Comparison of Paliperidone Palmitate from Different Crystallization Processes and Effect on Formulations In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Crystallization Processes of Paliperidone Palmitate
2.3. Characterization of Paliperidone Palmitate
2.3.1. Contact Angle Evaluation
2.3.2. Granular Evaluation
2.3.3. Crystallinity Evaluation
Differential Scanning Calorimetry
Infrared Spectroscopy
The Crystalline Properties
2.4. Preparation of Test Formulations
2.5. Characterization of Formulations
2.5.1. Particle Size Analyses
2.5.2. Dissolution Evaluation
In Vitro Release
Similarity Factor (f2)
2.6. Stability of Test Formulations
2.7. Pharmacokinetics In Vivo
2.7.1. Animal
2.7.2. Pharmacokinetics Study
2.7.3. Measurement of Paliperidone in Blood
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Paliperidone Palmitate
3.1.1. Surface Free Energy Evaluation
3.1.2. Granular Evaluation
3.1.3. Crystallinity Evaluation
DSC
IR
XRPD
3.2. Characterization of Test Formulations
3.2.1. Analysis of Particle Size
3.2.2. Evaluation of Dissolution
In Vitro Release
Analysis of Similarity Factor (f2)
3.3. Stability of Test Formulations
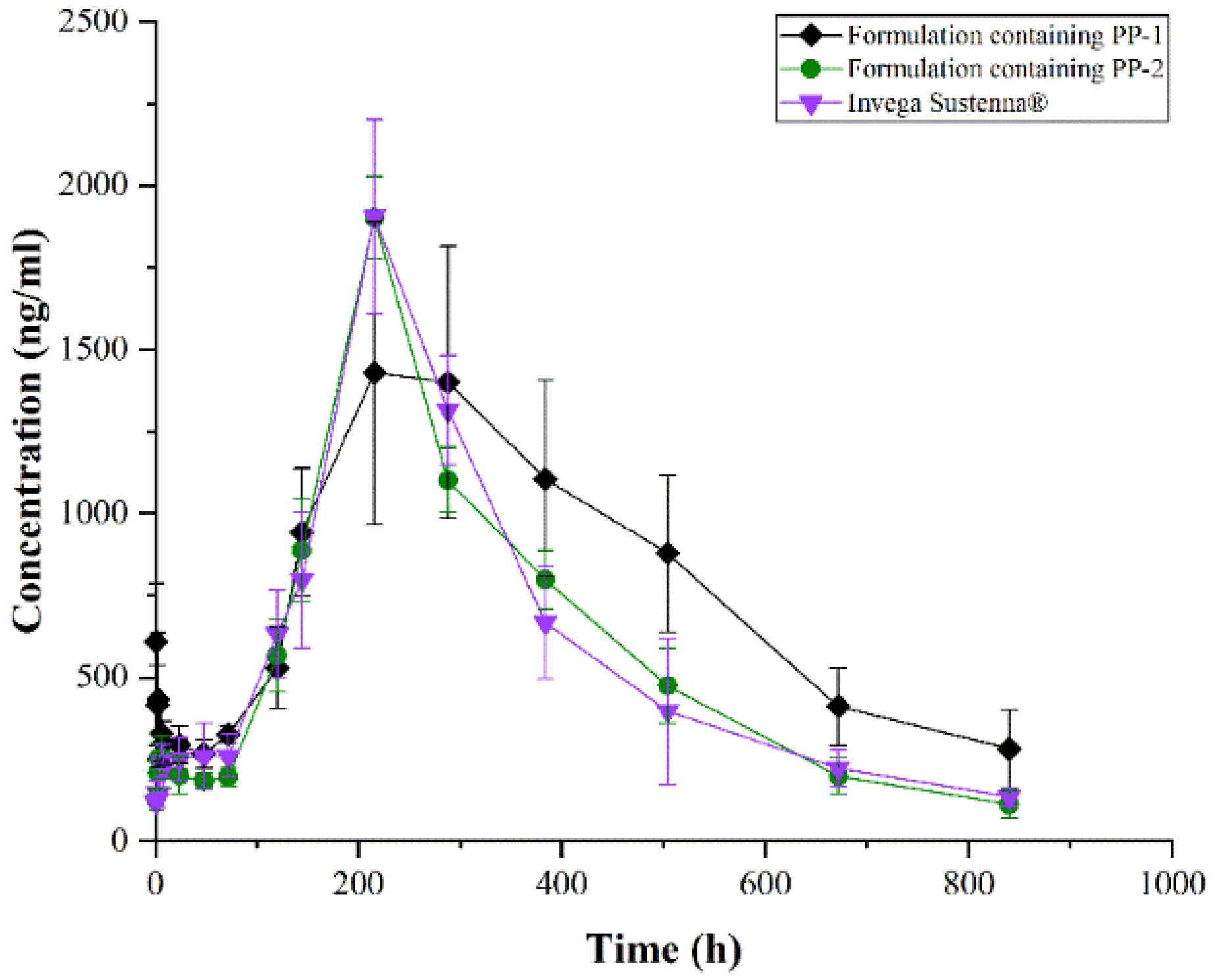
3.4. Pharmacokinetic In Vivo
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hough, D.; Gopal, S.; Vijapurkar, U.; Lim, P.; Morozova, M.; Eerdekens, M. Paliperidone palmitate maintenance treatment in delaying the time-to-relapse in patients with schizophrenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr. Res. 2010, 116, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, J.A.; Bettinger, T.L.; Argo, T.R. Paliperidone extended-release tablets for the acute and maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 231–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.; Simpson, G.; Maciulis, V.; Kushner, S.; Vijapurkar, U.; Lim, P.; Eerdekens, M. Paliperidone extended-release tablets for prevention of symptom recurrence in patients with schizophrenia: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Psychopharm. 2007, 27, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, D.; Lindenmayer, J.P.; Gopal, S.; Melkote, R.; Lim, P.; Herben, V.; Yuen, E.; Eerdekens, M. Safety and tolerability of deltoid and gluteal injections of paliperidone palmitate in schizophrenia. Prog. Neuro-Psychoph. 2009, 33, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peitl, V.; Vlahović, D. Paliperidone Palmitate 6-month (PP6M). Arch. Psych. Res. 2021, 57, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, S.; Faraj, J.A.; Giovagnoli, S.; DeLuca, P.P. Development of Risperidone PLGA Microspheres. J. Drug Deliv. 2014, 2014, 620464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C. Recent advances in drug polymorphs: Aspects of pharmaceutical properties and selective crystallization. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 611, 121320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Rohani, S.; Gong, G.; Wang, J. Recent Developments in the Crystallization Process: Toward the Pharmaceutical Industry. Engineer 2017, 3, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Wu, D.; Tang, J.; Wu, W.; Heng, J.Y.Y.; Zhao, H. A novel colored talc filler: Preparation and surface property determination using two distinct methods. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 155, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, J.M.; Schvezov, C.E.; Rosenberger, M.R. Construction and calibration of a goniometer to measure contact angles and calculate the surface free energy in solids with uncertainty analysis. Int. J. Adhesion Adhes. 2018, 87, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karde, V.; Ghoroi, C. Influence of surface modification on wettability and surface energy characteristics of pharmaceutical excipient powders. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 475, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engers, D.; Teng, J.; Jimenez-Novoa, J.; Gent, P.; Hossack, S.; Campbell, C.; Thomson, J.; Ivanisevic, I.; Templeton, A.; Byrn, S.; et al. A Solid-State Approach to Enable Early Development Compounds: Selection and Animsal Bioavailability Studies of an Itraconazole Amorphous Solid Dispersion. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3901–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moes, J.; Koolen, S.; Huitema, A.; Schellen, J.; Beijnan, J.; Nuijen, B. Development of an oral solid dispersion formulation for use in low-dose metronomic chemotheraphy of paclitaxel. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xin, T.; Ye, T.; Yang, X.; Pan, W. Solid dispersion in the development of a nimodipine delayed-release tablet formulation. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 9, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Obaidi, H.; Lawrence, M.; Al-Saden, N.; Ke, P. Investigation of griseofulvin and hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose acetate succinate miscibility in ball milled solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 443, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, S.; Cathcart, H.; O’Reilly, N.J. Polymeric Amorphous Solid Dispersions: A Review of Amorphization, Crystallization, Stabilization, Solid-State Characterization, and Aqueous Solubilization of Biopharmaceutical Classification System Class II Drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baird, J.A.; Taylor, L.S. Evaluation of amorphous solid dispersion properties using thermal analysis techniques. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 396–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaujia, P.; Lau, G.; Ng, W.K.; Widjaja, E.; Schreyer, M.; Hanefeld, A.; Fischbach, M.; Saal, C.; Maio, M.; Tan, B.H.R. Investigating the effect of moisture protection on solid-state stability and dissolution of fenofibrate and ketoconazole solid dispersions using PXRD, HSDSC and Raman microscopy. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2011, 37, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Su, C.; Hageman, M.; Hussain, M.; Haskell, R.; Stefanski, K.; Qian, F. Drug-Polymer-Water Interaction and Its Implication for the Dissolution Performance of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, A.; Geppi, M.; Mooter, G. Structural and Dynamic Properties of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: The Role of Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Relaxometry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 2635–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, R.; Jery, Y. A Review of Inverse Gas Chromatography and its Development as a Tool to Characterize Anisotropic Surface Properties of Pharmaceutical Solids. KONA Powder Part J. 2013, 30, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meredith, P. Bioequivalence and other unresolved issues in generic drug substitution. Clin. Ther. 2003, 25, 2875–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brissos, S.; Veguilla, M.R.; Taylor, D.; Balanza-Martinez, V. The role of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in schizophrenia: A critical appraisal. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 4, 198–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paliperidone Palmitate Prescribing Information. 2009. Available online: http://www.invegasustenna.com/invegasustenna/shared/pi/invegasustenna.pdf (accessed on 31 July 2009).
- Haidar, Z.S. Mathematical modeling for pharmacokinetic predictions from controlled drug release nano systems: A comparative parametric study. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2018, 11, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa-Lobo, J.M. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, T.S.; Acharya, F. Optimizing similarity factor of in vitro drug release profile for development of early stage formulation of drug using linear regression mode. J. Math Ind. 2021, 11, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, G. Development and validation of a rapid and sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS method for the determination of paliperidone in beagle dog plasma. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 9, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, G.; Qi, J.; Wang, Y. Synergistic influence of noncationic surfactants on the wettability and functional groups of coal. Powder Tech. 2021, 385, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, C.; Liu, R.; Miao, Y. Experimental synthesis and performance comparison analysis of high-efficiency wetting enhancers for coal seam water injection. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, R.M.; Ahmed, I.; Bourassa, P.A.; Carola, K.V. An in vitro technique for measuring contact angles on the corneal surface and its application to evaluate corneal wetting properties of water-soluble polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 119, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hutchins, D.; Zhao, C.Y. Melting behaviour of differently-sized micro-particles in a pipe flow under constant heat flux. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 53, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Gao, H.; Qu, W.; Zhao, F.; Xue, Y.; Cui, Z.; Xiao, L.; Niu, S. A theoretical study on the size and morphology dependency of integral melting enthalpy and entropy of nanomaterials. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 138, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Progress in the development of stabilization strategies for nanocrystal preparations. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumru, M.; Küçük, V.; Kocademir, M.; Alfanda, H.M.; Altun, A.; Sarı, L. Experimental and theoretical studies on IR, Raman, and UV–Vis spectra of quinoline-7-carboxaldehyde. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 134, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Sun, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, J. Molecular spectrum of lanthanide complexes with 2,3-dichlorobenzoic acid and 2,2-bipyridine. Spectrochim. Acta A 2014, 5, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Randhawa, J.K. Preparation and characterization of Paliperidone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 102, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Chan, L.H.; González-García, G.; Vargas-Coronado, R.F.; Cervantes-Uc, J.M.; Hernández-Sánchez, F.; Marcos-Fernadez, A.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V. Characterization of model compounds and poly(amide-urea) urethanes based on amino acids by FTIR, NMR and other analytical techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 92, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, C.M.C.; Herrero, M.; Labajos, F.M.; Marques, A.T.; Rives, V. Preparation and properties of new flame retardant unsaturated polyester nanocomposites based on layered double hydroxides. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2009, 94, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadendla, R.R.; Pinnamaneni, P.; Morla, S.P.; Patchala, A. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Paliperidone Palmitate and Compatibility Studies with its Pharmaceutical Excipients. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 33, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, D.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Guo, M.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y. Development and comparison of intramuscularly long-acting paliperidone palmitate nanosuspensions with different particle size. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.; Kakumanu, V.K.; Bansal, A.K. Analytical techniques for quantification of amorphous/crystalline phases in pharmaceutical solids. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1641–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, B.H.L.; Müller, R.H. Lab-scale production unit design for nanosuspensions of sparingly soluble cytotoxic drugs. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1999, 2, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, T.; Dunne, A.; Butler, J. A review of methods used to compare dissolution profile data. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1998, 1, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasińska-Stroschein, M.; Kurczewska, U.; Orszulak-Michalak, D. Statistical Considerations Concerning Dissimilar Regulatory Requirements for Dissolution Similarity Assessment. The Example of Immediate-Release Dosage Forms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. Stability of nanosuspensions in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindfors, L.; Skantze, P.; Skantze, U.; Westergren, J.; Olsson, U. Amorphous drug nanosuspensions. 3. Particle dissolution and crystal growth. Langmuir 2007, 23, 9866–9874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, A.A.; Ahlneck, C.; Alderborn, G.; Nystrom, C. Increased metastable solubility of milled griseofulvin, depending on the formation of a disordered surface structure. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 111, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Peak Number | Location of PP-1 | Area | Location of PP-2 | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15.35 | 154.13 | 15.37 | 211.21 |
| 2 | 16.15 | 316.33 | 16.16 | 644.36 |
| 3 | 16.60 | 56.93 | 16.61 | 67.75 |
| 4 | 17.68 | 317.83 | 17.70 | 397.21 |
| 5 | 18.01 | 71.79 | 18.04 | 125.46 |
| 6 | 18.21 | 57.33 | 18.23 | 80.90 |
| 7 | 19.90 | 1437.40 | 19.90 | 1959.10 |
| 8 | 19.29 | 477.00 | 19.30 | 1091.10 |
| 9 | 19.76 | 125.69 | 19.78 | 352.45 |
| 10 | 20.47 | 463.88 | 20.49 | 720.66 |
| 11 | 21.19 | 250.30 | 21.44 | 557.91 |
| 12 | 21.53 | 847.53 | 21.61 | 660.21 |
| 13 | 23.30 | 535.30 | 23.32 | 688.01 |
| 14 | 24.03 | 395.63 | 24.04 | 610.21 |
| 15 | 25.37 | 198.73 | 25.41 | 317.66 |
| Sample Name | Span | d (0.1)/µm | d (0.5)/µm | d (0.9)/µm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formulation containing PP-1 | 2.513 | 0.174 | 0.767 | 2.100 |
| Formulation containing PP-2 | 2.597 | 0.168 | 0.825 | 2.310 |
| Invega Sustenna® | 2.457 | 0.188 | 0.785 | 2.118 |
| Time (min) | Drug Dissolution (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invega Sustenna® | Formulation Containing PP-1 | Invega Sustenna® | Formulation Containing PP-2 | |
| 1.5 | 8.63 | 9.87 | 8.63 | 11.30 |
| 5 | 21.92 | 22.83 | 21.92 | 23.67 |
| 10 | 37.03 | 36.66 | 37.03 | 36.15 |
| 15 | 47.62 | 47.06 | 47.62 | 45.68 |
| 20 | 56.46 | 55.09 | 56.46 | 53.08 |
| 30 | 68.66 | 65.80 | 68.66 | 63.30 |
| 45 | 79.27 | 76.37 | 79.27 | 73.72 |
| 60 | 85.14 | 82.73 | 85.14 | 79.72 |
| 90 | 90.17 | 89.14 | 90.17 | 87.81 |
| f2 | 85 | 72 | ||
| Pharmacokinetic Parameter | Formulation Containing PP-1 | Formulation Containing PP-2 | Invega Sustenna® |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 1428 ± 460 | 1902 ± 125 | 1905 ± 296 |
| AUC0–t (ng/mL·h) | 642,602 ± 107,866 | 498,846 ± 35,062 | 499,383 ± 89,611 |
| AUC0–∞ (ng/mL·h) | 918,380 ± 242,998 | 526,208 ± 48,097 | 533,923 ± 81,653 |
| MRT0–t (h) | 376 ± 23 | 325 ± 14 | 321 ± 7 |
| MRT0–∞ (h) | 822 ± 475 | 363 ± 30 | 378 ± 46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Wang, D.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Liu, N.; Gao, X.; Zheng, A.; Zhang, H.; Xiang, M. Comparison of Paliperidone Palmitate from Different Crystallization Processes and Effect on Formulations In Vitro and In Vivo. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051094
Shi J, Wang D, Tian Y, Wang Z, Gao J, Liu N, Gao X, Zheng A, Zhang H, Xiang M. Comparison of Paliperidone Palmitate from Different Crystallization Processes and Effect on Formulations In Vitro and In Vivo. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(5):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051094
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Junfeng, Dan Wang, Yang Tian, Zengming Wang, Jing Gao, Nan Liu, Xiang Gao, Aiping Zheng, Hui Zhang, and Meixian Xiang. 2022. "Comparison of Paliperidone Palmitate from Different Crystallization Processes and Effect on Formulations In Vitro and In Vivo" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 5: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051094
APA StyleShi, J., Wang, D., Tian, Y., Wang, Z., Gao, J., Liu, N., Gao, X., Zheng, A., Zhang, H., & Xiang, M. (2022). Comparison of Paliperidone Palmitate from Different Crystallization Processes and Effect on Formulations In Vitro and In Vivo. Pharmaceutics, 14(5), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14051094





