Meta-Analysis of Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Efflux Transporter Substrate Drugs: Does Delayed Gastric Emptying Influence Drug Transport Kinetics?
Abstract
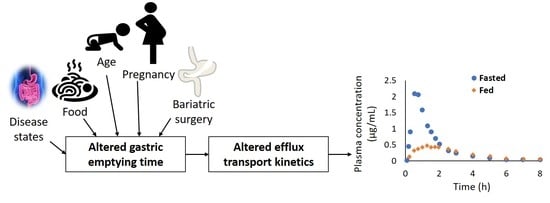
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Physicochemical, Biochemical, and Plasma Concentration Data for Drugs with Reported Clinical Food-Effect Studies
2.2. Identification of Solubility- and Permeability-Limited Drugs
2.3. Stratification of Drugs Based on Transport Saturation Index
2.4. Effect of Efflux Transport Saturation on Food-Effect for Permeability-Limited Drugs
2.5. Impact of High- versus Low-Fat Diets on Drug Absorption
3. Results
3.1. Stratification of Drugs Based on the Food-Effect Magnitude
Association of Efflux Transport Saturation on Food-Effect for Solubility- and Permeability-Limited Drugs
3.2. Impact of High-Fat versus Low-Fat Diets on Drug Absorption
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fuentes, A.; Pineda, M.; Venkata, K. Comprehension of Top 200 Prescribed Drugs in the US as a Resource for Pharmacy Teaching, Training and Practice. Pharmacy 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleisher, D.; Li, C.; Zhou, Y.; Pao, L.-H.; Karim, A. Drug, Meal and Formulation Interactions Influencing Drug Absorption after Oral Administration. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 36, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, E.L.; Budach, W.; Adamson, P.C.; Pitot, H.C.; Balis, F.M.; Rubin, J.; Murphy, R.F.; Poplack, D.G. Variability in the Oral Bioavailability of All-Trans-Retinoic Acid. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 49, 993–996. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhao, P.; Pan, Y.; Wagner, C. Predictive Performance of Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models for the Effect of Food on Oral Drug Absorption: Current Status. CPT:PSP 2018, 7, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Mojaverian, P.; Doedée, M.; Lin, E.; Weinryb, I.; Chiang, S.T.; Kowey, P.R. Bioavailability of Amiodarone Tablets Administered with and without Food in Healthy Subjects. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001, 87, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melander, A.; Brante, G.; Johansson, O.; Lindberg, T.; Wahlin-Boll, E. Influence of Food on the Absorption of Phenytoin in Man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1979, 15, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peloquin, C.A.; Namdar, R.; Singleton, M.D.; Nix, D.E. Pharmacokinetics of Rifampin under Fasting Conditions, with Food, and with Antacids. Chest 1999, 115, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekersky, I.; Dressler, D.; Mekki, Q.A. Effect of Low-and High-Fat Meals on Tacrolimus Absorption Following 5 Mg Single Oral Doses to Healthy Human Subjects. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 41, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidery, M.B.; Macdonald, I.A.; Blackshaw, P.E. Superior Mesenteric Artery Blood Flow and Gastric Emptying in Humans and the Differential Effects of High Fat and High Carbohydrate Meals. Gut 1994, 35, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cvijić, S.; Parojčić, J.; Langguth, P. Viscosity-Mediated Negative Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Poorly-Permeable Drugs with an Absorption Window in the Proximal Intestine: In Vitro Experimental Simulation and Computational Verification. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 61, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charman, W.N.; Porter, C.J.H.; Mithani, S.; Dressman, J.B. Physicochemical and Physiological Mechanisms for the Effects of Food on Drug Absorption: The Role of Lipids and PH. J. Pharm. Sci. 1997, 86, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marciani, L.; Cox, E.F.; Hoad, C.L.; Totman, J.J.; Costigan, C.; Singh, G.; Shepherd, V.; Chalkley, L.; Robinson, M.; Ison, R.; et al. Effects of Various Food Ingredients on Gall Bladder Emptying. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 1182–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abiru, H.; Sarna, S.K.; Condon, R.E. Contractile Mechanisms of Gallbladder Filling and Emptying in Dogs. Gastroenterology 1994, 106, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshitsugu, R.; Kikuchi, K.; Iwaya, H.; Fujii, N.; Hori, S.; Lee, D.G.; Ishizuka, S. Alteration of Bile Acid Metabolism by a High-Fat Diet Is Associated with Plasma Transaminase Activities and Glucose Intolerance in Rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mclean, A.J.; Mcnamara, P.J.; Dusouich, P.; Gibaldi, M.; Lalka, D.; Buffalo, N.Y. Food, Splanchnic Blood Flow, and Bioavailability of Drugs Subject to First-Pass Metabolism. Clin. Pharmacal. Ther. 1978, 24, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, C.K.; Edwards, D.J.; Mauriello, P.M.; Barde, S.H.; Foster, A.C.; Lanc, R.A.; Middleton, E.; Lalka, D. Effect of Food on Hepatic Blood Flow: Implications in the “Food Effect” Phenomenon. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1983, 34, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.Z.; Jang, G.R.; Tsunoda, S. Dietary Effects on Drug Metabolism and Transport. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 1071–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Guidance for Industry—Food-Effect Bioavailability and Fed Bioequivalence Studies. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/food-effect-bioavailability-and-fed-bioequivalence-studies (accessed on 5 August 2020).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER). Guidance for Industry—Assessing the Effects of Food on Drugs in INDs and NDAs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/assessing-effects-food-drugs-inds-and-ndas-clinical-pharmacology-considerations (accessed on 4 August 2020).
- Zhang, T.; Wells, E. A Review of Current Methods for Food Effect Prediction during Drug Development. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2020, 10, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S. The Use of Biorelevant Dissolution Media to Forecast the in Vivo Performance of a Drug. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bagchus, W.M.; Hust, R.; Maris, F.; Schnabel, P.G.; Houwing, N.S. Important Effect of Food on the Bioavailability of Oral Testosterone Undecanoate. Pharmacotherapy 2003, 23, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, R.H.; Turner, D.B.; Neuhoff, S.; Jamei, M. Incorporation of the Time-Varying Postprandial Increase in Splanchnic Blood Flow into a PBPK Model to Predict the Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics of Orally Administered High-Extraction Drugs. AAPS J. 2017, 19, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, J.M.; Wu, C.Y.; Benet, L.Z. Predicting Drug Disposition, Absorption/Elimination/Transporter Interplay and the Role of Food on Drug Absorption. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 717–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingels, F.; Deferme, S.; Destexhe, E.; Oth, M.; van den Mooter, G.; Augustijns, P. Simulated Intestinal Fluid as Transport Medium in the Caco-2 Cell Culture Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 232, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lown, K.S.; Bailey, D.G.; Fontana, R.J.; Janardan, S.K.; Adair, C.H.; Fortlage, L.A.; Brown, M.B.; Guo, W.; Watkins, P.B. Grapefruit Juice Increases Felodipine Oral Availability in Humans by Decreasing Intestinal CYP3A Protein Expression. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, J.S.; Donovan, J.L.; Lindsay Devane, C.; Taylor, R.M.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, J.-S.; Chavin, K.D. Effect of St John’s Wort on Drug Metabolism by Induction of Cytochrome P450 3A4 Enzyme. JAMA 2003, 290, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, U.; Seemann, D.; Oertel, R.; Miehlke, S.; Kuhlisch, E.; Fromm, M.; Kim, R.; Bailey, D.; Kirch, W. Grapefruit Juice Ingestion Significantly Reduces Talinolol Bioavailability. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 77, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennernäs, H.; Regårdh, C.G. Evidence for an Interaction between the Beta-Blocker Pafenolol and Bile Salts in the Intestinal Lumen of the Rat Leading to Dose-Dependent Oral Absorption and Double Peaks in the Plasma Concentration-Time Profile. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresser, G.; Bailey, D.G.; Leake, B.F.; Schwarz, U.I.; Dawson, P.A.; Freeman, D.J.; Kim, R.B. Fruit Juices Inhibit Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide–Mediated Drug Uptake to Decrease the Oral Availability of Fexofenadine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 71, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pao, L.H.; Zhou, S.Y.; Cook, C.; Kararli, T.; Kirchhoff, C.; Truelove, J.; Karim, A.; Fleisher, D. Reduced Systemic Availability of an Antiarrhythmic Drug, Bidisomide, with Meal Co-Administration: Relationship with Region-Dependent Intestinal Absorption. Pharm. Res. 1998, 15, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koziolek, M.; Grimm, M.; Becker, D.; Iordanov, V.; Zou, H.; Shimizu, J.; Wanke, C.; Garbacz, G.; Weitschies, W. Investigation of PH and Temperature Profiles in the GI Tract of Fasted Human Subjects Using the Intellicap® System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, K.L.R.; Keppler, D.; Hoffmaster, K.A.; Bow, D.A.J.; Cheng, Y.; Lai, Y.; Palm, J.E.; Stieger, B.; Evers, R. In Vitro Methods to Support Transporter Evaluation in Drug Discovery and Development. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kosa, R.E.; Lazzaro, S.; Bi, Y.; Tierney, B.; Gates, D.; Modi, S.; Costales, C.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Tremaine, L.M.; Varma, M.V. Simultaneous Assessment of Transporter-Mediated Drug-Drug Interactions Using a Probe Drug Cocktail in Cynomolgus Monkey. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otsuka, K.; Wagner, C.; Selen, A.; Dressman, J. Prediction of In-Vivo Pharmacokinetic Profile for Immediate and Modified Release Oral Dosage Forms of Furosemide Using an in-Vitro-in-Silico-in-Vivo Approach. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, R.; Awadallah, A.; Sunoqrot, S.; Tarawneh, O.; Nazzal, S.; AlBaraghthi, T.; al Sayyad, J.; Abbas, A. PH-Dependent Solubility and Dissolution Behavior of Carvedilol-Case Example of a Weakly Basic BCS Class II Drug. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCrindle, J.L.; Li, T.C.; Wa, K.; Barron, W.; Prescott, L.F. Effect of Food on the Absorption of Frusemide and Bumetanide in Man. Br J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 42, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Löbenberg, R.; Amidon, G.L. Modern Bioavailability, Bioequivalence and Biopharmaceutics Classification System. New Scientific Approaches to International Regulatory Standards. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinarov, Z.; Abdallah, M.; Agundez, J.; Allegaert, K.; Basit, A.W.; Braeckmans, M.; Ceulemans, J.; Corsetti, M.; Griffin, B.; Grimm, M.; et al. Impact of Gastrointestinal Tract Variability on Oral Drug Absorption and Pharmacokinetics: An UNGAP Review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 162, 105812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziolek, M.; Alcaro, S.; Augustijns, P.; Basit, A.W.; Grimm, M.; Hens, B.; Hoad, C.L.; Jedamzik, P.; Madla, C.M.; Maliepaard, M.; et al. The Mechanisms of Pharmacokinetic Food-Drug Interactions—A Perspective from the UNGAP Group. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menssen, H.D.; Quinlan, M.; Kemp, C.; Tian, X. Relative Bioavailability and Food Effect Evaluation for 2 Tablet Formulations of Asciminib in a 2-Arm, Crossover, Randomized, Open-Label Study in Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2019, 8, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damle, B.; Ravandi, F.; Kaul, S.; Sonnichsen, D.; Ferreira, I.; Brooks, D.; Stewart, D.; Alberts, D.; Pazdur, R. Effect of Food on the Oral Bioavailability of UFT and Leucovorin in Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 517–523. [Google Scholar]
- Purkins, L.; Wood, N.; Kleinermans, D.; Greenhalgh, K.; Nichols, D. Effect of Food on the Pharmacokinetics of Multiple-Dose Oral Voriconazole. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karim, A. Effects of Food on the Bioavailability of Theophylline from Controlled-Release Products in Adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1986, 78, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, Y.; Jian, Z.; Li, Q.; Gong, L.; Tang, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M. Systematic Investigation of the Effects of Long-Term Administration of a High-Fat Diet on Drug Transporters in the Mouse Liver, Kidney and Intestine. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Kosugi, Y.; Hirabayashi, H.; Moriwaki, T. Impact of P-Glycoprotein on Intestinal Absorption of an Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein Antagonist in Rats: Mechanisms of Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics and Food Effects. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, K. Chapter 12: Food effect. In Biopharmaceutics Modeling and Simulations Biopharmaceutics Modeling and Simulations: Theory, Practice, Methods, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 379–411. [Google Scholar]
- Daublain, P.; Feng, K.-I.; Altman, M.D.; Martin, I.; Mukherjee, S.; Nofsinger, R.; Northrup, A.B.; Tschirret-Guth, R.; Cartwright, M.; Mcgregor, C. Analyzing the Potential Root Causes of Variability of Pharmacokinetics in Preclinical Species. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 1634–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Tran, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Seo, S.; Zhu, H.; Zou, P. Biliary Excretion-Mediated Food Effects and Prediction. AAPS J. 2020, 22, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swearingen, D.; Aronoff, G.M.; Ciric, S.; Lal, R. Pharmacokinetics of Immediate Release, Extended Release, and Gastric Retentive Gabapentin Formulations in Healthy Adults. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2018, 56, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tayman, C.; Rayyan, M.; Allegaert, K. Neonatal Pharmacology: Extensive Interindividual Variability despite Limited Size. J. Pediatric Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 16, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchelor, H. Influence of Food on Paediatric Gastrointestinal Drug Absorption Following Oral Administration: A Review. Children 2015, 2, 244–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, D.M.; Williams, O.A.; Magides, A.D.; Reilly, C.S. Gastric Emptying Is Delayed at 8–12 Weeks’ Gestation. Br. J. Anaesth. 1994, 73, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolas, J.M.; Bouzom, F.; Hugues, C.; Ungell, A.L. Oral Drug Absorption in Pediatrics: The Intestinal Wall, Its Developmental Changes and Current Tools for Predictions. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2017, 38, 209–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimann, G. Enteral Absorption and Bioavailability in Children in Relation to Age. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1980, 18, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effinger, A.; O’Driscoll, C.M.; McAllister, M.; Fotaki, N. Impact of Gastrointestinal Disease States on Oral Drug Absorption-Implications for Formulation Design-a PEARRL Review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 674–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaffer, J.A.; Williams, S.E.; Turnberg, L.A.; Houston, J.B.; Rowland, M. Absorption of Prednisolone in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Gut 1983, 24, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt, S.; Heading, R.C.; Clements, J.A.; Tothill, P.; Prescott, L.F. Acetaminophen Absorption and Metabolism in Celiac Disease and Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1981, 30, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darwich, A.S.; Henderson, K.; Burgin, A.; Ward, N.; Whittam, J.; Ammori, B.J.; Ashcroft, D.M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Trends in Oral Drug Bioavailability Following Bariatric Surgery: Examining the Variable Extent of Impact on Exposure of Different Drug Classes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 74, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nóbrega, A.C.M.; Ferreira, B.R.S.; Oliveira, G.J.; Sales, K.M.O.; Santos, A.A.; Nobre e Souza, M.Â.; Braga, L.L.B.C.; de Almeida Troncon, L.A.E.; Souza, M.H.L.P. Dyspeptic Symptoms and Delayed Gastric Emptying of Solids in Patients with Inactive Crohn’s Disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Groups | Cmax Change (%) * | AUC Change (%) * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Median | 95% CI ⱡ | Mean | Median | 95% CI ⱡ | |
| Group 1 | 69.5 | 18 | [−21.6, 48.1] | 82.1 | 14.8 | [3.9, 39.9] |
| Group 2 | −15.4 ⱡⱡ | −21.9 ⱡⱡ | [−28, 10.4] | −7.4 ⱡⱡ | −1.2 ⱡⱡ | [−16.1, 8.2] |
| Group 3 | 619 | 44.5 | [25.8, 84] | 482.4 | 42.4 | [25, 87] |
| Group 4 | 9.2 | 8.8 | [−25, 19.3] | 23.5 | 7.8 | [−2, 12.5] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, S.; Prasad, B. Meta-Analysis of Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Efflux Transporter Substrate Drugs: Does Delayed Gastric Emptying Influence Drug Transport Kinetics? Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071035
Sharma S, Prasad B. Meta-Analysis of Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Efflux Transporter Substrate Drugs: Does Delayed Gastric Emptying Influence Drug Transport Kinetics? Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(7):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Sheena, and Bhagwat Prasad. 2021. "Meta-Analysis of Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Efflux Transporter Substrate Drugs: Does Delayed Gastric Emptying Influence Drug Transport Kinetics?" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 7: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071035
APA StyleSharma, S., & Prasad, B. (2021). Meta-Analysis of Food Effect on Oral Absorption of Efflux Transporter Substrate Drugs: Does Delayed Gastric Emptying Influence Drug Transport Kinetics? Pharmaceutics, 13(7), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13071035