Glu-Urea-Lys Scaffold Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Targeting PSMA for In Vivo Molecular MRI of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Materials
2.2. Chemistry
2.2.1. Di-Tert-Butyl L-Glutamate (1)
2.2.2. N6-Fmoc-N2-Boc-L-Lysine (2)
2.2.3. Tert-Butyl N6-Fmoc-L-Lysinate (3)
2.2.4. (Tert-Butyl-N6-Fmoc)-L-Lys-Urea-(Di-Tert-Butyl)-L-Glu (4)
2.2.5. (Tert-Butyl)-L-Lys-Urea-(Di-Tert-Butyl)-L-Glu (5)
2.2.6. Di-Tert-Butyl (((S)-1-(Tert-Butoxy)-6-(((4-Nitrophenoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)-1-Oxohexan-2-yl) Carbamoyl)-L-Glutamate (6)
2.2.7. (((S)-1-Carboxy-5-(((4-Nitrophenoxy)Carbonyl)Amino)Pentyl)Carbamoyl)-L-Glutamic Acid (PSMA-1)
2.2.8. Fe3O4 SPIONs
2.2.9. NH2-PEG2000-NH2
2.2.10. DPA-PEG-NH2
2.2.11. Fe3O4@DPA-PEG-NH2
2.2.12. Fe3O4@DPA-PEG-PSMA-1
2.3. Characterization
2.4. PSMA Biding Assay
2.4.1. Cytotoxicity Assay (MTT & LDH)
2.4.2. PSMA Molecular Binding Assay
2.4.3. Cell Binding Assay
2.4.4. Western Blot of PSMA
2.5. In Vivo MRI
2.5.1. Animal Model
2.5.2. In Vivo MRI
2.5.3. Histological Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
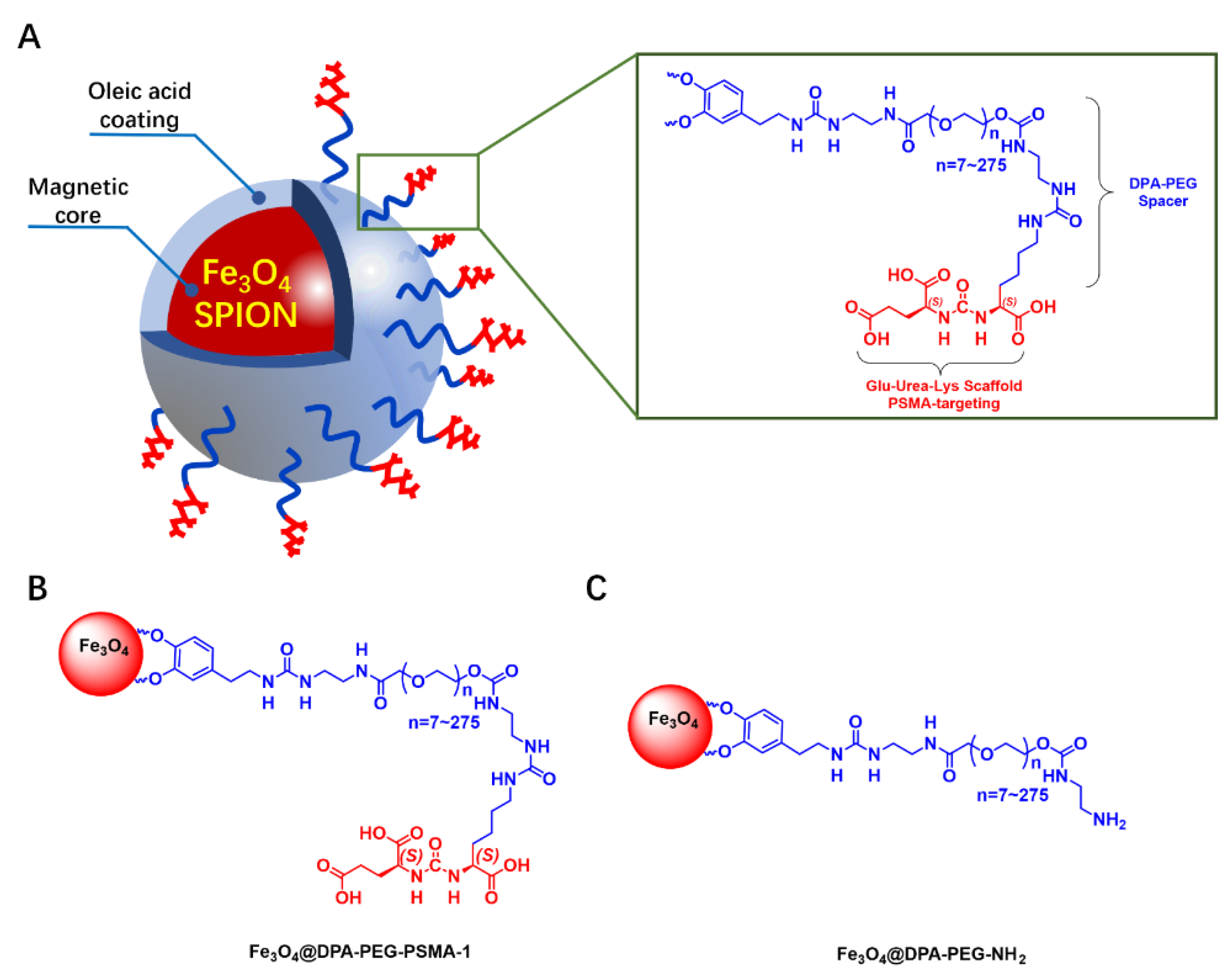
3.1.1. Design and Synthesis of MRI Probe
3.1.2. Characterization of SPIONs
3.2. PSMA Binding Assay
3.2.1. Molecular Binding Assay
3.2.2. Cell Binding Assay
3.3. MRI
3.3.1. In Vivo MRI
3.3.2. Histological Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, K.A.; Lake, A.J.; Scott, S.; Sherman, R.L.; Noone, A.M.; Howlader, N.; Henley, S.J.; Anderson, R.N.; Firth, A.U.; Ma, J. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, part I: National cancer statistics. Cancer 2018, 124, 2785–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, H.G.; Kramer, B.S.; Black, W.C. Epidemiologic Signatures in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1378–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negoita, S.; Feuer, E.J.; Mariotto, A.; Cronin, K.A.; Petkov, V.I.; Hussey, S.K.; Benard, V.; Henley, S.J.; Anderson, R.N.; Fedewa, S. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, part II: Recent changes in prostate cancer trends and disease characteristics. Cancer 2018, 124, 2801–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanti, S.; Minozzi, S.; Antoch, G.; Banks, I.; Briganti, A.; Carrio, I.; Chiti, A.; Clarke, N.; Eiber, M.; De Bono, J.; et al. Consensus on molecular imaging and theranostics in prostate cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e696–e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, R.E.; Williams, S.; Hicks, R.J. Molecular Imaging of Recurrent and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. In Seminars in Nuclear Medicine; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.Z.; Bagalkot, V.; Vasilliou, C.C.; Gu, F.; Alexis, F.; Zhang, L.; Shaikh, M.; Yuet, K.; Cima, M.J.; Langer, R. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle–aptamer bioconjugates for combined prostate cancer imaging and therapy. Chem. Med. Chem. Chem. Enabling Drug Discov. 2008, 3, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravaccini, S.; Puccetti, M.; Bocchini, M.; Ravaioli, S.; Celli, M.; Scarpi, E.; De Giorgi, U.; Tumedei, M.M.; Raulli, G.; Cardinale, L.; et al. PSMA expression: A potential ally for the pathologist in prostate cancer diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenboeck, S.M.; Rauscher, I.; Bluemel, C.; Fendler, W.P.; Rowe, S.P.; Pomper, M.G.; Asfhar-Oromieh, A.; Herrmann, K.; Eiber, M. PSMA Ligands for PET Imaging of Prostate Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütje, S.; Heskamp, S.; Cornelissen, A.S.; Poeppel, T.D.; Broek, S.A.M.W.V.D.; Rosenbaum-Krumme, S.; Bockisch, A.; Gotthardt, M.; Rijpkema, M.; Boerman, O.C. PSMA Ligands for Radionuclide Imaging and Therapy of Prostate Cancer: Clinical Status. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1388–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiber, M.; Herrmann, K.; Calais, J.; Hadaschik, B.; Giesel, F.L.; Hartenbach, M.; Hope, T.; Reiter, R.; Maurer, T.; Weber, W.A. Prostate cancer molecular imaging standardized evaluation (PROMISE): Proposed miTNM classification for the interpretation of PSMA-ligand PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Rajasekaran, A.K.; Moy, P.; Xia, Y.; Kim, S.; Navarro, V.; Rahmati, R.; Bander, N.H. Constitutive and antibody-induced internalization of prostate-specific membrane antigen. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4055–4060. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hillier, S.M.; Maresca, K.P.; Lu, G.; Merkin, R.D.; Marquis, J.C.; Zimmerman, C.N.; Eckelman, W.C.; Joyal, J.L.; Babich, J.W. 99mTc-labeled small-molecule inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen for molecular imaging of prostate cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.Y.; Gage, K.L.; Mease, R.C.; Senthamizhchelvan, S.; Holt, D.P.; Jeffrey-Kwanisai, A.; Endres, C.J.; Dannals, R.F.; Sgouros, G.; Lodge, M. Biodistribution, tumor detection, and radiation dosimetry of 18F-DCFBC, a low-molecular-weight inhibitor of prostate-specific membrane antigen, in patients with metastatic prostate cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, J.; Zeni, M.; Savio, E.; Engler, H. Synthesis of an Al(18)F radiofluorinated GLU-UREA-LYS(AHX)-HBED-CC PSMA ligand in an automated synthesis platform. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2018, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.S.; Chu, S.Y.; Jung, W.J.; Jeong, H.J.; Lee, K.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, M.H.; Chi, D.Y.; Ahn, H.; Lee, Y.J.; et al. F-18-labeled 1,2,3-triazole-linked Glu-urea-Lys-based PSMA ligands have good pharmacokinetic properties for positron emission tomography imaging of prostate cance. Prostate 2020, 80, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, R.A.; Derlin, T.; Lapa, C.; Sheikbahaei, S.; Higuchi, T.; Giesel, F.L.; Behr, S.; Drzezga, A.; Kimura, H.; Buck, A.K.; et al. F-Labeled, PSMA-Targeted Radiotracers: Leveraging the Advantages of Radiofluorination for Prostate Cancer Molecular Imaging. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.D.G.; Queiroz, M.A.; Nunes, R.F.; Marin, J.F.G.; Buchpiguel, C.A.; Cerri, G.G. Clinical perspectives of PSMA PET/MRI for prostate cancer. Clinics 2018, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüstemann, T.; Haberkorn, U.; Babich, J.; Mier, W. Targeting prostate cancer: Prostate-specific membrane antigen based diagnosis and therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 40–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J.; Guan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Duan, Y. In Vivo Molecular MRI Imaging of Prostate Cancer by Targeting PSMA with Polypeptide-Labeled Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9573–9587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.R.; Ngen, E.J.; Rotz, M.W.; Kakkad, S.; Lisok, A.; Pracitto, R.; Pullambhatla, M.; Chen, Z.; Shah, T.; Artemov, D.; et al. Synthesis and Evaluation of Gd(III) -Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents for Molecular Imaging of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 10778–10782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagesh, P.K.B.; Johnson, N.R.; Boya, V.K.N.; Chowdhury, P.; Othman, S.F.; Khalilzad-Sharghi, V.; Hafeez, B.B.; Ganju, A.; Khan, S.; Behrman, S.W.; et al. PSMA targeted docetaxel-loaded superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for prostate cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 144, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.R.; Pullambhatla, M.; Byun, Y.; Nimmagadda, S.; Green, G.; Fox, J.J.; Horti, A.; Mease, R.C.; Pomper, M.G. 68Ga-labeled inhibitors of prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) for imaging prostate cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5333–5341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.R.; Foss, C.A.; Castanares, M.; Mease, R.C.; Byun, Y.; Fox, J.J.; Hilton, J.; Lupold, S.E.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Pomper, M.G. Synthesis and evaluation of technetium-99m- and rhenium-labeled inhibitors of the prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4504–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.M.; Huber, D.L.; Monson, T.C.; Ali, A.-M.S.; Bisoffi, M.; Sillerud, L.O. Multifunctional iron platinum stealth immunomicelles: Targeted detection of human prostate cancer cells using both fluorescence and magnetic resonance imaging. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 4717–4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Abraham, S.; Campbell, M.; Zehbe, I.; Curiel, L. Development and characterization of an antibody-labeled super-paramagnetic iron oxide contrast agent targeting prostate cancer cells for magnetic resonance imaging. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolahi, M.; Shahbazi-Gahrouei, D.; Laurent, S.; Sermeus, C.; Firozian, F.; Allen, B.J.; Boutry, S.; Muller, R.N. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of MR molecular imaging probes using J591 mAb-conjugated SPIONs for specific detection of prostate cancer. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2013, 8, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Foss, C.A.; Byun, Y.; Nimmagadda, S.; Pullambhatla, M.; Fox, J.J.; Castanares, M.; Lupold, S.E.; Babich, J.W.; Mease, R.C.; et al. Radiohalogenated Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA)-Based Ureas as Imaging Agents for Prostate Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 7933–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.R.; Pullambhatla, M.; Shallal, H.; Lisok, A.; Mease, R.C.; Pomper, M.G. A Modular Strategy to Prepare Multivalent Inhibitors of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA). Oncotarget 2011, 2, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapidus, R.G.; Tiffany, C.W.; Isaacs, J.T.; Slusher, B.S. Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) enzyme activity is elevated in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2000, 45, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiber, M.; Fendler, W.P.; Rowe, S.P.; Calais, J.; Hofman, M.S.; Maurer, T.; Schwarzenboeck, S.M.; Kratowchil, C.; Herrmann, K.; Giesel, F.L. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Ligands for Imaging and Therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2017, 58, 67S–76S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, A.D.; Claypool, S.E.; Liu, R. The Smart Targeting of Nanoparticles. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6315–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Song, X. Synthesis and positron emission tomography evaluation of 18F-Glu-Urea-Lys, a prostate-specific membrane antigen-based imaging agent for prostate cancer Corrigendum in/10.3892/ol. 2015.4039. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 2299–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Synthesis of nearly monodisperse iron oxide and oxyhydroxide nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.Y.; Kwak, S.-Y. Assembly of magnetite nanocrystals into spherical mesoporous aggregates with a 3-D wormhole-like pore structure. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8320–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemen, M.; Brullot, W.; Luong, T.T.; Geukens, N.; Gils, A.; Verbiest, T. Improved functionalization of oleic acid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Nanopart Res. 2012, 14, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Peng, H.; Wen, Y.; Li, N. Re-examination of characteristic FTIR spectrum of secondary layer in bilayer oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.C.; Smith, J.B.; Pham, T.; Whitaker, R.D.; Sucato, C.A.; Hamilton, J.A.; Bartolak-Suki, E.; Wong, J.Y. Effect of PEG molecular weight on stability, T-2 contrast, cytotoxicity, and cellular uptake of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs). Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 119, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozandeh, P.; Aziz, A.A. Insight into Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.G.F.; Ciminelli, V.S.T.; Mohallem, N.D.S. A comparison of TEM and DLS methods to characterize size distribution of ceramic nanoparticles. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 733, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, X.N.; Zeng, S.; Ramamurthy, G.; Burda, C.; Basilion, J.P. Prostate-specific membrane antigen targeted gold nanoparticles for prostate cancer radiotherapy: Does size matter for targeted particles? Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 8119–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulińska-Litewka, J.; Łazarczyk, A.; Hałubiec, P.; Szafrański, O.; Karnas, K.; Karewicz, A. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles-Current and Prospective Medical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozikowski, A.P.; Zhang, J.; Nan, F.; Petukhov, P.A.; Grajkowska, E.; Wroblewski, J.T.; Yamamoto, T.; Bzdega, T.; Wroblewska, B.; Neale, J.H. Synthesis of Urea-Based Inhibitors as Active Site Probes of Glutamate Carboxypeptidase II: Efficacy as Analgesic Agents. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, S.; Asha Krishnan, M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chelvam, V. Comparison of prostate-specific membrane antigen ligands in clinical translation research for diagnosis of prostate cancer. Cancer Rep. 2019, 2, e1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Liu, F.; Kwon, H.; Byun, Y.; Minn, I.; Cai, X.; Zhang, J.; Pomper, M.G.; Yang, Z.; Xi, Z.; et al. (S)-3-(Carboxyformamido)-2-(3-(carboxymethyl)ureido)propanoic Acid as a Novel PSMA Targeting Scaffold for Prostate Cancer Imaging. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3563–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voinov, M.A.; Pagan, J.O.S.; Morrison, E.; Smirnova, T.I.; Smirnov, A.I. Surface-Mediated Production of Hydroxyl Radicals as a Mechanism of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Biotoxicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masur, S.; Zingsem, B.; Marzi, T.; Meckenstock, R.; Farle, M. Characterization of the oleic acid/iron oxide nanoparticle interface by magnetic resonance. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 415, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Ding, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Ye, L.; Zhang, M.; et al. Second-generation aptamer-conjugated PSMA-targeted delivery system for prostate cancer therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, B.W.C.; Cowin, G.J.; Soekmadji, C.; Jovanovic, L.; Vasireddy, R.S.; Ling, M.T.; Khatri, A.; Liu, T.; Thierry, B.; Russell, P.J. PSMA-targeting iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles enhance MRI of preclinical prostate cancer. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhou, T.; Sun, C.; Lin, H.; Yang, L.; Ren, B.W.; Chen, Z.; Gao, J. Iron-oxide-based twin nanoplates with strong T 2 relaxation shortening for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 18398–18406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, S.; Koul, V.; Choudhary, V.; Shishodia, G.; Bharti, A.C. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of folate-receptor-targeted SPION-polymer micelle hybrids for MRI contrast enhancement in cancer imaging. Nanotechnology 2013, 24, 015603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdarzadeh, M.; Atyabi, F.; Saei, A.A.; Varnamkhasti, B.S.; Omidi, Y.; Fateh, M.; Ghavami, M.; Shanehsazzadeh, S.; Dinarvand, R. Theranostic MUC-1 aptamer targeted gold coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy of colon cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 143, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Lee, J.S.; Liman, R.A.D.; Ruallo, J.M.S.; Villaflores, O.B.; Ger, T.R.; Hsiao, C.D. Potential Toxicity of Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spirou, S.V.; Lima, S.A.C.; Bouziotis, P.; Vranjes-Djuric, S.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Laurenzana, A.; Barbosa, A.I.; Garcia-Alonso, I.; Jones, C.; Jankovic, D.; et al. Recommendations for In Vitro and In Vivo Testing of Magnetic Nanoparticle Hyperthermia Combined with Radiation Therapy. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B. Pharmacokinetic parameters and tissue distribution of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janko, C.; Ratschker, T.; Nguyen, K.; Zschiesche, L.; Tietze, R.; Lyer, S.; Alexiou, C. Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (SPIONs) as Platform for the Targeted Multimodal Tumor Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Sample | Zeta Potential (mV) | |
|---|---|---|
| pH7.4 PBS | FBS | |
| Fe3O4 nanoparticles | −25.2 ± 0.3 | −23.0 ± 0.9 |
| Fe3O4@DPA-PEG-NH2 | 18.8 ± 0.7 | 19.2 ± 1.2 |
| Fe3O4@DPA-PEG-PSMA-1 | −22.4 ± 0.4 | −17.4 ± 0.7 |
| Compound | Ki |
|---|---|
| PSMA-1 | 2.4 ± 0.2 nM |
| Fe3O4@DPA-PEG-NH2 | >100 μg(Fe)/mL |
| Fe3O4@DPA-PEG-PSMA-1 | 0.38 ± 0.08 μg(Fe)/mL |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Huang, J.; Xiao, Q.; Hu, S.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.; Peng, J.; Chen, H. Glu-Urea-Lys Scaffold Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Targeting PSMA for In Vivo Molecular MRI of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102051
Zhou W, Huang J, Xiao Q, Hu S, Li S, Zheng J, Du Z, Peng J, Chen H. Glu-Urea-Lys Scaffold Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Targeting PSMA for In Vivo Molecular MRI of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102051
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Wei, Jiandong Huang, Qingwei Xiao, Shunmin Hu, Shijia Li, Jie Zheng, Zhiyun Du, Jiangling Peng, and Huixiong Chen. 2022. "Glu-Urea-Lys Scaffold Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Targeting PSMA for In Vivo Molecular MRI of Prostate Cancer" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102051
APA StyleZhou, W., Huang, J., Xiao, Q., Hu, S., Li, S., Zheng, J., Du, Z., Peng, J., & Chen, H. (2022). Glu-Urea-Lys Scaffold Functionalized Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Targeting PSMA for In Vivo Molecular MRI of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2051. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102051








