Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic Interaction Studies in Rats between the Drugs of Abuse γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Ketamine and Treatment Strategies for Overdose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Surgery
2.3. Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic Interaction Studies
2.3.1. Effect of Ketamine on the Sedative Effects of GHB
2.3.2. Effect of Ketamine on GHB Toxicokinetics, GHB-Induced Respiratory Depression, and Fatality
2.3.3. Effect of Ketamine on GHB Brain Concentrations
2.4. Potential Treatment Strategies for Overdose
2.4.1. Effect of MCT Inhibition on the Sedative Effects of GHB
2.4.2. Effect of Treatment Strategies on GHB Toxicokinetics, GHB-Induced Respiratory Depression, and Fatality
2.5. Sample Analysis
2.6. Data/Statistical Analysis
2.7. GHB Cell Uptake Studies
3. Results
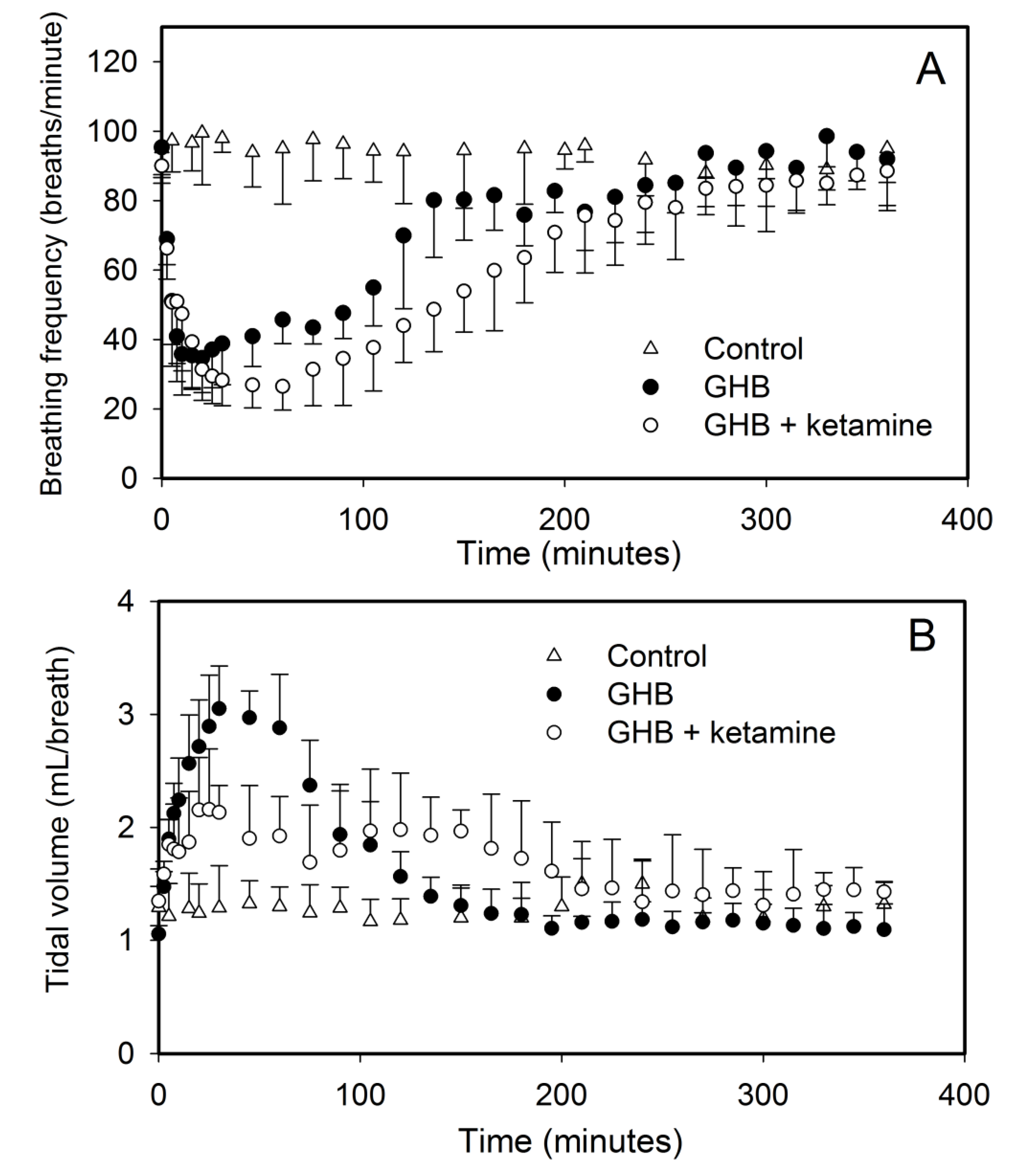
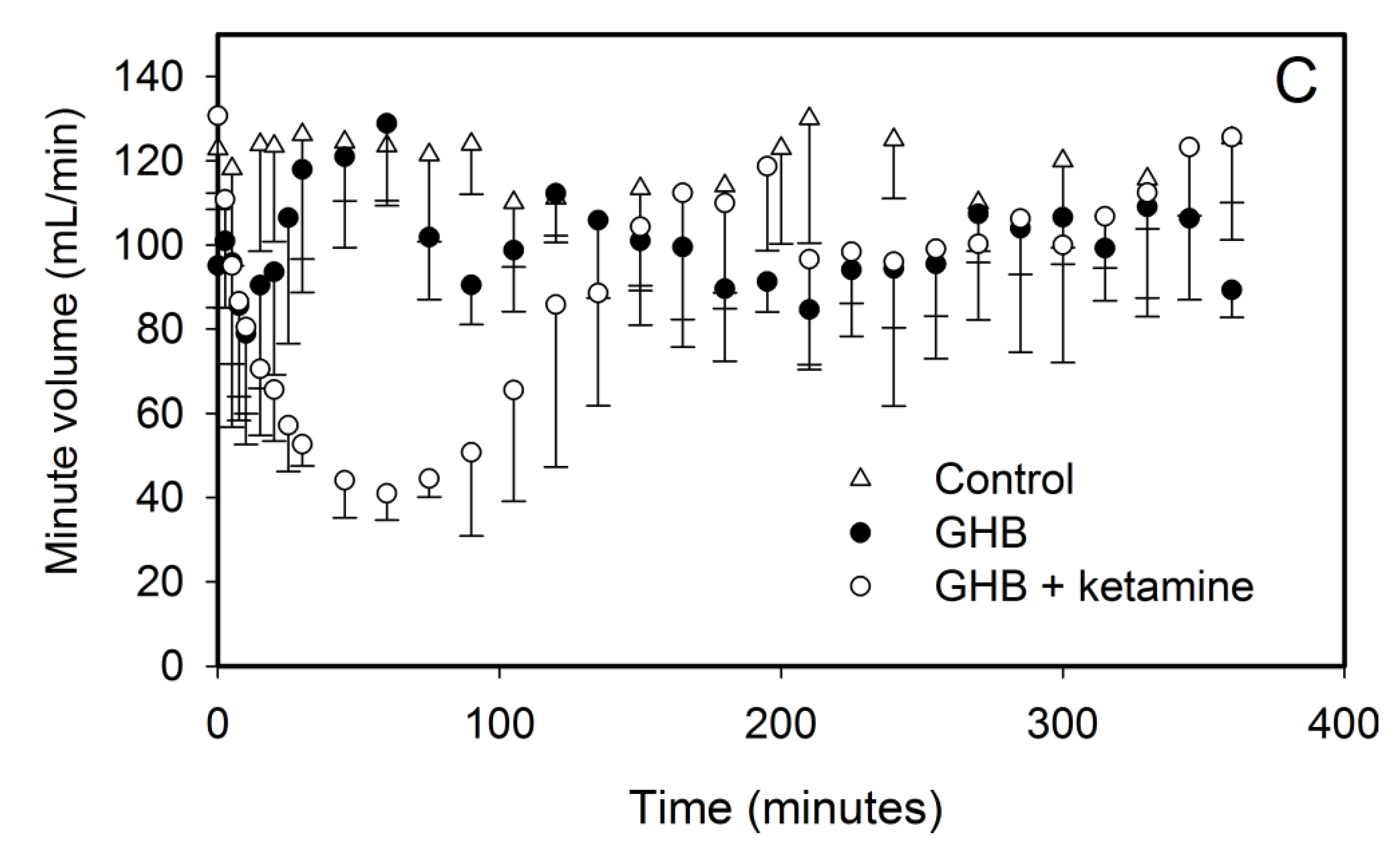
3.1. Effect of Ketamine on GHB Toxicokinetics/Toxicodynamics
3.1.1. Effect of Ketamine on GHB Toxicokinetics
3.1.2. Effect of Ketamine on GHB Toxicodynamics
3.2. Potential Treatment Strategies for Overdose
3.2.1. Monocarboxylate Transporter Inhibition
3.2.2. Specific Receptor Antagonism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galicia, M.; Nogue, S.; Miro, O. Liquid ecstasy intoxication: Clinical features of 505 consecutive emergency department patients. Emerg. Med. J. EMJ 2011, 28, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Stokes, S.A.; Woeckener, A. A tale of novel intoxication: Seven cases of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid overdose. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1998, 31, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zvosec, D.L.; Smith, S.W.; Porrata, T.; Strobl, A.Q.; Dyer, J.E. Case series of 226 gamma-hydroxybutyrate-associated deaths: Lethal toxicity and trauma. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2011, 29, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Anderson, I.B.; Dyer, J.E.; Barker, J.C.; Blanc, P.D. High-risk behaviors and hospitalizations among gamma hydroxybutyrate (GHB) users. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abus. 2007, 33, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, P.E.; Kerns, W.P., 2nd. Gamma hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) intoxication. Acad. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Soc. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2002, 9, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Sassenbroeck, D.K.; De Paepe, P.; Belpaire, F.M.; Buylaert, W.A. Characterization of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interaction between gamma-hydroxybutyrate and ethanol in the rat. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2003, 73, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morse, B.L.; Morris, M.E. Toxicokinetics/Toxicodynamics of gamma-hydroxybutyrate-ethanol intoxication: Evaluation of potential treatment strategies. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 346, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, D.M.; Nicolaou, M.; Dargan, P.I. Epidemiology of recreational drug toxicity in a nightclub environment. Subst. Use Misuse 2009, 44, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.M.; Greene, S.L.; Dargan, P.I. Five-year trends in self-reported recreational drugs associated with presentation to a UK emergency department with suspected drug-related toxicity. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Emerg. Med. 2013, 20, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lettieri, J.T.; Fung, H.L. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics and hypnotic effects of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate in the rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1979, 208, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.E.; Hu, K.; Wang, Q. Renal clearance of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in rats: Increasing renal elimination as a detoxification strategy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arena, C.; Fung, H.L. Absorption of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate and its prodrug gamma-butyrolactone: Relationship between in vitro transport and in vivo absorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 1980, 69, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.K.; Felmlee, M.A.; Morris, M.E. Monocarboxylate transporter-mediated transport of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2010, 38, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, I.; Boje, K.M. GHB (gamma-hydroxybutyrate) carrier-mediated transport across the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roiko, S.A.; Felmlee, M.A.; Morris, M.E. Brain uptake of the drug of abuse gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2012, 40, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Darling, I.M.; Morris, M.E. Transport of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in rat kidney membrane vesicles: Role of monocarboxylate transporters. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drozdzik, M.; Szelag-Pieniek, S.; Grzegolkowska, J.; Lapczuk-Romanska, J.; Post, M.; Domagala, P.; Mietkiewski, J.; Oswald, S.; Kurzawski, M. Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 (MCT1) in Liver Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Morris, M.E. Effects of L-lactate and D-mannitol on gamma-hydroxybutyrate toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics in rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2008, 36, 2244–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morse, B.L.; Vijay, N.; Morris, M.E. gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB)-induced respiratory depression: Combined receptor-transporter inhibition therapy for treatment in GHB overdose. Mol. Pharmacol. 2012, 82, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roiko, S.A.; Vijay, N.; Felmlee, M.A.; Morris, M.E. Brain extracellular gamma-hydroxybutyrate concentrations are decreased by L-lactate in rats: Role in the treatment of overdoses. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carai, M.A.; Colombo, G.; Brunetti, G.; Melis, S.; Serra, S.; Vacca, G.; Mastinu, S.; Pistuddi, A.M.; Solinas, C.; Cignarella, G.; et al. Role of GABA(B) receptors in the sedative/hypnotic effect of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 428, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaupmann, K.; Cryan, J.F.; Wellendorph, P.; Mombereau, C.; Sansig, G.; Klebs, K.; Schmutz, M.; Froestl, W.; van der Putten, H.; Mosbacher, J.; et al. Specific gamma-hydroxybutyrate-binding sites but loss of pharmacological effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate in GABA(B)(1)-deficient mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2722–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoyama, M.; Shimoyama, N.; Inturrisi, C.E.; Elliott, K. Oral ketamine produces a dose-dependent CNS depression in the rat. Life Sci. 1997, 60, PL9–PL14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shu, S.; Bayliss, D.A. HCN1 channel subunits are a molecular substrate for hypnotic actions of ketamine. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarton, E.; Teppema, L.J.; Olievier, C.; Nieuwenhuijs, D.; Matthes, H.W.; Kieffer, B.L.; Dahan, A. The involvement of the mu-opioid receptor in ketamine-induced respiratory depression and antinociception. Anesth. Analg. 2001, 93, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, D.L.; Malit, L.A.; Smith, T.C. Respiratory interactions of ketamine and morphine. Anesthesiology 1987, 66, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koek, W.; France, C.P. Cataleptic effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) and baclofen in mice: Mediation by GABA(B) receptors, but differential enhancement by N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists. Psychopharmacology 2008, 199, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, V.L.; Vermeyen, K.M.; Adriaensen, H.F.; Meert, T.F. Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on opioid-induced respiratory depression and acute antinociception in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2003, 74, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felmlee, M.A.; Roiko, S.A.; Morse, B.L.; Morris, M.E. Concentration-effect relationships for the drug of abuse gamma-hydroxybutyric acid. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 333, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, K.A.; Kilbane, E.M.; Jones, R.; Kunsman, G.W.; Levine, B.; Smith, M. Tissue distribution of ketamine in a mixed drug fatality. J. Forensic Sci. 1997, 42, 1183–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, B.R.; Wallage, H.R. Postmortem blood ketamine distribution in two fatalities. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Licata, M.; Pierini, G.; Popoli, G. A fatal ketamine poisoning. J. Forensic Sci. 1994, 39, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, E.E.; Nelson, T. An overview of gamma-hydroxybutyrate catabolism: The role of the cytosolic NADP(+)-dependent oxidoreductase EC 1.1.1.19 and of a mitochondrial hydroxyacid-oxoacid transhydrogenase in the initial, rate-limiting step in this pathway. Neurochem. Res. 1991, 16, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.T.; Chen, R.M. Mechanisms of ketamine-involved regulation of cytochrome P450 gene expression. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2010, 6, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rofael, H.Z. Effect of ketamine pretreatment on cocaine-mediated hepatotoxicity in rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 152, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchaipichat, V.; Raungrut, P.; Chau, N.; Janchawee, B.; Evans, A.M.; Miners, J.O. Effects of ketamine on human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in vitro predict potential drug-drug interactions arising from ketamine inhibition of codeine and morphine glucuronidation. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2011, 39, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Evans, A.M.; Wang, J.; Miners, J.O.; Upton, R.N.; Milne, R.W. Inhibition of morphine metabolism by ketamine. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2010, 38, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhart, D.Z.; Enerson, B.E.; Zhdankina, O.Y.; Leino, R.L.; Drewes, L.R. Expression of monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 by brain endothelium and glia in adult and suckling rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, E207–E213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, P.; Wilson, M.C.; Heddle, C.; Brown, M.H.; Barclay, A.N.; Halestrap, A.P. CD147 is tightly associated with lactate transporters MCT1 and MCT4 and facilitates their cell surface expression. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3896–3904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumi, K.; Furugen, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Otake, S.; Itagaki, S.; Iseki, K. Regulation of monocarboxylate transporter 1 in skeletal muscle cells by intracellular signaling pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 1568–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudoh, A.; Kudoh, E.; Katagai, H.; Takazawa, T. Ketamine suppresses norepinephrine-induced inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation via pathways involving protein kinase C. Anesth. Analg. 2002, 94, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.P.; Drewes, L.R. Modulation of monocarboxylic acid transporter-1 kinetic function by the cAMP signaling pathway in rat brain endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2053–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Suh, W.; Pan, Z.; You, G. Short-term and long-term effects of protein kinase C on the trafficking and stability of human organic anion transporter 3. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 3, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, G.; Bonner, S.; Gascoigne, A. Coma induced by abuse of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GBH or liquid ecstasy): A case report. BMJ 1997, 314, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovens, M.J.; Davies, A.J.; Wilson, M.C.; Murray, C.M.; Halestrap, A.P. AR-C155858 is a potent inhibitor of monocarboxylate transporters MCT1 and MCT2 that binds to an intracellular site involving transmembrane helices 7-10. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Treatment | Cplasma ketamine (µg/mL) | Cplasma GHB (mg/mL) | Cbrain GHB (mg/g) | GHB Brain/Plasma Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GHB alone | --- | 0.89 ± 0.05 | 0.21 ± 0.03 | 0.24 ± 0.02 |
| GHB + ketamine 0.1 mg/kg/min | 0.78 ± 0.05 | 0.92 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.02 |
| GHB + ketamine 0.287 mg/kg/min | 2.26 ± 0.21 | 0.90 ± 0.07 | 0.33 ± 0.05 * | 0.36 ± 0.05 * |
| GHB + ketamine 0.287 mg/kg/min + L-lactate | 2.67 ± 0.47 | 0.84 ± 0.04 | 0.17 ± 0.02 Ψ | 0.20 ± 0.02 Ψ |
| GHB + ketamine 0.287 mg/kg/min + AR-C155858 | 2.50 ± 0.30 | 0.37 ± 0.04 *Ψ | 0.03 ± 0.004 *Ψ | 0.08 ± 0.01 *Ψ |
| Toxicodynamic Parameter | GHB (n = 5) | GHB + Ketamine (n = 6) | GHB + Ketamine L-lactate (n = 4) | GHB + Ketamine AR-C155858 (n = 4) | GHB + Ketamine SCH50911 (n = 3) | GHB + Ketamine Naloxone (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency AUEC (breaths) | 5540 ± 1000 | 15,639 ± 1806 * | 5933 ± 2300 Ψ | 320.3 ± 135 *Ψ | 4534 ± 405 *Ψ | 11,358 ± 3800 |
| Frequency Emax (breaths/min) | 31 ± 5 | 22.6 ± 4.5 * | 34.5 ± 3.90 Ψ | 53.8 ± 7.31 *Ψ | 47.9 ± 5.6 Ψ | 22.3 ± 8.32 |
| Frequency Td (min) | 153 ± 12.5 | 326 ± 25.6 * | 124 ± 18.9 Ψ* | 17.5 ± 2.90 *Ψ | 140 ± 31.2 Ψ | 235 ± 45.8 |
| Cplasma (µg/mL) | Cbrain (µg/g) | GHB Brain/Plasma Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GHB | 379 ± 86.2 | 71.7 ± 9.89 | 0.19 ± 0.02 |
| GHB + ketamine 6 mg/kg | 277 ± 56.9 | 71.5 ± 8.47 | 0.26 ± 0.03 * |
| GHB + ketamine 20 mg/kg | 293 ± 35.1 | 82.6 ± 6.25 | 0.28 ± 0.01 * |
| Parameter | GHB | GHB + Ketamine | GHB + Ketamine + AR-C155858 | GHB + ketamine + L-Lactate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (mg.min/mL) | 101.9 ± 12.4 | 135.1 ± 14.4 * | 66.8 ± 4.39 * | 98.5 ± 5.73 Ψ |
| CLT (mL/min/kg) | 6.00 ± 0.74 | 4.49 ± 0.55 * | 9.01 ± 0.63 * | 6.10 ± 0.34 Ψ |
| CLR (mL/min/kg) | 1.68 ± 0.75 | 1.61 ± 0.29 | 4.10 ± 0.67 * | 2.32 ± 0.38 Ψ |
| CLM (mL/min/kg) | 4.31 ± 0.33 | 2.87 ± 0.28 * | 5.04 ± 0.86 Ψ | 3.77 ± 0.45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwatra, N.V.; Morris, M.E. Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic Interaction Studies in Rats between the Drugs of Abuse γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Ketamine and Treatment Strategies for Overdose. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050741
Kwatra NV, Morris ME. Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic Interaction Studies in Rats between the Drugs of Abuse γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Ketamine and Treatment Strategies for Overdose. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(5):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050741
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwatra, Nisha V., and Marilyn E. Morris. 2021. "Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic Interaction Studies in Rats between the Drugs of Abuse γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Ketamine and Treatment Strategies for Overdose" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 5: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050741
APA StyleKwatra, N. V., & Morris, M. E. (2021). Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic Interaction Studies in Rats between the Drugs of Abuse γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Ketamine and Treatment Strategies for Overdose. Pharmaceutics, 13(5), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13050741







