Improved Hygroscopicity and Bioavailability of Solid Dispersion of Red Ginseng Extract with Silicon Dioxide
Abstract
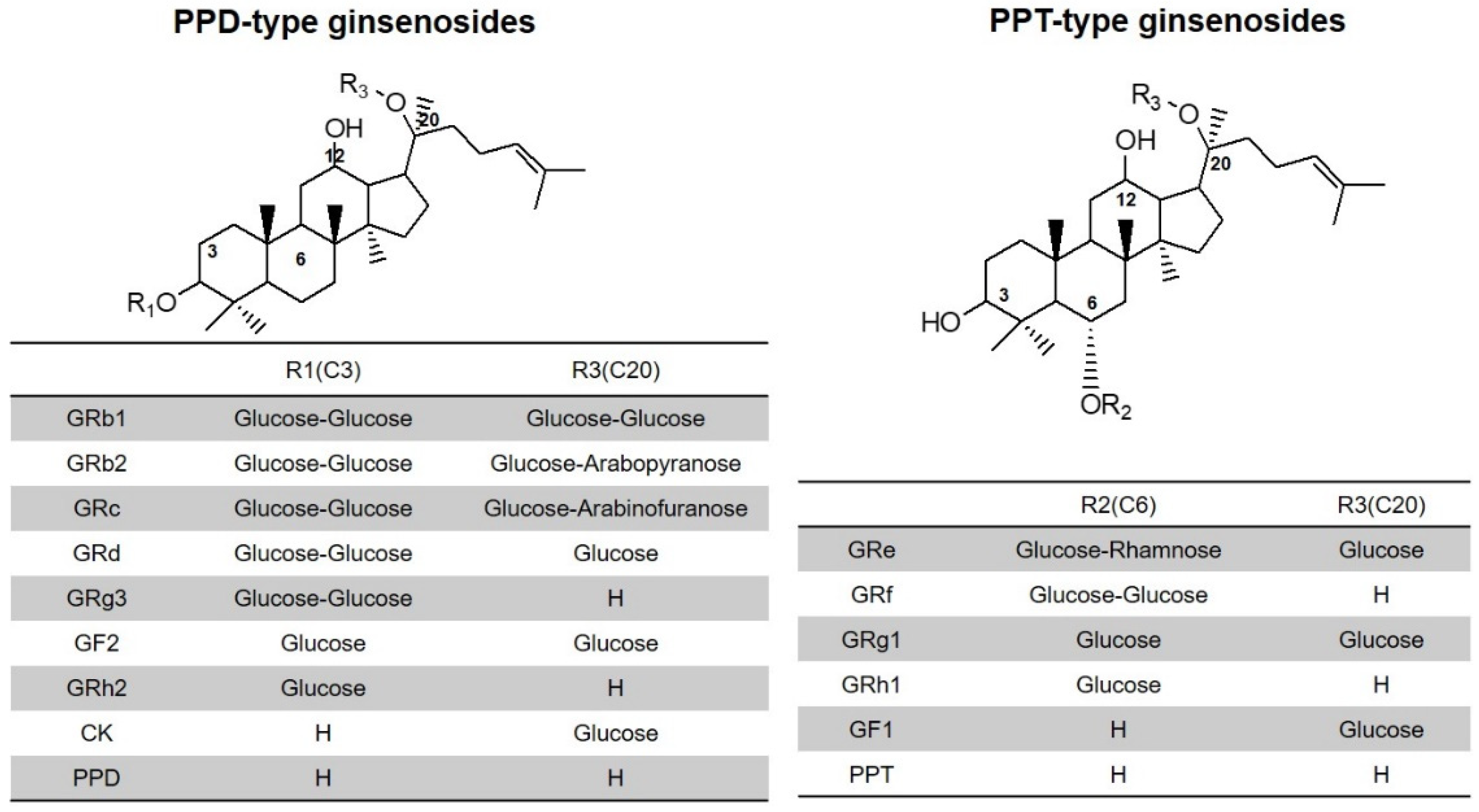
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solid Dispersion of Red Ginseng Extract
2.3. Hygroscopicity Test
2.4. Characterization of RGE Solid Dispersion
2.5. Intestinal Permeability Test
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Study
2.7. Stability of RGE-SiO2 Solid Dispersion
2.8. LC-MS/MS Analysis of Ginsenosides
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation of Solid Dispersion of RGE with Hydrophilic Carriers
3.2. Hygroscopicity Test
3.3. Characterization of RGE Solid Dispersion Formulation
3.3.1. XRD and DSC Analysis
3.3.2. Dissolution Rate of Ginsenoside from Solid Dispersion Formulations of RGE
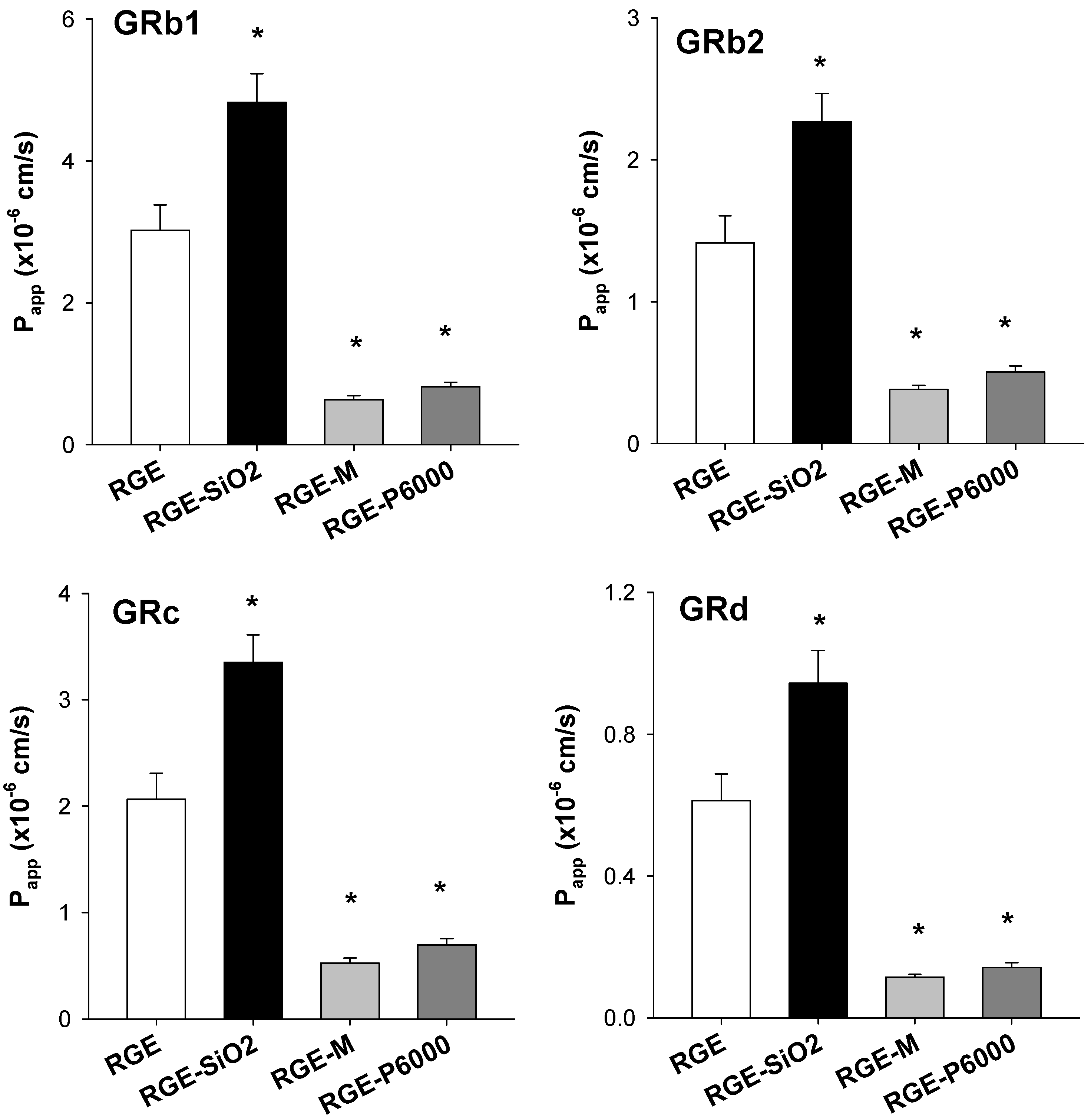
3.3.3. Intestinal Permeability of Ginsenoside from Solid Dispersion Formulations of RGE
3.4. Pharmacokinetics of Ginsenosides in RGE-SiO2
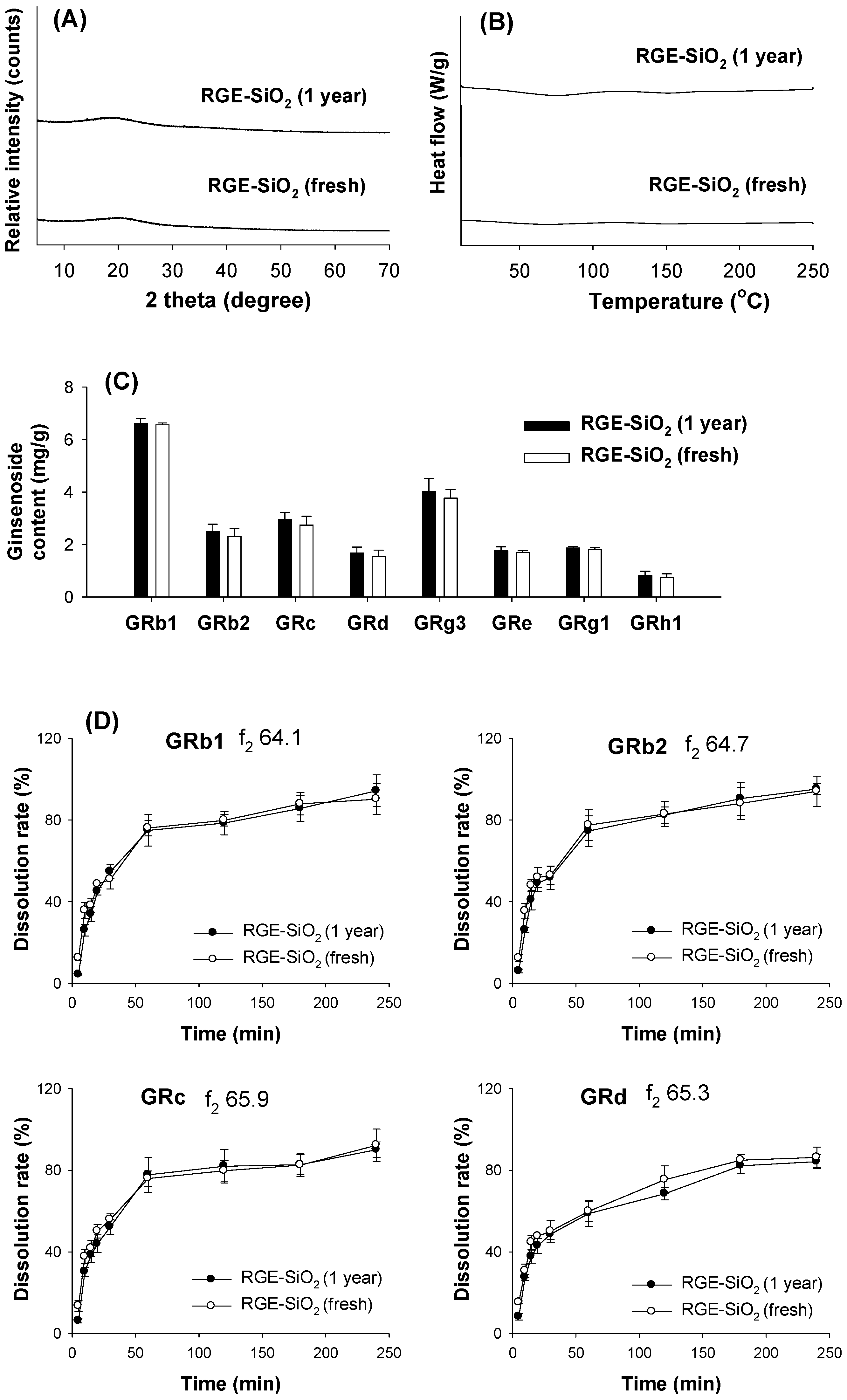
3.5. Stability of RGE-SiO2
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Won, H.J.; Kim, H.I.; Park, T.; Kim, H.; Jo, K.; Jeon, H.; Ha, S.J.; Hyun, J.M.; Jeong, A.; Kim, J.S.; et al. Non-clinical pharmacokinetic behavior of ginsenosides. J. Ginseng Res. 2019, 43, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.E.; Na, C.S.; Yoo, S.A.; Seo, S.H.; Son, H.S. Biotransformation of major ginsenosides in ginsenoside model culture by lactic acid bacteria. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, W.W.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, F.L.; Zhu, W.J.; Jiang, J.; Wu, S.; Yang, D.C.; Li, D.; Quan, L.H. Biotransformation of Panax ginseng extract by rat intestinal microflora: Identification and quantification of metabolites using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Detection of 13 ginsenosides (Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, Re, Rf, Rg1, Rg3, Rh2, F1, Compound K, 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol, and 20(S)-Protopanaxatriol) in human plasma and application of the analytical method to human pharmacokinetic studies following two week-repeated administration of red ginseng extract. Molecules 2019, 24, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, J.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides following repeated oral administration of red ginseng extract significantly differ between species of experimental animals. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2020, 43, 1335–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Yi, Y.S.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Role of ginsenosides, the main active components of Panax ginseng, in inflammatory responses and diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, T.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Yun, H.Y. Epidemiological study on cancer prevention by ginseng: Are all kinds of cancers preventable by ginseng? J. Korean Med. Sci. 2001, 16 (Suppl.), S19–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, Q.F.; Xu, Z.R.; Xu, K.Y.; Yang, Y.M. The efficacy of ginseng-related therapies in type 2 diabetes mellitus: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.Y.; Hong, M.; Sung, H.; Kim, S.; Suk, K.T. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng in chronic liver disease. J. Ginseng Res. 2017, 41, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Interactions of ginseng with therapeutic drugs. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 862–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xing, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Z. Pharmaceutical dispersion techniques for dissolution and bioavailability enhancement of poorly water-soluble drugs. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, D.H.; Kim, Y.-I.; Cho, K.H.; Poudel, B.K.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, D.-W.; Shin, Y.-J.; Bae, O.-N.; Yousaf, A.M.; Yong, C.S.; et al. A novel solid dispersion system for natural product-loaded medicine: Silymarin-loaded solid dispersion with enhanced oral bioavailability and hepatoprotective activity. J. Microencapsul. 2014, 31, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, I.S.; Cha, J.S.; Choi, M.K. Characterization, in vivo and in vitro evaluation of solid dispersion of curcumin containing d-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate and mannitol. Molecules 2016, 21, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vo, C.L.; Park, C.; Lee, B.J. Current trends and future perspectives of solid dispersions containing poorly water-soluble drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, P.; Pyo, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S. Overview of the manufacturing methods of solid dispersion technology for improving the solubility of poorly water-soluble drugs and application to anticancer drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cid, A.G.; Simonazzi, A.; Palma, S.D.; Bermúdez, J.M. Solid dispersion technology as a strategy to improve the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 363–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, W.; Jin, S.; Kwon, M.; Shin, C.H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Herb-drug interaction of red ginseng extract and ginsenoside Rc with valsartan in rats. Molecules 2020, 25, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, M.K.; Jin, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kang, W.Y.; Seong, S.J.; Yoon, Y.R.; Han, Y.H.; Song, I.S. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, Rc, Rd, and compound K after single or multiple administration of red ginseng extract in human beings. J. Ginseng Res. 2020, 44, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Xue, B.; Yang, C.; Miao, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Q.; Cai, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; He, H.; et al. Biopharmaceutical characters and bioavailability improving strategies of ginsenosides. Fitoterapia 2018, 129, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, C.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.M.; Jeon, H.; Won, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Micro-/nano-sized delivery systems of ginsenosides for improved systemic bioavailability. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Cheng, X.; Liang, X.; Liao, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Cao, Y. Intestinal absorption and pharmacokinetics study of long-circulating nanoparticles loaded with panax pseudoginseng saponins. China Pharm. 2014, 25, 4052–4055. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Jin, Z.C.; Yuan, Y.; Wei, H.M.; Xu, X.Y.; He, S.L.; Chen, S.T.; Hou, W.; Guo, Q.J.; Hua, B.J. Ginsenoside Rg3 serves as an adjuvant chemotherapeutic agent and VEGF inhibitor in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 7826753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Tong, D.; Che, D.; Pei, B.; Xia, X.; Yuan, G.; Jin, X. Ascorbyl palmitate/d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate monoester mixed micelles for prolonged circulation and targeted delivery of compound K for antilung cancer therapy in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Coasne, B.; Guyer, R.; Derome, D.; Carmeliet, J. Role of hydrogen bonding in hysteresis observed in sorption-induced swelling of soft nanoporous polymers. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Gong, T.; Zhang, K.; Lee, C. Graphene oxide papers with high water adsorption capacity for air dehumidification. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms. FDA Guidance Documents 1997. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/dissolution-testing-immediate-release-solid-oral-dosage-forms (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Choi, M.-K.; Song, I.-S. Recent advances in the formulation of sphingolipid anticancer therapeutics. J. Pharm. Investig. 2020, 50, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopp, M.M.; Nguyen, J.H.; Becker, C.; Francke, N.M.; Jørgensen, E.B.; Holm, P.; Holm, R.; Mu, H.; Rades, T.; Langguth, P. Influence of polymer molecular weight on in vitro dissolution behavior and in vivo performance of celecoxib:PVP amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 101, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateskumar, K.; Parasuraman, S.; Gunasunderi, R.; Sureshkumar, K.; Nayak, M.M.; Shah, S.A.A.; Khoo, K.; Kai, H.W. Acyclovir-Polyethylene Glycol 6000 Binary Dispersions: Mechanistic Insights. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 2085–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, B.; Shimpi, S.; Paradkar, A. Preparation and evaluation of glibenclamide-polyglycolized glycerides solid dispersions with silicon dioxide by spray drying technique. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredriksson, M.; Thybring, E.E. Scanning or desorption isotherms? Characterising sorption hysteresis of wood. Cellulose 2018, 25, 4477–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fredriksson, M.; Thybring, E.E. On sorption hysteresis in wood: Separating hysteresis in cell wall water and capillary water in the full moisture range. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, S.; Almukainzi, M.; Bou-Chacra, N.A.; Amidon, G.L.; Lee, B.-J.; Feng, J.; Kanfer, I.; Zuo, J.Z.; Wei, H.; Bolger, M.B.; et al. Provisional biopharmaceutical classification of some common herbs used in western medicine. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, I.S.; Nam, S.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Park, S.J.; Choi, M.K. Enhanced bioavailability and efficacy of silymarin solid dispersion in rats with acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morefield, E.; Seyer, J. Colloidal Silicon Dioxide. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 4th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Nepal, P.R.; Han, H.-K.; Choi, H.-K. Enhancement of solubility and dissolution of Coenzyme Q10 using solid dispersion formulation. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 383, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.H.; Kang, B.; Lee, S.; Jin, S.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Pharmacokinetics and intestinal metabolism of compound K in rats and mice. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, S.; Lee, S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Enhanced intestinal permeability and plasma concentration of metformin in rats by the repeated administration of red ginseng extract. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.L.; Sadrieh, N.; Yu, L. Impact of osmotically active excipients on bioavailability and bioequivalence of BCS class III drugs. AAPS J. 2013, 15, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaithianathan, S.; Haidar, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.; Avon, C.; Dowling, T.C.; Shao, C.; Kane, M.; Hoag, S.W.; Flasar, M.H.; et al. Effect of common excipients on the oral drug absorption of biopharmaceutics classification system class 3 drugs cimetidine and acyclovir. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adkin, D.A.; Davis, S.S.; Sparrow, R.A.; Huckle, P.D.; Wilding, I.R. The effect of mannitol on the oral bioavailability of cimetidine. J. Pharm. Sci. 1995, 84, 1405–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, I.S.; Jenkins, A.P.; Heduan, E.; Catt, S.D.; Segal, M.B.; Creamer, B. The effect of poorly absorbed solute on intestinal absorption. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1990, 25, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.L.; Blume, C.D.; Lin, E.T.; Holford, N.H.; Benet, L.Z. Relative bioavailability of chlorthalidone in humans: Adverse influence of polyethylene glycol. J. Pharm. Sci. 1982, 71, 533–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoin, C.; Tod, M.; Brion, N.; Louchahi, K.; Le Gros, V.; Petitjean, O. Pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin coadministered with a saline-polyethylene glycol solution in healthy volunteers. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 1995, 16, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragueneau, I.; Poirier, J.M.; Radembino, N.; Sao, A.B.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Jaillon, P. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic drug interactions between digoxin and macrogol 4000, a laxative polymer, in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, K.; Hirobe, S.; Okada, N.; Nakagawa, S. Analysis of skin permeability and toxicological properties of amorphous silica particles. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 1201–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.A.; Yoon, Y.H.; Choi, K.; Kwon, M.; Goo, S.H.; Cha, J.S.; Choi, M.K.; Lee, H.S.; Song, I.S. Enhanced oral bioavailability of morin administered in mixed micelle formulation with PluronicF127 and Tween80 in rats. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.; Lim, D.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, M.K.; Song, I.S. Enhanced intestinal absorption and pharmacokinetic modulation of berberine and its metabolites through the inhibition of P-glycoprotein and intestinal metabolism in rats using a berberine mixed micelle formulation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, N.; Pan, G.; Elmquist, W.F. Interactions of pluronic block copolymers on P-gp efflux activity: Experience with HIV-1 protease inhibitors. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 5421–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, M.; Morrison, R.A.; Chong, S. Commonly used surfactant, Tween 80, improves absorption of P-glycoprotein substrate, digoxin, in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.M.; Charman, W.N.; Porter, C.J.H. An in vitro examination of the impact of polyethylene glycol 400, Pluronic P85, and vitamin E d-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate on P-glycoprotein efflux and enterocyte-based metabolism in excised rat intestine. AAPS PharmSci 2002, 4, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.; Ensom, M.H. Post hoc power analysis: An idea whose time has passed? Pharmacotherapy 2001, 21, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.W.; Song, I.S.; Shin, H.J.; Yeo, C.W.; Cho, D.Y.; Shon, J.H.; Shin, J.G. The effect of SLCO1B1*15 on the disposition of pravastatin and pitavastatin is substrate dependent: The contribution of transporting activity changes by SLCO1B1*15. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2008, 18, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Compound | Retention Time (min) | Adduct | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ion (m/z) | Fragmentor Voltage (V) | Collision Energy (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRb1 | 3.4 | [M+Na]+ | 1131.6 | 365.1 | 165 | 65 |
| GRb2 | 4.2 | [M+Na]+ | 1101.6 | 335.1 | 185 | 60 |
| GRc | 3.6 | [M+Na]+ | 1101.6 | 335.1 | 185 | 60 |
| GRd | 4.8 | [M+Na]+ | 969.9 | 789.5 | 170 | 50 |
| GRe | 1.7 | [M+Na]+ | 969.9 | 789.5 | 170 | 50 |
| GRg1 | 1.8 | [M+Na]+ | 824.0 | 643.6 | 135 | 40 |
| GF2 | 5.9 | [M+Na]+ | 807.5 | 627.5 | 135 | 40 |
| GRg3 | 5.8 | [M+Na]+ | 807.5 | 365.2 | 165 | 60 |
| GRh1 | 3.2 | [M-2H2O+H]+ | 603.4 | 423.4 | 135 | 10 |
| GF1 | 3.7 | [M+Na]+ | 661.5 | 203.1 | 185 | 40 |
| GRh2 | 6.6 | [M-2H2O+H]+ | 587.4 | 407.4 | 135 | 15 |
| CK | 6.6 | [M+Na]+ | 645.5 | 203.1 | 160 | 35 |
| PPT | 5.4 | [M-2H2O+H]+ | 425.3 | 109.1 | 130 | 30 |
| PPD | 7.3 | [M-2H2O+H]+ | 411.3 | 109.1 | 125 | 25 |
| berberine (IS) | 3.5 | [M+H]+ | 336.1 | 320.0 | 135 | 30 |
| Ginsenosides | Ginsenoside Content (mg/g) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGE | RGE-SiO2 (p Value) | REG-M (p Value) | RGE-S (p Value) | RGE-L (p Value) | RGE-T (p Value) | ||||||
| PPD-type | GRb1 | 6.15 ± 2.41 | 5.58 ± 0.22 (0.651) | 5.73 ± 1.06 (0.760) | 5.95 ± 1.15 (0.883) | 6.36 ± 1.10 (0.883) | 6.25 ± 0.89 (0.941) | ||||
| GRb2 | 2.96 ± 1.03 | 2.53 ± 0.41 (0.462) | 2.93 ± 0.48 (0.951) | 3.03 ± 0.58 (0.907) | 3.11 ± 0.35 (0.907) | 3.27 ± 0.64 (0.634) | |||||
| GRc | 3.35 ± 1.02 | 2.85 ± 0.40 (0.398) | 3.23 ± 0.13 (0.819) | 3.52 ± 0.72 (0.794) | 3.35 ± 0.17 (0.794) | 3.44 ± 0.41 (0.874) | |||||
| GRd | 1.74 ± 0.79 | 1.41 ± 0.18 (0.455) | 1.63 ± 0.12 (0.806) | 1.81 ± 0.43 (0.873) | 1.87 ± 0.26 (0.873) | 1.73 ± 0.33 (0.981) | |||||
| GRg3 | 3.86 ± 2.19 | 3.31 ± 0.96 (0.663) | 3.48 ± 0.98 (0.759) | 3.92 ± 1.61 (0.968) | 3.83 ± 1.28 (0.968) | 3.84 ± 1.37 (0.987) | |||||
| PPT-type | GRe | 1.71 ± 0.63 | 1.74 ± 0.53 (0.941) | 1.72 ± 0.19 (0.984) | 1.79 ± 0.37 (0.836) | 1.74 ± 0.21 (0.836) | 1.79 ± 0.17 (0.810) | ||||
| GRg1 | 2.11 ± 0.69 | 1.86 ± 0.41 (0.546) | 2.00 ± 0.10 (0.757) | 2.12 ± 0.46 (0.977) | 2.20 ± 0.06 (0.977) | 2.16 ± 0.21 (0.892) | |||||
| GRh1 | 0.71 ± 0.22 | 0.61 ± 0.07 (0.432) | 0.70 ± 0.08 (0.996) | 0.73 ± 0.11 (0.869) | 0.73 ± 0.07 (0.869) | 0.76 ± 0.09 (0.678) | |||||
| Ginsenosides | Ginsenoside Content (mg/g) | ||||||||||
| RGE-HPC (p Value) | RGE-PVP (p Value) | RGE-PVPc (p Value) | RGE-P1500 (p Value) | RGE-P6000 (p Value) | |||||||
| PPD-type | GRb1 | 6.48 ± 1.31 (0.821) | 6.08 ± 1.06 (0.960) | 6.33 ± 0.89 (0.894) | 6.44 ± 0.64 (0.828) | 6.49 ± 1.29 (0.836) | |||||
| GRb2 | 3.12 ± 0.48 (0.793) | 2.96 ± 0.58 (0.998) | 3.24 ± 0.49 (0.640) | 3.25 ± 0.40 (0.622) | 2.98 ± 0.28 (0.978) | ||||||
| GRc | 3.31 ± 0.46 (0.943) | 3.46 ± 0.58 (0.859) | 3.40 ± 0.12 (0.918) | 3.53 ± 0.30 (0.740) | 3.62 ± 0.24 (0.678) | ||||||
| GRd | 1.87 ± 0.34 (0.767) | 1.69 ± 0.21 (0.906) | 1.75 ± 0.26 (0.978) | 1.72 ± 0.18 (0.973) | 1.82 ± 0.24 (0.878) | ||||||
| GRg3 | 3.76 ± 1.46 (0.941) | 3.67 ± 1.42 (0.888) | 3.89 ± 1.28 (0.981) | 3.59 ± 1.27 (0.840) | 3.89 ± 1.38 (0.980) | ||||||
| PPT-type | GRe | 1.68 ± 0.28 (0.925) | 1.74 ± 0.28 (0.924) | 1.74 ± 0.20 (0.939) | 1.81 ± 0.32 (0.796) | 1.71 ± 0.25 (0.995) | |||||
| GRg1 | 2.25 ± 0.51 (0.758) | 2.18 ± 0.39 (0.869) | 2.13 ± 0.27 (0.954) | 2.22 ± 0.38 (0.793) | 2.16 ± 0.39 (0.910) | ||||||
| GRh1 | 0.77 ± 0.13 (0.653) | 0.78 ± 0.07 (0.565) | 0.73 ± 0.08 (0.810) | 0.77 ± 0.05 (0.611) | 0.74 ± 0.10 (0.831) | ||||||
| Formulation | Parameters | GRb1 | GRb2 | GRc | GRd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGE | Cmax (ng/mL) | 9.5 ± 0.9 | 5.4 ± 1.7 | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 3.2 ± 1.4 |
| Tmax (h) | 5.0 ± 2.0 | 4.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 2.3 | 6.0 ± 2.3 | |
| AUC48h (ng × h/mL) | 222.5 ± 53.7 | 127.7 ± 31.6 | 138.6 ± 30.3 | 68.6 ± 33.4 | |
| t1/2 (h) | 16.1 ± 1.5 | 21.7 ± 3.6 | 19.2 ± 0.8 | 25.6 ± 16.4 | |
| MRT (h) | 16.8 ± 1.1 | 17.9 ± 0.9 | 16.9 ± 0.5 | 16.2 ± 1.0 | |
| RGE-SiO2 | Cmax (ng/mL) | 15.5 ± 1.9 * | 8.1 ± 2.1 * | 10.5 ± 1.9 * | 5.5 ± 2.6 * |
| Tmax (h) | 5.0 ± 2.0 | 5.0 ± 2.0 | 5.0 ± 2.0 | 7.0 ± 2.0 | |
| AUC48h (ng × h/mL) | 363.8 ± 78.7 * | 209.5 ± 57.7 * | 253.5 ± 65.2 * | 115.0 ± 50.7 * | |
| t1/2 (h) | 20.1 ± 4.2 | 24.9 ± 4.1 | 21.3 ± 2.8 | 28.9 ± 22.0 | |
| MRT (h) | 17.3 ± 0.7 | 19.1 ± 0.6 | 18.2 ± 0.6 | 16.6 ± 0.6 | |
| Relative BA (%) | 163.5 | 164.1 | 182.9 | 167.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.; Lee, C.H.; Lim, D.Y.; Lee, J.; Park, S.-J.; Song, I.-S.; Choi, M.-K. Improved Hygroscopicity and Bioavailability of Solid Dispersion of Red Ginseng Extract with Silicon Dioxide. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071022
Jin S, Lee CH, Lim DY, Lee J, Park S-J, Song I-S, Choi M-K. Improved Hygroscopicity and Bioavailability of Solid Dispersion of Red Ginseng Extract with Silicon Dioxide. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071022
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Sojeong, Chul Haeng Lee, Dong Yu Lim, Jaehyeok Lee, Soo-Jin Park, Im-Sook Song, and Min-Koo Choi. 2021. "Improved Hygroscopicity and Bioavailability of Solid Dispersion of Red Ginseng Extract with Silicon Dioxide" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071022
APA StyleJin, S., Lee, C. H., Lim, D. Y., Lee, J., Park, S.-J., Song, I.-S., & Choi, M.-K. (2021). Improved Hygroscopicity and Bioavailability of Solid Dispersion of Red Ginseng Extract with Silicon Dioxide. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071022







