Biosynthetic Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit the Malignant Behavior of Gastric Cancer Cells and Enhance the Therapeutic Effect of 5-Fluorouracil by Promoting Intracellular ROS Generation and Apoptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Materials
2.3. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8)
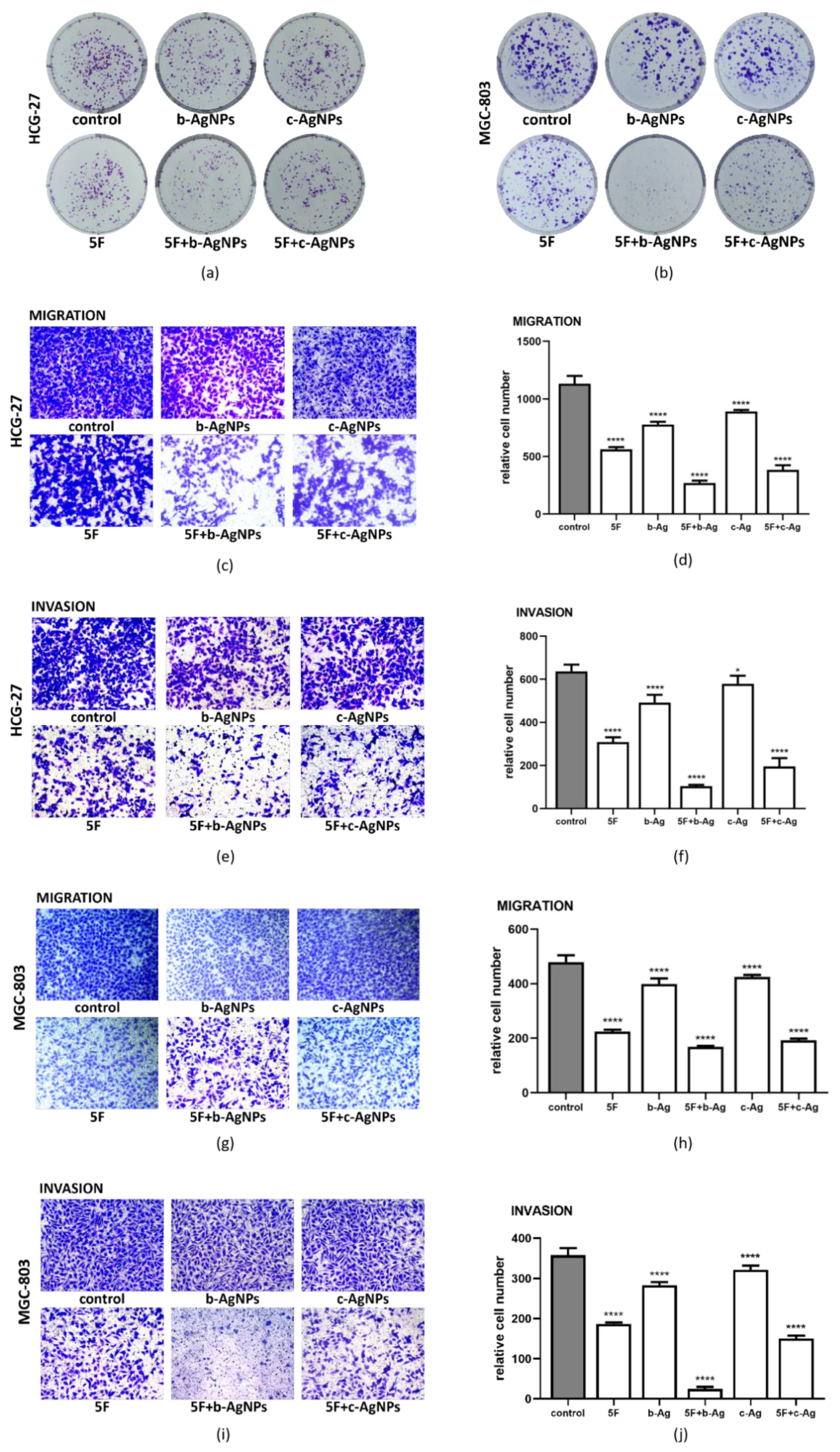
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.5. Transwell
2.6. DCFH-DA
2.7. Dihydroethidium (DHE)
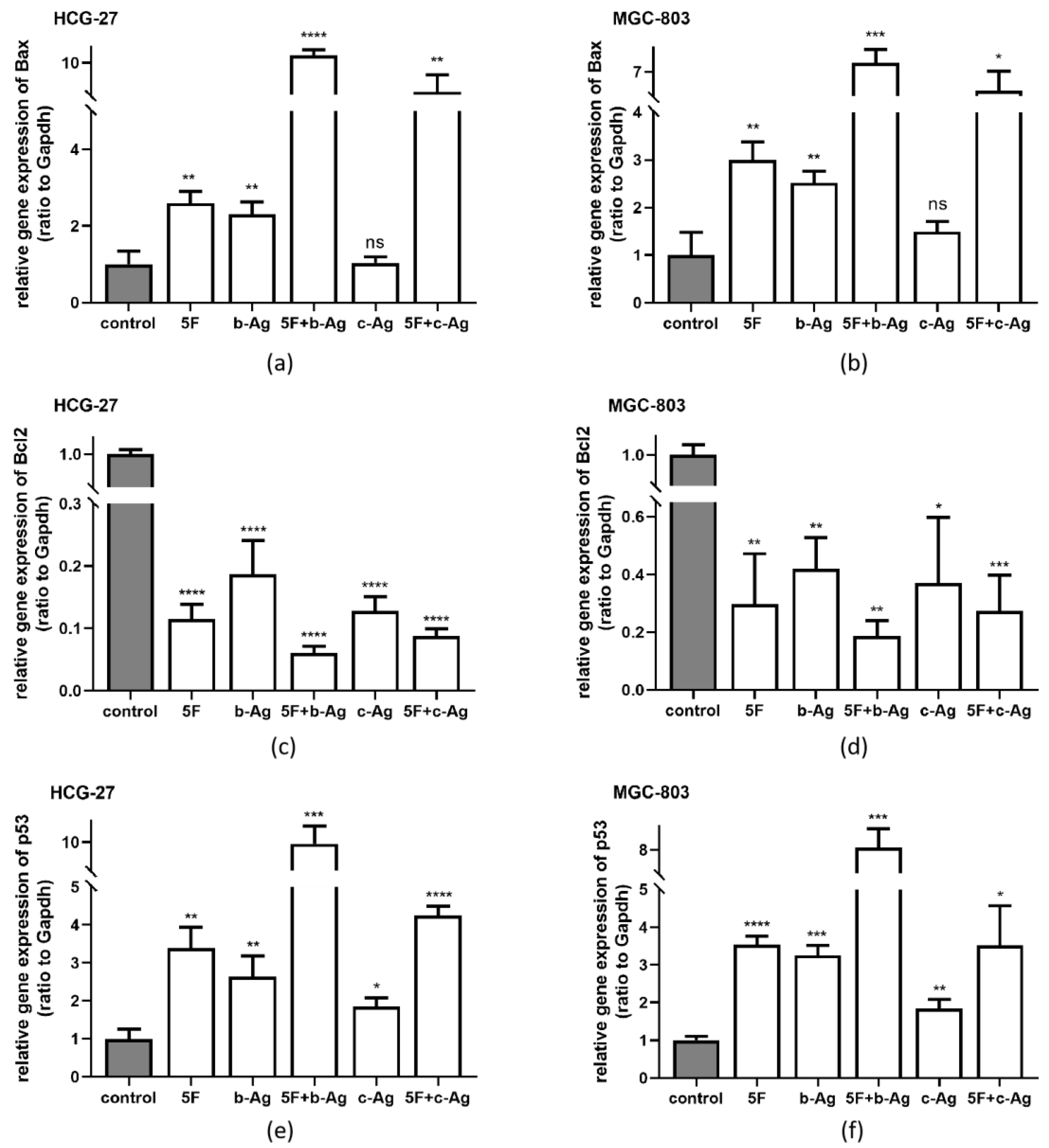
2.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.9. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
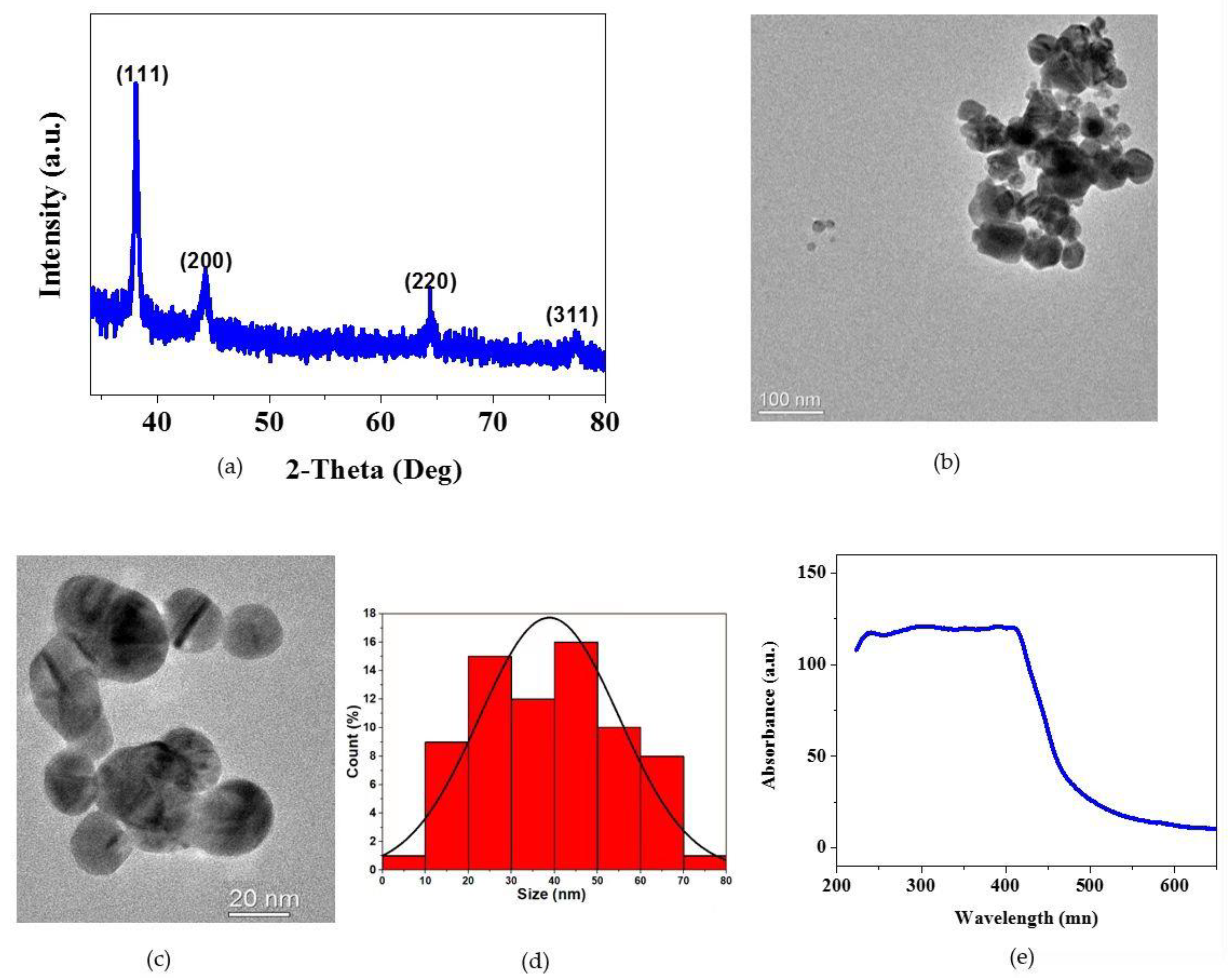
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of AgNPs
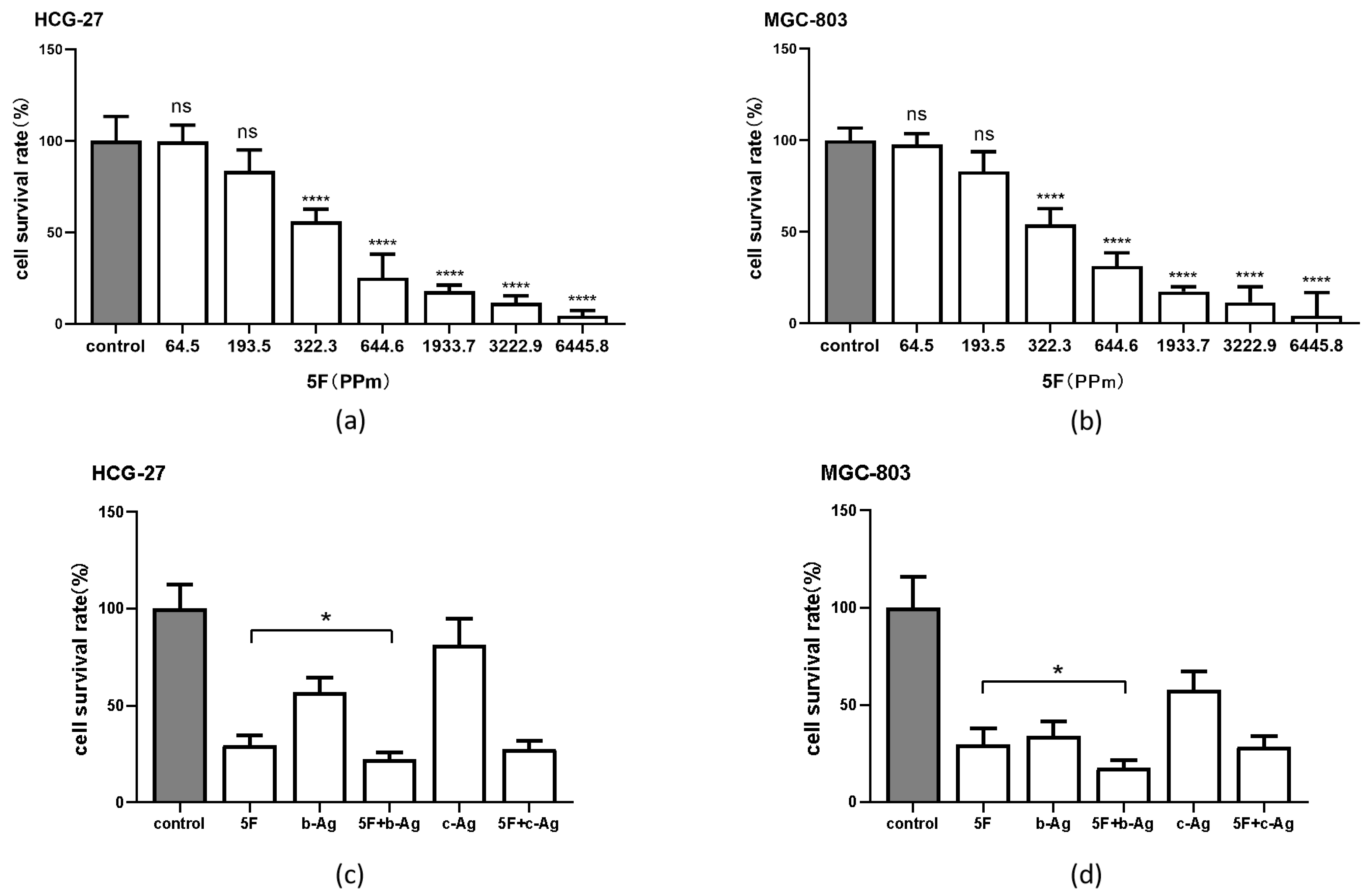
3.2. Cytotoxic Effect of AgNPs on Gastric Cancer Cells
3.3. Enhancement of 5F Cytotoxicity in Gastric Cancer Cells by AgNPs
3.4. Malignant Phenotype of Gastric Cancer Cells under AgNPs and 5F
3.5. Gastric Cancer Cell Apoptosis under AgNPs and 5F
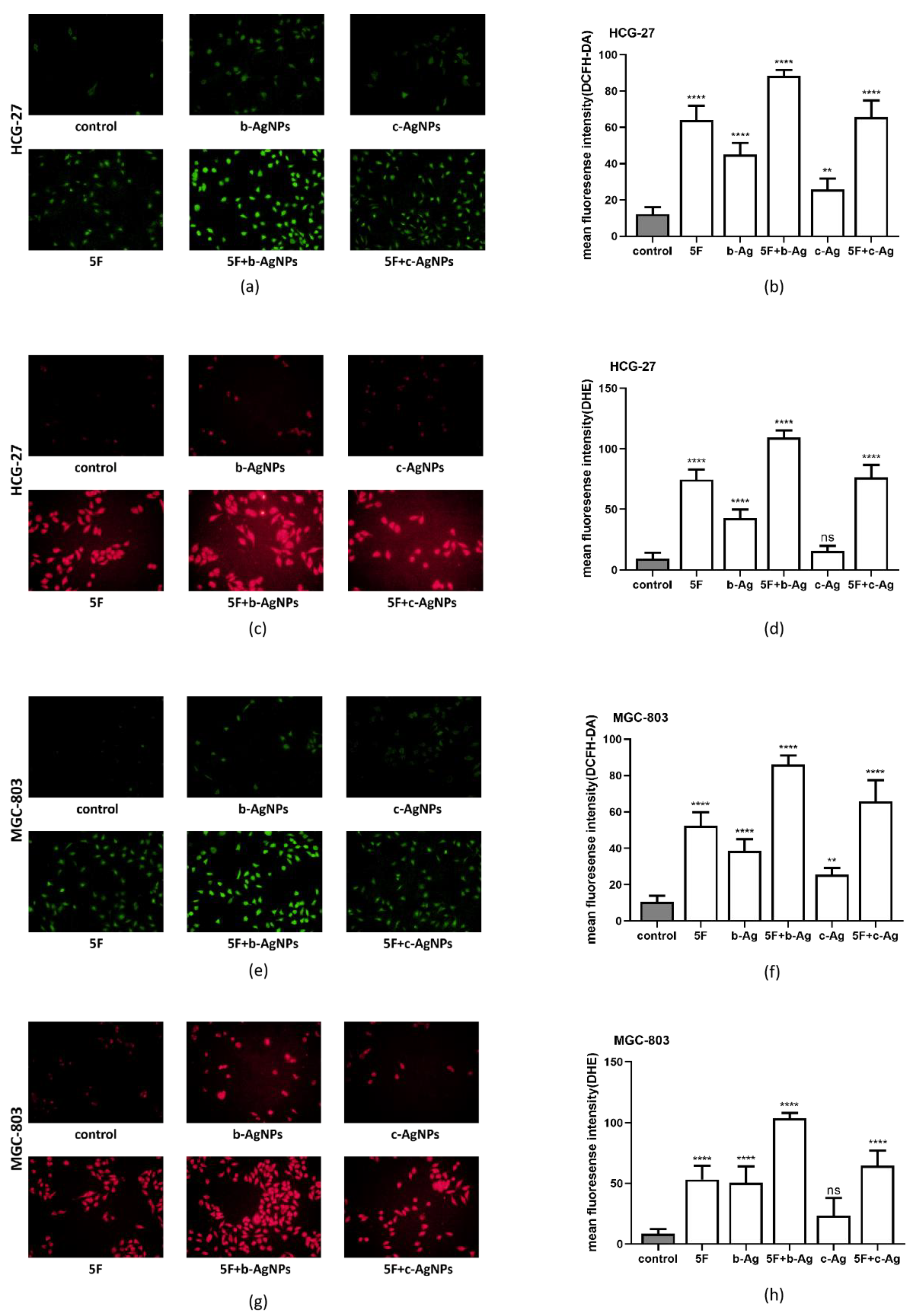
3.6. Intracellular ROS of Gastric Cancer Cells under AgNPs and 5F
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Su, J.; Meng, Q.; Yin, Q.; Chen, L.; Gu, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; et al. Cancer-Cell-Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Therapy of Homotypic Tumors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 9581–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Jafari, M.; Habibi, B. Ultrasensitive immunoassay of glycoprotein 125 (CA 125) in untreated human plasma samples using poly (CTAB-chitosan) doped with silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt B, 2048–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calatayud, D.G.; Neophytou, S.; Nicodemou, E.; Giuffrida, S.G.; Ge, H.; Pascu, S.I. Nano-Theranostics for the Sensing, Imaging and Therapy of Prostate Cancers. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 830133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy Chowdhury, N.; Cowin, A.J.; Zilm, P.; Vasilev, K. “Chocolate” Gold Nanoparticles-One Pot Synthesis and Biocompatibility. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J.A. Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilliard, S.A.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D.J. On the mechanism of tissue-specific mRNA delivery by selective organ targeting nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2109256118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, S.M.; Hashemi, S.A.; Ghasemi, Y.; Atapour, A.; Amani, A.M.; Savar Dashtaki, A.; Babapoor, A.; Arjmand, O. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles toward bio and medical applications: Review study. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S855–S872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Grzenia, A.; Wierzbicki, M.; Strojny-Cieslak, B.; Kalińska, A.; Gołębiewski, M.; Radzikowski, D.; Sawosz, E.; Jaworski, S. Silver and Copper Nanoparticles Inhibit Biofilm Formation by Mastitis Pathogens. Animals 2021, 11, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, S.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Singh, A.; Ahmad, I.; Rahman, M.; Anwar, M.; Jain, G.K.; Ahmad, F.; Khar, R.K. Cancer targeted metallic nanoparticle: Targeting overview, recent advancement and toxicity concern. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 1834–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinajero-Díaz, E.; Salado-Leza, D.; Gonzalez, C.; Velázquez, M.M.; López, Z.; Bravo-Madrigal, J.; Knauth, P.; Flores-Hernández, F.Y.; Herrera-Rodríguez, S.E.; Navarro, R.E.; et al. Green Metallic Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Evaluation Models and Cancer Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavas, S.; Quazi, S.; Karpiński, T.M. Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy: Current Progress and Challenges. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavaleta, C.; Ho, D.; Chung, E.J. Theranostic Nanoparticles for Tracking and Monitoring Disease State. SLAS Technol. 2018, 23, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondy, S.; David, V.; Verdier, M.; Mathonnet, M.; Perraud, A.; Christou, N. 5-Fluorouracil resistance mechanisms in colorectal cancer: From classical pathways to promising processes. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3142–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Voigt, W.; Jordan, K. Review: Chemotherapy-induced diarrhea: Pathophysiology, frequency and guideline-based management. Ther. Adv. Med Oncol. 2010, 2, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, R.A.; Wanderley, C.W.S.; Wong, D.V.T.; Mota, J.M.; Leite, C.A.V.G.; Souza, M.H.L.P.; Cunha, F.Q.; Lima-Júnior, R.C.P. Irinotecan- and 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis: Insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic perspectives. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Hu, H.; Liu, L.; Hong, D.; Zeng, S. Possible Pathways of Capecitabine-Induced Hand–Foot Syndrome. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2016, 29, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Drobni, Z.D.; Mosarla, R.; Alvi, R.M.; Lei, M.; Lou, U.Y.; Raghu, V.K.; Murphy, S.P.; Jones-O’Connor, M.; Hartmann, S.; et al. The Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes With 5-Fluorouracil-Associated Coronary Vasospasm. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2021, 3, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunenburg, C.A.T.C.; Van Der Wouden, C.H.; Nijenhuis, M.; Rhenen, M.H.C.-V.; De Boer-Veger, N.J.; Buunk, A.M.; Houwink, E.J.F.; Mulder, H.; Rongen, G.A.; Van Schaik, R.H.N.; et al. Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG) guideline for the gene–drug interaction of DPYD and fluoropyrimidines. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chowdhury, D.; Kotcherlakota, R.; Patra, S.; Vinothkumar, B.; Bhadra, M.P.; Sreedhar, B.; Patra, C.R. Potential theranostics application of bio-synthesized silver nanoparticles (4-in-1 system). Theranostics 2014, 4, 316–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, M.; Ishii, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Mori, Y.; Shimizu, S. Possible involvement of TRPM2 activation in 5-fluorouracil-induced myelosuppression in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 891, 173671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, H.; Yang, T.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Ke, H.; Ding, D.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H. Serum protein-based nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis and treatment. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 997–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhang, K.; Dai, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Erythrocyte–Cancer Hybrid Membrane Camouflaged Hollow Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for Prolonged Circulation Life and Homotypic-Targeting Photothermal/Chemotherapy of Melanoma. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5241–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Gao, L.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Hu, K. Nanoparticles: A New Approach to Upgrade Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Xiang, J. Aptamer-Functionalized Nanoparticles in Targeted Delivery and Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.-L.; Kang, C.-M.; Sun, Z.-Q.; Li, X.-H.; Dai, X.-Y.; Huang, R.-Y.; Zhao, J.-J.; Bei, Y.-R.; Huang, X.-Z.; Lu, Z.-F.; et al. TTDA inhibited apoptosis by regulating the p53-Bax/Bcl2 axis in glioma. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 331, 113380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Meng, W.; Bai, Z.; Rui, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, W.; Jin, X. Effect of CCNB1 silencing on cell cycle, senescence, and apoptosis through the p53 signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, V.; Moliné, T.; Somoza, R.; Paciucci, R.; Kondoh, H.; Lleonart, M.E. Oxidative stress and cancer: An overview. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanikoglu, A.; Ozben, H.; Hanikoglu, F.; Ozben, T. Hybrid Compounds & Oxidative Stress Induced Apoptosis in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 2118–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Feng, N. Red blood cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles: A novel drug delivery system for antitumor application. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| AgNO3 (μL) | AX (μL) | ddH2O (mL) | Concentration of b-Ag (PPm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12.5 | 37.5 | 4.95 | 64.5 |
| 37.5 | 112.5 | 4.85 | 193.5 |
| 62.5 | 187.5 | 4.75 | 322.3 |
| 125 | 375 | 4.5 | 644.6 |
| 375 | 1125 | 3.5 | 1933.7 |
| CX (μL) | ddH2O (mL) | Concentration of c-Ag (PPm) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.99 | 64.5 |
| 30 | 0.97 | 193.5 |
| 50 | 0.95 | 322.3 |
| 100 | 0.9 | 644.6 |
| 300 | 0.7 | 1933.7 |
| 5F (μg) | PBS (mL) | Concentration of 5F (PPm) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.34 | 1 | 64.5 |
| 1.02 | 1 | 193.5 |
| 1.7 | 1 | 322.3 |
| 3.4 | 1 | 644.6 |
| 10.2 | 1 | 1933.7 |
| 17 | 1 | 3222.9 |
| 34 | 1 | 6445.8 |
| Abbreviations | Drugs and Concentrations |
|---|---|
| Control | Without any drugs |
| 5F | 5-Fluorouracil (644.6 PPm) |
| b-Ag | Biosynthetic silver nanoparticles (322.3 PPm) |
| 5F + b-Ag | 5-Fluorouracil (644.6 PPm) + biosynthetic silver nanoparticles (322.3 PPm) |
| c-Ag | Chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles (322.3 PPm) |
| 5F + c-Ag | 5-Fluorouracil (644.6 PPm) + chemically synthesized silver nanoparticles (322.3 PPm) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Khan, S.U.; Luo, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, J.; Tong, Q. Biosynthetic Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit the Malignant Behavior of Gastric Cancer Cells and Enhance the Therapeutic Effect of 5-Fluorouracil by Promoting Intracellular ROS Generation and Apoptosis. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102109
Yuan J, Khan SU, Luo J, Jiang Y, Yang Y, Yan J, Tong Q. Biosynthetic Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit the Malignant Behavior of Gastric Cancer Cells and Enhance the Therapeutic Effect of 5-Fluorouracil by Promoting Intracellular ROS Generation and Apoptosis. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102109
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jingwen, Shahid Ullah Khan, Jiajun Luo, Yue Jiang, Yu Yang, Junfeng Yan, and Qiang Tong. 2022. "Biosynthetic Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit the Malignant Behavior of Gastric Cancer Cells and Enhance the Therapeutic Effect of 5-Fluorouracil by Promoting Intracellular ROS Generation and Apoptosis" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102109
APA StyleYuan, J., Khan, S. U., Luo, J., Jiang, Y., Yang, Y., Yan, J., & Tong, Q. (2022). Biosynthetic Silver Nanoparticles Inhibit the Malignant Behavior of Gastric Cancer Cells and Enhance the Therapeutic Effect of 5-Fluorouracil by Promoting Intracellular ROS Generation and Apoptosis. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2109. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102109







