Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of mRNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Vectors for mRNA Delivery
2.1. The Delivery of mRNA Requires Vectors
2.2. Selection of mRNA Delivery Vectors
2.2.1. Viral Vectors
2.2.2. Non-Viral Vectors
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Retrovirus | Stable integration into the genome, high transfection rate, long gene expression time, weak immunogenicity. | Only integrate into dividing cells, risk of insertional mutations, low delivery efficiency in vivo, small package capacity [9]. |
| Adenovirus | Capable of carrying relatively large gene fragments. | Immunogenic, complex operation, short gene expression time. |
| AAV | Weak immune response, high transfection rate, no integration of host DNA. | Small package capacity |
| Lentiviral | Stable integration into genome or dividing cells, long duration of gene expression, weak immunogenicity. | Risk of insertional mutations, low delivery efficiency in vivo [9]. |
| LNP | Protect mRNA from degradation by ribonucleases, high mRNA delivery efficiency, high yield, and easy scale-up of production. | Potential side effects, weak targeting and stability. |
| Protamine | Protect mRNA from degradation by ribonucleases and adjuvant activity of the protamine–mRNA complex. | Low delivery efficiency and low efficiency of mRNA translation. |
| Cationic polymer | Promote internalization through adsorption-mediated cellular endocytosis, effectively compress nucleic acids and protect them from enzymatic degradation through surface amine groups [48], and provide pH-buffering capacity through the large number of tertiary amine groups in the core [49]. | Mostly non-degradable and highly cytotoxic [50]. |
| Peptide | Highly functional. | Low delivery efficiency |
| Cationic nanoemulsion | Protects mRNA from degradation by ribonucleases, has the ability to protect and efficiently deliver nucleic acids, and can trigger a strong immune response as a vaccine adjuvant [51]. | High cytotoxicity |
| Cell-penetrating peptide | Low charge density and excellent ability to cross cell membranes. | Only a few peptides are effective and there is an urgent need to develop new effective compounds to expand the material pool for peptide delivery systems. |
| Exosome | Biocompatible and not easily cleared by immunity [52]. | Difficult to produce, isolate, and purify [53]. |
| Inorganic nanoparticle | Easily modified for surface modification and unique versatility. | Poor biocompatibility and difficult to biodegrade. |
3. Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)
3.1. The Development of LNPs
3.2. Components and Structural Features of LNPs
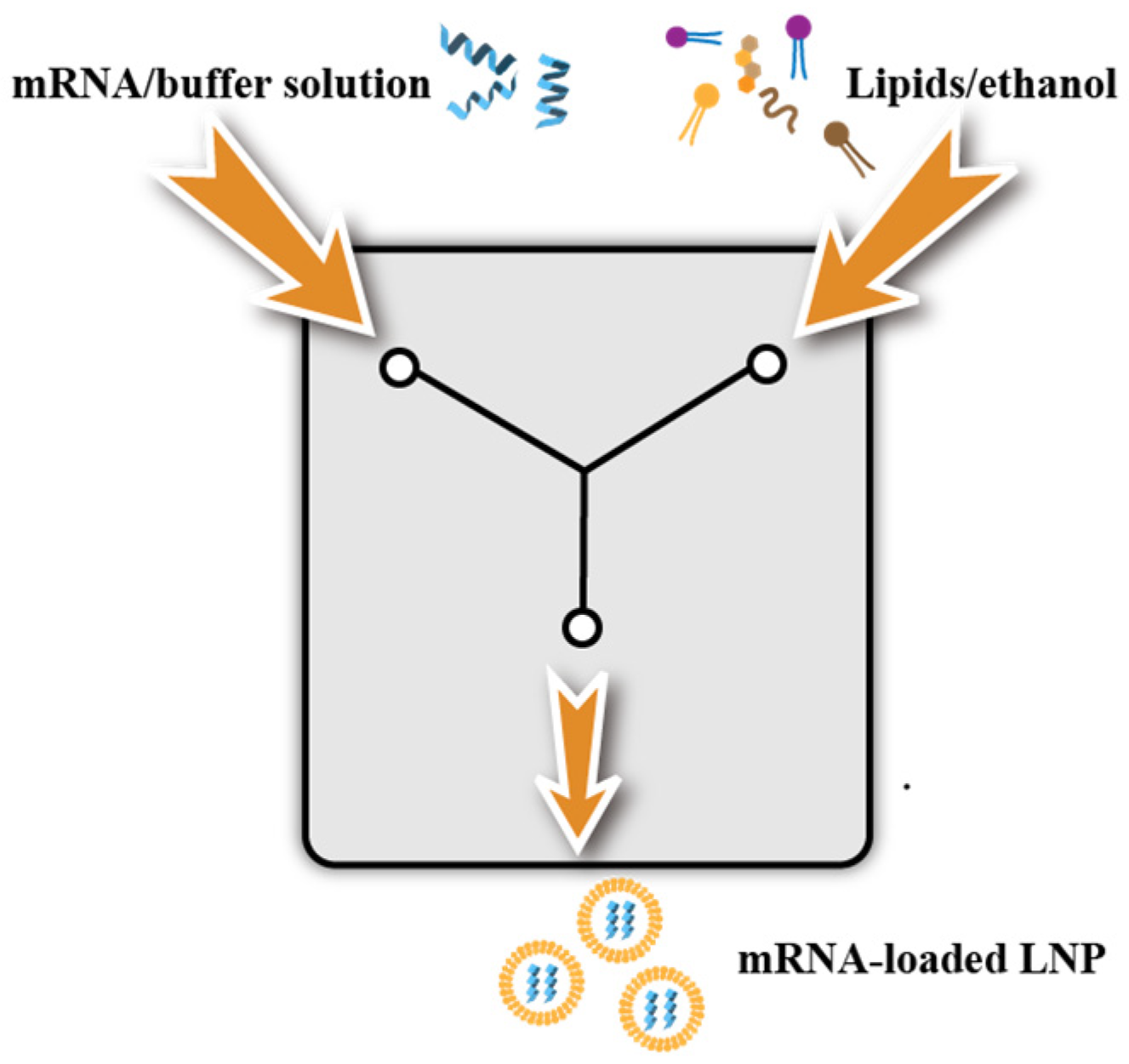
3.3. Preparation of LNPs
3.3.1. Ethanol Dilution Method and Manual Mixing Method
3.3.2. T-Mix Method
3.3.3. Microfluidics
4. The Factors Affecting the Efficiency of LNP@mRNA Delivery
4.1. Modification of mRNA
4.1.1. Nucleoside Modification
4.1.2. Adjusting the Cap Structure
4.1.3. Optimization of Regulation Elements for 5′ UTR and 3′ UTR
4.1.4. Design of the Open Reading Frame (ORF)
4.1.5. Adding A-Tail
4.2. Ionizable Lipids
4.2.1. The Effects of Ionizable Lipid Structure on the Efficiency of LNP Transfection
Head
Connecting Fragment
Tail
4.2.2. Key Points in the Design of Chemical Structures for Ionizable Lipids
pKa
Endosome Escape
4.2.3. Progress in the Study of Ionizable Lipids
4.3. PEGylated Lipids
4.4. Auxiliary Phospholipids
4.5. Cholesterol
4.6. Particle Size of LNPs
5. The Factors Affecting the Distribution of LNP@mRNA In Vivo
5.1. Route of Administration
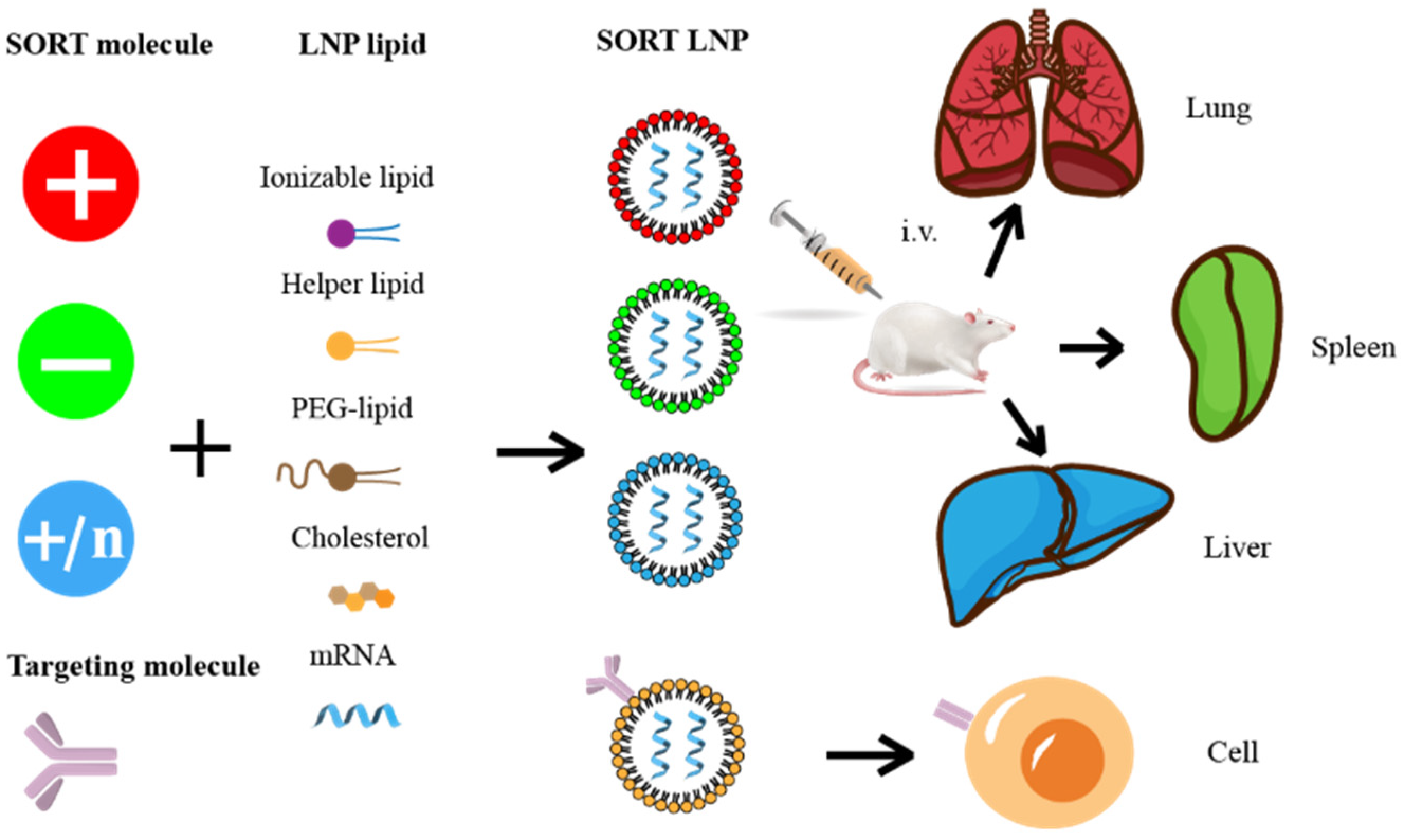
5.2. Targeted Molecular Modification
5.3. High-Throughput Screening and Design of Predictable LNP
5.4. Discovery of Novel Ionizable Lipids
6. Problems in Clinical Application of LNP@mRNA
6.1. Immune-Related Adverse Effects
6.2. Side Effects of PEG
6.3. Instability Issues of LNP@mRNA
7. Optimization of LNP@mRNA Recipes for Clinical Therapeutic Requirements
7.1. Optimization of LNP@mRNA Recipes
7.2. Designing Novel PEGylated Lipids
8. The Brief Landscape of LNP@mRNA in Clinical Gene Therapy
8.1. LNP@mRNA for Infectious Disease Treatment
8.2. LNP@mRNA for Cardiovascular Disease Treatment
8.3. LNP@mRNA for Liver Disease Treatment
8.4. LNP@mRNA Research for the Cancer Treatment
8.5. LNP@mRNA for Rare Disease Treatment
9. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wirth, T.; Parker, N.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. History of gene therapy. Gene 2013, 525, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaese, R.M.; Culver, K.W.; Miller, A.D.; Carter, C.S.; Fleisher, T.; Clerici, M.; Shearer, G.; Chang, L.; Chiang, Y.; Tolstoshev, P.; et al. T lymphocyte-directed gene therapy for ADA- SCID: Initial trial results after 4 years. Science 1995, 270, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Gao, H.; Tan, D.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.Z. mRNA cancer vaccines: Advances, trends and challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2969–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.Y.; Cheung, P.P.-H. Effectiveness of heterologous and homologous COVID-19 vaccine regimens: Living systematic review with network meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 377, e069989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Mateus, J.; Coelho, C.H.; Dan, J.M.; Moderbacher, C.R.; Gálvez, R.I.; Cortes, F.H.; Grifoni, A.; Tarke, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Humoral and cellular immune memory to four COVID-19 vaccines. Cell 2022, 185, 2434–2451.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruggi, G.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Ulmer, J.B.; Yu, D. mRNA as a Transformative Technology for Vaccine Development to Control Infectious Diseases. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunbar, C.E.; High, K.A.; Joung, J.K.; Kohn, D.B.; Ozawa, K.; Sadelain, M. Gene therapy comes of age. Science 2018, 359, eaan4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jinek, M.; Chylinski, K.; Fonfara, I.; Hauer, M.; Doudna, J.A.; Charpentier, E. A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 2012, 337, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posey, A.D., Jr.; Schwab, R.D.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Steentoft, C.; Mandel, U.; Engels, B.; Stone, J.D.; Madsen, T.D.; Schreiber, K.; Haines, K.M.; et al. Engineered CAR T Cells Targeting the Cancer-Associated Tn-Glycoform of the Membrane Mucin MUC1 Control Adenocarcinoma. Immunity 2016, 44, 1444–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hekele, A.; Bertholet, S.; Archer, J.; Gibson, D.G.; Palladino, G.; Brito, L.A.; Otten, G.R.; Brazzoli, M.; Buccato, S.; Bonci, A.; et al. Rapidly produced SAM(®) vaccine against H7N9 influenza is immunogenic in mice. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2013, 2, e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, M. Who discovered messenger RNA? Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, R526–R532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle In Vivo. Science 1990, 247, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phua, K.K.; Leong, K.W.; Nair, S.K. Transfection efficiency and transgene expression kinetics of mRNA delivered in naked and nanoparticle format. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dirisala, A.; Uchida, S.; Tockary, T.A.; Yoshinaga, N.; Li, J.; Osawa, S.; Gorantla, L.; Fukushima, S.; Osada, K.; Kataoka, K. Precise tuning of disulphide crosslinking in mRNA polyplex micelles for optimising extracellular and intracellular nuclease tolerability. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 670–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, A.; Cheng, Y.; Sylvestre, M.; Gustafson, H.H.; Puri, S.; Pun, S.H. Serum Nuclease Susceptibility of mRNA Cargo in Condensed Polyplexes. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Weissman, D. Recent advances in mRNA vaccine technology. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 65, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: The impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wadhwa, A.; Aljabbari, A.; Lokras, A.; Foged, C.; Thakur, A. Opportunities and Challenges in the Delivery of mRNA-Based Vaccines. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirisala, A.; Uchida, S.; Li, J.; Van Guyse, J.F.R.; Hayashi, K.; Vummaleti, S.V.C.; Kaur, S.; Mochida, Y.; Fukushima, S.; Kataoka, K. Effective mRNA Protection by Poly(l-ornithine) Synergizes with Endosomal Escape Functionality of a Charge-Conversion Polymer toward Maximizing mRNA Introduction Efficiency. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2022, 43, e2100754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Ashwanikumar, N.; Robinson, E.; DuRoss, A.; Sun, C.; Murphy-Benenato, K.E.; Mihai, C.; Almarsson, Ö.; Sahay, G. Boosting Intracellular Delivery of Lipid Nanoparticle-Encapsulated mRNA. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5711–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn, S.L.; Amaya, A.K.; Alexander, I.E.; Edelstein, M.; Abedi, M.R. Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide to 2017: An update. J. Gene Med. 2018, 20, e3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrman, S. Virus treatment questioned after gene therapy death. Nature 1999, 401, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hacein-Bey-Abina, S.; Von Kalle, C.; Schmidt, M.; McCormack, M.P.; Wulffraat, N.; Leboulch, P.; Lim, A.; Osborne, C.S.; Pawliuk, R.; Morillon, E.; et al. LMO2-associated clonal T cell proliferation in two patients after gene therapy for SCID-X1. Science 2003, 302, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.; Yang, S.; Hu, X.; Yin, D.; Dai, Y.; Qian, X.; Wang, D.; Pan, X.; Hong, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Lentiviral delivery of co-packaged Cas9 mRNA and a Vegfa-targeting guide RNA prevents wet age-related macular degeneration in mice. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Ling, S.; Wang, D.; Dai, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, X.; Paludan, S.R.; Hong, J.; Cai, Y. Targeting herpes simplex virus with CRISPR-Cas9 cures herpetic stromal keratitis in mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petsch, B.; Schnee, M.; Vogel, A.B.; Lange, E.; Hoffmann, B.; Voss, D.; Schlake, T.; Thess, A.; Kallen, K.J.; Stitz, L.; et al. Protective efficacy of in vitro synthesized, specific mRNA vaccines against influenza A virus infection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzebska, N.T.; Mellett, M.; Frei, J.; Kündig, T.M.; Pascolo, S. Protamine-Based Strategies for RNA Transfection. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1210–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, H.K.; Fan, Y.; Kim, J.; Amiji, M.M. Intranasal Delivery and Transfection of mRNA Therapeutics in the Brain Using Cationic Liposomes. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1996–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoerr, I.; Obst, R.; Rammensee, H.G.; Jung, G. In vivo application of RNA leads to induction of specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and antibodies. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Bryers, J.D. Scaffold-mediated delivery for non-viral mRNA vaccines. Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Duchardt, K.M.; Lorenz, C.; Pfeiffer, R.; Ojkić-Zrna, S.; Probst, J.; Kallen, K.J. Messenger RNA-based vaccines with dual activity induce balanced TLR-7 dependent adaptive immune responses and provide antitumor activity. J. Immunother. 2011, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wei, Y.; Gong, C. Polymeric Nanocarriers for Non-Viral Gene Delivery. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 739–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jere, D.; Jiang, H.L.; Arote, R.; Kim, Y.K.; Choi, Y.J.; Cho, M.H.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C.S. Degradable polyethylenimines as DNA and small interfering RNA carriers. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2009, 6, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armbruster, N.; Jasny, E.; Petsch, B. Advances in RNA Vaccines for Preventive Indications: A Case Study of A Vaccine Against Rabies. Vaccines 2019, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crommelin, D.J.A.; van Hoogevest, P.; Storm, G. The role of liposomes in clinical nanomedicine development. What now? Now what? J. Control. Release 2020, 318, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinc, A.; Maier, M.A.; Manoharan, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Jayaraman, M.; Barros, S.; Ansell, S.; Du, X.; Hope, M.J.; Madden, T.D.; et al. The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2019, 14, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J.C. Editorial: Drug Delivery: Too Much Complexity, Not Enough Reproducibility? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 15170–15171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, S.; Guevara, M.L.; Li, Z.; Mai, J.; Ferrari, M.; Pompa, P.P.; Shen, H. Lipopolyplex potentiates anti-tumor immunity of mRNA-based vaccination. Biomaterials 2017, 125, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, C. A Randomized, Open-Label, Controlled Phase I Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, Immunogenicity, and Immune-Boosting of the SW-BIC-213 mRNA Vaccine in Healthy People. Available online: http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=170605 (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Poliskey, J.A.; Crowley, S.T.; Ramanathan, R.; White, C.W.; Mathew, B.; Rice, K.G. Metabolically stabilized double-stranded mRNA polyplexes. Gene Ther. 2018, 25, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshinaga, N.; Uchida, S.; Dirisala, A.; Naito, M.; Osada, K.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K. mRNA loading into ATP-responsive polyplex micelles with optimal density of phenylboronate ester crosslinking to balance robustness in the biological milieu and intracellular translational efficiency. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassett, K.J.; Benenato, K.E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B.M.; Ketova, T.; et al. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of mRNA Vaccines. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- John, S.; Yuzhakov, O.; Woods, A.; Deterling, J.; Hassett, K.; Shaw, C.A.; Ciaramella, G. Multi-antigenic human cytomegalovirus mRNA vaccines that elicit potent humoral and cell-mediated immunity. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberli, M.A.; Reichmuth, A.M.; Dorkin, J.R.; Mitchell, M.J.; Fenton, O.S.; Jaklenec, A.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. Lipid Nanoparticle Assisted mRNA Delivery for Potent Cancer Immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ye, X.; Ni, H.; Zhang, J.; Ju, S.; Ding, W. Transfection Efficiency Evaluation and Endocytosis Exploration of Different Polymer Condensed Agents. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.P.; da Silva Santos, S.; da Silva, J.V.; Parise-Filho, R.; Igne Ferreira, E.; Seoud, O.E.; Giarolla, J. Dendrimers in the context of nanomedicine. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 573, 118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Yue, Y.; Rui, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wu, C. Effect of Chain Length on Cytotoxicity and Endocytosis of Cationic Polymers. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 2050–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, L.A.; Chan, M.; Shaw, C.A.; Hekele, A.; Carsillo, T.; Schaefer, M.; Archer, J.; Seubert, A.; Otten, G.R.; Beard, C.W.; et al. A cationic nanoemulsion for the delivery of next-generation RNA vaccines. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 2118–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaan6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Qin, Z.; Zhou, X.; Xiao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Xia, J. Exosome-mediated delivery of gene vectors for gene therapy. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, T.S.; Lee, A.C.; Akinc, A.; Bramlage, B.; Bumcrot, D.; Fedoruk, M.N.; Harborth, J.; Heyes, J.A.; Jeffs, L.B.; John, M.; et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2006, 441, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinc, A.; Querbes, W.; De, S.; Qin, J.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Jayaprakash, K.N.; Jayaraman, M.; Rajeev, K.G.; Cantley, W.L.; Dorkin, J.R.; et al. Targeted delivery of RNAi therapeutics with endogenous and exogenous ligand-based mechanisms. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hai, L.; Gao, Y.; Yu, G.; Sun, Y. Lipid nanomaterials-based RNA therapy and cancer treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B, 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaridou, E.; Heyes, J.; Lutwyche, P. Lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery: Current perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Tuyishime, S.; Muramatsu, H.; Kariko, K.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Madden, T.D.; Hope, M.J.; Weissman, D. Expression kinetics of nucleoside-modified mRNA delivered in lipid nanoparticles to mice by various routes. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thess, A.; Grund, S.; Mui, B.L.; Hope, M.J.; Baumhof, P.; Fotin-Mleczek, M.; Schlake, T. Sequence-engineered mRNA Without Chemical Nucleoside Modifications Enables an Effective Protein Therapy in Large Animals. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, T.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, M.; Cao, H.; Liang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Liang, X.J.; Weng, Y.; et al. Efficient hepatic delivery and protein expression enabled by optimized mRNA and ionizable lipid nanoparticle. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Ishihara, H. Difference in the lipid nanoparticle technology employed in three approved siRNA (Patisiran) and mRNA (COVID-19 vaccine) drugs. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 41, 100424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, M.N.; Kelly, H.G.; Wheatley, A.K.; Peng, S.; Pilkington, E.H.; Veldhuis, N.A.; Davis, T.P.; Kent, S.J.; Truong, N.P. Cellular Interactions of Liposomes and PISA Nanoparticles during Human Blood Flow in a Microvascular Network. Small 2020, 16, 2002861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa Magar, K.; Boafo, G.F.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; He, W. Liposome-based delivery of biological drugs. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viger-Gravel, J.; Schantz, A.; Pinon, A.C.; Rossini, A.J.; Schantz, S.; Emsley, L. Structure of Lipid Nanoparticles Containing siRNA or mRNA by Dynamic Nuclear Polarization-Enhanced NMR Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2018, 122, 2073–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eygeris, Y.; Patel, S.; Jozic, A.; Sahay, G. Deconvoluting Lipid Nanoparticle Structure for Messenger RNA Delivery. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4543–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Ashwanikumar, N.; Robinson, E.; Xia, Y.; Mihai, C.; Griffith, J.P.; Hou, S.; Esposito, A.A.; Ketova, T.; Welsher, K.; et al. Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M. Lipid nanoparticles: State of the art, new preparation methods and challenges in drug delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talarico, L.; Consumi, M.; Leone, G.; Tamasi, G.; Magnani, A. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Produced via a Coacervation Method as Promising Carriers for Controlled Release of Quercetin. Molecules 2021, 26, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaei, S.R.; Jackman, J.A.; Kim, M.; Yorulmaz, S.; Vafaei, S.; Cho, N.J. Biomembrane Fabrication by the Solvent-assisted Lipid Bilayer (SALB) Method. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 26, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, J.J.; Palmer, L.; Ossanlou, M.; MacLachlan, I.; Graham, R.W.; Zhang, Y.P.; Hope, M.J.; Scherrer, P.; Cullis, P.R. Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles: Construction and characterization. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffs, L.B.; Palmer, L.R.; Ambegia, E.G.; Giesbrecht, C.; Ewanick, S.; MacLachlan, I. A scalable, extrusion-free method for efficient liposomal encapsulation of plasmid DNA. Pharm. Res. 2005, 22, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeki, M.; Uno, S.; Niwa, A.; Okada, Y.; Tokeshi, M. Microfluidic technologies and devices for lipid nanoparticle-based RNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2022, 344, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, E.; Elia, U.; Peer, D. Principles for designing an optimal mRNA lipid nanoparticle vaccine. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2022, 73, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.R.; Muramatsu, H.; Nallagatla, S.R.; Bevilacqua, P.C.; Sansing, L.H.; Weissman, D.; Karikó, K. Incorporation of pseudouridine into mRNA enhances translation by diminishing PKR activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5884–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Naradikian, M.S.; Parkhouse, K.; Cain, D.W.; Jones, L.; Moody, M.A.; Verkerke, H.P.; Myles, A.; Willis, E.; et al. Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines induce potent T follicular helper and germinal center B cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1571–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauger, D.M.; Cabral, B.J.; Presnyak, V.; Su, S.V.; Reid, D.W.; Goodman, B.; Link, K.; Khatwani, N.; Reynders, J.; Moore, M.J.; et al. mRNA structure regulates protein expression through changes in functional half-life. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24075–24083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- CureVac Provides Update on Phase 2b/3 Trial of First-Generation COVID-19 Vaccine Candidate, CVnCoV. Available online: https://www.curevac.com/en/curevac-provides-update-on-phase-2b-3-trial-of-first-generation-COVID-19-vaccine-candidate-cvncov/ (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Bornewasser, L.; Domnick, C.; Kathschorr, S. Stronger together for in-cell translation: Natural and unnatural base modified mRNA. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 4753–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. Lipid Nanoparticle-mRNA Formulations for Therapeutic Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 4283–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, C.; Deng, B.; McComb, D.W.; Du, S.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Dong, Y. Vitamin lipid nanoparticles enable adoptive macrophage transfer for the treatment of multidrug-resistant bacterial sepsis. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Yang, F.; Huang, J.; Zou, L.; Zou, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, F.; et al. Highly efficient healing of critical sized articular cartilage defect in situ using a chemically nucleoside-modified mRNA-enhanced cell therapy. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katibah, G.E.; Qin, Y.; Sidote, D.J.; Yao, J.; Lambowitz, A.M.; Collins, K. Broad and adaptable RNA structure recognition by the human interferon-induced tetratricopeptide repeat protein IFIT5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12025–12030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuberth-Wagner, C.; Ludwig, J.; Bruder, A.K.; Herzner, A.M.; Zillinger, T.; Goldeck, M.; Schmidt, T.; Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Kerber, R.; Wolter, S.; et al. A Conserved Histidine in the RNA Sensor RIG-I Controls Immune Tolerance to N1-2’O-Methylated Self RNA. Immunity 2015, 43, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbas, Y.M.; Laudenbach, B.T.; Martínez-Montero, S.; Cencic, R.; Habjan, M.; Pichlmair, A.; Damha, M.J.; Pelletier, J.; Nagar, B. Structure of human IFIT1 with capped RNA reveals adaptable mRNA binding and mechanisms for sensing N1 and N2 ribose 2’-O methylations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aviv, H.; Voloch, Z.; Bastos, R.; Levy, S. Biosynthesis and stability of globin mRNA in cultured erythroleukemic Friend cells. Cell 1976, 8, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.; Sullivan, T.D. Half-lives of beta and gamma globin messenger RNAs and of protein synthetic capacity in cultured human reticulocytes. Blood 1985, 66, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kranz, L.M.; Diken, M.; Haas, H.; Kreiter, S.; Loquai, C.; Reuter, K.C.; Meng, M.; Fritz, D.; Vascotto, F.; Hefesha, H.; et al. Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy. Nature 2016, 534, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, G.; Coller, J. Codon optimality, bias and usage in translation and mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2018, 19, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, B. The CureVac Vaccine, and a Brief Tour through Some of the Wonders of Nature. 2021. Available online: https://berthub.eu/articles/posts/curevac-vaccine-and-wonders-of-biology (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Trepotec, Z.; Geiger, J.; Plank, C.; Aneja, M.K.; Rudolph, C. Segmented poly(A) tails significantly reduce recombination of plasmid DNA without affecting mRNA translation efficiency or half-life. RNA 2019, 25, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafez, I.M.; Maurer, N.; Cullis, P.R. On the mechanism whereby cationic lipids promote intracellular delivery of polynucleic acids. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tam, Y.Y.C.; Chen, S.; Cullis, P.R. Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2013, 5, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruner, S.M.; Cullis, P.R.; Hope, M.J.; Tilcock, C.P. Lipid polymorphism: The molecular basis of nonbilayer phases. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 1985, 14, 211–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Leung, J.; Chen, S.; Cullis, P.R.; van der Meel, R. Lipid nanoparticle technology for therapeutic gene regulation in the liver. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Li, K.; Hu, B.; Li, C.; Zhang, M.; Hussain, A.; Wang, X.; Cheng, Q.; Yang, F.; Ge, K.; et al. Membrane-destabilizing ionizable lipid empowered imaging-guided siRNA delivery and cancer treatment. Exploration 2021, 1, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.A.; Jayaraman, M.; Matsuda, S.; Liu, J.; Barros, S.; Querbes, W.; Tam, Y.K.; Ansell, S.M.; Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; et al. Biodegradable lipids enabling rapidly eliminated lipid nanoparticles for systemic delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semple, S.C.; Klimuk, S.K.; Harasym, T.O.; Dos Santos, N.; Ansell, S.M.; Wong, K.F.; Maurer, N.; Stark, H.; Cullis, P.R.; Hope, M.J.; et al. Efficient encapsulation of antisense oligonucleotides in lipid vesicles using ionizable aminolipids: Formation of novel small multilamellar vesicle structures. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1510, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Semple, S.C.; Akinc, A.; Chen, J.; Sandhu, A.P.; Mui, B.L.; Cho, C.K.; Sah, D.W.; Stebbing, D.; Crosley, E.J.; Yaworski, E.; et al. Rational design of cationic lipids for siRNA delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, M.; Ansell, S.M.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Butler, D.; Eltepu, L.; Matsuda, S.; Narayanannair, J.K.; et al. Maximizing the potency of siRNA lipid nanoparticles for hepatic gene silencing in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 8529–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinc, A.; Zumbuehl, A.; Goldberg, M.; Leshchiner, E.S.; Busini, V.; Hossain, N.; Bacallado, S.A.; Nguyen, D.N.; Fuller, J.; Alvarez, R.; et al. A combinatorial library of lipid-like materials for delivery of RNAi therapeutics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, S.; Kumarasinghe, E.S.; Salerno, T.; Mihai, C.; Ketova, T.; Senn, J.J.; Lynn, A.; Bulychev, A.; McFadyen, I.; Chan, J.; et al. A Novel Amino Lipid Series for mRNA Delivery: Improved Endosomal Escape and Sustained Pharmacology and Safety in Non-human Primates. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Yang, J.H.; Heartlein, M.W.; DeRosa, F.; Mir, F.F.; Fenton, O.S.; Anderson, D.G. Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for mRNA Delivery in Vivo with Fractional Factorial and Definitive Screening Designs. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7300–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Lee, S.; Zhang, D.; Siegwart, D.J. Lipid-Modified Aminoglycosides for mRNA Delivery to the Liver. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e1901487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Zhang, H.; Butowska, K.; Swingle, K.L.; Alameh, M.G.; Weissman, D.; Mitchell, M.J. An ionizable lipid toolbox for RNA delivery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Li, L.; Huang, Y.; Delcassian, D.; Chahal, J.; Han, J.; Shi, Y.; Sadtler, K.; Gao, W.; Lin, J.; et al. Delivery of mRNA vaccines with heterocyclic lipids increases anti-tumor efficacy by STING-mediated immune cell activation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- INNORNA. INNORNA: Explore Frontier of mRNA Application Based on Platform Technology. 2022. Available online: https://www.innorna.com/media/187.html (accessed on 15 September 2022).
- Xiao, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, M.; He, W. Liposome-based anchoring and core-encapsulation for combinatorial cancer therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4191–4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Yuan, X.; Wang, F.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W. The progress and perspective of strategies to improve tumor penetration of nanomedicines. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Jia, Y.; Farbiak, L.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, S.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, H.; Siegwart, D.J. Dendrimer-Based Lipid Nanoparticles Deliver Therapeutic FAH mRNA to Normalize Liver Function and Extend Survival in a Mouse Model of Hepatorenal Tyrosinemia Type I. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1805308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Witzigmann, D.; Leung, J.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. On the role of helper lipids in lipid nanoparticle formulations of siRNA. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 21733–21739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.B.; Zhang, S.; Kos, P.; Xiong, H.; Zhou, K.; Perelman, S.S.; Zhu, H.; Siegwart, D.J. Non-Viral CRISPR/Cas Gene Editing In Vitro and In Vivo Enabled by Synthetic Nanoparticle Co-Delivery of Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Yu, X.; Johnson, L.T.; Farbiak, L.; Siegwart, D.J. Membrane-destabilizing ionizable phospholipids for organ-selective mRNA delivery and CRISPR-Cas gene editing. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Sinoda, K.; Hatta, I. Effects of cholesterol on the lamellar and the inverted hexagonal phases of dielaidoylphosphatidylethanolamine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1289, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Misra, P.; Tanaka, E.; Zimmer, J.P.; Itty Ipe, B.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Renal clearance of quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braet, F.; Wisse, E.; Bomans, P.; Frederik, P.; Geerts, W.; Koster, A.; Soon, L.; Ringer, S. Contribution of high-resolution correlative imaging techniques in the study of the liver sieve in three-dimensions. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2007, 70, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moghimi, S.M.; Hunter, A.C.; Andresen, T.L. Factors controlling nanoparticle pharmacokinetics: An integrated analysis and perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 481–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belliveau, N.M.; Huft, J.; Lin, P.J.; Chen, S.; Leung, A.K.; Leaver, T.J.; Wild, A.W.; Lee, J.B.; Taylor, R.J.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. Microfluidic Synthesis of Highly Potent Limit-size Lipid Nanoparticles for In Vivo Delivery of siRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Novobrantseva, T.I.; Rosin, N.; Tam, Y.Y.; Hafez, I.M.; Wong, M.K.; Sugo, T.; Ruda, V.M.; Qin, J.; Klebanov, B.; et al. Influence of cationic lipid composition on gene silencing properties of lipid nanoparticle formulations of siRNA in antigen-presenting cells. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 2186–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Lin, P.J.C.; Sung, M.M.H.; Tam, Y.K.; Cullis, P.R. Influence of particle size on the in vivo potency of lipid nanoparticle formulations of siRNA. J. Control. Release 2016, 235, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez Arteta, M.; Kjellman, T.; Bartesaghi, S.; Wallin, S.; Wu, X.; Kvist, A.J.; Dabkowska, A.; Székely, N.; Radulescu, A.; Bergenholtz, J.; et al. Successful reprogramming of cellular protein production through mRNA delivered by functionalized lipid nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3351–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassett, K.J.; Higgins, J.; Woods, A.; Levy, B.; Xia, Y.; Hsiao, C.J.; Acosta, E.; Almarsson, Ö.; Moore, M.J.; Brito, L.A. Impact of lipid nanoparticle size on mRNA vaccine immunogenicity. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedmi, R.; Veiga, N.; Ramishetti, S.; Goldsmith, M.; Rosenblum, D.; Dammes, N.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Nahary, L.; Leviatan-Ben-Arye, S.; Harlev, M.; et al. A modular platform for targeted RNAi therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Qi, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, N.; Nan, F.; Zhang, H.; Tian, M.; Li, C.; Lu, H.; Jin, N. mRNA Vaccines Encoding the HA Protein of Influenza a H1N1 Virus Delivered by Cationic Lipid Nanoparticles Induce Protective Immune Responses in Mice. Vaccines 2020, 8, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurik, J.G.; Tombácz, I.; Yadegari, A.; Méndez Fernández, P.O.; Shewale, S.V.; Li, L.; Kimura, T.; Soliman, O.Y.; Papp, T.E.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. CAR T cells produced in vivo to treat cardiac injury. Science 2022, 375, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dammes, N.; Goldsmith, M.; Ramishetti, S.; Dearling, J.L.J.; Veiga, N.; Packard, A.B.; Peer, D. Conformation-sensitive targeting of lipid nanoparticles for RNA therapeutics. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-Contreras, O.A.; Greineder, C.F.; Kiseleva, R.Y.; Parhiz, H.; Walsh, L.R.; Zuluaga-Ramirez, V.; Myerson, J.W.; Hood, E.D.; Villa, C.H.; Tombacz, I.; et al. Selective targeting of nanomedicine to inflamed cerebral vasculature to enhance the blood-brain barrier. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3405–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhiz, H.; Shuvaev, V.V.; Pardi, N.; Khoshnejad, M.; Kiseleva, R.Y.; Brenner, J.S.; Uhler, T.; Tuyishime, S.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. PECAM-1 directed re-targeting of exogenous mRNA providing two orders of magnitude enhancement of vascular delivery and expression in lungs independent of apolipoprotein E-mediated uptake. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.Y.; Zhao, Q.H.; Dahotre, S.N.; Gamboa, L.; Bawage, S.S.; Silva Trenkle, A.D.; Zamat, A.; Phuengkham, H.; Ahmed, R.; Santangelo, P.J.; et al. In vivo mRNA delivery to virus-specific T cells by light-induced ligand exchange of MHC class I antigen-presenting nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm7950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sago, C.D.; Lokugamage, M.P.; Paunovska, K.; Vanover, D.A.; Monaco, C.M.; Shah, N.N.; Gamboa Castro, M.; Anderson, S.E.; Rudoltz, T.G.; Lando, G.N.; et al. High-throughput in vivo screen of functional mRNA delivery identifies nanoparticles for endothelial cell gene editing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 9944–9952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Farbiak, L.; Johnson, L.T.; Dilliard, S.A.; Siegwart, D.J. Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR-Cas gene editing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilliard, S.A.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D.J. On the mechanism of tissue-specific mRNA delivery by selective organ targeting nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, 2109256118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, O.S.; Kauffman, K.J.; Kaczmarek, J.C.; McClellan, R.L.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Tibbitt, M.W.; Zeng, M.D.; Appel, E.A.; Dorkin, J.R.; Mir, F.F.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Ionizable Lipid Materials for the In Vivo Delivery of Messenger RNA to B Lymphocytes. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Qiu, M.; Li, Y.; Glass, Z.; Xu, Q. Imidazole-Based Synthetic Lipidoids for In Vivo mRNA Delivery into Primary T Lymphocytes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 20083–20089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Muriph, R.; Ye, Z.; Huang, C.; Evans, J.; Henske, E.P.; Xu, Q. Lung-selective mRNA delivery of synthetic lipid nanoparticles for the treatment of pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, 2116271119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Lokugamage, M.P.; Hatit, M.Z.C.; Loughrey, D.; Paunovska, K.; Sato, M.; Cristian, A.; Dahlman, J.E. Nanoparticles containing constrained phospholipids deliver mRNA to liver immune cells in vivo without targeting ligands. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2020, 5, e10161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.; Jeong, M.; Hur, S.; Cho, Y.; Park, J.; Jung, H.; Seo, Y.; Woo, H.A.; Nam, K.T.; Lee, K.; et al. Engineered ionizable lipid nanoparticles for targeted delivery of RNA therapeutics into different types of cells in the liver. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerji, A.; Wickner, P.G.; Saff, R.; Stone, C.A., Jr.; Robinson, L.B.; Long, A.A.; Wolfson, A.R.; Williams, P.; Khan, D.A.; Phillips, E.; et al. mRNA Vaccines to Prevent COVID-19 Disease and Reported Allergic Reactions: Current Evidence and Suggested Approach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, G.; Kaliamurthi, S.; Peslherbe, G.H.; Wei, D.Q. Are the Allergic Reactions of COVID-19 Vaccines Caused by mRNA Constructs or Nanocarriers? Immunological Insights. Interdiscip. Sci. 2021, 13, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalberse, R.C. Structural biology of allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, K.J.; Mir, F.F.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Kaczmarek, J.C.; Hurtado, J.E.; Yang, J.H.; Webber, M.J.; Kowalski, P.S.; Heartlein, M.W.; DeRosa, F.; et al. Efficacy and immunogenicity of unmodified and pseudouridine-modified mRNA delivered systemically with lipid nanoparticles in vivo. Biomaterials 2016, 109, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halamoda-Kenzaoui, B.; Bremer-Hoffmann, S. Main trends of immune effects triggered by nanomedicines in preclinical studies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5419–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrams, M.T.; Koser, M.L.; Seitzer, J.; Williams, S.C.; DiPietro, M.A.; Wang, W.; Shaw, A.W.; Mao, X.; Jadhav, V.; Davide, J.P.; et al. Evaluation of efficacy, biodistribution, and inflammation for a potent siRNA nanoparticle: Effect of dexamethasone co-treatment. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahtinen, S.; Tong, A.J.; Himmels, P.; Oh, J.; Paler-Martinez, A.; Kim, L.; Wichner, S.; Oei, Y.; McCarron, M.J.; Freund, E.C.; et al. IL-1 and IL-1ra are key regulators of the inflammatory response to RNA vaccines. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedic, M.; Senn, J.J.; Lynn, A.; Laska, M.; Smith, M.; Platz, S.J.; Bolen, J.; Hoge, S.; Bulychev, A.; Jacquinet, E.; et al. Safety Evaluation of Lipid Nanoparticle-Formulated Modified mRNA in the Sprague-Dawley Rat and Cynomolgus Monkey. Vet. Pathol. 2018, 55, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szebeni, J. Complement activation-related pseudoallergy: A stress reaction in blood triggered by nanomedicines and biologicals. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 61, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zaifman, J.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Zhigaltsev, I.V.; Tam, Y.K.; Ciufolini, M.A.; Tam, Y.Y.C.; Cullis, P.R. Dexamethasone prodrugs as potent suppressors of the immunostimulatory effects of lipid nanoparticle formulations of nucleic acids. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Mao, X.; Davide, J.P.; Ng, B.; Cai, M.; Burke, P.A.; Sachs, A.B.; Sepp-Lorenzino, L. Mechanistically probing lipid-siRNA nanoparticle-associated toxicities identifies Jak inhibitors effective in mitigating multifaceted toxic responses. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semple, S.C.; Harasym, T.O.; Clow, K.A.; Ansell, S.M.; Klimuk, S.K.; Hope, M.J. Immunogenicity and rapid blood clearance of liposomes containing polyethylene glycol-lipid conjugates and nucleic Acid. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambegia, E.; Ansell, S.; Cullis, P.; Heyes, J.; Palmer, L.; MacLachlan, I. Stabilized plasmid-lipid particles containing PEG-diacylglycerols exhibit extended circulation lifetimes and tumor selective gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1669, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Allison, S.J.; Milner, J. RNA Interference by Single- and Double-stranded siRNA With a DNA Extension Containing a 3’ Nuclease-resistant Mini-hairpin Structure. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 2, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nogueira, S.S.; Schlegel, A.; Maxeiner, K.; Weber, B.; Barz, M.; Schroer, M.A.; Blanchet, C.E.; Svergun, D.I.; Ramishetti, S.; Peer, D.; et al. Polysarcosine-Functionalized Lipid Nanoparticles for Therapeutic mRNA Delivery. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 10634–10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoff, R.N.; Calina, D.; Kanduc, D.; Briggs, M.B.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.; Svistunov, A.A.; Tsatsakis, A. RETRACTED: Why are we vaccinating children against COVID-19? Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1665–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Marioli, M.; Zhang, K. Analytical characterization of liposomes and other lipid nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, J.; Sorensen, K.; Wolff, S.P. Peroxide accumulation in detergents. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1994, 29, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ball, R.L.; Bajaj, P.; Whitehead, K.A. Achieving long-term stability of lipid nanoparticles: Examining the effect of pH, temperature, and lyophilization. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 12, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascolo, S. Vaccination with messenger RNA (mRNA). In Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and Innate Immunity; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 221–235. [Google Scholar]
- Wayment-Steele, H.K.; Kim, D.S.; Choe, C.A.; Nicol, J.J.; Wellington-Oguri, R.; Watkins, A.M.; Parra Sperberg, R.A.; Huang, P.S.; Participants, E.; Das, R. Theoretical basis for stabilizing messenger RNA through secondary structure design. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10604–10617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Ludwig, J.; Weissman, D. Generating the optimal mRNA for therapy: HPLC purification eliminates immune activation and improves translation of nucleoside-modified, protein-encoding mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baiersdörfer, M.; Boros, G.; Muramatsu, H.; Mahiny, A.; Vlatkovic, I.; Sahin, U.; Karikó, K. A Facile Method for the Removal of dsRNA Contaminant from In Vitro-Transcribed mRNA. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, P.; Hou, X.; Yan, J.; Du, S.; Xue, Y.; Li, W.; Xiang, G.; Dong, Y. Long-term storage of lipid-like nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayesh, K.; Austin, H.; Pieter, C.; Blair, L.; Terri, P.; Pamela, W. Compositions and Systems Comprising Transfection-Competent Vesicles Free of Organic-Solvents and Detergents and Methods Related Thereto. U.S. Patent 2022/0118112 A1, 21 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Yao, W.; Han, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, W.; Xu, P.; et al. Lyophilized mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccines with long-term stability and high antigenicity against SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Leal, J.; Soto, M.R.; Smyth, H.D.C.; Ghosh, D. Aerosolizable Lipid Nanoparticles for Pulmonary Delivery of mRNA through Design of Experiments. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokugamage, M.P.; Vanover, D.; Beyersdorf, J.; Hatit, M.Z.C.; Rotolo, L.; Echeverri, E.S.; Peck, H.E.; Ni, H.; Yoon, J.K.; Kim, Y.; et al. Optimization of lipid nanoparticles for the delivery of nebulized therapeutic mRNA to the lungs. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jozic, A.; Sahay, G. Naturally Derived Membrane Lipids Impact Nanoparticle-Based Messenger RNA Delivery. Cell. Mol. Bioeng. 2020, 13, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimaraes, P.P.G.; Zhang, R.; Spektor, R.; Tan, M.; Chung, A.; Billingsley, M.M.; El-Mayta, R.; Riley, R.S.; Wang, L.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. Ionizable lipid nanoparticles encapsulating barcoded mRNA for accelerated in vivo delivery screening. J. Control. Release 2019, 316, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiba, A.; Toyooka, M.; Sato, Y.; Maeki, M.; Tokeshi, M.; Harashima, H. The use of design of experiments with multiple responses to determine optimal formulations for in vivo hepatic mRNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; Jiang, Y.; Duncan, R.G.; Brigham, B.; Fishman, S.; Nair, J.K.; Akinc, A.; Barros, S.A.; Kasperkovitz, P.V. Shielding of Lipid Nanoparticles for siRNA Delivery: Impact on Physicochemical Properties, Cytokine Induction, and Efficacy. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadati, R.; Dadashzadeh, S.; Abbasian, Z.; Soleimanjahi, H. Accelerated blood clearance of PEGylated PLGA nanoparticles following repeated injections: Effects of polymer dose, PEG coating, and encapsulated anticancer drug. Pharm. Res. 2013, 30, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zukancic, D.; Suys, E.J.A.; Pilkington, E.H.; Algarni, A.; Al-Wassiti, H.; Truong, N.P. The Importance of Poly(ethylene glycol) and Lipid Structure in Targeted Gene Delivery to Lymph Nodes by Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo-Rodríguez, A.; Solinís, M.; Rodríguez-Gascón, A. Applications of lipid nanoparticles in gene therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2016, 109, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espeseth, A.S.; Cejas, P.J.; Citron, M.P.; Wang, D.; DiStefano, D.J.; Callahan, C.; Donnell, G.O.; Galli, J.D.; Swoyer, R.; Touch, S.; et al. Modified mRNA/lipid nanoparticle-based vaccines expressing respiratory syncytial virus F protein variants are immunogenic and protective in rodent models of RSV infection. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aldrich, C.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Huang, K.B.; Bica, M.A.; Loeliger, E.; Schoenborn-Kellenberger, O.; Walz, L.; Leroux-Roels, G.; von Sonnenburg, F.; Oostvogels, L. Proof-of-concept of a low-dose unmodified mRNA-based rabies vaccine formulated with lipid nanoparticles in human volunteers: A phase 1 trial. Vaccine 2021, 39, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Sonwane, A.A.; Dahiya, S.S.; Patel, C.L.; Saini, M.; Rai, A.; Gupta, P.K. Induction of immune responses and protection in mice against rabies using a self-replicating RNA vaccine encoding rabies virus glycoprotein. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanBlargan, L.A.; Himansu, S.; Foreman, B.M.; Ebel, G.D.; Pierson, T.C.; Diamond, M.S. An mRNA Vaccine Protects Mice against Multiple Tick-Transmitted Flavivirus Infections. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3382–3392.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizvi, F.; Everton, E.; Smith, A.R.; Liu, H.; Osota, E.; Beattie, M.; Tam, Y.; Pardi, N.; Weissman, D.; Gouon-Evans, V. Murine liver repair via transient activation of regenerative pathways in hepatocytes using lipid nanoparticle-complexed nucleoside-modified mRNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwitz, C.; Kranz, L.M. mRNA Cancer Vaccines-Messages that Prevail. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 405, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Billingsley, M.M.; Mitchell, M.J. Biomaterials for vaccine-based cancer immunotherapy. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, S.Y.; Seo, Y.; Kim, M.H.; Chang, J.; Lee, H. Adjuvant incorporated lipid nanoparticles for enhanced mRNA-mediated cancer immunotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, X.; Ruan, Z.; Pu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Matsui, A.; Zhu, L.; Amoozgar, Z.; et al. Combining p53 mRNA nanotherapy with immune checkpoint blockade reprograms the immune microenvironment for effective cancer therapy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; Hou, X.; Du, S.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, W.; Deng, B.; McComb, D.W.; et al. Biomimetic nanoparticles deliver mRNAs encoding costimulatory receptors and enhance T cell mediated cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billingsley, M.M.; Singh, N.; Ravikumar, P.; Zhang, R.; June, C.H.; Mitchell, M.J. Ionizable Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated mRNA Delivery for Human CAR T Cell Engineering. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newick, K.; O’Brien, S.; Moon, E.; Albelda, S.M. CAR T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haanen, J.B. CT002—BNT211: A Phase I trial to evaluate safety and efficacy of CLDN6 CAR-T cells and CARVac-mediated in vivo expansion in patients with CLDN6-positive advanced solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2022, 82 (Suppl. 12), CT002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V. CAR T-Cell Therapy Plus Amplifying Vaccine Shows Initial Safety, Efficacy in Solid Tumors. 12 November 2021. Available online: https://www.cgtlive.com/view/car-t-cell-therapy-plus-amplifying-vaccine-safety-efficacy-solid-tumors (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Auricchio, A.; Smith, A.J.; Ali, R.R. The Future Looks Brighter After 25 Years of Retinal Gene Therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voretigene neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in patients with RPE65-mediated inherited retinal dystrophy: A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.W.; Grompe, M. Adeno-associated virus finds its disease. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.; Ryals, R.C.; Weller, K.K.; Pennesi, M.E.; Sahay, G. Lipid nanoparticles for delivery of messenger RNA to the back of the eye. J. Control. Release 2019, 303, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Liu, S.; Wei, T.; Cheng, Q.; Siegwart, D.J. Theranostic dendrimer-based lipid nanoparticles containing PEGylated BODIPY dyes for tumor imaging and systemic mRNA delivery in vivo. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.; Szoka, F.C. Nucleic acid delivery: The missing pieces of the puzzle? Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilleron, J.; Querbes, W.; Zeigerer, A.; Borodovsky, A.; Marsico, G.; Schubert, U.; Manygoats, K.; Seifert, S.; Andree, C.; Stöter, M.; et al. Image-based analysis of lipid nanoparticle-mediated siRNA delivery, intracellular trafficking and endosomal escape. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Kim, J.; Herrera, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Kabanov, A.V.; Sahay, G. Brief update on endocytosis of nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 144, 90–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Let’s Talk about Lipid Nanoparticles. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 99. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41578-021-00281-4 (accessed on 5 October 2022). [CrossRef]





| Technology Path | Vaccine Name | Companies | First Posted | Clinical Trial Number | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA vaccines | Comirnaty BNT162B2 | Pfizer (New York, NY, USA)/BioNTech SE (Mainz, Germany) | Approved. Emergency use authorization in several countries around the world | ||
| Spikevax mRNA-1273 | ModernaTX, Inc. (Cambridge, MA, USA) | ||||
| mRNA-1273.351 | ModernaTX, Inc. (Cambridge, MA, USA) | 28 May 2020 | NCT04405076 | Phase II | |
| SYS6006 | CSPC ZhongQi Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shijiazhuang, China) | 30 June 2022 | NCT05439824 | Phase II | |
| CanSino Biologics Inc. (Tianjin, China) | 13 May 2022 | NCT05373472 | Phase II | ||
| ABO1009-DP | Suzhou Abogen Biosciences Co., Ltd. (Suzhou, China) | 28 June 2022 | NCT05434585 | Phase I | |
| ABO-CoV.617.2 | |||||
| LVRNA009 | AIM Vaccine Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) | 6 May 2022 | NCT05364047 | Phase I | |
| RQ3013 | Walvax Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Kunming, China) | 31 May 2022 | NCT05396573 | Phase I | |
| PTX-COVID19-B | Providence Therapeutics Holdings Inc. (Toronto, ON, Canada) | 21 February 2021 | NCT04765436 | Phase I | |
| CV0501 | GlaxoSmithKline (Brentford, England) | 28 July 2022 | NCT05477186 | Phase I | |
| Lyophilized mRNA vaccine | RH109 | Wuhan Recogen Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China) | 9 May 2022 | NCT05366296 | Phase I |
| Viral Vectors | Non-Viral Vectors | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | High transfection efficiency | Low toxicity, low immune response, low chance of exogenous gene integration, no size limitation of gene insert, easy to use, easy to prepare, easy to store and test, high safety, high potential, low cost, simple preparation and modifiability |
| Disadvantages | Potentially carcinogenic, autoimmunogenicity, cytopathic changes, small genetic capacity, toxic side effects, high preparation costs | Low transfection efficiency |
| Name | Cost | Scalability | Encapsulation Efficiency | Reproducibility | Polydispersity Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol dilution method | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | High |
| Manual mixing method | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| T-mix method | Low | High | High | High | Moderate |
| Microfluidics | High | High | High | High | Low |
| Institution | Name | Indication | mRNA Encoding | Route of Administration | Delivery Vector | Clinical Trial Number (Phase) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ModernaTX, Inc. | mRNA-1647 | Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infection | Human cytomegalovirus envelope glycoprotein H | i.m. | LNP V1GL | NCT03382405 (I) NCT04232280 (II) |
| mRNA-1443 | LNP | NCT03382405 (I) | ||||
| mRNA-1653 | Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) and human parainfluenza 3 virus (PIV3) | hMPV and PIV3 membrane fusion protein | i.m. | LNP | NCT03392389 (I) NCT04144348 (I) | |
| VAL-506440; mRNA-1440 | Influenza A virus (H10N8) | Influenza hemagglutinin H10N8 | i.m. | LNP | NCT03076385 (I) | |
| VAL-339851; mRNA-1851 | Influenza A virus (H7N9) | Influenza hemagglutinin H7N9 | i.m. | LNP | NCT03345043 (I) | |
| mRNA-1345 | Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) | RSV pre-infused F protein | i.m. | LNP | NCT04528719 (I) | |
| VAL-181388; mRNA-1388; | Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) | Anti-CHKV monoclonal antibody | i.m. | LNP | NCT03325075 (I) | |
| mRNA-1944 | Prevention of CHIKV infection | CHIKV-specific monoclonal neutralizing antibody (CHKV-24) | i.m. | LNP | NCT03829384 (I) | |
| mRNA-1325; | Zika virus | PrM and E | i.m. | LNP | NCT03014089 (I) | |
| mRNA-1893 | i.m. | LNP V1GL | NCT04064905 (I) | |||
| mRNA-2752 | Solid tumor malignancies or lymphoma/ovarian cancer | Human OX40L, IL-23, and IL-36γ | Intratumoral injection | LNP | NCT03739931 (1) | |
| mRNA-2416 | Human OX40L | Intratumoral injection | LNP | NCT03323398 (I/II) | ||
| mRNA-4157 | Melanoma | Personalized | i.m. | LNP | NCT03897881 (II) | |
| Solid tumors | Personalized | i.m. | LNP | NCT03313778 (I) | ||
| BioNTech SE | Lipo-MERIT | Melanoma | Four selected malignant melanoma-associated antigens: New York-ESO 1 (NY-ESO-1), tyrosinase, melanoma-associated antigen A3 (MAGE-A3), and trans-membrane phosphatase with tensin homology (TPTE) | i.m. | Lipoplex | NCT02410733 (I) |
| CureVac | CV7202 | Rabies | Rabies virus glycoprotein (RABV-G) | i.m. | LNP | NCT03713086 (I) |
| GlaxoSmithKline | RG-SAM (CNE) vaccine (GSK3903133A) | Viral diseases | Rabies glycoprotein G (RG) | i.m. | CNE | NCT04062669 (I) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, L.; Gong, L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, W. Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122682
Yang L, Gong L, Wang P, Zhao X, Zhao F, Zhang Z, Li Y, Huang W. Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122682
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Lei, Liming Gong, Ping Wang, Xinghui Zhao, Feng Zhao, Zhijie Zhang, Yunfei Li, and Wei Huang. 2022. "Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of mRNA" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122682
APA StyleYang, L., Gong, L., Wang, P., Zhao, X., Zhao, F., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., & Huang, W. (2022). Recent Advances in Lipid Nanoparticles for Delivery of mRNA. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2682. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122682






