Formulation Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Dasatinib
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
Preparation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions
2.3. Morphology
2.4. X-ray Powder Diffraction
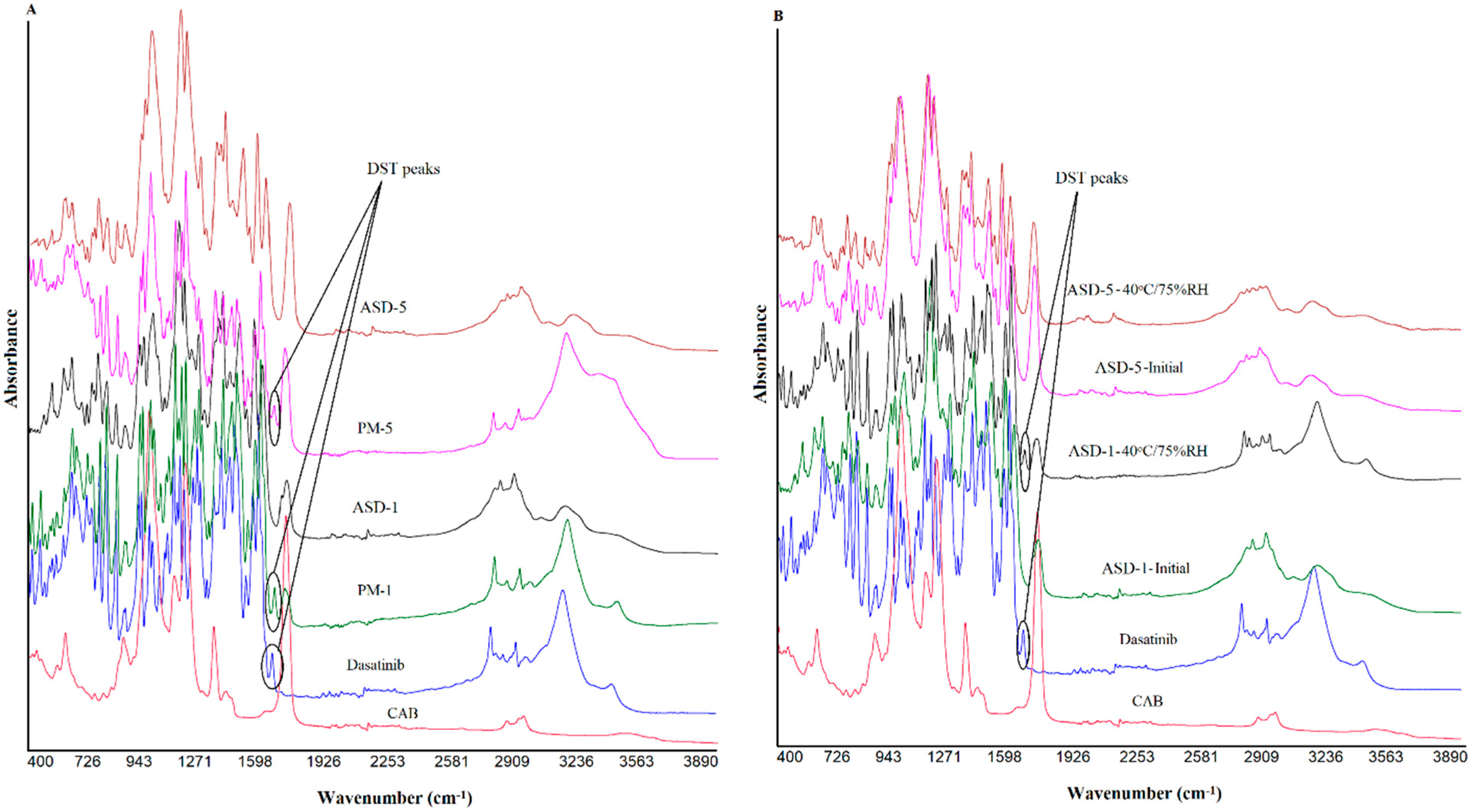
2.5. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
2.6. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.8. Near-Infrared (NIR) Hyperspectroscopy
2.9. Assay
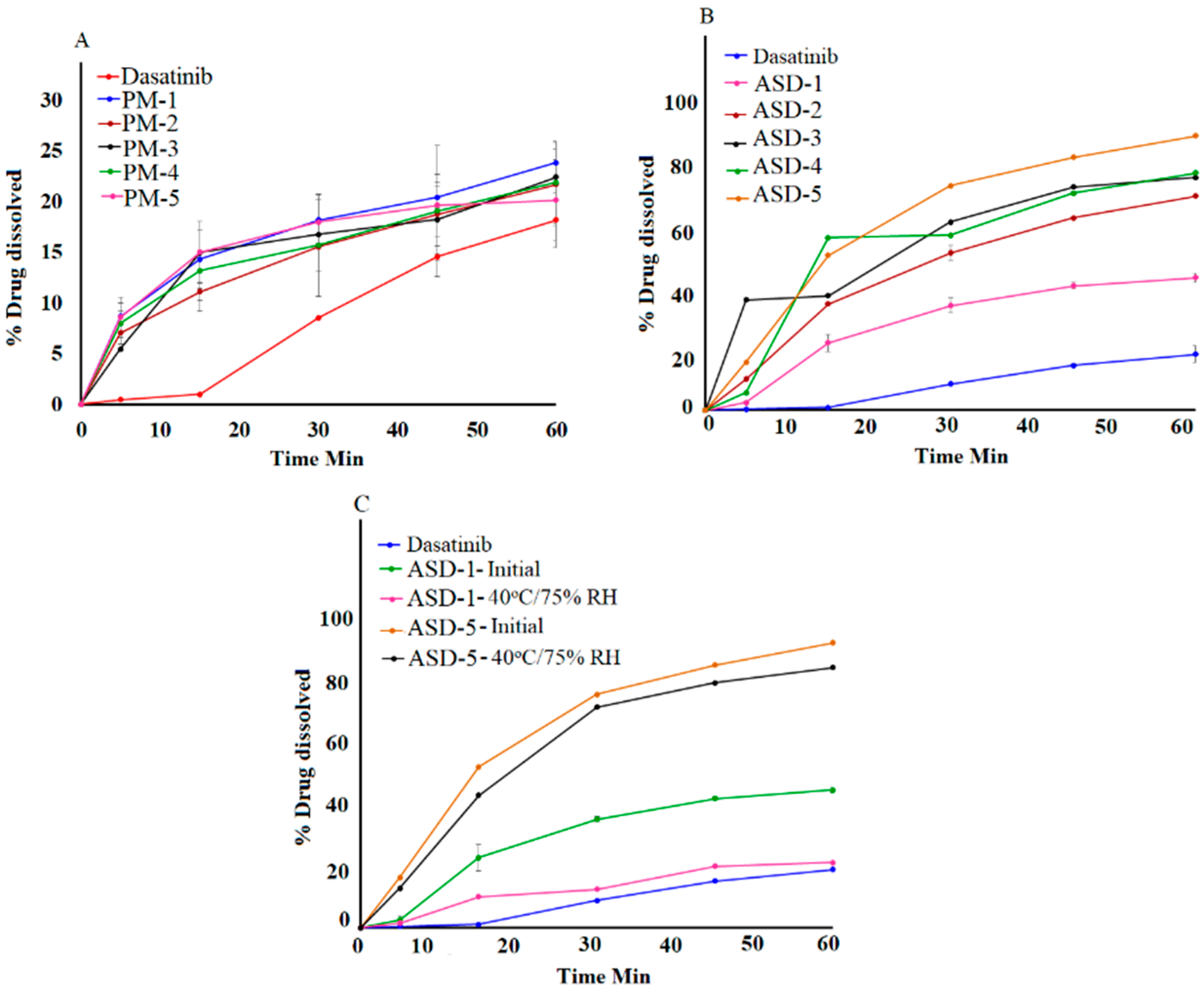
2.10. Dissolution
2.11. High Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.12. Stability Study
2.13. Pharmacokinetics
2.14. UPLC-MS Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ASD Characterizations
3.1.1. Morphology
3.1.2. X-ray Powder Diffraction
3.1.3. Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.4. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
3.1.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.1.6. Near-Infrared Hyperspectroscopy
3.1.7. Dissolution
3.1.8. Pharmacokinetics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lombardo, L.J.; Lee, F.Y.; Chen, P.; Norris, D.; Barrish, J.C.; Behnia, K.; Castaneda, S.; Cornelius, L.A.M.; Das, J.; Doweyko, A.M.; et al. Discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methylphenyl)-2-[[6-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)–piperazin-1-yl]-2–methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino] thiazole 5–carboxamide (BMS-354825), a dual Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical assays. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6658–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drugs@FDA. FDA Approved Drugs. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/ (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Tokarski, J.S.; Newitt, J.A.; Chang, C.Y.J.; Cheng, J.D.; Wittekind, M.; Kiefer, S.E.; Kish, K.; Lee, F.Y.; Borzillerri, R.; Lombardo, L.J.; et al. The structure of dasatinib (BMS-354825) bound to activated ABL kinase domain elucidates its inhibitory activity against imatinib-resistant ABL mutants. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5790–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talpaz, M.; Shah, N.P.; Kantarjian, H.; Donato, N.; Nicoll, J.; Paquette, R.; Cortes, J.; O’Brien, S.; Nicaise, C.; Bleickardt, E.; et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA. Sprycel—Dasatinib—Scientific Discussion. 2006. Available online: https://www.bms.com/assets/bms/ca/documents/productmonograph/SPRYCEL_EN_PM.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Dharani, S.; Rahman, Z.; Ali, S.F.B.; Afrooz, H.; Khan, M.A. Quantitative estimation of phenytoin sodium disproportionation in the formulations using vibration spectroscopies and multivariate methodologies. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 25, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrignelli, A.; Sanarica, F.; Lopalco, A.; Lopedota, A.; Laquintana, V.; Franco, M.; Boccanegra, B.; Mantuano, P.; De Luca, A.; Denora, N. Dasatinib/HP-β-CD inclusion complex based aqueous formulation as a promising tool for the treatment of paediatric neuromuscular disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, V.; Alayoubi, A.; Siddiqui, A.; Nazzal, S. Powdered self-emulsified lipid formulations of meloxicam as solid dosage forms for oral administration. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2013, 39, 1681–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, R.N.; Mehta, P.P.; Kumar, A. Efavirenz self-nano-emulsifying drug delivery system: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2016, 17, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Sharma, P.; Sharma, J.; Lamba, A.K.; Lamba, H.S. Development, characterization and solubility study of solid dispersion of Quercetin by solvent evaporation method. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 10128–10133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, S.E.; Jang, W.S.; Byeon, J.C.; Jeong, H.M.; Park, J.S. Use of acidifier and solubilizer in tadalafil solid dispersion to enhance the in vitro dissolution and oral bioavailability in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.S.; Yoon, D.S.; Sohn, J.Y.; Park, J.S.; Choi, J.S. Development and evaluation of targeting ligands surface modified paclitaxel nanocrystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2017, 72, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Han, H.K. Nanomedicines: Current status and future perspectives in aspect of drug delivery and pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remenar, J.F.; Peterson, M.L.; Stephens, P.W.; Zhang, Z.; Zimenkov, A.Y.; Hickey, M.B. Celecoxib: Nicotinamide dissociation: Using excipients to capture the cocrystal’s potential. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunashima, D.; Yamashita, K.; Ogawara, K.I.; Sako, K.; Higaki, K. Preparation of extended release solid dispersion formulations of tacrolimus using ethylcellulose and hydroxypropylmethylcellulose by solvent evaporation method. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Iyer, R.M.; Mair, H.J.; Choi, D.; Tian, H.; Diodone, R.; Fahnrich, K.; Pabst-Ravot, A.; Tang, K.; Scheubel, E. Improved human bioavailability of vemurafenib, a practically insoluble drug, using an amorphous polymer-stabilized solid dispersion prepared by a solvent-controlled coprecipitation process. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 967–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jermain, S.V.; Brough, C.; Williams, R.O., III. Amorphous solid dispersions and nanocrystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery—An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanetz, N.A. Stabilization of solid dispersions of nimodipine and polyethylene glycol 2000. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 28, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.B.; Rathi, S.; Jyothi, V.G.S.S.; Shastri, N.R. Cellulose based polymers in development of amorphous solid dispersions. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 14, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodarski, K.; Sawicki, W.; Paluch, K.J.; Tajber, L.; Grembecka, M.; Hawelek, L.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Grzybowska, K.; Talik, E.; Paluch, M. The influence of amorphization methods on the apparent solubility and dissolution rate of tadalafil. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 62, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.; Pyo, Y.C.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.E.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.S. Overview of the Manufacturing Methods of Solid Dispersion Technology for Improving the Solubility of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs and Application to Anticancer Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Quiñones, R.; Matzger, A.J. Structural and physicochemical aspects of dasatinib hydrate and anhydrate phases. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 2122–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipcik, O.S.; Martaus, A.; Jegorov, A.; Gavenda, A.; Aronhime, J.; Vraspír, R.; Koltai, T.; Faustmann, J.; Gabriel, R. Polymorphs of Dasatinib and Process for Preparation Thereof. U.S. Patent No. US20100256158A1, 5 July 2011. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20100256158A1/en (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Jimenez, S.G.; Fernandez, L.A.; Calzada, J.V. Pharmaceutical Composition Comprising Amorphous Dasatinib. PCT No. WO2017108605, 29 June 2017. Available online: https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2017108605 (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Dwivedi, S.D.; Singh, K.K.; Singh, N.K.; Patil, A.K. Process for Preparation of Amorphous Form of Dasatinib. U.S. Patent No. US9249134B2, 2 February 2016. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US9249134B2/en (accessed on 5 July 2022).
- Mohamed, E.M.; Khuroo, T.; Afrooz, H.; Dharani, S.; Sediri, K.; Cook, P.; Arunagiri, R.; Khan, M.A.; Rahman, Z. Development of a Multivariate Predictive Dissolution Model for Tablets Coated with Cellulose Ester Blends. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raouf, R.; Wahab, Z.A.; Ibrahim, N.A.; Talib, Z.A.; Chieng, B.W. Transparent Blend of Poly(Methylmethacrylate)/Cellulose Acetate Butyrate for the Protection from Ultraviolet. Polymers 2016, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, W.L.; Riegelman, S. Pharmaceutical Applications of Solid Dispersion Systems. J. Pharm. Sci. 1971, 60, 1281–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Ohárriz, M.C.; Martín, C.; Goñi, M.M.; Rodríguez-Espinosa, C.; Tros-Ilarduya, M.C.; Zornoza, A. Influence of Polyethylene Glycol 4000 on the Polymorphic Forms of Diflunisal. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogal, S.A.; Gurjar, P.N.; Yamgar, D.S.; Kamod, A.C. Solid Dispersion Technique for Improving Solubility of Some Poorly Soluble Drugs. Der Pharm. Lett. 2012, 4, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Shete, S.; Gadhave, V.; Gaikwad, D. Enhancement of Solubility and Dissolution Rate of Simvastatin by Ternary Solid Dispersion Technique. J. Pharm. Sci. Innovation. 2015, 3, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- ICH. Guidance for Industry—Q2B Validation of Analytical Procedures: Methodology; Unites States Patent Office: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2005; p. 1996.
- USP41-NF36; General Chapters: <1225> Validation of Compendial Procedures. Pharmacopeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2018; pp. 7665–7671.
- Nirali, G.P.; Abu, T.M.S. Moisture sorption by polymeric excipients commonly used in amorphous solid dispersion and its effect on glass transition temperature: I. Polyvinylpyrrolidone and related copolymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 616, 121532. [Google Scholar]
- Haldon, R.A.; Schell, W.J.; Simha, R. Transitions in glasses at low temperatures. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B 1967, 1, 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, E.; Worku, Z.A.; Healy, A.M. Physicochemical Properties of Poly-Vinyl Polymers and Their Influence on Ketoprofen Amorphous Solid Dispersion Performance: A Polymer Selection Case Study. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.X.; Yang, M.; Van Den Berg, F.; Pajander, J.; Rades, T.; Rantanen, J. Influence of solvent evaporation rate and formulation factors on solid dispersion physical stability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 44, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.D.; Tran, P.H.L. Molecular Interactions in Solid Dispersions of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Sato, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Ozaki, Y. FTIR Study on Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in Biodegradable Polymer Blends of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) and Poly(4-vinylphenol). Macromolecules 2010, 43, 3897–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutsyk, A.M.; Ilchenko, O.O.; Yuzvenko, Y.M.; Obukhovsky, V.V.; Nikonova, V.V. Vibration spectroscopy of complex formation in aqueous solutions of isopropanol. Ukr. J. Phys. 2018, 63, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Mohan, C.; Kanamsrinivasan, M.; Gulati, M. Physiochemical characterization and release rate studies of solid dispersions of ketoconazole with pluronic F127 and PVP K-30. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2011, 10, 685–694. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, L.M.; Videa, M.; Sosa, N.G.; Ramírez, J.H.; Castro, S. Long-term stability of new co-amorphous drug binary systems: Study of glass transitions as a function of composition and shelf time. Molecules 2016, 21, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, K.; Ashe, J.S.; Matzger, A.J. Far-Infrared Spectroscopy as a Probe for Polymorph Discrimination. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westad, F.; Schmidt, A.; Kermit, M. Incorporating chemical band-assignment in near infrared spectroscopy regression models. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2008, 16, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Hattori, Y.; Otsuka, M. Characterization of ternary amorphous solid dispersion containing hypromellose phthalate and erythritol prepared by hot melt extrusion using melting point depression. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 101797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Murai, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Miyagishima, T.; Shindo, M.; Ogawa, K.; Nagashima, T.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, R.; the Inter-Michinoku Dasatinib Study Group (IMIDAS); et al. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dasatinib in the Chronic Phase of Newly Diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, L.J.; Cui, D.; Wu, C.; Luo, R.; Manning, J.A.; Bonacorsi, S.J.; Lago, M.; Allentoff, A.; Lee, F.Y.F.; McCann, B.; et al. Metabolism and disposition of dasatinib after oral administration to humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2008, 36, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M. Therapeutic drug monitoring of imatinib, nilotinib, and dasatinib for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Formulation | % DST | % CAB | Drug to Carrier Ratio | Estimated Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASD-1 | 50 | 50 | 1:1 | 217 °C | 4.2 ± 0.2 |
| ASD-2 | 33.3 | 66.7 | 1:2 | 231 °C | 3.4 ± 0.1 |
| ASD-3 | 25 | 75 | 1:3 | 237 °C | 2.8 ± 0.2 |
| ASD-4 | 20 | 80 | 1:4 | 241 °C | 2.3 ± 0.3 |
| ASD-5 | 16.6 | 83.4 | 1:5 | 243 °C | 1.8 ± 0.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dharani, S.; Mohamed, E.M.; Khuroo, T.; Rahman, Z.; Khan, M.A. Formulation Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Dasatinib. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112450
Dharani S, Mohamed EM, Khuroo T, Rahman Z, Khan MA. Formulation Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Dasatinib. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(11):2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112450
Chicago/Turabian StyleDharani, Sathish, Eman M. Mohamed, Tahir Khuroo, Ziyaur Rahman, and Mansoor A. Khan. 2022. "Formulation Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Dasatinib" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 11: 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112450
APA StyleDharani, S., Mohamed, E. M., Khuroo, T., Rahman, Z., & Khan, M. A. (2022). Formulation Characterization and Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions of Dasatinib. Pharmaceutics, 14(11), 2450. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112450







