Smart Injectable Chitosan Hydrogels Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Drug Loading of Chitosan Hydrogel
2.3. Physicochemical Characterization of the Modified Hydrogel
Drug Content, Visual Inspection, and PH Determination
2.4. Rheological Studies
2.5. Injectability
2.6. In Vitro Release of 5-FU
2.7. In Vitro Antitumor Activity (MTT Assay)
2.8. In Vivo Antitumor Studies
2.8.1. Animal Preparation
2.8.2. Tumor Volume and Growth Measurement
2.8.3. Effects on the Lifespan
2.8.4. Histopathological Appraisals and Traits
2.8.5. Tumor Markers Detection in Blood
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Formulation of Thermosensitive Hydrogel Systems
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization of the Modified Hydrogel System
Drug Content, Visual Inspection, and pH Determination
3.3. Rheological Studies
3.4. In Vitro Drug Release
3.5. Injectability
3.6. In Vitro Antitumor Activity
3.7. In Vivo Antitumor Activity
3.7.1. Effect of Cytotoxicity on Relative Tumor Volume
3.7.2. Cytotoxic Impact on Rat’s Body Weight and Mortality
3.7.3. Histopathological Appraisals and Traits
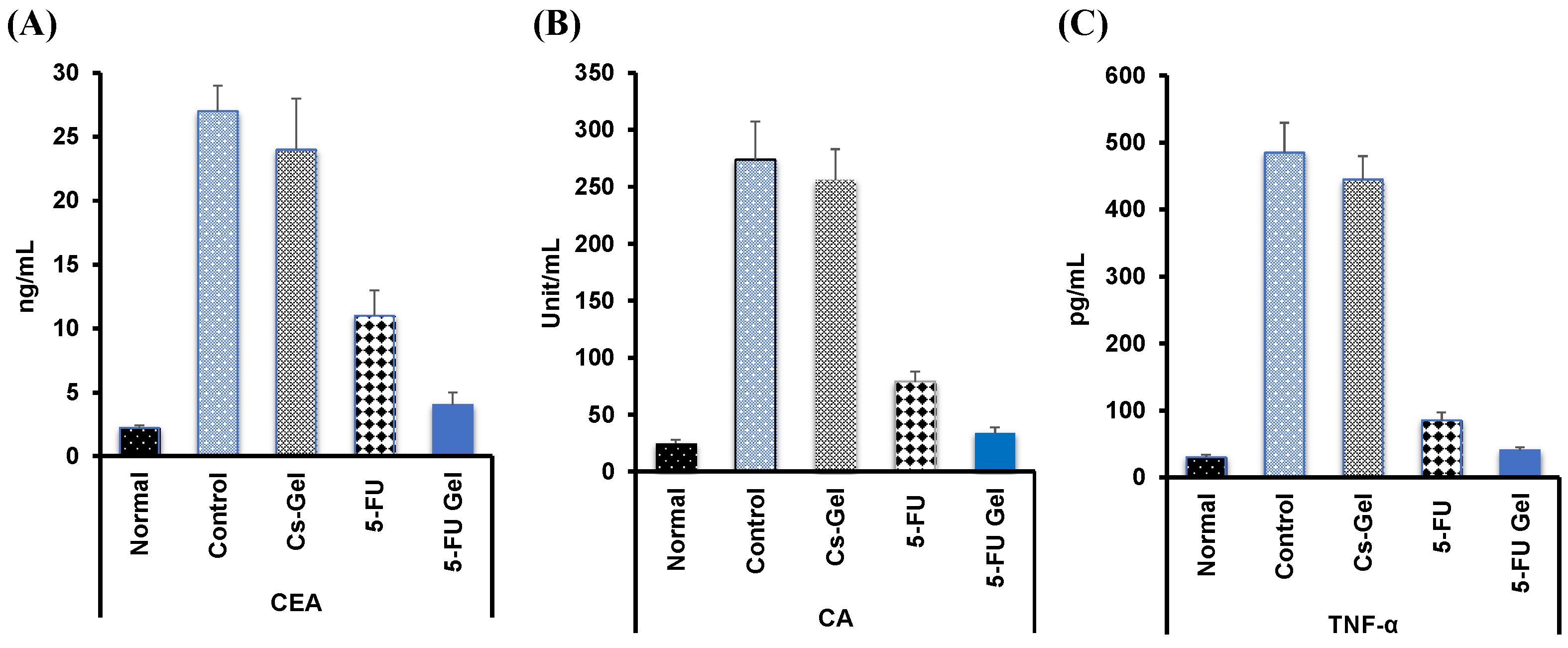
3.7.4. Tumor Markers Detection in Blood
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kassani, S.H.; Kassani, P.H.; Wesolowski, M.J.; Schneider, K.A.; Deters, R. Breast cancer diagnosis with transfer learning and global pooling. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 519–524. [Google Scholar]
- Kamalakannan, J.; Babu, M.R. Classification of breast abnormality using decision tree based on GLCM features in mammograms. Int. J. Comput. Aided Eng. Technol. 2018, 10, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, B.L.; Judson, I. Surgery and imatinib in the management of GIST: Emerging approaches to adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2004, 11, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, E.; DeVita, V.T., Jr. Physicians’ Cancer Chemotherapy Drug Manual 2019; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midena, E.; Degli Angeli, C.; Valenti, M.; De Belvis, V.; Boccato, P. Treatment of conjunctival squamous cell carcinoma with topical 5-fluorouracil. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 84, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.S.; Flaks, J.G.; Barner, H.D.; Loeb, M.R.; Lichtenstein, J. The mode of action of 5-fluorouracil and its derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1958, 44, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ta, H.T.; Dass, C.R.; Dunstan, D.E. Injectable chitosan hydrogels for localised cancer therapy. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Qin, L.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Cui, W.; Li, F.; Xiang, N.; He, X. Injectable thermosensitive hydrogel-based drug delivery system for local cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, H.; Naficy, S. Drug Delivery Based on Stimuli-Responsive Injectable Hydrogels for Breast Cancer Therapy: A Review. Gels 2022, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel-Gariepy, E.; Shive, M.; Bichara, A.; Berrada, M.; Le Garrec, D.; Chenite, A.; Leroux, J.C. A thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogel for the local delivery of paclitaxel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, S.K.S.; Rai, A.K.; Singh, S. Formulation of Thermosensitive Hydrogel Containing Cyclodextrin for Controlled Drug Delivery of Camptothecin. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, Y.I.; Park, S.; Jeong, S.Y.; Yoo, H.S. In vivo and in vitro anti-cancer activity of thermo-sensitive and photo-crosslinkable doxorubicin hydrogels composed of chitosan-doxorubicin conjugates. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 73, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, U.V.; Udupa, N. Methotrexate loaded chitosan and chitin microspheres—In vitro characterization and pharmacokinetics in mice bearing Ehrlich ascites carcinoma. J. Microencapsul. 1998, 15, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, B.; Dong, S. Assembly Pattern of Supramolecular Hydrogel Induced by Lower Critical Solution Temperature Behavior of Low-Molecular-Weight Gelator. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z. Thermo-sensitive hydrogels for delivering biotherapeutic molecules: A review. Saudi Pharm. J. 2019, 27, 990–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Biswas, S.; Nurus Sakib, M.; Rashid, T.U. Chitosan based bioactive materials in tissue engineering applications—A review. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. A review on chitosan and its nanocomposites in drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, M.; Hicks, E.A.; Rambarran, T.; Sheardown, H. Thermo-sensitivity and erosion of chitosan crosslinked poly[N-isopropylacrylamide-co-(acrylic acid)-co-(methyl methacrylate)] hydrogels for application to the inferior fornix. Acta Biomater. 2022, 141, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, N.M.; Awad, G.A.; Mortada, N.D.; Abd Elhady, S.S. Enhanced bioavailability of metoclopramide HCl by intranasal administration of a mucoadhesive in situ gel with modulated rheological and mucociliary transport properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 32, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malli, S.; Bories, C.; Pradines, B.; Loiseau, P.M.; Ponchel, G.; Bouchemal, K. In situ forming pluronic(R) F127/chitosan hydrogel limits metronidazole transmucosal absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherif, A.Y.; Mahrous, G.M.; Alanazi, F.K. Novel in-situ gel for intravesical administration of ketorolac. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karatas, A.; Boluk, A.; Algan, A. Poloxamer/Chitosan In Situ Gelling System for Ocular Delivery of Ofloxacin. Curr. Drug Ther. 2015, 9, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Joung, Y.K.; Na, J.S.; Lee, M.C.; Park, K.D. Thermosensitive chitosan-Pluronic hydrogel as an injectable cell delivery carrier for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Couce, J.; Tomas, M.; Fuentes, G.; Que, I.; Almirall, A.; Cruz, L.J. Chitosan/Pluronic F127 Thermosensitive Hydrogel as an Injectable Dexamethasone Delivery Carrier. Gels 2022, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokhade, A.P.; Shelke, N.B.; Patil, S.A.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Novel hydrogel microspheres of chitosan and pluronic F-127 for controlled release of 5-fluorouracil. J. Microencapsul. 2007, 24, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Anwar, N. Highly Porous pH-Responsive Carboxymethyl Chitosan-Grafted-Poly (Acrylic Acid) Based Smart Hydrogels for 5-Fluorouracil Controlled Delivery and Colon Targeting. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2019, 2019, 6579239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Sabbagh, C.; Seguin, J.; Agapova, E.; Kramerich, D.; Boudy, V.; Mignet, N. Thermosensitive hydrogels for local delivery of 5-fluorouracil as neoadjuvant or adjuvant therapy in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 157, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Chenite, A.; Felt-Baeyens, O.; Mayer, J.; Gurny, R. Pseudo-thermosetting chitosan hydrogels for biomedical application. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 288, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laftah, W.A.; Hashim, S.; Ibrahim, A.N. Polymer hydrogels: A review. Polym. -Plast. Technol. Eng. 2011, 50, 1475–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlt, C. A simple capillary viscometer. Phys. Educ. 1975, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, K. Pharmaceutical Studies on the Availability of Sildenafil Citrate from Certain Topical Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 2016, 7, 199–221. [Google Scholar]
- Baloglu, E.; Karavana, S.Y.; Hyusein, I.Y.; Kose, T. Design and formulation of mebeverine HCl semisolid formulations for intraorally administration. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramstack, J.M.; Riley, M.G.I.; Zale, S.E.; Hotz, J.M.; Johnson, O.L. Preparation of Injectable Suspensions Having Improved Injectability. Patent Application No. US6495164B1, 21 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. In Cancer Cell Culture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Sladowski, D.; Steer, S.J.; Clothier, R.H.; Balls, M. An improved MIT assay. J. Immunol. Methods 1993, 157, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (U.S.). Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; Institute for Laboratory Animal Research (U.S.); National Academies Press (U.S.); Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Research Council (U.S.): Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Volume 25, 220p. [Google Scholar]
- Arregui, J.R.; Kovvasu, S.P.; Betageri, G.V. Daptomycin Proliposomes for Oral Delivery: Formulation, Characterization, and In Vivo Pharmacokinetics. AAPS PharmSciTech 2018, 19, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abba, M.C.; Zhong, Y.; Lee, J.; Kil, H.; Lu, Y.; Takata, Y.; Simper, M.S.; Gaddis, S.; Shen, J.; Aldaz, C.M. DMBA induced mouse mammary tumors display high incidence of activating Pik3caH1047 and loss of function Pten mutations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 64289–64299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faustino-Rocha, A.; Oliveira, P.A.; Pinho-Oliveira, J.; Teixeira-Guedes, C.; Soares-Maia, R.; Da Costa, R.G.; Colaco, B.; Pires, M.J.; Colaco, J.; Ferreira, R. Estimation of rat mammary tumor volume using caliper and ultrasonography measurements. Lab. Anim. 2013, 42, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Cai, Y.; Yuan, M.; Ma, L.; Qiu, M.; Su, J. Development of a 5-fluorouracil-loaded PLGA microsphere delivery system by a solid-in-oil-in-hydrophilic oil (S/O/hO) novel method for the treatment of tumors. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2405–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Habib, F.; Hassan, M.; Abou El Ela, A.; El Sayeh, A.; Abdel Raheem, R. Different topical formulations of ketorolac tromethamine for anti-inflammatory application and clinical efficacy. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2014, 9, 705–719. [Google Scholar]
- Jagetia, G.C.; Baliga, M.S. Evaluation of anticancer activity of the alkaloid fraction of Alstonia scholaris (Sapthaparna) in vitro and in vivo. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 2006, 20, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Suvarna, K.S.; Layton, C.; Bancroft, J.D. Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Dai, D.; Chen, B.; Tang, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, W. Clinicopathological and Prognostic Significance of Cancer Antigen 15-3 and Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis including 12,993 Patients. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 9863092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montesano, R.; Soulie, P.; Eble, J.A.; Carrozzino, F. Tumour necrosis factor alpha confers an invasive, transformed phenotype on mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 3487–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Ali, Z. Normal Ranges for Acute Phase Reactants (Interleukin-6, Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha and C-reactive Protein) in Umbilical Cord Blood of Healthy Term Neonates at the Mount Hope Women’s Hospital, Trinidad. West Indian Med. J. 2014, 63, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Amin, M.A.; Maswadeh, H.; Alwehaibi, M.N.; Al-Harbi, S.N.; Alharbi, Z.A.; Mohammed, H.A.; Mehany, A.B.M.; Saleem, I. Cetuximab Conjugated with Octreotide and Entrapped Calcium Alginate-beads for Targeting Somatostatin Receptors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, D.C.; Davies, N.M.; Tucker, I.G. Mechanisms by which cyclodextrins modify drug release from polymeric drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Vermani, K.; Garg, S. Hydrogels: From controlled release to pH-responsive drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ding, J. Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hryniuk, W.; Bush, H. The importance of dose intensity in chemotherapy of metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1984, 2, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilurzo, F.; Selmin, F.; Minghetti, P.; Adami, M.; Bertoni, E.; Lauria, S.; Montanari, L. Injectability evaluation: An open issue. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Lum, J.J.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Thompson, C.B. The biology of cancer: Metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A.; Parveen, A. Thermosensitive Chitosan-Based Injectable Hydrogel as an Efficient Anticancer Drug Carrier. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 20450–20460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, J.; Lv, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Chitosan-based nanoparticles for improved anticancer efficacy and bioavailability of mifepristone. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adhikari, H.S.; Yadav, P.N. Anticancer Activity of Chitosan, Chitosan Derivatives, and Their Mechanism of Action. Int. J. Biomater. 2018, 2018, 2952085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sriwastawa, B.; Bhati, L.; Pandey, S.; Pandey, P.; Bannerjee, S.K. Drug delivery systems: An updated review. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Gel Composition | Drug Content | PH | Viscosity (Pa/s) | Gel Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gel (A): (Cs/β-GP) | 102.20 ± 3.80 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | 100.80 ± 1.26 | 29.3 ± 1.5 |
| Gel (B): (Cs/β-GP + PL) | 98.70 ± 2.85 | 6.8 ± 0.2 | 120.34 ± 2.34 | 29.3 ± 1.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdellatif, A.A.H.; Mohammed, A.M.; Saleem, I.; Alsharidah, M.; Al Rugaie, O.; Ahmed, F.; Osman, S.K. Smart Injectable Chitosan Hydrogels Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030661
Abdellatif AAH, Mohammed AM, Saleem I, Alsharidah M, Al Rugaie O, Ahmed F, Osman SK. Smart Injectable Chitosan Hydrogels Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(3):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030661
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdellatif, Ahmed A. H., Ahmed M. Mohammed, Imran Saleem, Mansour Alsharidah, Osamah Al Rugaie, Fatma Ahmed, and Shaaban K. Osman. 2022. "Smart Injectable Chitosan Hydrogels Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Breast Cancer" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 3: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030661
APA StyleAbdellatif, A. A. H., Mohammed, A. M., Saleem, I., Alsharidah, M., Al Rugaie, O., Ahmed, F., & Osman, S. K. (2022). Smart Injectable Chitosan Hydrogels Loaded with 5-Fluorouracil for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Pharmaceutics, 14(3), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14030661










