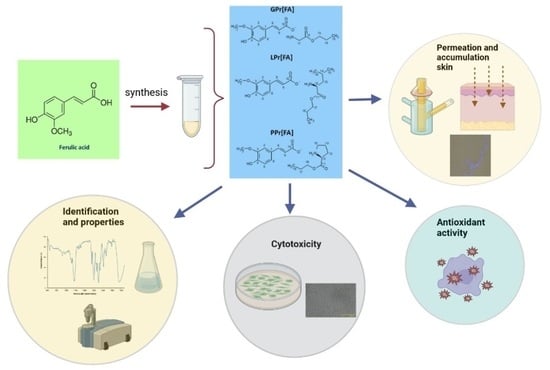
New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of the Amino Acid Propyl Ester Ferulates AAPr[FA]



2.3. Methods Used for Identification and Characterization of Ferulic Acid Derivatives
2.4. Hydrogel and Emulsion Preparation with Ferulic Acid and Its Derivatives
Stability of Hydrogels and Emulsion
2.5. Antioxidant Activity and Total Polyphenols Content
2.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.5.2. Total Polyphenols Content Assay
2.6. Skin Permeation Studies
2.6.1. Skin Preparation and Characteristics before Permeation Studies
2.6.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.6.3. Skin Permeation Experiments
2.6.4. Accumulation in the Skin
2.6.5. Fluorescent Microscopy
2.7. Cytotoxicity of FA and Its Derivatives by Cell Culture Study
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characteristics of Ferulic Acid Derivatives
3.2. Evaluation of Free Radical Scavenging Activity of Ferulic Acid Derivatives
3.3. Stability of Hydrogels and Emulsion
3.4. Skin Penetration Study
3.5. Cell Culture Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zduńska, K.; Dana, A.; Kolodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. Antioxidant Properties of Ferulic Acid and Its Possible Application. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 31, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Rui, Y.; Guo, S.; Luan, F.; Liu, R.; Zeng, N. Ferulic Acid: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Derivatives. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkez, H.; Arslan, M.E.; Barboza, J.N.; Kahraman, C.Y.; de Sousa, D.P.; Mardinoğlu, A. Therapeutic Potential of Ferulic Acid in Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 860–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zduńska-Pęciak, K.; Kołodziejczak, A.; Rotsztejn, H. Two Superior Antioxidants: Ferulic Acid and Ascorbic Acid in Reducing Signs of Photoaging—A Split-face Comparative Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maya-Cano, D.A.; Arango-Varela, S.; Santa-Gonzalez, G.A. Phenolic Compounds of Blueberries (Vaccinium Spp) as a Protective Strategy against Skin Cell Damage Induced by ROS: A Review of Antioxidant Potential and Antiproliferative Capacity. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Makuch, E.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Bargiel, P.; et al. Epilobium angustifolium L. Extracts as Valuable Ingredients in Cosmetic and Dermatological Products. Molecules 2021, 26, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Ziemlewska, A.; Bujak, T.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z.; Hordyjewicz-Baran, Z. Cosmetic and Dermatological Properties of Selected Ayurvedic Plant Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsay, G.J.; Lin, S.-Y.; Li, C.-Y.; Mau, J.-L.; Tsai, S.-Y. Comparison of Single and Combined Use of Ergothioneine, Ferulic Acid, and Glutathione as Antioxidants for the Prevention of Ultraviolet B Radiation-Induced Photoaging Damage in Human Skin Fibroblasts. Processes 2021, 9, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Sood, A.; Lang, D.K.; Arora, R.; Kumar, N.; Diwan, V.; Saini, B. Natural Products as Sources of Multitarget Compounds: Advances in the Development of Ferulic Acid as Multitarget Therapeutic. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gogary, R.I.; Nasr, M.; Rahsed, L.A.; Hamzawy, M.A. Ferulic Acid Nanocapsules as a Promising Treatment Modality for Colorectal Cancer: Preparation and in Vitro/in Vivo Appraisal. Life Sci. 2022, 298, 120500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Cybulska, K.; Makuch, E.; Kucharski, Ł.; Różewicka-Czabańska, M.; Prowans, P.; Czapla, N.; Bargiel, P.; Petriczko, J.; Klimowicz, A. In Vitro Human Skin Penetration, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Ethanol-Water Extract of Fireweed (Epilobium angustifolium L.). Molecules 2021, 26, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Rakoczy, R.; Nowak, A.; Konopacki, M.; Klebeko, J.; Świątek, E.; Janus, E.; Duchnik, W.; Wenelska, K.; Kucharski, Ł.; et al. Transdermal Delivery Systems for Ibuprofen and Ibuprofen Modified with Amino Acids Alkyl Esters Based on Bacterial Cellulose. IJMS 2021, 22, 6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Nowak, A.; Klebeko, J.; Janus, E.; Duchnik, W.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Kucharski, Ł.; Prowans, P.; Petriczko, J.; Czapla, N.; et al. Assessment of the Effect of Structural Modification of Ibuprofen on the Penetration of Ibuprofen from Pentravan® (Semisolid) Formulation Using Human Skin and a Transdermal Diffusion Test Model. Materials 2021, 14, 6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebeko, J.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Nowak, A.; Janus, E.; Duchnik, W.; Adamiak-Giera, U.; Kucharski, Ł.; Prowans, P.; Petriczko, J.; Czapla, N.; et al. Permeability of Ibuprofen in the Form of Free Acid and Salts of L-Valine Alkyl Esters from a Hydrogel Formulation through Strat-MTM Membrane and Human Skin. Materials 2021, 14, 6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, B.; Grimshaw, S.; Hoptroff, M.; Paterson, S.; Arnold, D.; Cawley, A.; Adams, S.E.; Falciani, F.; Dadd, T.; Eccles, R.; et al. Alteration of Barrier Properties, Stratum Corneum Ceramides and Microbiome Composition in Response to Lotion Application on Cosmetic Dry Skin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janus, E.; Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. Enhancement of Ibuprofen Solubility and Skin Permeation by Conjugation with L-Valine Alkyl Esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7570–7584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.-W.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Hsieh, P.-W.; Fang, J.-Y. A Comparison of Skin Delivery of Ferulic Acid and Its Derivatives: Evaluation of Their Efficacy and Safety. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 399, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sha, Y. A Convenient Synthesis of Amino Acid Methyl Esters. Molecules 2008, 13, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, K.; Ou, J.; Huang, C.; Ou, S. Derivatives of Ferulic Acid: Structure, Preparation and Biological Activities. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2015, 5, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Domenico, F.; Di Domenico, F.; Perluigi, M.; Foppoli, C.; Blarzino, C.; Coccia, R.; De Marco, F.; Butterfield, D.A.; Cini, C. Protective Effect of Ferulic Acid Ethyl Ester against Oxidative Stress Mediated by UVB Irradiation in Human Epidermal Melanocytes. Free. Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, D.; Nandi, N.K.; Singh, B.; Singh, A.; Kumar, B.; Narang, R.K.; Singh, C. Ferulic Acid-Loaded Drug Delivery Systems for Biomedical Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintra, T.E.; Luís, A.; Rocha, S.N.; Lobo Ferreira, A.I.M.C.; Gonçalves, F.; Santos, L.M.N.B.F.; Neves, B.M.; Freire, M.G.; Ventura, S.P.M.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Enhancing the Antioxidant Characteristics of Phenolic Acids by Their Conversion into Cholinium Salts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demurtas, M.; Onnis, V.; Zucca, P.; Rescigno, A.; Lachowicz, J.I.; De Villiers Engelbrecht, L.; Nieddu, M.; Ennas, G.; Scano, A.; Mocci, F.; et al. Cholinium-Based Ionic Liquids from Hydroxycinnamic Acids as New Promising Bioactive Agents: A Combined Experimental and Theoretical Investigation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparica, R.; Júlio, A.; Baby, A.; Araújo, M.; Fernandes, A.; Costa, J.; Santos de Almeida, T. Choline-Amino Acid Ionic Liquids as Green Functional Excipients to Enhance Drug Solubility. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Świątek, E.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Janus, E.; Nowak, A.; Sobolewski, P.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. Novel Naproxen Salts with Increased Skin Permeability. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Klebeko, J.; Świątek, E.; Bilska, K.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Struk, Ł.; Wenelska, K.; Klimowicz, A.; et al. Influence of the Type of Amino Acid on the Permeability and Properties of Ibuprofenates of Isopropyl Amino Acid Esters. IJMS 2022, 23, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Bujak, T.; Ziemlewska, A.; Nizioł-Łukaszewska, Z. Positive Effect of Cannabis sativa L. Herb Extracts on Skin Cells and Assessment of Cannabinoid-Based Hydrogels Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suñer-Carbó, J.; Calpena-Campmany, A.; Halbaut-Bellowa, L.; Clares-Naveros, B.; Rodriguez-Lagunas, M.; Barbolini, E.; Zamarbide-Losada, J.; Boix-Montañés, A. Biopharmaceutical Development of a Bifonazole Multiple Emulsion for Enhanced Epidermal Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowak, A.; Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Perużyńska, M.; Cybulska, K.; Kucharska, E.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Piotrowska, K.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Sulikowski, T.; et al. Assessment of the Anti-Inflammatory, Antibacterial and Anti-Aging Properties and Possible Use on the Skin of Hydrogels Containing Epilobium angustifolium L. Extracts. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 896706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Makuch, E.; Kucharski, Ł.; Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Cybulska, K.; Sulikowski, T.; Moritz, M.; Klimowicz, A. Epilobium angustifolium L. Essential Oil—Biological Activity and Enhancement of the Skin Penetration of Drugs—In Vitro Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuch, E.; Nowak, A.; Günther, A.; Pełech, R.; Kucharski, Ł.; Duchnik, W.; Klimowicz, A. Enhancement of the Antioxidant and Skin Permeation Properties of Eugenol by the Esterification of Eugenol to New Derivatives. AMB Expr. 2020, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Klimowicz, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.L.; Florkowska, K.; Muzykiewicz, A.; Wira, D.; Zielonkabrzezicka, J.; Siedłowska, A.; Nadarzewska, K. Application of Green-Extraction Technique to Evaluate of Antioxidative Capacity of Wild Population of Fireweed (Epilobium angustifolium). Herba Pol. 2020, 65, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiao In, M.; Richardson, K.C.; Loewa, A.; Hedtrich, S.; Kaessmeyer, S.; Plendl, J. Histological and Functional Comparisons of Four Anatomical Regions of Porcine Skin with Human Abdominal Skin. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2019, 48, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi, U.; Kaiser, M.; Toll, R.; Mangelsdorf, S.; Audring, H.; Otberg, N.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Porcine Ear Skin: An in Vitro Model for Human Skin. Skin Res. Technol. 2007, 13, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badran, M.M.; Kuntsche, J.; Fahr, A. Skin Penetration Enhancement by a Microneedle Device (Dermaroller®) in Vitro: Dependency on Needle Size and Applied Formulation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 36, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, A.; Goodyear, B.; Ameen, D.; Joshi, V.; Michniak-Kohn, B. Strat-M® Synthetic Membrane: Permeability Comparison to Human Cadaver Skin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 547, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntsche, J.; Bunjes, H.; Fahr, A.; Pappinen, S.; Rönkkö, S.; Suhonen, M.; Urtti, A. Interaction of Lipid Nanoparticles with Human Epidermis and an Organotypic Cell Culture Model. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Amaro, M.I.; Healy, A.M.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Comparative Evaluation of Rivastigmine Permeation from a Transdermal System in the Franz Cell Using Synthetic Membranes and Pig Ear Skin with in Vivo-in Vitro Correlation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noreen, S.; Pervaiz, F.; Ashames, A.; Buabeid, M.; Fahelelbom, K.; Shoukat, H.; Maqbool, I.; Murtaza, G. Optimization of Novel Naproxen-Loaded Chitosan/Carrageenan Nanocarrier-Based Gel for Topical Delivery: Ex Vivo, Histopathological, and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopečná, M.; Macháček, M.; Nováčková, A.; Paraskevopoulos, G.; Roh, J.; Vávrová, K. Esters of Terpene Alcohols as Highly Potent, Reversible, and Low Toxic Skin Penetration Enhancers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davies, D.J.; Ward, R.J.; Heylings, J.R. Multi-Species Assessment of Electrical Resistance as a Skin Integrity Marker for in Vitro Percutaneous Absorption Studies. Toxicol. Vitr. 2004, 18, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertges, F.S.; da Penha Henriques do Amaral, M.; Rodarte, M.P.; Vieira Fonseca, M.J.; Sousa, O.V.; Pinto Vilela, F.M.; Alves, M.S. Assessment of Chemical Changes and Skin Penetration of Green Arabica Coffee Beans Biotransformed by Aspergillus Oryzae. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taokaew, S.; Nunkaew, N.; Siripong, P.; Phisalaphong, M. Characteristics and Anticancer Properties of Bacterial Cellulose Films Containing Ethanolic Extract of Mangosteen Peel. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2014, 25, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albaugh, V.L.; Mukherjee, K.; Barbul, A. Proline Precursors and Collagen Synthesis: Biochemical Challenges of Nutrient Supplementation and Wound Healing. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamane, T.; Morioka, Y.; Kitaura, Y.; Iwatsuki, K.; Shimomura, Y.; Oishi, Y. Branched-Chain Amino Acids Regulate Type I Tropocollagen and Type III Tropocollagen Syntheses via Modulation of MTOR in the Skin. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2018, 82, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Burghardt, R.C.; Johnson, G.A.; Kim, S.W.; Knabe, D.A.; Li, P.; Li, X.; McKnight, J.R.; Satterfield, M.C.; et al. Proline and Hydroxyproline Metabolism: Implications for Animal and Human Nutrition. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalinowska, M.; Piekut, J.; Bruss, A.; Follet, C.; Sienkiewicz-Gromiuk, J.; Świsłocka, R.; Rzączyńska, Z.; Lewandowski, W. Spectroscopic (FT-IR, FT-Raman, 1H, 13C NMR, UV/VIS), Thermogravimetric and Antimicrobial Studies of Ca(II), Mn(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II) Complexes of Ferulic Acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 122, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; He, J.; Yao, T.; Chang, W. RP-HPLC Determination of Octanol–Water Partition Coefficients for Bioactive Compounds from Chinese Herbal Medicines. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas-Boas, S.M.; Cordova, I.W.; Kurnia, K.A.; Almeida, H.H.S.; Gaschi, P.S.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Pinho, S.P.; Ferreira, O. Comparison of Two Computational Methods for Solvent Screening in Countercurrent and Centrifugal Partition Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1666, 462859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Fan, T. Sodium Ferulate Attenuates Lidocaine-Induced Corneal Endothelial Impairment. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4967318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Peng, Q.; Liu, J.; Alolga, R.N.; Zhou, W. A Novel Ferulic Acid Derivative Attenuates Myocardial Cell Hypoxia Reoxygenation Injury through a Succinate Dehydrogenase Dependent Antioxidant Mechanism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 856, 172417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.L.S.; Valente, D.; Moreira, H.R.; Pintado, M.; Costa, P. Effect of Squalane-Based Emulsion on Polyphenols Skin Penetration: Ex Vivo Skin Study. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 218, 112779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauce, R.; de Oliveira Pinto, C.A.S.; Velasco, M.V.R.; Rosado, C.; Baby, A.R. Ex Vivo Penetration Analysis and Anti-Inflammatory Efficacy of the Association of Ferulic Acid and UV Filters. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 156, 105578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Liu, X.; Fahr, A. Skin Delivery of Ferulic Acid from Different Vesicular Systems. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2010, 6, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Wong, A.B.H. Stabilization of Ferulic Acid in Topical Gel Formulation via Nanoencapsulation and PH Optimization. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saija, A. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Caffeic and Ferulic Acids as Topical Photoprotective Agents. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 199, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žilius, M.; Ramanauskienė, K.; Briedis, V. Release of Propolis Phenolic Acids from Semisolid Formulations and Their Penetration into the Human Skin In Vitro. Evid. -Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 958717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ossowicz-Rupniewska, P.; Bednarczyk, P.; Nowak, M.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Rokicka, J.; Klimowicz, A.; Czech, Z. Sustainable UV-Crosslinkable Acrylic Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives for Medical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Jung, E.-C.; Zhu, H.; Zou, Y.; Hui, X.; Maibach, H. Vehicle Effects on Human Stratum Corneum Absorption and Skin Penetration. Toxicol Ind. Health 2017, 33, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; White, E.T.; Howes, T.; Litster, J.D.; Marziano, I. Effect of Solvent Composition and Temperature on the Solubility of Ibuprofen in Aqueous Ethanol. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, R.M.; Herkenne, C.; Guy, R.H.; Hadgraft, J.; Oliveira, G.; Lane, M.E. Influence of Ethanol on the Solubility, Ionization and Permeation Characteristics of Ibuprofen in Silicone and Human Skin. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2009, 22, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bommannan, D.; Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Examination of the Effect of Ethanol on Human Stratum Corneum in Vivo Using Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Control. Release 1991, 16, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Garg, P.; Goyal, R.; Kaur, G.; Li, X.; Negi, P.; Valis, M.; Kuca, K.; Kulshrestha, S. A Novel Herbal Hydrogel Formulation of Moringa Oleifera for Wound Healing. Plants 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagórska-Dziok, M.; Kleczkowska, P.; Olędzka, E.; Figat, R.; Sobczak, M. Poly(Chitosan-Ester-Ether-Urethane) Hydrogels as Highly Controlled Genistein Release Systems. IJMS 2021, 22, 3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.; Clegg, J.R.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Hydrogels in the Clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2020, 5, e10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Champeau, M.; Seabra, A.B.; de Oliveira, M.G. Hydrogels for Topical Nitric Oxide Delivery. In Nitric Oxide Donors; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 313–330. ISBN 978-0-12-809275-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Janus, E.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; Klimowicz, A. The Effect of Alcohols as Vehicles on the Percutaneous Absorption and Skin Retention of Ibuprofen Modified with l-Valine Alkyl Esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 41727–41740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwansh, R.K.; Mukherjee, P.K.; Bahadur, S.; Biswas, R. Enhanced Permeability of Ferulic Acid Loaded Nanoemulsion Based Gel through Skin against UVA Mediated Oxidative Stress. Life Sci. 2015, 141, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanini, M.Z.; Pinho-Ribeiro, F.A.; Ivan, A.L.M.; Ferreira, V.S.; Vilela, F.M.P.; Vicentini, F.T.M.C.; Martinez, R.M.; Zarpelon, A.C.; Fonseca, M.J.V.; Faria, T.J.; et al. Efficacy of Topical Formulations Containing Pimenta Pseudocaryophyllus Extract against UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Hairless Mice. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2013, 127, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Serra, S.; Cristina Abreu, A.; Saavedra, M.J.; Salgado, A.; Simões, M. Evaluation of the Effects of Selected Phytochemicals on Quorum Sensing Inhibition and in Vitro Cytotoxicity. Biofouling 2014, 30, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truzzi, F.; Valerii, M.C.; Tibaldi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Abduazizova, V.; Spisni, E.; Dinelli, G. Are Supplements Safe? Effects of Gallic and Ferulic Acids on In Vitro Cell Models. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-H.; Park, J.-K.; Kim, K.-M.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, S. In Vitro and in Vivo Antithrombotic and Cytotoxicity Effects of Ferulic Acid. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, e22004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Gong, X.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; Du, W.; Kuang, G. Ferulic Acid Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis via Blockage of PI3K/Akt Pathway in Osteosarcoma Cell. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 968–980. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Yu, H.; Guo, W.; Kong, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. The Anticancer Effects of Ferulic Acid Is Associated with Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest and Autophagy in Cervical Cancer Cells. Cancer Cell. Int. 2018, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, D.; Jiang, R.; Li, H.; Wan, J.; Li, H. Ferulic Acid Exerts Antitumor Activity and Inhibits Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Ingredient | Emulsion | Hydrogel |
|---|---|---|
| FA or its derivatives * | 1 * | 1 * |
| HEC | - | 3 |
| Glycerin | 10 | 10 |
| Biobase | 6 | - |
| Grape seed oil | 20 | - |
| Beeswax | 7 | - |
| Ethanol 96% | 1 | 1 |
| Water up to | 100 | 100 |
| Compound | Molar Mass (g mol−1) | Tm (°C) | Tc (°C) | Td onset (°C) | Td max (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferulic acid | 194.18 | 178.15 | 125.22 | 217.0 | 251.2 | na |
| GPr[FA] | 311.33 | 152.91 | nd | 129.6 | 145.3 | na |
| LPr[FA] | 367.44 | 115.27 | nd | 126.0 | 156.0 | +9.6 |
| PPr[FA] | 351.39 | 109.76 | nd | 122.8 | 148.7 | −29.8 |
| Compound | Solubility g dm−3 | Solubility g FA dm−3 | log PO/W |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ferulic acid | 0.6729 ± 0.0828 | 0.6729 ± 0.0828 | 1.643 ± 0.003 |
| GPr[FA] | 9.5816 ± 1.5818 | 5.9760 ± 0.9866 | 0.582 ± 0.019 |
| LPr[FA] | 11.3416 ± 1.4321 | 5.9937 ± 0.7568 | 0.454 ± 0.009 |
| PPr[FA] | 76.3345 ± 6.1153 | 42.1828 ± 3.3793 | 0.447 ± 0.022 |
| Antioxidant Activity: | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Molar Ratio Antioxidant:DPPH | FA | GPr[FA] | LPr[FA] | PPr[FA] | ||||
| %RSA | mmol Trolox dm−3 | %RSA | mmol Trolox dm−3 | %RSA | mmol Trolox dm−3 | %RSA | mmol Trolox dm−3 | |
| 0.1 | 12.4 ± 0.001 a | 0.049 ± 0.001 a | 17.6 ± 0.001 a | 0.099 ± 0.001 a | 17.6 ± 0.001 a | 0.098 ± 0.001 a | 19.3 ± 0.001 a | 0.115 ± 0.001 a |
| 1.0 | 73.2 ± 0.001 b | 0.635 ± 0.001 b | 78.0 ± 0.001 b | 0.681 ± 0.001 b | 79.5 ± 0.001 b | 0.696 ± 0.001 b | 79.6 ± 0.001 b | 0.697 ± 0.001 b |
| 2.0 | 86.5 ± 0.001 b | 0.763 ± 0.001 b | 86.6 ± 0.001 b | 0.764 ± 0.001 b | 87.8 ± 0.001 b | 0.776 ± 0.001 b | 87.7 ± 0.001 b | 0.775 ± 0.001 b |
| Cumulative Permeation Mass (µg FA·cm−2) | |
|---|---|
| Ethanol | |
| FA | 368.57 ± 2.94 a |
| GPr[FA] | 378.26 ± 2.29 a |
| LPr[FA] | 415.12 ± 8.71 b |
| PPr[FA] | 427.00 ± 4.67 b |
| Hydrogel | |
| FA | 289.36 ± 38.50 a |
| GPr[FA] | 268.16 ± 12.71 a |
| LPr[FA] | 267.48 ± 24.57 a |
| PPr[FA] | 396.86 ± 42.13 b |
| Emulsion | |
| FA | 104.93 ± 7.63 a |
| GPr[FA] | 101.70 ± 26.47 a |
| LPr[FA] | 119.29 ± 19.72 a |
| PPr[FA] | 128.80 ± 19.86 a |
| Compounds | DPPH mmol Trolox dm−3 | Total Polyphenol mmol GA dm−3 |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | ||
| FA | 0.079 ± 0.010 a | 0.097 ± 0.002 a |
| GPr[FA] | 0.097 ± 0.021 b | 0.115 ± 0.001 b |
| LPr[FA] | 0.098 ± 0.011 a | 0.122 ± 0.002 c |
| PPr[FA] | 0.094 ± 0.002 a | 0.125 ± 0.001 c |
| Hydrogel | ||
| FA | 0.067 ± 0.004 a | 0.059 ± 0.003 a |
| GPr[FA] | 0.069 ± 0.002 a | 0.064 ± 0.001 b |
| LPr[FA] | 0.063 ± 0.009 a | 0.057 ± 0.002 a |
| PPr[FA] | 0.075 ± 0.012 a | 0.082 ± 0.001 c |
| Emulsion | ||
| FA | 0.057 ± 0.004 a | 0.047 ± 0.006 a |
| GPr[FA] | 0.059 ± 0.010 a | 0.051 ± 0.001 ab |
| LPr[FA] | 0.053 ± 0.005 a | 0.045 ± 0.004 a |
| PPr[FA] | 0.061 ± 0.007 a | 0.061 ± 0.002 b |
| Compounds | DPPH mmol Trolox dm−3 | Total Polyphenol mmol GA dm−3 |
|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | ||
| FA | 0.394 ± 0.004 b | 0.275 ± 0.015 c |
| GPr[FA] | 0.257 ± 0.026 a | 0.234 ± 0.002 b |
| LPr[FA] | 0.255 ± 0.038 a | 0.199 ± 0.004 a |
| PPr[FA] | 0.259 ± 0.007 a | 0.193 ± 0.005 a |
| Hydrogel | ||
| FA | 0.381 ± 0.011 b | 0.289 ± 0.006 c |
| GPr[FA] | 0.298 ± 0.009 a | 0.248 ± 0.010 b |
| LPr[FA] | 0.320 ± 0.030 ab | 0.233 ± 0.008 b |
| PPr[FA] | 0.351 ± 0.036 ab | 0.201 ± 0.007 a |
| Emulsion | ||
| FA | 0.300 ± 0.024 b | 0.202 ± 0.012 a |
| GPr[FA] | 0.235 ± 0.037 a | 0.264 ± 0.000 b |
| LPr[FA] | 0.257 ± 0.014 ab | 0.219 ± 0.003 a |
| PPr[FA] | 0.198 ± 0.006 a | 0.208 ± 0.021 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Janus, E.; Pinheiro, L.R.; Nowak, A.; Kucharska, E.; Świątek, E.; Podolak, N.; Perużyńska, M.; Piotrowska, K.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, Ł.; et al. New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010117
Janus E, Pinheiro LR, Nowak A, Kucharska E, Świątek E, Podolak N, Perużyńska M, Piotrowska K, Duchnik W, Kucharski Ł, et al. New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010117
Chicago/Turabian StyleJanus, Ewa, Luan Ramalho Pinheiro, Anna Nowak, Edyta Kucharska, Ewelina Świątek, Natalia Podolak, Magdalena Perużyńska, Katarzyna Piotrowska, Wiktoria Duchnik, Łukasz Kucharski, and et al. 2023. "New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010117
APA StyleJanus, E., Pinheiro, L. R., Nowak, A., Kucharska, E., Świątek, E., Podolak, N., Perużyńska, M., Piotrowska, K., Duchnik, W., Kucharski, Ł., & Klimowicz, A. (2023). New Ferulic Acid and Amino Acid Derivatives with Increased Cosmeceutical and Pharmaceutical Potential. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010117