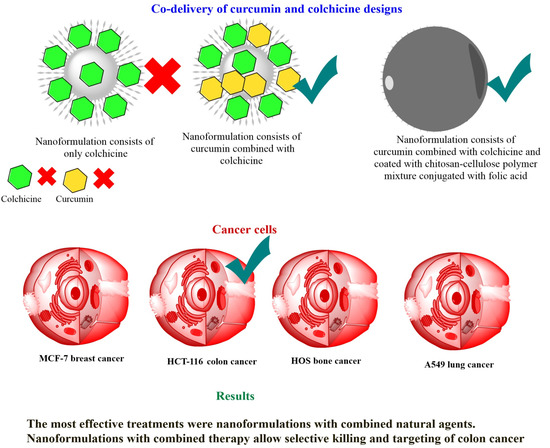
Co-Delivery System of Curcumin and Colchicine Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Promotes Anticancer and Apoptosis Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Phosphonate-Functionalized MSNs
2.2. Fabrication of Nanoformulations
2.2.1. Core Nanoformulations
2.2.2. Core-Shell Nanoformulation Preparation
2.3. Material Characterization
2.3.1. Instrumentation and Measurements
Electron Microscopy
X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
Surface Area
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
Thermal Properties
Zeta Potential
2.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.5. RT-qPCR Gene Expression Analysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Structure
3.2. XRD Characterization
3.3. STA-DSC Characterization
3.4. FTIR-ATR Characterization
3.5. Zeta Potential Measurement
3.6. In Vitro Anticancer Effects
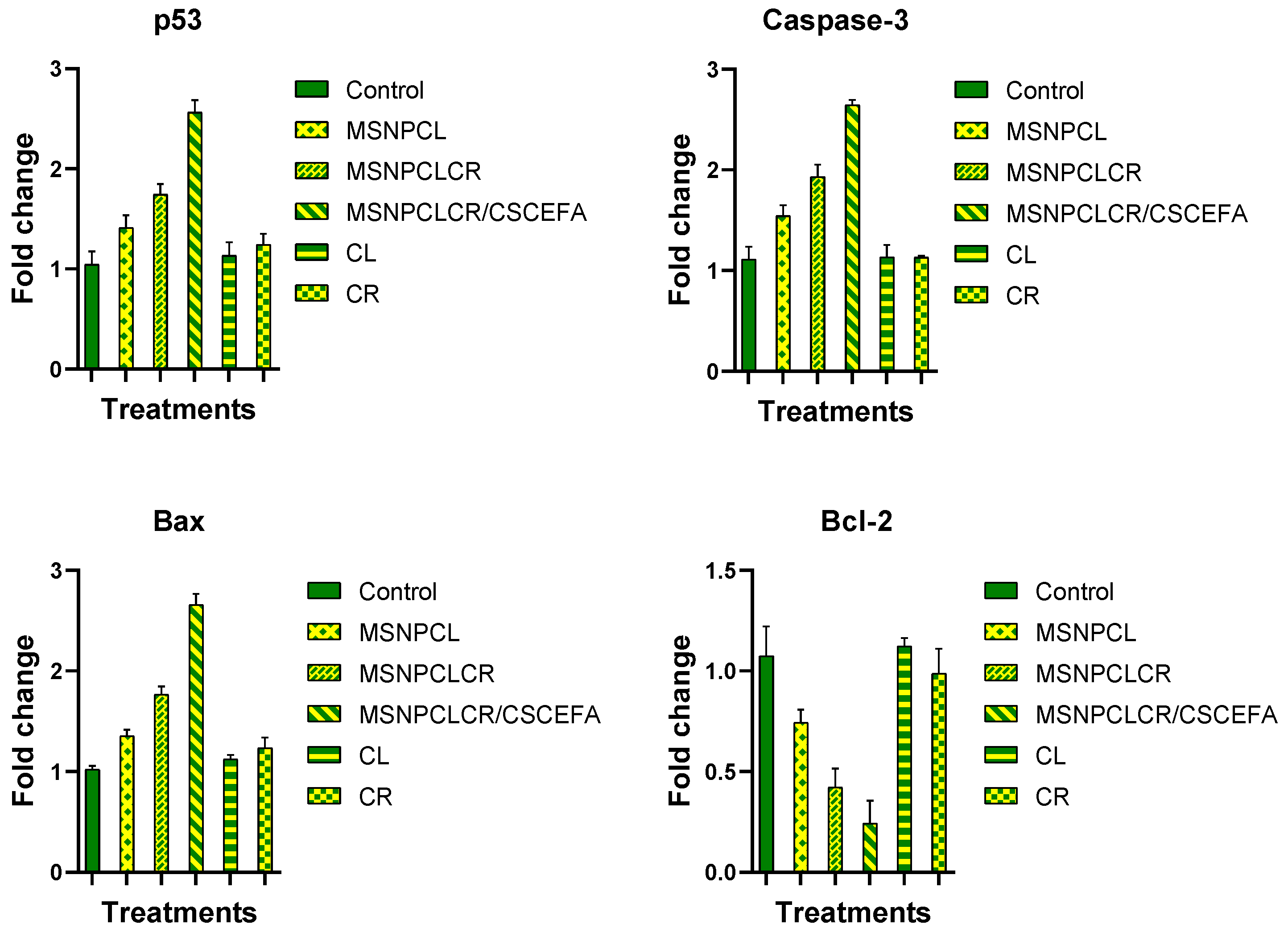
3.7. Apoptosis Induction Evaluations
3.7.1. Protein Expression by RT-PCR
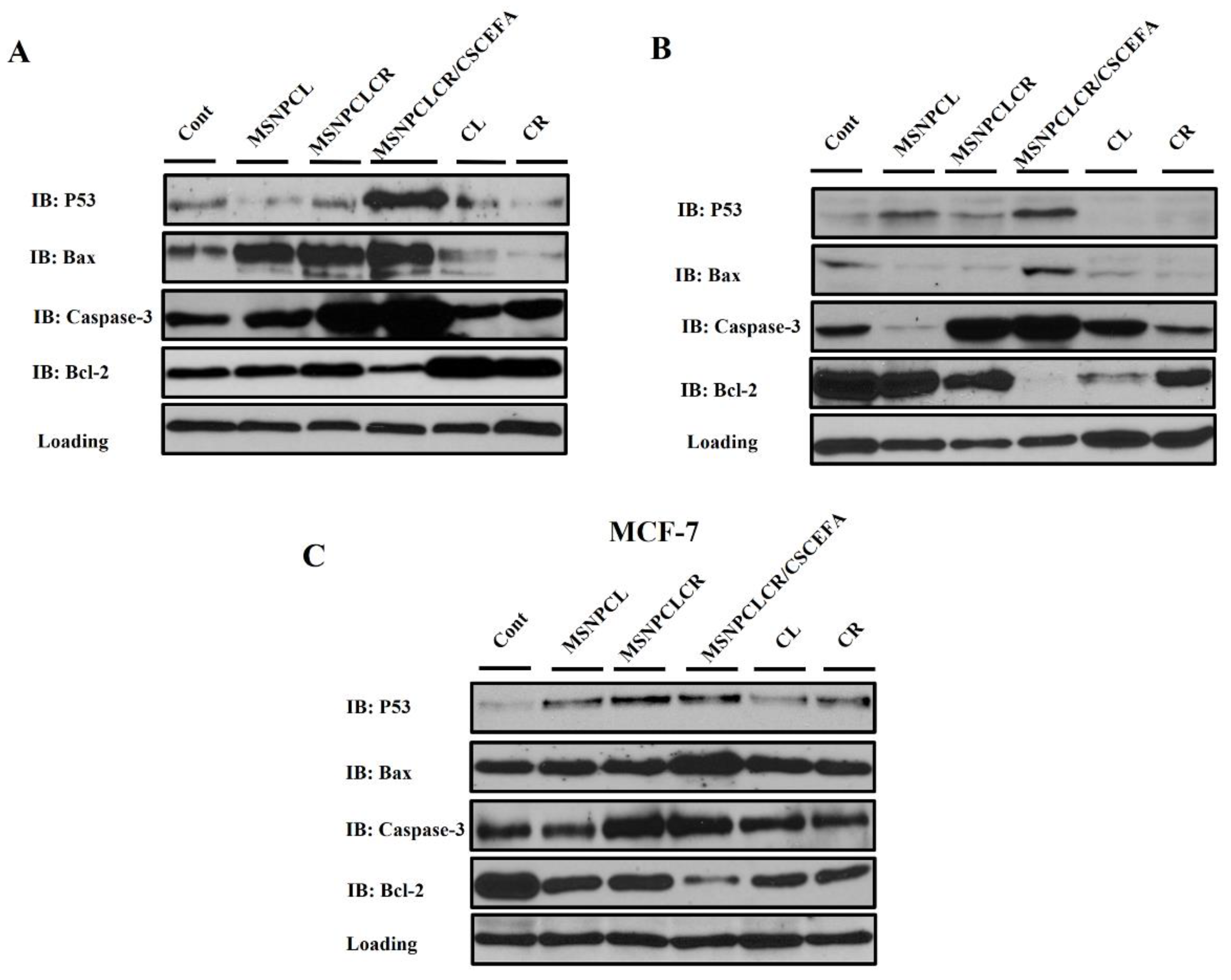
3.7.2. Protein Expression by Western Blotting
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinciguerra, D.; Jacobs, M.; Denis, S.; Mougin, J.; Guillaneuf, Y.; Lazzari, G.; Zhu, C.; Mura, S.; Couvreur, P.; Nicolas, J. Heterotelechelic polymer prodrug nanoparticles: Adaptability to different drug combinations and influence of the dual functionalization on the cytotoxicity. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.M.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-based combination therapy toward overcoming drug resistance in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.S.; Sun, J.H.; Yu, H.H.; Yu, S.Q. Co-delivery nanoparticles of anti-cancer drugs for improving chemotherapy efficacy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1909–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, C.M.; Aryal, S.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticle-assisted combination therapies for effective cancer treatment. Ther. Deliv. 2010, 1, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Kong, Y.Y.; Sun, J.H.; Huo, S.J.; Zhou, M.; Gui, Y.L.; Mu, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, S.Q.; Xu, Q. Co-delivery nanoparticles with characteristics of intracellular precision release drugs for overcoming multidrug resistance. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2081–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, F.; Vicent, M.J. Combination therapy: Opportunities and challenges for polymer-drug conjugates as anticancer nanomedicines. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, P.; Mohanty, C.; Sahoo, S.K. Nanotechnology-based combinational drug delivery: An emerging approach for cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2012, 17, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.L.; Nan, K.; Nie, G.; Chen, H. Enhanced anti-tumor efficacy by co-delivery of doxorubicin and paclitaxel with amphiphilic methoxy PEG-PLGA copolymer nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 8281–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Geng, D.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Cao, J. Co-delivery of etoposide and curcumin by lipid nanoparticulate drug delivery system for the treatment of gastric tumors. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3665–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AbouAitah, K.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Farghali, A.A.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Stefanek, A.; Gierlotka, S.; Opalinska, A.; Allayeh, A.K.; Ciach, T.; Lojkowski, W. Folic acid-conjugated mesoporous silica particles as nanocarriers of natural prodrugs for cancer targeting and antioxidant action. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26466–26490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouAitah, K.; Hassan, H.A.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Gohar, L.; Shaker, O.G.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Opalinska, A.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Targeted Nano-Drug Delivery of Colchicine against Colon Cancer Cells by Means of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Cancers 2020, 12, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahein, S.A.; Aboul-Enein, A.M.; Higazy, I.M.; Abou-Elella, F.; Lojkowski, W.; Ahmed, E.R.; Mousa, S.A.; AbouAitah, K. Targeted anticancer potential against glioma cells of thymoquinone delivered by mesoporous silica core-shell nanoformulations with pH-dependent release. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5503–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Gao, D.; Shen, J.; Wang, Q. A Review of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle Delivery Systems in Chemo-Based Combination Cancer Therapies. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 598722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Ge, Y.; Deng, K.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Ma, P.; Li, C.; et al. DNA-Hybrid-Gated Photothermal Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for NIR-Responsive and Aptamer-Targeted Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 20696–20706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guan, H.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cai, K. Hybrid Mesoporous–Microporous Nanocarriers for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance by Sequential Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.-J.; Li, L. Regulation of Ca2+ Signaling for Drug-Resistant Breast Cancer Therapy with Mesoporous Silica Nanocapsule Encapsulated Doxorubicin/siRNA Cocktail. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Deng, X.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Facile Fabrication Route of Janus Gold-Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers with Dual-Drug Delivery for Tumor Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.J.; Hartman, T.J.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Pietinen, P.; Barrett, M.J.; Taylor, P.R.; Virtamo, J.; Albanes, D. Null association between prostate cancer and serum folate, vitamin B6, vitamin B12, and homocysteine. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2003, 12, 1271–1272. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Low, P.S. Folate-mediated delivery of macromolecular anticancer therapeutic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta, F.; Lamers, G.E.; Morrhayim, J.; Chatzopoulou, A.; Schaaf, M.; den Dulk, H.; Backendorf, C.; Zink, J.I.; Kros, A. Folic acid-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cellular and nuclear targeted drug delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nadaf, A.H.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Jawarneh, S.; Bardaweel, S.; Mahmoud, N.N. Folic acid-hydrophilic polymer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles target doxorubicin delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E. Curcumin Combination Chemotherapy: The Implication and Efficacy in Cancer. Molecules 2019, 24, 2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bollu, V.S.; Barui, A.K.; Mondal, S.K.; Prashar, S.; Fajardo, M.; Briones, D.; Rodríguez-Diéguez, A.; Patra, C.R.; Gómez-Ruiz, S. Curcumin-loaded silica-based mesoporous materials: Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxic properties against cancer cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 63, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liang, Q.; Xie, S.; Liu, E.; Yu, Z.; Sun, L.; Shin, M.C.; Lee, S.J.; He, H.; Yang, V.C. Curcumin based combination therapy for anti-breast cancer: From in vitro drug screening to in vivo efficacy evaluation. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2016, 10, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Doxorubicin and curcumin co-delivery by lipid nanoparticles for enhanced treatment of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 93, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, S.; Jian, X.; Gao, X. Dual-Targeting Nanoparticles: Codelivery of Curcumin and 5-Fluorouracil for Synergistic Treatment of Hepatocarcinoma. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1284–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayet-Robert, M.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Leheurteur, M.; Gachon, F.; Planchat, E.; Abrial, C.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Durando, X.; Barthomeuf, C.; Chollet, P. Phase I dose escalation trial of docetaxel plus curcumin in patients with advanced and metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Epelbaum, R.; Schaffer, M.; Vizel, B.; Badmaev, V.; Bar-Sela, G. Curcumin and gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2010, 62, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalaut, V.S.; Sangwan, L.; Dahiya, K.; Ghalaut, P.S.; Dhankhar, R.; Saharan, R. Effect of imatinib therapy with and without turmeric powder on nitric oxide levels in chronic myeloid leukemia. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2012, 18, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, M.I.; Iwuji, C.; Irving, G.; Karmokar, A.; Higgins, J.A.; Griffin-Teal, N.; Thomas, A.; Greaves, P.; Cai, H.; Patel, S.R.; et al. Curcumin inhibits cancer stem cell phenotypes in ex vivo models of colorectal liver metastases, and is clinically safe and tolerable in combination with FOLFOX chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2015, 364, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, B.; Panda, D.; Gupta, S.; Banerjee, M. Anti-mitotic activity of colchicine and the structural basis for its interaction with tubulin. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Peng, W. Colchicine induces apoptosis in HT-29 human colon cancer cells via the AKT and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5939–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Granieri, L.; Pasculescu, A.; Datti, A.; Asa, S.L.; Xu, Z.; Ezzat, S. High-throughput drug library screening identifies colchicine as a thyroid cancer inhibitor. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19948–19959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Joo, Y.H.; Shin, E.Y.; Park, E.J.; Kim, M.S. Anticancer Effects of Colchicine on Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6269–6280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Wu, D.C.; Chuang, W.L. Anticancer effects of clinically acceptable colchicine concentrations on human gastric cancer cell lines. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aboul-Soud, M.A.M.; Al-Amri, M.Z.; Kumar, A.; Al-Sheikh, Y.A.; Ashour, A.E.; El-Kersh, T.A. Specific Cytotoxic Effects of Parasporal Crystal Proteins Isolated from Native Saudi Arabian Bacillus thuringiensis Strains against Cervical Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Hallouty, S.M.; Soliman, A.A.F.; Nassrallah, A.; Salamatullah, A.; Alkaltham, M.S.; Kamal, K.Y.; Hanafy, E.A.; Gaballa, H.S.; Aboul-Soud, M.A.M. Crude Methanol Extract of Rosin Gum Exhibits Specific Cytotoxicity against Human Breast Cancer Cells via Apoptosis Induction. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaad, H.I.; Zhou, L.; Carroll, R.J.; Wu, G. Rapid publication-ready MS-Word tables for one-way ANOVA. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- AbouAitah, K.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Kandeil, A.; Salman, A.M.M.; Wojnarowicz, J.; Ali, M.A.; Opalinska, A.; Gierlotka, S.; Ciach, T.; Lojkowski, W. Virucidal Action Against Avian Influenza H5N1 Virus and Immunomodulatory Effects of Nanoformulations Consisting of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Loaded with Natural Prodrugs. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 5181–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, R.; Tirrell, D.A. Designing materials for biology and medicine. Nature 2004, 428, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.M.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticle technologies for cancer therapy. In Drug Delivery; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 197, pp. 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossenta, M.; Busato, D.; Dal Bo, M.; Macor, P.; Toffoli, G. Novel Nanotechnology Approaches to Overcome Drug Resistance in the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Glypican 3 as a Useful Target for Innovative Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Guo, N.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Y. Active targeting co-delivery system based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for antitumor therapy in ovarian cancer stem-like cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H. Fabrication of a pH/Redox-Triggered Mesoporous Silica-Based Nanoparticle with Microfluidics for Anticancer Drugs Doxorubicin and Paclitaxel Codelivery. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1216–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Wang, P.-Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Wang, R.-R.; Xie, S.-Y. Nanoplatform-based natural products co-delivery system to surmount cancer multidrug-resistant. J. Control. Release 2021, 336, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Cai, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, S.; Fan, K.; Liu, Z.; et al. PEGylated Lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin: Design, characterization and its cytotoxic effect. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 536, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Hmadi, R.; Kareh, M.; Tohme, R.; Darwiche, N. Cell death mechanisms of plant-derived anticancer drugs: Beyond apoptosis. Apoptosis 2015, 20, 1531–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, H.; Shakeri, A.; Rashidi, B.; Jalili, A.; Banikazemi, Z.; Sahebkar, A. Phytosomal curcumin: A review of pharmacokinetic, experimental and clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, X.; Yan, Z.; Cao, C.; Luo, X. Involvement of p53-dependent apoptosis signal in antitumor effect of Colchicine on human papilloma virus (HPV)-positive human cervical cancer cells. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20194065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Ning, J.; Peng, L.; He, D. Effect of curcumin on Bcl-2 and Bax expression in nude mice prostate cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 9272–9278. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y. Synthesis of novel core-shell structured dual-mesoporous silica nanospheres and their application for enhancing the dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drugs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2014, 44, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Grohganz, H.; Gordon, K.C.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T. Coamorphous drug systems: Enhanced physical stability and dissolution rate of indomethacin and naproxen. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, O.M.; Bekhit, A.A.; Khattab, S.N.; Helmy, M.W.; Abdel-Ghany, Y.S.; Teleb, M.; Elzoghby, A.O. Synthesis of lactoferrin mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pemetrexed/ellagic acid synergistic breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 188, 110824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, A.; Canete, M.; Roca, A.G.; Calero, M.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Serna, C.J.; Morales Mdel, P.; Miranda, R. The influence of surface functionalization on the enhanced internalization of magnetic nanoparticles in cancer cells. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 115103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.-G.; Wei, W.; Lv, P.-P.; Yue, H.; Wang, L.-Y.; Su, Z.-G.; Ma, G.-H. Surface Charge Affects Cellular Uptake and Intracellular Trafficking of Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2440–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Xie, Q.R.; Xia, W.; Gu, H. Delivering hydrophilic and hydrophobic chemotherapeutics simultaneously by magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles to inhibit cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Zhang, S.; Xue, X.; Zhu, X.; Song, S.; Wang, B.; Jiang, L.; Qin, M.; Liang, H.; Gao, L. Quercetin and doxorubicin co-delivery using mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of gastric carcinoma chemotherapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5113–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hengartner, M.O. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000, 407, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, R.W.; Ruefli, A.A.; Lowe, S.W. Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell 2002, 108, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, S.W.; Lin, A.W. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McIlwain, D.R.; Berger, T.; Mak, T.W. Caspase functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thornberry, N.A. Caspases: Key mediators of apoptosis. Chem. Biol. 1998, 5, R97–R103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Lazebnik, Y. Caspases: Enemies within. Science 1998, 281, 1312–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, P.; Mishra, M.; Kyprianou, N. Targeting caspases in cancer therapeutics. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.L.; Wu, Q.; Vega, V.B.; Chiu, K.P.; Ng, P.; Zhang, T.; Shahab, A.; Yong, H.C.; Fu, Y.; Weng, Z.; et al. A global map of p53 transcription-factor binding sites in the human genome. Cell 2006, 124, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, C.; Hogarth, L.A.; Mackenzie, K.L.; Hall, A.G.; Lock, R.B. p21(WAF1) modulates drug-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 3602–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaux, D.L.; Cory, S.; Adams, J.M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 1988, 335, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, A.-L.; Gdynia, G.; Salou, M.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Duglova, K.; Heller, A.; Keim, S.; Kautz, N.; Jassowicz, A.; Elssner, C.; et al. Bcl-xL is an oncogenic driver in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rampino, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Ionov, Y.; Li, Y.; Sawai, H.; Reed, J.C.; Perucho, M. Somatic Frameshift Mutations in the BAX Gene in Colon Cancers of the Microsatellite Mutator Phenotype. Science 1997, 275, 967–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

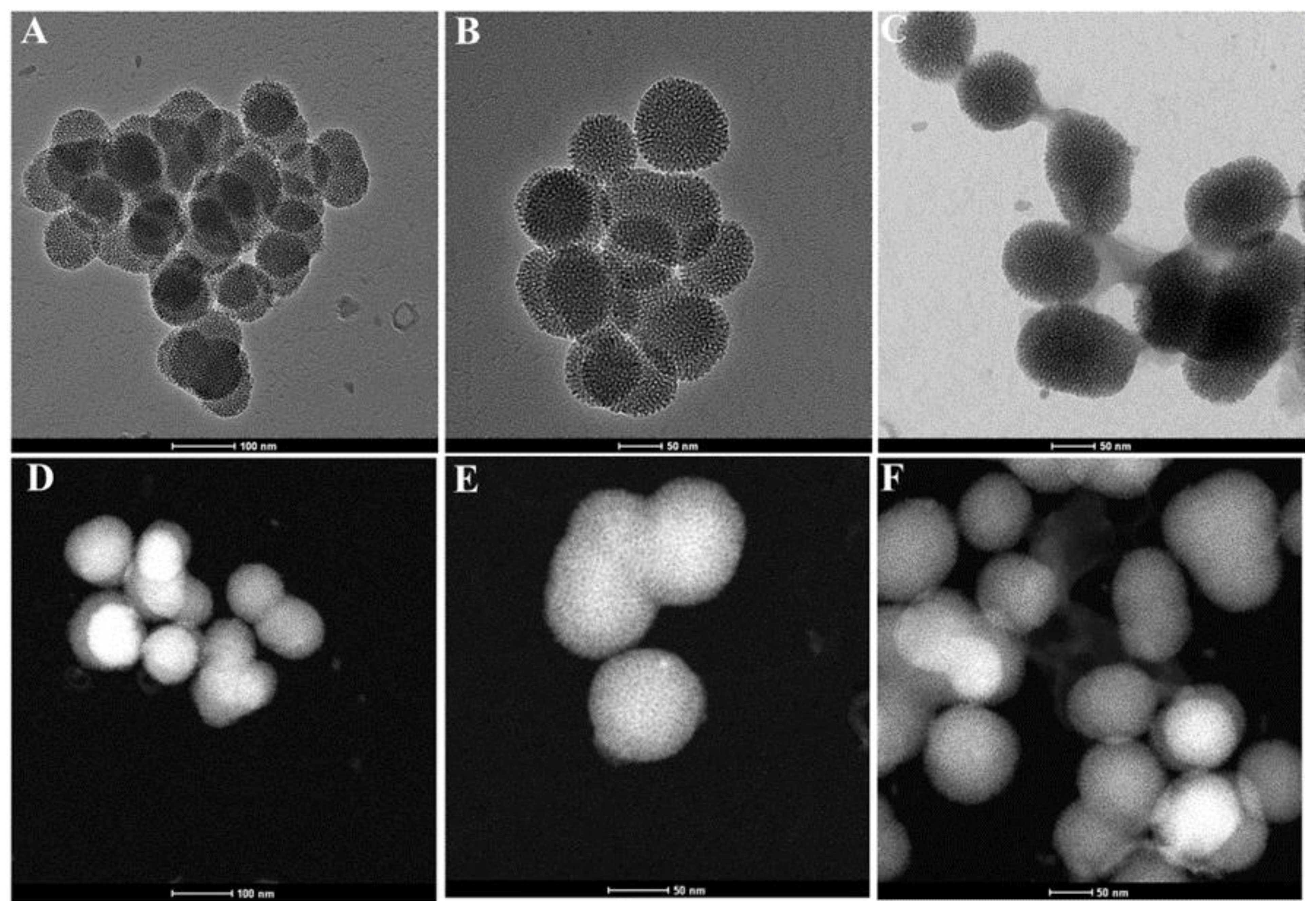
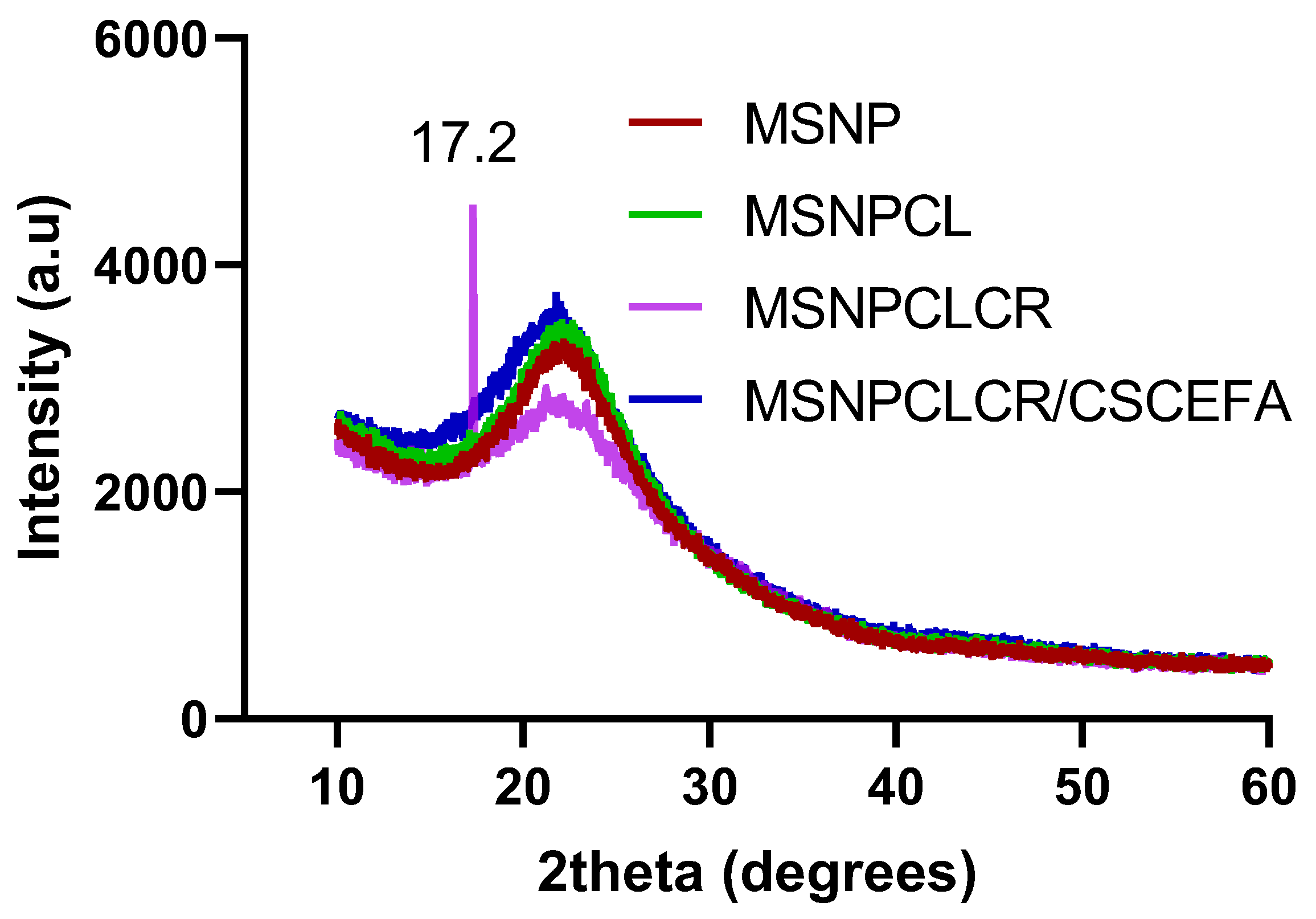






| Formula | Preparation Conditions | Weight Loss wt.% a Total Prodrug Content (TPC wt.%) | SBET (m2/g) b | Total Pore Volume c (CC/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug: Nanoparticles Ratio | Volume/Solvent | Temperature/ Stirring Speed | ||||
| MSNP | 21.5 | 206.2 | 0.689 | |||
| F1: MSNPCL | 1:3 | 10 mL CL/d. water | RT (24 h)/270 rpm | 32.4 TPC ~ 10.9 | 144.3 | 0.528 |
| F2: MSNPCLCR | 300 mg MSNPCL/ethanol containing 100 mg CR RT (24 h)/250 rpm | 50.5 TPC ~ 18.1 | 15.1 | 0.165 | ||
| F3: MSNPCLCR/CSCEFA | MSNPCLCR was resuspended in CS-CE-FA/ RT (24 h)/250 rpm | 60.8 TPC ~ 18.1 10.3 (as shell coating) | 1.0 | 0.188 | ||
| Treatments | Cancer Cell Line | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | HCT-116 | HOS | A549 | |
| MSNPCL | 65.3 ± 0.05 | 4.8 ± 0.05 | 68.7 ± 0.06 | 17.1 ± 0.05 |
| MSNPCLCR | 23.7 ± 0.05 | 6.2 ± 0.05 | 18.6 ± 0.05 | 16.6 ± 0.05 |
| MSNPCLCR/CSCEFA | 20.2 ± 0.06 | 4.1 ± 0.05 | 12.0 ± 0.05 | 16.6 ± 0.06 |
| CL | 101.3 ± 0.14 | 92.6 ± 0.15 | 111.0 ± 0.08 | 89.0 ± 0.07 |
| CR | 98.8 ± 0.13 | 116.7 ± 0.16 | 47.9 ± 0.05 | 38.6 ± 0.06 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AbouAitah, K.; Soliman, A.A.F.; Swiderska-Sroda, A.; Nassrallah, A.; Smalc-Koziorowska, J.; Gierlotka, S.; Lojkowski, W. Co-Delivery System of Curcumin and Colchicine Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Promotes Anticancer and Apoptosis Effects. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122770
AbouAitah K, Soliman AAF, Swiderska-Sroda A, Nassrallah A, Smalc-Koziorowska J, Gierlotka S, Lojkowski W. Co-Delivery System of Curcumin and Colchicine Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Promotes Anticancer and Apoptosis Effects. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122770
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbouAitah, Khaled, Ahmed A. F. Soliman, Anna Swiderska-Sroda, Amr Nassrallah, Julita Smalc-Koziorowska, Stanislaw Gierlotka, and Witold Lojkowski. 2022. "Co-Delivery System of Curcumin and Colchicine Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Promotes Anticancer and Apoptosis Effects" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122770
APA StyleAbouAitah, K., Soliman, A. A. F., Swiderska-Sroda, A., Nassrallah, A., Smalc-Koziorowska, J., Gierlotka, S., & Lojkowski, W. (2022). Co-Delivery System of Curcumin and Colchicine Using Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Promotes Anticancer and Apoptosis Effects. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2770. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122770