Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of PVA/CMC-Na Blend Film
2.2. Preparation of Li-HAMNs
2.3. Characterization of Li-HAMNs
2.3.1. The Thickness of the PVA/CMC-Na Blend Film
2.3.2. The Morphology of Li-HAMNs
2.3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3.4. Swelling Rate and Wettability of PVA/CMC-Na Blend Film
2.3.5. Adhesive Performance of the PVA/CMC-Na Blend Film In Vitro
2.3.6. Mechanical Strength of Li-HAMNs
2.4. Drug Loading of Microneedle Patch
2.5. Cytotoxicity Test of Li-HAMNs
2.6. Animal
2.7. Mucosa Insertion Test and LDC Retention In Vivo
2.8. Tail-Flick Test
2.9. Stability Evaluation
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Li-HAMNs
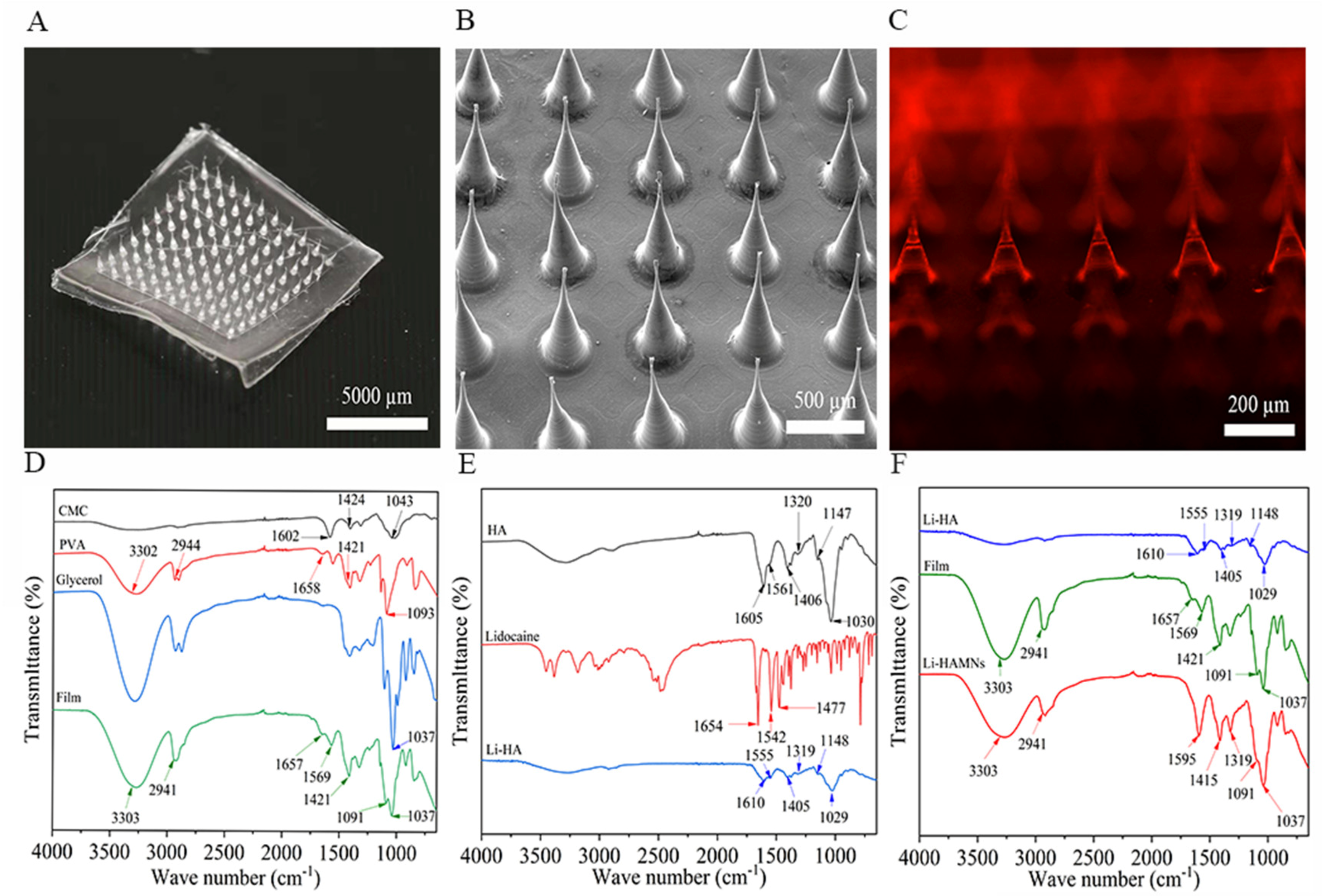
3.1.1. Morphology and Drug Loading of Li-HAMNs
3.1.2. FTIR Analysis of the Li-HAMNs
3.1.3. Swelling Performance and Wettability Test of PVA/CMC-Na Blended Film
3.1.4. Mechanics Strength of Li-HAMNs
3.2. Cytotoxicity Test of Li-HAMNs
3.3. Mucosa Insertion Test and LDC Retention In Vivo
3.4. Tail-Flick Experiment
3.5. Stability Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scrivani, S.J.; Spierings, E.L. Classification and Differential Diagnosis of Oral and Maxillofacial Pain. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 28, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeni, R.Z.; Zheng, M.; Lio, D.C.; Wiraja, C.; Mohd Yusoff, M.F.; Koh, W.T.; Liu, Y.; Goh, B.T.; Xu, C. Targeted Delivery of Anesthetic Agents to Bone Tissues using Conductive Microneedles Enhanced Iontophoresis for Painless Dental Anesthesia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberger, K.; Krause, K.; Maier, K.; Zschocke, I.; Radtke, M.; Augustin, M. Local anesthetic effects of Lidocaine cream: Randomized controlled trial using a standardized prick pain. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2012, 23, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Kang, G.; Jang, M.; Um, D.J.; Shin, J.; Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Jung, H.; Ahn, H.; Gong, S.; et al. Development of Lidocaine-Loaded Dissolving Microneedle for Rapid and Efficient Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochsner, K.N.; Ludlow, D.H.; Knierim, K.; Hanelin, J.; Ramachandran, T.; Glover, G.C.; Mackey, S.C. Neural correlates of individual differences in pain-related fear and anxiety. Pain 2006, 120, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negi, P.; Singh, B.; Sharma, G.; Beg, S.; Katare, O.P. Biocompatible lidocaine and prilocaine loaded-nanoemulsion system for enhanced percutaneous absorption: QbD-based optimisation, dermatokinetics and in vivo evaluation. J. Microencapsul. 2015, 32, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Kamboj, S.; Thakur, K.; Negi, P.; Raza, K.; Katare, O.P. Delivery of Thermoresponsive-Tailored Mixed Micellar Nanogel of Lidocaine and Prilocaine with Improved Dermatokinetic Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy in Topical Anaesthesia. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaie, S.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Davaran, S.; Kouhsoltani, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Nanoethosomes for Dermal Delivery of Lidocaine. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abou-Okeil, A.; Rehan, M.; El-Sawy, S.M.; El-Bisi, M.K.; Ahmed-Farid, O.A.; Abdel-Mohdy, F.A. Lidocaine/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex as drug delivery system. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.M.; Lee, C.; Lahiji, S.F.; Jung, U.W.; Chung, G.; Jung, H. Dissolving Microneedles for Rapid and Painless Local Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Yu, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, W.; Wu, T. Engineering Electrospun Nanofibers for the Treatment of Oral Diseases. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 797523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrañeta, E.; McCrudden, M.T.; Courtenay, A.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles: A New Frontier in Nanomedicine Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, D.D.; Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Guo, X.D. Insulin delivery systems combined with microneedle technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, A.; Das, D.B. Potential of biodegradable microneedles as a transdermal delivery vehicle for lidocaine. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 1351–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Kim, S.; Kang, G.; Lahiji, S.F.; Jang, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, J.M.; Cho, S.N.; Jung, H. Centrifugal Lithography: Self-Shaping of Polymer Microstructures Encapsulating Biopharmaceutics by Centrifuging Polymer Drops. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, J.S.; Lim, W.X.; Zou, S.; Foo, W.Y.; Pan, J.; Kang, L. Microneedle integrated transdermal patch for fast onset and sustained delivery of lidocaine. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4272–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangol, M.; Yang, H.; Li, C.G.; Lahiji, S.F.; Kim, S.; Ma, Y.; Jung, H. Innovative polymeric system (IPS) for solvent-free lipophilic drug transdermal delivery via dissolving microneedles. J. Control. Release 2016, 223, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Lahiji, S.F.; Ha, N.Y.; Yang, H.; Kang, G.; Nguyen, H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, M.S.; et al. Comparative Study of Two Droplet-Based Dissolving Microneedle Fabrication Methods for Skin Vaccination. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1701381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Ohta, J.; Imada, K.; Akamatsu, S.; Tsuchida, N.; Inoue, G.; Inoue, N.; Takada, K. Dissolving microneedles to obtain rapid local anesthetic effect of lidocaine at skin tissue. J. Drug Target. 2013, 21, 770–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Brown, K.; Siebenaler, K.; Determan, A.; Dohmeier, D.; Hansen, K. Development of lidocaine-coated microneedle product for rapid, safe, and prolonged local analgesic action. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serpe, L.; Jain, A.; de Macedo, C.G.; Volpato, M.C.; Groppo, F.C.; Gill, H.S.; Franz-Montan, M. Influence of salivary washout on drug delivery to the oral cavity using coated microneedles: An in vitro evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshazly, E.H.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Zhang, S.; Ke, L.; Gong, R. Fabrication of folate-phytosterol-carboxymethyl cellulose nanoparticles derived from plant material as carrier of anticancer drug. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maver, T.; Kurečič, M.; Pivec, T.; Maver, U.; Gradišnik, L.; Gašparič, P.; Kaker, B.; Bratuša, A.; Hribernik, S.; Stana Kleinschek, K. Needleless electrospun carboxymethyl cellulose/polyethylene oxide mats with medicinal plant extracts for advanced wound care applications. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4487–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allafchian, A.; Hosseini, H.; Ghoreishi, S.M. Electrospinning of PVA-carboxymethyl cellulose nanofibers for flufenamic acid drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Fawal, G.; Hong, H.; Song, X.; Wu, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Mo, X.; Wang, H. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Hydroxyethylcellulose Containing Ethosomes as a Scaffold for Transdermal Drug Delivery Applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2020, 191, 1624–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.; Mahmoud, K.H.; Fatah, A.A.; Hassen, A.D. DSC, TGA and dielectric properties of carboxymethyl cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol blends. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2011, 406, 4068–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, G.; Lu, J.; Liang, H. Preparation and Characterization of Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Polyvinyl Alcohol Blend Film as a Potential Coating Material. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2013, 52, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Che, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, C. Effect of Na2CO3 on the Microstructure and Macroscopic Properties and Mechanism Analysis of PVA/CMC Composite Film. Polymers 2020, 12, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Luo, H.; Lu, W.; Luan, H.; Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Pi, J.; Lim, C.Y.; Wang, H. Rapidly dissolvable microneedle patches for transdermal delivery of exenatide. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 3348–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Cui, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, C.; Han, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, B.; Fan, G.; et al. Coadministration of an Adhesive Conductive Hydrogel Patch and an Injectable Hydrogel to Treat Myocardial Infarction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, H.; Mao, J.; Li, Y.; Hussain, M.; Zhu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tao, J.; Zhu, J. Enhanced in vitro efficacy for inhibiting hypertrophic scar by bleomycin-loaded dissolving hyaluronic acid microneedles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6604–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhao, W.; Dong, Z.; Ji, Y.; Li, M.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yuan, C.; Deng, J.; Zhao, P.; et al. A biodegradable antibacterial alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan/Kangfuxin sponges for promoting blood coagulation and full-thickness wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Zheng, W.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Sui, K.; Shen, P.; Li, P.; Zhou, Q. Marine polysaccharide-based composite hydrogels containing fucoidan: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, and biocompatible evaluation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1978–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, L.; Franz-Montan, M.; Alcântara, A.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Castro, S.R.; Guilherme, V.A.; Muniz, B.V.; Rodrigues da Silva, G.H.; de Paula, E. Hybrid nanofilms as topical anesthetics for pain-free procedures in dentistry. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, P.; Alves, T.; Pegoraro, T.A.; Costa, Y.M.; Bonfante, E.A.; de Almeida, A. Measurement properties of gingival biotype evaluation methods. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogden, K.A.; Squier, C.; Ebrary, I. Human Oral Mucosa: Development, Structure and Function. Br. J. Surg. 2011, 15, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carla Santos, S.; Fávaro-Moreira, N.C.; Abdalla, H.B.; Augusto, G.; Costa, Y.M.; Volpato, M.C.; Groppo, F.C.; Gill, H.S.; Franz-Montan, M. A crossover clinical study to evaluate pain intensity from microneedle insertion in different parts of the oral cavity. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 592, 120050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Takano, T.; Tasaka, A.; Ueda, T.; Sakurai, K. Evaluation of participants’ perception and taste thresholds with a zirconia palatal plate. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2016, 60, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Newehy, M.H.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Alotaiby, S.; El-Hamshary, H.; Moydeen, M.; Al-Deyab, S. Preparation of biocompatible system based on electrospun CMC/PVA nanofibers as controlled release carrier of diclofenac sodium. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2016, 53, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.; Barbosa-Stancioli, E.F.; Piscitelli Mansur, A.A.; Vasconcelos, W.L.; Mansur, H.S. Design of novel hybrid organic-inorganic nanostructured biomaterials for immunoassay applications. Biomed. Mater. 2006, 1, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Negi, Y.S.; Bhardwaj, N.K.; Choudhary, V. Synthesis and characterization of methylcellulose/PVA based porous composite. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 88, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamnongkan, T.; Kantarot, K.; Niemtang, K.; Pansila, P.P.; Wattanakornsiri, A. Kinetics and mechanism of adsorptive removal of copper from aqueous solution with poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 3386–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsasulak, S.; Tongsin, P.; Intasanta, N.; Yoovidhya, T. Effect of glycerol on solution properties governing morphology, glass transition temperature, and tensile properties of electrospun zein film. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilli, R.; Kacuráková, M.; Mathlouthi, M.; Navarini, L.; Paoletti, S. FTIR studies of sodium hyaluronate and its oligomers in the amorphous solid phase and in aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Res. 1994, 263, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.; Döll-Boscardin, P.M.; Fiorin, B.C.; Nadal, J.M.; Farago, P.V.; Paula, J.P. Development and characterization of hyaluronic acid-lysine nanoparticles with potential as innovative dermal filling. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kevadiya, B.D.; Joshi, G.V.; Mody, H.M.; Bajaj, H.C. Biopolymer–clay hydrogel composites as drug carrier: Host–guest intercalation and in vitro release study of lidocaine hydrochloride. Appl. Clay. Sci. 2011, 52, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, P.D.; Luu, D.; Ye, R.; Buchta, R. Drug release from hydroethanolic gels. Effect of drug’s lipophilicity (logP), polymer-drug interactions and solvent lipophilicity. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 396, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Huwaij, R.; Assaf, S.; Salem, M.; Sallam, A. Mucoadhesive dosage form of lidocaine hydrochloride: I. Mucoadhesive and physicochemical characterization. Drug Dev. Ind. 2007, 33, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Patel, R.B.; Parikh, J.R.; Patel, B.G. Formulation consideration and skin retention study of microemulsion containing tazarotene for targeted therapy of acne. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 46, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Hao, J. Design and Development of Lidocaine Microemulsions for Transdermal Delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.C.; Lin, W.M.; Shu, J.C.; Tsai, S.W.; Chen, C.H.; Tsai, M.T. Formulation of two-layer dissolving polymeric microneedle patches for insulin transdermal delivery in diabetic mice. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2017, 105, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olkkola, K.T.; Isohanni, M.H.; Hamunen, K.; Neuvonen, P.J. The effect of erythromycin and fluvoxamine on the pharmacokinetics of intravenous lidocaine. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 100, 1352–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz-Montan, M.; Serpe, L.; Martinelli, C.C.; da Silva, C.B.; Santos, C.P.; Novaes, P.D.; Volpato, M.C.; de Paula, E.; Lopez, R.F.; Groppo, F.C. Evaluation of different pig oral mucosa sites as permeability barrier models for drug permeation studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 81, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, T.; Yu, X.; Yi, X.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Hao, Y.; Wang, W. Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040686
Zhu T, Yu X, Yi X, Guo X, Li L, Hao Y, Wang W. Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(4):686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040686
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Tingting, Xixi Yu, Xin Yi, Xiaoli Guo, Longhao Li, Yuanping Hao, and Wanchun Wang. 2022. "Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 4: 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040686
APA StyleZhu, T., Yu, X., Yi, X., Guo, X., Li, L., Hao, Y., & Wang, W. (2022). Lidocaine-Loaded Hyaluronic Acid Adhesive Microneedle Patch for Oral Mucosal Topical Anesthesia. Pharmaceutics, 14(4), 686. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14040686





