Explaining the Release Mechanism of Ritonavir/PVPVA Amorphous Solid Dispersions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Modeling
2.1. Solid–Liquid Equilibrium
2.2. Vapor–Liquid Equilibrium
2.3. Liquid–Liquid Equilibrium
2.4. Glass Transition
2.5. PC-SAFT
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Ball Milling
3.2.2. Vacuum Compression Molding (VCM)
3.2.3. Spray Drying
3.2.4. Cloud-Point Measurements
3.2.5. Storage at Humid Conditions
3.2.6. Gravimetric Water-Sorption Measurements
3.2.7. Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry (mDSC)
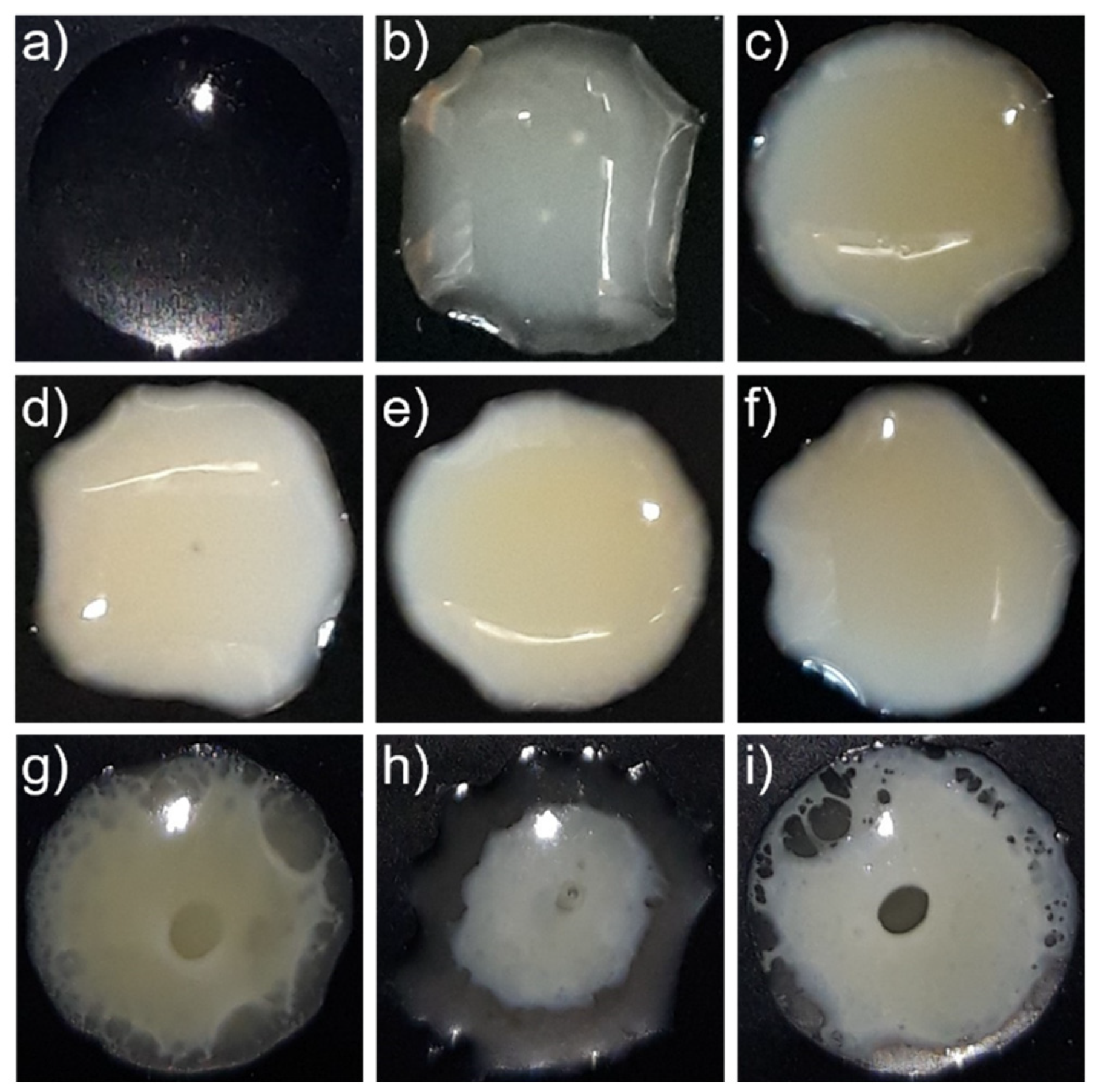
3.2.8. Dissolution Experiments
4. Results and Discussion
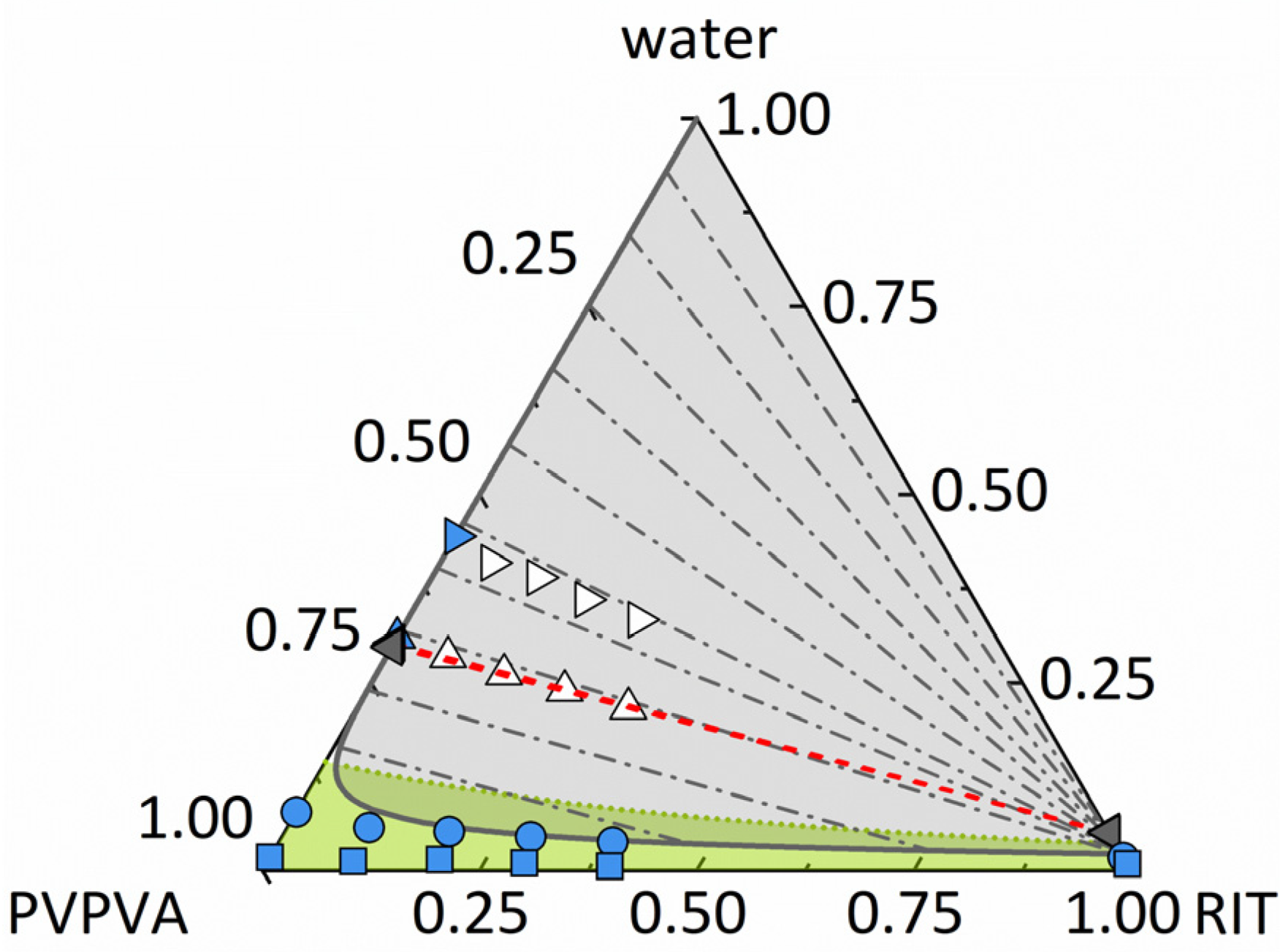
4.1. Ternary Phase Diagram of RIT/PVPVA/Water
4.1.1. Amorphous Phase Separation and Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation in the Ternary Phase Diagram
4.1.2. Prediction of the Ternary Phase Diagram
4.1.3. Experimental Validation of the Ternary Phase Diagram
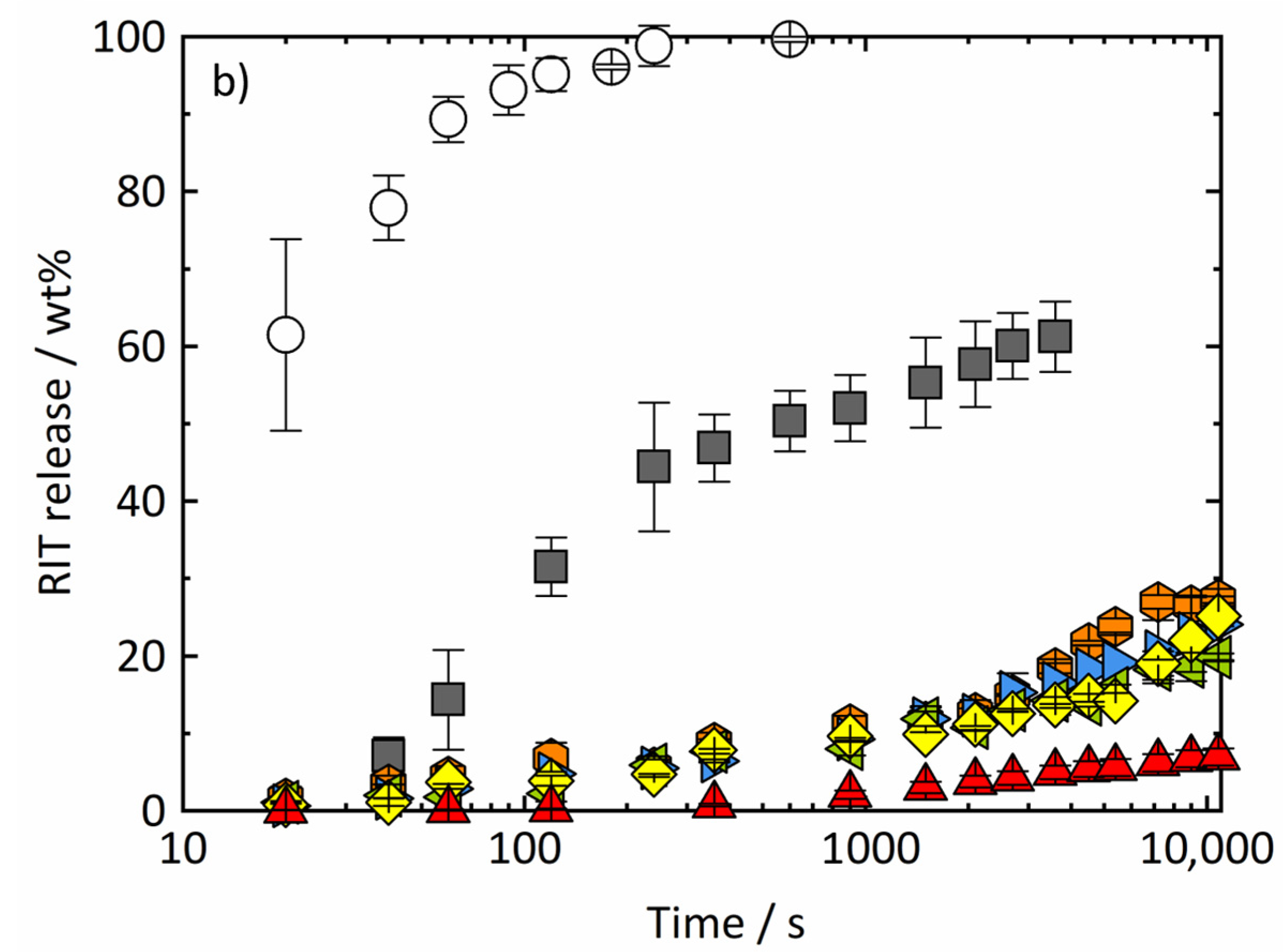
4.2. Dissolution Experiments
4.2.1. Dissolution of RIT/PVPVA ASDs
4.2.2. Release Mechanism of RIT/PVPVA ASDs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Brouwers, J.; Brewster, M.E.; Augustijns, P. Supersaturating drug delivery systems: The answer to solubility-limited oral bioavailability? J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 2549–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indulkar, A.S.; Lou, X.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Insights into the Dissolution Mechanism of Ritonavir-Copovidone Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Importance of Congruent Release for Enhanced Performance. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochmann, E.S.; Steidel, A.; Rosenblatt, K.M.; Gessner, D.; Liepold, B. Assessment of the amorphous solid dispersion erosion behavior following a novel small-scale predictive approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 158, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, C.; Lou, X.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Mo, H.; Indulkar, A.S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Insights into the Dissolution Behavior of Ledipasvir-Copovidone Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Role of Drug Loading and Intermolecular Interactions. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 5054–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, S.; Mugheirbi, N.A.; Zemlyanov, D.Y.; Kestur, U.S.; Taylor, L.S. Congruent release of drug and polymer: A “sweet spot” in the dissolution of amorphous solid dispersions. J. Control. Release 2019, 298, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, S.; Bapat, P.; Moseson, D.E.; Kestur, U.S.; Taylor, L.S. Exploring the Role of Surfactants in Enhancing Drug Release from Amorphous Solid Dispersions at Higher Drug Loadings. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.R.; Ma, Y.; Lee, P.I. Impact of phase separation morphology on release mechanism of amorphous solid dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 136, 104955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Borchardt, T.B. Direct Visualization of Drug-Polymer Phase Separation in Ritonavir-Copovidone Amorphous Solid Dispersions Using in situ Synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence Imaging of Thin Films. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4751–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indulkar, A.S.; Gao, Y.; Raina, S.A.; Zhang, G.G.Z.; Taylor, L.S. Exploiting the Phenomenon of Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation for Enhanced and Sustained Membrane Transport of a Poorly Water-Soluble Drug. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzer, J.; Hupfeld, S.; Vasskog, T.; Tho, I.; Hölig, P.; Mägerlein, M.; Fricker, G.; Brandl, M. In situ formation of nanoparticles upon dispersion of melt extrudate formulations in aqueous medium assessed by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tho, I.; Liepold, B.; Rosenberg, J.; Maegerlein, M.; Brandl, M.; Fricker, G. Formation of nano/micro-dispersions with improved dissolution properties upon dispersion of ritonavir melt extrudate in aqueous media. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Deac, A.; Zhang, G.G.Z. Assessing Physical Stability of Colloidal Dispersions Using a Turbiscan Optical Analyzer. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baird, J.A.; van Eerdenbrugh, B.; Taylor, L.S. A classification system to assess the crystallization tendency of organic molecules from undercooled melts. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 3787–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKelvey, C.A.; Kesisoglou, F. Enabling an HCV Treatment Revolution and the Frontiers of Solid Solution Formulation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohrn, S.; Luebbert, C.; Lehmkemper, K.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Solvent influence on the phase behavior and glass transition of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 158, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giauque, W.F.; Stout, J.W. The Entropy of Water and the Third Law of Thermodynamics. The Heat Capacity of Ice from 15 to 273 °K. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1936, 58, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwei, T.K. The effect of hydrogen bonding on the glass transition temperatures of polymer mixtures. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Lett. Ed. 1984, 22, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.; Taylor, J.S. Ideal copolymers and the second-order transitions of synthetic rubbers. i. non-crystalline copolymers. J. Appl. Chem. 1952, 2, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simha, R.; Boyer, R.F. On a General Relation Involving the Glass Temperature and Coefficients of Expansion of Polymers. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, K.; Verreck, G.; Peeters, J.; Brewster, M.; van den Mooter, G. Increased physical stability and improved dissolution properties of itraconazole, a class II drug, by solid dispersions that combine fast- and slow-dissolving polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Zografi, G. The relationship between the glass transition temperature and the water content of amorphous pharmaceutical solids. Pharm. Res. 1994, 11, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallbrucker, A.; Mayer, E.; Johari, G.P. The heat capacity and glass transition of hyperquenched glassy water. Philos. Mag. 1989, 60, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Spanton, S.; Henry, R.; Quick, J.; Dziki, W.; Porter, W.; Morris, J. Ritonavir: An extraordinary example of conformational polymorphism. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.; Sadowski, G. Application of the Perturbed-Chain SAFT Equation of State to Associating Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 5510–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmkemper, K.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Heinzerling, O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Long-Term Physical Stability of PVP- and PVPVA-Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameretti, L.F.; Sadowski, G. Modeling of aqueous amino acid and polypeptide solutions with PC-SAFT. Chem. Eng. Process. 2008, 47, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelot, D. Sur le mélange des gaz. Comptes Rendus Hebd. Des Séances De L’académie Des Sci. 1898, 126, 1703–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Lorentz, H.A. Ueber die Anwendung des Satzes vom Virial in der kinetischen Theorie der Gase. Ann. Phys. 1881, 248, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prudic, A.; Ji, Y.; Luebbert, C.; Sadowski, G. Influence of humidity on the phase behavior of API/polymer formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbach, J.P.; Sandler, S.I. Using Molecular Orbital Calculations To Describe the Phase Behavior of Cross-associating Mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1998, 37, 2917–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mini Spray Dryer B-290: Technical Data Sheet; BÜCHI Labortechnik AG: Flawil, Switzerland, 2014.
- Greenspan, L. Humidity Fixed Points of Binary Saturated Aqueous Solutions. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stan Sect. A 1977, 81A, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, R.; Lorenz, H.; Myerson, A.S. Solubility Measurement Using Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4854–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, H.S.; Taylor, L.S. Phase Behavior of Ritonavir Amorphous Solid Dispersions during Hydration and Dissolution. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 2842–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolbert, F.; Stecker, J.; Luebbert, C.; Sadowski, G. Viscosity of ASDs at humid conditions. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 154, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilevbare, G.A.; Taylor, L.S. Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation in Highly Supersaturated Aqueous Solutions of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs: Implications for Solubility Enhancing Formulations. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, L.S.; Langkilde, F.W.; Zografi, G. Fourier transform Raman spectroscopic study of the interaction of water vapor with amorphous polymers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritters, L.; Reichl, S. Influence of amorphous solid Dispersions of Paracetamol and PVP VA 64 on the thermoresponsive Behaviour of the Polymer. In Proceedings of the SPhERe Proceedings: 3rd International Symposium on Pharmaceutical Engineering Research, Braunschweig, Germany, 25–27 September 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Ren, J.; Novak, J.M.; Kemp, E.; Johnson, G.; Klinzing, G.; Johnson, M.A.; Xu, W. The Effect of Inorganic Salt on Disintegration of Tablets with High Loading of Amorphous Solid Dispersion Containing Copovidone. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Component | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RIT form II [15] | 398.12 | 63.20 | 224.16 |
| water [16] | 273.15 | 6.01 | 38.08 |
| RIT | 1150 * | 325.99 † |
| PVPVA | 1190 [20] | 380.74 † |
| water | 1000 [21] | 138.00 [22] |
| Mixture | ||
|---|---|---|
| RIT/PVPVA | −18.83 | 0.56 |
| RIT/water | −304.87 | 0.66 |
| PVPVA/water | 34.82 | 1.34 |
| Component | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIT [15] | 721 | 0.0220 | 3.900 | 305.787 | 1041.0 | 0.02 | 4/4 |
| PVPVA [25] | 65,000 | 0.0372 | 2.947 | 205.271 | 0 | 0.02 | 653/653 |
| water [26] | 18.015 | 0.0669 | * | 353.950 | 2425.7 | 0.0451 | 1/1 |
| Mixture | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| RIT/PVPVA [15] | 0 | 0 | 0.019 |
| RIT/water [15] | 0 | 0.00006 | −0.059 |
| PVPVA/water † | −7.0045 × 10−6 | 0.0052677 | −1.103909 |
| 10 | −22.32 | 13.54 | −27.87 | 13.50 | 0 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 20 | −21.41 | 15.82 | −27.08 | 15.62 | 0 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 30 | −23.13 | 14.44 | −26.78 | 14.21 | 0 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 40 | −22.83 | 14.85 | −26.30 | 14.49 | 0 | 0.70 | 0.30 | 0.95 | 0 | 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krummnow, A.; Danzer, A.; Voges, K.; Dohrn, S.; Kyeremateng, S.O.; Degenhardt, M.; Sadowski, G. Explaining the Release Mechanism of Ritonavir/PVPVA Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091904
Krummnow A, Danzer A, Voges K, Dohrn S, Kyeremateng SO, Degenhardt M, Sadowski G. Explaining the Release Mechanism of Ritonavir/PVPVA Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091904
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrummnow, Adrian, Andreas Danzer, Kristin Voges, Stefanie Dohrn, Samuel O. Kyeremateng, Matthias Degenhardt, and Gabriele Sadowski. 2022. "Explaining the Release Mechanism of Ritonavir/PVPVA Amorphous Solid Dispersions" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091904
APA StyleKrummnow, A., Danzer, A., Voges, K., Dohrn, S., Kyeremateng, S. O., Degenhardt, M., & Sadowski, G. (2022). Explaining the Release Mechanism of Ritonavir/PVPVA Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1904. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091904








