Click-Chemistry Cross-Linking of Hyaluronan Graft Copolymers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.1.1. Grafting Procedure for the Preparation of HA(270)-FA-Pg Copolymers
2.1.2. Click-Chemistry Cross-Linking of HA-FA-Pg Graft Copolymers
2.1.3. HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-10 Material
2.1.4. HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-20 Material
2.1.5. HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-40 Material
2.1.6. HA(8.7)-FA-HEG-CL-20 Material
2.1.7. Diethyl 3,3′-(((((3,6,9,12,15-Pentaoxaheptadecane-1,17-Diyl)Bis(1H-1,2,3-Triazole-1,4-Diyl))Bis(Methylene))Bis(Oxy))Bis(3-Methoxy-4,1-Phenylene))(2E,2′E)-Diacrylate (6)
2.1.8. Ethyl (E)-3-(4-((1-(17-Azido-3,6,9,12,15-Pentaoxaheptadecyl)-1H-1,2,3-Triazol-4-Yl)Methoxy)-3-Methoxyphenyl)Acrylate (7)
2.1.9. (2E,2′E)-3,3′-(((((3,6,9,12,15-Pentaoxaheptadecane-1,17-Diyl)Bis(1H-1,2,3-Triazole-1,4-Diyl))Bis(Methylene))Bis(Oxy))Bis(3-Methoxy-4,1-Phenylene))Diacrylic Acid (3)
2.1.10. (E)-3-(4-((1-(17-Azido-3,6,9,12,15-Pentaoxaheptadecyl)-1H-1,2,3-Triazol-4-Yl)Methoxy)-3-Methoxyphenyl)Acrylic Acid (4)
2.2. SEC-MALS
2.3. Swelling Performance
2.3.1. Swelling Kinetics
2.3.2. Total Water
2.3.3. Free and Bound Water
2.4. Rheological Analysis
2.5. Thermal Behavior
2.6. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Test
3. Results and Discussion
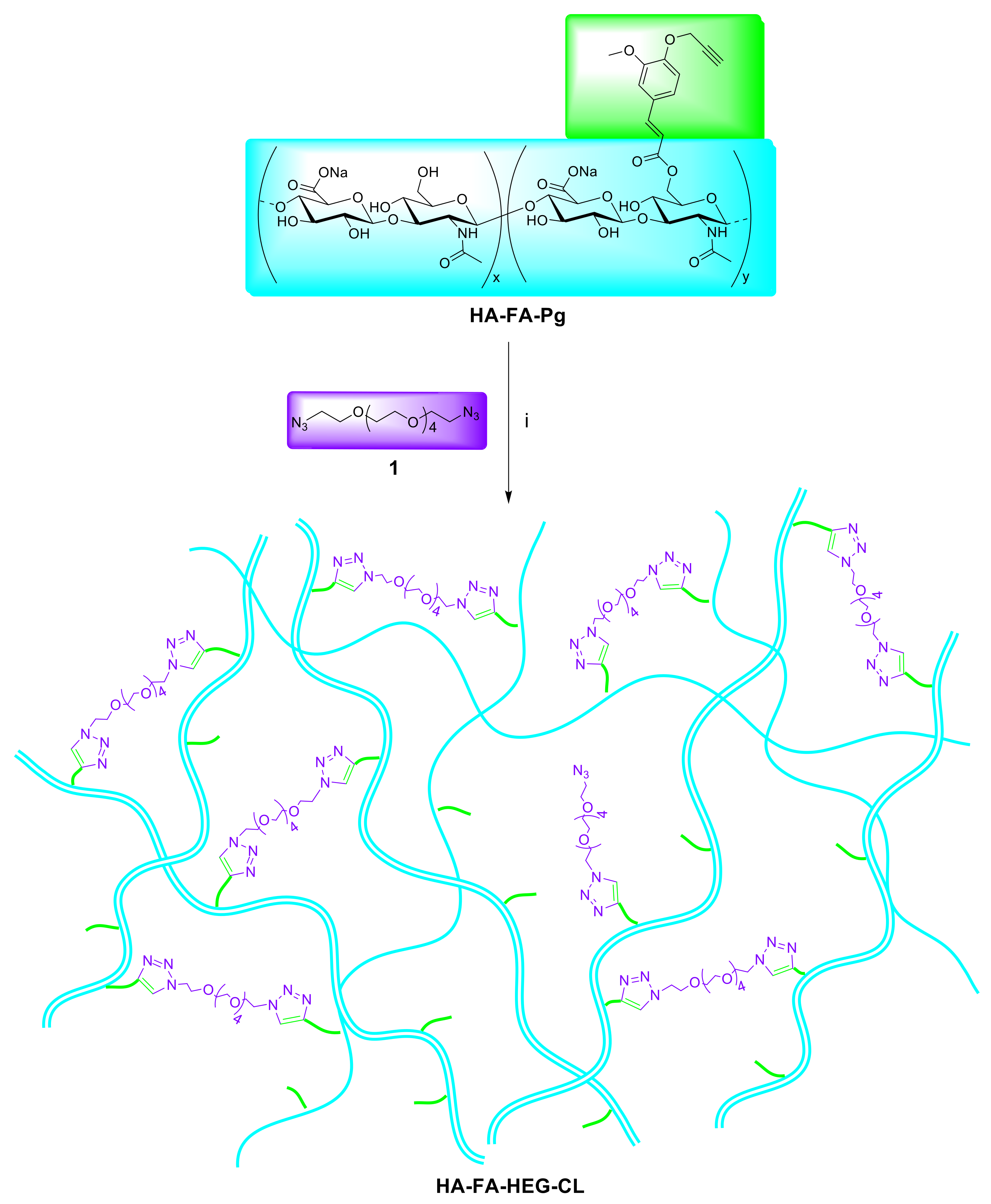
3.1. Synthesis of HA(270)-FA-Pg and HA-FA-HEG-CL Derivatives

| Copolymer | HA (g) | HA (mmol) | 2/HA Ratio (%) | Grafting Degree a (%) | Convers. b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA(270)-FA-Pg-10 | 1.0 | 2.49 | 12.5 | 10 | 80 |
| HA(270)-FA-Pg-20 | 1.0 | 2.49 | 25 | 20 | 80 |
| HA(270)-FA-Pg-40 | 1.0 | 2.49 | 50 | 40 | 80 |
3.2. Structure of HA-FA-Pg and HA-FA-HEG-CL Derivatives




3.3. Molecular Characterization of HA(270)-FA-Pg Derivatives
3.4. Swelling Performance
3.5. Rheological Analysis
3.6. Thermal Behavior
| Sample | 30–200 °C (%) | 200–400 °C (%) | 400–600 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-10 | 13 ± 1 | 43 ± 3 | 7 ± 1 |
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-20 | 15 ± 2 | 43 ± 3 | 7 ± 1 |
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-40 | 18 ± 2 | 46 ± 2 | 7 ± 2 |
| HA(8.7)-FA-HEG-CL-20 | 22 ± 3 | 43 ± 2 | 8 ± 2 |
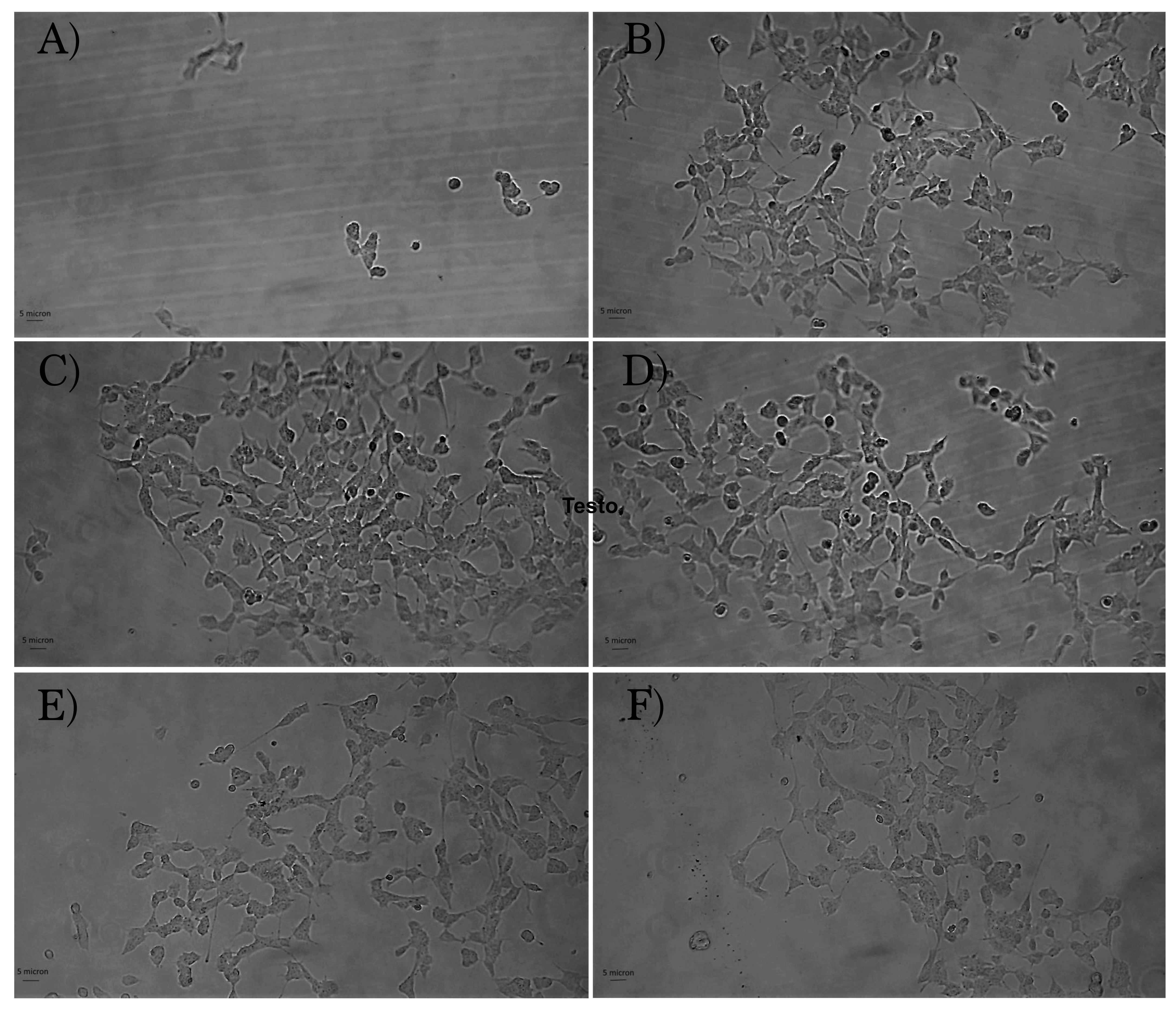
3.7. In Vitro Cytotoxicity: Cell Viability and Morphology
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dicker, K.T.; Gurski, L.A.; Pradhan-Bhatt, S.; Witt, R.L.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Hyaluronan: A simple polysaccharide with diverse biological functions. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1558–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, M.; Joester, D.; Geiger, B.; Addadi, L. Spatial and Temporal Sequence of Events in Cell Adhesion: From Molecular Recognition to Focal Adhesion Assembly. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasvani, S.; Kulkarni, P.; Rawtani, D. Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery, route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 151, 1012–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombino, S.; Servidio, C.; Curcio, F.; Cassano, R. Strategies for Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogel Design in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilarska, A.; Lewandowska-Łańcucka, J.; Horak, W.; Nowakowska, M. Collagen/chitosan/hyaluronic acid–based injectable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications–design, physicochemical and biological characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 170, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunmanee, S.; Jeong, Y.; Park, H. Crosslinking method of hyaluronic-based hydrogel for biomedical applications. J. Tissue Eng. 2017, 8, 2041731417726464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de O. Buanafina, M.M. Feruloylation in Grasses: Current and Future Perspectives. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 861–872. [Google Scholar]
- Grabber, J.H.; Ralph, J.; Hatfield, R.D. Cross-Linking of Maize Walls by Ferulate Dimerization and Incorporation into Lignin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6106–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G.; Fry, S.C. Phenolic Components of the Plant Cell Wall; Kwang, W., Jeon, J.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; Volume 151, pp. 229–267. ISBN 0074-7696. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, S.; Abraham, T.E. Ferulic Acid: An Antioxidant Found Naturally in Plant Cell Walls and Feruloyl Esterases Involved in its Release and Their Applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2004, 24, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramanti, E.; Fulgentini, L.; Bizzarri, R.; Lenci, F.; Sgarbossa, A. β-Amyloid Amorphous Aggregates Induced by the Small Natural Molecule Ferulic Acid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 13816–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noel, A.; Borguet, Y.P.; Raymond, J.E.; Wooley, K.L. Poly(carbonate–amide)s Derived from Bio-Based Resources: Poly(ferulic acid-co-tyrosine). Macromolecules 2014, 47, 2974–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelli, A.; Grisci, G.; Paolino, M.; Giuliani, G.; Donati, A.; Mendichi, R.; Artusi, R.; Demiranda, M.; Zanardi, A.; Giorgi, G.; et al. Hyaluronan derivatives bearing variable densities of ferulic acid residues. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4489–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valacchi, G.; Grisci, G.; Sticozzi, C.; Lim, Y.; Paolino, M.; Giuliani, G.; Mendichi, R.; Belmonte, G.; Artusi, R.; Zanardi, A.; et al. Wound healing properties of hyaluronan derivatives bearing ferulate residues. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7037–7045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelli, A.; Paolino, M.; Grisci, G.; Razzano, V.; Giuliani, G.; Donati, A.; Bonechi, C.; Mendichi, R.; Battiato, S.; Samperi, F.; et al. Hyaluronan-coated polybenzofulvene brushes as biomimetic materials. Polym. Chem. 2016, 7, 6529–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Giammona, G.; Paolino, M.; Cappelli, A. Design and development of hyaluronan-functionalized polybenzofulvene nanoparticles as CD44 receptor mediated drug delivery system. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzano, V.; Paolino, M.; Reale, A.; Giuliani, G.; Artusi, R.; Caselli, G.; Visintin, M.; Makovec, F.; Donati, A.; Villafiorita-Monteleone, F.; et al. Development of Imidazole-Reactive Molecules Leading to a New Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorophore Based on the Cinnamic Scaffold. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 5453–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelli, A.; Paolino, M.; Reale, A.; Razzano, V.; Grisci, G.; Giuliani, G.; Donati, A.; Bonechi, C.; Lamponi, S.; Mendichi, R.; et al. Hyaluronan-based graft copolymers bearing aggregation-induced emission fluorogens. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5864–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paolino, M.; Licciardi, M.; Savoca, C.; Giammona, G.; Modica De Mohac, L.; Reale, A.; Giuliani, G.; Komber, H.; Donati, A.; Leone, G.; et al. Hyaluronan Graft Copolymers Bearing Fatty-Acid Residues as Self-Assembling Nanoparticles for Olanzapine Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atrei, A.; Innocenti, C.; Lamponi, S.; Paesano, S.; Leone, G.; Reale, A.; Paolino, M.; Cappelli, A. Covalent hyaluronic-based coating of magnetite nanoparticles: Preparation, physicochemical and biological characterization. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 107, 110271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendichi, R.; Giacometti Schieroni, A. Use of a multi-detector size exclusion chromatography system for the characterization of complex polymers. Curr. Trends Polym. Sci. 2001, 6, 17–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt, P.J. Light scattering and the absolute characterization of macromolecules. Anal. Chim. Acta 1993, 272, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xue, F.; Cheng, R. States of water in partially swollen poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogels. Polymer 2005, 46, 12026–12031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.; Consumi, M.; Pepi, S.; Pardini, A.; Bonechi, C.; Tamasi, G.; Donati, A.; Lamponi, S.; Rossi, C.; Magnani, A. Enriched Gellan Gum hydrogel as visco-supplement. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 115347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10995-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for Cytotoxicity: In Vitro Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Lamponi, S.; Baratto, M.C.; Miraldi, E.; Baini, G.; Biagi, M. Chemical Profile, Antioxidant, Anti-Proliferative, Anticoagulant and Mutagenic Effects of a Hydroalcoholic Extract of Tuscan Rosmarinus officinalis. Plants 2021, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joram Mendoza, D.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Browne, C.; Singh Raghuwanshi, V.; Simon, G.P.; Garnier, G.; Allais, F. Grafting Nature-Inspired and Bio-Based Phenolic Esters onto Cellulose Nanocrystals Gives Biomaterials with Photostable Anti-UV Properties. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 6552–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.; Bidini, A.; Lamponi, S.; Magnani, A. States of water, surface and rheological characterisation of a new biohydrogel as articular cartilage substitute. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2013, 24, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Mo, X.; Song, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, C.; Ouyang, B.; Tu, B.; Luo, L.; et al. An interpenetrating network-strengthened and toughened hydrogel that supports cell-based nucleus pulposus regeneration. Biomaterials 2017, 136, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, G.; Consumi, M.; Pepi, S.; Pardini, A.; Bonechi, C.; Tamasi, G.; Donati, A.; Rossi, C.; Magnani, A. Poly-vinyl alcohol (PVA) crosslinked by trisodium trimetaphosphate (STMP) and sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP): Effect of molecular weight, pH and phosphorylating agent on length of spacing arms, crosslinking density and water interaction. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1202, 127264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamponi, S.; Leone, G.; Consumi, M.; Greco, G.; Magnani, A. In Vitro Biocompatibility of New PVA-Based Hydrogels as Vitreous Body Substitutes. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | dn/dc (mL/g) | Mp (kg/mol) | Mw (kg/mol) | Mw/Mn | Rec. Mass a (%) | Grafting b (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA(270) c | 0.150 | 188 | 274 | 3.89 | 94 | 0 |
| HA(270)-FA-Pg-10 d | 0.140 | 278 | 330 | 2.09 | 80 | 10 |
| HA(270)-FA-Pg-20 d | 0.140 | 359 | 387 | 2.21 | 68 | 20 |
| HA(270)-FA-Pg-40 d | 0.140 | 347 | 288 | 2.49 | 21 | 40 |
| Sample | 30–120 °C WC (%) | Wsg (mg) | Wtot (mg) | Wf (mg) | Wff-Wbf (%) | Wnf (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-10 | 98 | 17.8 | 17.4 (100%) | 16.2 (93%) | 98-2 | 1.2 (7%) |
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-20 | 97 | 13.8 | 13.4 (100%) | 11.5 (87%) | 82-18 | 1.8 (13%) |
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-40 | 93 | 8.37 | 7.78 (100%) | 6.95 (90%) | 88-12 | 0.82 (10%) |
| HA(8.7)-FA-HEG-CL-20 | 97 | 19.4 | 18.8 (100%) | 18.0 (95%) | 97-3 | 0.88 (8%) |
| Sample | G′ (2.5 Hz) (Pa) | G″(2.5 Hz) (Pa) | η 0.1 (Pa.s) | Shear Thinning Ratio (η0.1/η250) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-10 | 356 ± 9 | 59 ± 24 | 44 ± 11 | 156 ± 26 |
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-20 | 887 ± 11 | 266 ± 18 | 136 ± 48 | 4690 ± 154 |
| HA(270)-FA-HEG-CL-40 | 708 ± 14 | 147 ± 39 | 138 ± 52 | 9428 ± 269 |
| HA(8.7)-FA-HEG-CL-20 | 13 ± 2 | 0.25 ± 0.09 | 0.47 ± 0.05 | 390 ± 16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saletti, M.; Paolino, M.; Ballerini, L.; Giuliani, G.; Leone, G.; Lamponi, S.; Andreassi, M.; Bonechi, C.; Donati, A.; Piovani, D.; et al. Click-Chemistry Cross-Linking of Hyaluronan Graft Copolymers. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051041
Saletti M, Paolino M, Ballerini L, Giuliani G, Leone G, Lamponi S, Andreassi M, Bonechi C, Donati A, Piovani D, et al. Click-Chemistry Cross-Linking of Hyaluronan Graft Copolymers. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051041
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaletti, Mario, Marco Paolino, Lavinia Ballerini, Germano Giuliani, Gemma Leone, Stefania Lamponi, Marco Andreassi, Claudia Bonechi, Alessandro Donati, Daniele Piovani, and et al. 2022. "Click-Chemistry Cross-Linking of Hyaluronan Graft Copolymers" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051041
APA StyleSaletti, M., Paolino, M., Ballerini, L., Giuliani, G., Leone, G., Lamponi, S., Andreassi, M., Bonechi, C., Donati, A., Piovani, D., Schieroni, A. G., Magnani, A., & Cappelli, A. (2022). Click-Chemistry Cross-Linking of Hyaluronan Graft Copolymers. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051041










