Local Drug Delivery in Bladder Cancer: Advances of Nano/Micro/Macro-Scale Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Colloidal Nano- and Micro-Sized Delivery Systems
Additional Techniques to Improve Therapeutic Effect of Nano- and Micro Delivery Systems
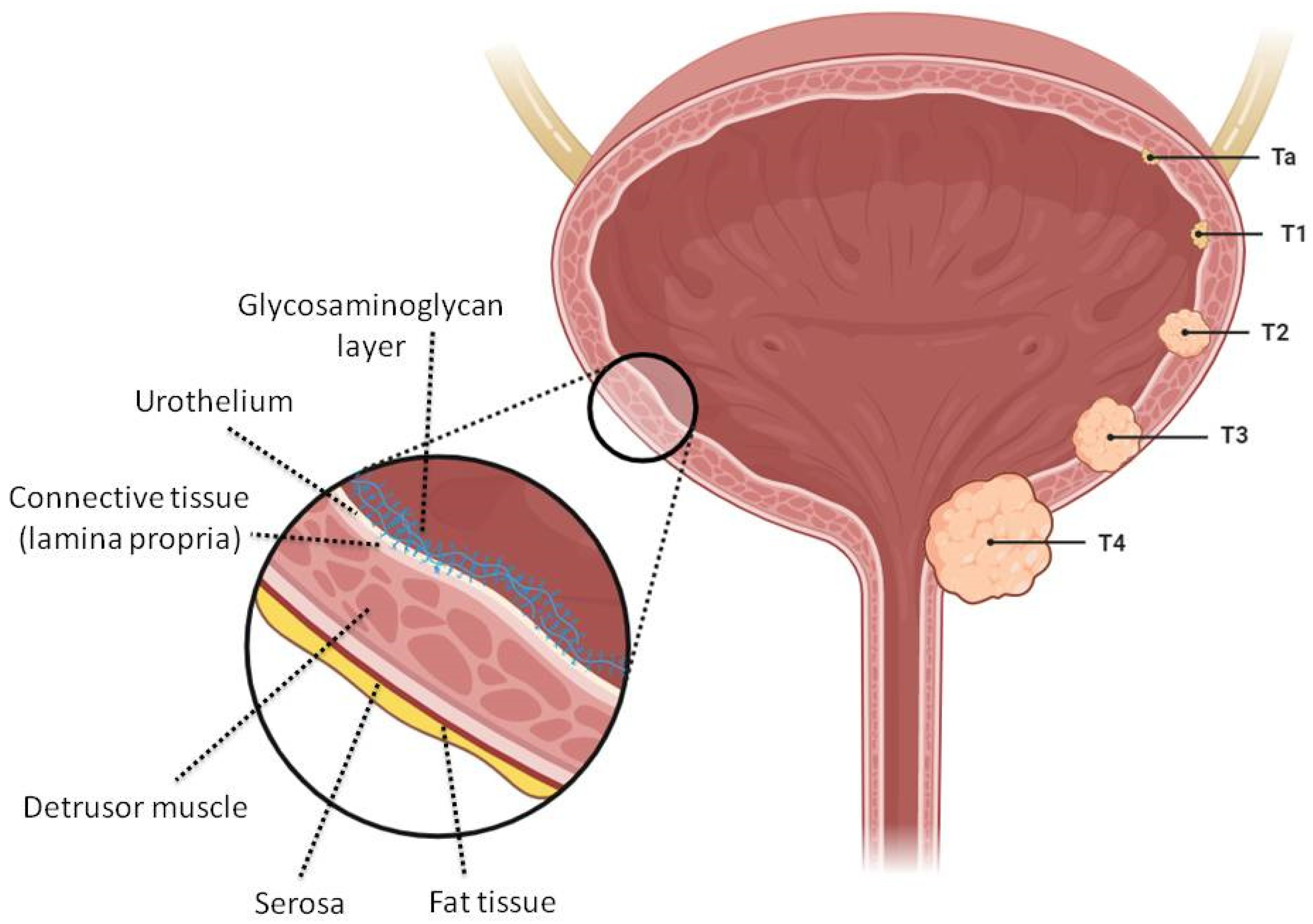
3. Reservoir-Type Intravesical Delivery Systems
3.1. Biodegradable Systems
3.1.1. Ion-Sensitive Formulations
3.1.2. Thermosensitive Formulations

3.1.3. Combined Particle–Hydrogel Systems for Intravesical Delivery
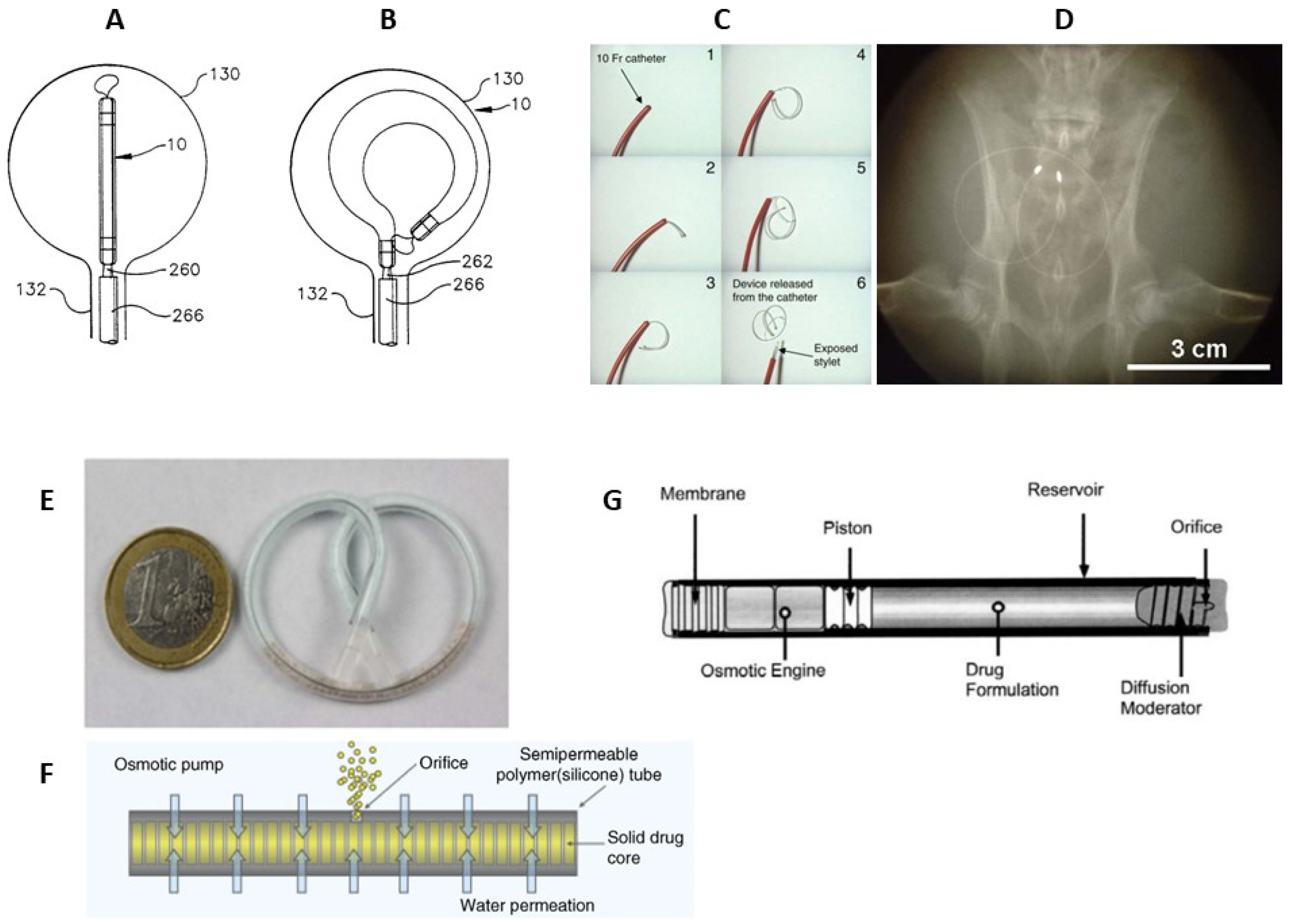
3.2. Non-Biodegradable Indwelling Devices
3.2.1. Elastomer-Based Devices

3.2.2. Osmotic Pumps
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoogstraten, L.M.C.; Vrieling, A.; van der Heijden, A.G.; Kogevinas, M.; Richters, A.; Kiemeney, L.A. Global trends in the epidemiology of bladder cancer: Challenges for public health and clinical practice. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 287–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidian, H.; Haghdoost, A.A.; Daroudi, R.; Raadabadi, M.; Ebadzadeh, M.R.; Zendehdel, K. Estimating the Prevalence of Bladder Cancer by Stage in Iran as a Developing Country. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2022, 36, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halaseh, S.A.; Halaseh, S.; Alali, Y.; Ashour, M.E.; Alharayzah, M.J. A Review of the Etiology and Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: All You Need To Know. Cureus 2022, 14, e27330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, K.; Kitchen, M.O.; Mathias, S.-J.; Khanim, F.L.; Bryan, R.T. Novel intravesical therapeutics in the treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: Horizon scanning. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 912438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez-Escrig, J.L.; Kelly, J.D.; Neal, D.E.; King, S.M.; Davies, B.R. Evaluation of the Therapeutic Potential of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Gefitinib in Preclinical Models of Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4874–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, H.; Mir, M.C.; Barata, P.C.; Stephenson, A.J.; Campbell, S.C.; Fergany, A.; Dreicer, R.; Garcia, J.A. Phase II trial of continuous treatment with sunitinib in patients with high-risk (BCG-refractory) non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 37, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallinger, C.; Trommeshauser, D.; Marzin, K.; Liesener, A.; Kaiser, R.; Stopfer, P. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Nintedanib in Healthy Volunteers and Patients with Advanced Cancer. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacche, M.M.; Srikrishna, S.; Cardozo, L. Novel targeted bladder drug-delivery systems: A review. Res. Rep. Urol. 2015, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palugan, L.; Cerea, M.; Cirilli, M.; Moutaharrik, S.; Maroni, A.; Zema, L.; Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Filippin, I.; Foppoli, A.; et al. Intravesical drug delivery approaches for improved therapy of urinary bladder diseases. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Xue, D. Current Researches on Nanodrug Delivery Systems in Bladder Cancer Intravesical Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 879828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfraz, M.; Qamar, S.; Rehman, M.U.; Tahir, M.A.; Ijaz, M.; Ahsan, A.; Asim, M.H.; Nazir, I. Nano-Formulation Based Intravesical Drug Delivery Systems: An Overview of Versatile Approaches to Improve Urinary Bladder Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.W.; Lee, H.H.; Park, E.Y.; Park, W.S.; Kim, S.H.; Joung, J.Y.; Chung, J.; Seo, H.K. Clinical Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Intravesical Mitomycin-C Therapy Immediately before Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor in Patients with Nonmuscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: Preliminary Results of a Prospective, Randomized Phase II Study. J. Urol. 2023, 209, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Shen, T.; Wientjes, M.G.; O’Donnell, M.A.; Au, J.L.S. Intravesical treatments of bladder cancer: Review. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GuhaSarkar, S.; Banerjee, R. Intravesical drug delivery: Challenges, current status, opportunities and novel strategies. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.-C.; Lee, K.-H.; Lee, W.-C.; Yeh, T.-C.; Kuo, Y.-C.; Chiang, B.-J.; Liao, C.-H.; Meng, E.; Kao, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-C.; et al. Treating Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury Patients—When Intravesical Botox Injection or Urethral Botox Injection Are Indicated. Toxins 2023, 15, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wientjes, M.G.; Li, J.; Au, J.L.S. Bladder tissue pharmacokinetics of intravesical mitomycin C and suramin in dogs. AAPS J. 2010, 12, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wientjes, M.G.; Dalton, J.T.; Badalament, R.A.; Drago, J.R.; Au, J.L.S. Bladder Wall Penetration of Intravesical Mitomycin C in Dogs. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4347–4354. [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes, M.G.; Dalton, J.T.; Badalament, R.A.; Dasani, B.M.; Drago, J.R.; Au, J.L.S. A Method to Study Drug Concentration–Depth Profiles in Tissues: Mitomycin C in Dog Bladder Wall. Pharm. Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. 1991, 8, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Wientjes, M.G.; Badalament, R.A.; Au, J.L.S. Penetration of intravesical doxorubicin in human bladders. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1996, 37, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Neoh, K.G.; Xu, L.; Lu, S.; Kang, E.T.; Mahendran, R.; Chiong, E. Functionalized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Mucoadhesive and Sustained Drug Release Properties for Potential Bladder Cancer Therapy. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6151–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Neoh, K.G.; Xu, L.; Kang, E.T.; Chiong, E. Polymeric nanoparticles with encapsulated superparamagnetic iron oxide and conjugated cisplatin for potential bladder cancer therapy. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 2513–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homhuan, A.; Harashima, H.; Yano, I. Cellular attachment and internalization of cationic liposomes containing mycobacterial cell wall. ScienceAsia 2008, 34, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Zarrabi, A.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Taheriazam, A.; Mirzaei, S.; Hashemi, M.; Hushmandi, K.; Makvandi, P.; Nazarzadeh Zare, E.; Sharifi, E.; et al. (Nano)platforms in bladder cancer therapy: Challenges and opportunities. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2023, 8, e10353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.; Zhang, S.; Lei, Q.; Wu, S. State-of-the-Art Advances of Nanomedicine for Diagnosis and Treatment of Bladder Cancer. Biosensors 2022, 12, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdoğar, N.; Iskit, A.B.; Eroğlu, H.; Sargon, M.F.; Mungan, N.A.; Bilensoy, E. Antitumor efficacy of bacillus calmette-guerin loaded cationic nanoparticles for intravesical immunotherapy of bladder tumor induced rat model. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 10156–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Hou, J.; Sun, B.; Zhu, B.; Qiao, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X. Paclitaxel/Chitosan Nanosupensions Provide Enhanced Intravesical Bladder Cancer Therapy with Sustained and Prolonged Delivery of Paclitaxel. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1992–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, K.; Jiao, B.; Luo, K.; Ren, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Q.; Gan, Z. Mucoadhesive nanoparticles based on ROS activated gambogic acid prodrug for safe and efficient intravesical instillation chemotherapy of bladder cancer. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, B.; Liu, K.; Gong, H.; Ding, Z.; Xu, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, G.; Yu, Q.; Gan, Z. Bladder cancer selective chemotherapy with potent NQO1 substrate co-loaded prodrug nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2022, 347, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogar, N.; Iskit, A.B.; Eroglu, H.; Sargon, M.F.; Mungan, N.A.; Bilensoy, E. Cationic core-shell nanoparticles for intravesical chemotherapy in tumor-induced rat model: Safety and efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Metwally, A.A.; Fahmy, R.H.; Osman, R. Chitosan-coated nanodiamonds: Mucoadhesive platform for intravesical delivery of doxorubicin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 245, 116528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.T.; Liu, J.; Shimizu, S.; Kaimakliotis, H.Z.; Wheeler, M.A.; Hittelman, A.B.; Weiss, R.M.; Steinbach, J.M. Surface-modified nanoparticles enhance transurothelial penetration and delivery of survivin siRNA in treating bladder cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 13, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Deng, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Y.; Miao, H.; Ren, F.; et al. Cannabidiol effectively promoted cell death in bladder cancer and the improved intravesical adhesion drugs delivery strategy could be better used for treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, M.K.; Bogataj, M.; Veranič, P.; Mrhar, A. Permeability of pig urinary bladder wall: Time and concentration dependent effect of chitosan. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1685–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugabe, C.; Matsui, Y.; So, A.I.; Gleave, M.E.; Baker, J.H.E.; Minchinton, A.I.; Manisali, I.; Liggins, R.; Brooks, D.E.; Burt, H.M. In vivo evaluation of mucoadhesive nanoparticulate docetaxel for intravesical treatment of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2788–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Neoh, K.G.; Kang, E.T.; Mahendran, R.; Chiong, E. Mucoadhesive polyacrylamide nanogel as a potential hydrophobic drug carrier for intravesical bladder cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 72, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Zhang, R.; Wu, G.; Sui, X.; Wang, J.; Kim, N.Y.; Blake, S.; De, D.; Xie, T.; Cao, Y.; et al. Intravesical delivery of KDM6A-mRNA via mucoadhesive nanoparticles inhibits the metastasis of bladder cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2112696119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yuan, S.; Deng, D.; Ou, T.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Lei, Q.; Wang, X.; Shen, W.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Fluorinated Polyethylenimine to Enable Transmucosal Delivery of Photosensitizer-Conjugated Catalase for Photodynamic Therapy of Orthotopic Bladder Tumors Postintravesical Instillation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lei, Q.; Wang, F.; Deng, D.; Wang, S.; Tian, L.; Shen, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, S. Fluorinated Polymer Mediated Transmucosal Peptide Delivery for Intravesical Instillation Therapy of Bladder Cancer. Small 2019, 15, 1900936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, S.; Deng, D.; Xiao, Z.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Lei, Q.; Gao, S.; Huang, G.; Zhang, E.; et al. Fluorinated Chitosan to Enhance Transmucosal Delivery of Sonosensitizer-Conjugated Catalase for Sonodynamic Bladder Cancer Treatment Post-intravesical Instillation. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, S.; Li, G.; Xu, M.; Deng, D.; Xiao, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, E.; Xie, L.; et al. Transmucosal Delivery of Self-Assembling Photosensitizer–Nitazoxanide Nanocomplexes with Fluorinated Chitosan for Instillation-Based Photodynamic Therapy of Orthotopic Bladder Tumors. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 1485–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Luo, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, X.; Zeng, G.; Liu, Z.; Wu, S. Photoactivated H2Nanogenerator for Enhanced Chemotherapy of Bladder Cancer. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8135–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Tao, T.; Deng, D.; Zhang, S.; Chao, Y.; Dai, Y.; Li, Y.; Tao, R.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Z.; et al. Collagen-targeted tumor-specific transepithelial penetration enhancer mediated intravesical chemoimmunotherapy for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaganapathy, B.R.; Chancellor, M.B.; Nirmal, J.; Dang, L.; Tyagi, P. Bladder uptake of liposomes after intravesical administration occurs by endocytosis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vila-Caballer, M.; Codolo, G.; Munari, F.; Malfanti, A.; Fassan, M.; Rugge, M.; Balasso, A.; de Bernard, M.; Salmaso, S. A pH-sensitive stearoyl-PEG-poly(methacryloyl sulfadimethoxine)-decorated liposome system for protein delivery: An application for bladder cancer treatment. J. Control. Release 2016, 238, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.R.; Yang, G.; Place, R.F.; Charisse, K.; Epstein-Barash, H.; Manoharan, M.; Li, L.C. Intravesical delivery of small activating RNA formulated into lipid nanoparticles inhibits orthotopic bladder tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5069–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, J.; Nishiyama, H.; Yano, I.; Nakaya, A.; Kohama, H.; Kawai, K.; Joraku, A.; Nakamura, T.; Harashima, H.; Akaza, H. The therapeutic effects of R8-liposome-BCG-CWS on BBN-induced rat urinary bladder carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar]
- Bersani, S.; Vila-Caballer, M.; Brazzale, C.; Barattin, M.; Salmaso, S. PH-sensitive stearoyl-PEG-poly(methacryloyl sulfadimethoxine) decorated liposomes for the delivery of gemcitabine to cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldybekov, D.B.; Tonglairoum, P.; Opanasopit, P.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Mucoadhesive maleimide-functionalised liposomes for drug delivery to urinary bladder. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 111, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldybekov, D.B.; Filippov, S.K.; Radulescu, A.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Maleimide-functionalised PLGA-PEG nanoparticles as mucoadhesive carriers for intravesical drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 143, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oefelein, M.; Huynh, D.; Dickstein, R.; Bean, K. Mp72-01 Phase 1 Outcomes of a Novel Third Generation Liposomal Paclitaxel Formulation (Tsd-001) in Low-Intermediate Risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer (Nmibc) Patients. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03081858 (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Rieger, C.; Kunhardt, D.; Kaufmann, A.; Schendel, D.; Huebner, D.; Erdmann, K.; Propping, S.; Wirth, M.P.; Schwenzer, B.; Fuessel, S.; et al. Characterization of different carbon nanotubes for the development of a mucoadhesive drug delivery system for intravesical treatment of bladder cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; He, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, C.; Jing, P. In vitro and in vivo studies of pirarubicin-loaded SWNT for the treatment of bladder cancer. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Wei, W.; Cao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, P.; Xie, D.; Wu, P.; Liu, B.; et al. Treatment of bladder cancer by geoinspired synthetic chrysotile nanocarrier-delivered circPRMT5 siRNA. Biomater. Res. 2022, 26, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; Chang, L.C.; Wu, P.C. Co-delivery of cisplatin and gemcitabine via viscous nanoemulsion for potential synergistic intravesical chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveleva, M.S.; Lobanov, M.E.; Gusliakova, O.I.; Plastun, V.O.; Prikhozhdenko, E.S.; Sindeeva, O.A.; Gorin, D.A.; Mayorova, O.A. Mucoadhesive Emulsion Microgels for Intravesical Drug Delivery: Preparation, Retention at Urothelium, and Biodistribution Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 25354–25368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Yeh, T.K.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Lyness, G.; Xin, Y.; Wientjes, M.G.; Bergdall, V.; Couto, G.; Alvarez-Berger, F.; et al. Paclitaxel gelatin nanoparticles for intravesical bladder cancer therapy. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, J.M.; Barlow, L.J.; Laudano, M.A.; Mann, M.J.; Petrylak, D.P.; Benson, M.C. A phase I trial of intravesical nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel in the treatment of bacillus Calmette-Guérin refractory nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, J.M.; Holder, D.D.; Ghandour, R.A.; Barlow, L.J.; Ahn, J.J.; Kates, M.; Badalato, G.M.; Roychoudhury, A.; Decastro, G.J.; Benson, M.C. Phase II trial of intravesical nanoparticle albumin bound paclitaxel for the treatment of nonmuscle invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder after bacillus calmette-guérin treatment failure. J. Urol. 2014, 192, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKiernan, J.; Onyeji, I.; Lascano, D.; Ahn, J.; Holder, D.; Abate-Shen, C.; RoyChoudhury, A.; Decastro, G.J. Lb-S&T-03 a Phase 1/2 Study of Albumin-Bound Rapamycin Nanoparticles in Bacillus Calmette-Guerin Refractory Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. J. Urol. 2016, 195, e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, P.; Luo, L.; Cheng, H.; Li, Y.; Du, T.; Zou, B.; Gou, M. Efficient intravesical therapy of bladder cancer with cationic doxorubicin nanoassemblies. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 4535–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Han, R.; Yang, C.; Liu, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qian, Z. RGD peptide modified platinum nanozyme Co-loaded glutathione-responsive prodrug nanoparticles for enhanced chemo-photodynamic bladder cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2023, 293, 121975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Li, Y.P.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Goodwin, N.; Gao, T.; White, R.D.V.; Lam, K.S.; Pan, C.X. Tumor-targeting multifunctional micelles for imaging and chemotherapy of advanced bladder cancer. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05519241 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Qiu, X.; Cao, K.; Lin, T.; Chen, W.; Yuan, A.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Guo, H. Drug delivery system based on dendritic nanoparticles for enhancement of intravesical instillation. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 7365–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, X. Poly(amidoamine)-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a mucoadhesive drug delivery system for potential bladder cancer therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 189, 110832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Fa, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Lu, Y.H.; Chiang, Y.H.; Yang, C.M.; Wu, L.C.; et al. Thiolated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Immunoadjuvant to Enhance Efficacy of Intravesical Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2204643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.T.; Hoimes, C.J.; Kaimakliotis, H.Z.; Cheng, C.J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, J.; Wheeler, M.A.; Kelly, W.K.; Tew, G.N.; Saltzman, W.M.; et al. Nanoparticles for urothelium penetration and delivery of the histone deacetylase inhibitor belinostat for treatment of bladder cancer. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, D.; Liu, F.; Wu, Y.; Peng, X.; Song, F. Recent advances of redox-responsive nanoplatforms for tumor theranostics. J. Control. Release 2021, 332, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Yan, L.; Ding, J.; Hou, Y.; Chen, X. Positively charged polypeptide nanogel enhances mucoadhesion and penetrability of 10-hydroxycamptothecin in orthotopic bladder carcinoma. J. Control. Release 2017, 259, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, F.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Hou, Y.; Wang, C.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Mucoadhesive Cationic Polypeptide Nanogel with Enhanced Penetration for Efficient Intravesical Chemotherapy of Bladder Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, F.; Qiu, H.; Xu, W.; Li, P.; Hou, Y.; Ding, J.; Chen, X. Synergistically Enhanced Mucoadhesive and Penetrable Polypeptide Nanogel for Efficient Drug Delivery to Orthotopic Bladder Cancer. Research 2020, 2020, 8970135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Lai, W.F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Qi, X.; et al. R11 modified tumor cell membrane nanovesicle-camouflaged nanoparticles with enhanced targeting and mucus-penetrating efficiency for intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, P.; Hou, D.; Yan, Y.; Yue, K.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, T.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, P.; et al. Bacteria-inspired transformable nanoparticle targets and covers residual tumor against bladder cancer recurrence. Nano Today 2022, 45, 101551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Cho, S.H.; Hahn, S.K. Urease-Powered Polydopamine Nanomotors for Intravesical Therapy of Bladder Diseases. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 6683–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, S.; Shu, Q.; Wu, S. Strategies to get drugs across bladder penetrating barriers for improving bladder cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Chancellor, M.B.; Seki, S.; Yoshimura, N.; Tyagi, P.; Huang, L.; Lavelle, J.P.; De Groat, W.C.; Fraser, M.O. Intravesical protamine sulfate and potassium chloride as a model for bladder hyperactivity. Urology 2003, 61, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, Ö.; Özdiler, E.; Özen, S.; Göğüş, O. Transmurally absorbed intravesical chemotherapy with dimethylsulfoxide in an animal model. Int. J. Urol. 1999, 6, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannantoni, A.; Di Stasi, S.M.; Stephen, R.L.; Navarra, P.; Scivoletto, G.; Mearini, E.; Porena, M. Intravesical Capsaicin Versus Resiniferatoxin In Patients With Detrusor Hyperreflexia: A Prospective Randomized Study. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 1710–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Chancellor, M.B.; Li, Z.; de Groat, W.C.; Yoshimura, N.; Fraser, M.O.; Huang, L. Urodynamic and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of Intravesical Capsaicin Delivery Using Thermosensitive Hydrogel and Liposomes. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, F.C.; Wein, A.J.; McKenna, B.A.W.; Whitmore, K.; Levin, R.M. Indigocarmine as a Quantitative Indicator of Urothelial Integrity. J. Urol. 1991, 145, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri, D.; Lee, H.J.; El-Gemmal, S.; Backhouse, C.; Tay, A.; John, B.; Perry, M.J.; Ayres, B.E.; Issa, R. Cystectomy outcomes in patients who have failed Radiofrequency-induced Thermo-chemotherapeutic Effect Mitomycin-C (RITE-MMC) treatment for high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (HRNMIBC)–Does it complicate surgery and adversely impact oncological o. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 39, 300.e15–300.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.S.; Kelly, J.D. Intravesical device-assisted therapies for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricksen, K. Device-assisted intravesical therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2019, 8, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.A. Radiofrequency-induced Thermochemotherapy for Recurrent Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A New Treatment for an Unmet Need? Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Valenberg, F.J.P.; van der Heijden, A.G.; Lammers, R.J.M.; Falke, J.; Arends, T.J.H.; Oosterwijk, E.; Witjes, J.A. Intravesical radiofrequency induced hyperthermia enhances mitomycin C accumulation in tumour tissue. Int. J. Hyperth. 2018, 34, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyev, F.; Bondar, O.; Chystiakov, R.; Lysenko, V.; Stavnychyi, O.; Varbanets, V. The impact of different adjuvant intravesical therapy methods on tumor biology in patients with high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2021, 74, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brummelhuis, I.S.G.; Wimper, Y.; Witjes-van Os, H.G.J.M.; Arends, T.J.H.; van der Heijden, A.G.; Witjes, J.A. Long-Term Experience with Radiofrequency-Induced Hyperthermia Combined with Intravesical Chemotherapy for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01094964 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Tan, W.S.; Panchal, A.; Buckley, L.; Devall, A.J.; Loubière, L.S.; Pope, A.M.; Feneley, M.R.; Cresswell, J.; Issa, R.; Mostafid, H.; et al. Radiofrequency-induced Thermo-chemotherapy Effect versus a Second Course of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin or Institutional Standard in Patients with Recurrence of Non–muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer Following Induction or Maintenance Bacillus Calmette-Guérin Th. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Xu, M.-Y.; Sun, J.-X.; Liu, C.-Q.; Xu, J.-Z.; An, Y.; Zhong, X.-Y.; Ma, S.-Y.; He, H.-D.; Xia, Q.-D.; et al. Hyperthermia intravesical chemotherapy acts as a promising alternative to bacillus Calmette–Guérin instillation in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A network meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1164932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasi, S.M.; Giannantoni, A.; Stephen, R.L.; Capelli, G.; Navarra, P.; Massoud, R.; Vespasiani, G. Intravesical Electromotive Mitomycin C Versus Passive Transport Mitomycin C for High Risk Superficial Bladder Cancer: A Prospective Randomized Study. J. Urol. 2003, 170, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasi, S.M.; Giannantoni, A.; Massoud, R.; Dolci, S.; Navarra, P.; Vespasiani, G.; Stephen, R.L. Electromotive versus passive diffusion of mitomycin C into human bladder wall: Concentration-depth profiles studies. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 4912–4918. [Google Scholar]
- Bachir, B.G.; Dragomir, A.; Aprikian, A.G.; Tanguay, S.; Fairey, A.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Breau, R.H.; Black, P.C.; Kassouf, W. Contemporary cost-effectiveness analysis comparing sequential bacillus Calmette-Guerin and electromotive mitomycin versus bacillus Calmette-Guerin alone for patients with high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer 2014, 120, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazzara, M.; Nazaraj, A.; Scarcia, M.; Cardo, G.; Carando, R.; Ludovico, G.M. Electromotive Drug Administration of Mitomycin C (EMDA/MMC) versus Intravesical Immunotherapy with Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) in Intermediate and High Risk Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Urol. Int. 2023, 107, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvet, T.; Mari, A.; Lajkosz, K.; Wallis, C.J.; Kuk, C.; Erlich, A.; Krimus, L.; Fleshner, N.E.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Zlotta, A.R. Sequential administration of Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) and Electromotive Drug Administration (EMDA) of mitomycin C (MMC) for the treatment of high-grade nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer after BCG failure. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2020, 38, 850.e9–850.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgarejo Segura, M.T.; Morales Martínez, A.; Yáñez Castillo, Y.; Arrabal Polo, M.Á.; Gómez Lechuga, P.; Pareja Vílchez, M.; Arrabal Martín, M. Conductive hyperthermic chemotherapy versus electromotive drug administration of mitomycin C as intravesical adjuvant treatment of patients with intermediate or high-risk non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2023, 41, 109.e1–109.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Gudeloglu, A.; Kiziloz, H.; Kuntz, G.M.; Miller, A.; Konety, B.R.; Dahm, P. Intravesical electromotive drug administration for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Jhang, J.-F.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kuo, H.-C. Low-Energy Shock Wave Plus Intravesical Instillation of Botulinum Toxin A for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome: Pathophysiology and Preliminary Result of a Novel Minimally Invasive Treatment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashef, A.; Barakat, N.; Khater, S.M.; Awadalla, A.; Belal, F.; El-Assmy, A.M.; Sheir, K.Z.; Shokeir, A.A. Effect of low-energy shock wave therapy on intravesical epirubicin delivery in a rat model of bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2021, 127, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04644835 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Bhandari, P.; Novikova, G.; Goergen, C.J.; Irudayaraj, J. Ultrasound beam steering of oxygen nanobubbles for enhanced bladder cancer therapy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakakos, T.; Peterson, C.; Lawson, G.; Ji, C.; Goodwin, S. Intravesical administration of doxorubicin to swine bladder using magnetically targeted carriers. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2003, 51, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, N.; Wang, M.; Jin, Y.; Ding, J.; Gao, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Cui, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, N.; et al. Magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes with controlled release of epirubicin: An intravesical instillation system for bladder cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Z.; Tang, S.; Xie, L.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Lu, D.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Magnetic-Powered Janus Cell Robots Loaded with Oncolytic Adenovirus for Active and Targeted Virotherapy of Bladder Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2201042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierzbicka, A.; Krakos, M.; Wilczek, P.; Bociaga, D. A comprehensive review on hydrogel materials in urology: Problems, methods, and new opportunities. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2023, 111, 730–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, M.; Nazari, B.; Miller, D.W. Injectable hydrogel-based drug delivery systems for local cancer therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, O.M.; Lau, W.M.; Mostafid, H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Advances in intravesical drug delivery systems to treat bladder cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, H.; Guo, H.; Li, D.; Hou, Y.; Kuang, T.; Ding, J. Intravesical Hydrogels as Drug Reservoirs. Trends Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.M.; Cook, M.T. In situ gelling drug delivery systems for topical drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 184, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroǧlu, M.; Öztürk, E.; Özdemýr, N.; Denkbap, E.B.; Doǧan, I.; Acar, A.; Güzel, M. Mitomycin-C-loaded alginate carriers for bladder cancer chemotherapy: In vivo studies. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2005, 20, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Li, Z.; Chancellor, M.; De Groat, W.C.; Yoshimura, N.; Huang, L. Sustained Intravesical Drug Delivery Using Thermosensitive Hydrogel. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenite, A. Rheological characterisation of thermogelling chitosan/glycerol-phosphate solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 46, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Chitosan/β-glycerophosphate in situ gelling mucoadhesive systems for intravesical delivery of mitomycin-C. Int. J. Pharm. X 2019, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Sun, P.; Li, P.; Xue, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Jin, X. A magnetic chitosan hydrogel for sustained and prolonged delivery of Bacillus Calmette-Guérin in the treatment of bladder cancer. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10258–10266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Sun, P.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Suo, N.; Yang, M.; Zhang, D.; Jin, X. A new drug delivery system for Mitomycin C to improve intravesical instillation. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Wu, J.; Zhao, X.; Lian, H.; Yuan, A.; Tang, X.; Zhao, S.; Guo, H.; Hu, Y. In situ floating hydrogel for intravesical delivery of adriamycin without blocking urinary tract. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 103, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goo, Y.T.; Yang, H.M.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, H.K.; Chang, I.H.; Choi, Y.W. Optimization of a floating poloxamer 407-based hydrogel using the Box-Behnken design: In vitro characterization and in vivo buoyancy evaluation for intravesical instillation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 163, 105885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, H.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Guo, S.; et al. Floating hydrogel with self-generating micro-bubbles for intravesical instillation. Materials 2016, 9, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.R.; Yoon, H.Y.; Chang, I.H.; Whang, Y.M.; Cho, M.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Choi, Y.W. Poloxamer 407 Hydrogels for Intravesical Instillation to Mouse Bladder: Gel-Forming Capacity and Retention Performance. Korean J. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 15, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, X.; Lian, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Hu, Y.; Guo, H. Visualized intravesical floating hydrogel encapsulating vaporized perfluoropentane for controlled drug release. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2820–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, K.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, P.; Gou, M.; Wei, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, B.; Du, Y.; et al. Delivering instilled hydrophobic drug to the bladder by a cationic nanoparticle and thermo-sensitive hydrogel composite system. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, C.; Ilem Ozdemir, D.; Baloglu, E.; Karavana, S.Y.; Sen, S.; Waldner, C.; Ay Şenyiğit, Z.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Design and evaluation of an intravesical delivery system for superficial bladder cancer: Preparation of gemcitabine HCl-loaded chitosan–thioglycolic acid nanoparticles and comparison of chitosan/poloxamer gels as carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-P.; Leu, Y.-L.; Fang, C.-L.; Chen, C.-H.; Fang, J.-Y. Thermosensitive Hydrogels Composed of Hyaluronic Acid and Gelatin as Carriers for the Intravesical Administration of Cisplatin. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanii, H.; Hashimoto, K. Studies on in vitro metabolism of acrylamide and related compounds. Arch. Toxicol. 1981, 48, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, B.; Bae, Y.H.; Kim, S.W. In situ gelation of PEG-PLGA-PEG triblock copolymer aqueous solutions and degradation thereof. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 50, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, M.T.; Schmidt, S.A.; Lee, E.; Samprasit, W.; Opanasopit, P.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V. Synthesis of mucoadhesive thiol-bearing microgels from 2-(acetylthio)ethylacrylate and 2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate: Novel drug delivery systems for chemotherapeutic agents to the bladder. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6599–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupt, M.; Thommes, M.; Heidenreich, A.; Breitkreutz, J. Lipid-based intravesical drug delivery systems with controlled release of trospium chloride for the urinary bladder. J. Control. Release 2013, 170, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Shang, L.; Shan, D.Y.; Che, X. Long-term floating control-released intravesical preparation of 5-fluorouracil for the local treatment of bladder cancer. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GuhaSarkar, S.; More, P.; Banerjee, R. Urothelium-adherent, ion-triggered liposome-in-gel system as a platform for intravesical drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 245, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.Y.; Chang, I.H.; Goo, Y.T.; Kim, C.H.; Kang, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Song, S.H.; Whang, Y.M.; Choi, Y.W. Intravesical delivery of rapamycin via folate-modified liposomes dispersed in thermo-reversible hydrogel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 6249–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavana, S.Y.; Şenyiğit, Z.A.; Çalışkan, Ç.; Sevin, G.; Özdemir, D.İ.; Erzurumlu, Y.; Şen, S.; Baloğlu, E. Gemcitabine hydrochloride microspheres used for intravesical treatment of superficial bladder cancer: A comprehensive in vitro/ex vivo/in vivo evaluation. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2018, 12, 1959–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevli, K.K.; Shore, N.D.; Trainer, A.; Smith, A.B.; Saltzstein, D.; Ehrlich, Y.; Raman, J.D.; Friedman, B.; D’Anna, R.; Morris, D.; et al. Primary Chemoablation of Low-Grade Intermediate-Risk Nonmuscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Using UGN-102, a Mitomycin-Containing Reverse Thermal Gel (Optima II): A Phase 2b, Open-Label, Single-Arm Trial. J. Urol. 2022, 207, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pre-TURBT TC-3 Gel Intravesical Instillation in NMIBC (OPTIMA). Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01803295 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- A Phase 2b Study of UGN-102 for Low Grade Intermediate Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (OPTIMA II). Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03558503 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01803295 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05243550 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04688931 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Kim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Wentworth, A.; Babaee, S.; Wong, K.; Collins, J.E.; Chu, J.; Ishida, K.; Kuosmanen, J.; Jenkins, J.; et al. Biodegradable ring-shaped implantable device for intravesical therapy of bladder disorders. Biomaterials 2022, 288, 121703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Goyanes, A.; Trenfield, S.J.; Diaz-Gomez, L.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Gaisford, S.; Basit, A.W. Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing of a bladder device for intravesical drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, I.S.; Lee, H.; Engelmayr, G.C.; Macaya, D.; Bettinger, C.J.; Cima, M.J. Zero-order controlled release of ciprofloxacin-HCl from a reservoir-based, bioresorbable and elastomeric device. J. Control. Release 2010, 146, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Langer, R. In vivo degradation characteristics of poly(glycerol sebacate). J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part A 2003, 66, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman-Yildir, J.; Fischer, B.; Breitkreutz, J. Development of sustained-release drug-loaded intravesical inserts via semi-solid micro-extrusion 3D-printing for bladder targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 622, 121849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, J.C.; Jain, P.; Shore, N.; Anderson, J.; Giesing, D.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.; Daniel, K.; White, S.; Larrivee-Elkins, C.; et al. Continuous Intravesical Lidocaine Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome: Safety and Efficacy of a New Drug Delivery Device. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 143ra100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.; Kohan, A.; Moldwin, R.; Radecki, D.; Geib, T.; Peters, K.M. Safety, tolerability, and efficacy of LiRIS 400 mg in women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome with or without Hunner lesions. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2021, 40, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method for Delivering a Medication. U.S. Patent No. 6,183,461, 6 February 2001.
- Method and Apparatus for Placement and Activation of a Medical Device within a Body Cavity. U.S. Patent No. 6,139,535, 31 October 2000.
- Adis R&D Profile. Oxybutynin Intravesical—Situs. Drugs R D 2002, 3, 82–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cima, M.J. An intravesical device for the sustained delivery of lidocaine to the bladder. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, K.; Seifu, Y.; Cutie, C.; Radecki, D. MP72-16 Safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of LIRIS® 400 MG in women with ulcerative interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2016, 195, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimberg, D.C.; Shah, A.; Inman, B.A. Overview of Taris GemRIS, a Novel Drug Delivery System for Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshmand, S.; Pohar, K.S.; Steinberg, G.D.; Aron, M.; Cutie, C. Effect of GemRIS (gemcitabine-releasing intravesical system, TAR-200) on antitumor activity in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, e16000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03404791 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02720367 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02722538 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03518320 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04658862 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05714202 (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Available online: https://www.urologytimes.com/view/phase-3-trial-to-evaluate-tar-200-cetrelimab-for-muscle-invasive-bladder-cancer (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Wright, J.C.; Tao Leonard, S.; Stevenson, C.L.; Beck, J.C.; Chen, G.; Jao, R.M.; Johnson, P.A.; Leonard, J.; Skowronski, R.J. An in vivo/in vitro comparison with a leuprolide osmotic implant for the treatment of prostate cancer. J. Control. Release 2001, 75, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.; Matsuura, J.; Berry, S.; Lucas, C. DUROS® Osmotic Implant for the Delivery of Peptides and Proteins. In Peptides: The Wave of the Future; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 29, pp. 944–945. [Google Scholar]
- Rohloff, C.M.; Alessi, T.R.; Yang, B.; Dahms, J.; Carr, J.P.; Lautenbach, S.D. DUROS® Technology Delivers Peptides and Proteins at Consistent Rate Continuously for 3 to 12 Months. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukierski, M.J.; Johnson, P.A.; Beck, J.C. Chronic (60-week) toxicity study of DUROS leuprolide implants in dogs. Int. J. Toxicol. 2001, 20, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Chester, A.; Skowronski, R.; Lucas, C. Long-Term Controlled Delivery of Therapeutic Agents via an Implantable Osmotically Driven System: The DUROS implant. In Modified-Release Drug Delivery Technology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 657–669. ISBN 9780203910337. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marchenko, I.V.; Trushina, D.B. Local Drug Delivery in Bladder Cancer: Advances of Nano/Micro/Macro-Scale Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122724
Marchenko IV, Trushina DB. Local Drug Delivery in Bladder Cancer: Advances of Nano/Micro/Macro-Scale Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(12):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122724
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarchenko, Irina V., and Daria B. Trushina. 2023. "Local Drug Delivery in Bladder Cancer: Advances of Nano/Micro/Macro-Scale Drug Delivery Systems" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 12: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122724
APA StyleMarchenko, I. V., & Trushina, D. B. (2023). Local Drug Delivery in Bladder Cancer: Advances of Nano/Micro/Macro-Scale Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics, 15(12), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122724






