Two Novel PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Endothelial Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) Targeting
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis
2.1.1. General Considerations
2.1.2. Synthesis of MacroP
2.1.3. Synthesis of NAMP
2.2. Radiochemistry
2.2.1. General Considerations
2.2.2. Radiolabeling
2.3. In Vitro Tests
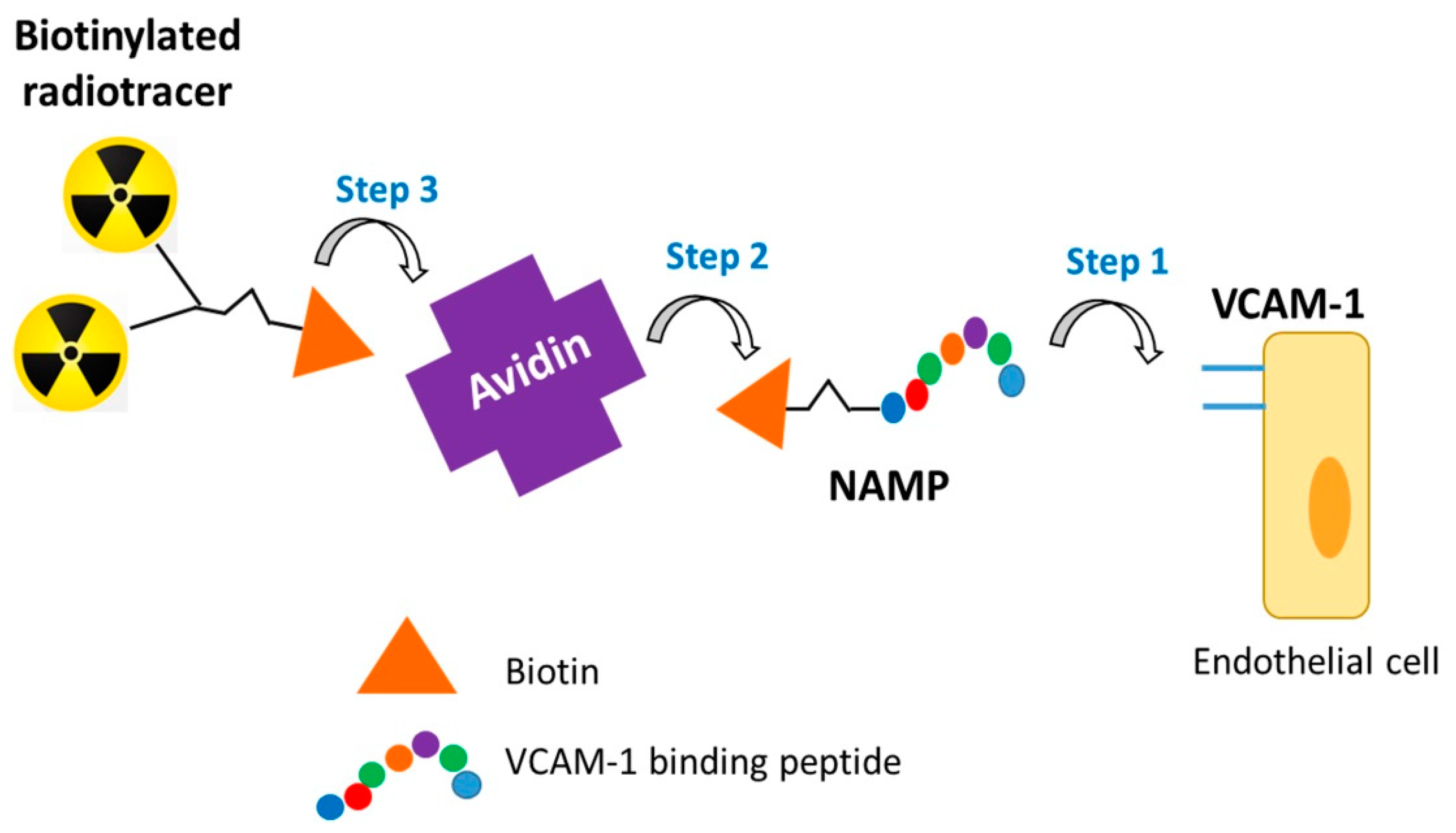
2.3.1. NAMP–Avidin Binding
2.3.2. NAMP–Avidin–BisDOTA Complex Formation
2.3.3. NAMP–Avidin–68Ga-BisDOTA Complex Formation
2.3.4. Cell Culture
2.3.5. In Vitro Test of 68Ga-MacroP on HUVEC
2.3.6. In Vitro Test of NAMP–avidin–68Ga-BisDOTA on HUVEC
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of MacroP and NAMP
3.1.1. Synthesis and Characterization of MacroP
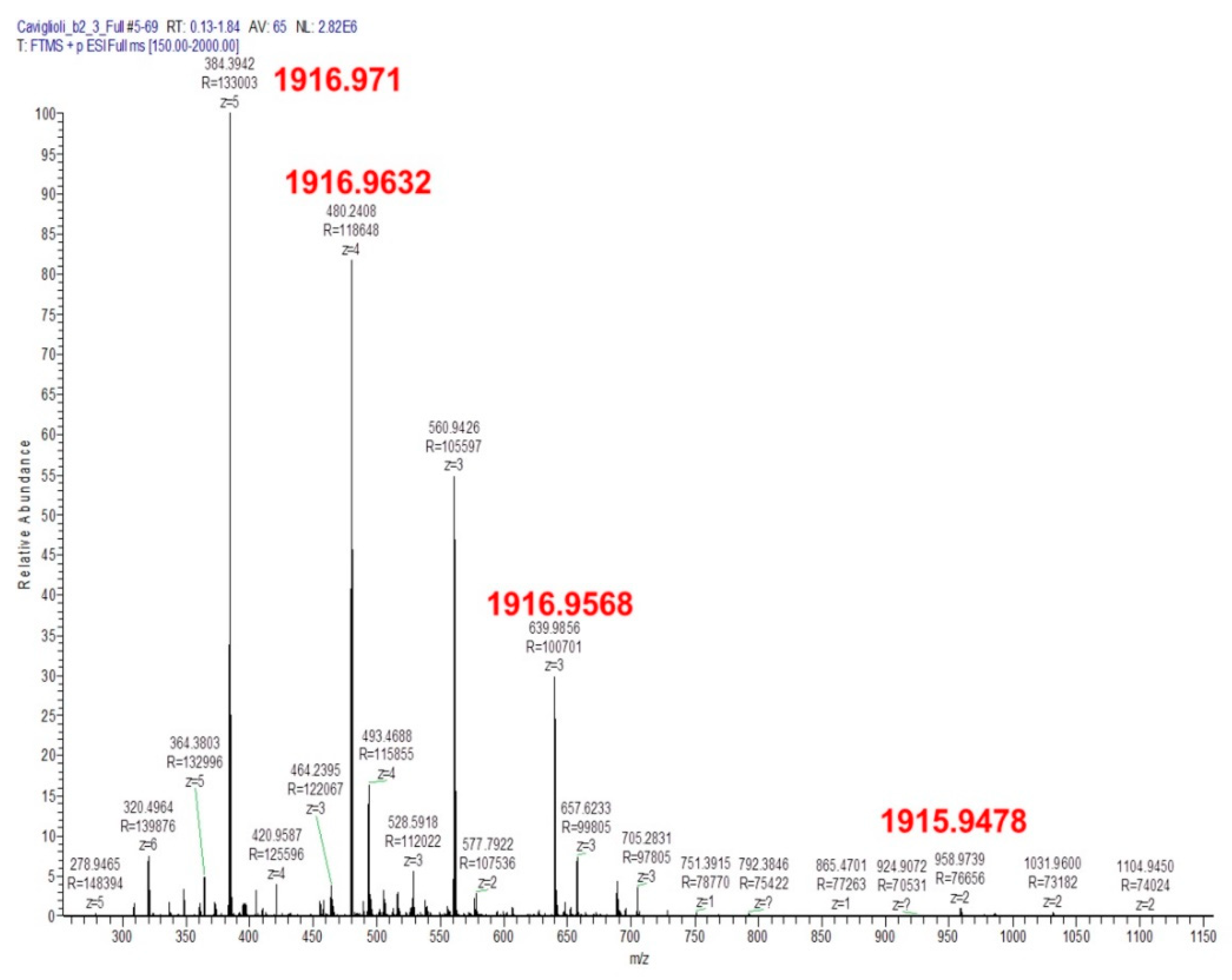
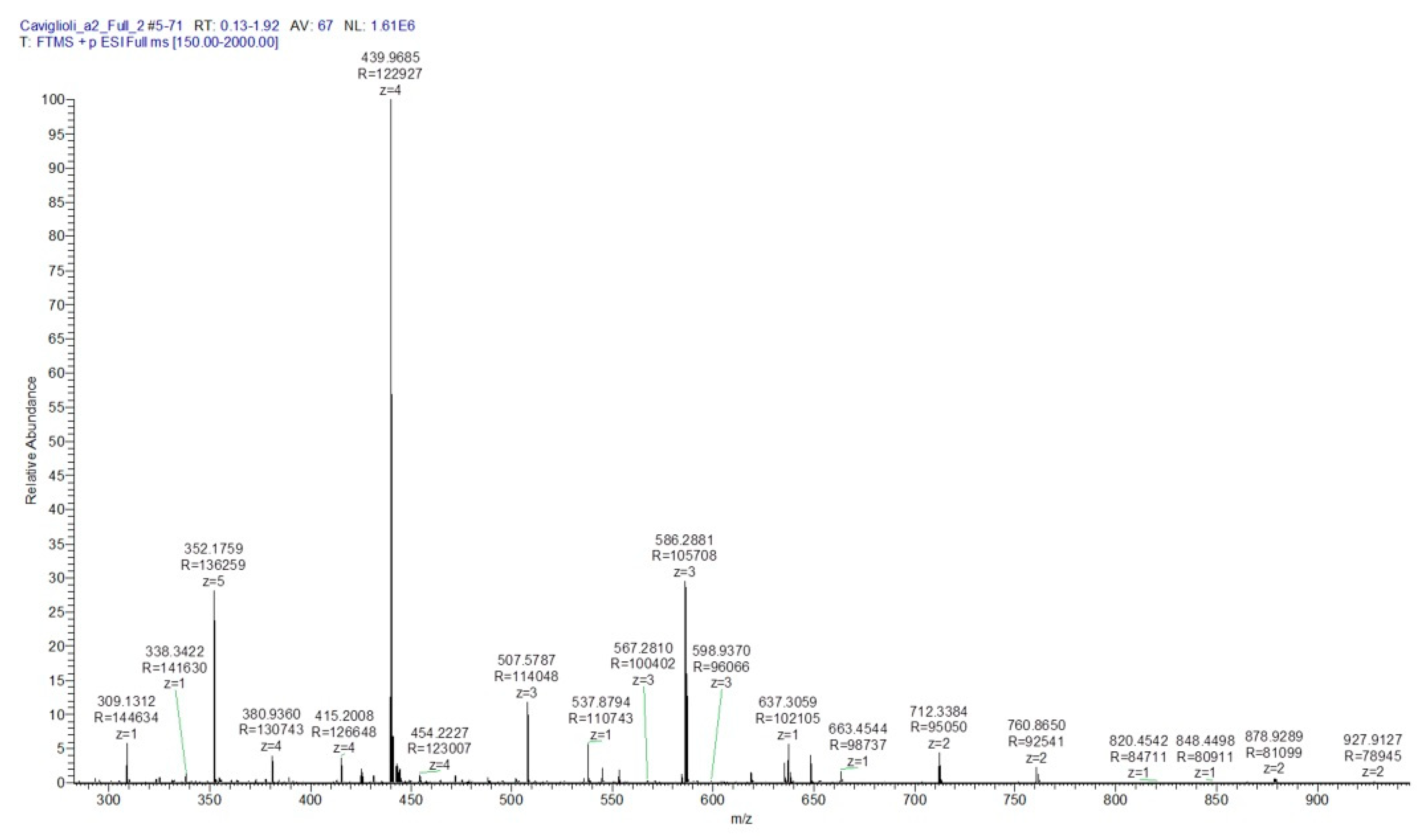
3.1.2. Synthesis and Characterization of NAMP and Precursors
3.2. Radiochemistry
3.2.1. Radiolabeling of MacroP
3.2.2. Radiolabeling of BisDOTA
3.3. In Vitro Tests
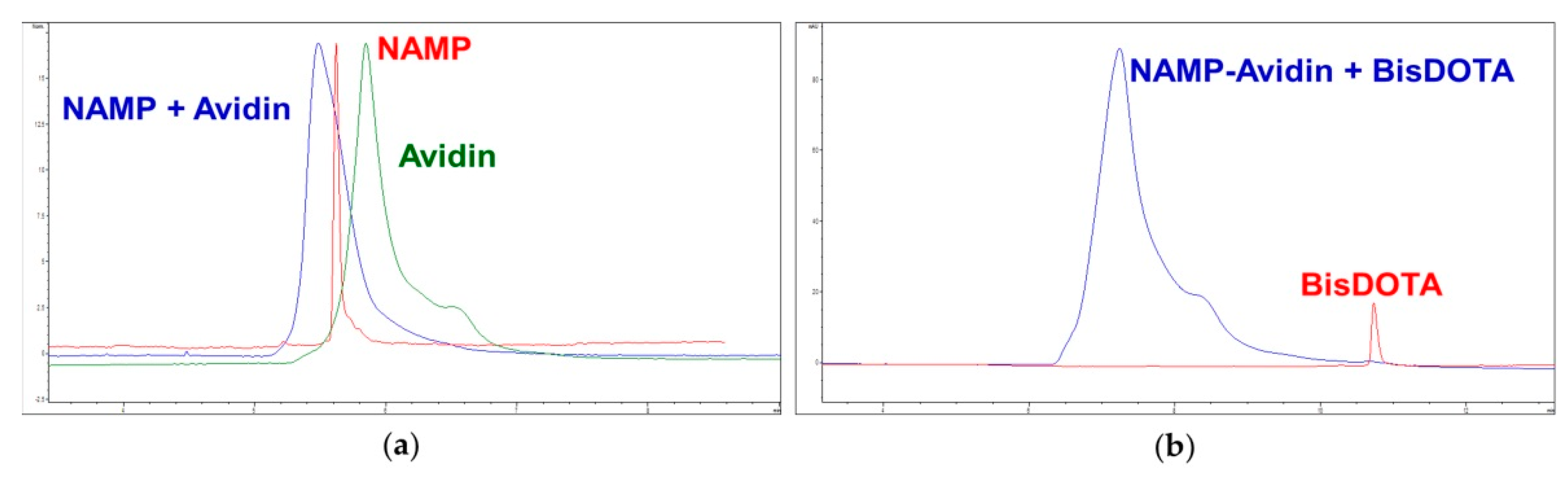
3.3.1. NAMP–avidin and NAMP–avidin–BisDOTA Complex Formation
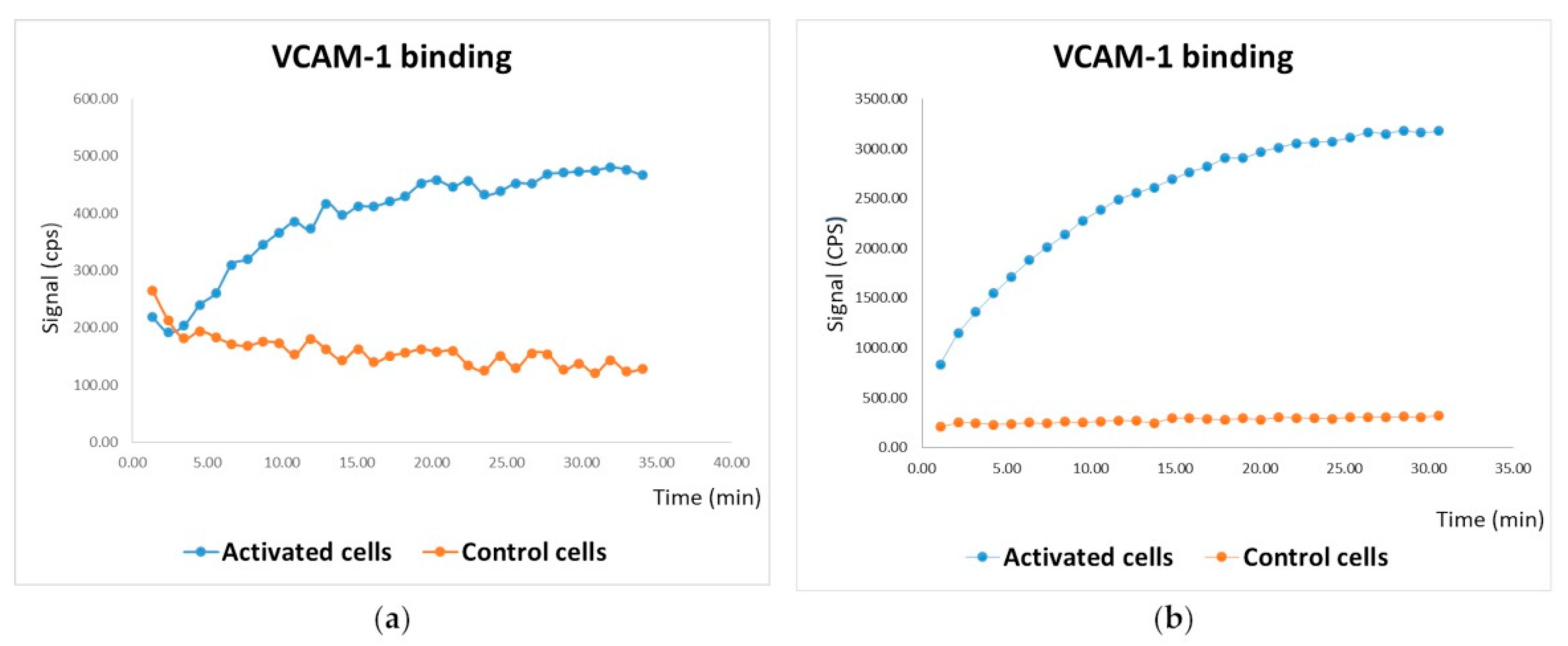
3.3.2. In Vitro Tests on HUVEC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barquera, S.; Pedroza-Tobias, A.; Medina, C.; Hernandez-Barrera, L.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Lozano, R.; Moran, A.E. Global overview of the epidemiology of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2015, 46, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkina, E.; Ley, K. Vascular adhesion molecules in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2292–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cybulsky, M.I.; Gimbrone, M.A. Endothelial expression of a mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecule during atherogenesis. Science 1991, 251, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osborn, L.; Hession, C.; Tizard, R.; Vassallo, C.; Luhowskyj, S.; Chirosso, G.; Lobb, R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell 1989, 59, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulsky, M.I.; Iiyama, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, S.; Chen, M.; Iiyama, M.; Davis, V.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Connelly, P.W.; Milstone, D.S. A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2001, 107, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ailuno, G.; Baldassari, S.; Zuccari, G.; Schlich, M.; Caviglioli, G. Peptide-based nanosystems for vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 targeting: A real opportunity for therapeutic and diagnostic agents in inflammation associated disorders. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailuno, G.; Zuccari, G.; Baldassari, S.; Lai, F.; Caviglioli, G. Anti-Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 nanosystems: A promising strategy against inflammatory based diseases. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2021, 21, 2793–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asati, S.; Pandey, V.; Soni, V. RGD peptide as a targeting moiety for theranostic purpose: An update study. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.A.; Nahrendorf, M.; Yu, A.M.; Reynolds, F.; Weissleder, R. In vivo phage display selection yields atherosclerotic plaque targeted peptides for imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2006, 8, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altai, M.; Membreno, R.; Cook, B.; Tolmachev, V.; Zeglis, B.M. Pretargeted Imaging and Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhoeven, M.; Seimbille, Y.; Dalm, S.U. Therapeutic Applications of Pretargeting. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paganelli, G.; Chinol, M. Radioimmunotherapy: Is avidin-biotin pretargeting the preferred choice among pretargeting methods? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caviglioli, G.; Chinol, M.; Baldassari, S.; Garaboldi, L.; Zuccari, G.; Petretto, A.; Drava, G.; Sinico, C.; Paganelli, G. A new microdispersed albumin derivative potentially useful for radio-guided surgery of occult breast cancer lesions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Ngai, M.H.; Song, Z.Y.; MarcAry, P.A.; Hobley, J.; Lear, M.J. Practical synthesis of maleimides and coumarin-linked probes for protein and antibody labelling via reduction of native disulfides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 3400–3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratesi, A.; Bucelli, F.; Mori, I.; Chinol, M.; Verdoliva, A.; Paganelli, G.; Rivieccio, V.; Gariboldi, L.; Ginanneschi, M. Biotin derivatives carrying two chelating DOTA units. Synthesis, in vitro evaluation of biotinidases resistance, avidin binding, and radiolabeling tests. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cossu, V.; Marini, C.; Piccioli, P.; Rocchi, A.; Bruno, S.; Orengo, A.M.; Emionite, L.; Bauckneht, M.; Grillo, F.; Capitanio, S.; et al. Obligatory role of endoplasmic reticulum in brain FDG uptake. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1184–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalecki, W. Synthesis of norbiotinamine and its derivatives. Bioconjug. Chem. 1996, 7, 2780–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailuno, G.; Baldassari, S.; Zuccari, G.; Di Francesco, V.; Decuzzi, P.; Caviglioli, G. Poster Communication. In Proceedings of the NanoInnovation 2020 Conference, Rome, Italy, 15–18 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Storch, D.; Schmitt, J.S.; Waldherr, C.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. Preclinical evaluation of somatostatin analogs bearing two macrocyclic chelators for high specific activity labeling with radiometals. Radiochim. Acta 2007, 95, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.L.; Xiong, C.Y.; Zhou, M.; Lu, W.; Huang, Q.; Ku, G.; Zhao, J.; Flores, L.G.; Ni, Y.C.; Li, C. Small-Animal PET of Tumor Damage Induced by Photothermal Ablation with Cu-64-Bis-DOTA-Hypericin. J. Nucl. Med. 2011, 52, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prinsen, K.; Cona, M.M.; Cleynhens, J.; Vanbilloen, H.; Li, J.J.; Dyubankova, N.; Lescrinier, E.; Bormans, G.; Ni, Y.C.; Verbruggen, A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 68Ga labeled bis-DOTA-3,3′-(benzylidene)-bis-(1H-indole-2-carbohydrazide) as a PET tracer for in vivo visualization of necrosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3216–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafer, D.E.; Inman, J.K.; Lees, A. Reaction of Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine (TCEP) with maleimide and α-haloacyl groups: Anomalous elution of TCEP by gel filtration. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 282, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tyagarajan, K.; Pretzer, E.; Wiktorowicz, J.E. Thiol-reactive dyes for fluorescence labeling of proteomic samples. Electrophoresis 2003, 24, 2348–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.P.; Podgórski, M.; Chatani, S.; Gong, T.; Xi, W.; Fenoli, C.R.; Bowman, C.N. The thiol-Michael addition click reaction: A powerful and widely used tool in materials chemistry. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 724–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantner, T.; Watts, A.G. Characterization of reactions between water-soluble trialkylphosphines and thiol alkylating reagents: Implications for protein-conjugation reactions. Bioconj. Chem. 2016, 27, 2400–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chinol, M.; Casalini, P.; Maggiolo, M.; Canevari, S.; Omodeo, E.S.; Caliceti, P.; Veronese, F.M.; Cremonesi, M.; Chiolerio, F.; Nardone, E.; et al. Biochemical modifications of avidin improve pharmacokinetics and biodistribution, and reduce immunogenicity. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, A.; Barve, A.; Zhao, Z.; Jin, W.; Cheng, K. Comparison of avidin, neutravidin, and streptavidin as nanocarriers for efficient siRNA delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pastorino, S.; Baldassari, S.; Ailuno, G.; Zuccari, G.; Drava, G.; Petretto, A.; Cossu, V.; Marini, C.; Alfei, S.; Florio, T.; et al. Two Novel PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Endothelial Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) Targeting. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071025
Pastorino S, Baldassari S, Ailuno G, Zuccari G, Drava G, Petretto A, Cossu V, Marini C, Alfei S, Florio T, et al. Two Novel PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Endothelial Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) Targeting. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071025
Chicago/Turabian StylePastorino, Sara, Sara Baldassari, Giorgia Ailuno, Guendalina Zuccari, Giuliana Drava, Andrea Petretto, Vanessa Cossu, Cecilia Marini, Silvana Alfei, Tullio Florio, and et al. 2021. "Two Novel PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Endothelial Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) Targeting" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071025
APA StylePastorino, S., Baldassari, S., Ailuno, G., Zuccari, G., Drava, G., Petretto, A., Cossu, V., Marini, C., Alfei, S., Florio, T., Sambuceti, G., & Caviglioli, G. (2021). Two Novel PET Radiopharmaceuticals for Endothelial Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) Targeting. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1025. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071025











