Water-in-Oil Nano-Emulsions Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification: New Insights on the Formulation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials
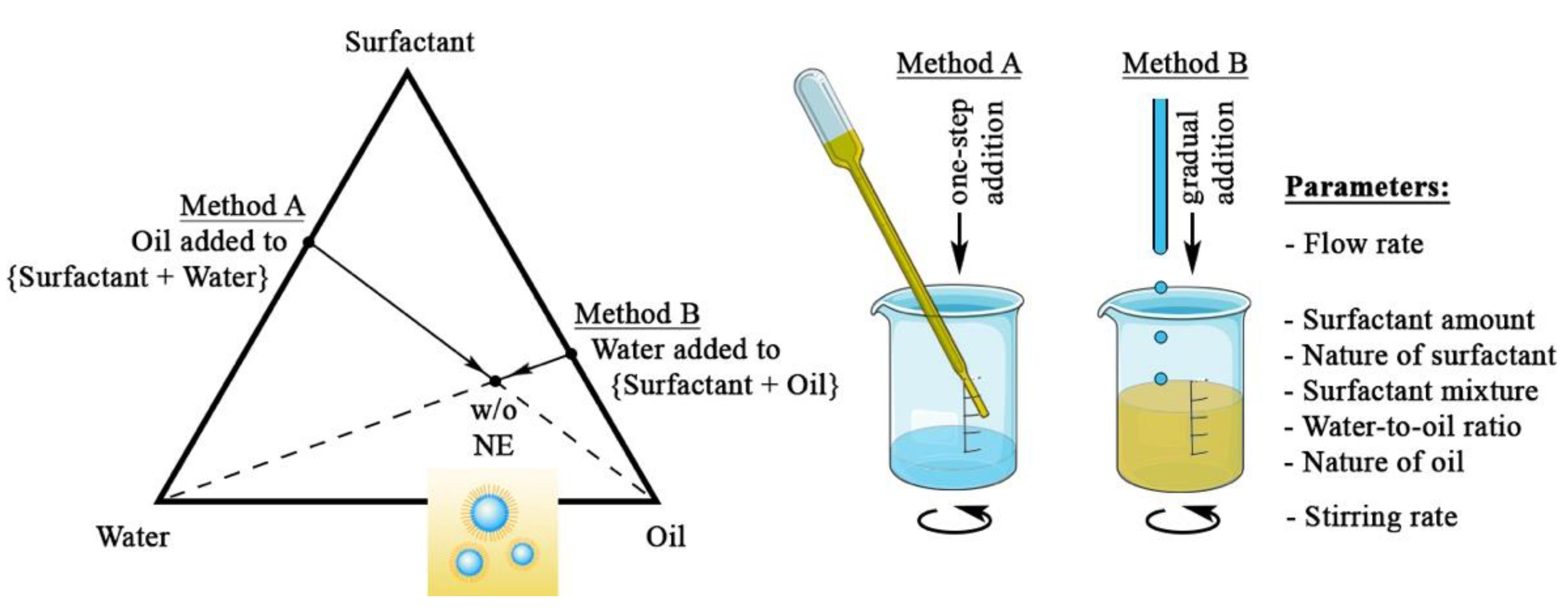
2.2. Methodology
2.3. Dynamic Light Scattering
3. Results and Discussion
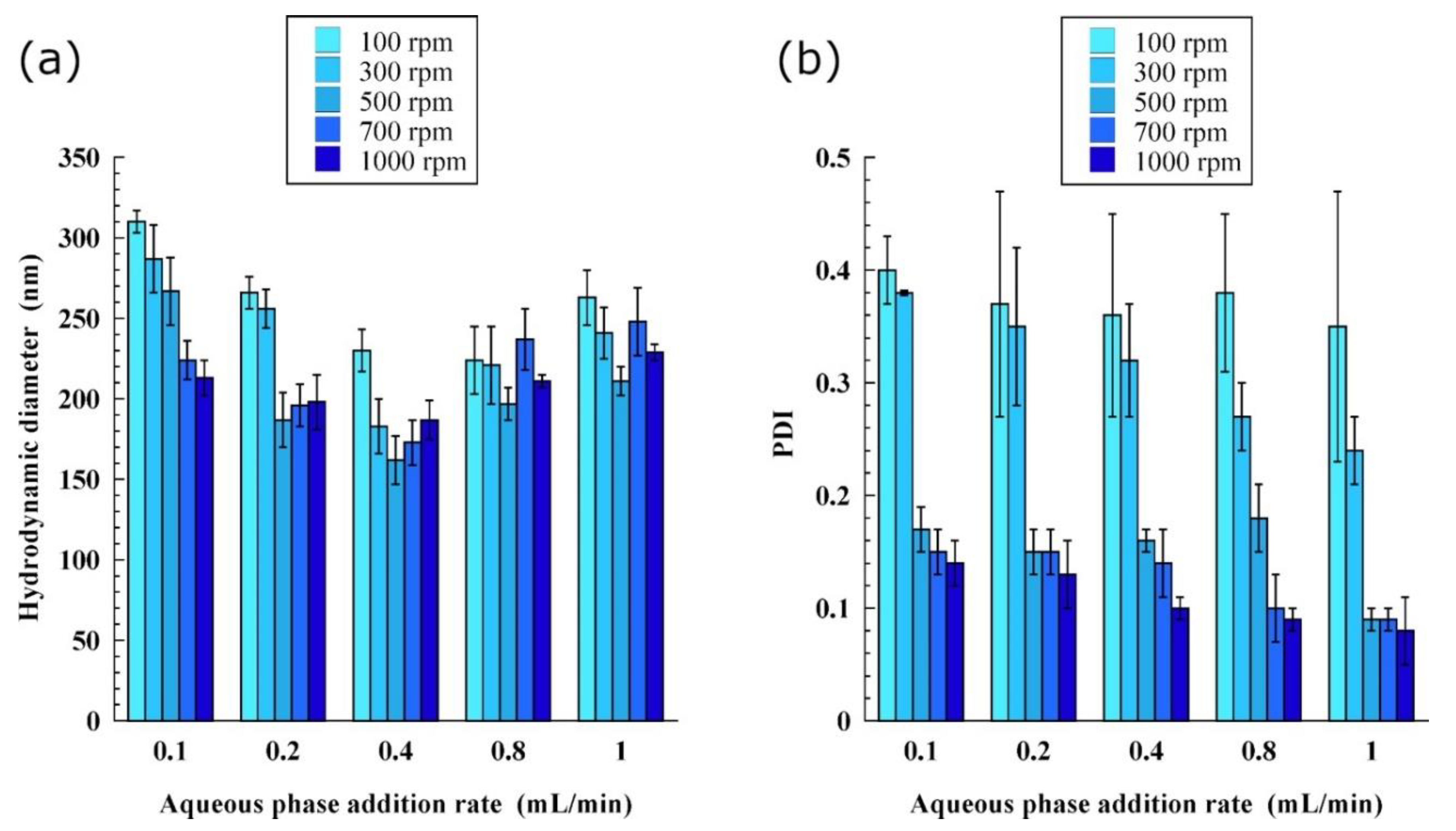
3.1. Impact of the Process Parameters
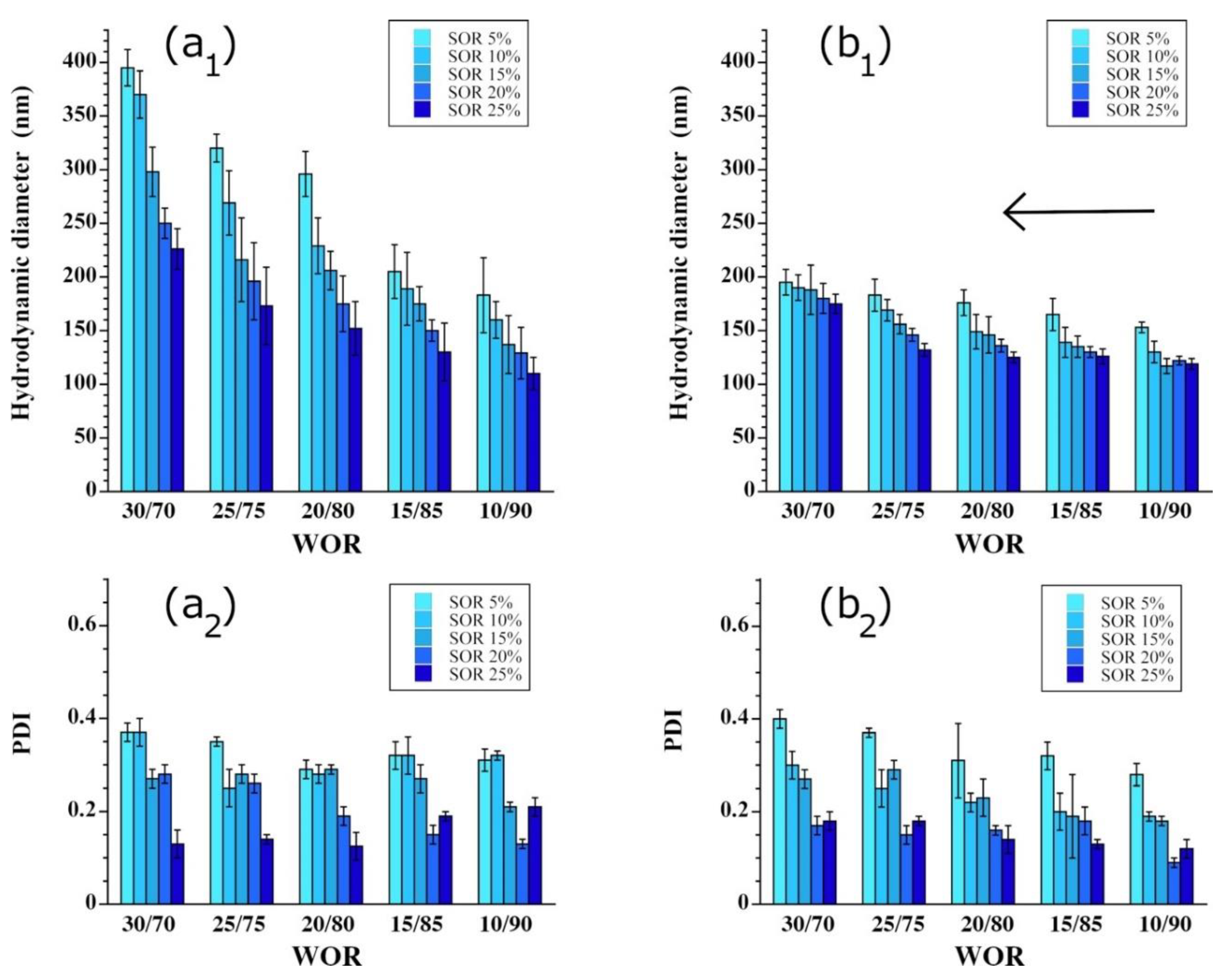
3.2. Impacts of the Surfactant-to-Oil Ratio, the Nature of Surfactants, and the Surfactant Mixture
3.3. Impact of the Surfactant Mixture
3.4. Impact of the Fraction of the Disperse Aqueous Phase
3.5. Impact of the Nature of the Oil
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, H.; Webster, T.J. Nanomedicine for implants: A review of studies and necessary experimental tools. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 354–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Siddiqui, F.A. Nanomedicine and drug delivery: A mini review. Int. Nano Lett. 2014, 4, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, D.; Chen, H.; Du, D.; Mao, C.; Wan, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Hydrogel-thickened nanoemulsion system for topical delivery of lipophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 353, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ramachandran, C.; Weiner, N.D.; Roessler, B.J. Topical transport of hydrophilic compounds using water-in-oil nanoemulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 220, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Mojzisova, H.; Porcher, E.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Reverse micelle-loaded lipid nano-emulsions: New technology for nano-encapsulation of hydrophilic materials. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrignaud, S.; Anton, N.; Gayet, P.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Reverse micelle-loaded lipid nanocarriers: A novel drug delivery system for the sustained release of doxorubicin hydrochloride. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, S.; Anton, N.; Akram, S.; Er-Rafik, M.; Anton, H.; Klymchenko, A.; Yu, W.; Vandamme, T.F.T.F.; Serra, C.A.C.A. A new method for the formulation of double nanoemulsions. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.; Serra, C.A.; Vandamme, T.F.; Yu, W.; Anton, N. Double emulsions prepared by two–step emulsification: History, state-of-the-art and perspective. J. Control. Release 2019, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, S.; Wang, X.; Vandamme, T.F.; Collot, M.; Rehman, A.U.; Messaddeq, N.; Mély, Y.; Anton, N. Toward the Formulation of Stable Micro and Nano Double Emulsions through a Silica Coating on Internal Water Droplets. Langmuir 2019, 35, 2313–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, M.; Dudhe, R.; Sharma, P.K. Nanoemulsion: An advanced mode of drug delivery system. 3 Biotech 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouchemal, K.; Briançon, S.; Perrier, E.; Fessi, H. Nano-emulsion formulation using spontaneous emulsification: Solvent, oil and surfactant optimisation. Int. J. Pharm. 2004, 280, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donsì, F. Chapter 11—Applications of Nanoemulsions in Foods. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 349–377. ISBN 978-0-12-811838-2. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, Z.; McClements, D.J.; Jafari, S.M. Chapter 12—Application of Nanoemulsions in Formulation of Pesticides. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 379–413. ISBN 978-0-12-811838-2. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, K.; Pattnaik, S.; Swain, K. Chapter 13—Application of Nanoemulsions in Drug Delivery. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 415–433. ISBN 978-0-12-811838-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sonneville-Aubrun, O.; Yukuyama, M.N.; Pizzino, A. Chapter 14—Application of Nanoemulsions in Cosmetics. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 435–475. ISBN 978-0-12-811838-2. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Espí, R.; Álvarez-Bermúdez, O. Chapter 15—Application of Nanoemulsions in the Synthesis of Nanoparticles. In Nanoemulsions; Jafari, S.M., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 477–515. ISBN 978-0-12-811838-2. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsions versus microemulsions: Terminology, differences, and similarities. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.F. Nano-Emulsions; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 9783319153384. [Google Scholar]
- Anton, N.; Benoit, J.-P.; Saulnier, P. Design and production of nanoparticles formulated from nano-emulsion templates-A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 128, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooster, T.J.; Golding, M.; Sanguansri, P. Impact of Oil Type on Nanoemulsion Formation and Ostwald Ripening Stability. Langmuir 2008, 24, 12758–12765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, P. Ostwald ripening in emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 75, 107–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welin-Berger, K.; Bergenståhl, B. Inhibition of Ostwald ripening in local anesthetic emulsions by using hydrophobic excipients in the disperse phase. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 200, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadros, T.; Izquierdo, P.; Esquena, J.; Solans, C. Formation and stability of nano-emulsions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 108–109, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solans, C.; Solé, I. Nano-emulsions: Formation by low-energy methods. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 17, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Akram, S.; Vandamme, T.F. Transitional Nanoemulsification Methods. Nanoemulsions 2018, 77–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulotta, A.; Saberi, A.H.; Nicoli, M.C.; McClements, D.J. Nanoemulsion-Based Delivery Systems for Polyunsaturated (ω-3) Oils: Formation Using a Spontaneous Emulsification Method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Badruddoza, Z.; Doyle, P.S. A General Route for Nanoemulsion Synthesis using Low Energy Methods at Constant Temperature. Langmuir 2017, 33, 7118–7123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttoff, M.; Saberi, A.H.; McClements, D.J. Formation of vitamin D nanoemulsion-based delivery systems by spontaneous emulsification: Factors affecting particle size and stability. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrnia, M.-A.; Jafari, S.-M.; Makhmal-Zadeh, B.S.; Maghsoudlou, Y. Crocin loaded nano-emulsions: Factors affecting emulsion properties in spontaneous emulsification. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 84, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.F. The universality of low-energy nano-emulsification. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 377, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, N.; Vandamme, T.F. Nano-emulsions and micro-emulsions: Clarifications of the critical differences. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahtz, J.; Gunes, D.Z.; Syrbe, A.; Mosca, N.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Quantification of Spontaneous W/O Emulsification and its Impact on the Swelling Kinetics of Multiple W/O/W Emulsions. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5787–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owusu Apenten, R.K.; Zhu, Q.-H. Interfacial parameters for selected Spans and Tweens at the hydrocarbon—water interface. Food Hydrocoll. 1996, 10, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Patra, A. Cadmium Sulfide Aggregates through Reverse Micelles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marze, S. Relaxation Processes of PGPR at the Water/Oil Interface Inferred by Oscillatory or Transient Viscoelasticity Measurements. Langmuir 2009, 25, 12066–12072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients—7th Edition. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2013, 18, 544. [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akram, S.; Anton, N.; Omran, Z.; Vandamme, T. Water-in-Oil Nano-Emulsions Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification: New Insights on the Formulation Process. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071030
Akram S, Anton N, Omran Z, Vandamme T. Water-in-Oil Nano-Emulsions Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification: New Insights on the Formulation Process. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071030
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkram, Salman, Nicolas Anton, Ziad Omran, and Thierry Vandamme. 2021. "Water-in-Oil Nano-Emulsions Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification: New Insights on the Formulation Process" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071030
APA StyleAkram, S., Anton, N., Omran, Z., & Vandamme, T. (2021). Water-in-Oil Nano-Emulsions Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification: New Insights on the Formulation Process. Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1030. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071030








