Development of Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Hydrogel for Buccal Delivery of (S)-Ketamine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.3. Preparation of Artificial Media for Hydrogel Studies
2.3.1. Artificial Saliva Preparation
2.3.2. Mucin Solution Preparation
2.4. Gelling Temperature Study
2.5. In Vitro Evaluation of Mucoadhesion
2.5.1. Flow Measurements
2.5.2. Oscillatory Measurements
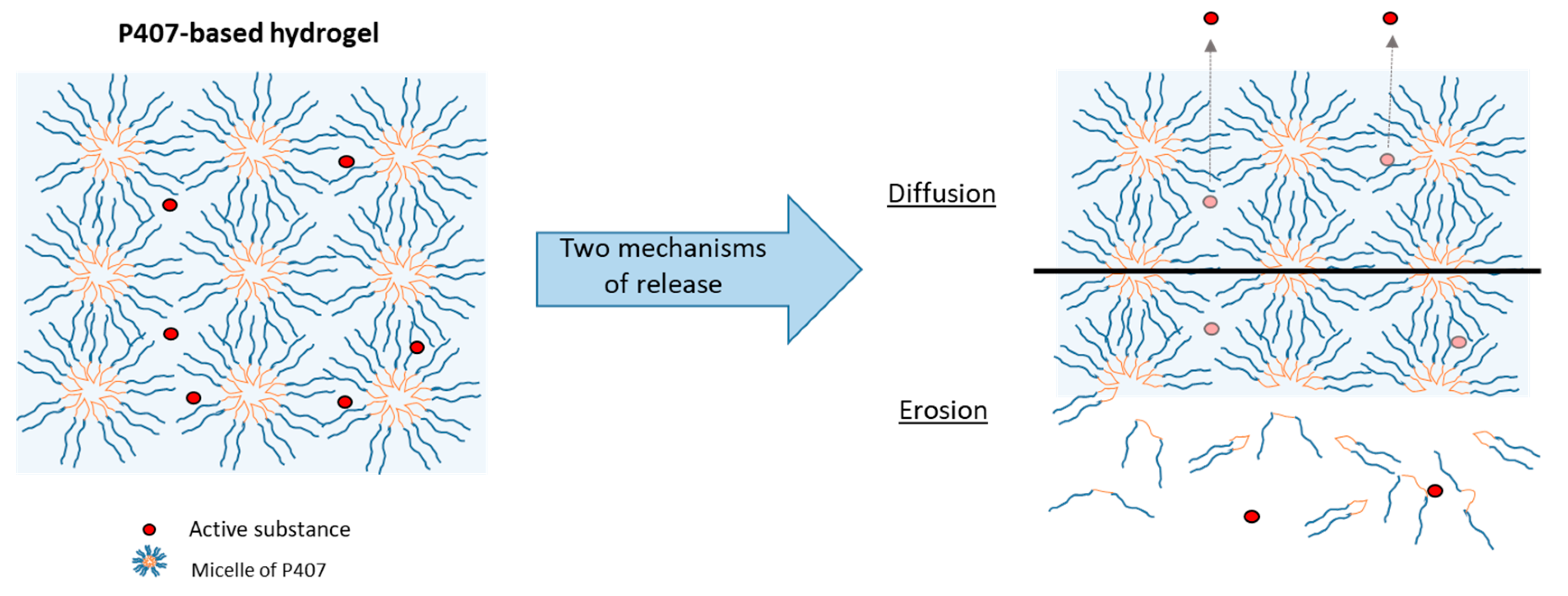
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Relation between Concentration of Poloxamer and Gelling Temperature
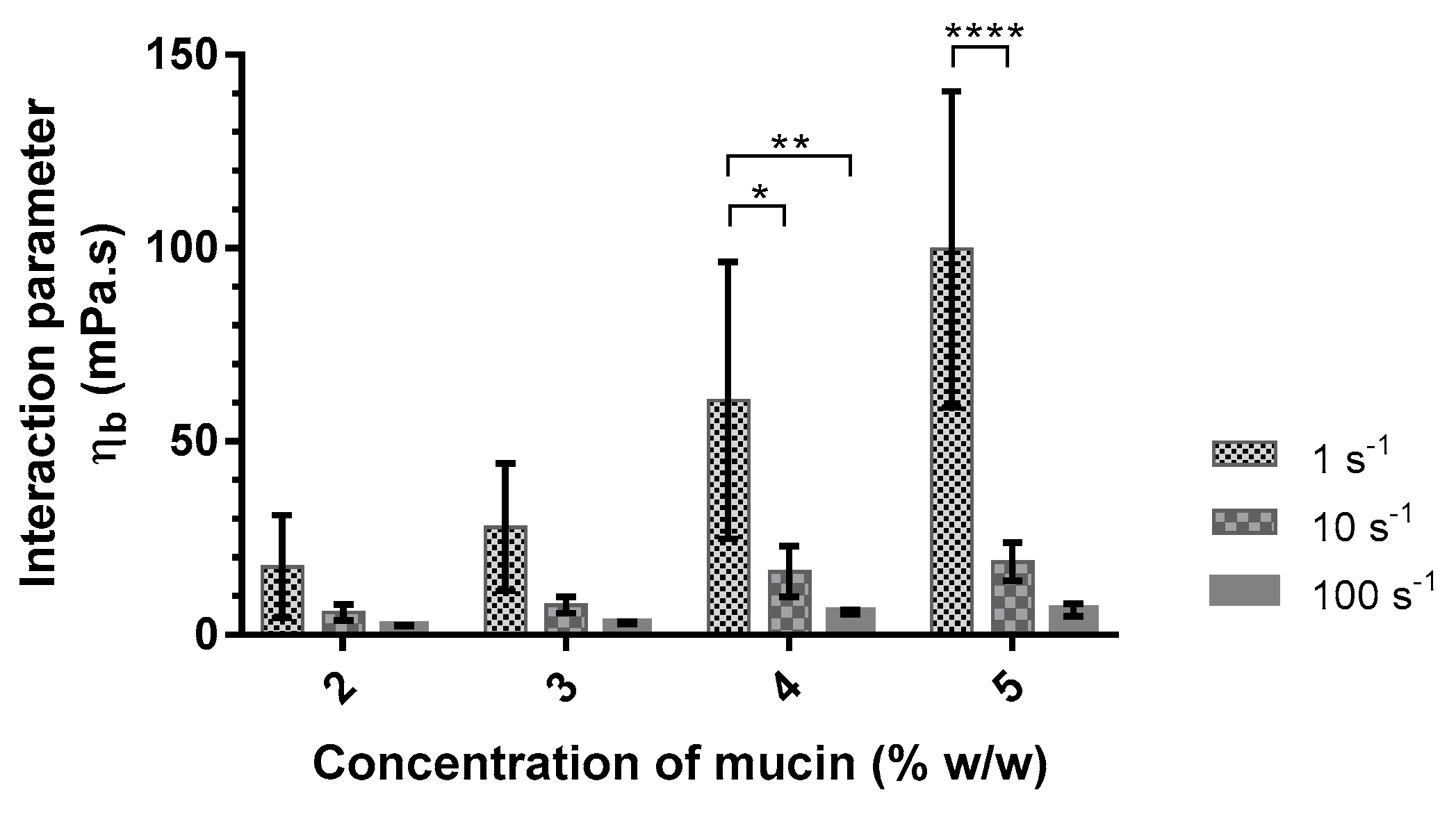
3.2. Mucoadhesive Properties
3.2.1. Mucoadhesive Properties of Alginate
3.2.2. Mucoadhesive Properties of P407–Alginate Association
3.3. Effect of P407 Batches on Rheological Parameters
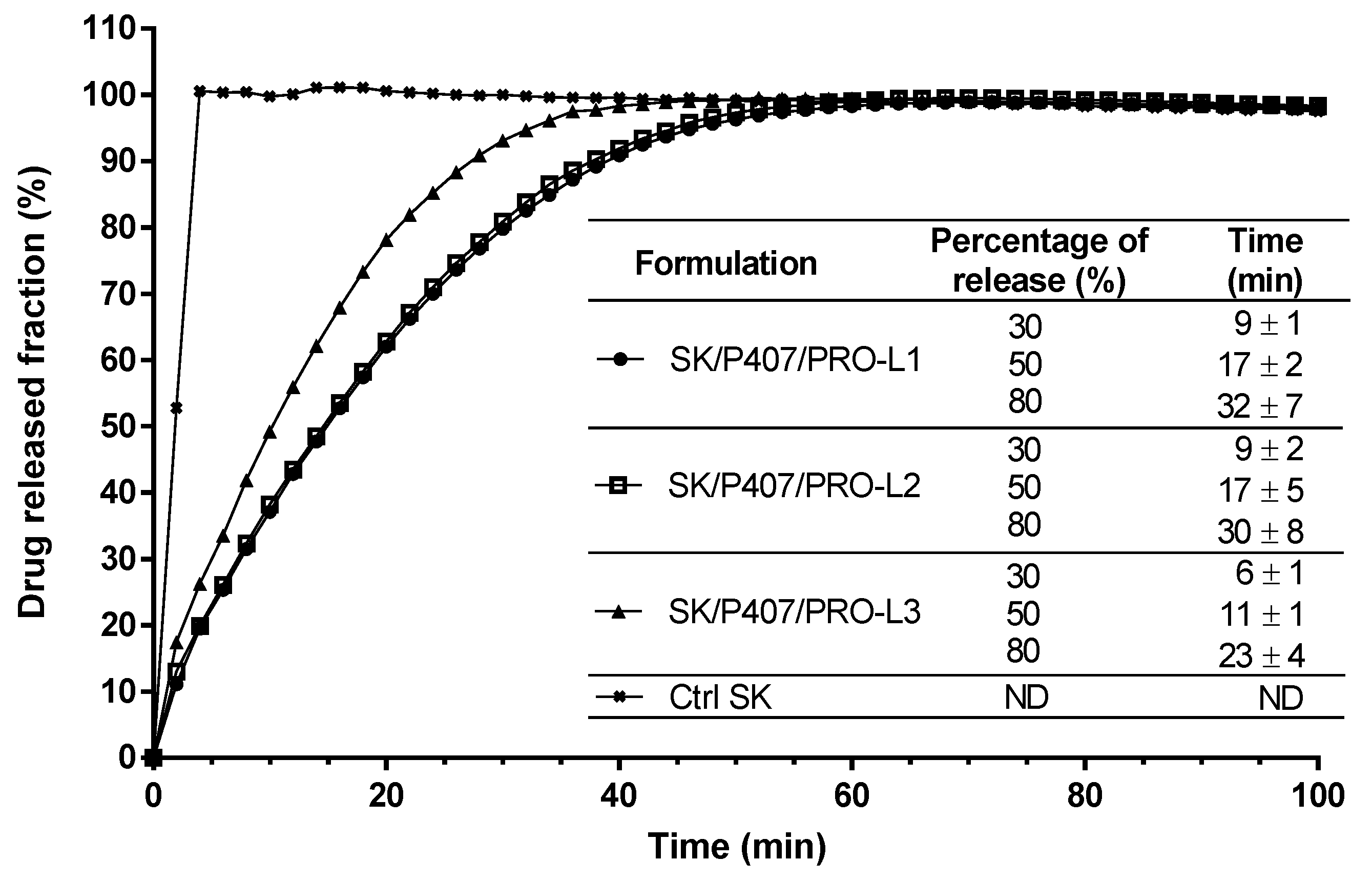
3.4. Effect of P407 Batches on Drug Release Profiles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gai, N.; Naser, B.; Hanley, J.; Peliowski, A.; Hayes, J.; Aoyama, K. A Practical Guide to Acute Pain Management in Children. J. Anesth. 2020, 34, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, B.S.; Calligaris, L.; Green, S.M.; Barbi, E. Current Concepts in Management of Pain in Children in the Emergency Department. Lancet 2016, 387, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, B.; Green, S.M. Procedural Sedation and Analgesia in Children. Lancet 2006, 367, 766–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.M.; Rothrock, S.G.; Harris, T.; Hopkins, G.A.; Garrett, W.; Sherwin, T. Intravenous Ketamine for Pediatric Sedation in the Emergency Department: Safety Profile with 156 Cases. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1998, 5, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.M.; Rothrock, S.G.; Lynch, E.L.; Ho, M.; Harris, T.; Hestdalen, R.; Hopkins, G.A.; Garrett, W.; Westcott, K. Intramuscular Ketamine for Pediatric Sedation in the Emergency Department: Safety Profile in 1022 Cases. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1998, 31, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M.A.; Hagelberg, N.M.; Olkkola, K.T.; Saari, T.I. Ketamine: A Review of Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Anesthesia and Pain Therapy. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 1059–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, W.; Buxhoeveden, M.; Dhillon, S. Ketamine: A Versatile Tool for Anesthesia and Analgesia. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 33, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mion, G.; Villevieille, T. Ketamine Pharmacology: An Update (Pharmacodynamics and Molecular Aspects, Recent Findings). CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2013, 19, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaji, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Koyano, K.; Yokoyama, T.; Nakanishi, H. Preferential Inhibitory Effects of S-Ketamine on Both NMDA Receptor Currents and Neuropathic Pain. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 68, e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich Zeilhofer, H.; Swandulla, D.; Geisslinger, G.; Brune, K. Differential Effects of Ketamine Enantiomers on NMDA Receptor Currents in Cultured Neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 213, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanta, S.; Kinnunen, M.; Backman, J.T.; Kalso, E. Population Pharmacokinetics of S-Ketamine and Norketamine in Healthy Volunteers after Intravenous and Oral Dosing. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltoniemi, M.A.; Saari, T.I.; Hagelberg, N.M.; Laine, K.; Kurkinen, K.J.; Neuvonen, P.J.; Olkkola, K.T. Rifampicin Has a Profound Effect on the Pharmacokinetics of Oral S-Ketamine and Less on Intravenous S-Ketamine. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 111, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlerick, L.; Devreese, M.; Peremans, K.; Dockx, R.; Croubels, S.; Duchateau, L.; Polis, I. Pharmacokinetics, Absolute Bioavailability and Tolerability of Ketamine after Intranasal Administration to Dexmedetomidine Sedated Dogs. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza Ferreira, S.B.; Moço, T.D.; Borghi-Pangoni, F.B.; Junqueira, M.V.; Bruschi, M.L. Rheological, Mucoadhesive and Textural Properties of Thermoresponsive Polymer Blends for Biomedical Applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 55, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braccini, I.; Pérez, S. Molecular Basis of Ca2+ -Induced Gelation in Alginates and Pectins: The Egg-Box Model Revisited. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popeski-Dimovski, R. Work of Adhesion between Mucin Macromolecule and Calcium-Alginate Gels on Molecular Level. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 123, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caetano, L.; Almeida, A.; Gonçalves, L. Effect of Experimental Parameters on Alginate/Chitosan Microparticles for BCG Encapsulation. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horniblow, R.D.; Latunde-Dada, G.O.; Harding, S.E.; Schneider, M.; Almutairi, F.M.; Sahni, M.; Bhatti, A.; Ludwig, C.; Norton, I.T.; Iqbal, T.H.; et al. The Chelation of Colonic Luminal Iron by a Unique Sodium Alginate for the Improvement of Gastrointestinal Health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mascaraque, G.L.; Martínez-Sanz, M.; Hogan, S.A.; López-Rubio, A.; Brodkorb, A. Nano- and Microstructural Evolution of Alginate Beads in Simulated Gastrointestinal Fluids. Impact of M/G Ratio, Molecular Weight and PH. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmolka, I.R. Artificial Skin I. Preparation and Properties of Pluronic F-127 Gels for Treatment of Burns. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1972, 6, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxen, E.; Mosgaard, M.D.; Pedersen, A.M.L.; Jacobsen, J. Mucin Dispersions as a Model for the Oromucosal Mucus Layer in in Vitro and Ex Vivo Buccal Permeability Studies of Small Molecules. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 121, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.E.; Gallo, J.M. A Simple Rheological Method for the in Vitro Assessment of Mucin Polymer Bioadhesive Bond Strength. Pharm. Res. 1990, 07, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi da Silva, J.; Ferreira, S.; Reis, A.; Cook, M.; Bruschi, M. Assessing Mucoadhesion in Polymer Gels: The Effect of Method Type and Instrument Variables. Polymers 2018, 10, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägerström, H.; Edsman, K. Limitations of the Rheological Mucoadhesion Method: The Effect of the Choice of Conditions and the Rheological Synergism Parameter. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 18, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Zou, A.; Li, W.; Yao, C.; Xie, S. DDSolver: An Add-In Program for Modeling and Comparison of Drug Dissolution Profiles. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-P.; Ma, M.-C.; Chow, S.-C. Statistical Evaluation of Similarity Factor F2 as a Criterion for Assessment of Similarity Between Dissolution Profiles. Drug Inf. J. 1997, 31, 1255–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Dumortier, G.; Maury, M.; Mignet, N.; Boudy, V. Influence of Additives on a Thermosensitive Hydrogel for Buccal Delivery of Salbutamol: Relation between Micellization, Gelation, Mechanic and Release Properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 467, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrami, M.; D’Agostino, I.; Milcovich, G.; Fiorentino, S.; Farra, R.; Asaro, F.; Lapasin, R.; Grassi, G.; Grassi, M. Physical Characterization of Alginate–Pluronic F127 Gel for Endoluminal NABDs Delivery. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuliano, E.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Mucosal Applications of Poloxamer 407-Based Hydrogels: An Overview. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, E159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baus, R.A.; Zahir-Jouzdani, F.; Dünnhaupt, S.; Atyabi, F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Mucoadhesive Hydrogels for Buccal Drug Delivery: In Vitro-in Vivo Correlation Study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 142, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, F. A Rheological Examination of the Mucoadhesive/Mucus Interaction: The Effect of Mucoadhesive Type and Concentration. J. Control. Release 1998, 50, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Robinson, J.R. Physico-Chemical Properties of Water Insoluble Polymers Important to Mucin/Epithelial Adhesion. J. Control. Release 1985, 2, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demouveaux, B.; Gouyer, V.; Magnien, M.; Plet, S.; Gottrand, F.; Narita, T.; Desseyn, J.-L. La structure des mucines conditionne les propriétés viscoélastiques des gels de mucus. Médecine/Sciences 2018, 34, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuongfuchat, A.; Jamieson, A.M.; Blackwell, J.; Gerken, T.A. Rheological Studies of the Interaction of Mucins with Alginate and Polyacrylate. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 284, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callens, C.; Ceulemans, J.; Ludwig, A.; Foreman, P.; Remon, J.P. Rheological Study on Mucoadhesivity of Some Nasal Powder Formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 55, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. Development and In-Vitro Evaluation of Sustained Release Poloxamer 407 (P407) Gel Formulations of Ceftiofur. J. Control. Release 2002, 85, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathematical Models of Drug Release. In Strategies to Modify the Drug Release from Pharmaceutical Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 63–86. ISBN 978-0-08-100092-2.
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Evaluation of Mathematical Models Describing Drug Release from Estradiol Transdermal Systems. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Mathematical Modeling of Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Sahlin, J.J. A Simple Equation for the Description of Solute Release. III. Coupling of Diffusion and Relaxation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 57, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Type of Alginate | Viscosity (1) (mPa·s) | M/G Ratio | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protanal LF 10/60 | 30–60 | 0.4–0.7 | [17] |
| Manucol DH | 40–90 | 1.5–1.8 | [18,19] |
| Keltone LVCR | 100–300 (2%) | 1.5–2.3 | [17] |
| Sample Name | Batches of P407 | Concentration of P407 (% wP407/wwater) | Grades of Alginate | Concentration of Alginate (% w/w) | Concentration of SK (% w/w) | Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SK/PRO/P4071 | L1 | 15.0 | PRO | 0.10 | 9.23 | Rheological study |
| SK/PRO/P4072 | 15.5 | |||||
| SK/PRO/P4073 | 16.0 | |||||
| SK/PRO/P4074 | 16.5 | |||||
| SK/PRO/P4075 | 17.0 | |||||
| P407 | L1 | 16.0 | - | - | - | Mucoadhesion |
| P407/PRO10 | L1 | 16.0 | PRO | 0.10 | ||
| P407/PRO15 | 0.15 | |||||
| P407/PRO20 | 0.20 | |||||
| P407/KEL10 | L1 | 16.0 | KEL | 0.10 | ||
| P407/KEL15 | 0.15 | |||||
| P407/KEL20 | 0.20 | |||||
| P407/MAN10 | L1 | 16.0 | MAN | 0.10 | ||
| P407/MAN15 | 0.15 | |||||
| P407/MAN20 | 0.20 | |||||
| SK/PRO/P407-L1 | L1 | 16.0 | PRO | 0.10 | 9.23 | Rheological study and in vitro drug release |
| SK/PRO/P407-L2 | L2 | |||||
| SK/PRO/P407-L3 | L3 |
| Models | Equations | Parameters | Numbering |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higuchi | (5) | ||
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | (6) | ||
| Hopfenberg | (7) | ||
| Peppas–Sahlin | (8) | ||
| Makoid–Banakar | (9) |
| Aqueous Media | Concentrations of Mucin (%w/w) | ηm (mPa·s) | ηt (mPa·s) | ηb (mPa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphate buffer | 2 | 3.5 ± 0.3 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 0.7 ± 1.4 |
| 3 | 6.0 ± 0.8 | 8.7 ± 1.4 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | |
| 4 | 9.3 ± 0.4 | 15.2 ± 1.4 * | 4.4 ± 1.1 * | |
| 5 | 14.7 ± 2.1 | 20.7 ± 4.7 **** | 4.5 ± 1.8 *** | |
| Artificialsaliva | 2 | 7.3 ± 6.1 | 26.9 ± 10.5 | 17.6 ± 13.3 |
| 3 | 8.3 ± 1.8 | 38.1 ± 18.2 | 27.8 ± 16.5 | |
| 4 | 12.1 ± 1.6 | 74.6 ± 35.6 * | 60.6 ± 35.8 * | |
| 5 | 19.3 ± 1.4 | 121.0 ± 41.0 **** | 99.7 ± 40.9 *** |
| Mathematical Models | Parameters | Batches of P407 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 | L2 | L3 | ||
| Higuchi | 13.556 | 13.774 | 16.281 | |
| R2adj | 0.941 | 0.947 | 0.950 | |
| AIC | 91.6 | 90.1 | 54.5 | |
| Korsmeyer–Peppas | 7.347 | 7.772 | 10.261 | |
| 0.707 | 0.693 | 0.680 | ||
| R2adj | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.999 | |
| AIC | 34.3 | 29.0 | 16.1 | |
| Hopfenberg | 0.008 | 0.008 | 0.005 | |
| 5.449 | 6.050 | 13.589 | ||
| R2adj | 0.997 | 0.995 | 0.990 | |
| AIC | 49.4 | 56.9 | 39.1 | |
| Peppas–Sahlin | 7.384 | 7.884 | 9.799 | |
| 1.385 | 1.322 | 1.767 | ||
| R2adj | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.999 | |
| AIC | 48.2 | 42.4 | 18.8 | |
| Makoid–Banakar | 6.193 | 6.963 | 8.638 | |
| 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.000 | ||
| 0.814 | 0.763 | 0.825 | ||
| R2adj | 1.000 | 0.999 | 0.998 | |
| AIC | 22.1 | 28.1 | 49.2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thouvenin, A.; Toussaint, B.; Marinovic, J.; Gilles, A.-L.; Dufaÿ Wojcicki, A.; Boudy, V. Development of Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Hydrogel for Buccal Delivery of (S)-Ketamine. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102039
Thouvenin A, Toussaint B, Marinovic J, Gilles A-L, Dufaÿ Wojcicki A, Boudy V. Development of Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Hydrogel for Buccal Delivery of (S)-Ketamine. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102039
Chicago/Turabian StyleThouvenin, Agathe, Balthazar Toussaint, Jelena Marinovic, Anne-Laure Gilles, Amélie Dufaÿ Wojcicki, and Vincent Boudy. 2022. "Development of Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Hydrogel for Buccal Delivery of (S)-Ketamine" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102039
APA StyleThouvenin, A., Toussaint, B., Marinovic, J., Gilles, A.-L., Dufaÿ Wojcicki, A., & Boudy, V. (2022). Development of Thermosensitive and Mucoadhesive Hydrogel for Buccal Delivery of (S)-Ketamine. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2039. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102039





