Iodine Nanoparticles (Niodx™) for Radiotherapy Enhancement of Glioblastoma and Other Cancers: An NCI Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
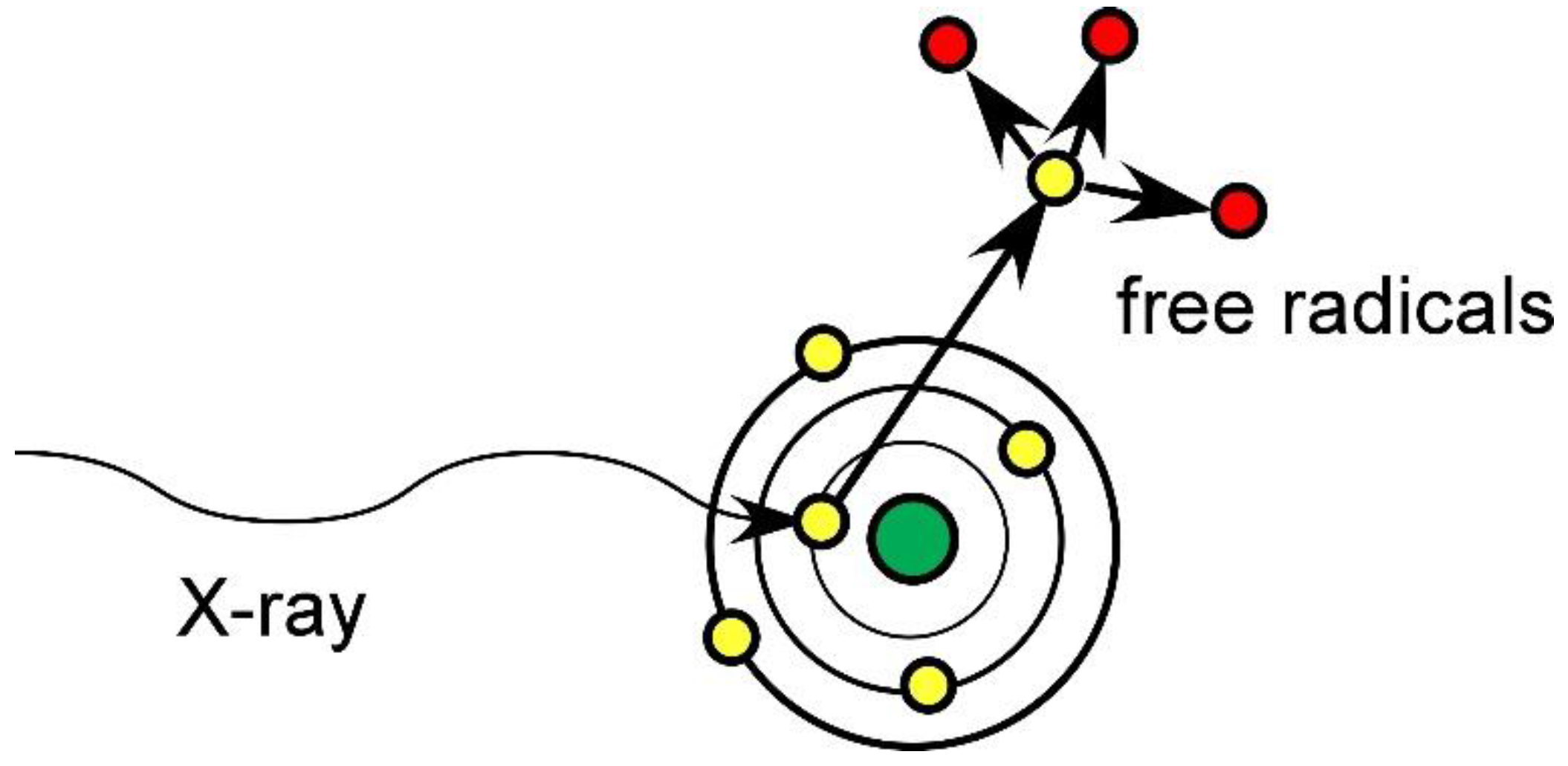
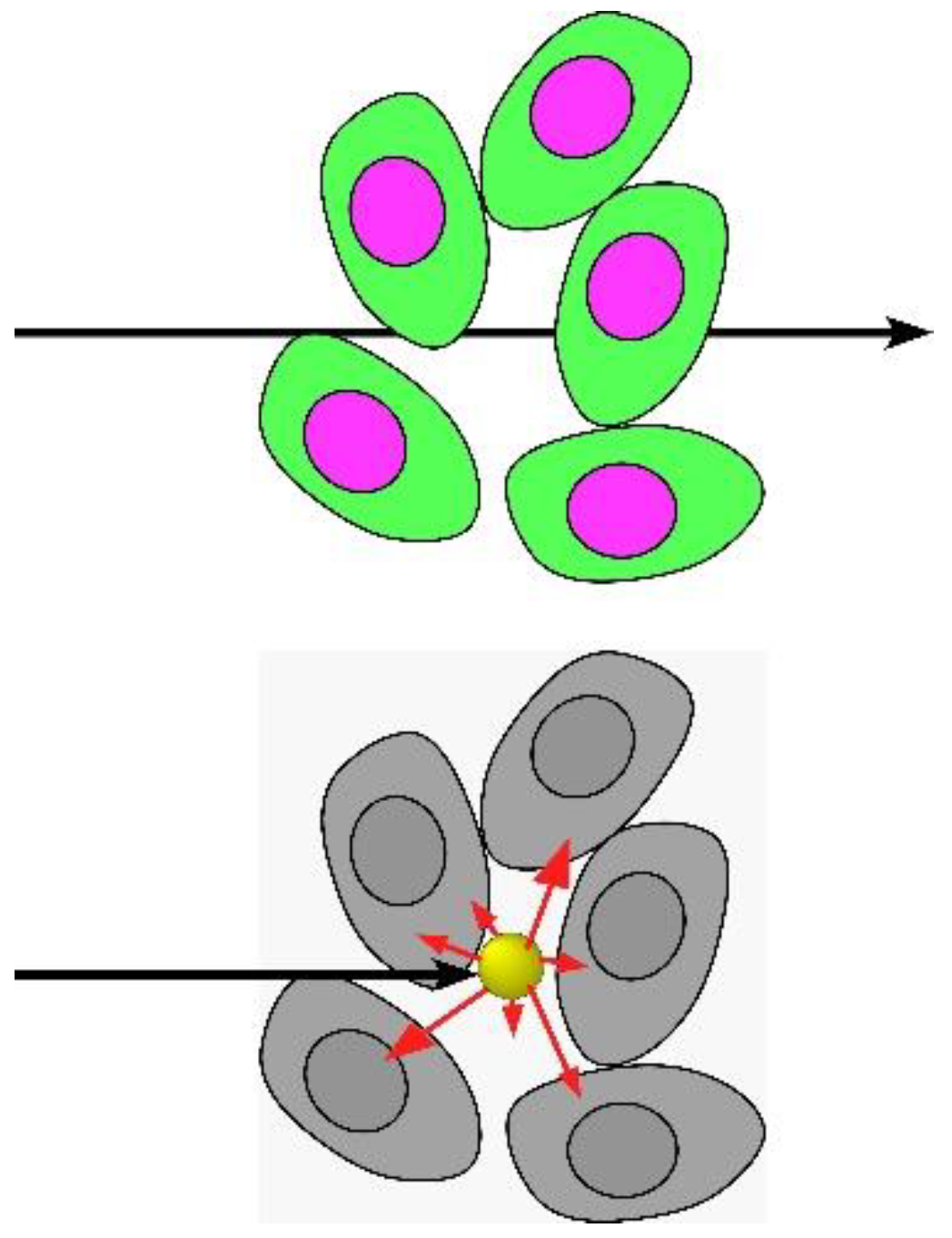
1.1. Mechanism
1.2. Gold Nanoparticle Imaging and Radiotherapy
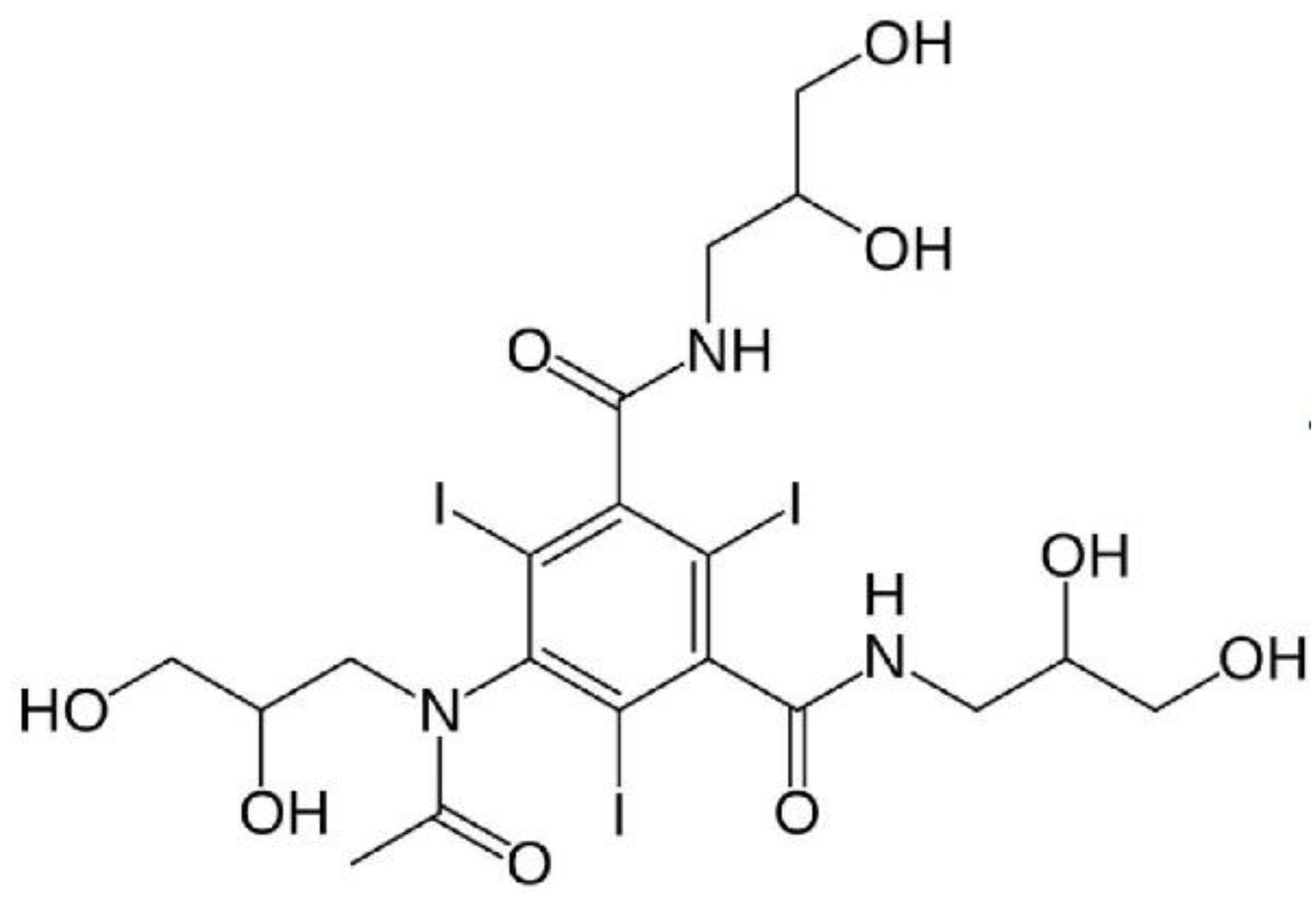
1.3. Iodine Nanoparticles
1.4. Iodine Nanoparticle Imaging
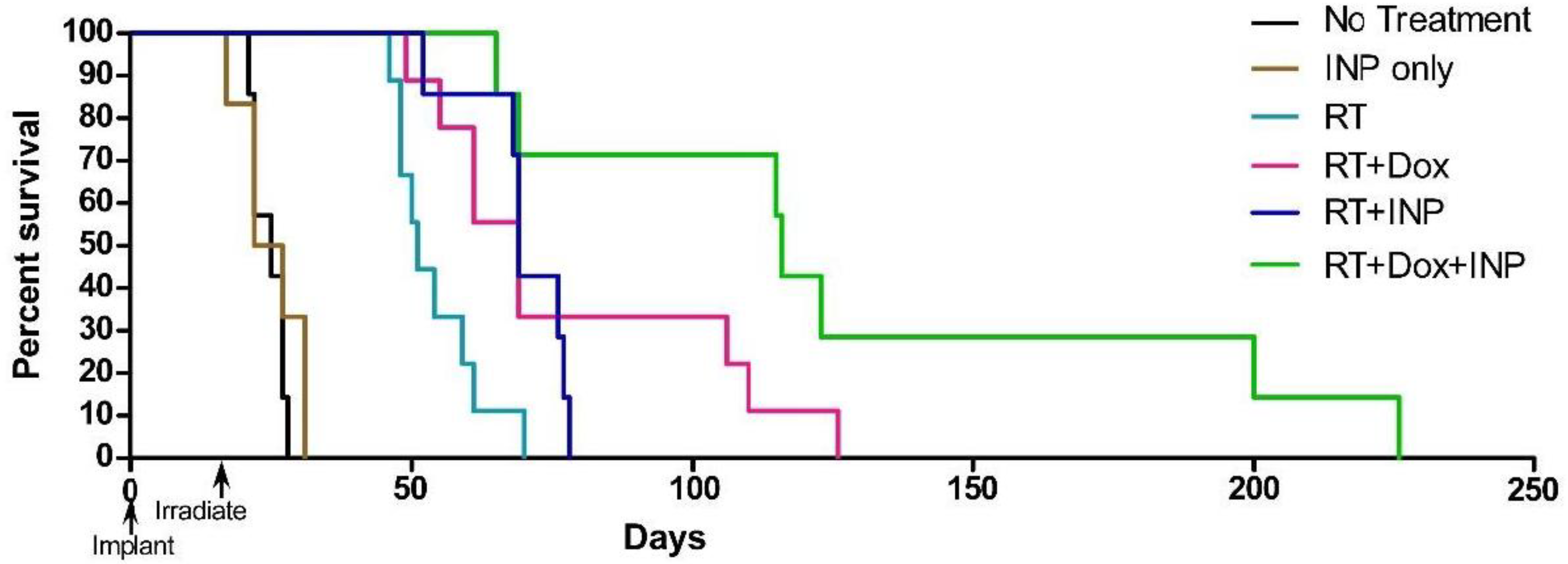
1.5. Iodine Nanoparticle Glioma Therapy
1.6. Iodine Nanoparticle Radiotherapy Synergy with Drugs
1.7. Iodine Nanoparticle Targeting
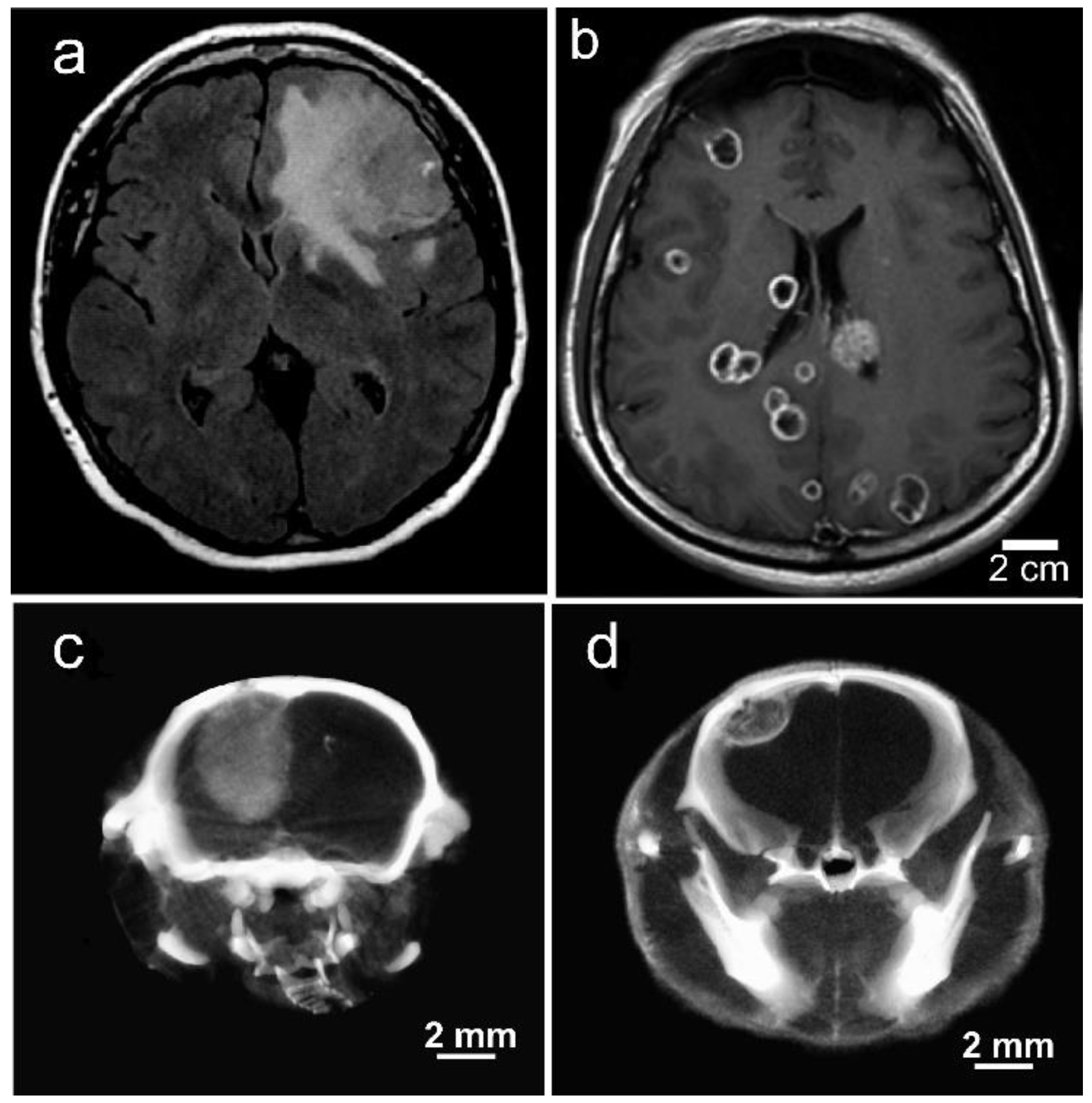
1.8. Iodine-Enhanced Radiotherapy of Brain Metastases
1.9. Iodine Nanoparticle Targeting to Brain Metastases
1.10. Optimal X-ray Energy
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. National Cancer Institute Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Study of Niodx
3.1.1. Sterility, Endotoxin, and Beta-Glucans
3.1.2. Physicochemical Characterization
3.1.3. In Vitro Toxicity Studies
3.1.4. In Vitro Immunological Characterization
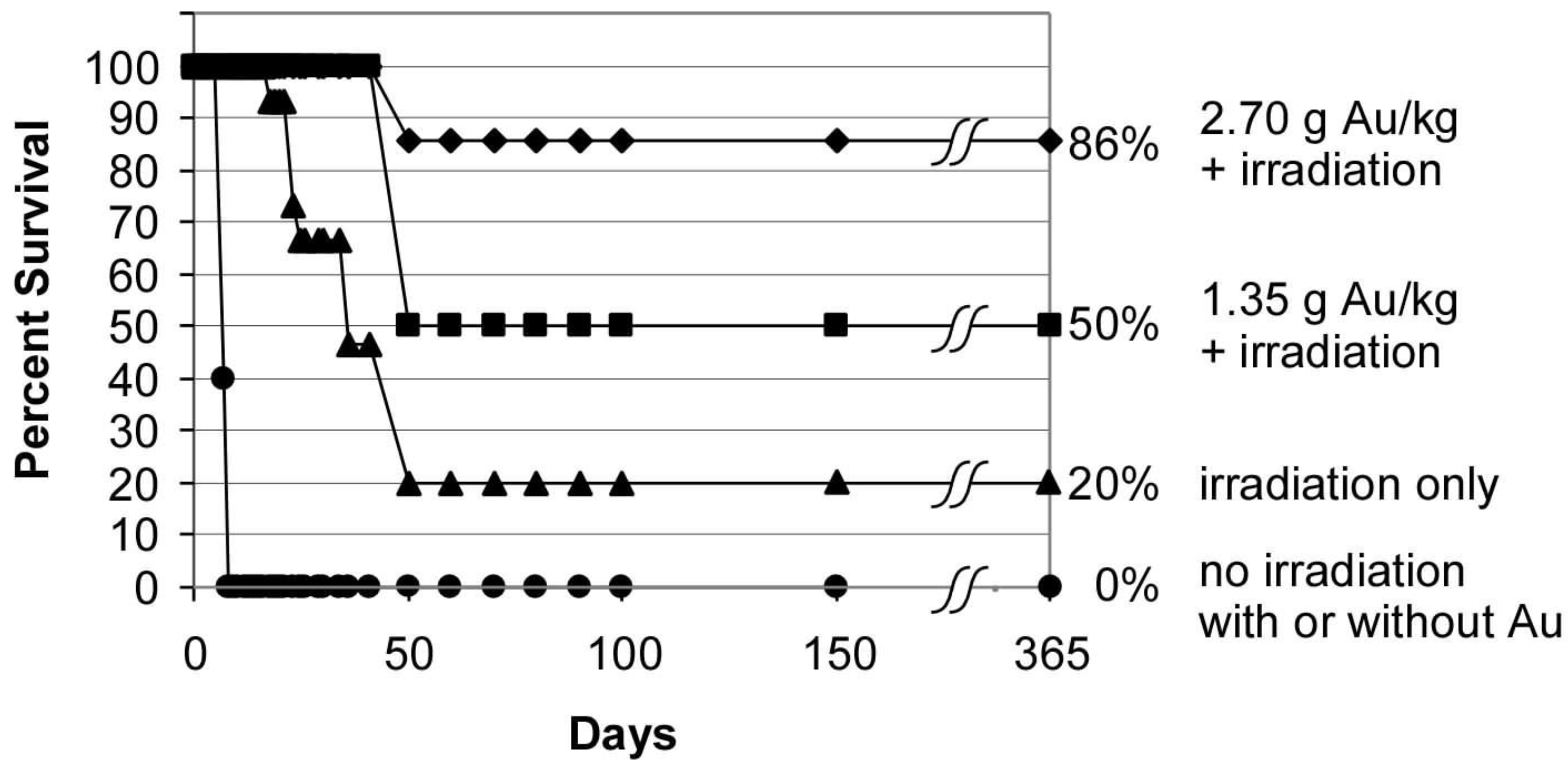
3.1.5. Multidose Toxicity Study (ADME-Tox)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karlsson, J.; Luly, K.M.; Tzeng, S.Y.; Green, J.J. Nanoparticle designs for delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics as brain cancer therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 113999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevastre, A.S.; Costachi, A.; Tataranu, L.G.; Brandusa, C.; Artene, S.A.; Stovicek, O.; Alexandru, O.; Danoiu, S.; Sfredel, V.; Dricu, A. Glioblastoma pharmacotherapy: A multifaceted perspective of conventional and emerging treatments (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boateng, F.; Ngwa, W. Delivery of Nanoparticle-Based Radiosensitizers for Radiotherapy Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butterworth, K.T.; McMahon, S.J.; Currell, F.J.; Prise, K.M. Physical basis and biological mechanisms of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. Nanoscale. 2012, 4, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, D.; Sebastian, S.; Le, Q.V.; Thierry, B.; Kempson, I. Chemical Mechanisms of Nanoparticle Radiosensitization and Radioprotection: A Review of Structure-Function Relationships Influencing Reactive Oxygen Species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kempson, I. Mechanisms of nanoparticle radiosensitization. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, S.; Connolly, C.; Schettino, G.; Butterworth, K.T.; Prise, K.M. Biological mechanisms of gold nanoparticle radiosensitization. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Ramirez-Loera, C.; Malouff, T.D.; Seneviratne, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Trifiletti, D.M. Novel Strategies for Nanoparticle-Based Radiosensitization in Glioblastoma. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuemann, J.; Bagley, A.F.; Berbeco, R.; Bromma, K.; Butterworth, K.T.; Byrne, H.L.; Chithrani, B.D.; Cho, S.H.; Cook, J.R.; Favaudon, V.; et al. Roadmap for metal nanoparticles in radiation therapy: Current status, translational challenges, and future directions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 21RM02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mu, X.; He, H.; Zhang, X.D. Cancer Radiosensitizers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 24–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Ridwan, S.M.; Stanishevskiy, F.Y.; Smilowitz, H.M. Iodine nanoparticle radiotherapy of human breast cancer growing in the brains of athymic mice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiers, F.W. The influence of energy absorption and electron range on dosage in irradiated bone. Brit. J. Radiol. 1949, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos Mello, R.; Callisen, H.; Winter, J.; Kagan, A.R.; Norman, A. Radiation dose enhancement in tumors with iodine. Med. Phys. 1983, 10, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.H.; Norman, A.; Ingram, M.; Aoki, C.; Solberg, T.; Mesa, A. First radiotherapy of human metastatic brain tumors delivered by a computerized tomography scanner (CTRx). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 45, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.F.; Balosso, J.; Renier, M.; Elleaume, H.; Estève, F.; Berkvens, P.; Nemoz, C.; Brochard, T.; Tessier, A.; Verry, C.; et al. Synchrotron Stereotactic Radiation Therapy: A Report on Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial Achievements, Ongoing Developments, and Long-Term Prospects. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, E624–E625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obeid, L.; Deman, P.; Tessier, A.; Balosso, J.; Esteve, F.; Adam, J.F. Absolute perfusion measurements and associated iodinated contrast agent time course in brain metastasis: A study for contrast-enhanced radiotherapy. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.B.; Kivisaari, L.; Kormano, M. Contrast enhancement pharmacokinetics of six ionic and nonionic contrast media. Investig. Radiol. 1983, 18, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Slatkin, D.N.; Smilowitz, H.M. The use of gold nanoparticles to enhance radiotherapy in mice. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, N309–N315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J. Intestinal stem cell injury and protection during cancer therapy. Transl. Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 384–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Smilowitz, H.M.; O’Connor, M.J.; Dilmanian, F.A.; Slatkin, D.N. Gold nanoparticle imaging and radiotherapy of brain tumors in mice. Nanomedicine (London) 2013, 8, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Ridwan, S.M.; Stanishevskiy, Y.; Smilowitz, N.R.; Davis, J.; Smilowitz, H.M. Small, Long Blood Half-Life Iodine Nanoparticle for Vascular and Tumor Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fleming, C.J.; Salisbury, E.L.; Kirwan, P.; Painter, D.M.; Barnetson, R.S. Chrysiasis after low-dose gold and UV light exposure. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1996, 34, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadrup, N.; Lam, H.R. Oral toxicity of silver ions, silver nanoparticles and colloidal silver—A review. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 68, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.B.; Watson, A.D. Metal-Based X-ray Contrast Media. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2353–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, A.; Khan, R.; Ghosh, M.K. Blood brain barrier: A challenge for effectual therapy of brain tumors. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hainfeld, J.F.; Ridwan, S.M.; Stanishevskiy, Y.; Panchal, R.; Slatkin, D.N.; Smilowitz, H.M. Iodine nanoparticles enhance radiotherapy of intracerebral human glioma in mice and increase efficacy of chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashton, J.R.; Castle, K.D.; Qi, Y.; Kirsch, D.G.; West, J.L.; Badea, C.T. Dual-Energy CT Imaging of Tumor Liposome Delivery After Gold Nanoparticle-Augmented Radiation Therapy. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1782–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heggannavar, G.B.; Hiremath, C.G.; Achari, D.D.; Pangarkar, V.G.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Development of Doxorubicin-Loaded Magnetic Silica-Pluronic F-127 Nanocarriers Conjugated with Transferrin for Treating Glioblastoma across the Blood-Brain Barrier Using an in Vitro Model. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8017–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, S.; Karagiannis, T.C. Transferrin receptor-mediated endocytosis: A useful target for cancer therapy. J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, E.A.; Davis, M.E. Method of establishing breast cancer brain metastases affects brain uptake and efficacy of targeted, therapeutic nanoparticles. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2019, 4, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choudhury, H.; Pandey, M.; Chin, P.X.; Phang, Y.L.; Cheah, J.Y.; Ooi, S.C.; Mak, K.K.; Pichika, M.R.; Kesharwani, P.; Hussain, Z.; et al. Transferrin receptors-targeting nanocarriers for efficient targeted delivery and transcytosis of drugs into the brain tumors: A review of recent advancements and emerging trends. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 1545–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Liu, R.; Xia, G.; Wang, F.; Chen, B. Applications of daunorubicin-loaded PLGA-PLL-PEG-Tf nanoparticles in hematologic malignancies: An in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Huang, G. Liposome encapsulated of temozolomide for the treatment of glioma tumor: Preparation, characterization and evaluation. Drug Discov. Ther. 2015, 9, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lam, F.C.; Morton, S.W.; Wyckoff, J.; Vu Han, T.L.; Hwang, M.K.; Maffa, A.; Balkanska-Sinclair, E.; Yaffe, M.B.; Floyd, S.R.; Hammond, P.T. Enhanced efficacy of combined temozolomide and bromodomain inhibitor therapy for gliomas using targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wu, H.; Peng, B.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Deng, G.; Zou, P.; Liu, J.; Chen, A.T.; Li, D.; et al. Vessel-Targeting Nanoclovers Enable Noninvasive Delivery of Magnetic Hyperthermia-Chemotherapy Combination for Brain Cancer Treatment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 8111–8118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridwan, S.M.; Hainfeld, J.F.; Ross, V.; Stanishevskiy, Y.; Smilowitz, H.M. Novel Iodine nanoparticles target vascular mimicry in intracerebral triple negative human MDA-MB-231 breast tumors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Assay Cascade Protocols. Available online: https://ncl.cancer.gov/resources/assay-cascade-protocols (accessed on 7 February 2022).
- Krause, W.; Press, W.R. Influence of contrast media on blood coagulation. Investig. Radiol. 1997, 32, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
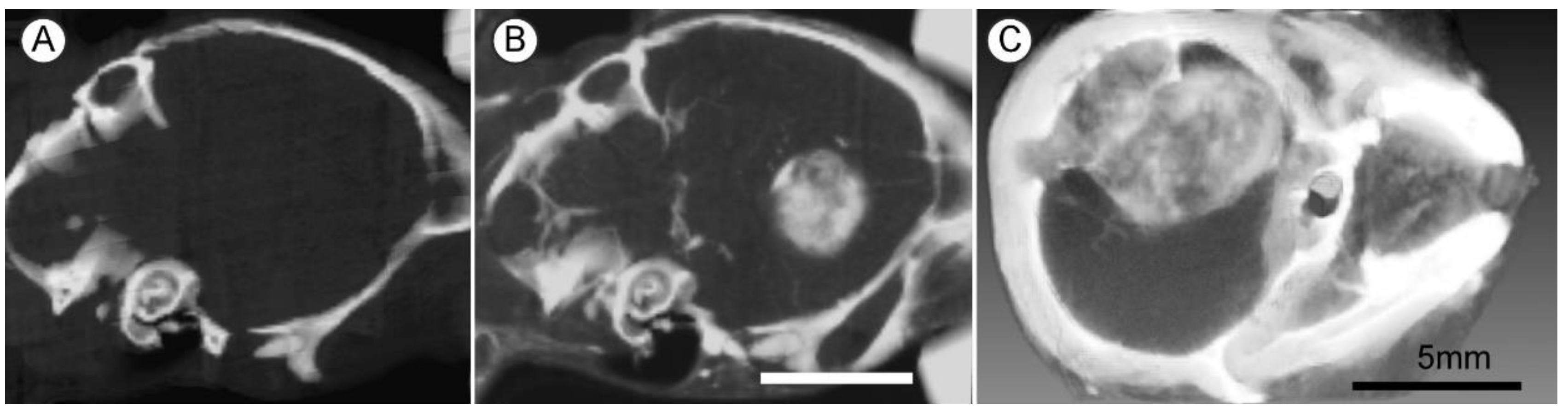
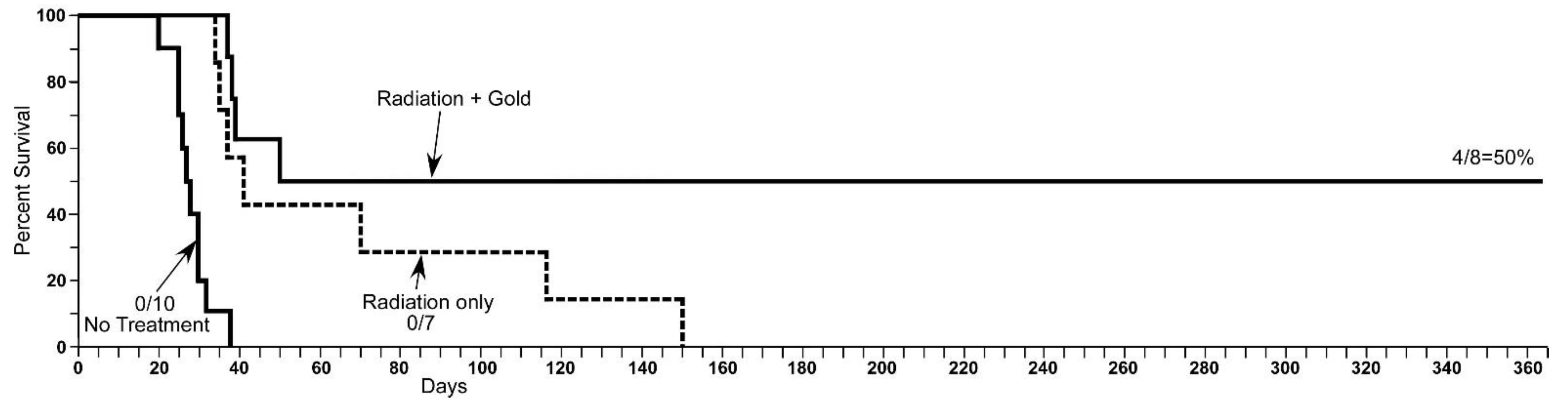

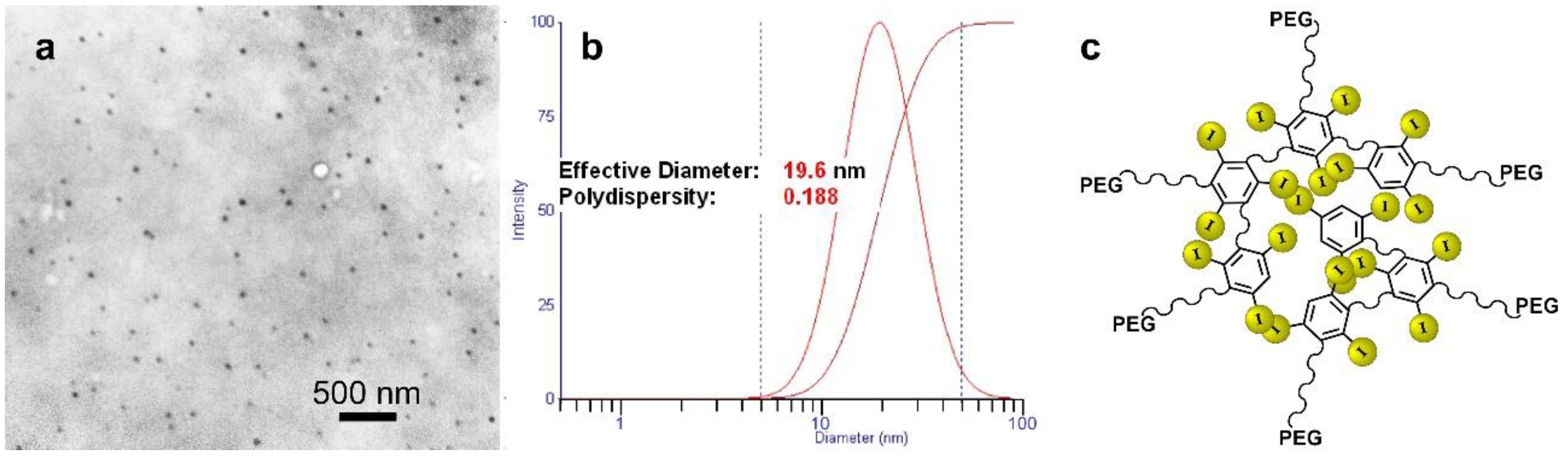
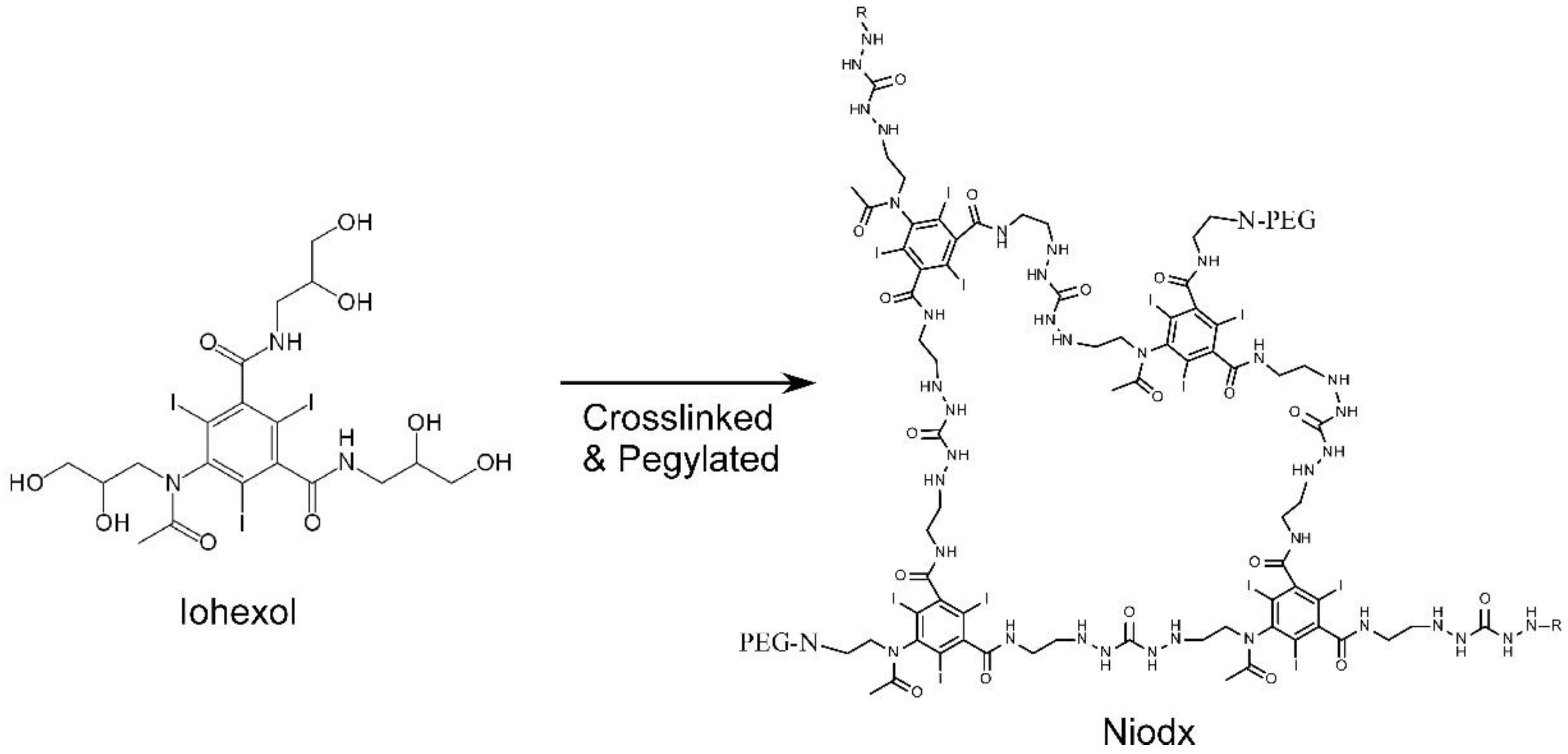


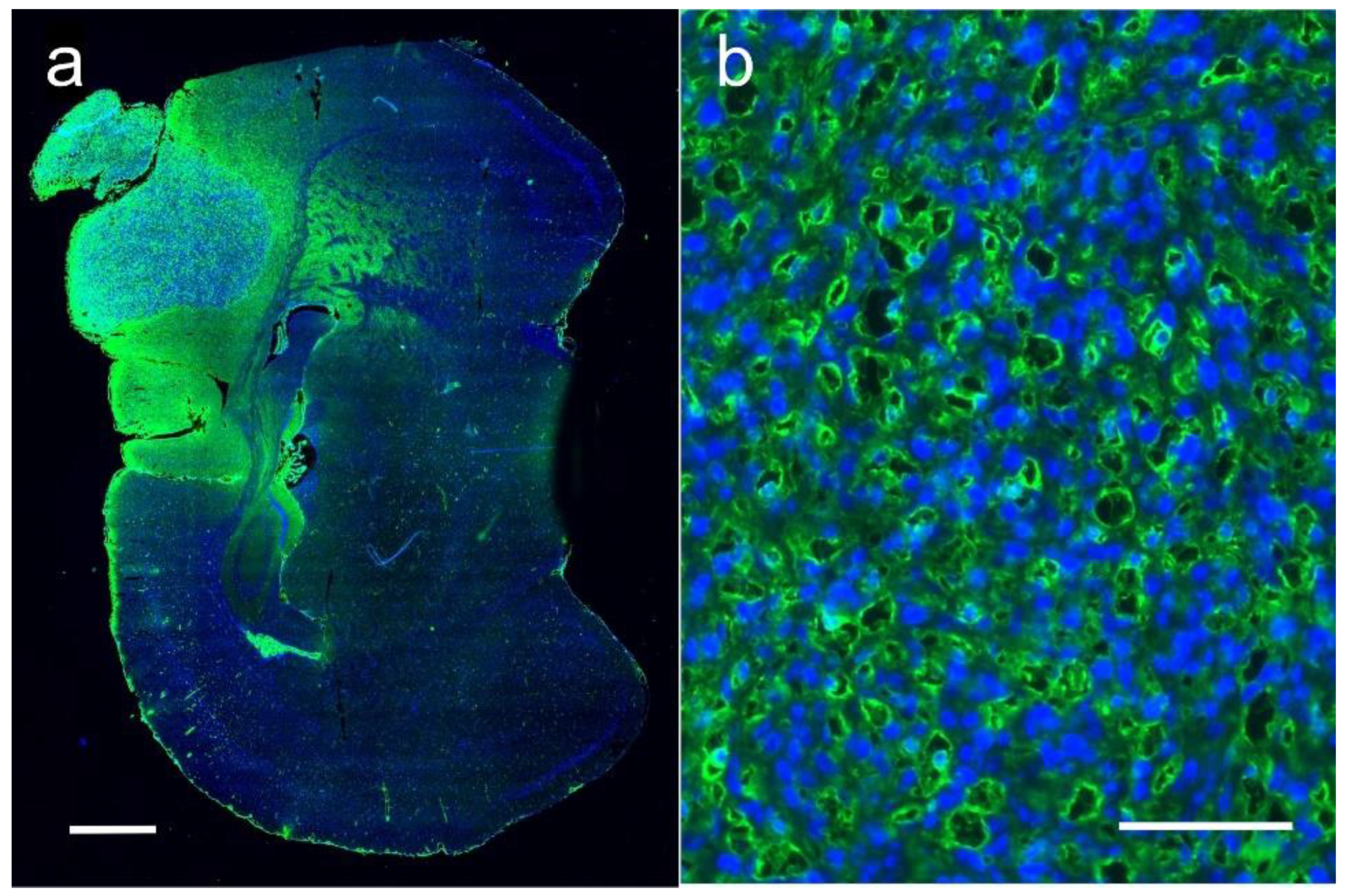
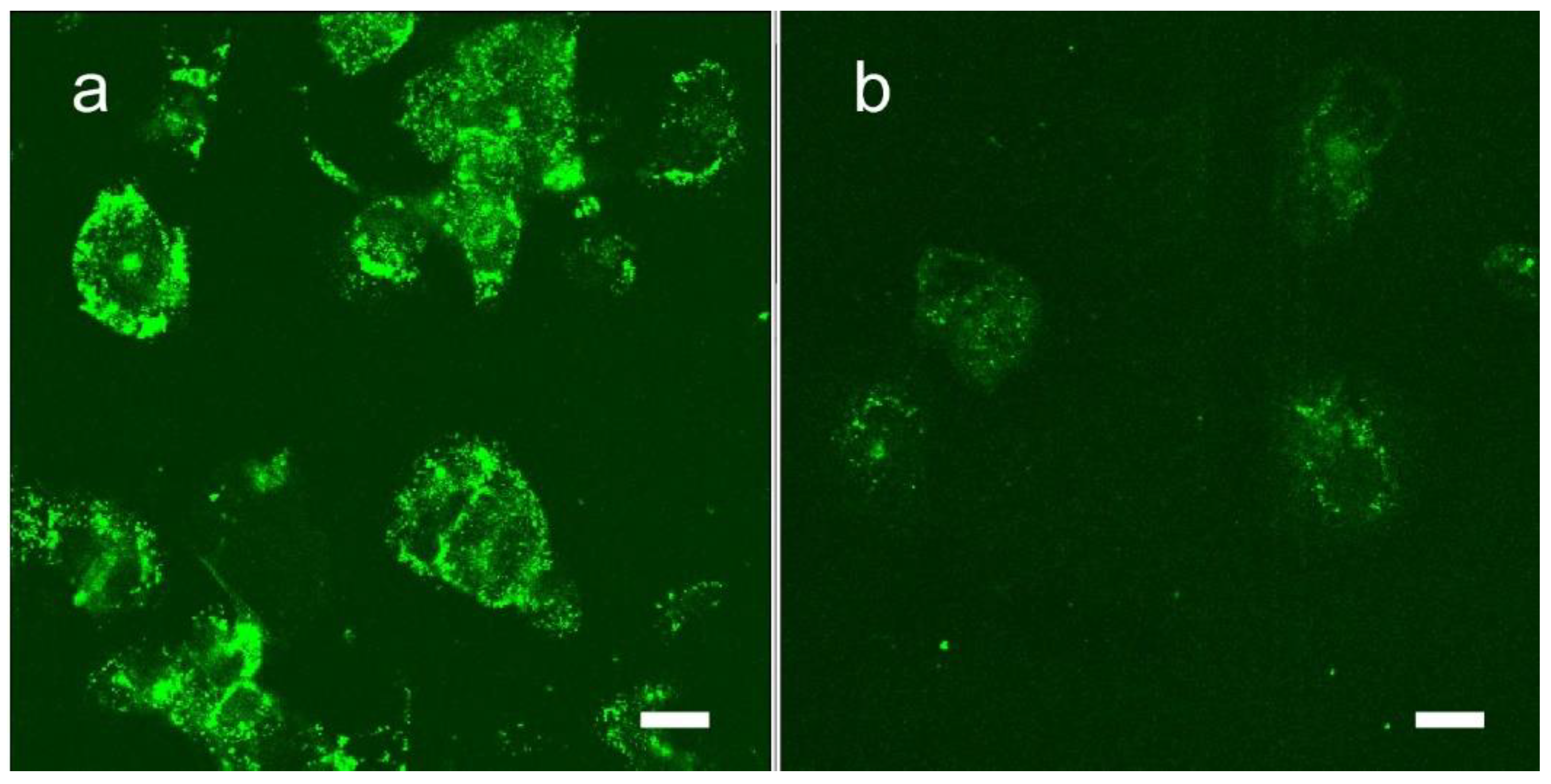
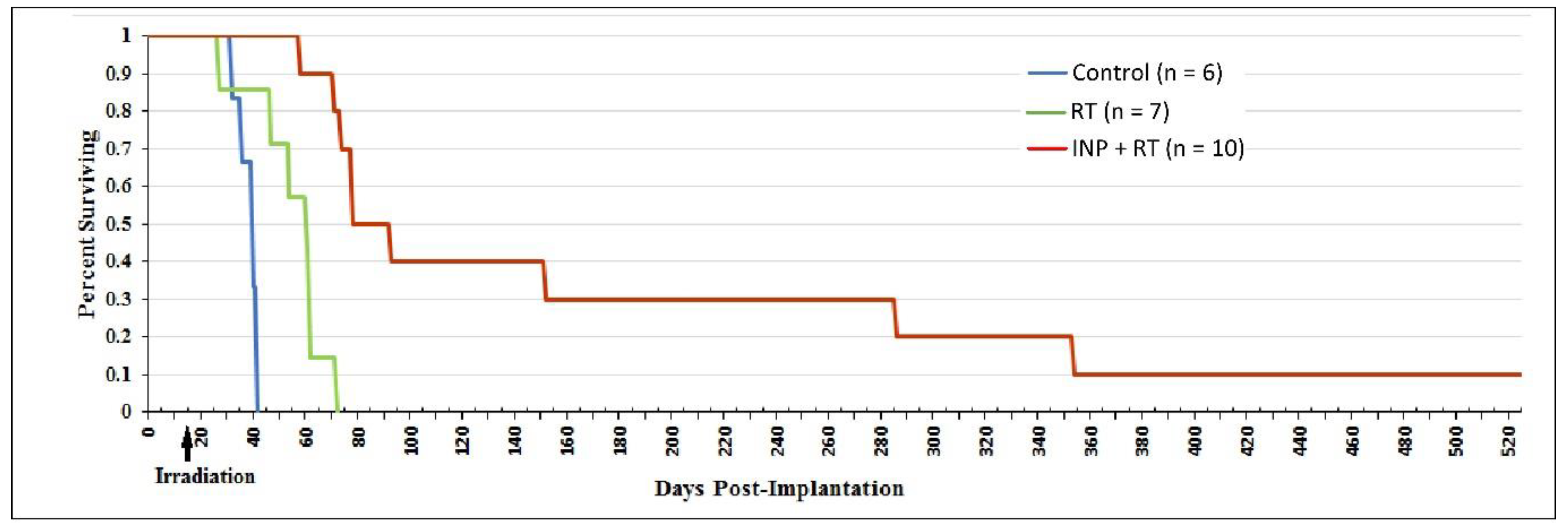
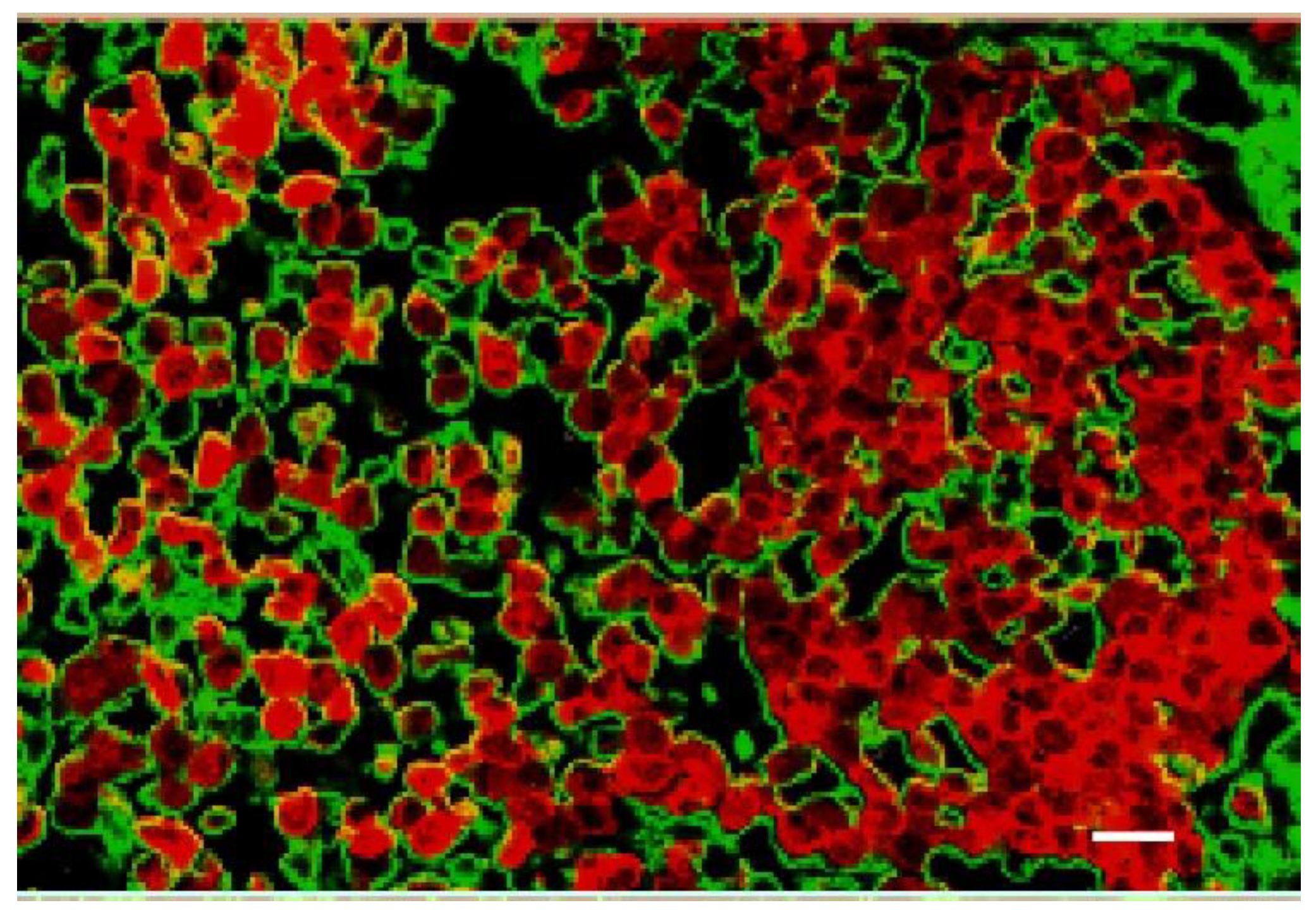
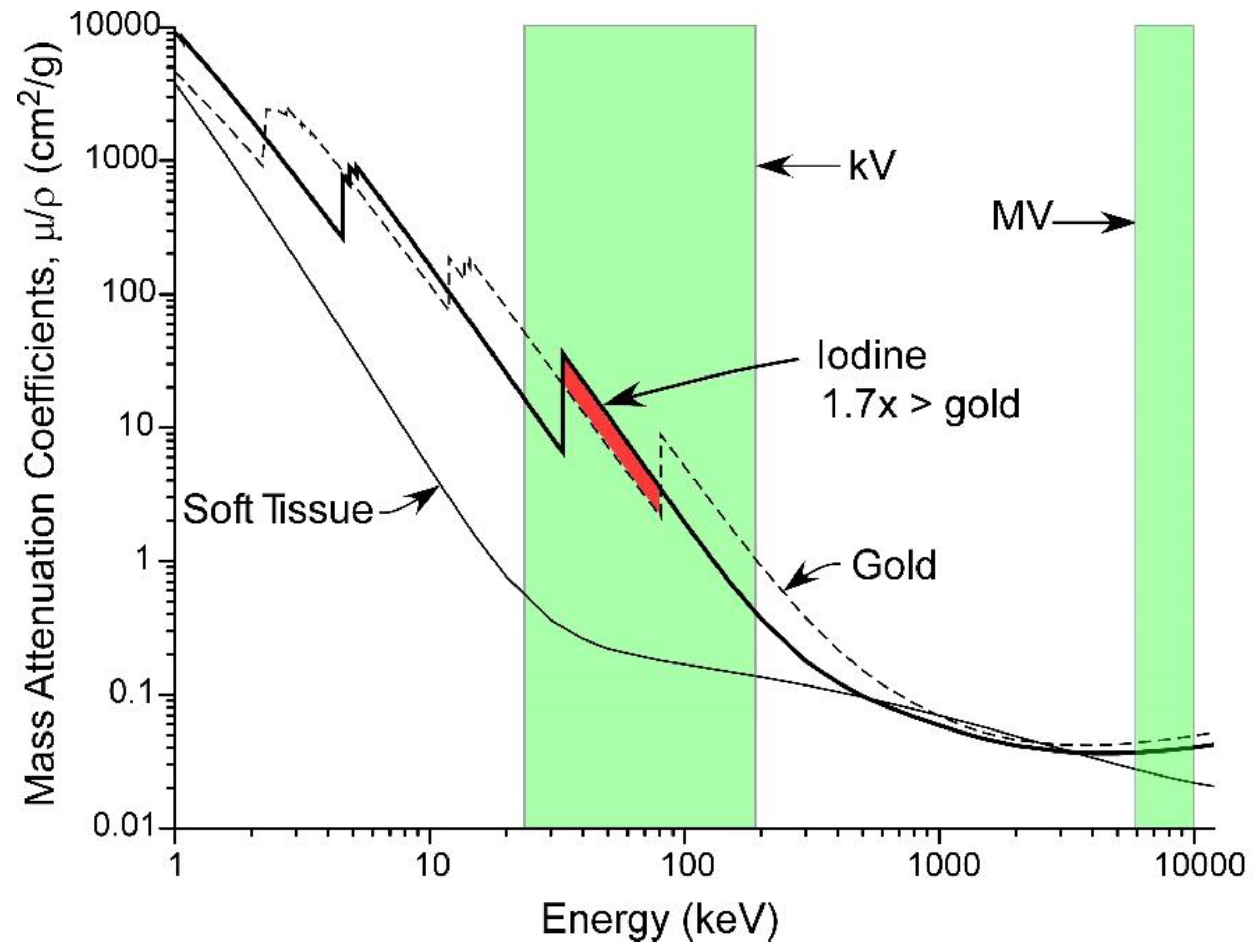
| Tumor Center (Average) | Growing Edge (Average) | Peaks at Growing Edge (Average) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| %Iodine | 1.13 ± 0.35 | 2.9 ± 0.54 | 4.52 ± 0.07 |
| DEF | 2.77 | 5.48 | 8.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hainfeld, J.F.; Ridwan, S.M.; Stanishevskiy, Y.; Smilowitz, H.M. Iodine Nanoparticles (Niodx™) for Radiotherapy Enhancement of Glioblastoma and Other Cancers: An NCI Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Study. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030508
Hainfeld JF, Ridwan SM, Stanishevskiy Y, Smilowitz HM. Iodine Nanoparticles (Niodx™) for Radiotherapy Enhancement of Glioblastoma and Other Cancers: An NCI Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Study. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(3):508. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030508
Chicago/Turabian StyleHainfeld, James F., Sharif M. Ridwan, Yaroslav Stanishevskiy, and Henry M. Smilowitz. 2022. "Iodine Nanoparticles (Niodx™) for Radiotherapy Enhancement of Glioblastoma and Other Cancers: An NCI Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Study" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 3: 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030508
APA StyleHainfeld, J. F., Ridwan, S. M., Stanishevskiy, Y., & Smilowitz, H. M. (2022). Iodine Nanoparticles (Niodx™) for Radiotherapy Enhancement of Glioblastoma and Other Cancers: An NCI Nanotechnology Characterization Laboratory Study. Pharmaceutics, 14(3), 508. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030508






