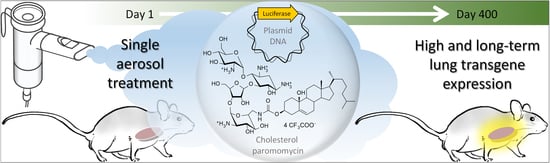
Aerosol-Mediated Non-Viral Lung Gene Therapy: The Potential of Aminoglycoside-Based Cationic Liposomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plasmid DNA
2.3. Animal Experimentation: Ethical Approval and Experimental Animals
2.4. Preparation of Liposomes
2.5. Preliminary Physicochemical Characterizations of Liposomes and Lipoplexes
2.6. Preparation of pDNA Lipoplexes for Aerosol Delivery
2.7. Aerosol Delivery
2.8. Gel Retardation Assays
2.9. Analysis of Luciferase Expression in Living Animals
2.10. Analysis of Luciferase Expression in Lung Homogenates and Cell Lines
2.11. Histology
2.12. Additional Experimental Details
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. A Rational Testing Plan Was Followed
3.2. Original Cationic Lipids Were Synthetized
3.3. Cationic Lipids and Colipids with Structural Diversity Were Considered
3.4. All Combinations of Lipidic Compounds Cannot Be Stably Formulated at High Concentrations
3.5. All Lipidic Formulations Were Not Stable When Mixed with Highly Concentrated pDNA
3.6. All Lipoplexes Showing Colloidal Stability Were Suitable for Delivery via Aerosol
3.7. All the Aerosols Performed Were Safe for the Animals
3.8. Aerosolized Formulations Demonstrated Diverse Abilities to Transfect Lungs In Vivo
3.9. Further Studies Detailed the Interest of CholP/DOPE for Aerosol Lung Gene Delivery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cutting, G.R. Cystic Fibrosis Genetics: From Molecular Understanding to Clinical Application. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mall, M.A.; Mayer-Hamblett, N.; Rowe, S.M. Cystic Fibrosis: Emergence of Highly Effective Targeted Therapeutics and Potential Clinical Implications. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 201, 1193–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alton, E.W.; Boyd, A.C.; Davies, J.C.; Gill, D.R.; Griesenbach, U.; Harman, T.E.; Hyde, S.; McLachlan, G. Gene Therapy for Respiratory Diseases: Progress and a Changing Context. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alton, E.W.; Armstrong, D.K.; Ashby, D.; Bayfield, K.J.; Bilton, D.; Bloomfield, E.V.; Boyd, A.C.; Brand, J.; Buchan, R.; Calcedo, R.; et al. Repeated Nebulisation of Non-Viral CFTR Gene Therapy in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2b Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2015, 3, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alton, E.W.; Beekman, J.M.; Boyd, A.C.; Brand, J.; Carlon, M.S.; Connolly, M.M.; Chan, M.; Conlon, S.; Davidson, H.E.; Davies, J.C.; et al. Preparation for a First-in-Man Lentivirus Trial in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Thorax 2017, 72, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, L.A.; Nunez-Alonso, G.A.; McLachlan, G.; Hyde, S.C.; Gill, D.R. Aerosol Delivery of DNA/Liposomes to the Lung for Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. Clin. Dev. 2014, 25, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenbach, U.; Alton, E.W. Moving Forward: Cystic Fibrosis Gene Therapy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, R52–R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mottais, A.; Berchel, M.; Sibiril, Y.; Laurent, V.; Gill, D.; Hyde, S.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Montier, T.; Le Gall, T. Antibacterial Effect and DNA Delivery Using a Combination of an Arsonium-Containing Lipophosphoramide with an N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Silver Complex-Potential Benefits for Cystic Fibrosis Lung Gene Therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottais, A.; Berchel, M.; Le Gall, T.; Sibiril, Y.; d’Arbonneau, F.; Laurent, V.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Montier, T. Antibacterial and Transfection Activities of Nebulized Formulations Incorporating Long N-Alkyl Chain Silver N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 567, 118500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.R.; Marshall, J.; Siegel, C.S.; Jiang, C.; Yew, N.S.; Nichols, M.R.; Nietupski, J.B.; Ziegler, R.J.; Lane, M.B.; Wang, K.X.; et al. Detailed Analysis of Structures and Formulations of Cationic Lipids for Efficient Gene Transfer to the Lung. Hum. Gene Ther. 1996, 7, 1701–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, N.N.; De Smedt, S.C.; Cheng, S.H.; Demeester, J. Pegylated GL67 Lipoplexes Retain Their Gene Transfection Activity after Exposure to Components of CF Mucus. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLachlan, G.; Davidson, H.; Holder, E.; Davies, L.A.; Pringle, I.A.; Sumner-Jones, S.G.; Baker, A.; Tennant, P.; Gordon, C.; Vrettou, C.; et al. Pre-Clinical Evaluation of Three Non-Viral Gene Transfer Agents for Cystic Fibrosis after Aerosol Delivery to the Ovine Lung. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 996–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alton, E.W.; Baker, A.; Baker, E.; Boyd, A.C.; Cheng, S.H.; Coles, R.L.; Collie, D.D.S.; Davidson, H.; Davies, J.C.; Gill, D.R.; et al. The Safety Profile of a Cationic Lipid-Mediated Cystic Fibrosis Gene Transfer Agent Following Repeated Monthly Aerosol Administration to Sheep. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10267–10277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alton, E.W.; Boyd, A.C.; Cheng, S.H.; Davies, J.C.; Davies, L.A.; Dayan, A.; Gill, D.R.; Griesenbach, U.; Higgins, T.; Hyde, S.C.; et al. Toxicology Study Assessing Efficacy and Safety of Repeated Administration of Lipid/DNA Complexes to Mouse Lung. Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alton, E.W.; Boyd, A.C.; Cheng, S.H.; Cunningham, S.; Davies, J.C.; Gill, D.R.; Griesenbach, U.; Higgins, T.; Hyde, S.C.; Innes, J.A.; et al. A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase IIB Clinical Trial of Repeated Application of Gene Therapy in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Thorax 2013, 68, 1075–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, D.R.; Hyde, S.C. Delivery of Genes into the CF Airway. Thorax 2014, 69, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mével, M.; Neveu, C.; Goncalves, C.; Yaouanc, J.J.; Pichon, C.; Jaffrès, P.A.; Midoux, P. Novel Neutral Imidazole-Lipophosphoramides for Transfection Assays. Chem. Comm. 2008, 27, 3124–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Gall, T.; Berchel, M.; Le Hir, S.; Fraix, A.; Salaün, J.Y.; Férec, C.; Lehn, P.; Jaffres, P.-A.; Montier, T. Arsonium-Containing Lipophosphoramides, Poly-Functional Nano-Carriers for Simultaneous Antibacterial Action and Eukaryotic Cell Transfection. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 1513–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Corre, S.S.; Berchel, M.; Belmadi, N.; Denis, C.; Haelters, J.-P.; Le Gall, T.; Lehn, P.; Montier, T.; Jaffrès, P.-A. Cationic Lipophosphoramidates with Two Different Lipid Chains: Synthesis and Evaluation as Gene Carriers. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picquet, E.; Le Ny, K.; Delépine, P.; Montier, T.; Yaouanc, J.J.; Cartier, D.; des Abbayes, H.; Férec, C.; Clément, J.C. Cationic Lipophosphoramidates and Lipophosphoguanidines Are Very Efficient for in Vivo DNA Delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2005, 16, 1051–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, T.; Loizeau, D.; Picquet, E.; Carmoy, N.; Yaouanc, J.J.; Burel-Deschamps, L.; Delepine, P.; Giamarchi, P.; Jaffres, P.A.; Lehn, P.; et al. A Novel Cationic Lipophosphoramide with Diunsaturated Lipid Chains: Synthesis, Physicochemical Properties, and Transfection Activities. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1496–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, M.F.; Carmoy, N.; Le Gall, T.; Fraix, A.; Berchel, M.; Lorilleux, C.; Couthon-Gourvès, H.; Bellaud, P.; Fautrel, A.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; et al. The Gene Transfection Properties of a Lipophosphoramidate Derivative with Two Phytanyl Chains. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6240–6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gall, T.; Barbeau, J.; Barrier, S.; Berchel, M.; Lemiègre, L.; Jeftić, J.; Meriadec, C.; Artzner, F.; Gill, D.R.; Hyde, S.C.; et al. Effects of a Novel Archaeal Tetraether-Based Colipid on the in Vivo Gene Transfer Activity of Two Cationic Amphiphiles. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 2973–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchel, M.; Le Gall, T.; Haelters, J.-P.; Lehn, P.; Montier, T.; Jaffrès, P.-A. Cationic Lipophosphoramidates Containing a Hydroxylated Polar Headgroup for Improving Gene Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, M.F.; Le Gall, T.; Carmoy, N.; Berchel, M.; Hyde, S.C.; Gill, D.R.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Lehn, P.; Montier, T. Efficient in Vivo Transfection and Safety Profile of a CpG-Free and Codon Optimized Luciferase Plasmid Using a Cationic Lipophosphoramidate in a Multiple Intravenous Administration Procedure. Biomaterials 2015, 59, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesenbach, U.; Sumner-Jones, S.G.; Holder, E.; Munkonge, F.M.; Wodehouse, T.; Smith, S.N.; Wasowicz, M.Y.; Pringle, I.; Casamayor, I.; Chan, M.; et al. Limitations of the Murine Nose in the Development of Nonviral Airway Gene Transfer. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2010, 43, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, C.; Berchel, M.; Gosselin, M.-P.; Malard, V.; Cheradame, H.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; Guégan, P.; Pichon, C.; Midoux, P. Lipopolyplexes Comprising Imidazole/Imidazolium Lipophosphoramidate, Histidinylated Polyethyleneimine and SiRNA as Efficient Formulation for SiRNA Transfection. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desigaux, L.; Sainlos, M.; Lambert, O.; Chevre, R.; Letrou-Bonneval, E.; Vigneron, J.P.; Lehn, P.; Lehn, J.M.; Pitard, B. Self-Assembled Lamellar Complexes of SiRNA with Lipidic Aminoglycoside Derivatives Promote Efficient SiRNA Delivery and Interference. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16534–16539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mével, M.; Sainlos, M.; Chatin, B.; Oudrhiri, N.; Hauchecorne, M.; Lambert, O.; Vigneron, J.-P.; Lehn, P.; Pitard, B.; Lehn, J.-M. Paromomycin and Neomycin B Derived Cationic Lipids: Synthesis and Transfection Studies. J. Control Release 2012, 158, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, E.L.; Loomis, K.H.; Bhosle, S.M.; Vanover, D.; Baumhof, P.; Pitard, B.; Zurla, C.; Santangelo, P.J. Proximity Ligation Assays for In Situ Detection of Innate Immune Activation: Focus on In Vitro-Transcribed MRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids 2019, 14, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhosle, S.M.; Loomis, K.H.; Kirschman, J.L.; Blanchard, E.L.; Vanover, D.A.; Zurla, C.; Habrant, D.; Edwards, D.; Baumhof, P.; Pitard, B.; et al. Unifying in Vitro and in Vivo IVT MRNA Expression Discrepancies in Skeletal Muscle via Mechanotransduction. Biomaterials 2018, 159, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, K.E.; Bhosle, S.M.; Zurla, C.; Beyersdorf, J.; Rogers, K.A.; Vanover, D.; Xiao, P.; Araínga, M.; Shirreff, L.M.; Pitard, B.; et al. Visualization of Early Events in MRNA Vaccine Delivery in Non-Human Primates via PET-CT and near-Infrared Imaging. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habrant, D.; Peuziat, P.; Colombani, T.; Dallet, L.; Gehin, J.; Goudeau, E.; Evrard, B.; Lambert, O.; Haudebourg, T.; Pitard, B. Design of Ionizable Lipids to Overcome the Limiting Step of Endosomal Escape: Application in the Intracellular Delivery of MRNA, DNA, and SiRNA. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3046–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Réthoré, G.; Montier, T.; Le Gall, T.; Delépine, P.; Cammas-Marion, S.; Lemiègre, L.; Lehn, P.; Benvegnu, T. Archaeosomes Based on Synthetic Tetraether-like Lipids as Novel Versatile Gene Delivery Systems. Chem. Commun. 2007, 20, 2054–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demazeau, M.; Quesnot, N.; Ripoche, N.; Rauch, C.; Jeftić, J.; Morel, F.; Gauffre, F.; Benvegnu, T.; Loyer, P. Efficient Transfection of Xenobiotic Responsive Element-Biosensor Plasmid Using Diether Lipid and Phosphatidylcholine Liposomes in Differentiated HepaRG Cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 524, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, S.C.; Pringle, I.A.; Abdullah, S.; Lawton, A.E.; Davies, L.A.; Varathalingam, A.; Nunez-Alonso, G.; Green, A.M.; Bazzani, R.P.; Sumner-Jones, S.G.; et al. CpG-Free Plasmids Confer Reduced Inflammation and Sustained Pulmonary Gene Expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, B.D.; Loffing, J.; Schwiebert, E.M.; Loffing-Cueni, D.; Halpin, P.A.; Karlson, K.H.; Ismailov, I.I.; Guggino, W.B.; Langford, G.M.; Stanton, B.A. Membrane Trafficking of the Cystic Fibrosis Gene Product, Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator, Tagged with Green Fluorescent Protein in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 21759–21768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danos, O.; Davies, K.; Lehn, P.; Mulligan, R. The ARRIVE Guidelines, a Welcome Improvement to Standards for Reporting Animal Research. J. Gene Med. 2010, 12, 559–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snouwaert, J.N.; Brigman, K.K.; Latour, A.M.; Malouf, N.N.; Boucher, R.C.; Smithies, O.; Koller, B.H. An Animal Model for Cystic Fibrosis Made by Gene Targeting. Science 1992, 257, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Szoka, F.C., Jr. Mechanism of DNA Release from Cationic Liposome/DNA Complexes Used in Cell Transfection. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 5616–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuhorn, I.S.; Oberle, V.; Visser, W.H.; Engberts, J.B.F.N.; Bakowsky, U.; Polushkin, E.; Hoekstra, D. Phase Behavior of Cationic Amphiphiles and Their Mixtures with Helper Lipid Influences Lipoplex Shape, DNA Translocation, and Transfection Efficiency. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 2096–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koltover, I.; Salditt, T.; Rädler, J.O.; Safinya, C.R. An Inverted Hexagonal Phase of Cationic Liposome-DNA Complexes Related to DNA Release and Delivery. Science 1998, 281, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, M.J.; Nantz, M.H.; Balasubramaniam, R.P.; Gruenert, D.C.; Malone, R.W. Cholesterol Enhances Cationic Liposome-Mediated DNA Transfection of Human Respiratory Epithelial Cells. Biosci. Rep. 1995, 15, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Fiardo, P.; Hervouet, C.; Marsault, R.; Franken, P.R.; Cambien, B.; Guglielmi, J.; Warnez-Soulie, J.; Darcourt, J.; Pourcher, T.; Colombani, T.; et al. Evaluation of Tetrafunctional Block Copolymers as Synthetic Vectors for Lung Gene Transfer. Biomaterials 2015, 45, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, I.; Riou, M.; Hacquin, O.; Chevaleyre, C.; Barc, C.; Pezant, J.; Pinard, A.; Fassy, J.; Rezzonico, R.; Mari, B.; et al. Tetrafunctional Block Copolymers Promote Lung Gene Transfer in Newborn Piglets. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierrat, P.; Wang, R.; Kereselidze, D.; Lux, M.; Didier, P.; Kichler, A.; Pons, F.; Lebeau, L. Efficient in Vitro and in Vivo Pulmonary Delivery of Nucleic Acid by Carbon Dot-Based Nanocarriers. Biomaterials 2015, 51, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mastorakos, P.; da Silva, A.L.; Chisholm, J.; Song, E.; Choi, W.K.; Boyle, M.P.; Morales, M.M.; Hanes, J.; Suk, J.S. Highly Compacted Biodegradable DNA Nanoparticles Capable of Overcoming the Mucus Barrier for Inhaled Lung Gene Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8720–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konstan, M.W.; Davis, P.B.; Wagener, J.S.; Hilliard, K.A.; Stern, R.C.; Milgram, L.J.H.; Kowalczyk, T.H.; Hyatt, S.L.; Fink, T.L.; Gedeon, C.R.; et al. Compacted DNA Nanoparticles Administered to the Nasal Mucosa of Cystic Fibrosis Subjects Are Safe and Demonstrate Partial to Complete Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Regulator Reconstitution. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 1255–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesenbach, U.; Vicente, C.C.; Roberts, M.J.; Meng, C.; Soussi, S.; Xenariou, S.; Tennant, P.; Baker, A.; Baker, E.; Gordon, C.; et al. Secreted Gaussia Luciferase as a Sensitive Reporter Gene for in Vivo and Ex Vivo Studies of Airway Gene Transfer. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2614–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, L.A.; McLachlan, G.; Sumner-Jones, S.G.; Ferguson, D.; Baker, A.; Tennant, P.; Gordon, C.; Vrettou, C.; Baker, E.; Zhu, J.; et al. Enhanced Lung Gene Expression after Aerosol Delivery of Concentrated PDNA/PEI Complexes. Mol. Ther. 2008, 16, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mével, M.; Breuzard, G.; Yaouanc, J.J.; Clément, J.C.; Lehn, P.; Pichon, C.; Jaffrès, P.A.; Midoux, P. Synthesis and Transfection Activity of New Cationic Phosphoramidate Lipids: High Efficiency of an Imidazolium Derivative. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezanet, C.; Kempf, J.; Mingeot-Leclercq, M.-P.; Décout, J.-L. Amphiphilic Aminoglycosides as Medicinal Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellucci, M.C.; Volonterio, A. Aminoglycosides: From Antibiotics to Building Blocks for the Synthesis and Development of Gene Delivery Vehicles. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmont, P.; Aissaoui, A.; Hauchecorne, M.; Oudrhiri, N.; Petit, L.; Vigneron, J.P.; Lehn, J.M.; Lehn, P. Aminoglycoside-Derived Cationic Lipids as Efficient Vectors for Gene Transfection in Vitro and in Vivo. J. Gen Med. 2002, 4, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainlos, M.; Belmont, P.; Vigneron, J.P.; Lehn, P.; Lehn, J.M. Aminoglycoside-Derived Cationic Lipids for Gene Transfection: Synthesis of Kanamycin A Derivatives. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 2003, 2764–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainlos, M.; Hauchecorne, M.; Oudrhiri, N.; Zertal-Zidani, S.; Aissaoui, A.; Vigneron, J.P.; Lehn, J.M.; Lehn, P. Kanamycin A-Derived Cationic Lipids as Vectors for Gene Transfection. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gall, T.; Baussanne, I.; Halder, S.; Carmoy, N.; Montier, T.; Lehn, P.; Decout, J.L. Synthesis and Transfection Properties of a Series of Lipidic Neamine Derivatives. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 2032–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beuzelin, D.; Pitard, B.; Kaeffer, B. Oral Delivery of MiRNA With Lipidic Aminoglycoside Derivatives in the Breastfed Rat. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatin, B.; Mével, M.; Devallière, J.; Dallet, L.; Haudebourg, T.; Peuziat, P.; Colombani, T.; Berchel, M.; Lambert, O.; Edelman, A.; et al. Liposome-Based Formulation for Intracellular Delivery of Functional Proteins. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallet, L.; Decossas, M.; Taveau, J.-C.; Lecomte, S.; Poussard, S.; Lambert, O.; Pitard, B. Single Lipoaminoglycoside Promotes Efficient Intracellular Antibody Delivery: A Comprehensive Insight into the Mechanism of Action. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombani, T.; Peuziat, P.; Dallet, L.; Haudebourg, T.; Mével, M.; Berchel, M.; Lambert, O.; Habrant, D.; Pitard, B. Self-Assembling Complexes between Binary Mixtures of Lipids with Different Linkers and Nucleic Acids Promote Universal MRNA, DNA and SiRNA Delivery. J. Control Release 2017, 249, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mével, M.; Haudebourg, T.; Colombani, T.; Peuziat, P.; Dallet, L.; Chatin, B.; Lambert, O.; Berchel, M.; Montier, T.; Jaffrès, P.-A.; et al. Important Role of Phosphoramido Linkage in Imidazole-Based Dioleyl Helper Lipids for Liposome Stability and Primary Cell Transfection. J. Gene Med. 2016, 18, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopaczynska, M.; Schulz, A.; Fraczkowska, K.; Kraszewski, S.; Podbielska, H.; Fuhrhop, J.H. Selective Condensation of DNA by Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. Eur. Biophys. J. 2016, 45, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Afonso, D.; Le Gall, T.; Couthon-Gourvès, H.; Grélard, A.; Prakash, S.; Berchel, M.; Kervarec, N.; Dufourc, E.J.; Montier, T.; Jaffrès, P.-A. Triggering Bilayer to Inverted-Hexagonal Nanostructure Formation by Thiol-Ene Click Chemistry on Cationic Lipids: Consequences on Gene Transfection. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 4516–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlins, E.L.; Hogan, B.L.M. Ciliated Epithelial Cell Lifespan in the Mouse Trachea and Lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L231–L234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, N.; Donnelley, M.; Cmielewski, P.; Roscioli, E.; Rout-Pitt, N.; McIntyre, C.; Bertoncello, I.; Parsons, D.W. Role of Basal Cells in Producing Persistent Lentivirus-Mediated Airway Gene Expression. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herweijer, H.; Zhang, G.; Subbotin, V.M.; Budker, V.; Williams, P.; Wolff, J.A. Time Course of Gene Expression after Plasmid DNA Gene Transfer to the Liver. J. Gene Med. 2001, 3, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Ludtke, J.J.; Acsadi, G.; Williams, P.; Jani, A. Long-Term Persistence of Plasmid DNA and Foreign Gene Expression in Mouse Muscle. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1992, 1, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrom, J.E.; Hegge, J.; Zhang, G.; Noble, M.; Budker, V.; Lewis, D.L.; Herweijer, H.; Wolff, J.A. A Facile Nonviral Method for Delivering Genes and SiRNAs to Skeletal Muscle of Mammalian Limbs. Mol. Ther. 2004, 10, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, R.; Laurent, V.; Roquefort, P.; Haute, T.; Ramel, S.; Gall, T.L.; Aubry, T.; Montier, T. Optimizations of In Vitro Mucus and Cell Culture Models to Better Predict In Vivo Gene Transfer in Pathological Lung Respiratory Airways: Cystic Fibrosis as an Example. Pharmaceutics 2020, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, R.; Roquefort, P.; Ramel, S.; Laurent, V.; Haute, T.; Le Gall, T.; Aubry, T.; Montier, T. Apparent Yield Stress of Sputum as a Relevant Biomarker in Cystic Fibrosis. Cells 2021, 10, 3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, A.V.; Midoux, P.; Gras, D.; Si-Tahar, M.; Bréa, D.; Attucci, S.; Khelloufi, M.-K.; Ramphal, R.; Diot, P.; Gauthier, F.; et al. Poly-L-Lysine Compacts DNA, Kills Bacteria, and Improves Protease Inhibition in Cystic Fibrosis Sputum. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerem, E.; Konstan, M.W.; De Boeck, K.; Accurso, F.J.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Wilschanski, M.; Elborn, J.S.; Melotti, P.; Bronsveld, I.; Fajac, I.; et al. Ataluren for the Treatment of Nonsense-Mutation Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheer, S.M.; Waugh, J.; Noble, S. Inhaled Tobramycin (TOBI): A Review of Its Use in the Management of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infections in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Drugs 2003, 63, 2501–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, L.A.; Hyde, S.C.; Nunez-Alonso, G.; Bazzani, R.P.; Harding-Smith, R.; Pringle, I.A.; Lawton, A.E.; Abdullah, S.; Roberts, T.C.; McCormick, D.; et al. The Use of CpG-Free Plasmids to Mediate Persistent Gene Expression Following Repeated Aerosol Delivery of PDNA/PEI Complexes. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5618–5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| # | CL | Counter Ion | MW 1 | Geo.2 | Headgroup | Z+ 3 | Lipid Domain | cLogP 4 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DOPAs | 1 I− | 872 | C | Trimethyl-arsonium | Pc (1) | (C18:1)2 | 14.2 | [20] |
| 2 | DOGB | 1 Cl− | 756 | C | Glycine betaine | Pc (1) | (C18:1)2 | 8.5 | [23] |
| 3 | DOPIm | 1 Br− | 787 | C | Imidazolium | Pc (1) | (C18:1)2 | 10.1 | [27] |
| 4 | DOSP | 4 CF3COO− | 1672 | T | Paromomycin | Pa (4) | (C18:1)2 | −6.8 | [28] |
| 5 | CholAs | 1 I− | 705 | L | Trimethyl-arsonium | Pc (1) | Chol | 9.2 | This study |
| 6 | CholIm | 1 I− | 620 | L | Imidazolium | Pc (1) | Chol | 4.5 | This study |
| 7 | CholP | 4 CF3COO− | 1484 | T | Paromomycin | Pa (4) | Chol | −12.4 | [29] |
| 8 | CholT | 4 CF3COO− | 1336 | L | Tobramycin | Pa (4) | Chol | −10.5 | [33] |
| 9 | CholK | 3 CF3COO− | 1239 | L | Kanamycin | Pa (3) | Chol | −8.1 | [30,31,32] |
| 10 | CholKB | 4 CF3COO− | 1352 | L | Kanamycin B | Pa (4) | Chol | −11.2 | [30,31,32] |
| 11 | CholRi | 3 CF3COO− | 1209 | T | Ribostamycin | Pa (3) | Chol | −7.5 | [29] |
| 12 | GL67 | 2 Cl− | 629 | T | Spermine | Pa (2) | Chol | 0.9 | [10] |
| Lipidic Formulation Composition | Physicochemistry | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F# | CL | [CL] 1 | Colipid(s) 2 | MR 3 | [DP5K] 4 | Size 5 | PdI 6 | Zeta 7 |
| F1 | CholAs | 15.0 | None | Na | 5 | 178 | 0.20 | +50 |
| F2 | CholIm | 30.0 | DOPE | 3/2 | 10 | 108 | 0.21 | +50 |
| F3 | DOSP | 3.7 | DOPI | 1/1 | 5 | 309 | 0.52 | Nd |
| F4 | DOPIm | 30.0 | Chol/DOPE | 1/1/1 | 10 | 353 | 0.51 | +50 |
| F5 | DOPAs | 30.0 | None | Na | 5 | 136 | 0.26 | +69 |
| F6 | DOSP | 7.5 | DOPE | 1/1 | 10 | 254 | 0.42 | Nd |
| F7 | DOSP | 7.5 | Tetraether | 5/1 | 10 | 117 | 0.25 | +54 |
| F8 | DOGB | 30.0 | Tetraether | 10/1 | 5 | 190 | 0.32 | +28 |
| F9 | DOSP | 15.0 | DOPI | 1/1 | 10 | 126 | 0.20 | +53 |
| F10 | DOSP | 7.5 | DOPI | 1/1 | 5 | 92 | 0.26 | +67 |
| F11 | CholP | 7.5 | Diether | 1/2 | 10 | 220 | 0.46 | Nd |
| F12 | DOPIm | 30.0 | DOPI | 1/1 | 5 | 135 | 0.22 | +38 |
| F13 | CholRi | 10.0 | DOPE | 1/2 | 10 | Nd | Nd | Nd |
| F14 | CholKB | 7.5 | DOPE | 1/2 | 10 | Nd | Nd | Nd |
| F15 | CholP | 7.5 | DOPE | 1/1 | 10 | 143 | 0.29 | +53 |
| F16 | CholP | 7.5 | DOPI | 1/1 | 10 | 172 | 0.31 | +57 |
| F17 | CholK | 10.0 | DOPE | 1/2 | 10 | Nd | Nd | Nd |
| F18 | GL67 | 15.0 | DOPE | 1/2 | 5 | 294 | 0.27 | +55 |
| F19 | CholT | 7.5 | DOPE | 1/2 | 10 | Nd | Nd | Nd |
| F20 | CholP | 7.5 | DOPE | 1/2 | 10 | 256 | 0.12 | Nd |
| Lipid + pDNA Formulation Composition | Physicochemistry | In Vivo Evaluation 9 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F# + L 1 | CL | Colipid(s) 2 | MR 3 | PR 4 | CR 5 | Size 6 | PdI 7 | Zeta 8 | D1 | D7 | D14/28 | Group |
| F1 + L | CholAs | None | Na | 1 | 1 | 325 | 0.36 | +37 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Gr1 |
| F2 + L | CholIm | DOPE | 3/2 | 2 | 2 | 160 | 0.29 | +22 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Gr1 |
| F3 + L | DOSP | DOPI | 1/1 | 1 | 1 | 307 | 0.52 | Nd | 5 | 2 | 1 | Gr1 |
| F4 + L | DOPIm | Chol/DOPE | 1/1/1 | 2 | 2 | 197 | 0.18 | +21 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Gr1 |
| F5 + L | DOPAs | None | Na | 1 | 2 | 245 | 0.50 | +38 | 1 | 3 | 1 | Gr1 |
| F6 + L | DOSP | DOPE | 1/1 | 2 | 2 | 289 | 0.36 | Nd | 1 | 4 | 5 | Gr2 |
| F7 + L | DOSP | Tetraether | 5/1 | 2 | 2 | 224 | 0.63 | Nd | 1 | 3 | 2 | Gr2 |
| F8 + L | DOGB | Tetraether | 10/1 | 1 | 2 | 190 | 0.32 | +28 | 1 | 5 | 7 | Gr2 |
| F9 + L | DOSP | DOPI | 1/1 | 2 | 4 | 481 | 0.76 | +1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | Gr2 |
| F10 + L | DOSP | DOPI | 1/1 | 1 | 2 | 153 | 0.29 | +5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Gr2 |
| F11 + L | CholP | Diether | 1/2 | 2 | 2 | 193 | 0.39 | Nd | 1 | Nd | 3 | Gr2 |
| F12 + L | DOPIm | DOPI | 1/1 | 1 | 2 | 192 | 0.33 | +43 | 2 | Nd | 1 | Gr2 |
| F13 + L | CholRi | DOPE | 1/2 | 2 | 2 | Nd | Nd | Nd | 1 | 6 | 4 | Gr2 |
| F14 + L | CholKB | DOPE | 1/2 | 2 | 2 | Nd | Nd | Nd | 1 | 3 | 2 | Gr3 |
| F15 + L | CholP | DOPE | 1/1 | 2 | 2 | 307 | 0.52 | Nd | 1 | 1 | 1 | Gr3 |
| F16 + L | CholP | DOPI | 1/1 | 2 | 2 | 259 | 0.33 | Nd | 2 | Nd | 1 | Gr3 |
| F17 + L | CholK | DOPE | 1/2 | 2 | 2 | Nd | Nd | Nd | 1 | 3 | 5 | Gr3 |
| F18 + L | GL67 | DOPE | 1/2 | 1 | 2 | 262 | 0.22 | +30 | 1 | 3 | 4 | Gr3 |
| F19 + L | CholT | DOPE | 1/2 | 2 | 2 | Nd | Nd | Nd | 1 | 3 | 8 | Gr3 |
| F20 + L | CholP | DOPE | 1/2 | 2 | 2 | 168 | 0.27 | Nd | 1 | 1 | 2 | Gr4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Le Gall, T.; Berchel, M.; Davies, L.; Mottais, A.; Ghanem, R.; Fautrel, A.; Gill, D.; Hyde, S.; Lehn, P.; Lehn, J.-M.; et al. Aerosol-Mediated Non-Viral Lung Gene Therapy: The Potential of Aminoglycoside-Based Cationic Liposomes. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010025
Le Gall T, Berchel M, Davies L, Mottais A, Ghanem R, Fautrel A, Gill D, Hyde S, Lehn P, Lehn J-M, et al. Aerosol-Mediated Non-Viral Lung Gene Therapy: The Potential of Aminoglycoside-Based Cationic Liposomes. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleLe Gall, Tony, Mathieu Berchel, Lee Davies, Angélique Mottais, Rosy Ghanem, Alain Fautrel, Deborah Gill, Steve Hyde, Pierre Lehn, Jean-Marie Lehn, and et al. 2022. "Aerosol-Mediated Non-Viral Lung Gene Therapy: The Potential of Aminoglycoside-Based Cationic Liposomes" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010025
APA StyleLe Gall, T., Berchel, M., Davies, L., Mottais, A., Ghanem, R., Fautrel, A., Gill, D., Hyde, S., Lehn, P., Lehn, J.-M., Lemiègre, L., Benvegnu, T., Jaffrès, P.-A., Pitard, B., & Montier, T. (2022). Aerosol-Mediated Non-Viral Lung Gene Therapy: The Potential of Aminoglycoside-Based Cationic Liposomes. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010025