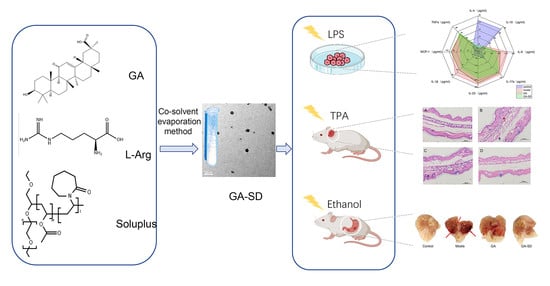
Enhancement of the Bioavailability and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Glycyrrhetinic Acid via Novel Soluplus®—A Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals and Cell Line
2.3. Fabrication of GA-SD
2.4. Drug Loading Analysis
2.5. Characterizations of GA-SD
2.5.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potentials
2.5.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.5.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5.4. X-ray Diffraction
2.5.5. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis
2.5.6. Stability Studies
2.5.7. Solubility of Formulation
2.6. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.7. Construction of Mouse Ear Edema Model
2.8. Histopathology
2.9. Analysis of Serum Biochemical Parameters
2.10. Construction of Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer Model
2.11. Assessment of Gastric Tissue Injury and Histopathological Examination
2.12. Immunohistochemical (IHC) Staining
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of GA-SD
3.2. Physicochemical Characterization
3.2.1. Particle Size and Zeta Potentials
3.2.2. XRD and FT-IR Analysis
3.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2.4. Stability of GA-SD
3.2.5. Solubility GA-SD
3.3. Anti-Inflammatory Effect In Vitro
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy on TPA-Induced Mouse Ear Edema
3.5. The Biosafety of GA-SD
3.5.1. Histopathological Results from the Liver and Kidney
3.5.2. Effect of GA-SD on Liver and Kidney Function
3.6. Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy on Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer Model
3.6.1. Effect of GA-SD on the Pathological Features of Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcer Model
3.6.2. Histopathological Examination of Gastric Tissues
3.6.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis of Gastric Tissues
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ptaschinski, C.; Lukacs, N.W. Acute and chronic inflammation induces disease pathogenesis. In Molecular Pathology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Kao, T.-C.; Lo, W.-H.; Yen, G.-C. Glycyrrhizic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid modulate lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by suppression of NF-κB through PI3K p110δ and p110γ inhibitions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 7726–7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, W.R. The role of leukotrienes in inflammation. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 121, 684–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasneem, S.; Liu, B.; Li, B.; Choudhary, M.I.; Wang, W. Molecular pharmacology of inflammation: Medicinal plants as anti-inflammatory agents. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 139, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.-C.; Shyu, M.-H.; Yen, G.-C. Glycyrrhizic acid and 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid inhibit inflammation via PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling and glucocorticoid receptor activation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8623–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Guo, L.; Li, H.; Chen, D.-F. Bupleurum polysaccharides attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation via modulating Toll-like receptor 4 signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Wei, H.; Löbenberg, R.; Kanfer, I.; Lee, V.H.; Amidon, G.L.; Zuo, Z. Establishing the pharmaceutical quality of Chinese herbal medicine: A provisional BCS classification. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1623–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Nassiri-Asl, M. Pharmacological effects of Glycyrrhiza spp. and its bioactive constituents: Update and review. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 1868–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.-N.; Li, L.; Qiu, Y.-F.; Miao, J.-H.; Gao, X.-Q.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z.-X.; Xu, Y.-L.; Shao, D.-H.; Wei, J.-C. Glycyrrhetinic acid extracted from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch. induces the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 in Ana-1 murine macrophages. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 13, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Luo, S.; Lv, X.; Deng, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G. Formulation of injectable glycyrrhizic acid-hydroxycamptothecin micelles as new generation of DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor for enhanced antitumor activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 571, 118693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Kong, Y.; Sui, H.; Feng, J.; Zhu, R.; Wang, W.J.D.D.; Research, T. Enhanced oral bioavailability of glycyrrhetinic acid via nanocrystal formulation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, A.; Kumar, N.K.; Suryanarayanan, R.J. Crosslinking: An avenue to develop stable amorphous solid dispersion with high drug loading and tailored physical stability. J. Control. Release 2019, 311, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, T.; Sarmento, B.; Costa, P. Solid dispersions as strategy to improve oral bioavailability of poor water soluble drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, Y.B.; Liavitskaya, T.; Vyazovkin, S. Polyvinylpyrrolidone affects thermal stability of drugs in solid dispersions. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 551, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Han, C. The Effect of PVP Molecular Weight on Dissolution Behavior and Physicochemical Characterization of Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersions. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2020, 2020, 8859658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Mai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.J.P. Mechanism and improved dissolution of glycyrrhetinic acid solid dispersion by alkalizers. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Sun, E.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Jia, X.-B.; Zhang, Z.-H. Improved oral bioavailability and anticancer efficacy on breast cancer of paclitaxel via Novel Soluplus®—Solutol® HS15 binary mixed micelles system. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.K.; Balogh, A.; Vajna, B.; Farkas, A.; Patyi, G.; Kramarics, Á.; Marosi, G. Comparison of electrospun and extruded Soluplus®-based solid dosage forms of improved dissolution. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonde, G.V.; Ajmal, G.; Yadav, S.K.; Mittal, P.; Singh, J.; Bakde, B.V.; Mishra, B.J.C.; Biointerfaces, S.B. Assessing the viability of Soluplus® self-assembled nanocolloids for sustained delivery of highly hydrophobic lapatinib (anticancer agent): Optimisation and in-vitro characterisation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotz, E.; Tateosian, N.L.; Salgueiro, J.; Bernabeu, E.; Gonzalez, L.; Manca, M.L.; Amiano, N.; Valenti, D.; Manconi, M.; García, V.; et al. Pulmonary delivery of rifampicin-loaded soluplus micelles against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Adu-Frimpong, M.; Ji, H.; Toreniyazov, E.; Wang, Q.; Yu, J.; Xu, X. Enhancement of oral bioavailability and anti-hyperuricemic activity of aloe emodin via novel Soluplus®—Glycyrrhizic acid mixed micelle system. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamma, R.N.; Basha, M. Soluplus®: A novel polymeric solubilizer for optimization of carvedilol solid dispersions: Formulation design and effect of method of preparation. Powder Technol. 2013, 237, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water soluble drugs—Part 1: Preparation, stability and dissolution enhancement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, J.; Danjou, P.-E.; Landy, D.; Ruellan, S.; Auezova, L.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Fourmentin, S. The effect of cyclodextrin complexation on the solubility and photostability of nerolidol as pure compound and as main constituent of cabreuva essential oil. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, P.; Zhang, C.; Ju, C.; Su, Z.; Bao, Y.; Gao, J.; Sun, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, C. Solubility and bioavailability enhancement study of lopinavir solid dispersion matrixed with a polymeric surfactant-Soluplus. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 134, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagianni, A.; Kachrimanis, K.; Nikolakakis, I. Co-amorphous solid dispersions for solubility and absorption improvement of drugs: Composition, preparation, characterization and formulations for oral delivery. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Ding, D.; Salvi, R. Cytotoxic effects of dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) on cochlear organotypic cultures. Hear. Res. 2008, 236, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, M.; Xu, S.; Shi, J.; Mao, X.; Yao, X.; Liu, C. Luteolin alters macrophage polarization to inhibit inflammation. Inflammation 2020, 43, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, H.; Bian, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, S.; Zheng, X.; Du, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ouyang, D. Molecular interactions for the curcumin-polymer complex with enhanced anti-inflammatory effects. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, M.M.; Vazquez, J.H.; Kennon-McGill, S.; McCullough, S.S.; James, L.P.; McGill, M.R. Pre-treatment twice with liposomal clodronate protects against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity through a pre-conditioning effect. Liver Res. 2020, 4, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-S.; Seo, C.-S.; Baek, E.B.; Rho, J.-H.; Won, Y.-S.; Kwun, H.-J.; Medicine, A. Gastroprotective effect of myricetin on ethanol-induced acute gastric injury in rats. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 9968112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, L.-J.; Liu, Z.-Q. Nanocarriers: A general strategy for enhancement of oral bioavailability of poorly absorbed or pre-systemically metabolized drugs. Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Akayleh, F.; Al-Naji, I.; Adwan, S.; Al-Remawi, M.; Shubair, M. Enhancement of curcumin solubility using a novel solubilizing polymer Soluplus®. J. Pharm. Innov. 2020, 17, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazunori, K.; Masayuki, Y.; Teruo, O.; Yasuhisa, S. Block copolymer micelles as vehicles for drug delivery. J. Control. Release 1993, 24, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albadarin, A.B.; Potter, C.B.; Davis, M.T.; Iqbal, J.; Korde, S.; Pagire, S.; Paradkar, A.; Walker, G. Development of stability-enhanced ternary solid dispersions via combinations of HPMCP and Soluplus® processed by hot melt extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Biopharmaceutics. Amino acids as co-amorphous stabilizers for poorly water-soluble drugs—Part 2: Molecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, H.; Wu, W.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Müllertz, A.; Rades, T. Application of a salt coformer in a co-amorphous drug system dramatically enhances the glass transition temperature: A case study of the ternary system carbamazepine, citric acid, and l-arginine. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2036–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tong, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. Effect and mechanism of penetration enhancement of organic base and alcohol on Glycyrrhetinic acid in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 399, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Ju, X.; Yang, D.; Kong, Y.; Tang, X. Effect of the third component on the aging and crystallization of cinnarizine-soluplus® binary solid dispersion. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; He, Q.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wan, Z.; Yang, X. Food-grade emulsions and emulsion gels prepared by soy protein-pectin complex nanoparticles and glycyrrhizic acid nanofibrils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1051–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, E.; Ramasamy, P.; Devi, T.U.; Meenakshi, R.; Chandramohan, A.; Spectroscopy, B. Synthesis, growth, structure and spectroscopic characterization of a new organic nonlinear optical hydrogen bonding complex crystal: 3-Carboxyl anilinium p-toluene sulfonate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 125, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisca, D.; Croitor, L.; Coropceanu, E.B.; Fonari, M.S. Four Cu (II) coordination polymers with biocompatible isonicotinamide and picolinate ligands in interplay with anionic and neutral linkers. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 132, 108864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, A.A.; Saad, G.R.; Abdelhamid, I.A.; Elwahy, A.H.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Elsabee, M.Z. Chitosan Schiff bases-based polyelectrolyte complexes with graphene quantum dots and their prospective biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, N.-Q.; Lai, H.-W.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, B.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H.-M.; Li, Z.-Q.; Qi, X.-R. Technology. On the inherent properties of Soluplus and its application in ibuprofen solid dispersions generated by microwave-quench cooling technology. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, W.; Han, C.; Sui, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Dong, Y. Preparation of glycyrrhetinic acid liposomes using lyophilization monophase solution method: Preformulation, optimization, and in vitro evaluation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.; Cheung, C.; Chui, W.; Tsao, S.; Nicholls, J.; Chan, Y.; Chan, R.; Long, H.; Poon, L.; Guan, Y. Proinflammatory cytokine responses induced by influenza A (H5N1) viruses in primary human alveolar and bronchial epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, Y.-h.; Yang, Z.-Q. The cytokine storm of severe influenza and development of immunomodulatory therapy. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev.™ Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tirpude, N.V.; Kulurkar, P.M.; Sharma, R.; Padwad, Y. Berberis lycium fruit extract attenuates oxi-inflammatory stress and promotes mucosal healing by mitigating NF-κB/c-Jun/MAPKs signalling and augmenting splenic Treg proliferation in a murine model of dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 2663–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carstens, M.G.; Rijcken, C.J.; Nostrum, C.F.; Hennink, W.E. Pharmaceutical micelles: Combining longevity, stability, and stimuli sensitivity. In Multifunctional Pharmaceutical Nanocarriers; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 263–308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Firempong, C.K.; Feng, C.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.; Yu, J. Enhanced oral bioavailability of capsaicin in mixed polymeric micelles: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 8, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Jiang, M.; Yu, R.; Deng, T.; Yu, C. Bioenzyme-responsive l-arginine-based carbon dots: The replenishment of nitric oxide for nonpharmaceutical therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7432–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.; Kathawala, K.; Li, J.; Chen, C.; Shan, Z.; Cao, X.; Wang, Y.-J.; Garg, S.; Zhou, X.-F. Self-nanomicellizing solid dispersion of edaravone: Part II: In vivo assessment of efficacy against behavior deficits and safety in Alzheimer’s disease model. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J.; Teng, Y.; Lin, Q.; Fu, Y.; Gong, T. Soluplus® based 9-nitrocamptothecin solid dispersion for peroral administration: Preparation, characterization, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 477, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, I.; Chakrabarti, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Toxicology, C. Genotoxicity and biocompatibility of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Influence of surface modification on biodistribution, retention, DNA damage and oxidative stress. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, A.-T.H.; Mohafrash, S.M.; Chandrasekaran, N. Safety of natural insecticides: Toxic effects on experimental animals. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4308054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Santana, G.; Bax, J.C.; Fernandes, D.C.S.; Bacellar, D.T.L.; Hooper, C.; Dias, A.A.S.O.; Silva, C.B.; de Souza, A.M.; Ramos, S.; Santos, R.A. Clinical hematological and biochemical parameters in Swiss, BALB/c, C57BL/6 and B6D2F1 Mus musculus. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2020, 3, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Li, J.; An, C.; Hu, K.; Tang, M. Pharmacology. Acute and sub-chronic toxicity studies of the extract of Thunberg Fritillary Bulb. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 68, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanda, M.R.; Kim, I.-S.; Ahn, D.; Tae, H.-J.; Nam, H.-H.; Choo, B.-K.; Kim, K.; Park, B.-Y. Anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective roles of rabdosia inflexa through downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadić, V.M.; Dobrić, S.; Marković, G.M.; Ðorđević, S.M.; Arsić, I.A.; Menković, N.R.; Stević, T. Anti-inflammatory, gastroprotective, free-radical-scavenging, and antimicrobial activities of hawthorn berries ethanol extract. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7700–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, A.C.; Miguel, F.; Mendonça, S.; Pedrazzoli, J., Jr.; Gurgueira, S.A. Oxidative stress expression status associated to Helicobacter pylori virulence in gastric diseases. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Xu, D.; Xu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, S. Novel role of Zn (II)-curcumin in enhancing cell proliferation and adjusting proinflammatory cytokine-mediated oxidative damage of ethanol-induced acute gastric ulcers. Chem. Interact. 2012, 197, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.I.; Abd El-Ghffar, E.A. Spirulina ameliorates aspirin-induced gastric ulcer in albino mice by alleviating oxidative stress and inflammation. Biomed. Pharm. 2019, 109, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lv, R.; Xu, X.; Ge, Q.; Lin, S. Tricholoma matsutake-Derived Peptides Show Gastroprotective Effects against Ethanol-Induced Acute Gastric Injury. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 14985–14994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Group | GA | GA-SD |
|---|---|---|
| Saturated solubility(mg/mL) | 6.62 × 10−3 | 37.6 ± 0.03 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Li, R.; Rao, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, L.; Wu, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Liang, H.; et al. Enhancement of the Bioavailability and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Glycyrrhetinic Acid via Novel Soluplus®—A Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091797
Wang H, Li R, Rao Y, Liu S, Hu C, Zhang Y, Meng L, Wu Q, Ouyang Q, Liang H, et al. Enhancement of the Bioavailability and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Glycyrrhetinic Acid via Novel Soluplus®—A Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091797
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hao, Runwei Li, Yuan Rao, Saixing Liu, Chunhui Hu, Yong Zhang, Linchao Meng, Qilin Wu, Qiuhong Ouyang, Hao Liang, and et al. 2022. "Enhancement of the Bioavailability and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Glycyrrhetinic Acid via Novel Soluplus®—A Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersion" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091797
APA StyleWang, H., Li, R., Rao, Y., Liu, S., Hu, C., Zhang, Y., Meng, L., Wu, Q., Ouyang, Q., Liang, H., & Qin, M. (2022). Enhancement of the Bioavailability and Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Glycyrrhetinic Acid via Novel Soluplus®—A Glycyrrhetinic Acid Solid Dispersion. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091797