Ibrutinib Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis in a BTK-Independent Manner
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
2.2. In Vitro Angiogenesis Assay
2.3. Cell-Viability Assay
2.4. Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Immunoblot Analysis
2.6. RNA-Seq Analysis
2.7. Apoptosis Analysis
2.8. Xenograft Model Analysis
2.9. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
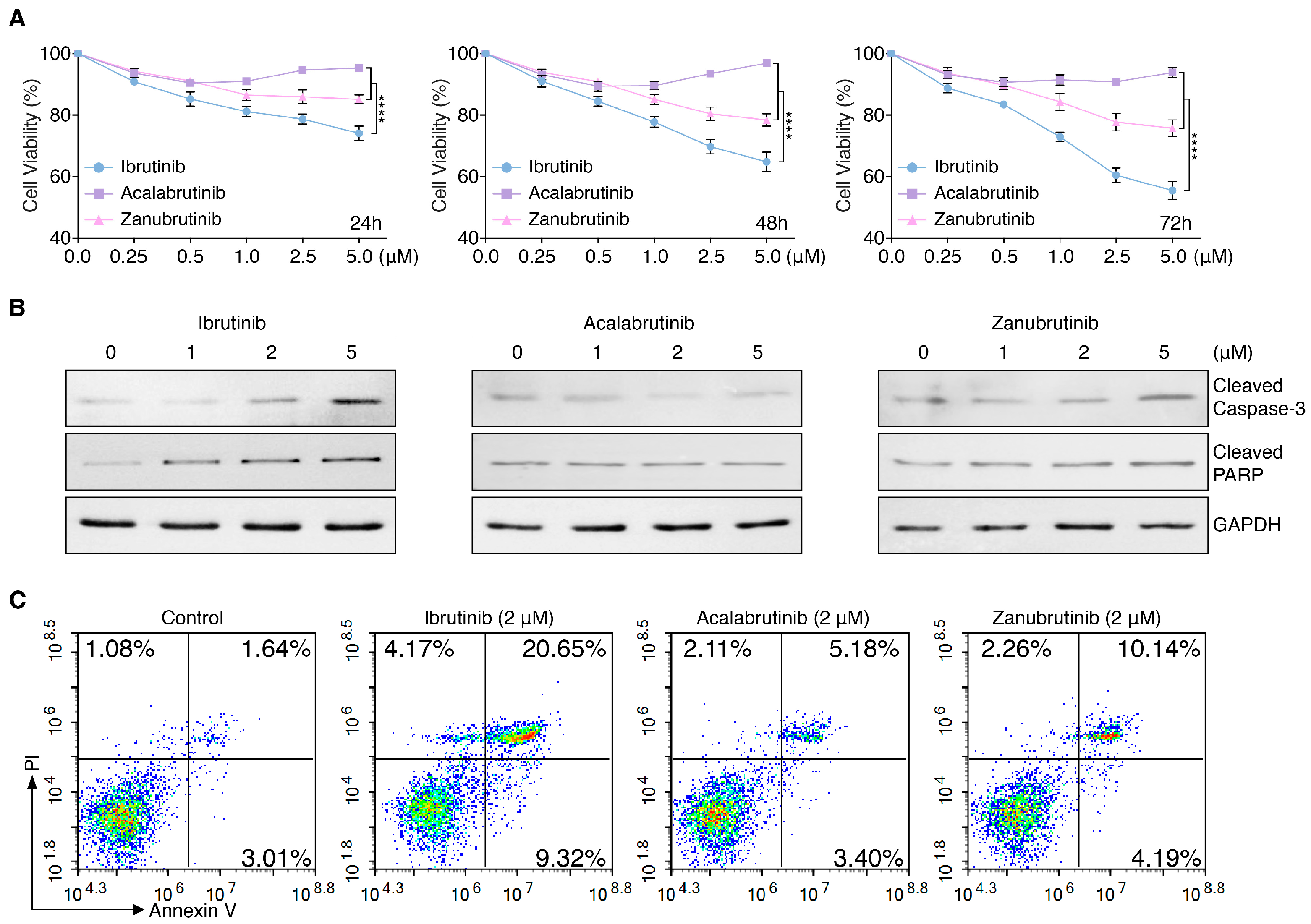
3.1. BTKis Differentially Induce Apoptosis in Endothelial Cells
3.2. RNA-Seq Identifies BTKi-Regulated Apoptotic Genes
3.3. BTKis Have Distinct Capacities to Induce Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction
3.4. Ibrutinib Induces Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction via Upregulating BMP4
3.5. Targeting BMP4 Inhibits the Capability of Ibrutinib to Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction
3.6. Ibrutinib Inhibits Ovarian and Breast Cancer Progression In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Li, L.R.; Young, K.H. New agents and regimens for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal Singh, S.; Dammeijer, F.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langerbeins, P.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Cramer, P.; Furstenau, M.; Al-Sawaf, O.; von Tresckow, J.; Fink, A.M.; Kreuzer, K.A.; Vehling-Kaiser, U.; et al. The CLL12 trial: Ibrutinib vs placebo in treatment-naive, early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2022, 139, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, R.H.; Buggy, J.J.; Sharman, J.P.; Smith, S.M.; Boyd, T.E.; Grant, B.; Kolibaba, K.S.; Furman, R.R.; Rodriguez, S.; Chang, B.Y.; et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib (PCI-32765) has significant activity in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, S.E.M.; Montraveta, A.; Niemann, C.U.; Mora-Jensen, H.; Gulrajani, M.; Krantz, F.; Mantel, R.; Smith, L.L.; McClanahan, F.; Harrington, B.K.; et al. The Bruton Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor Acalabrutinib Demonstrates Potent On-Target Effects and Efficacy in Two Mouse Models of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2831–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, C.S.; Trotman, J.; Opat, S.; Burger, J.A.; Cull, G.; Gottlieb, D.; Harrup, R.; Johnston, P.B.; Marlton, P.; Munoz, J.; et al. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. Blood 2019, 134, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levade, M.; David, E.; Garcia, C.; Laurent, P.A.; Cadot, S.; Michallet, A.S.; Bordet, J.C.; Tam, C.; Sie, P.; Ysebaert, L.; et al. Ibrutinib treatment affects collagen and von Willebrand factor-dependent platelet functions. Blood 2014, 124, 3991–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Harrington, B.; O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Schuh, A.; Devereux, S.; Chaves, J.; Wierda, W.G.; Awan, F.T.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Acalabrutinib (ACP-196) in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xiang, B.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, W.; Zou, D.; Lv, F.; Guo, W.; Liu, A.; Li, C.; et al. Zanubrutinib monotherapy for relapsed or refractory non-germinal center diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobie, G.; Kuriri, F.A.; Omar, M.M.A.; Alanazi, F.; Gazwani, A.M.; Tang, C.P.S.; Sze, D.M.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Tam, C.; Jackson, D.E. Ibrutinib, but not zanubrutinib, induces platelet receptor shedding of GPIb-IX-V complex and integrin αIIbβ3 in mice and humans. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 4298–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bye, A.P.; Unsworth, A.J.; Desborough, M.J.; Hildyard, C.A.T.; Appleby, N.; Bruce, D.; Kriek, N.; Nock, S.H.; Sage, T.; Hughes, C.E.; et al. Severe platelet dysfunction in NHL patients receiving ibrutinib is absent in patients receiving acalabrutinib. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kinoshita, T.; Gururaja, T.; Sukbuntherng, J.; James, D.; Lu, D.; Whang, J.; Versele, M.; Chang, B.Y. The effect of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors on collagen-induced platelet aggregation, BTK, and tyrosine kinase expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (TEC). Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 101, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroi, M.; Jung, S.M.; Okuma, M.; Shinmyozu, K. A patient with platelets deficient in glycoprotein VI that lack both collagen-induced aggregation and adhesion. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 84, 1440–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, B.T.; Ellmeier, W.; Watson, S.P. Tec regulates platelet activation by GPVI in the absence of Btk. Blood 2003, 102, 3592–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Goldmann, L.; Brandl, R.; Spannagl, M.; Weber, C.; Siess, W.; von Hundelshausen, P. Effects of the Btk-Inhibitors Remibrutinib (LOU064) and Rilzabrutinib (PRN1008) With Varying Btk Selectivity Over Tec on Platelet Aggregation and in vitro Bleeding Time. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 749022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Series, J.; Garcia, C.; Levade, M.; Viaud, J.; Sie, P.; Ysebaert, L.; Payrastre, B. Differences and similarities in the effects of ibrutinib and acalabrutinib on platelet functions. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2292–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, N.; Yu, D.; Zhou, C.; Shi, G.; Zhang, B.; Wei, M.; Liu, J.; Luo, L.; et al. Discovery of Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111), a Novel, Potent, and Selective Covalent Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 7923–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Simons, M. Regulation of vascular integrity. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, N.R.; Whitehead, K.J.; Li, D.Y. Endogenous endothelial cell signaling systems maintain vascular stability. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zuo, N.; Yang, H.; Fang, S.; Shi, J. Extracellular Traps Increase Burden of Bleeding by Damaging Endothelial Cell in Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 841445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, N.; Wang, L.; Esko, J.; Giordano, F.J.; Huang, Y.; Gerber, H.P.; Ferrara, N.; Johnson, R.S. Loss of HIF-1alpha in endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven VEGF autocrine loop necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, R.; Osawa, T.; Wang, F.; Nishii, R.; Das, B.; Tsuchida, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Takahashi, T.; Inoue, T.; Wada, Y.; et al. BMP4/Thrombospondin-1 loop paracrinically inhibits tumor angiogenesis and suppresses the growth of solid tumors. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3803–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paydas, S. Management of adverse effects/toxicity of ibrutinib. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 136, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomero, J.; Vegliante, M.C.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Eguileor, A.; Castellano, G.; Planas-Rigol, E.; Jares, P.; Ribera-Cortada, I.; Cid, M.C.; Campo, E.; et al. SOX11 promotes tumor angiogenesis through transcriptional regulation of PDGFA in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2014, 124, 2235–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyono, M.; Shibuya, M. Bone morphogenetic protein 4 mediates apoptosis of capillary endothelial cells during rat pupillary membrane regression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4627–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhammer, T.; Bataille, F.; Spruss, T.; Eissner, G.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Functional implication of BMP4 expression on angiogenesis in malignant melanoma. Oncogene 2007, 26, 4158–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezzola, S.; Di Somma, M.; Corsini, M.; Leali, D.; Ravelli, C.; Polli, V.A.B.; Grillo, E.; Presta, M.; Mitola, S. VEGFR2 activation mediates the pro-angiogenic activity of BMP4. Angiogenesis 2019, 22, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varikuti, S.; Singh, B.; Volpedo, G.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Jha, B.K.; Saljoughian, N.; Viana, A.G.; Verma, C.; Hamza, O.; Halsey, G.; et al. Ibrutinib treatment inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis by inducing conversion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells to dendritic cells. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, N. The effect of ibrutinib on radiosensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells by targeting EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucha, M.A.; Wu, A.T.; Lee, W.H.; Wang, L.S.; Lin, W.W.; Yuan, C.C.; Yeh, C.T. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (Btk) Inhibitor Ibrutinib Suppresses Stem-like Traits in Ovarian Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13255–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempero, M.; Oh, D.Y.; Tabernero, J.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Hendifar, A.; Waldschmidt, D.T.; Starling, N.; Bachet, J.B.; Chang, H.M.; et al. Ibrutinib in combination with nab-paclitaxel and gemcitabine for first-line treatment of patients with metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma: Phase III RESOLVE study. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.W.; Tan, E.; Zhou, J.-M.; Schell, M.J.; Martinez, M.; Yu, J.; Carballido, E.; Mehta, R.; Strosberg, J.; Imanirad, I.; et al. A phase 1/2 trial of ibrutinib in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with mismatch repair proficient metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Sui, L.; Yu, J. Ibrutinib Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis in a BTK-Independent Manner. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091876
Liu J, Liu Z, Zhang J, Chen X, Chen J, Sui L, Yu J. Ibrutinib Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis in a BTK-Independent Manner. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091876
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jia, Zhuojun Liu, Jing Zhang, Xiaofang Chen, Junge Chen, Linlin Sui, and Jian Yu. 2022. "Ibrutinib Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis in a BTK-Independent Manner" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091876
APA StyleLiu, J., Liu, Z., Zhang, J., Chen, X., Chen, J., Sui, L., & Yu, J. (2022). Ibrutinib Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumorigenesis in a BTK-Independent Manner. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1876. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091876






