The Association of Biochemical and Genetic Biomarkers in VEGF Pathway with Depression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Assessments
2.2. Laboratory Measurements
2.2.1. Genotyping
2.2.2. Protein Measurement
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
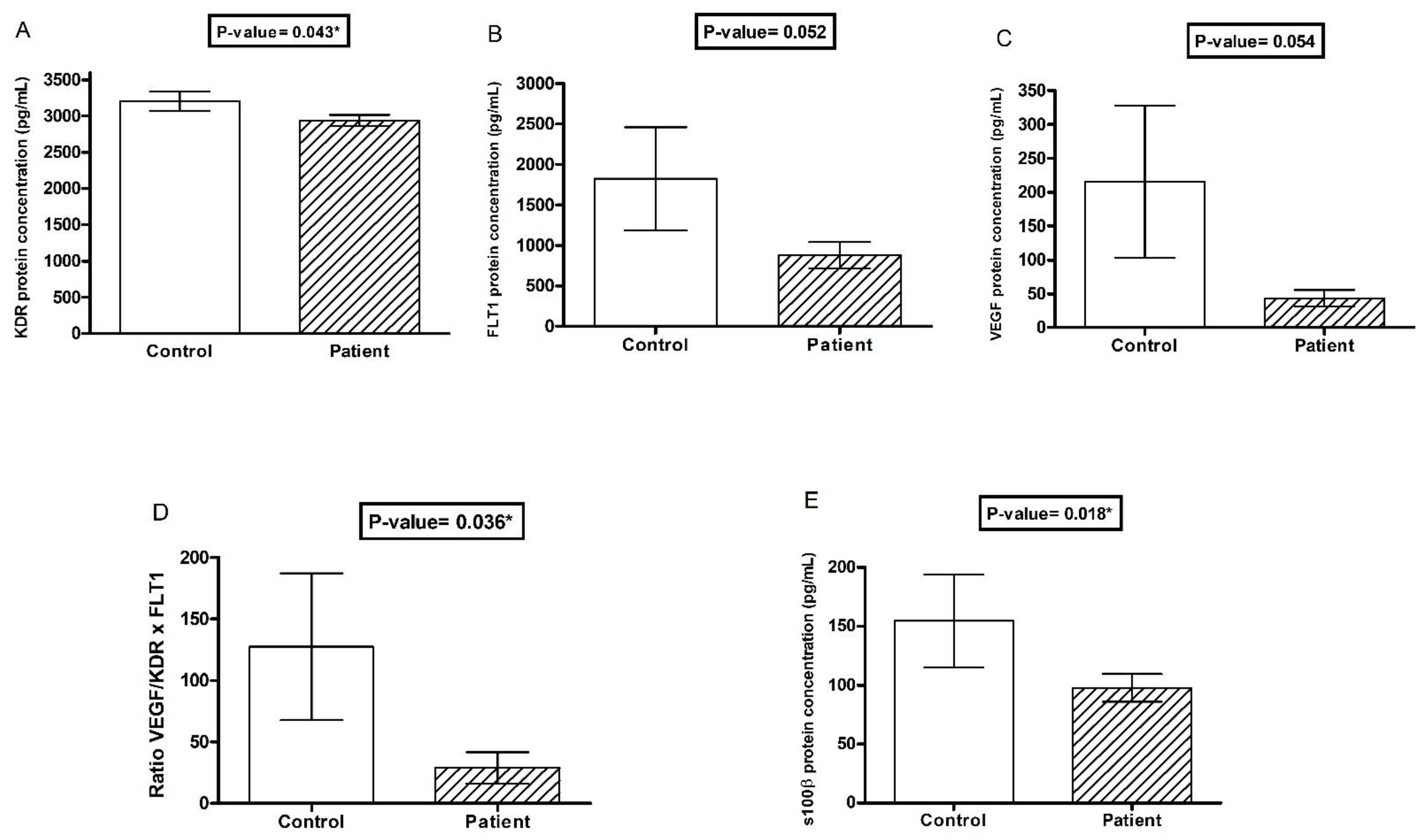
3.2. Association of VEGF Markers with Depression
3.3. Correlations between VEGF and Its Inhibitors, VEGF and S100β, in the Depressive Group
3.4. VEGF and S100β with GRID-HAM21, BSI, and Number of Suicide Attempts in the Depressive Group
3.5. Case–Control Genetic Study
3.6. No Association between Number of Suicide Attempts and Genetic Polymorphisms in the Depressive Group
3.7. Rs699947 Contributes to Variations in Plasma VEGF Concentrations in Patients
3.8. Association of FLT1 rs7993418 Polymorphism with Symptom Intensity in Depressives
3.9. Case-Control Study of Haplotypes: KDR and VEGF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.; Vos, T.; Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Flaxman, A.D.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2197–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnett, R. Depression. Lancet 2019, 393, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leading Causes of Death Reports. 2016. Available online: https://wisqars.cdc.gov/fatal-leading (accessed on 22 March 2022).
- Xie, T.; Stathopoulou, M.G.; de Andrés, F.; Siest, G.; Murray, H.; Martin, M.; Cobaleda, J.; Delgado, A.; Lamont, J.; Peñas-LIedó, E.; et al. VEGF-related polymorphisms identified by GWAS and risk for major depression. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karege, F.; Perret, G.; Bondolfi, G.; Schwald, M.; Bertschy, G.; Aubry, J.M. Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in major depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 2002, 109, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeben, A.; Landuyt, B.; Highley, M.S.; Wildiers, H.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; De Bruijn, E.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 549–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitsillou, E.; Bresnehan, S.M.; Kagarakis, E.A.; Wijoyo, S.J.; Liang, J.; Hung, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. The cellular and molecular basis of major depressive disorder: Towards a unified model for understanding clinical depression. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Jiao, X.; Zuzga, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Fong, D.M.; Young, D.; During, M.J. VEGF links hippocampal activity with neurogenesis, learning and memory. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Mao, X.O.; Xie, L.; Greenberg, D.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) stimulates neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11946–11950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mackenzie, F.; Ruhrberg, C. Diverse roles for VEGF-A in the nervous system. Development 2012, 139, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Storkebaum, E.; Lambrechts, D.; Carmeliet, P. VEGF: Once regarded as a specific angiogenic factor, now implicated in neuroprotection. Bioessays 2004, 26, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, D.A.; Jin, K. Experiencing VEGF. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 792–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, D.R.; Rapaport, M.H.; Miller, B.J. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients: Comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol. Psychiatry 2016, 21, 1696–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Suchankova, P.; Ekman, A.; Erhardt, S.; Sellgren, C.; Samuelsson, M.; Westrin, A.; Minthon, L.; Hansson, O.; Träskman-Bendz, L.; et al. Low IL-8 is associated with anxiety in suicidal patients: Genetic variation and decreased protein levels. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2015, 131, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janelidze, S.; Ventorp, F.; Erhardt, S.; Hansson, O.; Minthon, L.; Flax, J.; Samuelsson, M.; Traskman-Bendz, L.; Brundin, L. Altered chemokine levels in the cerebrospinal fluid and plasma of suicide attempters. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.D.; Shelton, R.C.; Duman, R.S. Functional biomarkers of depression: Diagnosis, treatment, and pathophysiology. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 2375–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jonsdottir, I.H.; Hägg, D.A.; Glise, K.; Ekman, R. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) and growth factors called into question as markers of prolonged psychosocial stress. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juengst, S.B.; Kumar, R.G.; Failla, M.D.; Goyal, A.; Wagner, A.K. Acute inflammatory biomarker profiles predict depression risk following moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2015, 30, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahl, K.G.; Bens, S.; Ziegler, K.; Rudolf, S.; Kordon, A.; Dibbelt, L.; Schweiger, U. Angiogenic factors in patients with current major depressive disorder comorbid with borderline personality disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Hussain, B.; Chang, J. Peripheral inflammation and blood-brain barrier disruption: Effects and mechanisms. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, H.J.; Fischer, S.; Marti, H.H. Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression causes vascular leakage in the brain. Brain A J. Neurol. 2002, 125, 2549–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, A.T.; Gurfein, B.T.; Zhang, Y.; Zameer, A.; John, G.R. VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1977–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engelhardt, S.; Patkar, S.; Ogunshola, O.O. Cell-specific blood-brain barrier regulation in health and disease: A focus on hypoxia. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1210–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Davies, K.; Powers, C.; Bruggen, N.; Chopp, M. VEGF enhances angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in the ischemic brain. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Donato, R.; Sorci, G.; Riuzzi, F.; Arcuri, C.; Bianchi, R.; Brozzi, F.; Tubaro, C.; Giambanco, I. S100B’s double life: Intracellular regulator and extracellular signal. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1793, 1008–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroeter, M.L.; Abdul-Khaliq, H.; Krebs, M.; Diefenbacher, A.; Blasig, I.E. Serum markers support disease-specific glial pathology in major depression. J. Affect Disord. 2008, 111, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanner, A.A.; Marchi, N.; Fazio, V.; Mayberg, M.R.; Koltz, M.T.; Siomin, V.; Stevens, G.H.; Masaryk, T.; Aumayr, B.; Ayumar, B.; et al. Serum S100beta: A noninvasive marker of blood-brain barrier function and brain lesions. Cancer 2003, 97, 2806–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iga, J.; Ueno, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Numata, S.; Tayoshi-Shibuya, S.; Kinouchi, S.; Nakataki, M.; Song, H.; Hokoishi, K.; Tanabe, H.; et al. Gene expression and association analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor in major depressive disorder. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 31, 658–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventriglia, M.; Zanardini, R.; Pedrini, L.; Placentino, A.; Nielsen, M.G.; Gennarelli, M.; Bocchio-Chiavetto, L. VEGF serum levels in depressed patients during SSRI antidepressant treatment. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APA, A.P.A. Manual Diagnóstico e Estatístico de Transtornos Mentais: DSM-5, 5th ed.; Artmed: Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2014; Volume 5, p. 948. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, D.V.; Lecrubier, Y.; Sheehan, K.H.; Amorim, P.; Janavs, J.; Weiller, E.; Hergueta, T.; Baker, R.; Dunbar, G.C. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): The development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59 (Suppl. S20), 22–33, quiz 34–57. [Google Scholar]
- Amorim, P. Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI): Validation of a short structured diagnostic psychiatric interview. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2000, 22, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henrique-Araújo, R.; Osório, F.L.; Gonçalves Ribeiro, M.; Soares Monteiro, I.; Williams, J.B.; Kalali, A.; Alexandre Crippa, J.; Oliveira, I.R. Transcultural Adaptation of GRID Hamilton Rating Scale For Depression (GRID-HAMD) to Brazilian Portuguese and Evaluation of the Impact of Training Upon Inter-Rater Reliability. Innov. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 11, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, D.P.; Fink, L.; Handelsman, L.; Foote, J.; Lovejoy, M.; Wenzel, K.; Sapareto, E.; Ruggiero, J. Initial reliability and validity of a new retrospective measure of child abuse and neglect. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 1132–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, D.P.; Stein, J.A.; Newcomb, M.D.; Walker, E.; Pogge, D.; Ahluvalia, T.; Stokes, J.; Handelsman, L.; Medrano, M.; Desmond, D.; et al. Development and validation of a brief screening version of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire. Child Abuse Negl. 2003, 27, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi-Oliveira, R.; Stein, L.M.; Pezzi, J.C. Translation and content validation of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire into Portuguese language. Rev. Saude Publica 2006, 40, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasconcellos, V.; Lacchini, R.; Jacob-Ferreira, A.; Sales, M.; Ferreira-Sae, M.; Schreiber, R.; Nadruz, W.; Tanus-Santos, J. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase haplotypes associated with hypertension do not predispose to cardiac hypertrophy. DNA Cell Biol. 2010, 29, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; He, H.; Yang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, F.; Lyu, J. Changes in the global burden of depression from 1990 to 2017: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 126, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.D.; Huang, X.; Fox, K.R.; Franklin, J.C. Depression and hopelessness as risk factors for suicide ideation, attempts and death: Meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 212, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update; World Health Organization (WHO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz de Almodovar, C.; Lambrechts, D.; Mazzone, M.; Carmeliet, P. Role and therapeutic potential of VEGF in the nervous system. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 607–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacQueen, G.; Santaguida, P.; Keshavarz, H.; Jaworska, N.; Levine, M.; Beyene, J.; Raina, P. Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Failed Antidepressant Treatment Response in Major Depressive Disorder, Dysthymia, and Subthreshold Depression in Adults. Can. J. Psychiatry 2017, 62, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, C.; Zonca, V.; Riva, M.A.; Cattaneo, A. Blood biomarkers and treatment response in major depression. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 18, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Toups, M.; Nemeroff, C.B. The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron 2020, 107, 234–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Z.; Lan, T.; Li, Y.; Bai, M.; Liu, J.; et al. Major depression accompanied with inflammation and multiple cytokines alterations: Evidences from clinical patients to macaca fascicularis and LPS-induced depressive mice model. J. Affect Disord. 2020, 271, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevo, O.; Lee, D.K.; Caniggia, I. Attenuation of VEGFR-2 expression by sFlt-1 and low oxygen in human placenta. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, B.H.; Hong, J.P.; Hwang, J.A.; Ham, B.J.; Na, K.S.; Kim, W.J.; Trigo, J.; Kim, Y.K. Alterations in plasma vascular endothelial growth factor levels in patients with schizophrenia before and after treatment. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 228, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Ameele, S.; Coppens, V.; Schuermans, J.; De Boer, P.; Timmers, M.; Fransen, E.; Sabbe, B.; Morrens, M. Neurotrophic and inflammatory markers in bipolar disorder: A prospective study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 84, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.J.F.; Boulle, F.; Steinbusch, H.W.; van den Hove, D.L.A.; Kenis, G.; Lanfumey, L. Neurotrophic factors and neuroplasticity pathways in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 2195–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Picker, L.J.; Morrens, M.; Chance, S.A.; Boche, D. Microglia and Brain Plasticity in Acute Psychosis and Schizophrenia Illness Course: A Meta-Review. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machado-Vieira, R.; Soeiro-De-Souza, M.G.; Richards, E.M.; Teixeira, A.L.; Zarate, C.A. Multiple levels of impaired neural plasticity and cellular resilience in bipolar disorder: Developing treatments using an integrated translational approach. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 15, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monday, H.R.; Younts, T.J.; Castillo, P.E. Long-Term Plasticity of Neurotransmitter Release: Emerging Mechanisms and Contributions to Brain Function and Disease. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 41, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagihara, H.; Takao, K.; Walton, N.M.; Matsumoto, M.; Miyakawa, T. Immature dentate gyrus: An endophenotype of neuropsychiatric disorders. Neural Plast. 2013, 2013, 318596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyama, S.; Bang, E.; Kato, T.; Li, X.Y.; Duman, R.S. Neurotrophic and Antidepressant Actions of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Require Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 86, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, G.C.; Greenstein, D.; Kadriu, B.; Yuan, P.; Park, L.T.; Gould, T.D.; Zarate, C.A. Treatment of depression with ketamine does not change plasma levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor or vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 280, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjörs Dahlman, A.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Glise, K.; Jonsdottir, I.H. Growth factors and neurotrophins in patients with stress-related exhaustion disorder. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 109, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidese, S.; Hattori, K.; Sasayama, D.; Tsumagari, T.; Miyakawa, T.; Matsumura, R.; Yokota, Y.; Ishida, I.; Matsuo, J.; Yoshida, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid neuroplasticity-associated protein levels in patients with psychiatric disorders: A multiplex immunoassay study. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoporis, J.N.; Izhar, S.; Proteau, G.; Slaughter, G.; Parker, T.G. S100B-RAGE dependent VEGF secretion by cardiac myocytes induces myofibroblast proliferation. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2012, 52, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsberg, P.J.; Strbian, D.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L. Mast Cells as Early Responders in the Regulation of Acute Blood–Brain Barrier Changes after Cerebral Ischemia and Hemorrhage. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lasek-Bal, A.; Jedrzejowska-Szypulka, H.; Student, S.; Warsz-Wianecka, A.; Zareba, K.; Puz, P.; Bal, W.; Pawletko, K.; Lewin-Kowalik, J. The importance of selected markers of inflammation and blood-brain barrier damage for short-term ischemic stroke prognosis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKittrick, C.M.; Lawrence, C.E.; Carswell, H.V.O. Mast cells promote blood brain barrier breakdown and neutrophil infiltration in a mouse model of focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015, 35, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.W.; Bae, S.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.W. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)alpha: Its protein stability and biological functions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2004, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Jin, K.; Xie, L.; Childs, J.; Mao, X.O.; Logvinova, A.; Greenberg, D.A. VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.Y.; Guo, X. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of neuroprotection by vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 79, 180–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manoonkitiwongsa, P.S.; Schultz, R.L.; McCreery, D.B.; Whitter, E.F.; Lyden, P.D. Neuroprotection of ischemic brain by vascular endothelial growth factor is critically dependent on proper dosage and may be compromised by angiogenesis. J. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2004, 24, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shahbazi, M.; Fryer, A.A.; Pravica, V.; Brogan, I.J.; Ramsay, H.M.; Hutchinson, I.V.; Harden, P.N. Vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms are associated with acute renal allograft rejection. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Bossche, M.J.A.; Emsell, L.; Dols, A.; Vansteelandt, K.; De Winter, F.L.; Van den Stock, J.; Sienaert, P.; Stek, M.L.; Bouckaert, F.; Vandenbulcke, M. Hippocampal volume change following ECT is mediated by rs699947 in the promotor region of VEGF. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambrechts, D.; Storkebaum, E.; Morimoto, M.; Del-Favero, J.; Desmet, F.; Marklund, S.L.; Wyns, S.; Thijs, V.; Andersson, J.; van Marion, I.; et al. VEGF is a modifier of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice and humans and protects motoneurons against ischemic death. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, D.; Qiao, Z.; Qi, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, L.; Song, X.; Zhao, E.; Zhang, J.; et al. Epistatic Interaction Between 5-HT1A and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Gene Polymorphisms in the Northern Chinese Han Population With Major Depressive Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrechts, D.; Claes, B.; Delmar, P.; Reumers, J.; Mazzone, M.; Yesilyurt, B.T.; Devlieger, R.; Verslype, C.; Tejpar, S.; Wildiers, H.; et al. VEGF pathway genetic variants as biomarkers of treatment outcome with bevacizumab: An analysis of data from the AViTA and AVOREN randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuselinck, B.; Jean-Baptiste, J.; Schöffski, P.; Couchy, G.; Meiller, C.; Rolland, F.; Allory, Y.; Joniau, S.; Verkarre, V.; Elaidi, R.; et al. Validation of VEGFR1 rs9582036 as predictive biomarker in metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma patients treated with sunitinib. BJU Int. 2016, 118, 890–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yu, H.; Lou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, B.; Yang, Y.; Hui, R. Polymorphisms of KDR gene are associated with coronary heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Awaida, W.; Ahmed, A.A.; Hamza, A.A.; Amber, K.I.; Al-Ameer, H.J.; Jarrar, Y.; Fatima, G.; Maslat, A.O.; Gushchina, Y.; Al Bawareed, O.; et al. Association of KDR rs1870377 genotype with clopidogrel resistance in patients with post percutaneous coronary intervention. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saoud, H.; Aflouk, Y.; Ben Afia, A.; Gaha, L.; Bel Hadj Jrad, B. Association of VEGF-A and KDR polymorphisms with the development of schizophrenia. Hum. Immunol. 2022, 83, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, V.C.A.; Lourenc, G.J.; Brito, A.B.C.; Vasconcelos, V.L.; Maldaun, M.V.C.; Tedeschi, H.; Marie, S.K.N.; Shinjo, S.M.O.; Lima, C.S.P. Associations of VEGFA and KDR single-nucleotide polymorphisms and increased risk and aggressiveness of high-grade gliomas. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2019, 41, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowacka, M.; Obuchowicz, E. BDNF and VEGF in the pathogenesis of stress-induced affective diseases: An insight from experimental studies. Pharmacol. Rep. 2013, 65, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, G.C.; Prueitt, W.L.; Minhajuddin, A.; Patel, S.S.; Czysz, A.H.; Furman, J.L.; Mason, B.L.; Rush, A.J.; Jha, M.K.; Trivedi, M.H. Childhood maltreatment and impact on clinical features of major depression in adults. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 293, 113412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, D.A.; Brunwasser, S.M.; Hollon, S.D.; Weersing, V.R.; Clarke, G.N.; Dickerson, J.F.; Beardslee, W.R.; Gladstone, T.R.; Porta, G.; Lynch, F.L.; et al. Effect of a Cognitive-Behavioral Prevention Program on Depression 6 Years After Implementation Among At-Risk Adolescents: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Clinical Feature | Control (n = 114) | Depressive (n = 160) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 37.9 ± 16.3 | 41.7 ± 12.1 | 0.011 * |
| Gender (female) n (%) | 79 (70%) | 127 (79.3%) | 0.028 * |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m²) | 27.1 ± 5.1 | 28.7 ± 8.3 | 0.113 |
| Education (years) | 15.1 ± 3.7 | 10.7 ± 4.8 | <0.001 * |
| Early-life Stress (yes) n (%) | 9 (8.6%) | 83 (52.0%) | <0.001 * |
| Ethnicity (whites) | 69 (63.3%) | 91 (57.0%) | 0.619 |
| Current smokers | 7 (6.4%) | 20 (13.5%) | 0.064 |
| Alcohol consumption | 6 (5.5%) | 2 (1.4%) | 0.078 |
| Illegal drugs abuse (yes) | 0 (0%) | 1 (0%) | 1.000 |
| Familiar history of depression (yes) n (%) | - | 88 (59%) | - |
| Depression pharmacological treatment n (%) | |||
| SSRI or SNRI or atypical antidepressants | - | 110 (68.7%) | - |
| Anxiolytics | - | 73 (45.3%) | - |
| Tricyclic antidepressants | - | 29 (18%) | - |
| Antipsychotics | - | 52 (32.5%) | - |
| Mood stabilizers | - | 50 (31.2%) | - |
| Thyroid hormone | - | 20 (12.4%) | |
| Suicidal attempts GRID-HAMD21 | - 0.55 ± 0.92 | 1.5 ± 2.20 18.0 ± 9.8 | - <0.001 * |
| BSI | - | 7.2 ± 9.7 | - |
| Dependent Variables | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRID-HAMD21 Score | BSI Score | Number of Suicide Attempts | ||||
| Independent variables | R²: 0.25 | RMSE: 8.91 | R²: 0.25 | RMSE: 8.80 | R²: 0.28 | RMSE: 1.77 |
| β | P | β | P | β | P | |
| Age (years) | −0.06 | 0.378 | −0.22 | 0.003 | −0.03 | 0.027 |
| Gender (female) | 0.01 | 0.997 | 1.35 | 0.177 | 0.06 | 0.729 |
| Education (years) | −0.46 | 0.011 * | −0.47 | 0.009 | −0.12 | 0.001 |
| Early-life stress (yes) | 1.56 | 0.052 | 2.28 | 0.005 | 0.42 | 0.011 |
| Pharmacological treatment | ||||||
| SSRI or SNRI or atypical antidepressants | 0.72 | 0.416 | 0.75 | 0.405 | 0.27 | 0.146 |
| Anxiolytics | 2.73 | 0.001 * | 0.84 | 0.318 | −0.02 | 0.863 |
| Tricyclic antidepressants | 0.40 | 0.691 | 1.02 | 0.306 | 0.55 | 0.007 |
| Antipsychotics | −0.18 | 0.834 | 1.20 | 0.179 | 0.08 | 0.645 |
| Mood stabilizers | 0.26 | 0.760 | 0.51 | 0.568 | 0.20 | 0.265 |
| Genetic Markers | ||||||
| KDR rs2071559 | ||||||
| GG | −0.80 | 0.927 | −0.20 | 0.817 | 0.05 | 0.750 |
| AG + AA | 0.80 | 0.927 | 0.20 | 0.817 | −0.05 | 0.750 |
| KDR rs2305948 | ||||||
| TT | 3.51 | 0.212 | 0.26 | 0.923 | −0.33 | 0.548 |
| CT + CC | −3.51 | 0.212 | −0.26 | 0.923 | 0.33 | 0.548 |
| KDR rs1870377 | ||||||
| AA | −1.29 | 0.522 | −2.04 | 0.305 | −0.14 | 0.740 |
| TA + TT | 1.29 | 0.522 | 2.04 | 0.305 | 0.14 | 0.740 |
| FLT1 rs7993418 | ||||||
| GG. | −2.73 | 0.040 * | −1.49 | 0.252 | 0.17 | 0.517 |
| AG + AA | 2.73 | 0.040 * | 1.49 | 0.252 | −0.17 | 0.517 |
| VEGF rs2010963 | ||||||
| CC | 0.51 | 0.645 | 0.21 | 0.856 | −0.02 | 0.900 |
| GC + GG | −0.51 | 0.645 | −0.21 | 0.856 | 0.02 | 0.900 |
| VEGF rs699947 | ||||||
| AA | −0.73 | 0.551 | −0.11 | 0.926 | −0.45 | 0.076 |
| CA + CC | 0.73 | 0.551 | 0.11 | 0.926 | 0.45 | 0.076 |
| Dependent Variables | ||
|---|---|---|
| VEGF (pg/mL) | ||
| Independent variables | R²: 0.19 | RMSE: 126 |
| β | P | |
| Age (years) | −1.72 | 0.163 |
| Gender (female) | 6.71 | 0.707 |
| Education (years) | 3.21 | 0.253 |
| Early-life stress (yes) | 2.80 | 0.827 |
| Pharmacological treatment | ||
| SSRI or SNRI or atypical antidepressants | −11.31 | 0.430 |
| Anxiolytics | −3.81 | 0.781 |
| Tricyclic antidepressants | 9.22 | 0.568 |
| Antipsychotics | −10.53 | 0.448 |
| Mood stabilizers | −6.84 | 0.627 |
| Genetic Markers | ||
| VEGF rs2010963 | ||
| GG | −10.96 | 0.675 |
| GC | 3.09 | 0.860 |
| CC | 2827.97 | 0.742 |
| Global p−Value: 0.915 | ||
| VEGF rs699947 | ||
| CC | 97.05 | 0.002 * |
| CA | −48.98 | 0.012 * |
| AA | −48.06 | 0.056 |
| Global p−Value: 0.006 * | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, F.D.D.; Ferezin, L.P.; Pereira, S.C.; Figaro-Drumond, F.V.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Menezes, I.C.; Baes, C.v.W.; Coeli-Lacchini, F.B.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Juruena, M.F.; et al. The Association of Biochemical and Genetic Biomarkers in VEGF Pathway with Depression. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122757
Nunes FDD, Ferezin LP, Pereira SC, Figaro-Drumond FV, Pinheiro LC, Menezes IC, Baes CvW, Coeli-Lacchini FB, Tanus-Santos JE, Juruena MF, et al. The Association of Biochemical and Genetic Biomarkers in VEGF Pathway with Depression. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122757
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Fernanda Daniela Dornelas, Letícia Perticarrara Ferezin, Sherliane Carla Pereira, Fernanda Viana Figaro-Drumond, Lucas Cézar Pinheiro, Itiana Castro Menezes, Cristiane von Werne Baes, Fernanda Borchers Coeli-Lacchini, José Eduardo Tanus-Santos, Mário Francisco Juruena, and et al. 2022. "The Association of Biochemical and Genetic Biomarkers in VEGF Pathway with Depression" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122757
APA StyleNunes, F. D. D., Ferezin, L. P., Pereira, S. C., Figaro-Drumond, F. V., Pinheiro, L. C., Menezes, I. C., Baes, C. v. W., Coeli-Lacchini, F. B., Tanus-Santos, J. E., Juruena, M. F., & Lacchini, R. (2022). The Association of Biochemical and Genetic Biomarkers in VEGF Pathway with Depression. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2757. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122757










