Exploitation of Design-of-Experiment Approach for Design and Optimization of Fast-Disintegrating Tablets for Sublingual Delivery of Sildenafil Citrate with Enhanced Bioavailability Using Fluid-Bed Granulation Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Preparation of Sildenafil FDSTs
2.4. Characterization of Fast-Disintegrating Granules
2.4.1. Mean Granule Size (d50)
2.4.2. Bulk Density (ρb)
2.4.3. Flowability
2.5. Tablet Characterization
2.5.1. Content Uniformity (CU)
2.5.2. Weight Variation and Thickness Uniformity
2.5.3. Breaking Force (BF)
2.5.4. Friability
2.5.5. In Vitro Disintegration Test
2.5.6. In Vitro Dissolution Test
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Study in Rabbits
2.6.1. Animal Experiment
2.6.2. Plasma Treatment and Drug Analysis
2.6.3. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection of Excipients
3.2. Validation of Drug Analytical Method
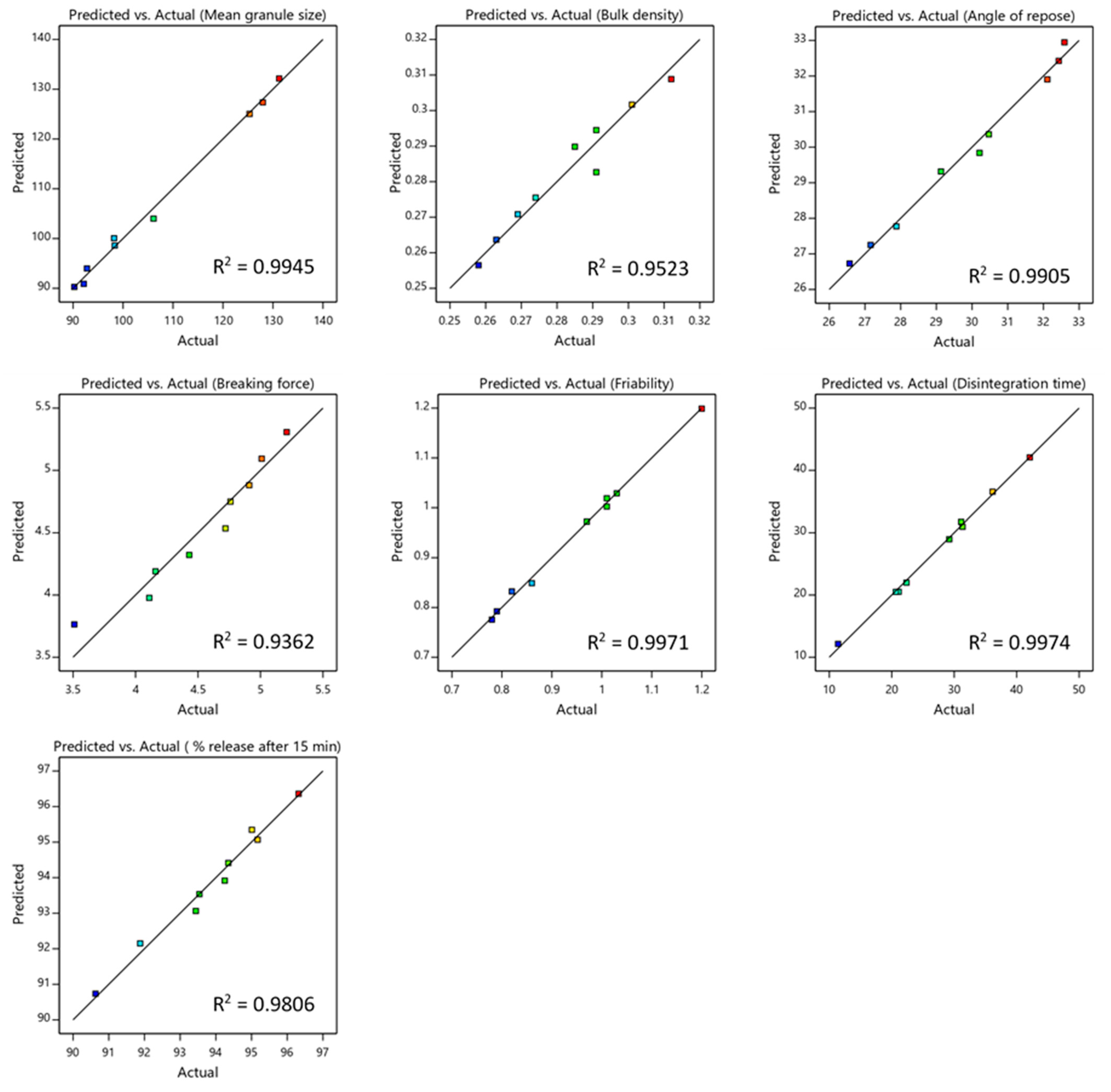
3.3. Statistical and Diagnostic Analysis of the Models
3.4. Granule Characterization
3.5. Tablet Characterization
3.5.1. Weight Variation, Thickness and Content Uniformity
3.5.2. Breaking Force and Friability
3.5.3. In Vitro Disintegration Study
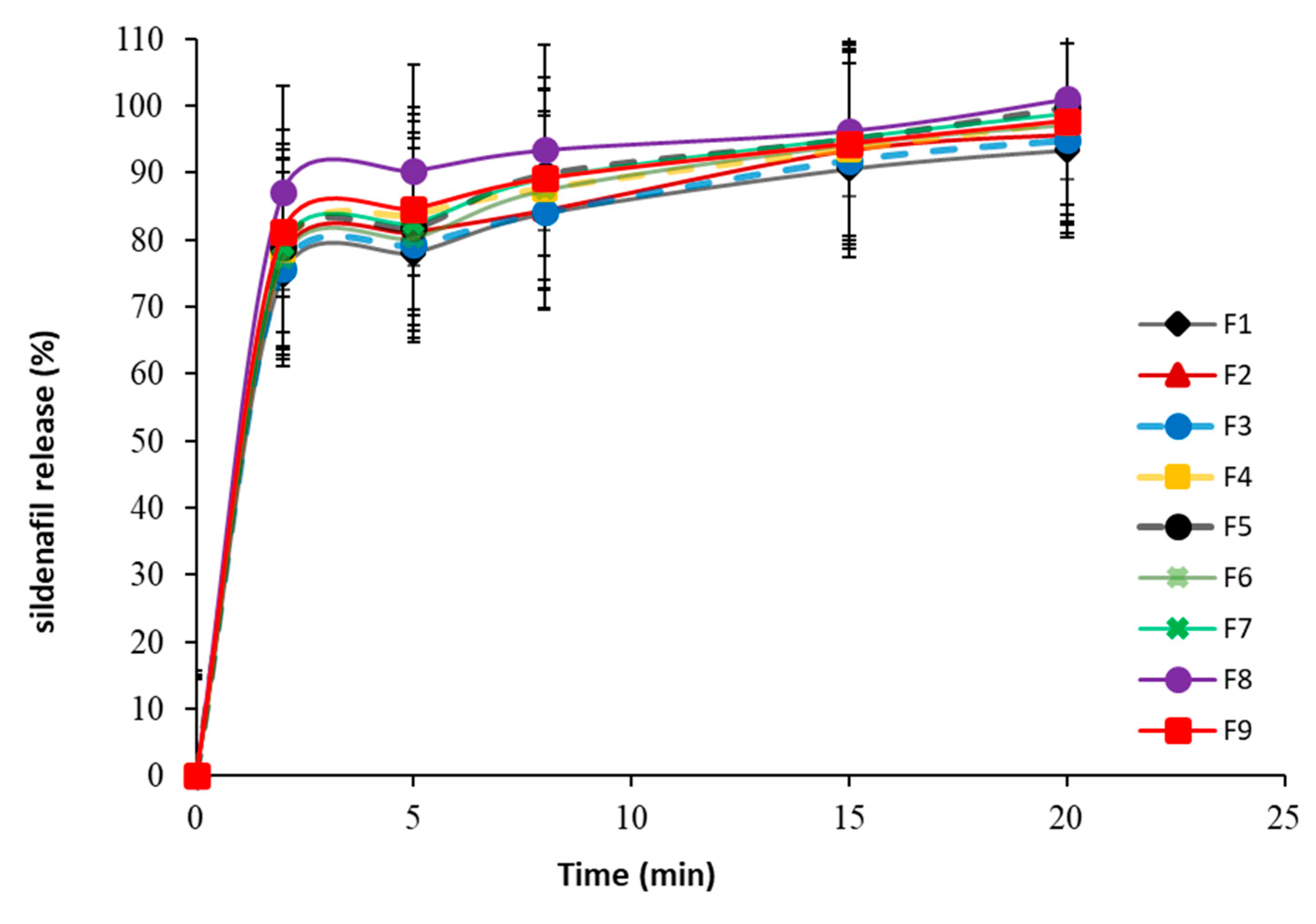
3.5.4. In Vitro Dissolution Study
3.5.5. Optimization of Independent Variables
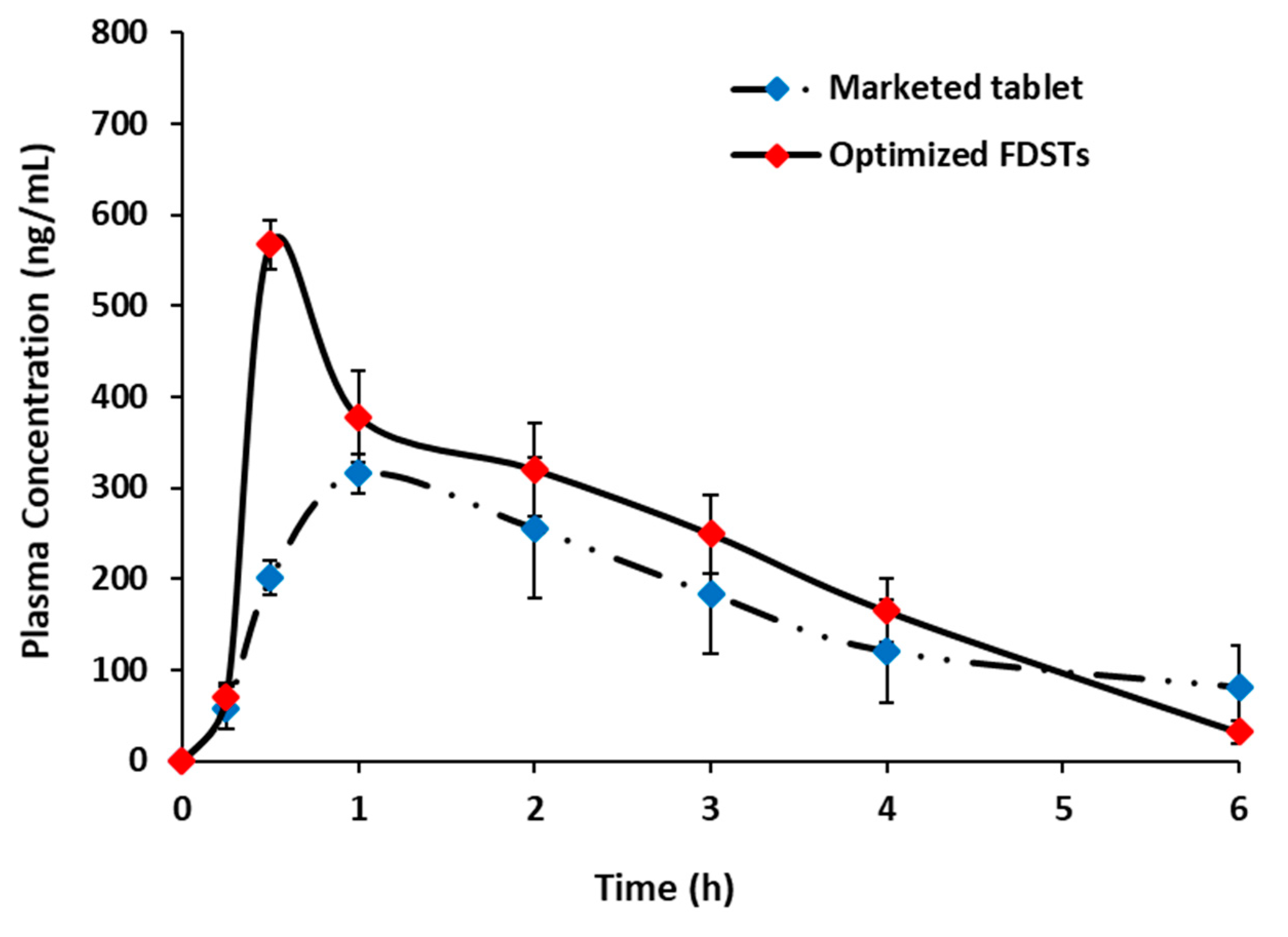
3.5.6. Pharmacokinetic Assessment of Optimized Formulation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raheem, O.A.; Natale, C.; Dick, B.; Reddy, A.G.; Yousif, A.; Khera, M.; Baum, N. Novel Treatments of Erectile Dysfunction: Review of the Current Literature. Sex. Med. Rev. 2021, 9, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaglione, F.; Donde, S.; Hassan, T.A.; Jannini, E.A. Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: Pharmacology and Clinical Impact of the Sildenafil Citrate Orodispersible Tablet Formulation. Clin. Ther. 2017, 39, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Peng, E.; Liao, Z.; Tang, Z. Do Urologists Really Recognize the Association between Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Disease? Sex. Med. 2020, 8, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jannini, E.A.; Droupy, S. Needs and Expectations of Patients with Erectile Dysfunction: An Update on Pharmacological Innovations in Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibition with Focus on Sildenafil. Sex. Med. 2019, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawatdee, S.; Atipairin, A.; Yoon, A.S.; Srichana, T. Enhanced dissolution of sildenafil dry foam tablets. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 11, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chow, M.S.S.; Zuo, Z. Mechanistic analysis of pH-dependent solubility and trans-membrane permeability of amphoteric compounds: Application to sildenafil. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 352, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, M.-T.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Chen, R.-N.; Chou, P.-Y.; Ho, H.-O. Rapid-Onset Sildenafil Sublingual Drug Delivery Systems: In Vitro Evaluation and In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rabbits. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2774–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Sun, C.C. The efficient development of a sildenafil orally disintegrating tablet using a material sparing and expedited approach. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, N.M.; Sanad, R.A.B.; Kharshoum, R.M.; Zineldin, M.A. Development of Salbutamol Sulphate fast disintegrating sublingual tablets with enhanced bioavailability and improved clinical efficacy for potential treatment of asthma. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 41, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, H.; Ye, Q.; Shi, C.; Zhang, X.; Pan, W. Carvedilol-loaded polyvinylpyrrolidone electrospun nanofiber film for sublingual delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Siati, M.; Saugo, M.; Franzolin, N. The start of pharmacological activity after sublingual administration of sildenafil citrate in 30 patients affected by erectile dysfunction. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. Organo Uff. Soc. Ital. Ecogr. Urol. Nefrol. 2003, 75, 18–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mandić, J.; Pirnat, V.; Luštrik, M.; German Ilić, I.; Vrečer, F.; Gašperlin, M.; Gašperlin, M.; Pobirk, A.Z. Solidification of SMEDDS by fluid bed granulation and manufacturing of fast drug release tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, Y.; Irisawa, Y.; Okimoto, K.; Osawa, T.; Yamashita, S. A new formulation for orally disintegrating tablets using a suspension spray-coating method. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 382, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalaiwe, A.; Fayed, M.H.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alsulays, B.B.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Tawfeek, H.M.; Khafagy, E.-S. Application of design of experiment approach for investigating the effect of partially pre-gelatinized starch on critical quality attributes of rapid orally disintegrating tablets. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Levins, C.; Pafiakis, S.; Zacour, B.; Bindra, D.S.; Trinh, J.; Buckley, D.; Gour, S.; Sharif, S.; Stamato, H. Enhancing tablet disintegration characteristics of a highly water-soluble high-drug-loading formulation by granulation process. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazumder, S.; Pavurala, N.; Manda, P.; Xu, X.; Cruz, C.N.; Krishnaiah, Y.S.R. Quality by Design approach for studying the impact of formulation and process variables on product quality of oral disintegrating films. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 527, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aodah, A.H.; Fayed, M.H.; Alalaiwe, A.; Alsulays, B.B.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.-S. Design, Optimization, and Correlation of In Vitro/In Vivo Disintegration of Novel Fast Orally Disintegrating Tablet of High Dose Metformin Hydrochloride Using Moisture Activated Dry Granulation Process and Quality by Design Approach. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafagy, E.-S.; Fayed, M.H.; Alrabahi, S.H.; Gad, S.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Aldawsari, M. Defining design space for optimization of escitalopram ultra-fast melting tablet using suspension spray-coating technique: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States. Pharmacopiae (USP 38-NF-33); United States: North Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shdefat, R.; Ali, B.E.; Anwer, M.K.; Fayed, M.H.; Alalaiwe, A.; Soliman, G.A. Sildenafil citrate-Glycyrrhizin/Eudragit binary spray dried microparticles: A sexual behavior studies on male rats. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dali, M.M.; Moench, P.A.; Mathias, N.R.; Stetsko, P.I.; Heran, C.L.; Smith, R.L. A rabbit model for sublingual drug delivery: Comparison with human pharmacokinetic studies of propranolol, verapamil and captopril. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, E.-J.; Kim, J.-Y.; Rhee, Y.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Park, C.-W.; Park, E.-S. Preparation of sildenafil citrate microcapsules and in vitro/in vivo evaluation of taste masking efficiency. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 466, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelian, A.; Wasilewska, K.; Wesoły, M.; Ciosek-Skibińska, P.; Winnicka, K. Taste-masking assessment of orally disintegrating tablets and lyophilisates with cetirizine dihydrochloride microparticles. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, P.M.; Liew, C.V.; Heng, P.W.S. Review of Disintegrants and the Disintegration Phenomena. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2545–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thoorens, G.; Krier, F.; Leclercq, B.; Carlin, B.; Evrard, B. Microcrystalline cellulose, a direct compression binder in a quality by design environment—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rachid, O.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Simons, F.E.R.; Simons, K.J. Rapidly-disintegrating sublingual tablets of epinephrine: Role of non-medicinal ingredients in formulation development. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Sun, C.C. Systematic evaluation of common lubricants for optimal use in tablet formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 117, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyttä, K.M.; Lakio, S.; Wikström, H.; Sulemanji, A.; Fransson, M.; Ketolainen, J.; Tajarobi, P. Comparison between twin-screw and high-shear granulation—The effect of filler and active pharmaceutical ingredient on the granule and tablet properties. Powder Technol. 2020, 376, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, K.; Kanada, K.; Uchida, S.; Yamada, M.; Namiki, N. Formulation study for orally disintegrating tablet using partly pregelatinized starch binder. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 59, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solaiman, A.; Suliman, A.S.; Shinde, S.; Naz, S.; Elkordy, A.A. Application of general multilevel factorial design with formulation of fast disintegrating tablets containing croscaremellose sodium and Disintequick MCC-25. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, Z.; Tas, C.; Tasdemir, U.; Erol, H.; Ozkan, C.K.; Savaser, A.; Ozkan, Y. Formulation of zolmitriptan sublingual tablets prepared by direct compression with different polymers: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbillemont, B.; Everaert, H.; De Beer, T. New advances in the characterization of lyophilised orally disintegrating tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 579, 119153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trubiano, P.C. Swelling Starches as Tablet Disintegrants. U.S. Patent No. 4,369,308, 18 January 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Kalný, M.; Grof, Z.; Štěpánek, F. Microstructure based simulation of the disintegration and dissolution of immediate release pharmaceutical tablets. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queiroz, A.L.P.; Wood, B.; Faisal, W.; Farag, F.; Garvie-Cook, H.; Glennon, B.; Vucen, S.; Crean, A.M. Application of percolation threshold to disintegration and dissolution of ibuprofen tablets with different microcrystalline cellulose grades. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 589, 119838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhodairy, K.A.; Hassan, M.A.; Afifi, S.A. Formulation and optimization of orodispersible tablets of flutamide. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairy, B.K.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Alalaiwe, A.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Alsulays, B.B.; Alshetaili, A.S.; Alshehri, S.M.; Fayed, M.H. Enhancing the Poor Flow and Tableting Problems of High Drug-Loading Formulation of Canagliflozin Using Continuous Green Granulation Process and Design-of-Experiment Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredenberg, S.; Duberg, M.; Lennernäs, B.; Lennernäs, H.; Pettersson, A.; Westerberg, M.; Nyström, C. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a new sublingual tablet system for rapid oromucosal absorption using fentanyl citrate as the active substance. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 20, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, K.M.; Mosli, H.A.; Hassan, A.H. Soy polysaccharide as a novel superdisintegrant in sildenafil citrate sublingual tablets: Preparation, characterization, and in vivo evaluation. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| QTPP Element | Target | CQAs | Justification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dosage form | Fast-disintegrating sublingual tablets | Breaking force | Hard enough |
| Appearance | Uncoated tablets | Friability | <1% |
| Strength | 50 mg | Disintegration time | <30 s |
| Route of administration | Sublingual | Drug release | More than 80% in 15 min |
| Proposed indications | Erectile dysfunction | - | - |
| Dosage frequency | Immediately before sexual activity | - | - |
| Coded Levels | PGS Levels (%) | MCC Levels (%) |
|---|---|---|
| −1 | 5 | 10 |
| 0 | 10 | 35 |
| 1 | 15 | 60 |
| Formula | PGS Levels (%) | MCC (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 10 |
| 2 | 5 | 35 |
| 3 | 5 | 60 |
| 4 | 10 | 10 |
| 5 | 10 | 35 |
| 6 | 10 | 60 |
| 7 | 15 | 10 |
| 8 | 15 | 35 |
| 9 | 15 | 60 |
| Ingredients | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sildenafil citrate | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 | 16.66 |
| Partially pre-gelatinized starch | 5 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Micro crystalline cellulose | 10 | 35 | 60 | 10 | 35 | 60 | 10 | 35 | 60 |
| Sodium stearyl fumarate | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| D-mannitol up to | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Response | Model | F-Ratio | p-Value | R2 | Adjusted R2 | Predicted R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean granule size (d50) | Quadratic | 2.92 | 0.0014 | 0.9945 | 0.9853 | 0.9495 |
| Bulk density | Linear | 0.5821 | 0.0001 | 0.9523 | 0.9364 | 0.9118 |
| Angle of repose | Linear | 2.10 | <0.0001 | 0.9905 | 0.9873 | 0.9774 |
| Breaking force | Linear | 0.6099 | 0.0003 | 0.9362 | 0.9149 | 0.8436 |
| Friability | Quadratic | 0.060 | 0.0005 | 0.9971 | 0.9924 | 0.9736 |
| Disintegration time | Quadratic | 4.020 | 0.0005 | 0.9974 | 0.9931 | 0.9703 |
| Drug release at 15 min | Quadratic | 0.5776 | 0.0090 | 0.9806 | 0.9484 | 0.8142 |
| Formula | Mean Granule Size (µm) (mean ± SD) | Bulk Density (gcm−3) (mean ± SD) | Angle of Repose (Degree) (mean ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 90.25 ± 0.225 | 0.258 ± 0.013 | 32.59 ± 0.162 |
| 2 | 92.14 ± 0.255 | 0.274 ± 0.011 | 32.43 ± 0.335 |
| 3 | 92.78 ± 0.239 | 0.291 ± 0.008 | 32.11 ± 0.193 |
| 4 | 98.34 ± 0.157 | 0.263 ± 0.014 | 30.47 ± 0.106 |
| 5 | 98.21 ± 0.297 | 0.291 ± 0.006 | 30.21 ± 0.113 |
| 6 | 106.11 ± 0.413 | 0.301 ± 0.023 | 29.13 ± 0.241 |
| 7 | 125.32 ± 0.365 | 0.269 ± 0.012 | 27.88 ± 0.264 |
| 8 | 127.97 ± 0.421 | 0.285 ± 0.034 | 27.16 ± 0.375 |
| 9 | 131.25 ± 0.522 | 0.321 ± 0.016 | 26.57 ± 0.316 |
| Variables | Coefficient Estimate | Sum of Squares | Standard Error | F-Value | p-Value | 95% CI Low | 95% CI High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean granule size “d50” (Quadratic model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 100.06 | - | 1.50 | - | - | 95.28 | 104.85 |
| X1 | 18.23 | 1993.63 | 0.8233 | 490.23 | 0.0002 | 15.61 | 20.85 |
| X2 | 2.71 | 93.90 | 0.8233 | 10.8 | 0.0462 | 0.0850 | 5.33 |
| X1 X2 | 0.850 | 2.89 | 1.01 | 0.4611 | −2.36 | 4.06 | |
| Bulk density (Linear model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 0.2827 | - | 0.0015 | - | - | 0.2790 | 0.2864 |
| X1 | 0.0072 | 0.0003 | 0.0019 | 14.93 | 0.0083 | 0.0026 | 0.0117 |
| X2 | 0.0190 | 0.0022 | 0.0019 | 104.95 | <0.0001 | 0.0145 | 0.0235 |
| Angle of repose (Linear model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 29.84 | - | 0.0861 | - | - | 29.63 | 30.05 |
| X1 | −2.59 | 40.15 | 0.1055 | 601.57 | <0.0001 | −2.84 | −2.33 |
| X2 | −0.5217 | 1.63 | 0.1055 | 24.47 | 0.0026 | −0.7797 | −0.2636 |
| Formula | Weight (mg ± SD) | Thickness (mm ± SD) | CU ** (% ± SD) | Breaking Force (KP ± SD) | Friability (% ± SD) | DT *** (S ± SD) | % Release after 15 min (% ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 299.52 ± 1.16 | 3.33 ± 0.013 | 98.96 ± 1.36 | 3.51 ± 0.85 | 1.30 ± 0.07 | 42.11 ± 0.73 | 90.63 ± 4.15 |
| 2 | 297.82 ± 1.40 | 3.32 ± 0.007 | 100.51 ± 0.96 | 4.11 ± 0.65 | 1.03 ± 0.13 | 31.34 ± 0.67 | 93.44 ± 2.17 |
| 3 | 300.91 ± 1.69 | 3.34 ± 0.004 | 97.33 ± 1.94 | 4.16 ± 0.76 | 0.97 ± 0.16 | 36.16 ± 0.92 | 91.88 ± 3.36 |
| 4 | 299.71 ± 1.38 | 3.36 ± 0.03 | 99.58 ± 1.52 | 4.43 ± 0.58 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 31.12 ± 1.67 | 93.54 ± 3.55 |
| 5 | 299.81 ± 1.51 | 3.34 ± 0.005 | 98.69 ± 1.65 | 4.72 ± 0.88 | 0.86 ± 0.03 | 22.36 ± 0.42 | 95.01 ± 2.97 |
| 6 | 298.14 ± 1.60 | 3.35 ± 0.007 | 99.46 ± 1.92 | 4.76 ± 0.96 | 0.79 ± 0.06 | 29.21 ± 1.24 | 94.25 ± 3.28 |
| 7 | 298.35 ± 1.49 | 3.31 ± 0.008 | 100.53 ± 2.17 | 4.91 ± 0.79 | 1.01 ± 0.04 | 21.11 ± 1.13 | 95.17 ± 3.87 |
| 8 | 297.62 ± 1.28 | 3.33 ± 0.006 | 98.17 ± 2.14 | 5.01 ± 0.58 | 0.82 ± 0.03 | 11.41 ± 0.52 | 96.32 ± 4.01 |
| 9 | 301.21 ± 1.43 | 3.32 ± 0.04 | 99.22 ± 2.44 | 5.21 ± 0.73 | 0.78 ± 0.04 | 20.66 ± 0.79 | 94.35 ± 3.15 |
| Variables | Coefficient Estimate | Sum of Squares | Standard Error | F-Value | p-Value | 95% CI Low | 95% CI High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breaking force (Linear model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 4.54 | - | 0.0520 | - | - | 4.41 | 4.66 |
| X1 | 0.5583 | 1.87 | 0.0637 | 76.79 | 0.0001 | 0.4024 | 0.7142 |
| X2 | 0.2133 | 0.2731 | 0.0637 | 11.21 | 0.0155 | 0.0574 | 0.3692 |
| Friability (Quadratic model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 0.8489 | - | 0.0091 | - | - | 0.8200 | 0.8778 |
| X1 | −0.0983 | 0.0580 | 0.0050 | 391.61 | <0.0003 | −0.1141 | −0.0825 |
| X2 | −0.1133 | 0.0771 | 0.0050 | 520.20 | 0.0002 | −0.1291 | −0.0975 |
| Disintegration time (Quadratic model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 21.99 | - | 0.5776 | - | - | 20.15 | 23.83 |
| X1 | −9.41 | 530.72 | 0.3164 | 883.72 | <0.0001 | −10.41 | −8.40 |
| X2 | −1.39 | 11.51 | 0.3164 | 19.16 | 0.0221 | −2.39 | −0.3782 |
| X1 X2 | 1.38 | 7.56 | 0.3875 | 12.59 | 0.0381 | 0.1419 | 2.61 |
| Percent release after 15 min (Quadratic model) | |||||||
| Intercept | 95.35 | - | 0.2940 | - | - | 94.41 | 96.28 |
| X1 | 1.65 | 16.30 | 0.1611 | 104.74 | 0.0020 | 1.14 | 2.16 |
| X2 | 0.1900 | 0.2166 | 0.1611 | 1.39 | 0.3231 | −32.26 | 0.7026 |
| X1 X2 | −0.5175 | 1.070 | 19.73 | 6.88 | 0.0788 | −1.15 | 0.1102 |
| Variables | Target | Range | Weight | Importance Co-Efficient |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-put | ||||
| PGS | In range | 5–15% | 1 | - |
| MCC | In range | 10–60% | 1 | - |
| Out-put | ||||
| Breaking force | Maximize | 3.51–5.21 KP | 1 | +++ |
| Friability | Minimize | 0.78–1.2% | 1 | +++ |
| Disintegration time | Minimize | 11.41–42.11 s | 1 | +++ |
| Ingredients | % w/w | ||
| Sildenafil citrate | 16.66 | ||
| Partially pre-gelatinized starch | 15.00 | ||
| Micro crystalline cellulose | 46.62 | ||
| Sodium stearyl fumarate | 1.00 | ||
| D-mannitol up to | 100.00 | ||
| Responses | Predicted Values | Experimental Values (Mean ± SD) | Relative Error (%) |
| Breaking force (KP) | 5.193 | 5.382 ± 1.63 | −3.639 |
| Friability (%) | 0.791 | 0.753 ± 0.48 | 4.804 |
| Disintegration time (s) | 13.958 | 14.561 ± 0.84 | −4.320 |
| Percent release after 15 min (%) | 95.857 | 94.734 ± 2.76 | 1.171 |
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | Sildenafil Marketed Product (n = 6) | Optimized Sildenafil FDSTs (n = 6) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 327.92 ± 29.18 | 567.38 ± 27.36 ** |
| tmax (h) | 1.33 ± 0.51 | 0.50 ± 0.00 ** |
| K (h−1) | 0.29 ± 0.11 | 0.72 ± 0.09 ** |
| t1/2 (h) | 2.57 ± 0.73 | 0.97 ± 0.11 ** |
| AUC0–6 (ng.h/mL) | 1232.63 ± 393.38 | 1978.69 ± 261.37 ** |
| AUC0–∞ (ng.h/mL) | 1572.97 ± 631.21 | 2024.74 ± 280.74 ** |
| Relative bioavailability (F) based on AUC0–6 | - | 160.52% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlAli, A.S.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alalaiwe, A.; Almutairy, B.K.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Walbi, I.A.; Fayed, M.H. Exploitation of Design-of-Experiment Approach for Design and Optimization of Fast-Disintegrating Tablets for Sublingual Delivery of Sildenafil Citrate with Enhanced Bioavailability Using Fluid-Bed Granulation Technique. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060870
AlAli AS, Aldawsari MF, Alalaiwe A, Almutairy BK, Al-Shdefat R, Walbi IA, Fayed MH. Exploitation of Design-of-Experiment Approach for Design and Optimization of Fast-Disintegrating Tablets for Sublingual Delivery of Sildenafil Citrate with Enhanced Bioavailability Using Fluid-Bed Granulation Technique. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(6):870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060870
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlAli, Amer S., Mohammed F. Aldawsari, Ahmed Alalaiwe, Bjad K. Almutairy, Ramadan Al-Shdefat, Ismail A. Walbi, and Mohamed H. Fayed. 2021. "Exploitation of Design-of-Experiment Approach for Design and Optimization of Fast-Disintegrating Tablets for Sublingual Delivery of Sildenafil Citrate with Enhanced Bioavailability Using Fluid-Bed Granulation Technique" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 6: 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060870
APA StyleAlAli, A. S., Aldawsari, M. F., Alalaiwe, A., Almutairy, B. K., Al-Shdefat, R., Walbi, I. A., & Fayed, M. H. (2021). Exploitation of Design-of-Experiment Approach for Design and Optimization of Fast-Disintegrating Tablets for Sublingual Delivery of Sildenafil Citrate with Enhanced Bioavailability Using Fluid-Bed Granulation Technique. Pharmaceutics, 13(6), 870. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13060870









