Locust Bean Gum Nano-Based Hydrogel for Vaginal Delivery of Diphenyl Diselenide in the Treatment of Trichomoniasis: Formulation Characterization and In Vitro Biological Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Nanocapsule Suspensions
2.3. Characterization of Nanocapsule Suspensions
2.4. In Vitro Evaluation of Biological Properties
2.4.1. Anti-T. vaginalis Action
2.4.2. Antioxidant Potential
2.5. Hydrogels Preparation
2.6. Hydrogel Characterization
2.7. Mucoadhesion and Mucosa Permeation Evaluations
2.7.1. Nanocapsule Formulations
2.7.2. Hydrogel Formulations
2.8. Evaluation of Irritant Potential of the Formulations
2.9. Data Presentation and Statistical Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. General Characterization of Nanocapsule Suspensions
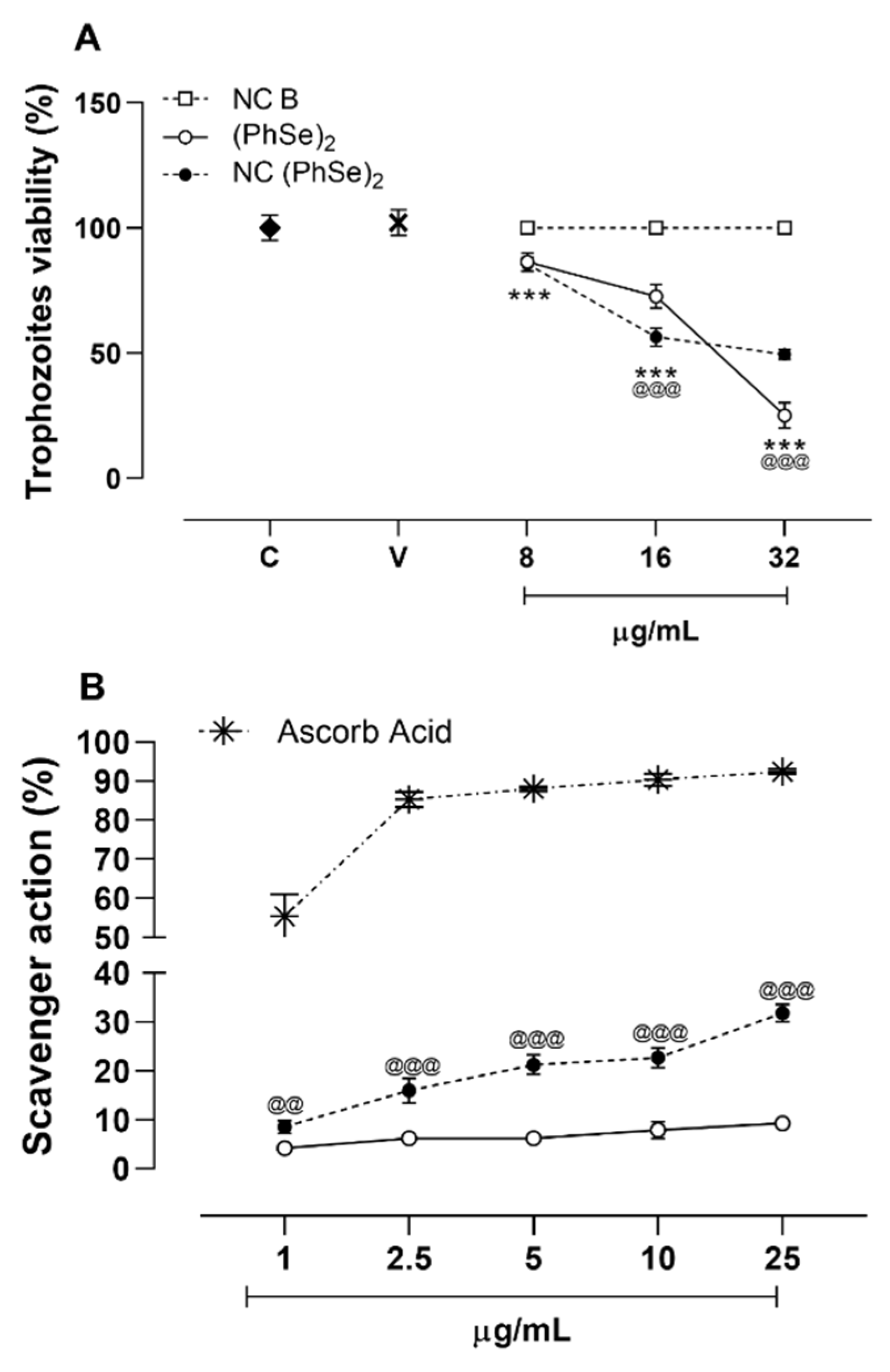
3.2. Anti-T. vaginalis Action and Antioxidant Properties of Nanocapsules
3.3. General Characterization of Hydrogels
3.4. Mucoadhesion Assessment
3.5. (PhSe)2 Mucosa Permeation
3.6. HET-CAM Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rowley, J.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Korenromp, E.; Low, N.; Unemo, M.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Chico, R.M.; Smolak, A.; Newman, L.; Gottlieb, S.; et al. Chlamydia, gonorrhoea, trichomoniasis and syphilis: Global prevalence and incidence estimates, 2016. Bull. World Health Organ. 2019, 97, 548–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Chung, C.H.; Lin, H.A.; Chen, R.M.; Tsao, C.H.; Chien, W.C.; Chiueh, T.S. Infection with Trichomonas vaginalis increases the risk of psychiatric disorders in women: A nationwide population-based cohort study. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masha, S.C.; Cools, P.; Sanders, E.J.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Crucitti, T. Trichomonas vaginalis and HIV infection acquisition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sex. Transm. Infect. 2019, 95, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, X. Trichomonas vaginalis infection-associated risk of cervical cancer: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2018, 228, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Küng, E.; Fürnkranz, U.; Walochnik, J. Chemotherapeutic options for the treatment of human trichomoniasis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 53, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.W.; Barbosa, N.V.; Rocha, J.B.T. Toxicology and pharmacology of synthetic organoselenium compounds: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 1179–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; da Silva, H.N.P.; Zeppenfeld, C.C.; Dornelles, J.L.; Henn, A.S.; Duarte, F.A.; da Costa, S.T.; Da Silva, A.S.; Cunha, M.A.; et al. Diphenyl diselenide dietary supplementation protects against fumonisin B 1-induced oxidative stress in brains of the silver catfish Rhamdia quelen. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 231, 1108738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.G.; Jardim, N.S.; Quines, C.B.; Nogueira, C.W. Diphenyl diselenide regulates Nrf2/Keap-1 signaling pathway and coun-teracts hepatic oxidative stress induced by bisphenol A in male mice. Environ. Res. 2018, 164, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe, R.L.; Jaramillo, M.L.; Galant, L.S.; Engel, D.; Dafre, A.L.; da Rocha, J.B.T.; Radi, R.; Farina, M.; de Bem, A.F. Diphenyl diselenide protects neuronal cells against oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction: Involvement of the glutathione-dependent antioxidant system. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.W.; Quinhones, E.B.; Jung, E.A.C.; Zeni, G.; Rocha, J.B.T. Anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activity of diphenyl diselenide. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, T.P.; Chassot, F.; Loreto, É.S.; Keller, J.T.; Azevedo, M.I.; Zeni, G.; Santurio, J.M.; Alves, S.H. Antifungal activities of diphenyl diselenide and ebselen alone and in combination with antifungal agents against Fusarium spp. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denardi, L.B.; Mario, D.A.N.; De Loreto, S.; Nogueira, C.W.; Santurio, J.M.; Alves, S.H. Antifungal Activities of Diphenyl Diselenide alone and in Combination with Fluconazole or Amphotericin B against Candida glabrata. Mycopathologia 2013, 176, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, G.; Jardim, N.S.; Sari, M.H.M.; Flores, E.F.; Prigol, M.; Nogueira, C.W. Diphenyl Diselenide Reduces Oxidative Stress and Tox-icity Caused by HSV-2 Infection in Mice. J. Cell Biochem. 2017, 118, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doleski, P.H.; Leal, D.B.R.; Machado, V.S.; Bottari, N.B.; Manzoni, A.G.; Casali, E.A.; Moritz, C.E.J.; Rocha, A.C.A.; Camillo, G.; Vogel, F.F.; et al. Diphenyl diselenide modulates nucleotidases, reducing inflammatory responses in the liver of Toxoplasma gondii-infected mice. Purinergic Signal. 2017, 13, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, C.W.; Rocha, J.B.T. Diphenyl diselenide a janus-faced molecule. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 21, 2055–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigol, M.; Nogueira, C.W.; Zeni, G.; Bronze, M.; Constantino, L. Physicochemical and Biochemical Profiling of Diphenyl Diselenide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 169, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prigol, M.; Brüning, C.A.; Martini, F.; Nogueira, C.W. Comparative Excretion and Tissue Distribution of Selenium in Mice and Rats Following Treatment with Diphenyl Diselenide. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2012, 150, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Thareja, S. In vitro and in vivo characterization of pharmaceutical nanocarriers used for drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 524–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyva-Gómez, G.; Piñón-Segundo, E.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L.; Mendoza-Elvira, S.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Approaches in Polymeric Nanoparticles for Vaginal Drug Delivery: A Review of the State of the Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, P.B.; dos Santos Ramos, M.A.; Bonifacio, B.V.; Negri KM, S.; Sato, M.R.; Bauab, T.M.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnological strategies for vaginal administration of drugs—A review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 2218–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; Censi, R.; di Martino, P. Polymeric Nanocapsules as Nanotechnological Alternative for Drug Deliv-ery System: Current Status, Challenges and Opportunities. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englert, A.V.; Verdi, C.M.; Santos, R.C.V.; Cruz, L.; Sari, M.H.M. Diphenyl Diselenide and Clotrimazole Co-loaded into Eudragit® RS 100 Nanocapsules Formulation Has Superior Antioxidant Potential and Promising Anti-candida Activity. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.; Cervi, V.F.; Sari, M.H.M.; Barbieri, A.V.; Ramos, A.P.; Copetti, P.M.; de Brum, G.F.; Nascimento, K.; Nadal, J.M.; Farago, P.V.; et al. Diphenyl diselenide loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) nanocapsules with selective antimelanoma activity: Development and cytotoxic evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, E.S.; Ferreira, L.M.; Denardi, L.B.; Sari, M.H.M.; Cervi, V.F.; Nogueira, C.W.; Alves, S.H.; Cruz, L. Mucoadhesive gellan gum hydrogel containing diphenyl diselenide-loaded nanocapsules presents improved anti-candida action in a mouse model of vulvovaginal candidiasis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 167, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldissera, M.D.; Souza, C.F.; Alessio, K.O.; Krawczak, K.W.; Abbad, L.B.; da Silva, A.S.; Bizzi, C.; Ourique, A.F.; Zeppenfeld, C.C.; Baldisserotto, B.; et al. Diphenyl diselenide-loaded nanocapsules in silver catfish feed enhance growth, improve muscle antioxidant/oxidant status and increase selenium deposition: Advantages of nanotechnology for fish health. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 4196–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.; Sari, M.H.M.; Cervi, V.F.; Prado, V.C.; Nadal, J.M.; Azambuja, J.H.; Da Silveira, E.F.; Nogueira, C.W.; Farago, P.V.; Braganhol, E.; et al. Design of Pegylated-Nanocapsules to Diphenyl Diselenide Administration: In Vitro Evidence of Hemocompatible and Selective Antiglioma Formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2020, 21, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.; da Rosa, L.V.C.; Müller, T.E.; de Menezes, C.C.; Sari, M.H.M.; Loro, V.L.; Nogueira, C.W.; Rosemberg, D.B.; Cruz, L. Zebrafish exposure to diphenyl diselenide-loaded polymeric nanocapsules caused no behavioral impairments and brain oxidative stress. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2019, 53, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.M.; Carvalho, S.G.; Araujo, V.H.S.; Carvalho, G.C.; Gremião, M.P.D.; Chorilli, M. Recent advances in hydrogels as strategy for drug delivery intended to vaginal infections. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 590, 119867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchemal, K.; Bories, C.; Loiseau, P.M. Strategies for Prevention and Treatment of Trichomonas vaginalis Infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Lima, J.A.; Paines, T.C.; Motta, M.H.; Weber, W.B.; Dos Santos, S.S.; Cruz, L.; da Silva, C.D.B. Novel Pemulen/Pullulan blended hydrogel containing clotrimazole-loaded cationic nanocapsules: Evaluation of mucoadhesion and vaginal permeation. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 79, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, M.; Manzoor, K.; Purwar, R.; Ikram, S. A review on latest innovations in natural gums based hydrogels: Preparations & applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 870–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermani, K.; Garg, S. The scope and potential of vaginal drug delivery. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 2000, 3, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenha, A.; Dionísio, M. Locust bean gum: Exploring its potential for biopharmaceutical applications. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2012, 4, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.-J.; Zayed, M.Z.; Zhu, H.-X.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.-P. Functional polysaccharides of carob fruit: A review. Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigon, C.; Marchiori, M.C.L.; Jardim, F.D.S.; Pegoraro, N.S.; Chaves, P.D.S.; Velho, M.C.; Beck, R.C.R.; Ourique, A.; Sari, M.H.M.; de Oliveira, S.M.; et al. Hydrogel containing silibinin nanocapsules presents effective anti-inflammatory action in a model of irritant contact dermatitis in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 137, 104969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmari, B.F.; Giuliani, L.M.; Reolon, J.B.; Rigo, G.V.; Tasca, T.; Cruz, L. Gellan gum-based hydrogel containing nanocapsules for vagi-nal indole-3-carbinol delivery in trichomoniasis treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 151, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.T.; Brown, M.B. Polymeric gels for intravaginal drug delivery. J. Control. Release. 2018, 270, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulmier, C. Selenium reagents and intermediates in organic synthesis. Angew. Chem. 1986, 100, 25–51. [Google Scholar]
- Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.P.; Ammoury, N.; Benita, S. Nanocapsule formation by interfacial polymer deposition follow-ing solvent displacement. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 55, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, L.S.; Bartgis, I.L. Axenic Cultivation of Trichomonas tenax, the Oral Flagellate of Man I. Establishment of Cultures. J. Protozool. 1962, 9, 442–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P.; Bhat, T.K. DPPH antioxidant assay revisited. Food Chem. 2009, 113, 1202–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghetti, G.S.; Knorst, M.T. Desenvolvimento e avaliação da estabilidade física de loções O/A contendo filtros solares. Rev. Bras. Ciências Farm. 2006, 42, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigo, L.A.; da Silva, C.R.; de Oliveira, S.M.; Cabreira, T.N.; da Silva CD, B.; Ferreira, J.; Beck RC, R. Nanoencapsulation of rice bran oil increases its protective effects against UVB radiation-induced skin injury in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Bio-pharm. 2015, 93, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, H.; Thongborisute, J.; Matsui, Y.; Sugihara, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Kawashima, Y. Novel mucoadhesion tests for polymers and polymer-coated particles to design optimal mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 1583–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanwat, R.; Shrivastava, B.; Pathak, K. Preparation and Evaluation of bioadhesive ocular inserts of aceclofenac. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2016, 41, 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Vieira, P.; Tasca, T.; Secor, W. Challenges and Persistent Questions in the Treatment of Trichomoniasis. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1249–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindamo, G.; Sapino, S.; Peira, E.; Chirio, D.; Gallarate, M. Recent Advances in Nanosystems and Strategies for Vaginal Delivery of Antimicrobials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, C.F.A.; De Souza, D.; Dornelles, L.; Nogueira, C.W.; Alves, M.P.; Prigol, M.; Rodrigues, O.E.D. Diphenyl Diselenide-Loaded Nanocapsules: Preparation and Biological Distribution. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 172, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, R.S.; Chandasana, H.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Rathi, C.; Kumar, D.; Mitra, K.; Shukla, P.K. Mucoadhesive nanoparticles for prolonged ocu-lar delivery of natamycin: In vitro and pharmacokinetics studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 432, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarturk, F. Mucoadhesive vaginal drug delivery systems. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2009, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, I.; Messina, F.; Nascimento, V.; Nacca, F.G.; Pietrella, D.; Lenardão, E.J.; Perin, G.; Sancineto, L. Synthetic Approaches to Organoselenium De-rivatives with Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Activity. Mini-Rev. Org. Chem. 2018, 16, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.M.; Sari, M.H.M.; Azambuja, J.H.; da Silveira, E.F.; Cervi, V.F.; Marchiori, M.C.L.; Maria-Engler, S.S.; Wink, M.R.; Azevedo, J.G.; Nogueira, C.W.; et al. Xanthan gum-based hydrogel containing nanocapsules for cutaneous diphenyl diselenide delivery in melanoma therapy. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 38, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, D.P.G.; Vieira, P.D.B.; Frasson, A.P.; Menezes, C.B.; Senger, F.R.; da Silva, G.N.S.; Gnoatto, S.C.B.; Tasca, T. Anti-Trichomonas vaginalis activity of betulinic acid derivatives. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malli, S.; Bories, C.; Bourge, M.; Loiseau, P.M.; Bouchemal, K. Surface-dependent endocytosis of poly(isobutylcyanoacrylate) nano-particles by Trichomonas vaginalis. International journal of pharmaceutics. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, V.D.; Jani, G.K.; Moradiya, N.G.; Randeria, N.P.; Nagar, B.J. Locust bean gum: A versatile biopolymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.H.M.; da Cruz Weber Fulco, B.; Ferreira, L.M.; Pegoraro, N.S.; da SilvaBrum, E.; Casola, K.K.; Marchiori, M.C.L.; Oliveira, S.M.; Nogueira, C.W.; Cruz, L.N. anoencapsulation potentiates the cutaneous anti-inflammatory effect of p,p’-methoxyl-diphenyl diselenide: Design, permeation, and in vivo studies of a nano-technological-based carrageenan gum hydrogel. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 153, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmałek, T.; Froelich, A.; Jadach, B.; Tatarek, A.; Gadziński, P.; Falana, A.; Gralińska, K.; Ekert, M.; Puri, V.; Wrotyńska-Barczyńska, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Polymer-Based Vaginal Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ahsan, F. The vagina as a route for systemic drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2005, 103, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, J.-P. Antibacterial treatment of bacterial vaginosis: Current and emerging therapies. Int. J. Women’s Health 2011, 3, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavletic, A.J.; Hawes, S.E.; Geske, J.A.; Bringe, K.; Polack, S.H. Experience with routine vaginal pH testing in a family practice set-ting. Infectious diseases in obstetrics and gynecology. Infect. Dis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szymańska, E.; Orłowski, P.; Winnicka, K.; Tomaszewska, E.; Bąska, P.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J.; Basa, A.; Krzyżowska, M. Multifunctional Tannic Ac-id/Silver Nanoparticle-Based Mucoadhesive Hydrogel for Improved Local Treatment of HSV Infection: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, V.K.; Anis, A.; Banerjee, I.; Pramanik, K.; Bhattacharya, M.K.; Pal, K. Preparation and characterization of novel carbopol based bigels for topical delivery of metronidazole for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 44, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, N.B.; Kumar, R.P.; Kumar, N.U.; Brata, B.B. Development and Characterization of Bioadhesive Gel of Microencapsulated Metronidazole for Vaginal Use. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2010, 9, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, A.; Aggarwal, D.; Garg, S.; Singla, A.K. Spreading of semisolid formulations: An update. Pharm. Technol. 2002, 26, 84–105. [Google Scholar]
- Berginc, K.; Škalko-Basnet, N.; Basnet, P.; Kristl, A. Development and Evaluation of an In Vitro Vaginal Model for Assessment of Drug’s Biopharmaceutical Properties: Curcumin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2012, 13, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, A.M.; de Oliveira, E.G.; Coradini, K.; Bruinsmann, F.A.; Aguirre, T.; Lorenzoni, R.; Barcelos, R.C.S.; Roversi, K.; Rossato, D.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; et al. Chitosan hydrogels containing nanoencapsulated phenytoin for cutaneous use: Skin permeation/penetration and efficacy in wound healing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, C.B.; Frasson, A.P.; Tasca, T. Trichomoniasis—Are we giving the deserved attention to the most common non-viral sex-ually transmitted disease worldwide? Microbial. Cell. 2016, 3, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Parveen, R.; Chatterji, B.P. Toxicology of Nanoparticles in Drug Delivery. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2021, 9, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmeira-de-Oliveira, R.; Monteiro Machado, R.; Martinez-de-Oliveira, J.; Palmeira-de-Oliveira, A. Testing vaginal irritation with the Hen’s Egg Test-Chorioallantoic Membrane assay. ALTEX-Altern. Anim. Exp. 2018, 35, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Formulation | AS (nm) | PDI | pH | Drug Content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HG (PhSe)2 | - | - | 7.52 ± 0.10 | 1.08 ± 0.09 |
| HG NC B | 295 ± 24 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 6.16 ± 0.14 | - |
| HG NC (PhSe)2 | 237 ± 4 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | 6.20 ± 0.14 | 0.96 ± 0.01 |
| Formulation | Index | Sf (mm2/g) | |
| ɳ | Ƙ | ||
| HG (PhSe)2 | 0.565 ± 0.0209 | 8.08 × 104 ± 7565 | 3.43 ± 0.44 |
| HG NC B | 0.513 ± 0.0114 | 1.53 × 105 ± 9511 * | 2.94 ± 0.02 |
| HG NC (PhSe)2 | 0.503 ± 0.0580 | 1.55 × 105 ± 4410 * | 2.95 ± 0.08 |
| Formulation | Equations | ||
| Bingham | Casson | Ostwald | |
| HG (PhSe)2 | 0.982 ± 0.006 | 0.992 ± 0.004 | 0.998 ± 0.001 |
| HG NC B | 0.968 ± 0.006 | 0.984 ± 0.004 | 0.997 ± 0.002 |
| HG NC (PhSe)2 | 0.968 ± 0.006 | 0.985 ± 0.004 | 0.997 ± 0.001 |
| Sample | Irritation Score (IS) |
|---|---|
| (PhSe)2 | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| NC (PhSe)2 | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| NC B | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| HG NC (PhSe)2 | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| HG (PhSe)2 | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| HG NC B | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| NaCl 0.9% | 0.00 ± 0.0 |
| NaOH 0.1 M | 13.6 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reis, F.P.d.; Rigo, G.V.; Nogueira, C.W.; Tasca, T.; Sari, M.H.M.; Cruz, L. Locust Bean Gum Nano-Based Hydrogel for Vaginal Delivery of Diphenyl Diselenide in the Treatment of Trichomoniasis: Formulation Characterization and In Vitro Biological Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102112
Reis FPd, Rigo GV, Nogueira CW, Tasca T, Sari MHM, Cruz L. Locust Bean Gum Nano-Based Hydrogel for Vaginal Delivery of Diphenyl Diselenide in the Treatment of Trichomoniasis: Formulation Characterization and In Vitro Biological Evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(10):2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102112
Chicago/Turabian StyleReis, Fernanda Padoin dos, Graziela Vargas Rigo, Cristina Wayne Nogueira, Tiana Tasca, Marcel Henrique Marcondes Sari, and Letícia Cruz. 2022. "Locust Bean Gum Nano-Based Hydrogel for Vaginal Delivery of Diphenyl Diselenide in the Treatment of Trichomoniasis: Formulation Characterization and In Vitro Biological Evaluation" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 10: 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102112
APA StyleReis, F. P. d., Rigo, G. V., Nogueira, C. W., Tasca, T., Sari, M. H. M., & Cruz, L. (2022). Locust Bean Gum Nano-Based Hydrogel for Vaginal Delivery of Diphenyl Diselenide in the Treatment of Trichomoniasis: Formulation Characterization and In Vitro Biological Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 14(10), 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14102112










