Protocol to Induce the Temporary Opening of the Blood–Brain Barrier with Short-Time Focused Ultrasound in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
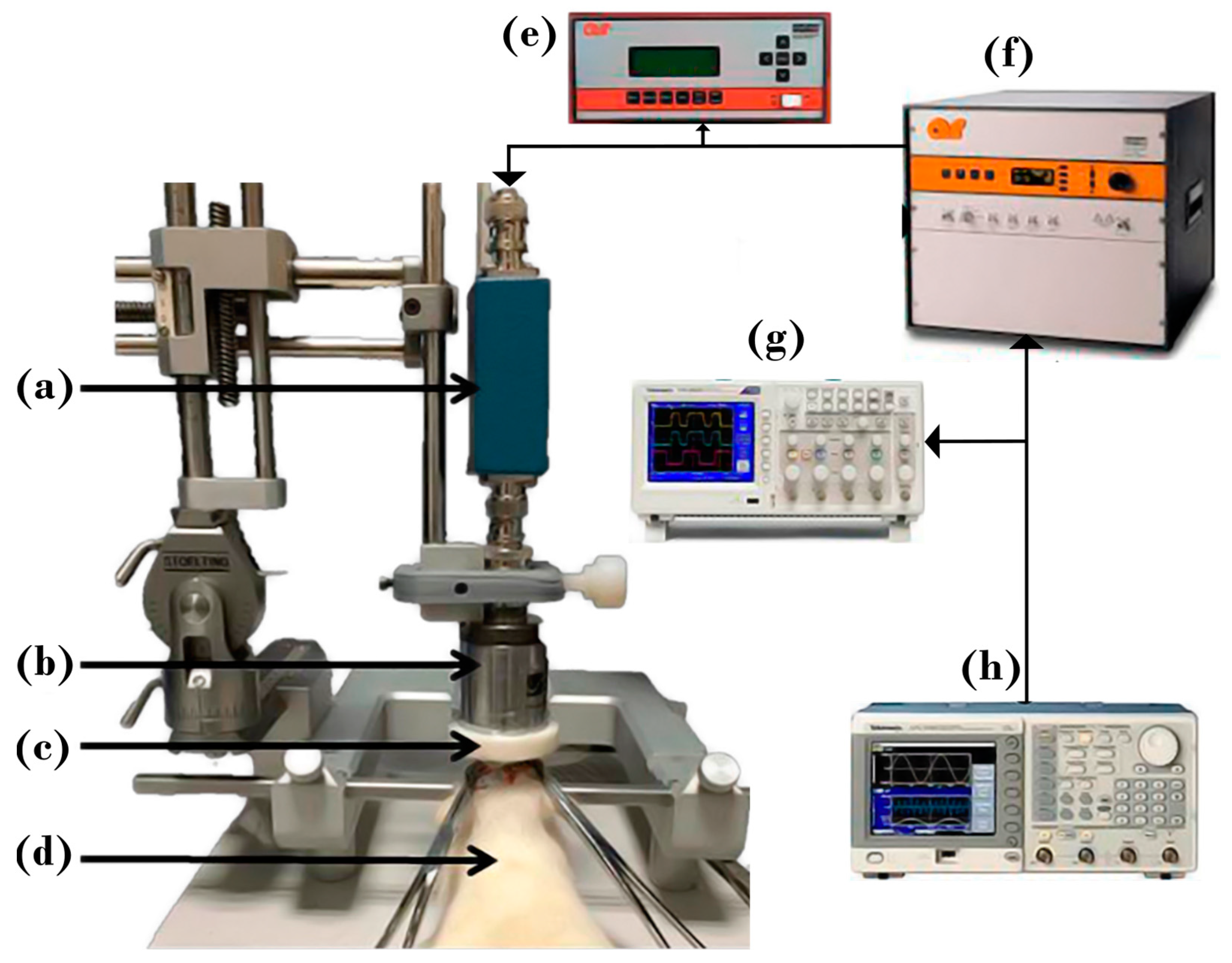
2.1. Experimental Setup
- 10 s, DC = 60%,
- 50 s, DC = 20%,
- 30 s, DC = 0% (rest),
- repeat steps 1 and 2.
2.2. Animal Preparation
BBB Opening Detection and Reversibility Analysis
2.3. Numerical Simulation
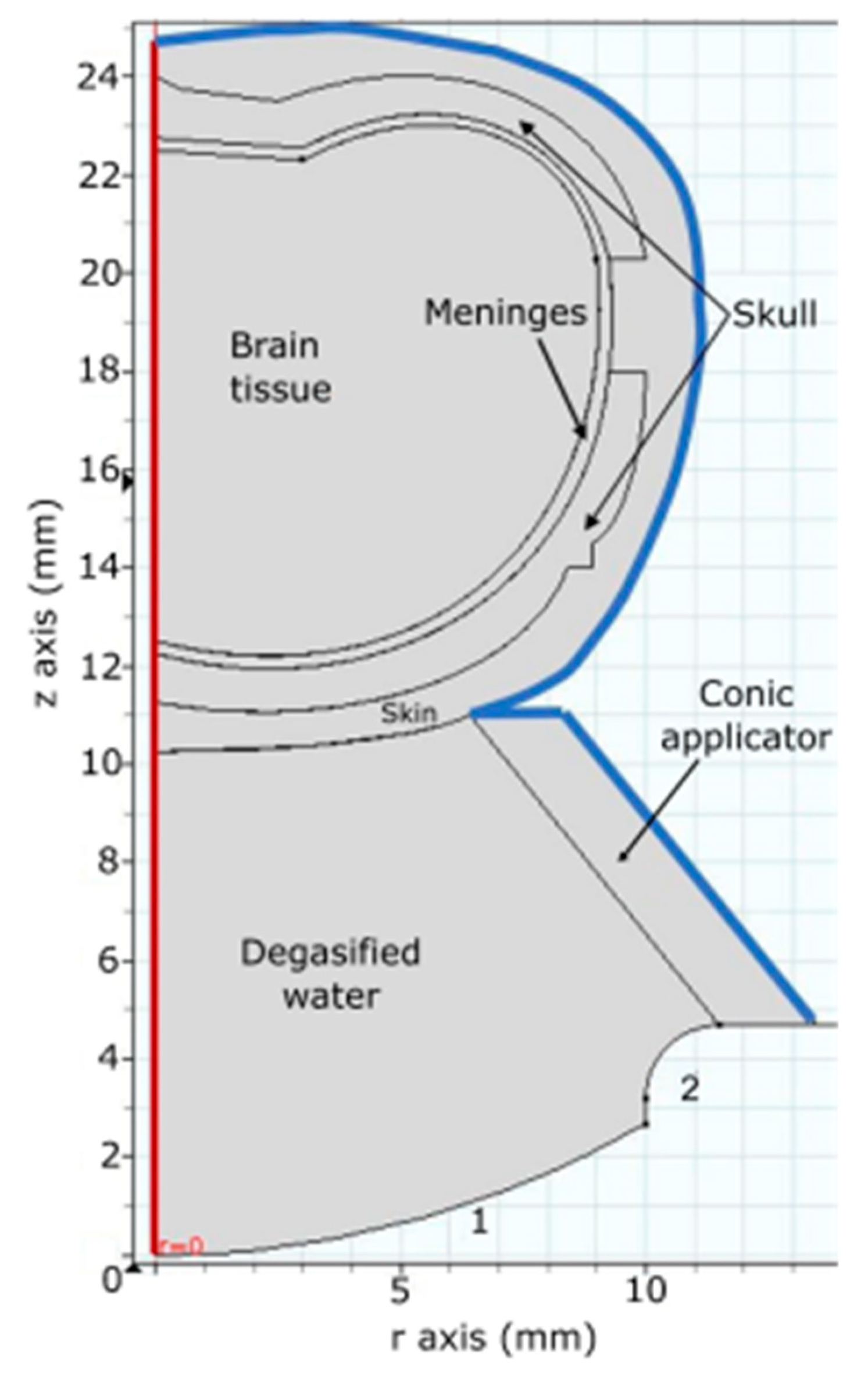
2.3.1. Acoustic Field Distribution
| Material | Speed of Sound (m/s) | Attenuation (Np/m) | Thermal Capacity, (J/kg·K) | Thermal Conductivity, k, (W/m·K) | Density, (kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 1500 | 0 | - | - | 997 |
| Polyurethane | 1900 | - | - | - | 35 |
| Skin | 1624 | 43.96 | 3391 | 0.37 | 1109 |
| Skull bone | 2814 | 113.36 | 1313 | 0.32 | 1908 |
| Meninges | 1545 | 34.18 | 2372 | 0.39 | 1027 |
| Brain | 1546 | 17.60 | 3696 | 0.49 | 1046 |
2.3.2. Bioheat Transfer
3. Results
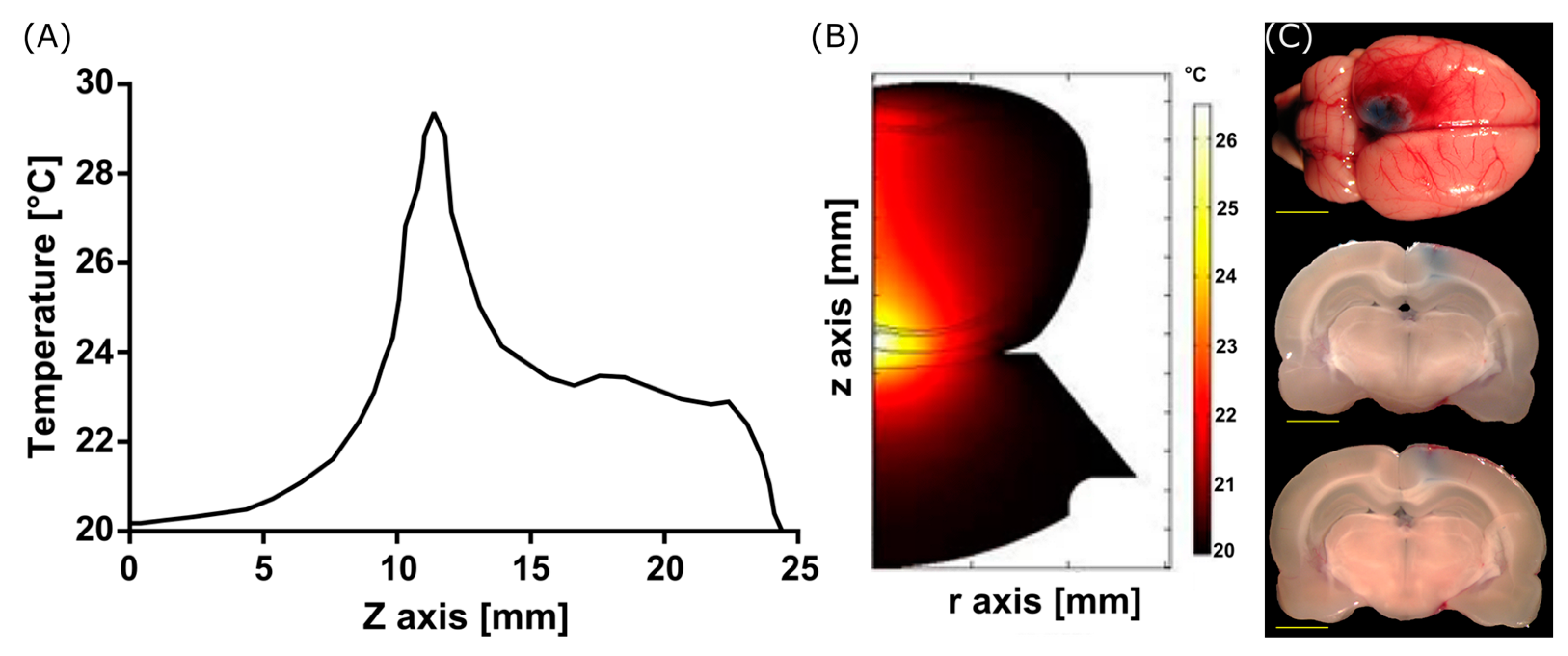
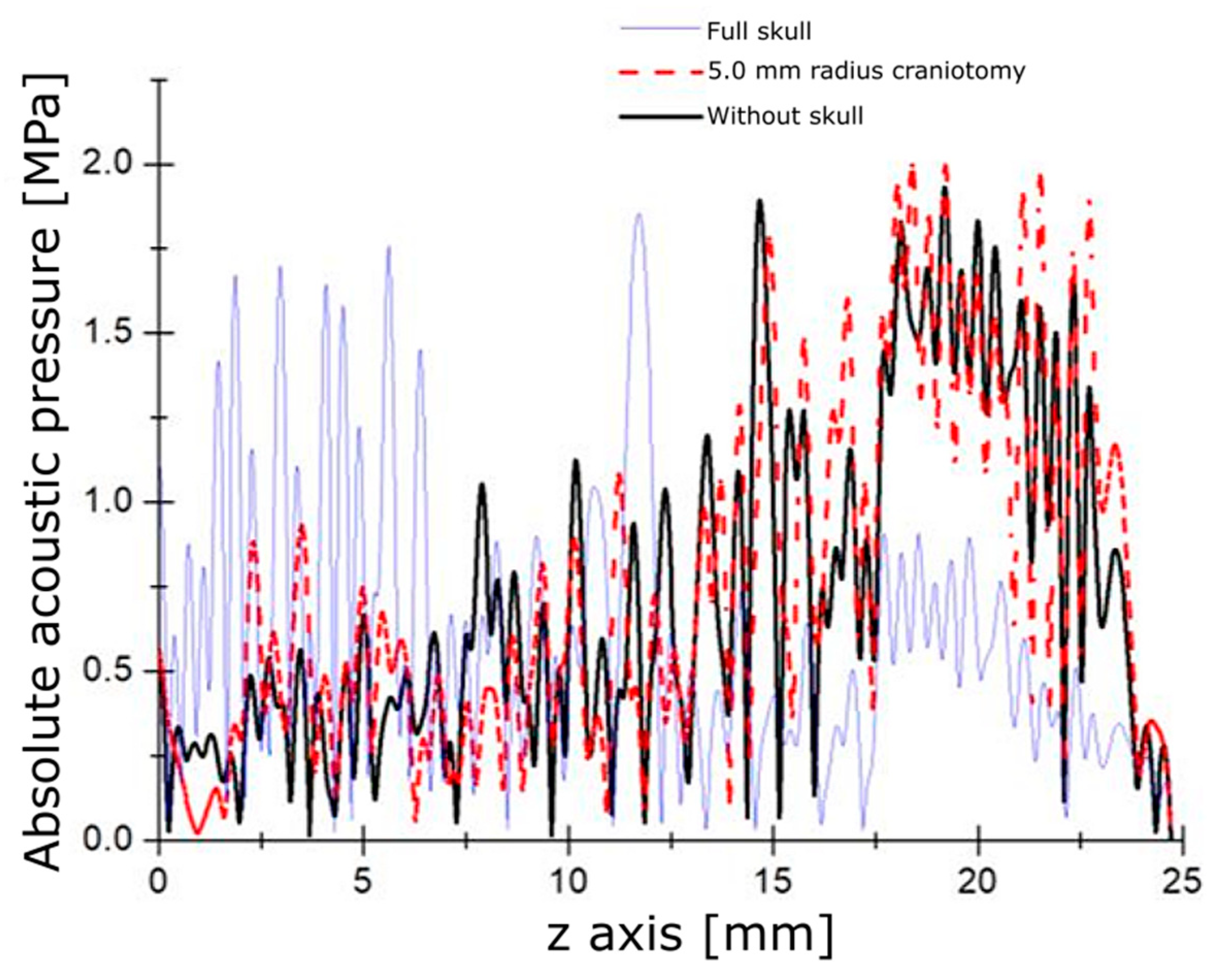
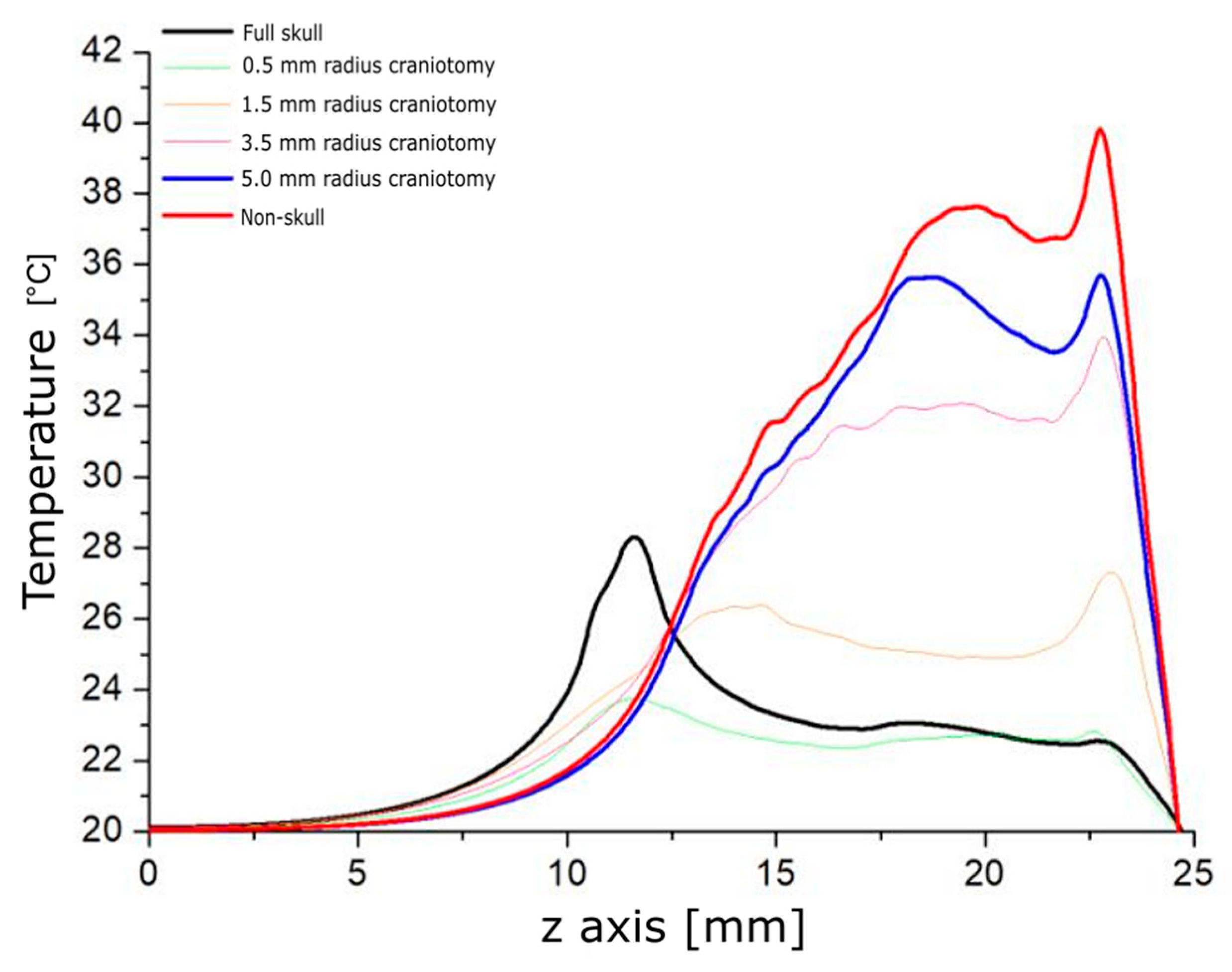
3.1. Modeling Acoustic Field and Temperature Distribution
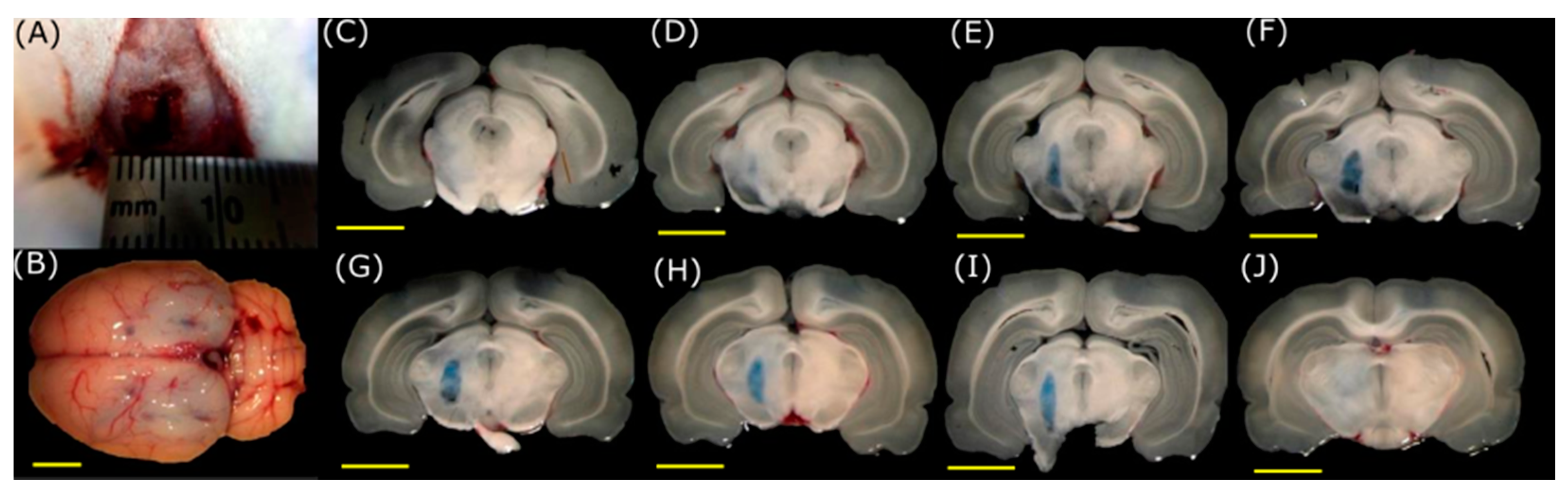
3.2. BBB Opening with FUS
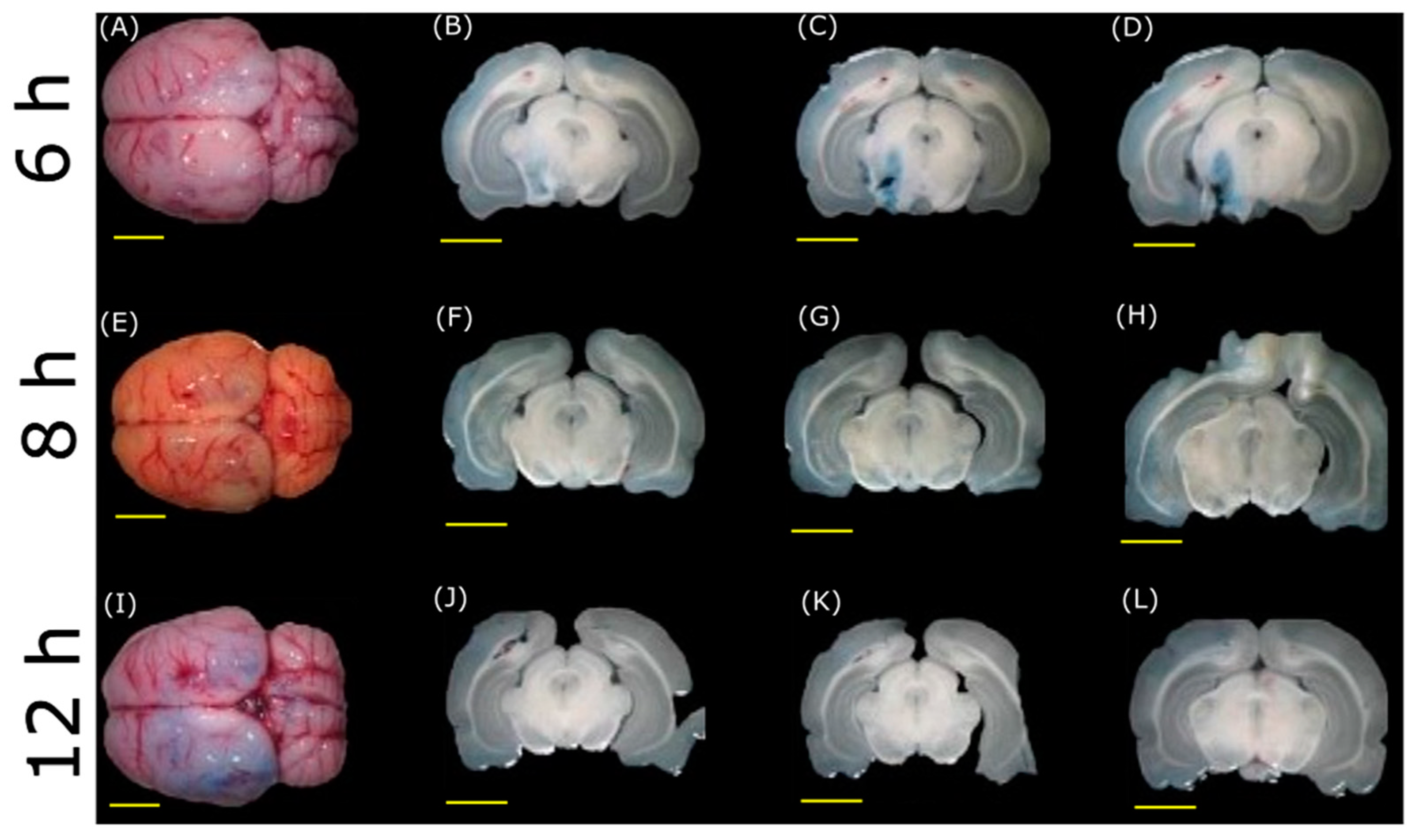
3.3. BBB Disruption Reversibility
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fahn, S.; Sulzer, D. Neurodegeneration and Neuroprotection in Parkinson Disease. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, A.; Simcox, E.; Turnbull, D. Ageing and Parkinson’s Disease: Why Is Advancing Age the Biggest Risk Factor? Ageing Res. Rev. 2014, 14, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corti, O.; Hampe, C.; Darios, F.; Ibanez, P.; Ruberg, M.; Brice, A. Parkinson’s Disease: From Causes to Mechanisms. Comptes Rendus-Biol. 2005, 328, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Dallapiazza, R.; De Vloo, P.; Lozano, A. Current Surgical Treatments for Parkinson’s Disease and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1342–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Fong, D.; Bannon, M.J.; Trudeau, L.E.; Gonzalez-Barrios, J.A.; Arango-Rodriguez, M.L.; Hernandez-Chan, N.G.; Reyes-Corona, D.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.; Navarro-Quiroga, I. NTS-Polyplex: A Potential Nanocarrier for Neurotrophic Therapy of Parkinson’s Disease. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 1052–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Ganesh, S.; Shahiwala, A.; Shah, S.P. Drug delivery to the central nervous system: A review. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 6, 252–273. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12935438/ (accessed on 12 September 2023). [PubMed]
- Vykhodtseva, N.; McDannold, N.; Hynynen, K. Progress and Problems in the Application of Focused Ultrasound for Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. Ultrasonics 2008, 48, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Rey, R. Fundamentos de Neurología y Neurocirugía; Editorial Magna Publicaciones: Tucumán, Argentina, 2002; ISBN 978-987-9390-19-1. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, W.S.; Marsman, D.S. Animal Welfare Considerations in Biomedical Research and Testing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sharma, P.; Maheshwari, R.; Tekade, M.; Shrivastava, S.K.; Tekade, R.K. Beyond the Blood-Brain Barrier; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timbie, K.F.; Mead, B.P.; Price, R.J. Drug and Gene Delivery across the Blood-Brain Barrier with Focused Ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2015, 219, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.J.; Pernot, M.; Brown, T.R.; Small, S.A.; Konofagou, E.E. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Molecular Delivery through the Blood-Brain Barrier Using Focused Ultrasound. Phys. Med. Biol. 2007, 52, 5509–5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Y.; Fu, W.M.; Yang, R.S.; Liou, H.C.; Kang, K.H.; Lin, W.L. Quantitative Evaluation of Focused Ultrasound with a Contrast Agent on Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2007, 33, 1421–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Wai, Y.Y.; Chen, W.S.; Chen, J.C.; Hsu, P.H.; Wu, X.Y.; Huang, W.C.; Yen, T.C.; Wang, J.J. Hemorrhage Detection During Focused-Ultrasound Induced Blood-Brain-Barrier Opening by Using Susceptibility-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynynen, K.; Mcdannold, N. Non-invasive MR Imaging–Guided Focal Opening of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Rabbits. Radiology 2001, 220, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etame, A.B.; Diaz, R.J.; Smith, C.A.; Mainprize, T.G.; Hynynen, K.; Rutka, J.T. Focused Ultrasound Disruption of the Blood-Brain Barrier: A New Frontier for Therapeutic Delivery in Molecular Neurooncology. Neurosurg. Focus 2012, 32, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meairs, S. Drug Delivery Across the Blood–Brain Barrier with Focused Ultrasound and Microbubbles. Blood Brain Barrier 2014, 10, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, A. Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening for Drug Delivery. Front. Neurol. Neurosci. 2015, 36, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Hynynen, K. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Induced by Focused Ultrasound and Circulating Preformed Microbubbles Appears to Be Characterized by the Mechanical Index. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, K.F.; Howles, G.P.; Qi, Y.; Palmeri, M.L.; Nightingale, K.R. Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Disruption Using a Diagnostic Ultrasound Scanner and Definity® in Mice. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2009, 35, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDannold, N.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Hynynen, K. Effects of Acoustic Parameters and Ultrasound Contrast Agent Dose on Focused-Ultrasound Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2008, 34, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.J.; Selert, K.; Gao, Z.; Samiotaki, G.; Baseri, B.; Konofagou, E.E. Non-invasive and Localized Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Using Focused Ultrasound Can Be Achieved at Short Pulse Lengths and Low Pulse Repetition Frequencies. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2011, 31, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.J.; Selert, K.; Vlachos, F.; Wong, A.; Konofagou, E.E. Non-invasive and Localized Neuronal Delivery Using Short Ultrasonic Pulses and Microbubbles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16539–16544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, R.; Vykhodtseva, N.; Hynynen, K. Influence of Exposure Time and Pressure Amplitude on Blood-Brain-Barrier Opening Using Transcranial Ultrasound Exposures. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2010, 1, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, F.; Tung, Y.; Konofagou, E. Permeability Dependence Study of the Focused Ultrasound-induced Blood–Brain Barrier Opening at Distinct Pressures and Microbubble Diameters Using DCE-MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2011, 66, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Samiotaki, G.; Olumolade, O.; Feshitan, J.A.; Konofagou, E.E. Microbubble Type and Distribution Dependence of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2014, 40, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.J.; Small, S.A.; Konofagou, E.E. 2F-5 Optimization of Blood-Brain Barrier Opening in Mice Using Focused Ultrasound. In Proceedings of the IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–6 October 2006; pp. 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiotaki, G.; Vlachos, F.; Tung, Y.S.; Feshitan, J.; Borden, M.; Konofagou, E.E. A Quantitative Pressure and Microbubble Size Dependence Study of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening Reversibility in Vivo Using MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2012, 2012, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.H.; Wang, J.J.; Lin, K.J.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, H.L. Multiple Low-Pressure Sonications to Improve Safety of Focused-Ultrasound Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption: In a 1.5-MHz Transducer Setup. IFMBE Proc. 2009, 23, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.H.; Liu, H.L.; Yen, T.C.; Yeh, C.K. Focused Ultrasound with Submicron Bubbles Producing Inertial Cavitation Suppression in Blood-Brain Barrier Opening Application. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 October 2011; pp. 1997–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.H.; Fan, C.H.; Ting, C.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Yeh, C.K. Dynamic Perfusion Assessment by Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound in Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1152–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samiotaki, G.; Konofagou, E.E. Dependence of the Reversibility of Focused-Ultrasound-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Opening on Pressure and Pulse Length in Vivo. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 2257–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.C.; Hsiao, M.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, J.C.; Liu, H.L. Investigation of the Effect of Acoustic Pressure and Sonication Duration on Focused-Ultrasound Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. IFMBE Proc. 2009, 23, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Alkins, R.; Schwartz, M.L.; Hynynen, K. Opening the Blood-Brain Barrier with MR Imaging-Guided Focused Ultrasound: Preclinical Testing on a Trans-Human Skull Porcine Model. Radiology 2017, 282, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.T.; Yarnell, A.; Kean, W.S.; Gold, E.; Lewis, B.; Ren, M.; McMullen, D.C.; Jacobowitz, D.M.; Pollard, H.B.; O’Neill, J.T.; et al. Craniotomy: True Sham for Traumatic Brain Injury, or a Sham of a Sham? J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagraoui, M.; Latoche, J.R.; Cartwright, N.G.; Sukumar, G.; Dalgard, C.L.; Schaefer, B.C. Controlled Cortical Impact and Craniotomy Induce Strikingly Similar Profiles of Inflammatory Gene Expression, but with Distinct Kinetics. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gelb, A.W.; Flexman, A.M.; Ji, F.; Meng, L. Definition, Evaluation, and Management of Brain Relaxation during Craniotomy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2016, 116, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.J.; Member, S.; Feshitan, J.A.; Baseri, B.; Wang, S.; Tung, Y.; Borden, M.A.; Konofagou, E.E. Microbubble-Size Dependence of Focused Ultrasound-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Opening in Mice In Vivo. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alecou, T.; Giannakou, M.; Damianou, C. Amyloid β Plaque Reduction with Antibodies Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier, Which Was Opened in 3 Sessions of Focused Ultrasound in a Rabbit Model. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 36, 2257–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelekanos, M.; Leinenga, G.; Odabaee, M.; Odabaee, M.; Saifzadeh, S.; Steck, R.; Götz, J. Establishing Sheep as an Experimental Species to Validate Ultrasound-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Opening for Potential Therapeutic Interventions. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2583–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsman, M.; Sereti, V.; Mühlenpfordt, M.; Johnsen, K.B.; Andresen, T.L.; Urquhart, A.J.; de Lange Davies, C. Focused Ultrasound and Microbubble Treatment Increases Delivery of Transferrin Receptor-Targeting Liposomes to the Brain. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5359386, Evans Blue Dye. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2023. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Evans-Blue-Dye (accessed on 10 November 2023).
- Hawkins, B.T.; Egleton, R.D. Fluorescence Imaging of Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 151, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marburg, S. Computational Acoustics of Noise Propagation in Fluids-Finite and Boundary Element Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-77447-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kocbach, J. Finite Element Modeling of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Transducers Influence of Geometry and Material Parameters on Vibration, Response Functions and Radiated Field; Department of Physics, University of Bergen: Bergen, Norway, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Giering, K.; Minet, O.; Lamprecht, I.; Muller, G. Review of Thermal Properties of Biological Tissues; SPIE Optical Engineering Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1995; Volume 44, pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, A.; Wili, P.; Maquer, G.; Zysset, P. The Thermal Conductivity of Cortical and Cancellous Bone. Eur. Cells Mater. 2018, 35, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleke, C.; Konofagou, E.E. In Vivo Feasibility of Real-Time Monitoring of Focused Ultrasound Surgery (FUS) Using Harmonic Motion Imaging (HMI). IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grudzenski, S.; Heger, S.; de Jonge, A.; Schipp, J.; Dumont, E.; Larrat, B.; Schad, L.; Platten, M.; Fatar, M. Simulation, Implementation and Measurement of Defined Sound Fields for Blood–Brain Barrier Opening in Rats. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2022, 48, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, N.; Zhang, Y.; Arcaro, M.; Becerra, L.; Borsook, D.; Livingstone, M.; McDannold, N. Focused Ultrasound Induced Opening of the Blood-Brain Barrier Disrupts Inter-Hemispheric Resting State Functional Connectivity in the Rat Brain. Neuroimage 2018, 178, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, J.A.; Gutiérrez, M.I.; Vera, A.; Hernández, D.A.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Martínez-Fong, D.; Leija, L. Protocol to Induce the Temporary Opening of the Blood–Brain Barrier with Short-Time Focused Ultrasound in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122733
Rodríguez JA, Gutiérrez MI, Vera A, Hernández DA, Gutiérrez JM, Martínez-Fong D, Leija L. Protocol to Induce the Temporary Opening of the Blood–Brain Barrier with Short-Time Focused Ultrasound in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(12):2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122733
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Jorge A., Mario I. Gutiérrez, Arturo Vera, Daniel A. Hernández, Juan M. Gutiérrez, Daniel Martínez-Fong, and Lorenzo Leija. 2023. "Protocol to Induce the Temporary Opening of the Blood–Brain Barrier with Short-Time Focused Ultrasound in Rats" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 12: 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122733
APA StyleRodríguez, J. A., Gutiérrez, M. I., Vera, A., Hernández, D. A., Gutiérrez, J. M., Martínez-Fong, D., & Leija, L. (2023). Protocol to Induce the Temporary Opening of the Blood–Brain Barrier with Short-Time Focused Ultrasound in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 15(12), 2733. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122733






