Anticancer Activity of the Choline Kinase Inhibitor PL48 Is Due to Selective Disruption of Choline Metabolism and Transport Systems in Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
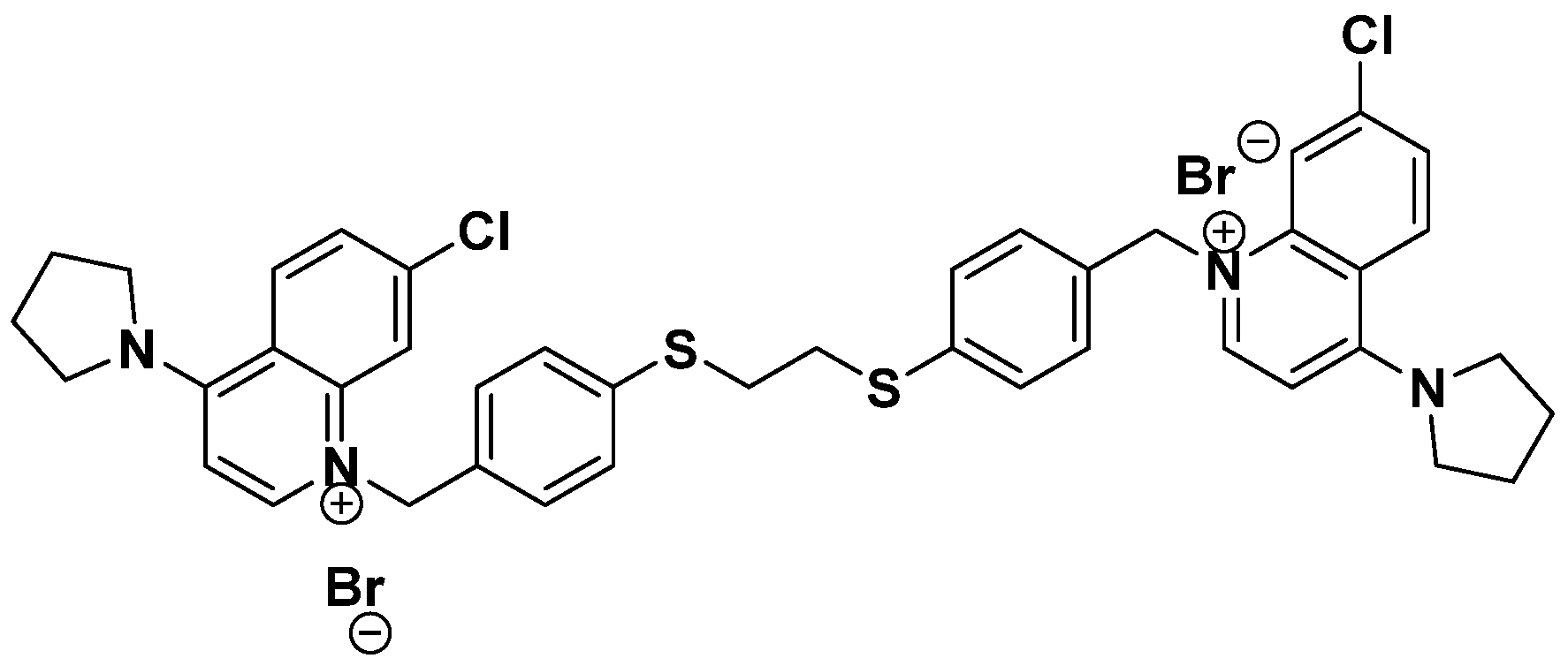
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Choline Uptake Assays
2.4. Cloning, Protein Expression and Purification of ChoKα1
2.5. Preparation of Cell Lysate Containing Soluble ChoKα
2.6. Determination of ChoKα Activity
2.7. Evaluation of the Antiproliferative Effect of PL48 in HepG2 and MCF7 Cell Lines
2.8. Immunoblotting Assay
2.9. Metabolic Labelling Assays
2.10. Other Analyses
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Functional Characteristics of Choline Uptake in MCF7 and HepG2 Cells
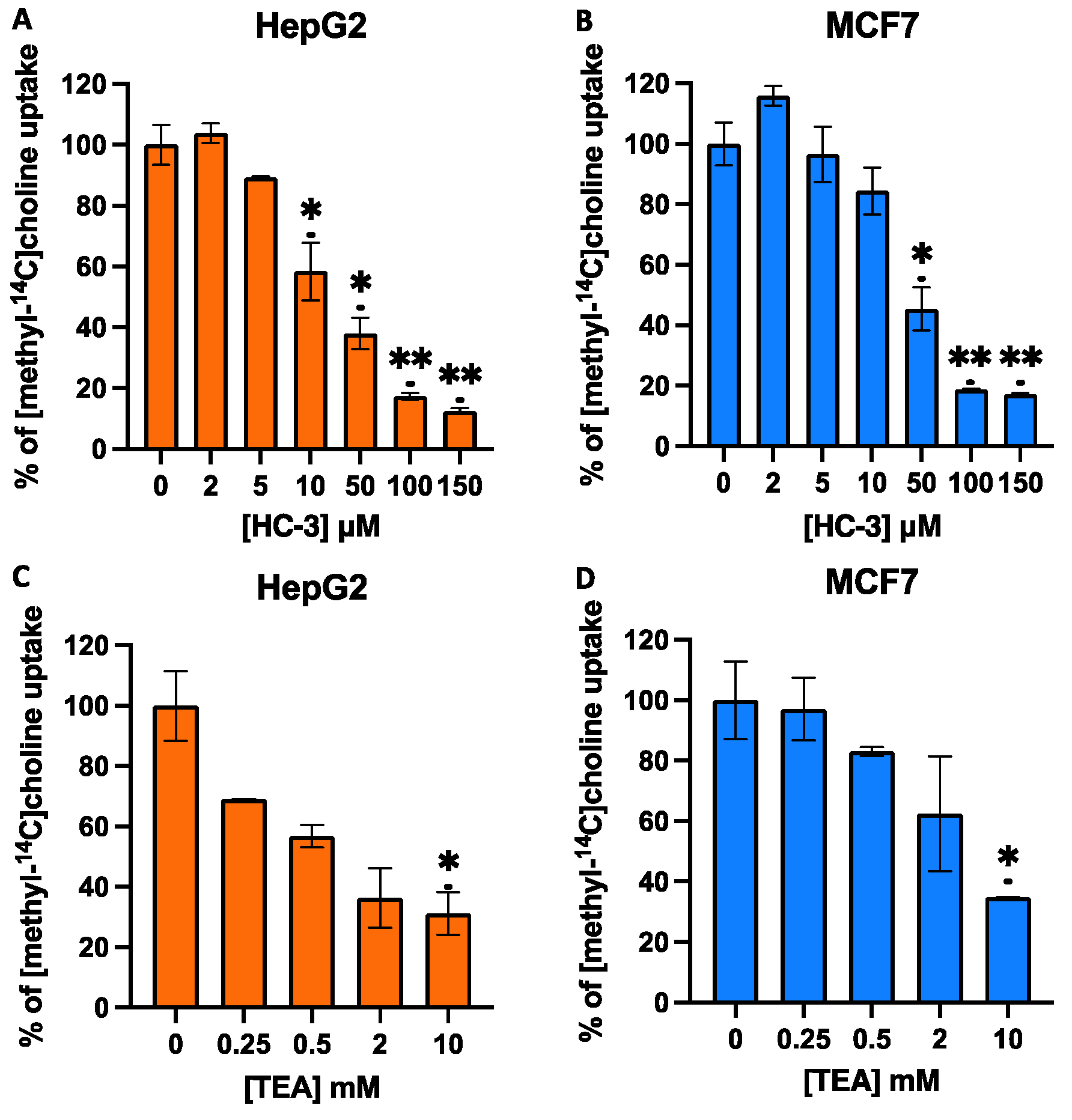
3.2. Effect of HC-3 and TEA on Choline Uptake in MCF7 and HepG2 Cells
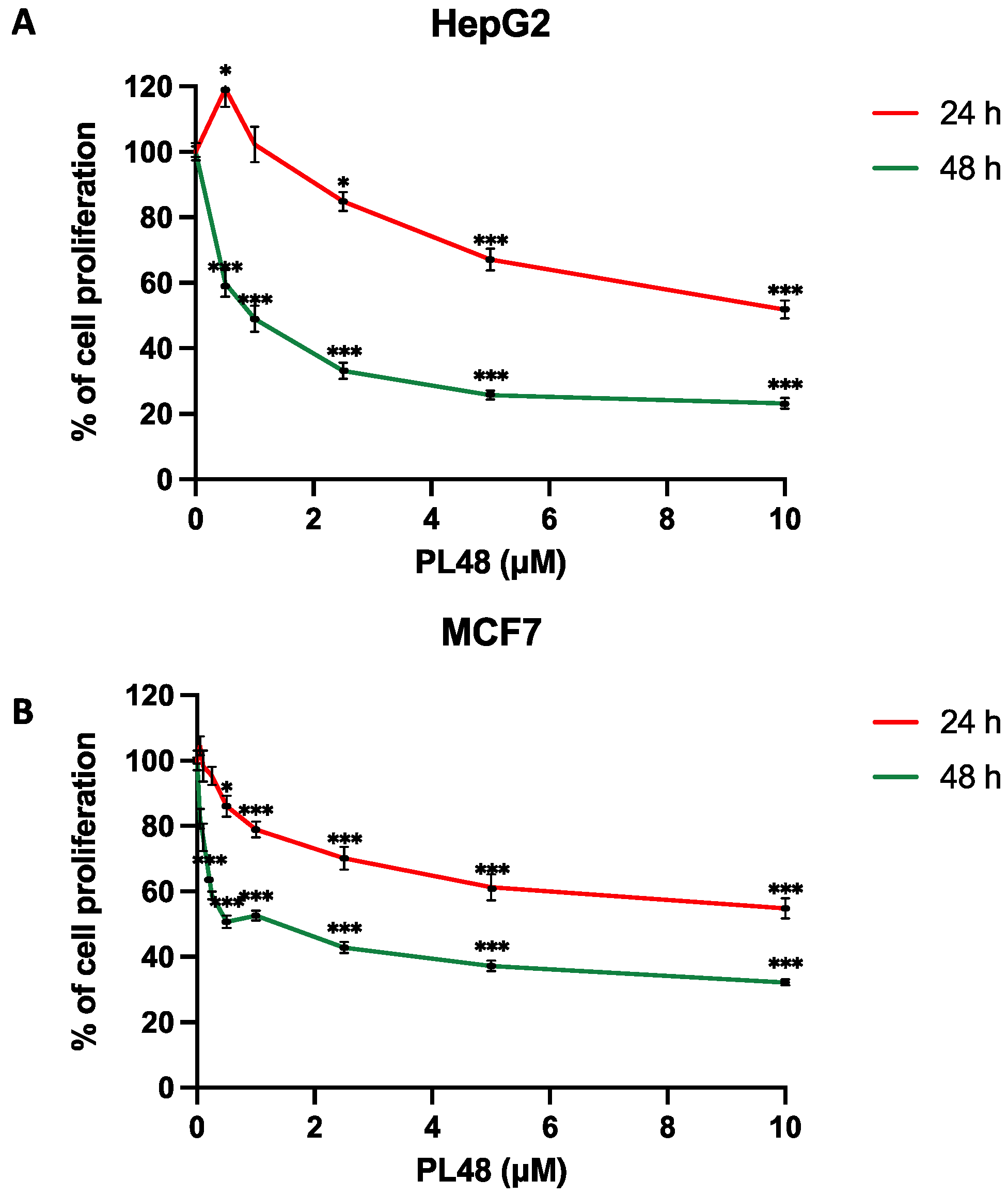
3.3. PL48 Inhibits Cell Growth in MCF7 and HepG2 Cells
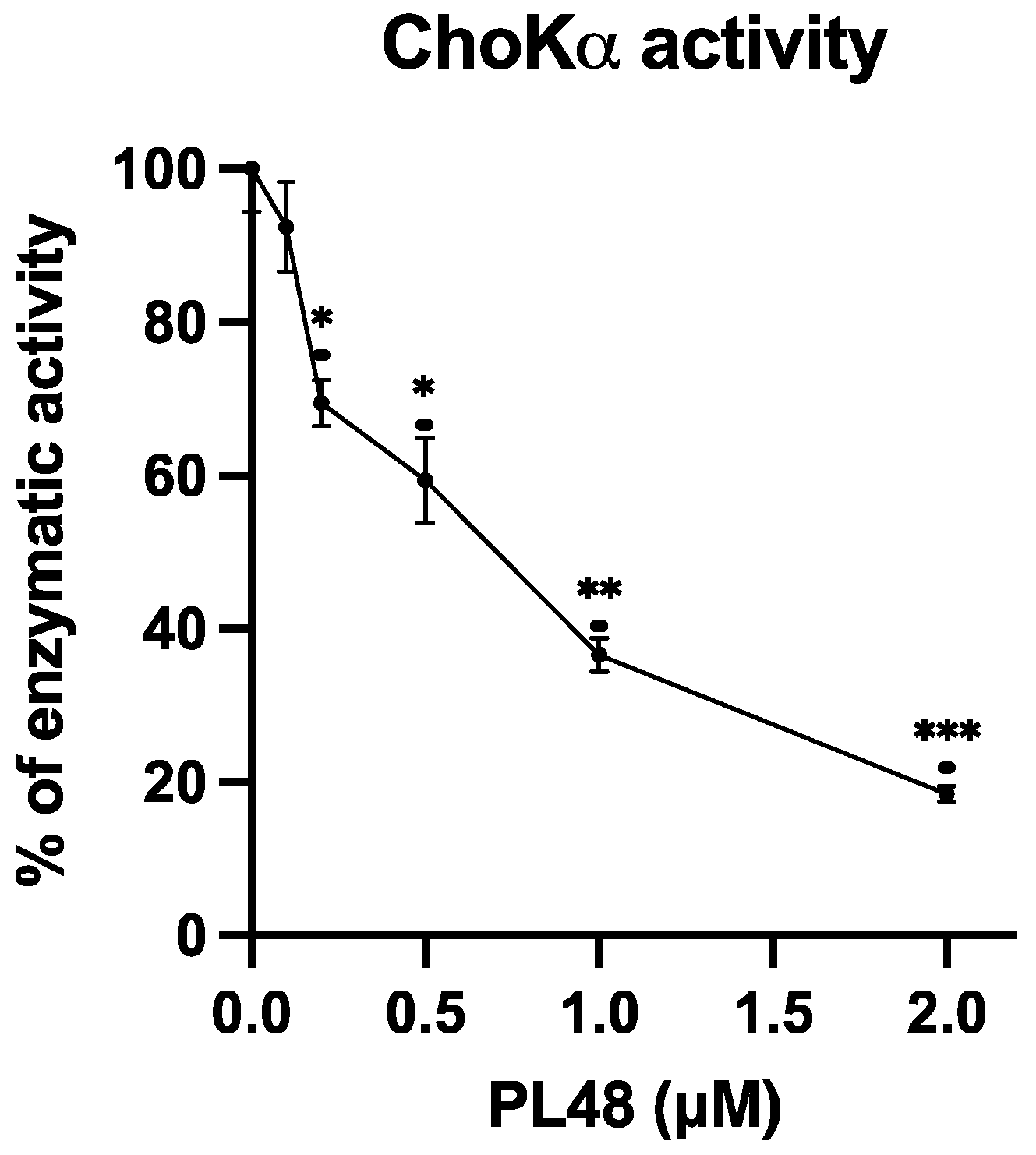
3.4. Inhibition of ChoKα1 by PL48
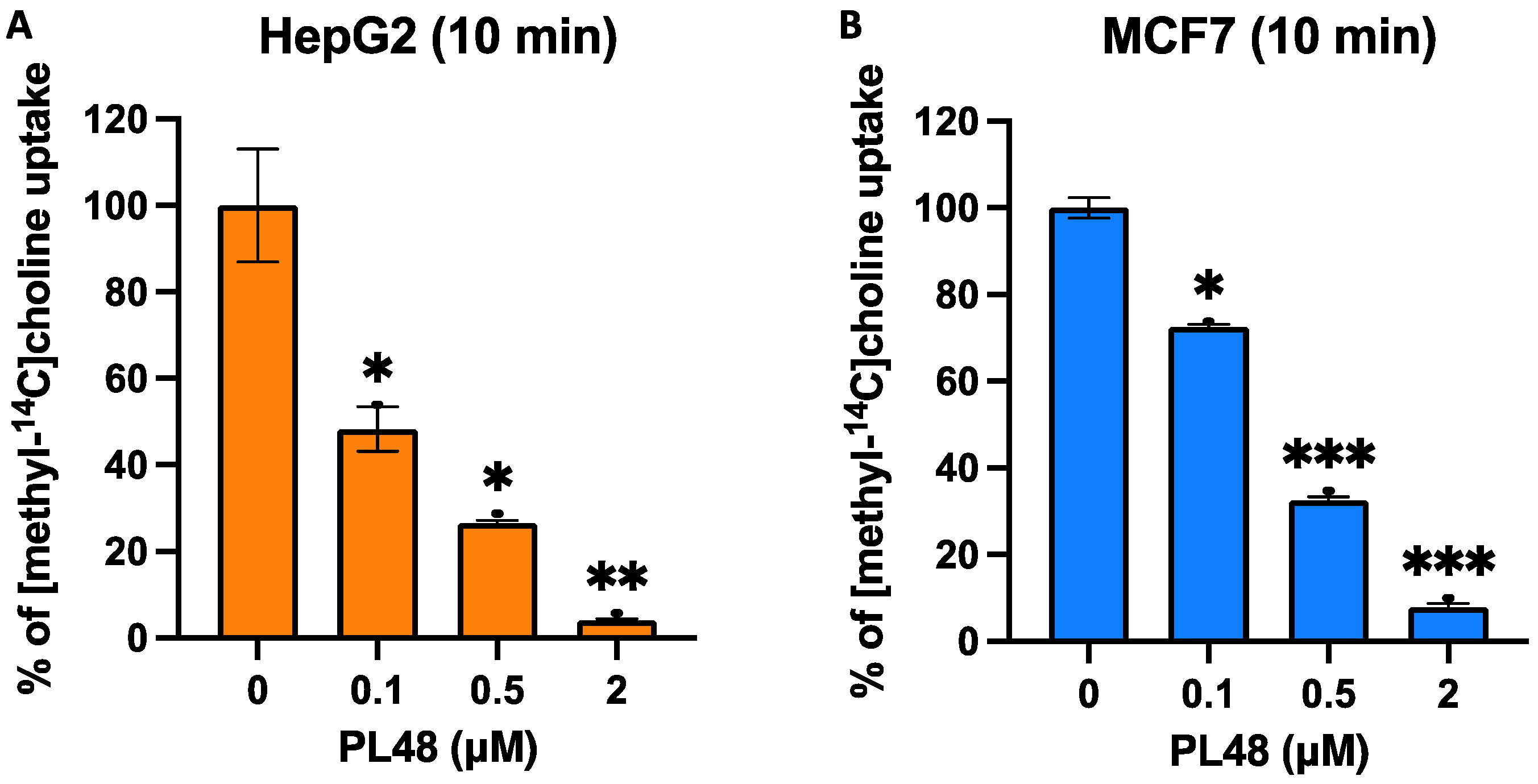
3.5. Effect of PL48 on Choline Uptake in HepG2 and MCF7 Cell Lines
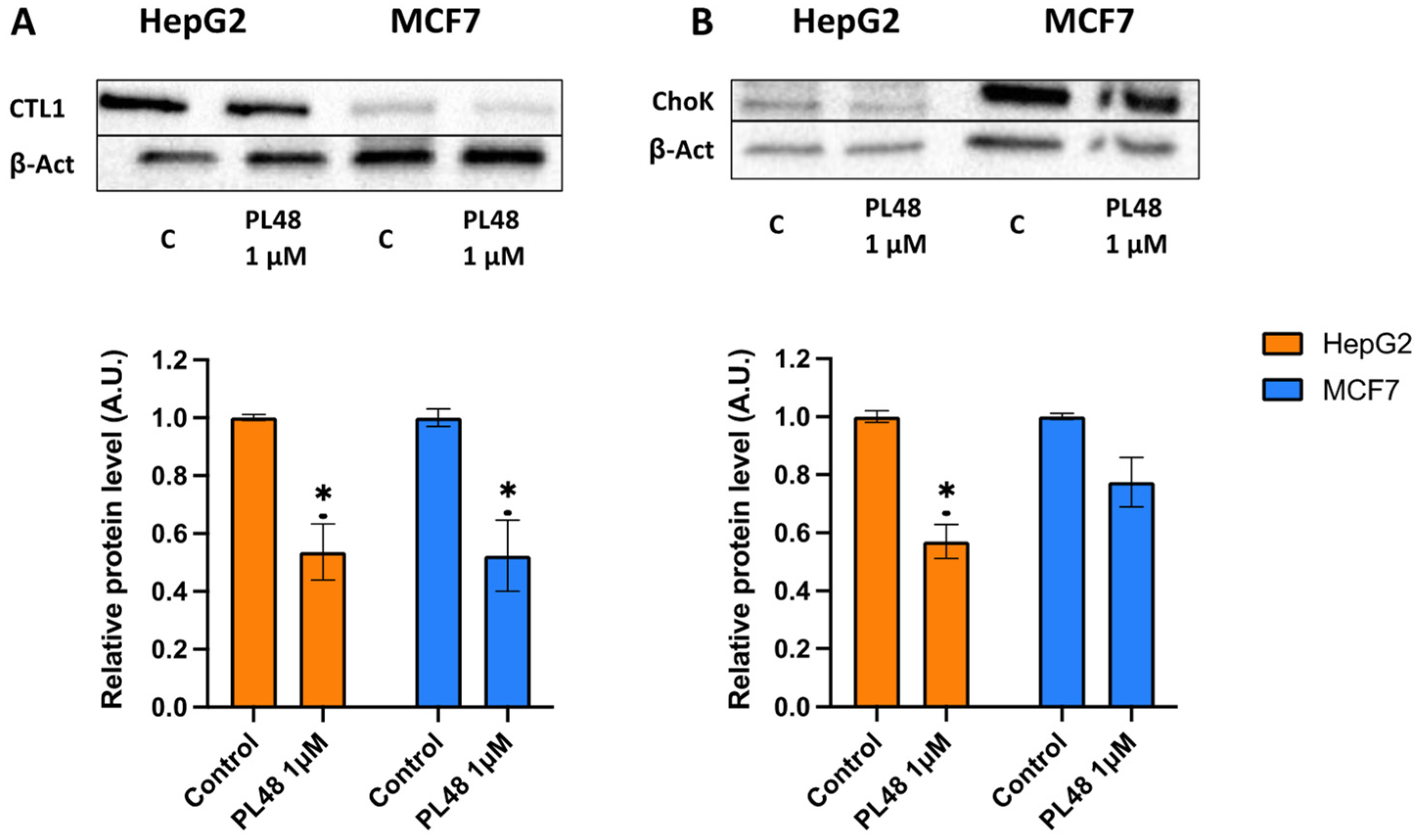
3.6. Effect of PL48 Treatment for 48 h on ChoKα and CTL1 Expression Levels in MCF7 and HepG2 Cells
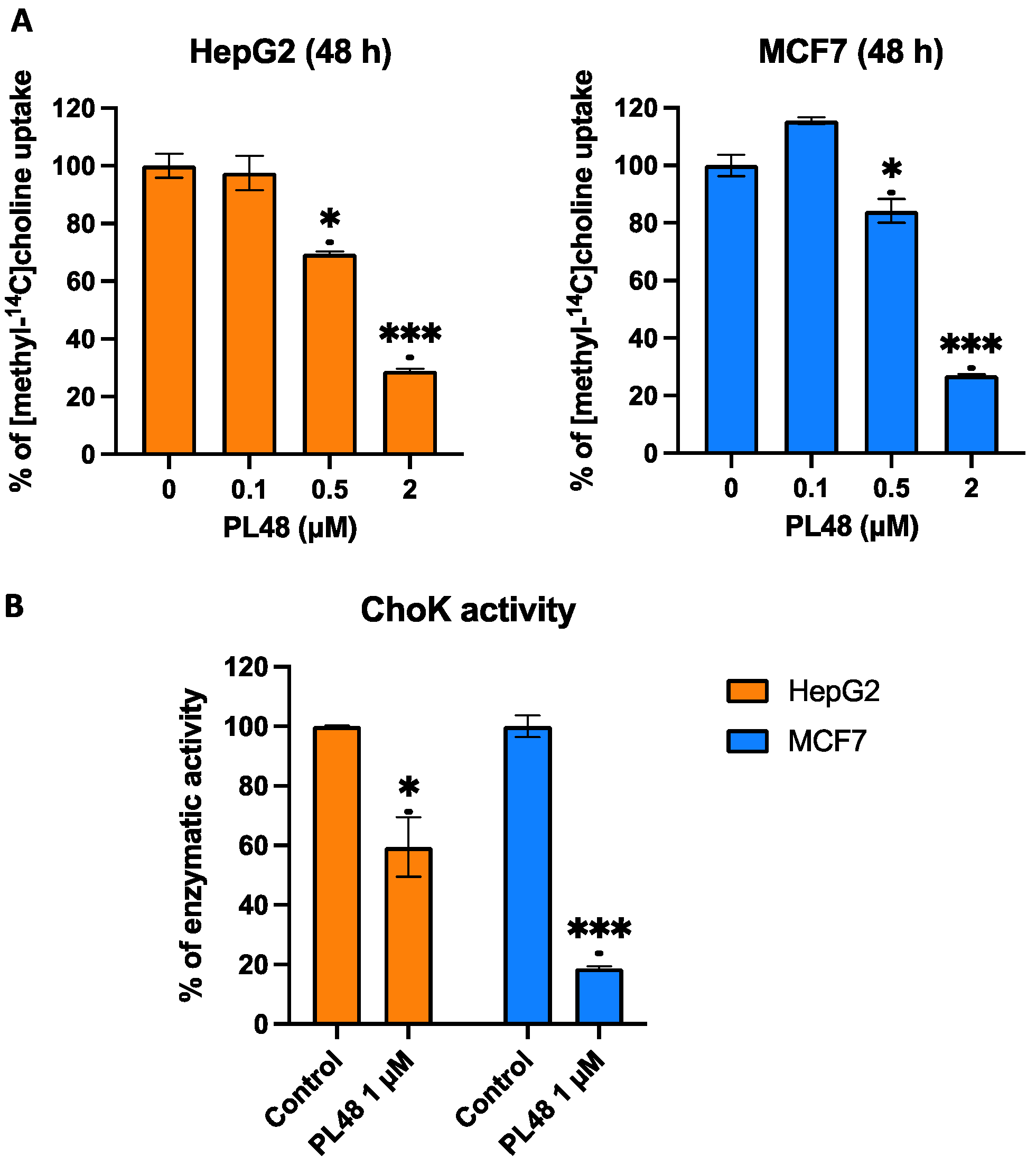
3.7. Effect of PL48 Treatment for 48 h on ChoKα and CTL1 Activities in MCF7 and HepG2 Cells
3.8. Effect of PL48 on Choline Metabolism in MCF7 and HepG2 Cells
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, L.; Salomone, S.; Libra, M. Evolution of Cancer Pharmacological Treatments at the Turn of the Third Millennium. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.; Sun, G.; Sun, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhong, R.; Peng, Y. Tumor Energy Metabolism and Potential of 3-Bromopyruvate as an Inhibitor of Aerobic Glycolysis: Implications in Tumor Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, G.; Sun, X.; Li, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhong, R.; Peng, Y. The Potential of Lonidamine in Combination with Chemotherapy and Physical Therapy in Cancer Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Glunde, K. Targeting Phospholipid Metabolism in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, M.; Rizwan, A.; Jiang, L.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Glunde, K. Molecular Effects of Doxorubicin on Choline Metabolism in Breast Cancer. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Molina, A.R.; Gutiérrez, R.; Ramos, M.A.; Silva, J.M.; Silva, J.; Bonilla, F.; Sánchez, J.J.; Lacal, J.C. Increased Choline Kinase Activity in Human Breast Carcinomas: Clinical Evidence for a Potential Novel Antitumor Strategy. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4317–4322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cecchetti, S.; Bortolomai, I.; Ferri, R.; Mercurio, L.; Canevari, S.; Podo, F.; Miotti, S.; Iorio, E. Inhibition of Phosphatidylcholine-Specific Phospholipase C Interferes with Proliferation and Survival of Tumor Initiating Cells in Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inazu, M. Choline Transporter-like Proteins CTLs/SLC44 Family as a Novel Molecular Target for Cancer Therapy. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2014, 35, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inazu, M. Functional Expression of Choline Transporters in the Blood–Brain Barrier. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, B.S.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Tempel, W.; Finerty, P.J.; MacKenzie, F.; Dimov, S.; Vedadi, M.; Park, H.-W. Crystal Structures of Human Choline Kinase Isoforms in Complex with Hemicholinium-3. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 16330–16340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arlauckas, S.P.; Popov, A.V.; Delikatny, E.J. Choline Kinase Alpha—Putting the ChoK-Hold on Tumor Metabolism. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 63, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awwad, H.M.; Geisel, J.; Obeid, R. The Role of Choline in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 45, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayub Khan, S.M.; Few, L.L.; See Too, W.C. Downregulation of Human Choline Kinase α Gene Expression by MiR-876-5p. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7442–7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mori, N.; Glunde, K.; Takagi, T.; Raman, V.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Choline Kinase Down-Regulation Increases the Effect of 5-Fluorouracil in Breast Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11284–11290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalcin, A.; Clem, B.; Makoni, S.; Clem, A.; Nelson, K.; Thornburg, J.; Siow, D.; Lane, A.N.; Brock, S.E.; Goswami, U.; et al. Selective Inhibition of Choline Kinase Simultaneously Attenuates MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signaling. Oncogene 2010, 29, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clem, B.F.; Clem, A.L.; Yalcin, A.; Goswami, U.; Arumugam, S.; Telang, S.; Trent, J.O.; Chesney, J. A Novel Small Molecule Antagonist of Choline Kinase-α That Simultaneously Suppresses MAPK and PI3K/AKT Signaling. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3370–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glunde, K.; Shah, T.; Winnard, P.T.; Raman, V.; Takagi, T.; Vesuna, F.; Artemov, D.; Bhujwalla, Z.M. Hypoxia Regulates Choline Kinase Expression through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Signaling in a Human Prostate Cancer Model. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio-Ruiz, B.; Figuerola-Conchas, A.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; Capitán-Cañadas, F.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Carrasco, M.P.; Gallo, M.Á.; Espinosa, A.; Marco, C.; Ruiz, C.; et al. Discovery of a New Binding Site on Human Choline Kinase A1: Design, Synthesis, Crystallographic Studies, and Biological Evaluation of Asymmetrical Bispyridinium Derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sola-Leyva, A.; López-Cara, L.C.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Ríos, A.; Marco, C.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P. Choline Kinase Inhibitors EB-3D and EB-3P Interferes with Lipid Homeostasis in HepG2 Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahún-Roncero, M.; Rubio-Ruíz, B.; Conejo-García, A.; Velázquez-Campoy, A.; Entrena, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R. Determination of Potential Scaffolds for Human Choline Kinase A1 by Chemical Deconvolution Studies. ChemBioChem 2013, 14, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino-Ortega, S.; Baglioni, E.; Mariotto, E.; Bortolozzi, R.; Serrán-Aguilera, L.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Carrasco-Jimenez, M.P.; Gallo, M.A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; Marco, C.; et al. Design, Synthesis, Crystallization and Biological Evaluation of New Symmetrical Biscationic Compounds as Selective Inhibitors of Human Choline Kinase A1 (ChoKα1). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serrán-Aguilera, L.; Mariotto, E.; Rubbini, G.; Castro Navas, F.F.; Marco, C.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P.; Ballarotto, M.; Macchiarulo, A.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; Viola, G.; et al. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, in Silico Modeling and Crystallization of Novel Small Monocationic Molecules with Potent Antiproliferative Activity by Dual Mechanism. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 207, 112797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haga, T. Molecular Properties of the High-Affinity Choline Transporter CHT1. J. Biochem. 2014, 156, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hedtke, V.; Bakovic, M. Choline Transport for Phospholipid Synthesis: An Emerging Role of Choline Transporter-like Protein 1. Exp. Biol. Med. 2019, 244, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saiki, I.; Yara, M.; Yamanaka, T.; Uchino, H.; Inazu, M. Functional Expression of Choline Transporter-Like Protein 1 in LNCaP Prostate Cancer Cells: A Novel Molecular Target. Biomol. Ther. 2020, 28, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, S.; Nishijima, N.; Hirai, K.; Shibata, K.; Hase, A.; Yamanaka, T.; Inazu, M. Anticancer Activity of Amb4269951, a Choline Transporter-Like Protein 1 Inhibitor, in Human Glioma Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-López, J.M.; Carrasco, M.P.; Segovia, J.L.; Marco, C. Hexadecylphosphocholine Inhibits Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis and the Proliferation of HepG2 Cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 4649–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiaffino-Ortega, S.; López-Cara, L.C.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Carrasco-Jimenez, M.P.; Gallo, M.A.; Espinosa, A.; Marco, C.; Entrena, A. New Non-Symmetrical Choline Kinase Inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7146–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Ruíz, B.; Conejo-García, A.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Carrasco-Jiménez, M.P.; Segovia, J.; Marco, C.; Gallo, M.A.; Espinosa, A.; Entrena, A. Design, Synthesis, Theoretical Calculations and Biological Evaluation of New Non-Symmetrical Choline Kinase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 50, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisel, S.H. Choline Phospholipids: Signal Transduction and Carcinogenesis 1. FASEB J. 1993, 7, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; Ronen, S.M. Choline Metabolism in Malignant Transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Wan, D.; Gu, J. Choline Transporters in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma: Expression and Functional Implications. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2007, 39, 668–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sinclair, C.J.; Chi, K.D.; Subramanian, V.; Ward, K.L.; Green, R.M. Functional Expression of a High Affinity Mammalian Hepatic Choline/Organic Cation Transporter. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, D.L.; Carroll, D.; Day, S.; Gray, H.; Sadarangani, P.; Murthi, S.; Job, C.; Baggett, B.; Raghunand, N.; Gillies, R.J. Characterization of Breast Cancers and Therapy Response by MRS and Quantitative Gene Expression Profiling in the Choline Pathway. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, V.; Yuan, Z.; Ramsubir, S.; Bakovic, M. Choline Transport for Phospholipid Synthesis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2006, 231, 490–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Zhong, Z.; Stubelius, A.; Sweeney, S.R.; Booshehri, L.M.; Antonucci, L.; Liu-Bryan, R.; Lodi, A.; Terkeltaub, R.; Lacal, J.C.; et al. Choline Uptake and Metabolism Modulate Macrophage IL-1β and IL-18 Production. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1350–1362.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiaffino-Ortega, S.; Mariotto, E.; Luque-Navarro, P.M.; Kimatrai-Salvador, M.; Rios-Marco, P.; Hurtado-Guerrero, R.; Marco, C.; Carrasco-Jimenez, M.P.; Viola, G.; López-Cara, L.C. Anticancer and Structure Activity Relationship of Non-Symmetrical Choline Kinase Inhibitors. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Navas, F.F.; Schiaffino-Ortega, S.; Carrasco-Jimenez, M.P.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Marco, C.; Espinosa, A.; Gallo, M.A.; Mariotto, E.; Basso, G.; Viola, G.; et al. New More Polar Symmetrical Bipyridinic Compounds: New Strategy for the Inhibition of Choline Kinase A1. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martín, R.; Campos, J.M.; Conejo-García, A.; Cruz-López, O.; Báñez-Coronel, M.; Rodríguez-González, A.; Gallo, M.A.; Lacal, J.C.; Espinosa, A. Symmetrical Bis-Quinolinium Compounds: New Human Choline Kinase Inhibitors with Antiproliferative Activity against the HT-29 Cell Line. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 3354–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Molina, A.R.R.; Sarmentero-Estrada, J.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; Tarón, M.; de Molina, V.R.; Cejas, P.; Skrzypski, M.; Gallego-Ortega, D.; de Castro, J.; Casado, E.; et al. Expression of Choline Kinase Alpha to Predict Outcome in Patients with Early-Stage Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Study. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, S.; Xie, P. ChoK-Full of Potential: Choline Kinase in B Cell and T Cell Malignancies. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glunde, K.; Serkova, N.J. Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers Identified in Cancer Choline Phospholipid Metabolism. Pharmacogenomics 2006, 7, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Ortega, D.; de Molina, A.R.; Ramos, M.A.; Valdes-Mora, F.; Barderas, M.G.; Sarmentero-Estrada, J.; Lacal, J.C. Differential Role of Human Choline Kinase α and β Enzymes in Lipid Metabolism: Implications in Cancer Onset and Treatment. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butler, L.M.; Perone, Y.; Dehairs, J.; Lupien, L.E.; de Laat, V.; Talebi, A.; Loda, M.; Kinlaw, W.B.; Swinnen, J.V. Lipids and Cancer: Emerging Roles in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Therapeutic Intervention. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 159, 245–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.S.; Eriksson, P.; Izquierdo-Garcia, J.L.; Brandes, A.H.; Ronen, S.M. HDAC Inhibition Induces Increased Choline Uptake and Elevated Phosphocholine Levels in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- See Too, W.C.; Wong, M.T.; Few, L.L.; Konrad, M. Highly Specific Antibodies for Co-Detection of Human Choline Kinase A1 and A2 Isoforms. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, C.S.; Yin, K.B.; Cun, S.T.W.; Ling, F.L. Expression Profiling of Choline and Ethanolamine Kinases in MCF7, HCT116 and HepG2 Cells, and the Transcriptional Regulation by Epigenetic Modification. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saeedi, F.; Welch, A.E.; Smith, T.A.D. [Methyl-3H]Choline Incorporation into MCF7 Tumour Cells: Correlation with Proliferation. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2005, 32, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Y.; Salem, N.; Corn, D.J.; Erokwu, B.; Tian, H.; Wang, F.; Lee, Z. Transport and Metabolism of Radiolabeled Choline in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 2077–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| HepG2 | MCF7 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ChoP | PC | Total | ChoP | PC | |
| Control | 32.11 ± 2.09 | 23.74 ± 1.56 | 7.15 ± 0.61 | 13.46 ± 0.99 | 9.64 ± 0.62 | 2.21 ± 0.62 |
| 1 μM PL48 | 20.89 ± 1.33 * | 16.3 ± 1.49 * | 3.37 ± 0.30 * | 10.22 ± 0.41 * | 6.70 ± 0.63 * | 2.38 ± 0.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
García-Molina, P.; Sola-Leyva, A.; Luque-Navarro, P.M.; Laso, A.; Ríos-Marco, P.; Ríos, A.; Lanari, D.; Torretta, A.; Parisini, E.; López-Cara, L.C.; et al. Anticancer Activity of the Choline Kinase Inhibitor PL48 Is Due to Selective Disruption of Choline Metabolism and Transport Systems in Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020426
García-Molina P, Sola-Leyva A, Luque-Navarro PM, Laso A, Ríos-Marco P, Ríos A, Lanari D, Torretta A, Parisini E, López-Cara LC, et al. Anticancer Activity of the Choline Kinase Inhibitor PL48 Is Due to Selective Disruption of Choline Metabolism and Transport Systems in Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(2):426. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020426
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcía-Molina, Pablo, Alberto Sola-Leyva, Pilar M. Luque-Navarro, Alejandro Laso, Pablo Ríos-Marco, Antonio Ríos, Daniela Lanari, Archimede Torretta, Emilio Parisini, Luisa C. López-Cara, and et al. 2022. "Anticancer Activity of the Choline Kinase Inhibitor PL48 Is Due to Selective Disruption of Choline Metabolism and Transport Systems in Cancer Cell Lines" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 2: 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020426
APA StyleGarcía-Molina, P., Sola-Leyva, A., Luque-Navarro, P. M., Laso, A., Ríos-Marco, P., Ríos, A., Lanari, D., Torretta, A., Parisini, E., López-Cara, L. C., Marco, C., & Carrasco-Jiménez, M. P. (2022). Anticancer Activity of the Choline Kinase Inhibitor PL48 Is Due to Selective Disruption of Choline Metabolism and Transport Systems in Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics, 14(2), 426. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14020426








