Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Study of Gallium-68- and Lutetium-177-Labeled VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors Based on Peptide A7R and Branched Peptidomimetic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Analytical Methods
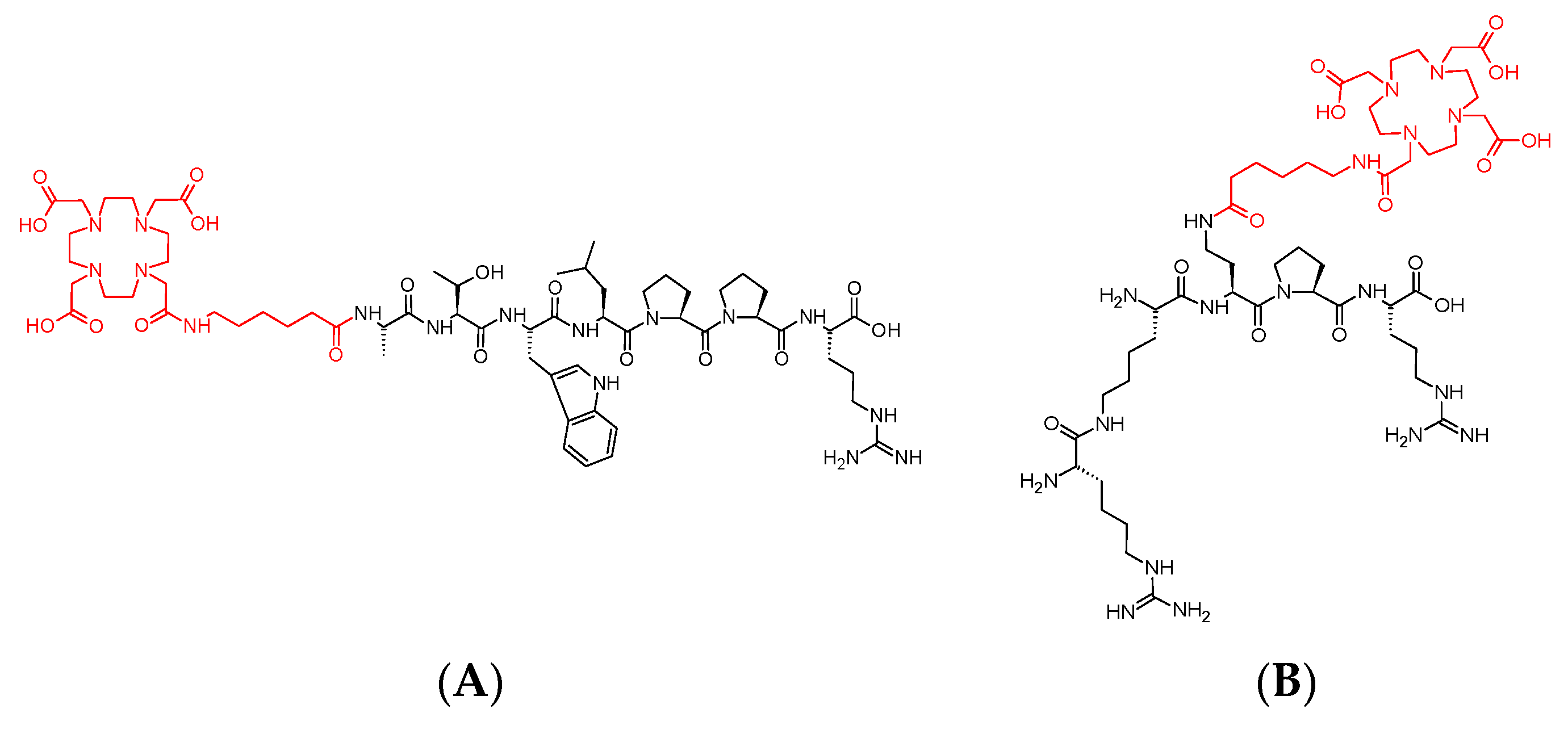
2.2.2. Syntheses
2.2.3. Physicochemical Properties Study of the Radioconjugates
3. Results
3.1. Syntheses of Conjugates 1 and 2
3.2. Syntheses of Radioconjugates
3.3. Synthesis of Cold References Compounds
3.4. Lipophilicity Studies
3.5. Stability Studies of Radioconjugates in PBS Buffer, Cysteine and Histidine
3.6. Stability Tests for 68Ga-1 and 68Ga-2 Radioconjugates
3.7. Stability Tests for 177Lu-1 and 177Lu-2 Radioconjugates
3.8. Stability Studies of Radioconjugates in Human Serum
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A7R | Ala-Thr-Trp-Leu-Pro-Pro-Arg-OH peptide |
| ACN | Acetonitrile |
| ADME | Absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion |
| Ahx | 6-aminohexanoic acid |
| Alloc | Allyloxycarbonyl group |
| Ao | Organic phase radioactivity |
| Aw | Aqueous phase radioactivity |
| Boc COOH | Tert-butyloxycarbonyl group Carboxyl group |
| Cys | Cysteine |
| Dab | 2,4-Diaminobutyric Acid |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DIC | N,N′-Di(propan-2-yl)methanediimine |
| DMF | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| DOTA | 2,2′,2″,2‴-(1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetrayl) tetraacetic acid |
| DOTA-tris(tBu)-NHS | tri-tert-butyl 2,2′,2″-(10-(2-((2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl) -1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triyl)triacetate |
| ESI-MS | Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analyses |
| Et3N | Triethylamine |
| Eβmax | Beta emitter with a maximum energy |
| Fmoc | 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl group |
| hArg | Homoarginine |
| HCl | Hydrogen chloride |
| His | Histidine |
| HOBt | 1H-1,2,3-Benzotriazol-1-ol |
| HS | Human Serum |
| IC50 L | Half maximal inhibitory concentration Lipophilicity |
| logP | Decimal logarithm of partition coefficient |
| m/z | Mass-to-charge ratio |
| mAb | Monoclonal antibodies |
| NH2 | Amino group |
| NRP-1 | Neuropilin-1 |
| P | Partition coefficient |
| Pbf | Pentamethyl-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-sulfonyl group |
| PBS PhOH | Phosphate-buffered saline Phenol |
| PhSiH3 | Phenylsilane |
| RP-HPLC | Reverse-Phase High Pressure Liquid Chromatography |
| RT | Retention time |
| RTKs | Receptor Tyrosine Kinases |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SH | Thiol group |
| SPPS | Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis |
| t1/2 | Half-life time |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| TIPS | Tri(propan-2-yl)silane |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VEGF-A165 | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A165 |
| VEGFR | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor |
| VEGFR-2 | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| ∑ | sigma; operator for summation |
References
- Ferrara, N. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in regulation of physiological angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2001, 280, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grünewald, F.S.; Prota, A.E.; Giese, A.; Ballmer-Hofer, K. Structure–function analysis of VEGF receptor activation and the role of coreceptors in angiogenic signaling. BBA—Proteins Proteom. 2010, 1804, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, S.; Driscoll, P.C. Targeting VEGF signalling via the neuropilin co-receptor. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2007, 62, 179–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, S.; Fidder, H.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Characterization of Novel Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) Receptors on Tumor Cells That Bind VEGF165 via Its Exon 7-encoded Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goel, H.L.; Mercurio, A.M. VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masłowska, K.; Halik, P.K.; Tymecka, D.; Misicka, A.; Gniazdowska, E. The Role of VEGF receptors as molecular target in nuclear medicine for cancer diagnosis and combination therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.F.; Vander Kooi, C.W. Neuropilin functions as an essential cell surface receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29120–29126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soker, S.; Takashima, S.; Miao, H.Q.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform-specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 1998, 92, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latil, A.; Bieche, I.; Pesche, S.; Valeri, A.; Fournier, G.; Cussenot, O.; Lidereau, R. VEGF overexpression in clinically localized prostate tumors and neuropilin-1 overexpression in metastatic forms. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 89, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, J.M.; Banerjee, S.; Saxena, N.K.; Cherian, R.; Banerjee, S.K. Neuropilin-1 is differentially expressed in myoepithelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells in preneoplastic and neoplastic human breast: A possible marker for the progression of breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 101, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, A.A.; Liu, W.B.; Fan, F.; Stoeltzing, O.; Reinmuth, N.; Bruns, C.J.; Bucana, C.D.; Evans, D.B.; Ellis, L.M. Expression and regulation of the novel vascular endothelial growth factor receptor neuropilin-1 by epidermal growth factor in human pancreatic carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 98, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.A.; Fan, F.; Liu, W.B.; Ahmad, S.A.; Stoeltzing, O.; Reinmuth, N.; Bielenberg, D.; Bucana, C.D.; Klagsburn, M.; Ellis, L.M. Neuropilin-1 in human colon cancer: Expression, regulation, and role in induction of angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jubb, A.M.; Strickland, L.A.; Liu, S.D.; Mak, J.; Schmidt, M.; Koeppen, H. Neuropilin-1 expression in cancer and development. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandclement, C.; Borg, C. Neuropilins: A new target for cancer therapy. Cancers 2011, 3, 1899–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puszko, A.K.; Sosnowski, P.; Pułka-Ziach, K.; Hermine, O.; Hopfgartner, G.; Lepelletier, Y.; Misicka, A. Urea moiety as amide bond mimetic in peptide-like inhibitors of VEGF-A165/NRP-1 complex. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 2493–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagri, A.; Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Watts, R.J. Neuropilins in tumor biology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1860–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soker, S.; Gollamudi-Payne, S.; Fidder, H.; Charmahelli, H.; Klagsbrun, M. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced endothelial cell proliferation by a peptide corresponding to the exon 7-encoded domain of VEGF165. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31582–31588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, K.M.; Figg, W.D. Angiogenesis inhibitors: Current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 222–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiselyov, A.; Balakin, K.V.; Tkachenko, S.E. VEGF/VEGFR signalling as a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortora, G.; Melisi, D.; Ciardiello, F. Angiogenesis: A target for cancer therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüegg, C.; Hasmim, M.; Lejeune, F.J.; Alghisi, G.C. Antiangiogenic peptides and proteins: From experimental tools to clinical drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1765, 155–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murukesh, N.; Dive, C.; Jayson, G.C. Biomarkers of angiogenesis and their role in the development of VEGF inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, K.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, B.; Xu, Y. Targeting VEGF–neuropilin interactions: A promising antitumor strategy. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Adjei, A.A. Targeting angiogenesis in cancer therapy: Moving beyond vascular endothelial growth factor. Oncologist 2015, 20, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayson, G.C.; Zweit, J.; Jackson, A.; Mulatero, C.; Julyan, P.; Ranson, M.; Broughton, L.; Wagstaff, J.; Hakannson, L.; Groenewegen, G.; et al. Molecular imaging and biological evaluation of HuMV833 anti-VEGF antibody: Implications for trial design of antiangiogenic antibodies. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1484–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, X.; Fu Wang, R. A concise review of current radiopharmaceuticals in tumor angiogenesis imaging. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 1032–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoforidis, J.B.; Briley, K.; Binzel, K.; Bhatia, P.; Wei, L.; Kumar, K.; Knopp, M.V. Systemic biodistribution and intravitreal pharmacokinetic properties of bevacizumab, ranibizumab, and aflibercept in a nonhuman primate model. Invst. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 5636–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Backer, M.V.; Backer, J.M. Imaging key biomarkers of tumor angiogenesis. Theranostics 2012, 2, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Féliz, L.R.; Tsimberidou, A.M. Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in the era of personalized medicine. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniess, T. Radiolabeled small molecule inhibitors of VEGFR-recent advances. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binétruy-Tournaire, R.; Demangel, C.; Malavaud, B.; Vassy, R.; Rouyre, S.; Kraemer, M.; Plouët, J.; Derbin, C.; Perret, G.; Mazie, J.C. Identification of a peptide blocking vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Starzec, A.; Vassy, R.; Martin, A.; Lecouvey, M.; Di Benedetto, M.; Crépin, M.; Perret, G.Y. Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of peptide inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Life Sci. 2006, 79, 2370–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teesalu, T.; Sugahara, K.N.; Kotamraju, V.R.; Ruoslahti, E. C-end rule peptides mediate neuropilin-1-dependent cell, vascular, and tissue penetration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16157–16162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jarvis, A.; Allerston, C.K.; Jia, H.; Herzog, B.; Garza-Garcia, A.; Winfield, N.; Ellard, K.; Aqil, R.; Lynch, R.; Chapman, C.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors of the neuropilin-1 vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorczyk, B.; Lipiński, P.F.; Puszko, A.K.; Tymecka, D.; Wilenska, B.; Dudka, W.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Triazolopeptides inhibiting the interaction between neuropilin-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-165. Molecules 2019, 24, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puszko, A.K.; Sosnowski, P.; Rignault-Bricard, R.; Hermine, O.; Hopfgartner, G.; Pułka-Ziach, K.; Lepelletier, Y.; Misicka, A. Urea-Peptide Hybrids as VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors with Improved Receptor Affinity and Biological Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puszko, A.K.; Sosnowski, P.; Raynaud, F.; Hermine, O.; Hopfgartner, G.; Lepelletier, Y.; Misicka, A. Does Cysteine Rule (CysR) Complete the CendR Principle? Increase in Affinity of Peptide Ligands for NRP-1 Through the Presence of N-Terminal Cysteine. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puszko, A.K.; Sosnowski, P.; Tymecka, D.; Raynaud, F.; Hermine, O.; Lepelletier, Y.; Misicka, A. Neuropilin-1 peptide-like ligands with proline mimetics, tested using the improved chemiluminescence affinity detection method. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, K.; Puszko, A.K.; Lipiński, P.F.; Laskowska, A.K.; Wileńska, B.; Witkowska, E.; Misicka, A. Design, synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation of a small cyclic peptide as inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor binding to neuropilin-1. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2843–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymecka, D.; Puszko, A.K.; Lipiński, P.F.; Fedorczyk, B.; Wilenska, B.; Sura, K.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Branched pentapeptides as potent inhibitors of the vascular endothelial growth factor 165 binding to Neuropilin-1: Design, synthesis and biological activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 158, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymecka, D.; Lipiński, P.F.; Fedorczyk, B.; Puszko, A.; Wileńska, B.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Structure-activity relationship study of tetrapeptide inhibitors of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A binding to Neuropilin-1. Peptides 2017, 94, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, K.; Puszko, A.K.; Lipiński, P.F.; Laskowska, A.K.; Wileńska, B.; Witkowska, E.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Structure-activity relationship study of a small cyclic peptide Hc[Lys-Pro-Glu]-Arg-OH: A potent inhibitor of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor interaction with Neuropilin-1. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorczyk, B.; Lipiński, P.F.; Tymecka, D.; Puszko, A.K.; Wilenska, B.; Perret, G.Y.; Misicka, A. Conformational latitude–activity relationship of KPPR tetrapeptide analogues toward their ability to inhibit binding of vascular endothelial growth factor 165 to neuropilin-1. J. Pept. Sci. 2017, 23, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzec, A.; Ladam, P.; Vassy, R.; Badache, S.; Bouchemal, N.; Navaza, A.; du Penhoat, C.H.; Perret, G.Y. Structure-function analysis of the antiangiogenic ATWLPPR peptide inhibiting VEGF165 binding to neuropilin-1 and molecular dynamics simulations of the ATWLPPR/neuropilin-1 complex. Peptides 2007, 28, 2397–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, F.; Farahani, A.M.; Rezazedeh, F.; Sadeghzadeh, N. Structural modifications of amino acid sequences of radiolabeled peptides for targeted tumor imaging. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 99, 103802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, D.H.; Singh, J. The carbodiimide method. In The Peptides: Analysis, Synthesis, Biology, Volume 1: Major Methods of Peptide; Gross, E., Meienhofer, J., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; Volume 1, pp. 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, E.; Colescott, R.L.; Bossinger, C.D.; Cook, P.I. Color test for detection of free terminal amino groups in the solid-phase synthesis of peptides. Anal. Biochem. 1970, 34, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, T. Qualitative test for monitoring coupling completeness in solid phase peptide synthesis using chloranil. Acta Chem. Scand. B 1979, 33, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izdebski, J.; Witkowska, E.; Kunce, D.; Orłowska, A.; Baranowska, B.; Radzikowska, M.; Smoluch, M. New potent hGH-RH analogues with increased resistance to enzymatic degradation. J. Pept. Sci. 2002, 8, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thieriet, N.; Alsina, J.; Giralt, E.; Guibé, F.; Albericio, F. Use of Alloc-amino Acids in Solid-Phase Peptide Synthesis. Tandem Deprotection-Coupling Reactions Using Neutral Conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 7275–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillings, N.; Hjelstuen, O.; Ballinger, J.; Behe, M.; Decristoforo, C.; Elsinga, P.; Ferrari, V.; Peitl, P.K.; Koziorowski, J.; Laverman, P.; et al. Guideline on current good radiopharmacy practice (cGRPP) for the small-scale preparation of radiopharmaceuticals. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2021, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency Guideline on the Non-Clinical Requirements for Radiopharmaceuticals. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/draft-guideline-non-clinical-requirements-radiopharmaceuticals-first-version_en.pdf (accessed on 14 December 2021).
- Balani, S.K.; Miwa, G.T.; Gan, L.-S.; Wu, J.-T.; Lee, F.W. Strategy of Utilizing In Vitro and In Vivo ADME Tools for Lead Optimization and Drug Candidate Selection. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibbitts, J.; Canter, D.; Graff, R.; Smith, A.; Khawil, L.A. Key factors influencing ADME properties of therapeutic proteins: A need for ADME characterization in drug discovery and development. mAbs 2016, 8, 229–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doogue, M.P.; Polasek, T.M. The ABCD of clinical pharmacokinetics. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2013, 4, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, E. Kinetics of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. J. Pharm. Sci. 1961, 50, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Clayton, J.M. Lipophilic character and biological activity of drugs II: The parabolic case. J. Pharm. Sci. 1973, 62, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, R.N. Determination of lipophilicity and its use as a predictor of blood–brain barrier penetration of molecular imaging agents. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2003, 5, 376–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, M.J. Lipophilicity in drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnott, J.A.; Planey, S.L. The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2012, 7, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, E.; Pajak, K.; Jóźwiak, K. Lipophilicity--methods of determination and its role in medicinal chemistry. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2013, 70, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.D.Y.; Terry, D.B.; Smith, L.H.; Markossian, S.; Grossman, A.; Brimacombe, K.; Arkin, M.; Auld, D.; Austin, C.P.; Baell, J.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Assessment of ADME and PK Properties During Lead Selection and Lead Optimization—Guidelines, Benchmarks and Rules of Thumb; Eli Lilly & Company and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences: Bethesda, ML, USA, 2004. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK326710/ (accessed on 17 December 2021).
- Pike, V. Radiotracers: Crossing the blood-brain barrier and surviving metabolism. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Misra, A.; Ganesh, S.; Shahiwala, A.; Shah, S.P. Drug delivery to the central nervous system: A review. J. Pharm Pharm. Sci. 2003, 6, 252–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]








| Conjugate | RT (min) (RP-HPLC System) | Signal Found (m/z) | Signal Calculated (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10.9 (1) | [M+3H]3+: 447.5 | [M+3H]3+: 447.0 |
| [M+2H]2+: 670.7 | M+2H]2+: 670.0 | ||
| [M−2H]2−: 668.6 | [M−2H]2−:668.0 | ||
| [M−H]−: 1337.9 | [M−H]−: 1337.9 | ||
| 2 | 9.3 (2) | [M+4H]4+: 293.2 | [M+4H]4-: 293.0 |
| [M+3H]3+: 390.6 | [M+3H]3+: 390.3 | ||
| [M+2H]2+: 585.4 | [M+2H]2+: 585.0 | ||
| [M−H]−: 1167.7 | [M−H]−: 1167.0 |
| Radioconjugate | RCY ± SD, n = 4 (%) | RCP ± SD, n = 4 (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 68Ga-1 | 93.3 ± 0.3 | 97.1 ± 0.9 |
| 177Lu-1 | 95.5 ± 1.2 | 99.8 ± 0.9 |
| 68Ga-2 | 91.5 ± 0.8 | 93.4 ± 0.3 |
| 177Lu-2 | 96.2 ± 2.6 | 99.3 ± 1.9 |
| Compound | RT (min) (RP-HPLC System) | Signal Found (m/z) | Signal Calculated (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ga-1 | 10.83 (3) | [M]+: 1405.60 and 1407.61 | [M]+: 1405.64 and 1407.64 |
| Lu-1 | 10.75 (3) | [M+H]+: 1511.63 | [M+H]+: 1511.66 |
| Ga-2 | 10.46 (4) | [M]+: 1235.60 and 1237.63 | [M]+: 1235.62 and 1237.62 |
| Lu-2 | 10.35 (4) | [M+H]+: 1341.59 | [M+H]+: 1341.62 |
| Radiocompound | RP-HPLC System | RT (min) | logP ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 68Ga-1 | 3 | 11.27 | −3.92 ± 0.03 |
| 177Lu-1 | 3 | 11.08 | −3.40 ± 0.14 |
| 68Ga-2 | 4 | 10.63 | −4.57 ± 0.05 |
| 177Lu-2 | 4 | 10.78 | −3.75 ± 0.08 |
| Radioconjugate | RCP ± SD, n = 3 (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| after 10 min | after 4.5 h | after 1 day | After 4 days | |
| 68Ga-1 | 65.3 ± 3.7 | 36.6 ± 1.4 | n/a | n/a |
| 68Ga-2 | 27.7 ± 2.0 | 3.6 ± 0.2 | n/a | n/a |
| 177Lu-1 | 39.2 ± 2.0 | --- | --- | 2.6 ± 0.2 |
| 177Lu-2 | 13.8 ± 1.5 | --- | 2.7 ± 0.1 | --- |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masłowska, K.; Witkowska, E.; Tymecka, D.; Halik, P.K.; Misicka, A.; Gniazdowska, E. Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Study of Gallium-68- and Lutetium-177-Labeled VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors Based on Peptide A7R and Branched Peptidomimetic. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010100
Masłowska K, Witkowska E, Tymecka D, Halik PK, Misicka A, Gniazdowska E. Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Study of Gallium-68- and Lutetium-177-Labeled VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors Based on Peptide A7R and Branched Peptidomimetic. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010100
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasłowska, Katarzyna, Ewa Witkowska, Dagmara Tymecka, Paweł Krzysztof Halik, Aleksandra Misicka, and Ewa Gniazdowska. 2022. "Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Study of Gallium-68- and Lutetium-177-Labeled VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors Based on Peptide A7R and Branched Peptidomimetic" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010100
APA StyleMasłowska, K., Witkowska, E., Tymecka, D., Halik, P. K., Misicka, A., & Gniazdowska, E. (2022). Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Study of Gallium-68- and Lutetium-177-Labeled VEGF-A165/NRP-1 Complex Inhibitors Based on Peptide A7R and Branched Peptidomimetic. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010100







