Liposomal Artificial Red Blood Cell-Based Carbon Monoxide Donor Is a Potent Renoprotectant against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of CO-HbV
2.2. Animals
2.3. Renoprotective Effect of CO-HbV against CDDP-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Mice
2.4. Determination of Biological Parameters
2.5. Histological Examinations
2.6. Western Blotting Analysis
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Influence of CO-HbV on Tumor Growth in B16-F10 Melanoma Cell-Bearing Mice
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Renoprotective Effect of CO-HbV on CDDP-Induced Nephrotoxicity
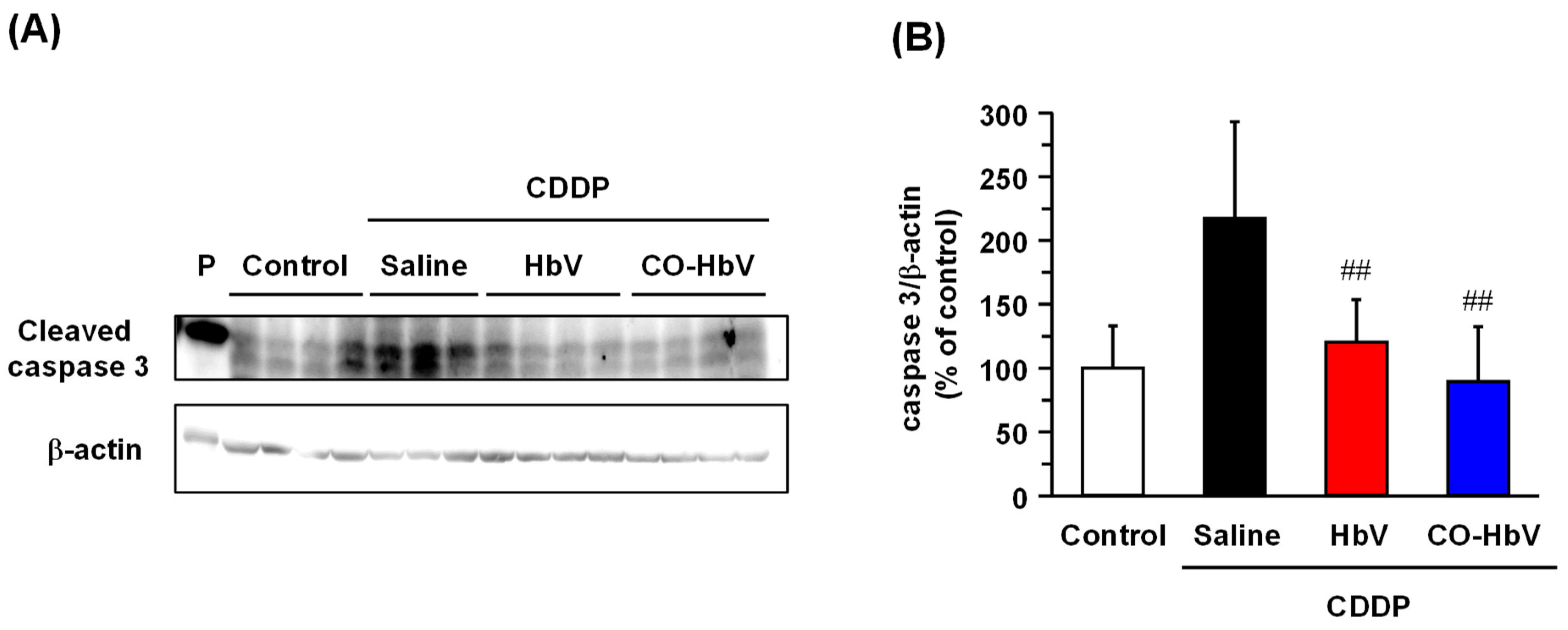
3.2. Protective Mechanism of CO-HbV against CDDP-Induced Nephrotoxicity
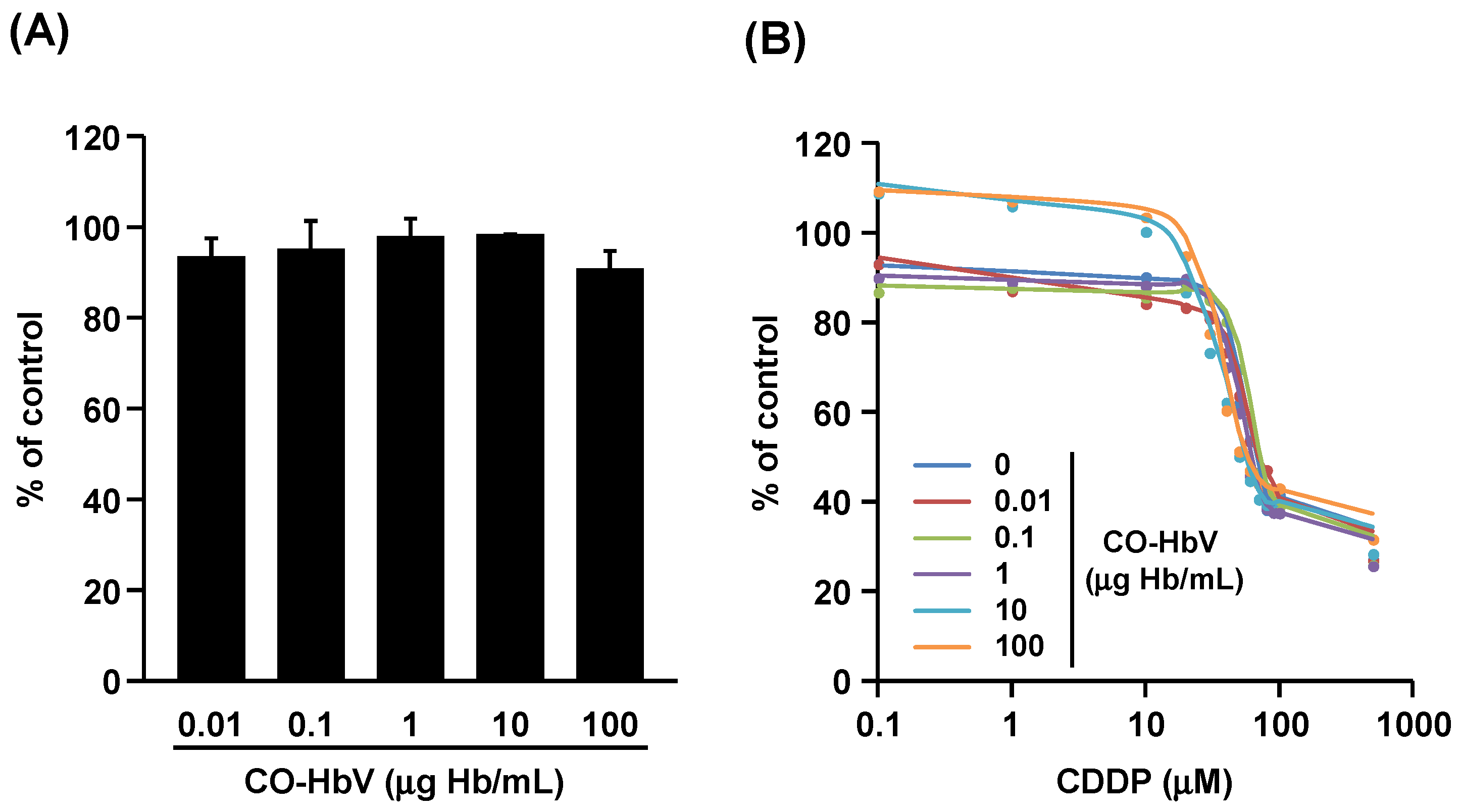
3.3. Effect of CO-HbV on Anti-Tumor Activity of CDDP against B16-F10 Melanoma Cells In Vitro
3.4. Effect of CO-HbV on Anti-Tumor Activity of CDDP in B16-F10 Melanoma Cell-Bearing Mice
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yao, X.; Panichpisal, K.; Kurtzman, N.; Nugent, K. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: A review. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2007, 334, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crona, D.J.; Faso, A.; Nishijima, T.F.; McGraw, K.A.; Galsky, M.D.; Milowsky, M.I. A Systematic Review of Strategies to Prevent Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity. Oncologist 2017, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Launay-Vacher, V.; Rey, J.B.; Isnard-Bagnis, C.; Deray, G.; Daouphars, M. Prevention of cisplatin nephrotoxicity: State of the art and recommendations from the European Society of Clinical Pharmacy Special Interest Group on Cancer Care. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 61, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horie, S.; Oya, M.; Nangaku, M.; Yasuda, Y.; Komatsu, Y.; Yanagita, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kuwano, H.; Nishiyama, H.; Ishioka, C.; et al. Guidelines for treatment of renal injury during cancer chemotherapy 2016. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2018, 22, 210–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamroun, A.; Lenain, R.; Bigna, J.J.; Speyer, E.; Bui, L.; Chamley, P.; Pottier, N.; Cauffiez, C.; Dewaeles, E.; Dhalluin, X.; et al. Prevention of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Drugs 2019, 79, 1567–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongnuanjan, P.; Soodvilai, S.; Fongsupa, S.; Chabang, N.; Vivithanaporn, P.; Tuchinda, P.; Soodvilai, S. Protective Effect of Panduratin A on Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis of Human Renal Proximal Tubular Cells and Acute Kidney Injury in Mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.Y.; Lou, D.Y.; Zhou, L.Q.; Wang, J.C.; Yang, B.; He, Q.J.; Wang, J.J.; Weng, Q.J. Natural products: Potential treatments for cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2021, 42, 1951–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, A.; Watanabe, H.; Tanaka, R.; Kondo, M.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Wu, Q.; Endo, M.; Ishima, Y.; Fukagawa, M.; Otagiri, M.; et al. Albumin fusion renders thioredoxin an effective anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory agent for preventing cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Chang, R.; Wu, H.; Lin, J.; Huang, Z. Exogenous Carbon Monoxide Decreases Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury and Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20595–20608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uddin, M.J.; Pak, E.S.; Ha, H. Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 protects mice against acute kidney injury through inhibition of ER stress. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taguchi, K.; Ogaki, S.; Nagasaki, T.; Yanagisawa, H.; Nishida, K.; Maeda, H.; Enoki, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Sekijima, H.; Ooi, K.; et al. Carbon monoxide rescues the developmental lethality of experimental rat models of rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2020, 372, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.E.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.H.; Han, W.K. Renoprotective Effects of Carbon Monoxide-Releasing Molecule 3 in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Cisplatin-Induced Toxicity. Transplant. Proc. 2017, 49, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayem, Y.; Johnson, T.R.; Mann, B.E.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Protection against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by a carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F789–F794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abuchowski, A. SANGUINATE (PEGylated Carboxyhemoglobin Bovine): Mechanism of Action and Clinical Update. Artif. Organs 2017, 41, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogaki, S.; Taguchi, K.; Watanabe, H.; Ishima, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Carbon monoxide-bound red blood cell resuscitation ameliorates hepatic injury induced by massive hemorrhage and red blood cell resuscitation via hepatic cytochrome P450 protection in hemorrhagic shock rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2199–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Use of Hemoglobin for Delivering Exogenous Carbon Monoxide in Medicinal Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2949–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Kure, T.; Okuda, C. Translational research of hemoglobin vesicles as a transfusion alternative. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Yamasaki, K.; Sakai, H.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. The Use of Hemoglobin Vesicles for Delivering Medicinal Gas for the Treatment of Intractable Disorders. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 2392–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Horinouchi, H.; Tsuchida, E.; Kobayashi, K. Hemoglobin vesicles and red blood cells as carriers of carbon monoxide prior to oxygen for resuscitation after hemorrhagic shock in a rat model. Shock 2009, 31, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, S.; Taguchi, K.; Sakai, H.; Tanaka, R.; Horinouchi, H.; Watanabe, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Carbon monoxide-bound hemoglobin-vesicles for the treatment of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6553–6562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, S.; Taguchi, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Wakayama, T.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Yamasaki, K.; Watanabe, H.; Sakai, H.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Evaluation of a new type of nano-sized carbon monoxide donor on treating mice with experimentally induced colitis. J. Control. Release 2016, 234, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, K.; Nagao, S.; Maeda, H.; Yanagisawa, H.; Sakai, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Wakayama, T.; Watanabe, H.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Biomimetic carbon monoxide delivery based on hemoglobin vesicles ameliorates acute pancreatitis in mice via the regulation of macrophage and neutrophil activity. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagao, S.; Taguchi, K.; Sakai, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Watanabe, H.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Carbon monoxide-bound hemoglobin vesicles ameliorate multiorgan injuries induced by severe acute pancreatitis in mice by their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5611–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watabe, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Sakai, H.; Enoki, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M.; Kohno, M.; Matsumoto, K. Bioinspired carbon monoxide delivery using artificial blood attenuates the progression of obliterative bronchiolitis via suppression of macrophage activation by IL-17A. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 170, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kure, T.; Sakai, H. Preparation of Artificial Red Blood Cells (Hemoglobin Vesicles) Using the Rotation-Revolution Mixer for High Encapsulation Efficiency. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, H.; Tomiyama, K.; Masada, Y.; Takeoka, S.; Horinouchi, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsuchida, E. Pretreatment of serum containing hemoglobin vesicles (oxygen carriers) to prevent their interference in laboratory tests. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2003, 41, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Lu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Hung, T.T.; Stenzel, M.H. Safety of nanoparticles based on albumin-polymer conjugates as a carrier of nucleotides for pancreatic cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6278–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSweeney, K.R.; Gadanec, L.K.; Qaradakhi, T.; Ali, B.A.; Zulli, A.; Apostolopoulos, V. Mechanisms of Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: Pathological Mechanisms, Pharmacological Interventions, and Genetic Mitigations. Cancers 2021, 13, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Chapman, G.B.; Peyton, K.J.; Schafer, A.I.; Durante, W. Antiapoptotic action of carbon monoxide on cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2003, 228, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.M.; Chapman, G.B.; Peyton, K.J.; Schafer, A.I.; Durante, W. Carbon monoxide inhibits apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 55, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Un, H.; Ugan, R.A.; Gurbuz, M.A.; Bayir, Y.; Kahramanlar, A.; Kaya, G.; Cadirci, E.; Halici, Z. Phloretin and phloridzin guard against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice through inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation. Life Sci. 2021, 266, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, T.; Razak, S.; Aldisi, D.; Shabbir, M.; Almajwal, A.; Al Kheraif, A.A.; Arshad, M. Acacia hydaspica R. Parker ethyl-acetate extract abrogates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by targeting ROS and inflammatory cytokines. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motterlini, R.; Otterbein, L.E. The therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.; Gao, H. Harnessing carbon monoxide-releasing platforms for cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegiel, B.; Gallo, D.; Csizmadia, E.; Harris, C.; Belcher, J.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Penacho, N.; Seth, P.; Sukhatme, V.; Ahmed, A.; et al. Carbon monoxide expedites metabolic exhaustion to inhibit tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 7009–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perše, M. Cisplatin Mouse Models: Treatment, Toxicity and Translatability. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Izumi, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Teramura, Y.; Sakai, H.; Kohno, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kawamura, M.; Adachi, T.; Ikeda, E.; et al. Systemic administration of hemoglobin vesicle elevates tumor tissue oxygen tension and modifies tumor response to irradiation. J. Surg. Res. 2009, 151, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K. Pharmaceutical Technology Innovation Strategy Based on the Function of Blood Transport Proteins as DDS Carriers for the Treatment of Intractable Disorders and Cancer. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1815–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taguchi, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Tsutsuura, M.; Hiraoka, K.; Watabe, Y.; Enoki, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Sakai, H.; Matsumoto, K. Liposomal Artificial Red Blood Cell-Based Carbon Monoxide Donor Is a Potent Renoprotectant against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010057
Taguchi K, Suzuki Y, Tsutsuura M, Hiraoka K, Watabe Y, Enoki Y, Otagiri M, Sakai H, Matsumoto K. Liposomal Artificial Red Blood Cell-Based Carbon Monoxide Donor Is a Potent Renoprotectant against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaguchi, Kazuaki, Yuto Suzuki, Moeko Tsutsuura, Kana Hiraoka, Yuki Watabe, Yuki Enoki, Masaki Otagiri, Hiromi Sakai, and Kazuaki Matsumoto. 2022. "Liposomal Artificial Red Blood Cell-Based Carbon Monoxide Donor Is a Potent Renoprotectant against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010057
APA StyleTaguchi, K., Suzuki, Y., Tsutsuura, M., Hiraoka, K., Watabe, Y., Enoki, Y., Otagiri, M., Sakai, H., & Matsumoto, K. (2022). Liposomal Artificial Red Blood Cell-Based Carbon Monoxide Donor Is a Potent Renoprotectant against Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Pharmaceutics, 14(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010057






