Rowan Berries: A Potential Source for Green Synthesis of Extremely Monodisperse Gold and Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Property
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
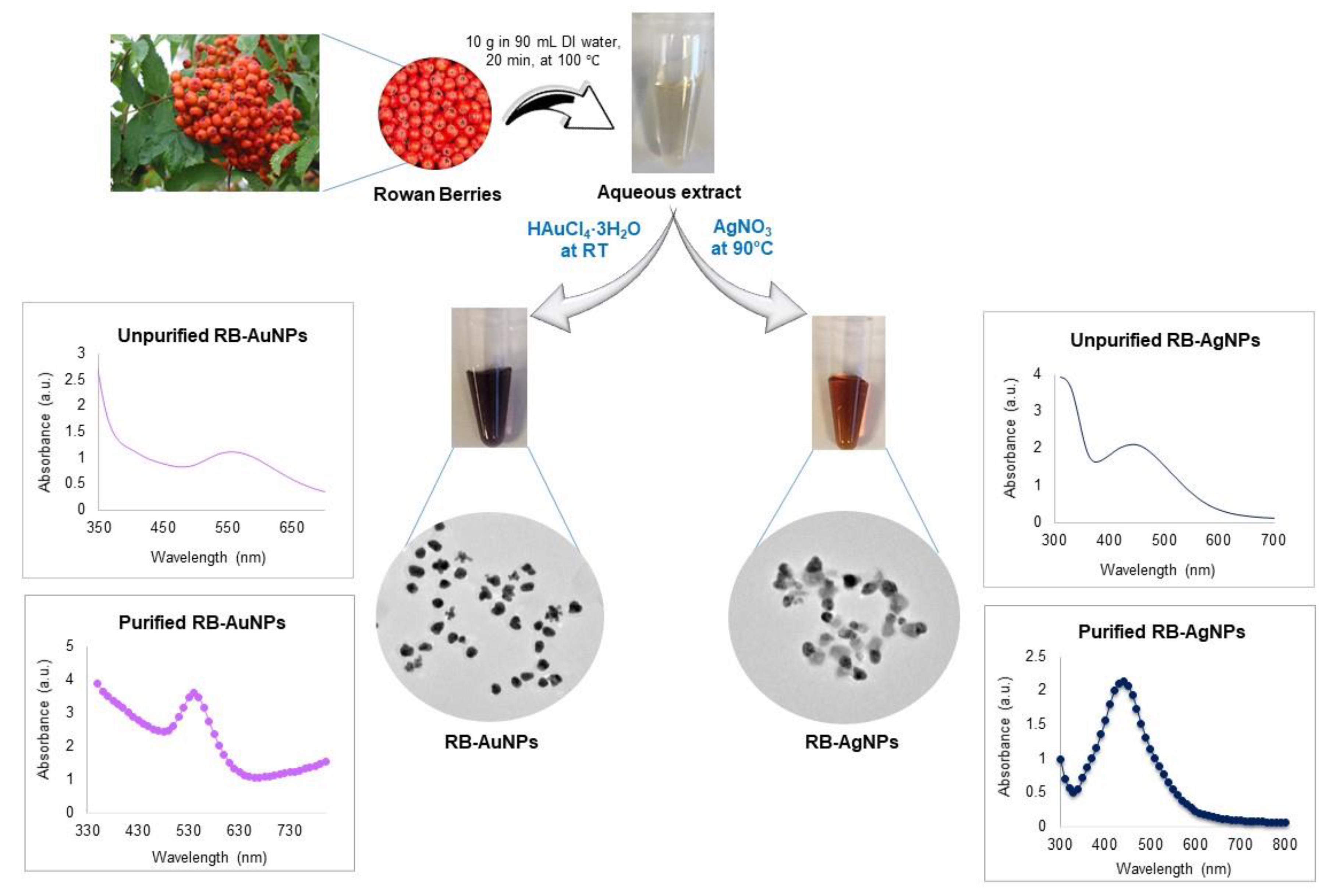
2.2. Green Synthesis of RB-AuNPs and RB-AgNPs
2.3. Analytical Characterization of RB-AuNPs and RB-AgNPs
2.3.1. UV-Vis Study
2.3.2. Single-Particle Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (sp-ICP-MS)
2.3.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX), and Elemental Mapping
2.3.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.3.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.3.7. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.3.8. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
2.4. Antibacterial Activity of RB-AgNPs
2.4.1. RB-AgNPs Effects on Gram-Negative Pathogens
2.4.2. Live and Dead Staining
2.4.3. SEM Analysis of Treated Cells
3. Results
3.1. Green Synthesis of RB-AuNPs and RB-AgNPs
3.2. Characterization of RB-AuNPs and RB-AgNPs
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of RB-AgNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.-C. Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles from Plants and Microorganisms. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Ahn, S.; Kang, J.P.; Veronika, S.; Huo, Y.; Singh, H.; Chokkaligam, M.; El-Agamy Farh, M.; Aceituno, V.C.; Kim, Y.J.; et al. In vitroanti-inflammatory activity of spherical silver nanoparticles and monodisperse hexagonal gold nanoparticles by fruit extract of Prunus serrulata: A green synthetic approach. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ssekatawa, K.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Kato, C.D.; Wampande, E.M.; Ejobi, F.; Nakavuma, J.L.; Maaza, M.; Sackey, J.; Nxumalo, E.; Kirabira, J.B. Green Strategy–Based Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Applications. Front. Nanotechnol. 2021, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Garnæs, J.; Tunjic, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.; Sultan, A.; Thygesen, A.; Mackevica, A.; Mateiu, R.V.; Daugaard, A.E.; et al. Green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles from Cannabis sativa (industrial hemp) and their capacity for biofilm inhibition. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3571–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailie, A.; Renaut, S.; Ubalijoro, E.; Guerrero-Analco, J.A.; Saleem, A.; Haddad, P.; Arnason, J.T.; Johns, T.; Cuerrier, A. Phytogeographic and genetic variation inSorbus, a traditional antidiabetic medicine—Adaptation in action in both a plant and a discipline. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarv, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Bhat, R. The Sorbus spp.—Underutilised Plants for Foods and Nutraceuticals: Review on Polyphenolic Phytochemicals and Antioxidant Potential. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šavikin, K.P.; Zdunić, G.M.; Krstić-Milošević, D.B.; Šircelj, H.; Stešević, D.D.; Pljevljakušić, D.S. Sorbus aucupariaandSorbus ariaas a Source of Antioxidant Phenolics, Tocopherols, and Pigments. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zymone, K.; Raudone, L.; Raudonis, R.; Marksa, M.; Ivanauskas, L.; Janulis, V. Phytochemical Profiling of Fruit Powders of Twenty Sorbus L. Cultivars. Molecules 2018, 23, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kylli, P.; Nohynek, L.; Puupponen-Pimiä, R.; Westerlund-Wikström, B.; McDougall, G.; Stewart, D.; Heinonen, M. Rowanberry Phenolics: Compositional Analysis and Bioactivities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11985–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, E.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Patras, A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A.; Tudor, C.; Sturza, R. The Influence of Temperature, Storage Conditions, pH, and Ionic Strength on the Antioxidant Activity and Color Parameters of Rowan Berry Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlcek, J.; Rop, O.; Jurikova, T.; Sochor, J.; Fišera, M.; Balla, S.; Baron, M.; Hrabe, J. Bioactive compounds in sweet rowanberry fruits of interspecific Rowan crosses. Open Life Sci. 2014, 9, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rónavári, A.; Igaz, N.; Adamecz, D.I.; Szerencsés, B.; Molnar, C.; Kónya, Z.; Pfeiffer, I.; Kiricsi, M. Green Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Biological Synthesis Approaches and Potentials for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdușel, A.-C.; Gherasim, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoantă, L.; Ficai, A.; Andronescu, E. Biomedical Applications of Silver Nanoparticles: An Up-to-Date Overview. Nanomater 2018, 8, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gherasim, O.; Puiu, R.A.; Bîrcă, A.C.; Burdușel, A.-C.; Grumezescu, A.M. An Updated Review on Silver Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. Nanomater 2020, 10, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.-J. Gold nanoparticles: Emerging paradigm for targeted drug delivery system. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Advances in gold nanoparticle technology as a tool for diagnostics and treatment of cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 21, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.X.; Shameli, K.; Yew, Y.P.; Teow, S.-Y.; Jahangirian, H.; Rafiee-Moghaddam, R.; Webster, T.J. Recent Developments in the Facile Bio-Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs) and Their Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Du, J.; Singh, P.; Yi, T.H. Ecofriendly synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Euphrasia officinalis leaf extract and its biomedical applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Yang, D.C. Microbial synthesis of Flower-shaped gold nanoparticles. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Garnæs, J.; Mijakovic, I. A Sustainable Approach for the Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Solibacillus isronensis sp. and Their Application in Biofilm Inhibition. Molecules 2020, 25, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Beshay, M.; Mokkapati, V.R.S.S.; Garnaes, J.; Olsson, M.E.; Sultan, A.; Mackevica, A.; Mateiu, R.V.; Lütken, H.; et al. Anti-biofilm effects of gold and silver nanoparticles synthesized by the Rhodiola rosea rhizome extracts. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S886–S899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Tian, B.; Li, T.; Dai, S.; Weng, Y.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, Y.; Pang, R.; Hua, Y. Biosynthesis of Au, Ag and Au–Ag bimetallic nanoparticles using protein extracts of Deinococcus radiodurans and evaluation of their cytotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1411–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amina, M.; Al Musayeib, N.M.; Alarfaj, N.A.; El-Tohamy, M.F.; Al-Hamoud, G.A. Antibacterial and Immunomodulatory Potentials of Biosynthesized Ag, Au, Ag-Au Bimetallic Alloy Nanoparticles Using the Asparagus racemosus Root Extract. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinath, K.; Kumaraguru, S.; Bhakyaraj, K.; Mohan, S.; Venkatesh, K.S.; Esakkirajan, M.; Kaleeswarran, P.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Govindarajan, M.; et al. Green synthesis of silver, gold and silver/gold bimetallic nanoparticles using the Gloriosa superba leaf extract and their antibacterial and antibiofilm activities. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Marroquín, D.; Cruz, D.M.; Nieto-Argüello, A.; Crua, A.V.; Chen, J.; Torres-Castro, A.; Webster, T.J.; Cholula-Díaz, J.L. Starch-mediated synthesis of mono- and bimetallic silver/gold nanoparticles as antimicrobial and anticancer agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2171–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbai, R.; Ramya Mathiyalagan, J.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Wang, C.; Singh, P.; Ahn, S.; Farh, M.E.A.; Yang, D.C. Green synthesis of multifunctional silver and gold nanoparticles from the oriental herbal adaptogen: Siberian ginseng. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3131–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, H.; Du, J.; Singh, P.; Yi, T.H. Role of green silver nanoparticles synthesized from Symphytum officinale leaf extract in protection against UVB-induced photoaging. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2018, 8, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomelí-Rosales, D.A.; Zamudio-Ojeda, A.; Cortes-Llamas, S.A.; Velázquez-Juárez, G. One-step synthesis of gold and silver non-spherical nanoparticles mediated by Eosin Methylene Blue agar. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chokkalingam, M.; Singh, P.; Huo, Y.; Soshnikova, V.; Ahn, S.; Kang, J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. Facile synthesis of Au and Ag nanoparticles using fruit extract of Lycium chinense and their anticancer activity. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albeladi, S.S.R.; Malik, M.A.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A. Facile biofabrication of silver nanoparticles using Salvia officinalis leaf extract and its catalytic activity towards Congo red dye degradation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 10031–10044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahardoli, A.; Karimi, N.; Sadeghi, F.; Fattahi, A. Green approach for synthesis of gold nanoparticles from Nigella arvensis leaf extract and evaluation of their antibacterial, antioxidant, cytotoxicity and catalytic activities. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles Using Some Selected Medicinal Plants from Southern Africa and Their Biological Applications. Plants 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, H.; Kumari, P.; Bontempi, E.; Yadav, S. Medicinal plants: Treasure trove for green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Bharath, L. Mechanism of plant-mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles—A review on biomolecules involved, characterisation and antibacterial activity. Chem. Interact. 2017, 273, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denev, P.; Kratchanova, M.; Ciz, M.; Lojek, A.; Vasicek, O.; Nedelcheva, P.; Blazheva, D.; Toshkova, R.; Gardeva, E.; Yossifova, L.; et al. Biological activities of selected polyphenol-rich fruits related to immunity and gastrointestinal health. Food Chem. 2014, 157, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.P.; Kim, Y.J.; Singh, P.; Huo, Y.; Soshnikova, V.; Markus, J.; Ahn, S.; Chokkalingam, M.; Lee, H.A.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis of gold and silver chloride nanoparticles mediated by Crataegus pinnatifida fruit extract: In vitro study of anti-inflammatory activities. Artif. Cells Nanomedicin Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1530–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soshnikova, V.; Kim, Y.J.; Singh, P.; Huo, Y.; Markus, J.; Ahn, S.; Castro-Aceituno, V.; Kang, J.; Chokkalingam, M.; Mathiyalagan, R.; et al. Cardamom fruits as a green resource for facile synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles and their biological applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Singh, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Wang, C.; Yang, D.C. Extracellular synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles by Sporosarcina koreensis DC4 and their biological applications. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 86, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shen, W.; Xue, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, J. Recent advances in synthetic methods and applications of silver nanostructures. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubey, S.P.; Lahtinen, M.; Särkkä, H.; Sillanpää, M. Bioprospective of Sorbus aucuparia leaf extract in development of silver and gold nanocolloids. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, Y.; Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Soshnikova, V.; Kang, J.; Markus, J.; Ahn, S.; Castro-Aceituno, V.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Chokkalingam, M.; et al. Biological synthesis of gold and silver chloride nanoparticles by Glycyrrhiza uralensis and in vitro applications. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2017, 46, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kang, H.; Buchman, J.T.; Rodriguez, R.S.; Ring, H.L.; He, J.; Bantz, K.C.; Haynes, C.L. Stabilization of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles: Preservation and Improvement of Plasmonic Functionalities. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 664–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Shin, H.-S. Facile green biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Pisum sativum L. outer peel aqueous extract and its antidiabetic, cytotoxicity, antioxidant, and antibacterial activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6679–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masum, M.I.; Siddiqa, M.M.; Ali, K.A.; Zhang, Y.; Abdallah, Y.; Ibrahim, E.; Qiu, W.; Yan, C.; Li, B. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Phyllanthus emblica Fruit Extract and Its Inhibitory Action Against the Pathogen Acidovorax oryzae Strain RS-2 of Rice Bacterial Brown Stripe. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisan, C.M.; Mocan, T.; Manolea, M.; Lasca, L.I.; Tăbăran, F.-A.; Mocan, L. Review on Silver Nanoparticles as a Novel Class of Antibacterial Solutions. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Interactions of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles with Bacterial Biofilms: Molecular Interactions behind Inhibition and Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Kim, Y.J.; Yang, D.C. A strategic approach for rapid synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles by Panax ginseng leaves. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]










Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Rowan Berries: A Potential Source for Green Synthesis of Extremely Monodisperse Gold and Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Property. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010082
Singh P, Mijakovic I. Rowan Berries: A Potential Source for Green Synthesis of Extremely Monodisperse Gold and Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Property. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(1):82. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010082
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Priyanka, and Ivan Mijakovic. 2022. "Rowan Berries: A Potential Source for Green Synthesis of Extremely Monodisperse Gold and Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antimicrobial Property" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 1: 82. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14010082






