Surface-Tailored Zein Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
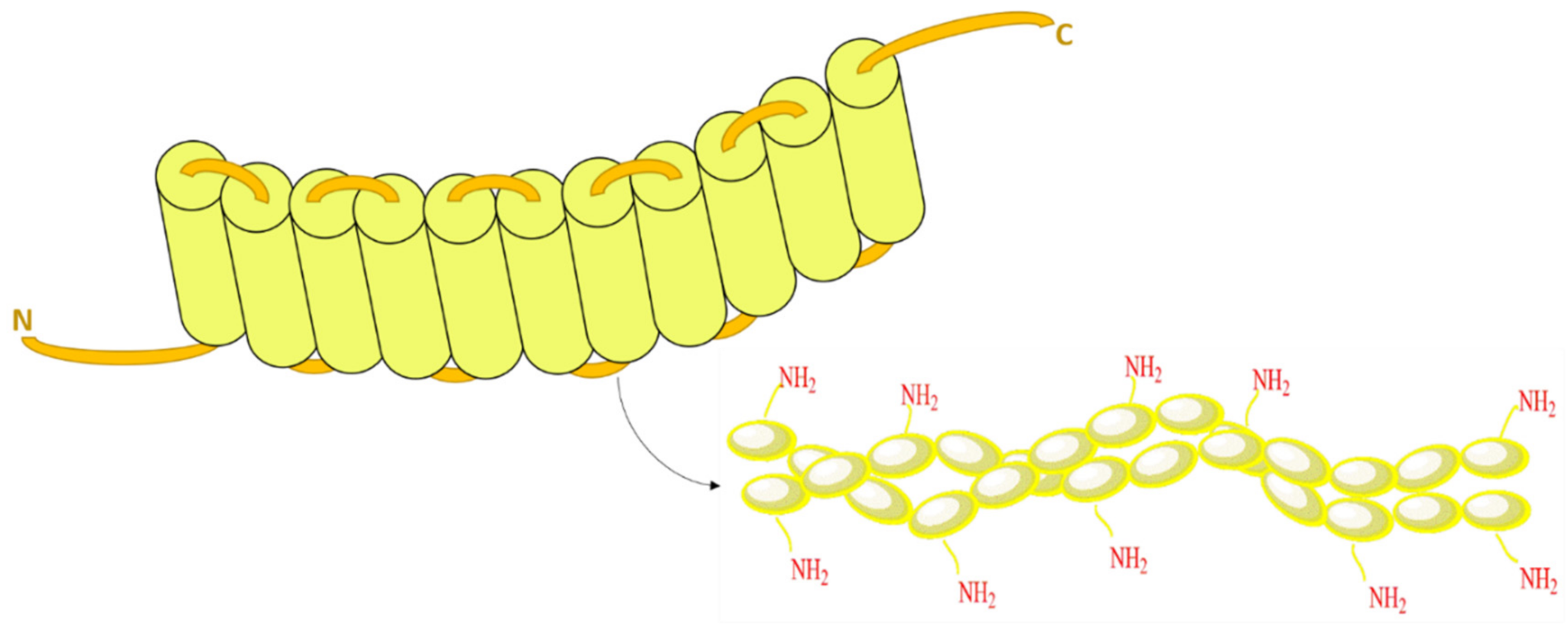
2. Structure of Zein
3. Factors Affecting the Structure and Integrity of Zein Protein
3.1. Temperature Effect
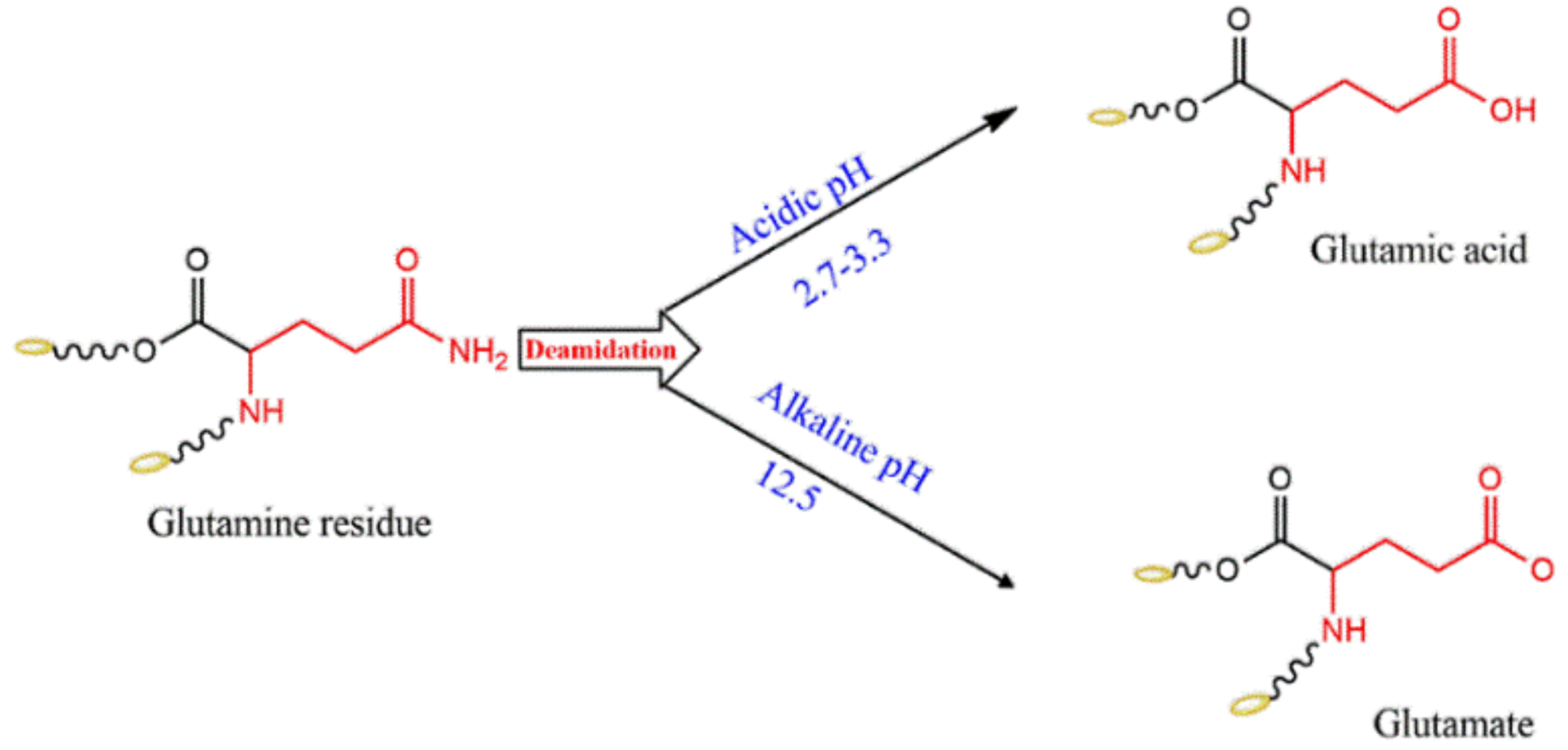
3.2. pH Effect
4. Zein Nanocomposite-Based Systems
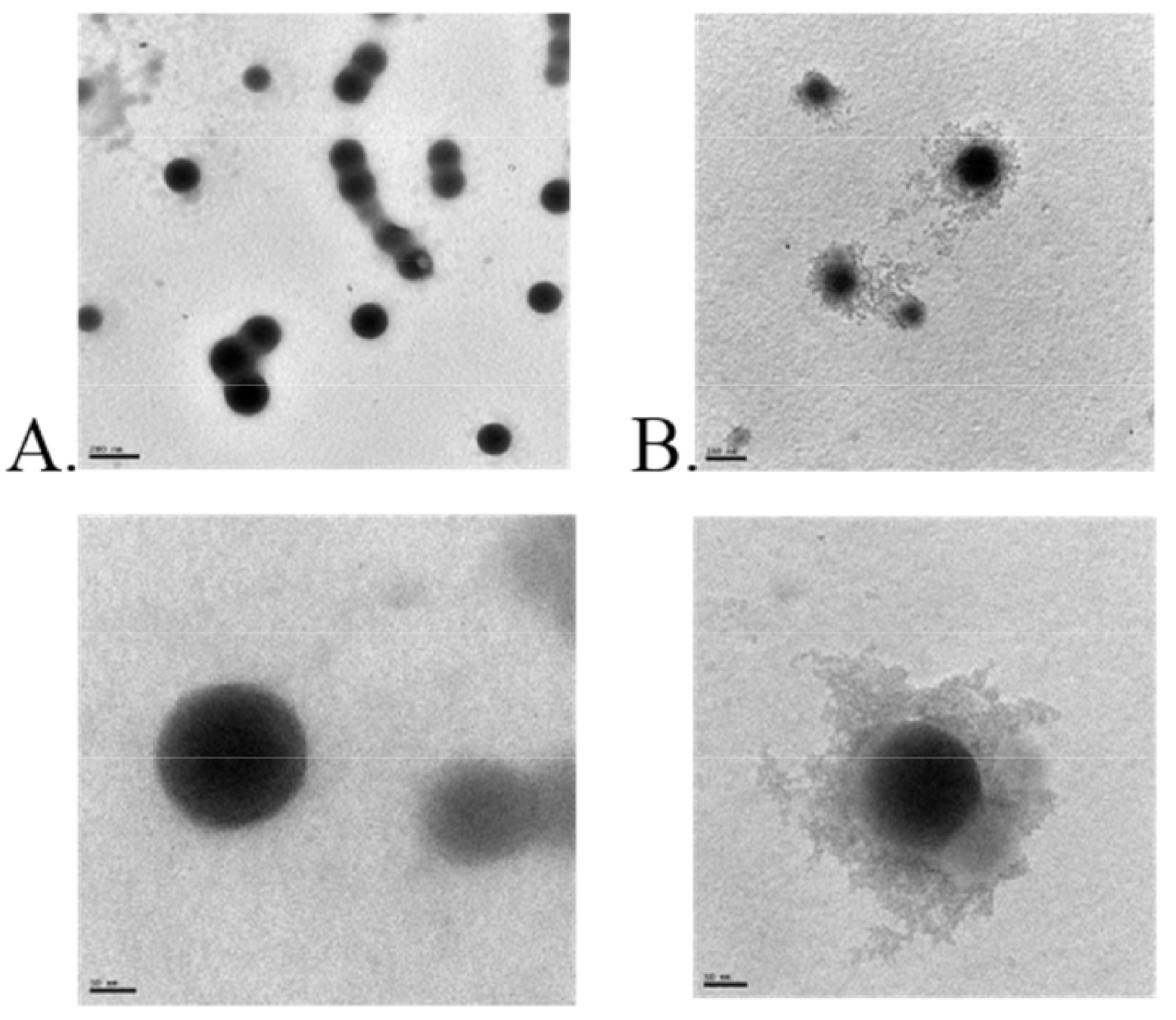
4.1. Zein Phospholipid Complex
4.2. Zein Protein Complex
4.3. Zein Polysaccharide Complex
5. Applications in Drug Delivery
5.1. Phytochemical Drug Delivery
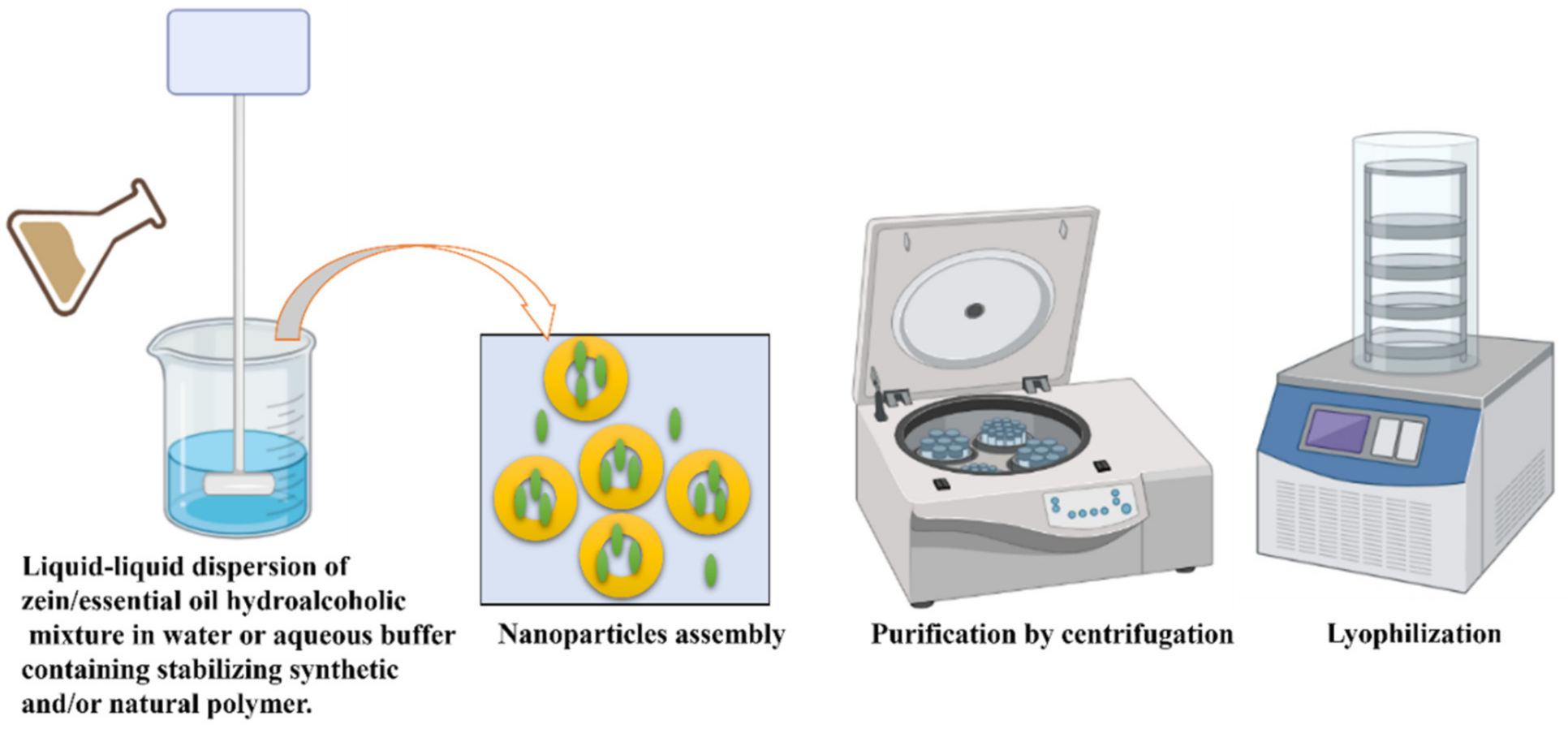
5.2. Essential Oil Delivery
5.3. Cytotoxic Drug Delivery
6. Zein in Cellular Imaging and Tissue Engineering
6.1. Bioimaging
6.2. Tissue Engineering
7. Surface Modified Zein Nanoparticles for Active Targeted Drug Delivery
7.1. Zein-Folic Acid
7.2. Zein-Lactoferrin
8. Antigenicity of Zein
9. Concluding Remarks and Future Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maham, A.; Tang, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y. Protein-Based Nanomedicine Platforms for Drug Delivery. Small 2009, 5, 1706–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasaai, M.R. Zein and zein -based nano-materials for food and nutrition applications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 79, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, M.; Tarakanova, A. Molecular Design of Soluble Zein Protein Sequences. Biophys. J. 2020, 118, 45a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissmueller, N.T.; Lu, H.D.; Hurley, A.; Prud’Homme, R.K. Nanocarriers from GRAS Zein Proteins to Encapsulate Hydrophobic Actives. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3828–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.-L.; Xu, Q.; Lu, Z.-Q.; Wang, J.-Y. Preparation of transparent zein films for cell culture applications. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2014, 120, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchaurraga, L.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Martin-Arbella, N.; Irache, J.M. Zein-based nanoparticles for the oral delivery of insulin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.; Hu, Y.; Tiwari, J.K.; Velikov, K.P. Synthesis and characterisation of zein–curcumin colloidal particles. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 6192–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, J.-Y. Basic study of corn protein, zein, as a biomaterial in tissue engineering, surface morphology and biocompatibility. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4691–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-López, P.; Murdan, S. Formulation and characterisation of zein microspheres as delivery vehicles. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2005, 15, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwestka, J.; Tschofen, M.; Vogt, S.; Marcel, S.; Grillari, J.; Raith, M.; Swoboda, I.; Stoger, E. Plant-derived protein bodies as delivery vehicles for recombinant proteins into mammalian cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Hollow nanoparticles from zein for potential medical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 18227–18235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Uyar, T. Antioxidant electrospun zein nanofibrous web encapsulating quercetin/cyclodextrin inclusion complex. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 53, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Podaralla, S.; Averineni, R.; Alqahtani, M.; Perumal, O. Synthesis of Novel Biodegradable Methoxy Poly(ethylene glycol)–Zein Micelles for Effective Delivery of Curcumin. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labib, G. Overview on zein protein: A promising pharmaceutical excipient in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Duan, W.; Lee, B.-J.; Tran, T.T. The use of zein in the controlled release of poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 566, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, R.; Palakurthi, S. Zein in controlled drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2014, 189, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Che, X.; Zhang, H.; Shi, N.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Kong, W. Zein-based films and their usage for controlled delivery: Origin, classes and current landscape. J. Control. Release 2015, 206, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Cheryan, M. Zein: The industrial protein from corn. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2001, 13, 171–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, N.; Jockusch, S.; Turro, N.J.; Somasundaran, P. Surfactant Interactions with Zein Protein. Langmuir 2003, 19, 5083–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, N.; Dickey, L.C. Extraction and solubility characteristics of zein proteins from dry-milled corn. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3757–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esen, A. Separation of Alcohol-Soluble Proteins (Zeins) from Maize into Three Fractions by Differential Solubility. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsushima, N.; Danno, G.-I.; Takezawa, H.; Izumi, Y. Three-dimensional structure of maize α-zein proteins studied by small-angle X-ray scattering. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) 1997, 1339, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cui, L.; Li, F.; Shi, N.; Li, C.; Yu, X.; Chen, Y.; Kong, W. Design, fabrication and biomedical applications of zein-based nano/micro-carrier systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 513, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.; Freag, M.; Mamdouh, H.; Elkhodairy, K. Zein-based Nanocarriers as Potential Natural Alternatives for Drug and Gene Delivery: Focus on Cancer Therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 23, 5261–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa De Almeida, C.; Catelam, K.T.; Lopes Cornélio, M.; Francisco, J.; Filho, L. Morphological and Structural Characteris-tics of Zein Biofilms with Added Xanthan Gum. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 48, 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Chuacharoen, T.; Sabliov, C.M. Zein nanoparticles as delivery systems for covalently linked and physically entrapped folic acid. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2017, 19, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, Y.-C.; Park, J.-H. Zein-alginate based oral drug delivery systems: Protection and release of therapeutic proteins. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Li, R.; Wei, Y.; Sun, C.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Fabrication of zein and rhamnolipid complex nanoparticles to enhance the stability and in vitro release of curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 77, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, J.; Yu, X.; Yagoub, A.E.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, H.; Gao, X.; Otu, P.N.Y. Heat and/or ultrasound pretreatments motivated enzymolysis of corn gluten meal: Hydrolysis kinetics and protein structure. LWT 2017, 77, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Dai, L.; He, X.; Liu, F.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Effect of heat treatment on physical, structural, thermal and morphological characteristics of zein in ethanol-water solution. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 58, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Dai, L.; Liu, F.; Gao, Y. Simultaneous treatment of heat and high pressure homogenization of zein in ethanol–water solution: Physical, structural, thermal and morphological characteristics. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 34, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; Paolino, D.; Iannone, M.; Palma, E.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Sodium deoxycholate-decorated zein nanoparticles for a stable colloidal drug delivery system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabra, V.; Arreguin, R.; Vazquez-Duhalt, R.; Farres, A. Effect of Alkaline Deamidation on the Structure, Surface Hydrophobicity, and Emulsifying Properties of the Z19 α-Zein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. Heat-induced self-assembly of zein nanoparticles: Fabrication, stabilization and potential application as oral drug delivery. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podaralla, S.; Perumal, O. Influence of Formulation Factors on the Preparation of Zein Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Effect of acid and base treatments on structural, rheological, and antioxidant properties of α-zein. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yao, P. High dispersity, stability and bioaccessibility of curcumin by assembling with deamidated zein peptide. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Sun, C.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Zein-hyaluronic acid binary complex as a delivery vehicle of quercetagetin: Fabrication, structural characterization, physicochemical stability and in vitro release property. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Rodríguez-Felix, F.; Juárez-Onofre, J.E.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Robles-García, M.A.; Borboa-Flores, J.; Wong-Corral, F.J.; Cinco-Moroyoqui, F.J.; Castro-Enríquez, D.D.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L. Zein-polysaccharide nanoparticles as matrices for antioxidant compounds: A strategy for prevention of chronic degenerative diseases. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 451–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y. The Interaction between Zein and Lecithin in Ethanol-Water Solution and Characterization of Zein–Lecithin Composite Colloidal Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podaralla, S.; Perumal, O. Preparation of zein nanoparticles by pH controlled nanoprecipitation. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Lakany, S.A.; Elgindy, N.A.; Helmy, M.W.; Abu-Serie, M.M.; Elzoghby, A.O. Lactoferrin-decorated vs PEGylated zein nanospheres for combined aromatase inhibitor and herbal therapy of breast cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.; Zhong, Q. Low energy, organic solvent-free co-assembly of zein and caseinate to prepare stable dispersions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.; Hosny, K.; Al-Sawahli, M.; Fahmy, U.A. Optimization of caseinate-coated simvastatin-zein nanoparticles: Improved bioavailability and modified release characteristics. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Wang, T.T.Y.; Wang, Q. Cellular Uptake and Transport of Zein Nanoparticles: Effects of Sodium Caseinate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7621–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, M.; Islam, M.S.; Podaralla, S.; Kaushik, R.S.; Reineke, J.; Woyengo, T.; Perumal, O. Food Protein Based Core–Shell Nanocarriers for Oral Drug Delivery: Effect of Shell Composition on in Vitro and in Vivo Functional Performance of Zein Nanocarriers. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 757–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, N.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Li, Z.; Li, C. Preparation and Characterization of Insulin-Loaded Zein/Carboxymethylated Short-Chain Amylose Complex Nanoparticles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9335–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoli, M.; Lima, R.; Fraceto, L.F. Zein Nanoparticles and Strategies to Improve Colloidal Stability: A Mini-Review. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusigale; Wang, T.; Hu, Q.; Xue, J.; Khan, M.A.; Liang, L.; Luo, Y. Partition and Stability of Folic Acid and Caffeic Acid in Hollow Zein Particles Coated with Chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Yue, C.; Fang, Z.; Hu, S.; Cheng, H.; Bakry, A.M.; Liang, L. Alginate/chitosan-coated zein nanoparticles for the delivery of resveratrol. J. Food Eng. 2019, 258, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.-E.; Park, D.-J.; Kim, B.-K. Effects of a chitosan coating on properties of retinol-encapsulated zein nanoparticles. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baspinar, Y.; Üstündas, M.; Bayraktar, O.; Sezgin, C. Curcumin and piperine loaded zein-chitosan nanoparticles: Development and in-vitro characterisation. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-F.; Chen, L.; Xu, M.-Z.; Zhang, J.-L.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Q.-Z.; Wei, X.-C.; Yuan, Y. The formation of zein-chitosan complex coacervated particles: Relationship to encapsulation and controlled release properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-J.; Yu, Y.-G.; Yin, S.-W.; Tang, C.-H.; Yang, X.-Q. Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Antioxidant Activity of Zein/Chitosan Nanoparticles Incorporated with Quercetin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12783–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Teng, Z.; Wang, Q. Development of Zein Nanoparticles Coated with Carboxymethyl Chitosan for Encapsulation and Controlled Release of Vitamin D3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Fang, S.; Zhao, X.; Liang, X.; Wu, D. Natamycin-loaded zein nanoparticles stabilized by carboxymethyl chitosan: Evaluation of colloidal/chemical performance and application in postharvest treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Piai, J.F.; Fajardo, A.R.; Fávaro, S.L.; Rubira, A.; Muniz, E. Preparation and Characterization of Zein and Zein-Chitosan Microspheres with Great Prospective of Application in Controlled Drug Release. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wang, T.T.; Teng, Z.; Chen, P.; Sun, J.; Wang, Q. Encapsulation of indole-3-carbinol and 3,3′-diindolylmethane in zein/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles with controlled release property and improved stability. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, E.; Brown, D.M.; Ramer-Tait, A.; Pannier, A.K. Chitosan-zein nano-in-microparticles capable of mediating in vivo transgene expression following oral delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 249, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication of biopolymer nanoparticles by antisolvent precipitation and electrostatic deposition: Zein-alginate core/shell nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 44, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vozza, G.; Khalid, M.; Byrne, H.J.; Ryan, S.; Frias, J.M. Nutraceutical formulation, characterisation, and in-vitro evaluation of methylselenocysteine and selenocystine using food derived chitosan:zein nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauzer, G.N. Selenomethionine: A Review of Its Nutritional Significance, Metabolism and Toxicity. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vozza, G.; Danish, M.; Byrne, H.J.; Frias, J.; Ryan, S.M. Application of Box-Behnken experimental design for the formulation and optimisation of selenomethionine-loaded chitosan nanoparticles coated with zein for oral delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, H.-T.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Chen, T.-H.; Hung, P.-F.; Pan, S.-H. Sorafenib-fortified zein–chondroitin sulphate biopolymer nanoparticles as a novel therapeutic system in gastric cancer treatment. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 57266–57274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Kang, N.-W.; Kim, H.; Kim, D.H.; Chae, J.-W.; Lee, W.; Song, G.Y.; Cho, C.-W.; Kim, D.-D.; Lee, J.-Y. Chondroitin sulfate-hybridized zein nanoparticles for tumor-targeted delivery of docetaxel. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 253, 117187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jing, Y.; Han, C.; Zhang, H.; Tian, Y. Encapsulation of curcumin in zein/ caseinate/sodium alginate nanoparticles with improved physicochemical and controlled release properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Wang, T.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, M.; Xue, J.; Luo, Y. Pectin coating improves physicochemical properties of caseinate/zein nanoparticles as oral delivery vehicles for curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Wang, T.; Hu, Q.; Luo, Y. Zein/caseinate/pectin complex nanoparticles: Formation and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, K.; Chen, W.; Song, F.; McClements, D.J.; Hu, K. Tailoring zein nanoparticle functionality using biopolymer coatings: Impact on curcumin bioaccessibility and antioxidant capacity under simulated gastrointestinal conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Guo, H. Preparation of new 5-fluorouracil-loaded zein nanoparticles for liver targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 404, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, B.; Whent, M.; Yu, L. (Lucy); Wang, Q. Preparation and characterization of zein/chitosan complex for encapsulation of α-tocopherol, and its in vitro controlled release study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 85, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado-López, P.; Murdan, S. Zein microspheres as drug/antigen carriers: A study of their degradation and erosion, in the presence and absence of enzymes. J. Microencapsul. 2006, 23, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, F.; Imhof, A.; Velikov, K. Color-tunable particles through affinity interactions between water-insoluble protein and soluble dyes. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 562, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Zhan, L.; Shao, P.; Xiang, N.; Sun, P.; Chen, H.; Gao, H. Electrospinning of zein-ethyl cellulose hybrid nanofibers with improved water resistance for food preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turasan, H.; Kokini, J.L. Advances in Understanding the Molecular Structures and Functionalities of Biodegradable Zein-Based Materials Using Spectroscopic Techniques: A Review. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 331–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Reddy, N.; Yang, Y. Cytocompatible Cross-Linking of Electrospun Zein Fibers for the Development of Water-Stable Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4042–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zou, L.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Enhancing the bioaccessibility of hydrophobic bioactive agents using mixed colloidal dispersions: Curcumin-loaded zein nanoparticles plus digestible lipid nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2016, 81, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Wang, J.-M.; Yang, X.-Q.; Guo, J.; Lin, Y. Amphiphilic zein hydrolysate as a novel nano-delivery vehicle for curcumin. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2636–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zhou, H.; Wei, Y.; Gao, Y.; McClements, D.J. Curcumin encapsulation in zein-rhamnolipid composite nanoparticles using a pH-driven method. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Fan, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Xu, Y.; Cao, Y. Fabrication of stable zein nanoparticles coated with soluble soybean polysaccharide for encapsulation of quercetin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. Physical, structural, thermal and morphological characteristics of zeinquercetagetin composite colloidal nanoparticles. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 77, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuacharoen, T.; Sabliov, C.M. Stability and controlled release of lutein loaded in zein nanoparticles with and without lecithin and pluronic F127 surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 503, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.J.; Ferruzzi, M.; Jones, O.G. Fate of lutein-containing zein nanoparticles following simulated gastric and intestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Sharma, G.; Kushwah, V.; Ghoshal, G.; Jain, A.; Singh, B.; Shivhare, U.S.; Jain, S.; Katare, O.P. Beta carotene-loaded zein nanoparticles to improve the biopharmaceutical attributes and to abolish the toxicity of methotrexate: A preclinical study for breast cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. 1), 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Ma, D.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; He, L.; Gao, Y.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication and characterization of protein-phenolic conjugate nanoparticles for co-delivery of curcumin and resveratrol. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 79, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhong, Q. A novel method of preparing stable zein nanoparticle dispersions for encapsulation of peppermint oil. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Niu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Ge, M.; Yang, T.; Yu, L.; Wang, Q. Fabrication, characterization and antimicrobial activities of thymol-loaded zein nanoparticles stabilized by sodium caseinate–chitosan hydrochloride double layers. Food Chem. 2014, 142, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of essential oils encapsulated in zein nanoparticles prepared by liquid–liquid dispersion method. LWT 2012, 48, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Dong, X.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, H.; Ho, P.-Y.; Wong, M.-S.; Wang, Y. Doxorubicin-loaded biodegradable self-assembly zein nanoparticle and its anti-cancer effect: Preparation, in vitro evaluation, and cellular uptake. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, L.; Wang, B.; Qian, J.; Fletcher, B.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Q.; Chen, W.; Hong, L. Preparation, characterization and preliminary pharmacokinetic study of pH-sensitive Hydroxyapatite/Zein nano-drug delivery system for doxorubicin hydrochloride. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, R.K.; Nguyen, H.T.; Jeong, J.-H.; Shin, B.S.; Ku, S.K.; Choi, H.-G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Synergistic anticancer activity of combined histone deacetylase and proteasomal inhibitor-loaded zein nanoparticles in metastatic prostate cancers. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarhini, M.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Elaissari, A. Protein-based nanoparticles: From preparation to encapsulation of active molecules. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 522, 172–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathy, R.G.; Sivakumar, B.; Brahatheeswaran, D.; Fukuda, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, S. Biocompatible fluorescent zein nanoparticles for simultaneous bioimaging and drug delivery application. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xie, Q. Facile encapsulation of hydroxycamptothecin nanocrystals into zein-based nanocomplexes for active targeting in drug delivery and cell imaging. Acta Biomater. 2017, 61, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadavi, M.; Hasannia, S.; Faghihi, S.; Mashayekhi, F.; Homazadeh, H.; Mostofi, S.B. Zein nanoparticle as a novel BMP6 derived peptide carrier for enhanced osteogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46 (Suppl. 1), 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turner, J.C.; Collins, G.; Blaber, E.A.; Almeida, E.A.; Arinzeh, T.L. Evaluating the cytocompatibility and differentiation of bone progenitors on electrospun zein scaffolds. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Jian, L.; Liao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y. Fabrication, characterization, physicochemical stability of zein-chitosan nanocomplex for co-encapsulating curcumin and resveratrol. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, Q.; McClements, D.J.; Han, Y.; Dai, L.; Mao, L.; Gao, Y. Co-delivery of curcumin and piperine in zein-carrageenan core-shell nanoparticles: Formation, structure, stability and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qing, J.; Han, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Gao, Y. Core-shell nanoparticles for co-encapsulation of coenzyme Q10 and piperine: Surface engineering of hydrogel shell around protein core. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Dai, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Y. Entrapment of curcumin in whey protein isolate and zein composite nanoparticles using pH-driven method. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 106, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Pan, C.; Ying, Z.; Yu, D.; Duan, X.; Huang, F.; Ling, J.; Ouyang, X.-K. Stabilization of zein nanoparticles with k-carrageenan and tween 80 for encapsulation of curcumin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Xiao, P.; Yu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, J.; Peng, H.; Deng, S. A novel pectin from Akebia trifoliata var. australis fruit peel and its use as a wall-material to coat curcumin-loaded zein nanoparticle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. Zein/soluble soybean polysaccharide composite nanoparticles for encapsulation and oral delivery of lutein. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, P.; Vaseeharan, B.; Vijayakumar, S.; Balan, B.; Govindarajan, M.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M.; Benelli, G. Biopolymer zein-coated gold nanoparticles: Synthesis, antibacterial potential, toxicity and histopathological effects against the Zika virus vector Aedes aegypti. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 173, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, G.; Xue, F.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication and characterization of zein/lactoferrin composite nanoparticles for encapsulating 7,8-dihydroxyflavone: Enhancement of stability, water solubility and bioaccessibility. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Z. Fabrication and characterization of zein/tea saponin composite nanoparticles as delivery vehicles of lutein. LWT 2020, 125, 109270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wu, H.; Hu, H.; Dong, Z.; Dang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Du, S.; Lu, Y. Zein nanoparticles as nontoxic delivery system for maytansine in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Sharkawi, F.Z.; Ewais, S.M.; Fahmy, R.H.; Rashed, L.A. PTEN and TRAIL genes loaded zein nanoparticles as potential therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Wang, T.; Fernandez, M.L.; Luo, Y. Development of tannic acid cross-linked hollow zein nanoparticles as potential oral delivery vehicles for curcumin. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-H.; Yang, Y.-N.; Ho, Y.-C.; Tsai, M.-L.; Mi, F.-L. Drug release and antioxidant/antibacterial activities of silymarin-zein nanoparticle/bacterial cellulose nanofiber composite films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 180, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, A.; Bonacci, S.; Paolino, D.; Celia, C.; Procopio, A.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Paclitaxel-loaded sodium deoxycholate-stabilized zein nanoparticles: Characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamel, N.M.; Helmy, M.W.; Abdelfattah, E.-Z.; Khattab, S.N.; Ragab, D.; Samaha, M.W.; Fang, J.-Y.; Elzoghby, A.O. Inhalable Dual-Targeted Hybrid Lipid Nanocore–Protein Shell Composites for Combined Delivery of Genistein and All-Trans Retinoic Acid to Lung Cancer Cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunab, J.; Fanb, Y.; Zhangb, P.; Zhangd, X.; Zhouc, Q.; Zhaoa, J.; Rena, L. Self-enriched mesoporous silica nanoparticle composite membrane with remarkable photodynamic antimicrobial performances. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 559, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-H.; Lee, M.-K.; Lim, S.-J. Enhanced Stability of Indocyanine Green by Encapsulation in Zein-Phosphatidylcholine Hybrid Nanoparticles for Use in the Phototherapy of Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, H.-Y.; Rejinold, N.S.; Lekshmi, K.M.; Cherukula, K.; Park, I.-K.; Kim, Y.-C. CD44 targeting biocompatible and biodegradable hyaluronic acid cross-linked zein nanogels for curcumin delivery to cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Control. Release 2018, 280, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, D.; Zhu, W.; Guan, S.; Fan, L.; Cai, D. Targeted delivery of honokiol by zein/hyaluronic acid core-shell nanoparticles to suppress breast cancer growth and metastasis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Guo, A.; Liu, Z.; Mao, L.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y.; Mackie, A. Structural design of zein-cellulose nanocrystals core–shell microparticles for delivery of curcumin. Food Chem. 2021, 357, 129849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.; Baião, A.; Monteiro, D.; Das Neves, J.; Sarmento, B. Zein nanoparticles as low-cost, safe, and effective carriers to improve the oral bioavailability of resveratrol. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. A stable polyamine-modified zein-based nanoformulation with high foliar affinity and lowered toxicity for sustained avermectin release. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3300–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.A.; Camara, M.C.; de Oliveira, J.L.; Campos, E.V.R.; Carvalho, L.B.; Proença, P.L.D.F.; Guilger-Casagrande, M.; Lima, R.; Nascimento, J.D.; Gonçalves, K.C.; et al. Zein based-nanoparticles loaded botanical pesticides in pest control: An enzyme stimuli-responsive approach aiming sustainable agriculture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 126004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, L.; Tong, M.; Lu, Y.; Ouyang, X.-K.; Ling, J. Encapsulation of curcumin using fucoidan stabilized zein nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro release performance. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 329, 115586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qin, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, T. Fabrication, characterization, physicochemical stability and simulated gastrointestinal digestion of pterostilbene loaded zein-sodium caseinate-fucoidan nanoparticles using pH-driven method. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, X.; Peng, X.; Liang, X.; Fang, S.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y. Development of antifungal gelatin-based nanocomposite films functionalized with natamycin-loaded zein/casein nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Liang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, H. Preparation and evaluation of lecithin/zein hybrid nanoparticles for the oral delivery of Panax notoginseng saponins. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 164, 105882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Su, Z.; Yang, C.; Ji, Y.; Liu, B.; Meng, X. Fabrication, characterization and properties of DHA-loaded nanoparticles based on zein and PLGA. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, R.; Wu, Z.; Xie, Q.-T.; Cheng, J.-S.; Zhang, B. Preparation and characterization of zein/carboxymethyl dextrin nanoparticles to encapsulate curcumin: Physicochemical stability, antioxidant activity and controlled release properties. Food Chem. 2021, 340, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, D.W.; Su, H.; Hildebrandt, I.J.; Weber, W.A.; Davis, M.E. Impact of tumor-specific targeting on the biodistribution and efficacy of siRNA nanoparticles measured by multimodality in vivo imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15549–15554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Pang, J.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Q.; Guan, G.; Jiang, Y. Self-Assembled Nanospheres of Folate-Decorated Zein for the Targeted Delivery of 10-Hydroxycamptothecin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8517–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wei, D.; Wang, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y. Self-assembly of zein microspheres with controllable particle size and narrow distribution using a novel built-in ultrasonic dialysis process. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y. Incorporation of 10-hydroxycamptothecin nanocrystals into zein microspheres. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 155, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, H.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, Y. Folate-conjugated zein/Fe3O4 nanocomplexes for the enhancement of cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of gefitinib. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14907–14921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, M.; Ren, J.; Hu, N.; Wang, Y. Bilayer Nanocarriers with Protein–Acid Conjugation for Prolonged Release and Enhanced Anticancer Effects. Langmuir 2019, 35, 3710–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soe, Z.C.; Ou, W.; Gautam, M.; Poudel, K.; Kim, B.K.; Pham, L.M.; Phung, C.D.; Jeong, J.-H.; Jin, S.G.; Choi, H.-G.; et al. Development of Folate-Functionalized PEGylated Zein Nanoparticles for Ligand-Directed Delivery of Paclitaxel. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, C.S.; Guedes, J.P.; Gonçalves, M.; Loureiro, L.; Castro, L.; Gerós, H.; Rodrigues, L.R.; Côrte-Real, M. Lactoferrin selectively triggers apoptosis in highly metastatic breast cancer cells through inhibition of plasmalemmal V-H+-ATPase. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62144–62158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, S.H.; Das, S.K. Role of Lactoferrin in the Carcinogenesis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer Clin. Trials 2016, 1, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sabra, S.A.; Elzoghby, A.O.; Sheweita, S.; Haroun, M.; Helmy, M.W.; Eldemellawy, M.A.; Xia, Y.; Goodale, D.; Allan, A.L.; Rohani, S. Self-assembled amphiphilic zein-lactoferrin micelles for tumor targeted co-delivery of rapamycin and wogonin to breast cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 128, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, R.; Pan, D.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, M. Nanoparticle ferritin-bound erastin and rapamycin: A nanodrug combining autophagy and ferroptosis for anticancer therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3779–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirumbolo, S. Anticancer properties of the flavone wogonin. Toxicology 2013, 314, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Pan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yin, X.; Yu, C.; Kong, W.; Zhang, Y. The Effect of Size, Dose, and Administration Route on Zein Nanoparticle Immunogenicity in BALB/c Mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9917–9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M.; Sciences, H.; Sciences, M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Yang, L.; Yi, J.-Z.; Xie, M.; Zhang, L.-M. Long-circulating zein-polysulfobetaine conjugate-based nanocarriers for enhancing the stability and pharmacokinetics of curcumin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 109, 110636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
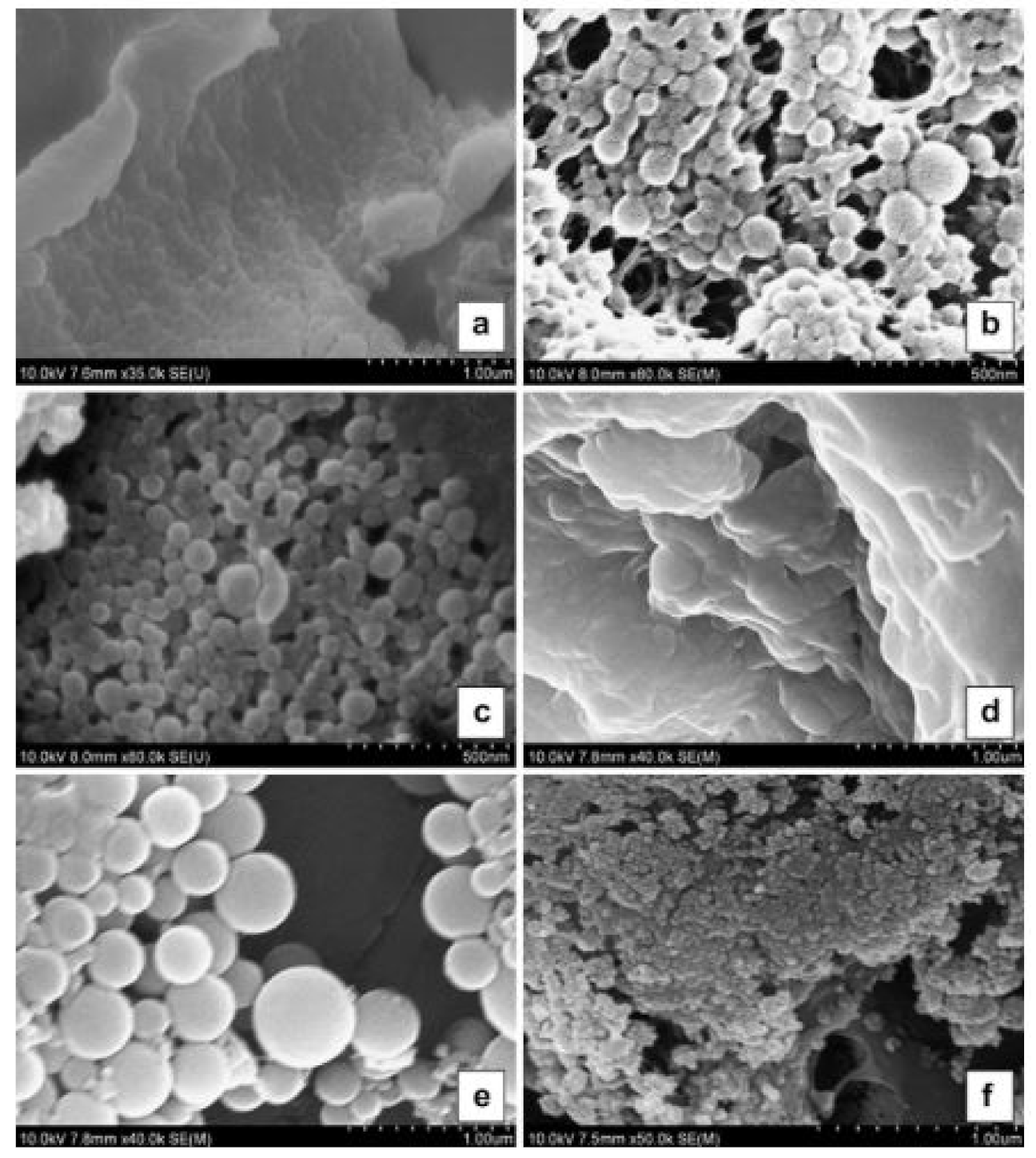



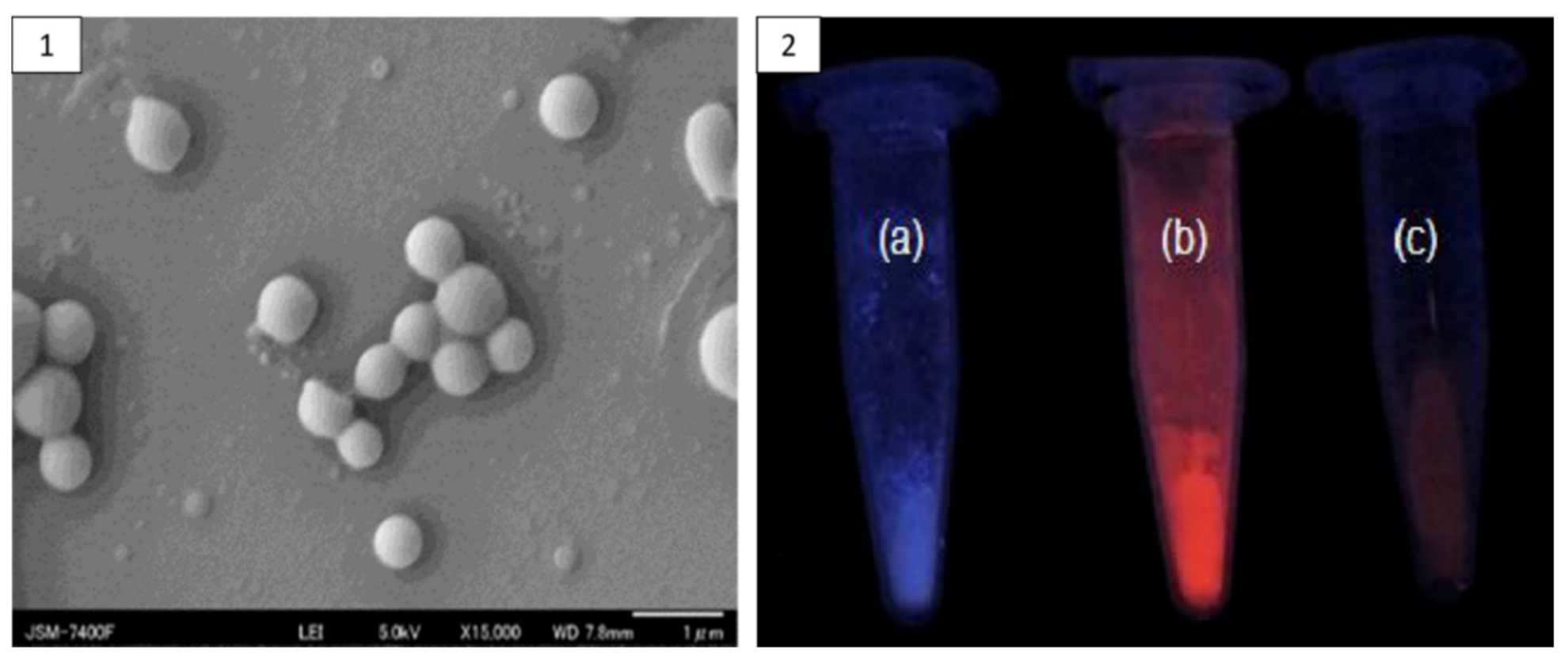

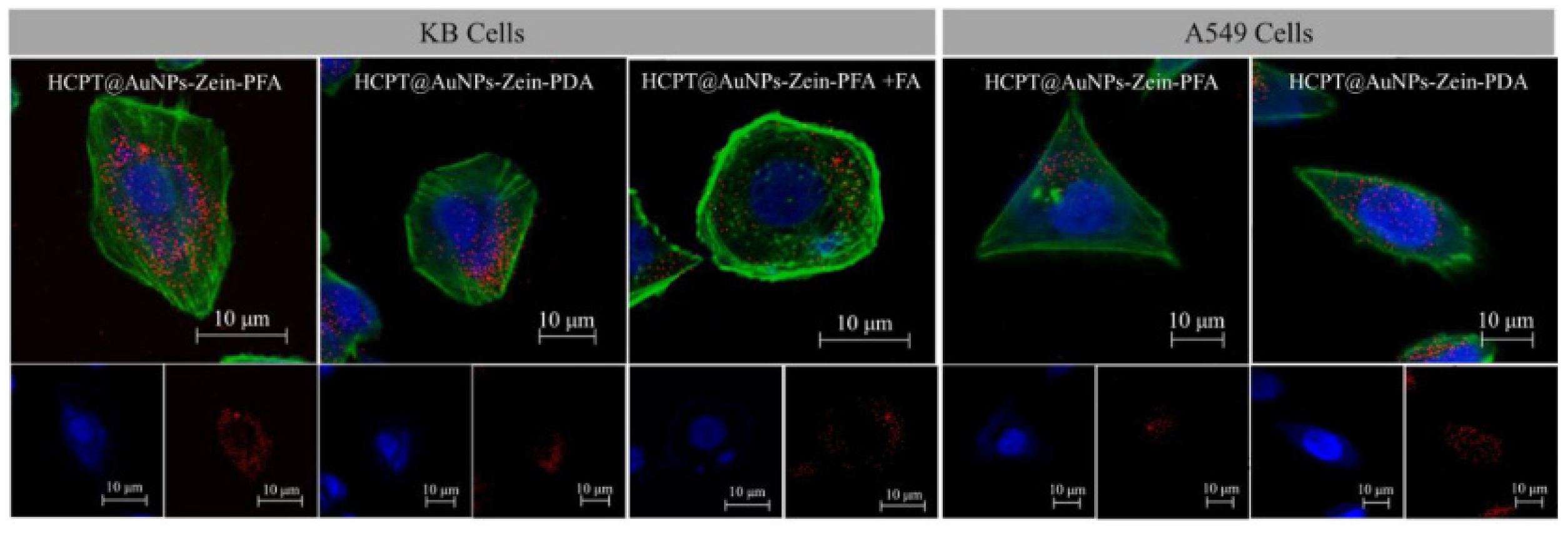
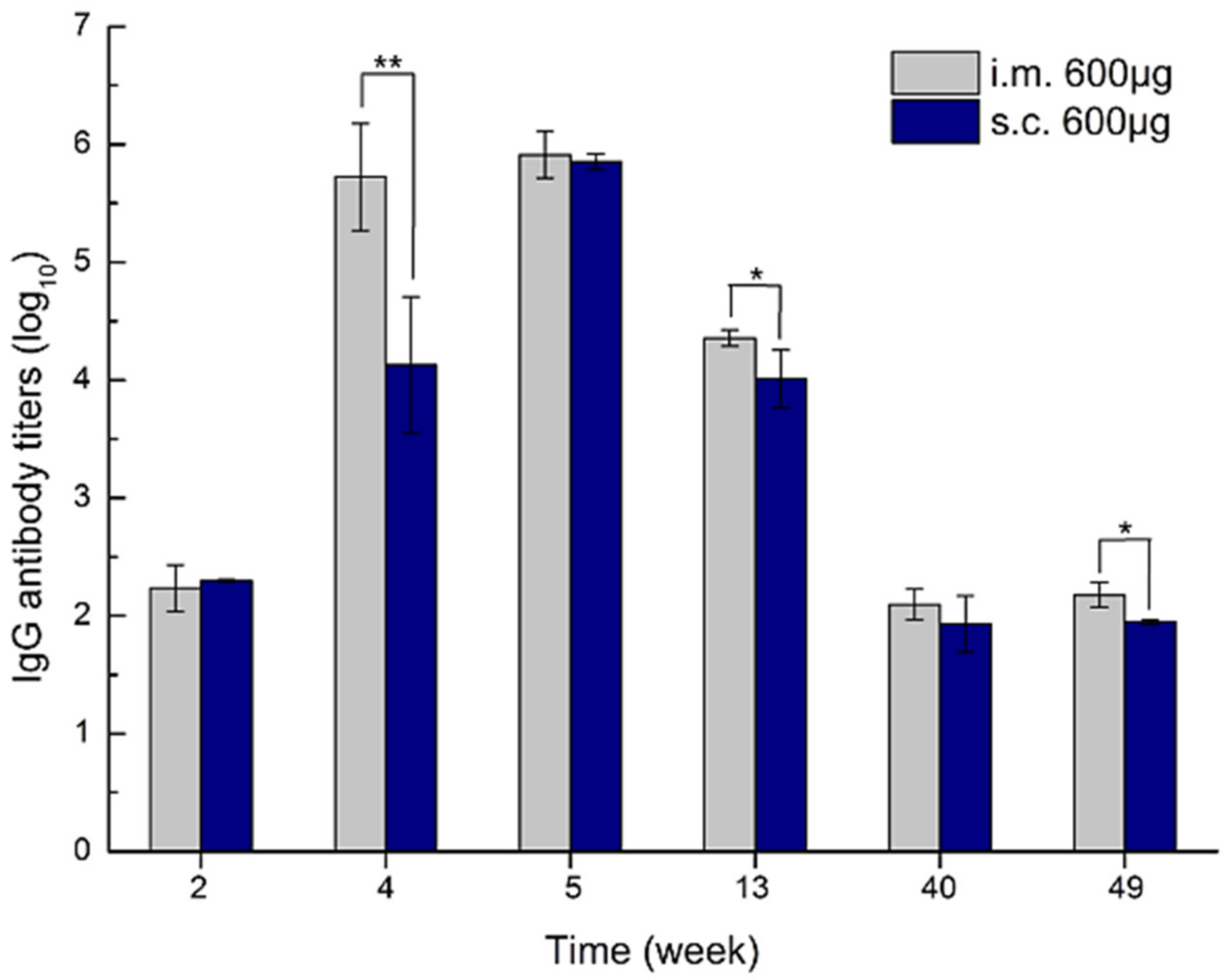
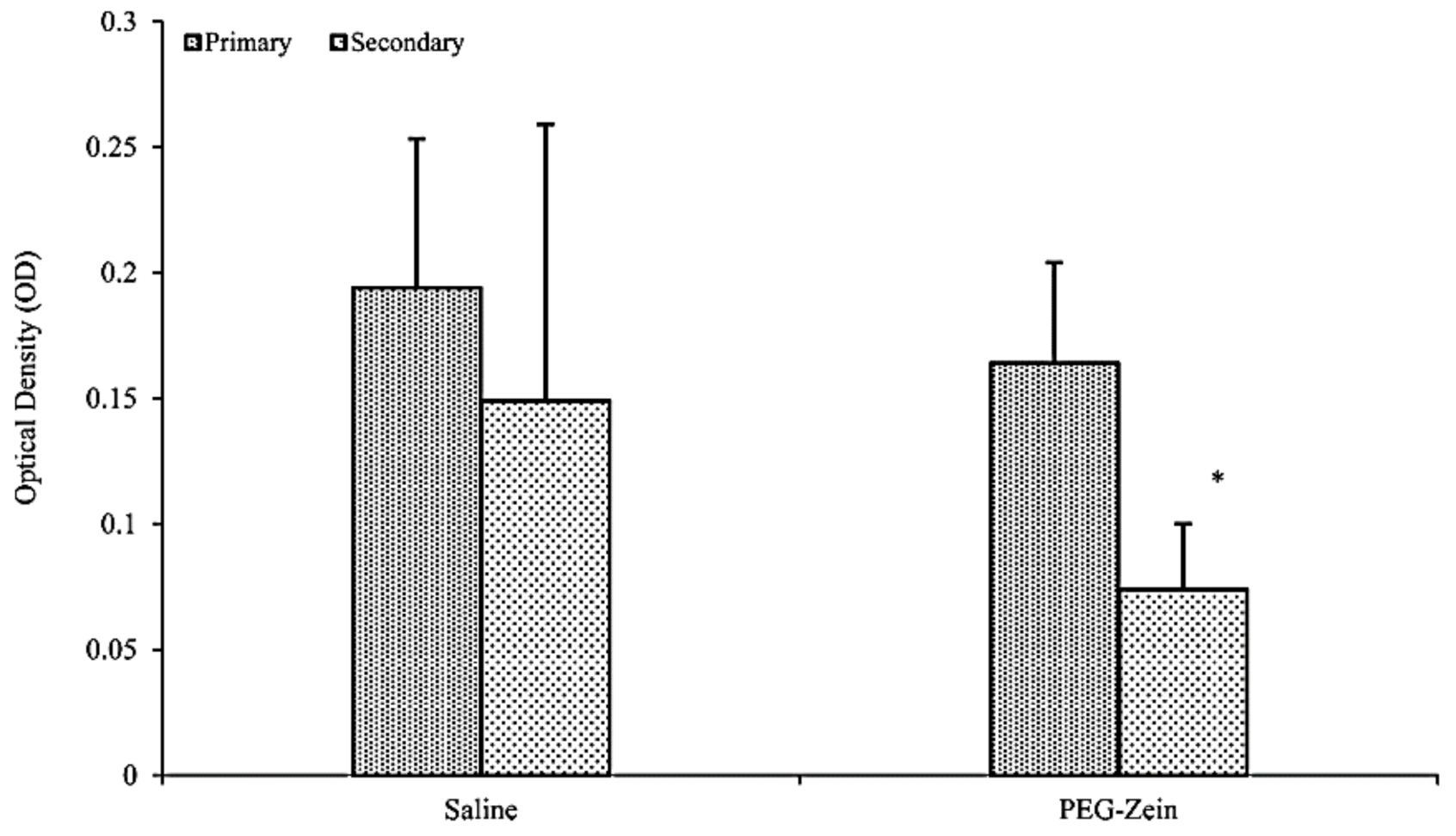
| Protein Fraction | Average Molecular Weights (kDa) | Percentage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-zein | 19–22 | up to 80% | [18,20,21,22] |
| β-zein | 17–18 | 10–15% | [18,20,21] |
| γ-zein | 27–28 | 5–10% | [18,21,22] |
| δ-zein | 9–10 | 3% | [21] |
| Zein Based Nanocomposite Platform | Application | Encapsulated Substance | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| zein/chitosan nano complex | oral drug and food delivery | curcumin and resveratrol | [97] |
| zein/carrageenan | oral drug delivery | curcumin and piperine coenzyme Q10 and piperine | [98,99] |
| hydrophilic whey isolate/zein | oral drug delivery | curcumin | [100] |
| zein/carrageenan/tween 80 | drug delivery | curcumin | [101] |
| pectin from Akebia trifoliata var. Australis fruit peel and zein | drug and food delivery | curcumin | [102] |
| deamidated zein peptide | drug and food delivery | curcumin | [37] |
| zein/soybean polysaccharide | drug delivery | lutein | [103] |
| zein/caseinate | oral and parenteral drug delivery | simvastatin | [44] |
| zein/gold nanoparticles | antibacterial and larvicidal | the whole nanocomposite | [104] |
| zein/lactoferrin | drug delivery | 7,8-dihydroxyflavone | [105] |
| zein/tea saponins | food and drug delivery | lutein | [106] |
| solid zein nanoparticles | drug delivery Gene delivery | maytansine PTEN and TRAIL genes | [107,108] |
| hollow zein nanoparticles | food and drug delivery | curcumin | [109] |
| zein/CMC | postharvest fruit preservation | natamycin | [56] |
| zein/bacterial cellulose | preservative and packaging | silymarin | [110] |
| zein/sodium deoxycholate | cytotoxic drug delivery | paclitaxel | [111] |
| lipid/zein core-shell nanocomposite | targeted pulmonary drug delivery | all-trans retinoic acid and genistein | [112] |
| mesoporous silica nanoparticles coated with zein polycarbolactone mixture | antimicrobial photodynamic therapy | methylene blue | [113] |
| zein/phosphatidylcholine hybrid nanoparticles | cancer photodynamic therapy | indocyanine green | [114] |
| zein/lactoferrin | functional food delivery | 7,8-dihydroxyflavone | [105] |
| zein/hyaluronic acid | targeted drug delivery | curcumin honokiol | [115,116] |
| zein-cellulose nanocrystals core-shell nanoparticles | functional food delivery | curcumin | [117] |
| zein nanoparticles | oral drug delivery | resveratrol | [118] |
| polyamine modified zein | pest management | avermectin | [119] |
| zein/pluronic F68 nanoparticles | pest management | limonene and carvacrol | [120] |
| zein/fucoidan nanocomplex | oral drug delivery | curcumin | [121] |
| zein/sodium caseinate/fucoidan nanoparticles | functional food delivery | pterostilbene | [122] |
| zein/caseinate gelatin nanocomposite films | antifungal drug delivery | natamycin | [123] |
| lecithin/zein hybrid nanoparticles | oral drug delivery | panax notoginseng saponin | [124] |
| zein/PLGA nanoparticles | functional food delivery | docosahexaenoic acid | [125] |
| zein/carboxymethyl dextrin nanoparticles | oral drug delivery | curcumin | [126] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelsalam, A.M.; Somaida, A.; Ayoub, A.M.; Alsharif, F.M.; Preis, E.; Wojcik, M.; Bakowsky, U. Surface-Tailored Zein Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091354
Abdelsalam AM, Somaida A, Ayoub AM, Alsharif FM, Preis E, Wojcik M, Bakowsky U. Surface-Tailored Zein Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(9):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091354
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelsalam, Ahmed M., Ahmed Somaida, Abdallah Mohamed Ayoub, Fahd M. Alsharif, Eduard Preis, Matthias Wojcik, and Udo Bakowsky. 2021. "Surface-Tailored Zein Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 9: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091354
APA StyleAbdelsalam, A. M., Somaida, A., Ayoub, A. M., Alsharif, F. M., Preis, E., Wojcik, M., & Bakowsky, U. (2021). Surface-Tailored Zein Nanoparticles: Strategies and Applications. Pharmaceutics, 13(9), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091354










