Development of a Library of Disulfide Bond-Containing Cationic Lipids for mRNA Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Biological Reagents
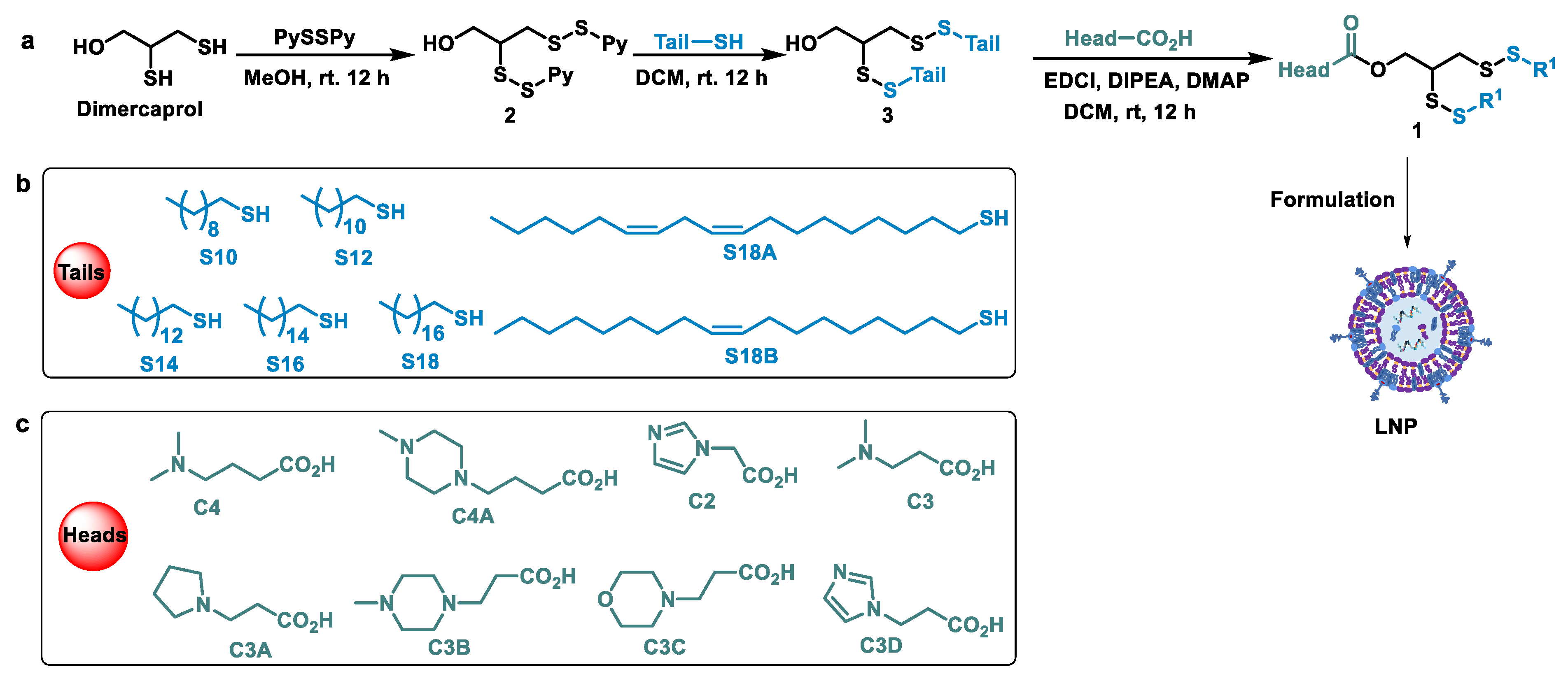
2.3. Synthesis of Disulfide Lipids
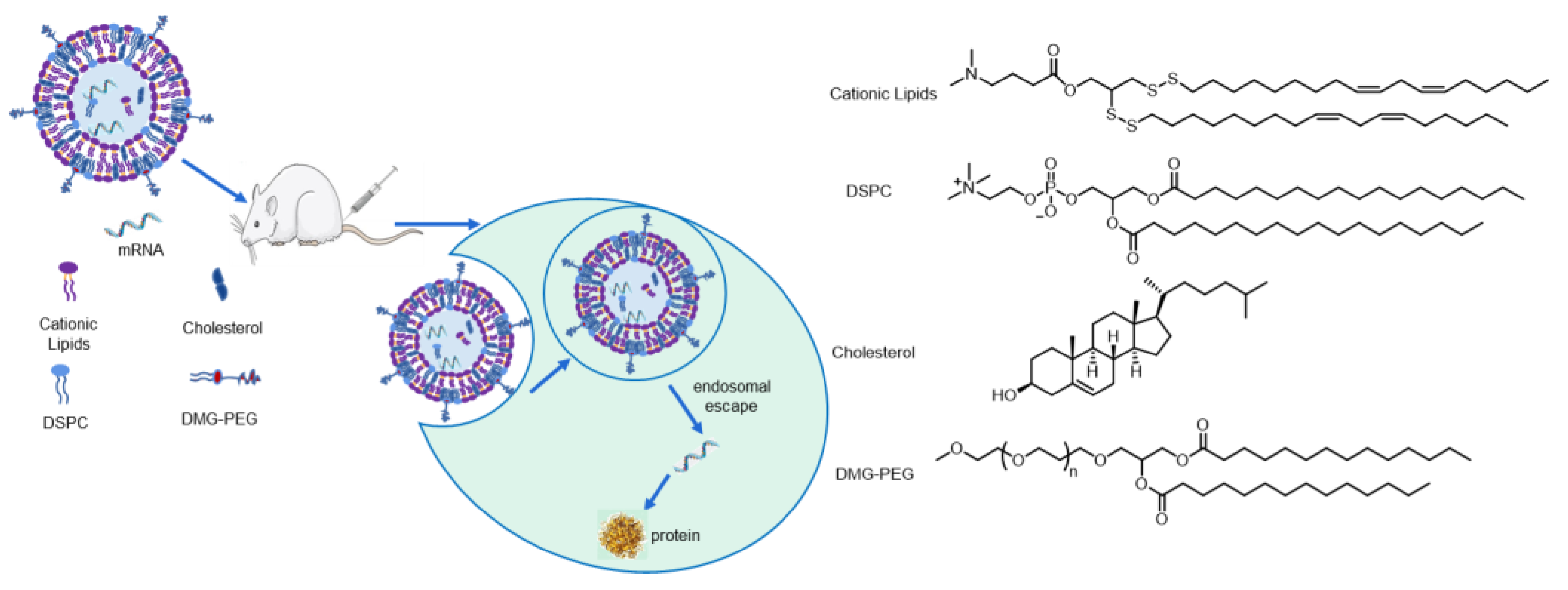
2.4. Lipid Nanoparticle (LNP) Formulation
2.5. Characterization of LNPs
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Firefly Luciferase Activity Assay
2.8. GSH-Triggered Bioreducible Lipid Degradation
2.9. Measurement of pKa via TNS
2.10. Cell Viability
2.11. In Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging
3. Results
3.1. Design and Syntheses of Lipids
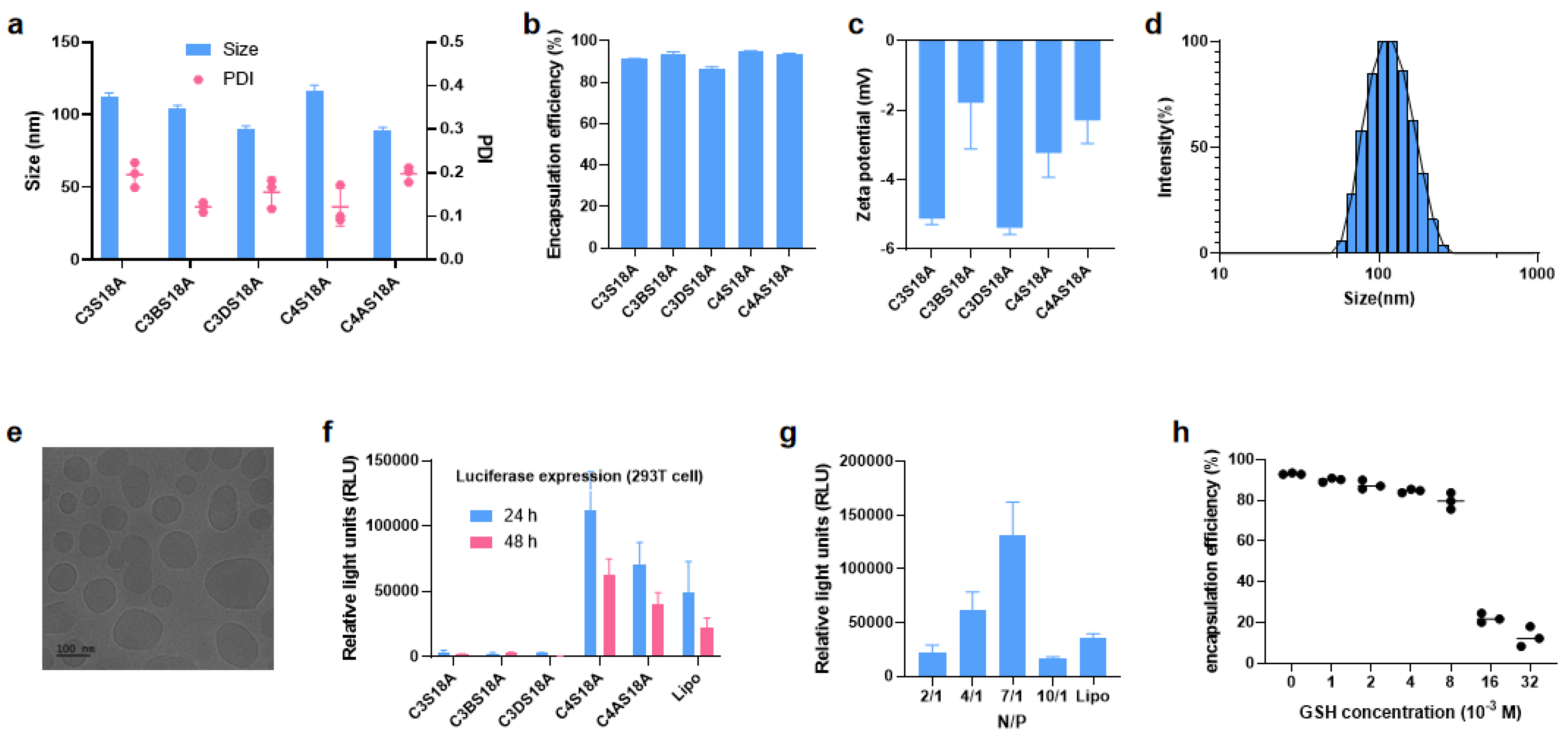
3.2. Screening of LNPs
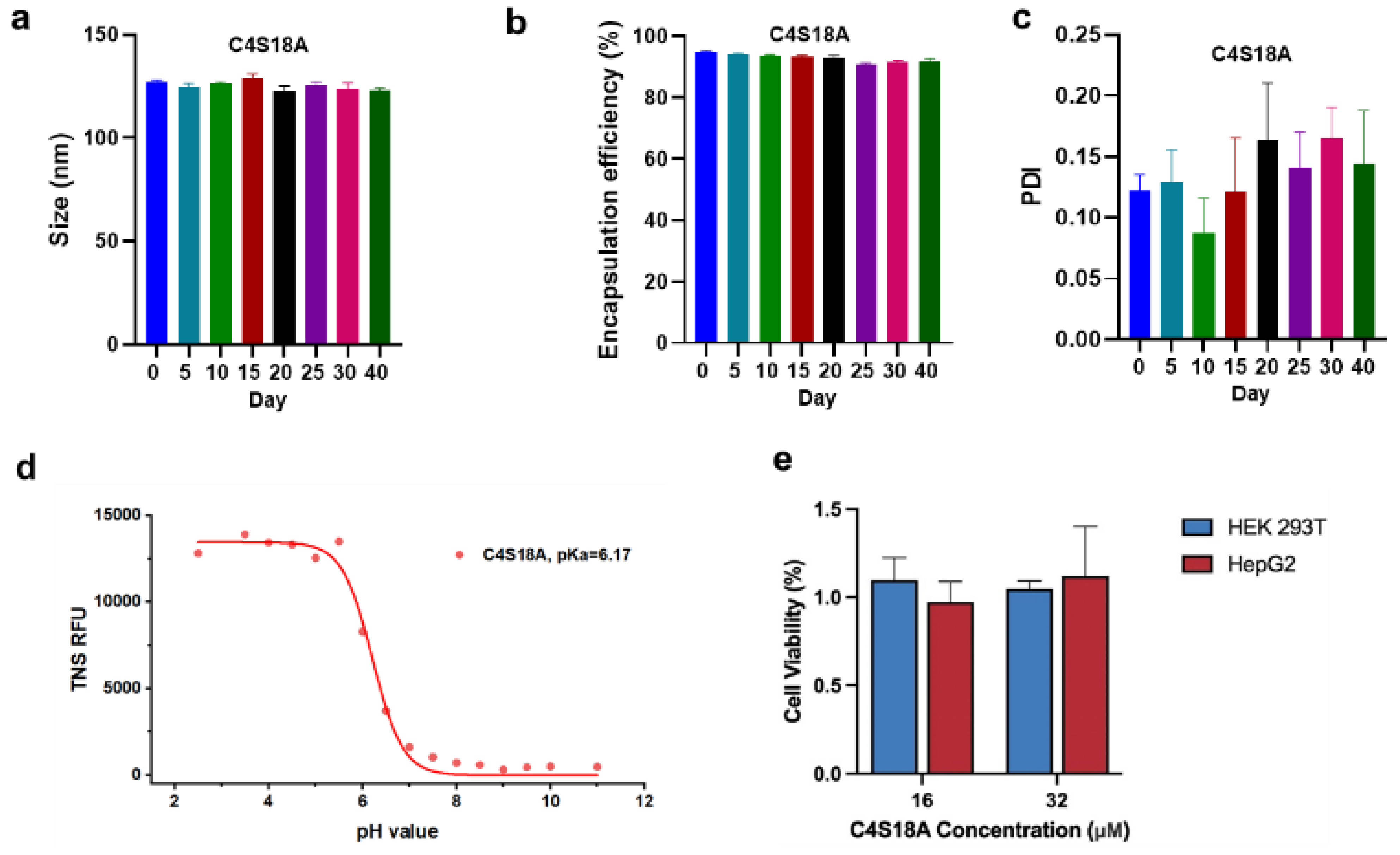
3.3. Stability and Biological Evaluation of mRNA-LNPs
3.4. In Vivo Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lamb, Y.N. BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanh Le, T.; Andreadakis, Z.; Kumar, A.; Gómez Román, R.; Tollefsen, S.; Saville, M.; Mayhew, S. The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Li, S.; Wen, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Z. Advances in development of mRNA-Based therapeutics. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2022, 440, 147–166. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Karikó, K.; Türeci, Ö. mRNA-based therapeutics-developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, S.; Tonnu, N.; Tachikawa, K.; Limphong, P.; Vega, J.B.; Karmali, P.P.; Chivukula, P.; Verma, I.M. Systemic delivery of factor IX messenger RNA for protein replacement therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E1941–E1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; An, D.; Galduroz, M.; Zhuo, J.; Liang, S.; Eybye, M.; Frassetto, A.; Kuroda, E.; Funahashi, A.; Santana, J.; et al. mRNA Therapy Improves Metabolic and Behavioral Abnormalities in a Murine Model of Citrin Deficiency. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1242–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberli, M.A.; Reichmuth, A.M.; Dorkin, J.R.; Mitchell, M.J.; Fenton, O.S.; Jaklenec, A.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R.; Blankschtein, D. Lipid Nanoparticle Assisted mRNA Delivery for Potent Cancer Immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2016, 17, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, S.Y.; Seo, Y.; Kim, M.H.; Chang, J.; Lee, H. Adjuvant incorporated lipid nanoparticles for enhanced mRNA-mediated cancer immunotherapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Yan, J.; Hou, X.; Du, S.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, W.; Deng, B.; McComb, D.W.; et al. Biomimetic nanoparticles deliver mRNAs encoding costimulatory receptors and enhance T cell mediated cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Song, C.-Q.; Dorkin, J.R.; Zhu, L.J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Park, A.; Yang, J.; Suresh, S.; Bizhanova, A.; et al. Therapeutic genome editing by combined viral and non-viral delivery of CRISPR system components in vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, Y.; Peer, D. Delivering the right message: Challenges and opportunities in lipid nanoparticles-mediated modified mRNA therapeutics—An innate immune system standpoint. Semin. Immunol. 2017, 34, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houseley, J.; Tollervey, D. The Many Pathways of RNA Degradation. Cell 2009, 136, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.B.; Siegwart, D.J. Design of synthetic materials for intracellular delivery of RNAs: From siRNA-mediated gene silencing to CRISPR/Cas gene editing. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 5310–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittrup, A.; Lieberman, J. Knocking down disease: A progress report on siRNA therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.E.; Ehrhardt, A.; Kay, M.A. Progress and problems with the use of viral vectors for gene therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, C.; Wang, C.; Jankovic, K.E.; Dong, Y. Lipids and Lipid Derivatives for RNA Delivery. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 12181–12277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Dorkin, J.R.; Wang, W.; Chang, P.H.; Webber, M.J.; Tang, B.C.; Yang, J.; Abutbul-Ionita, I.; Danino, D.; DeRosa, F.; et al. Poly(glycoamidoamine) Brushes Formulated Nanomaterials for Systemic siRNA and mRNA Delivery in Vivo. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, K.A.; Whitehead, K.A. Tools for translation: Non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Tu, J.; Wang, J.; Shajii, A.; Kong, N.; Feng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Xie, T.; Bharwani, Z.; et al. Glutathi-one-responsive prodrug nanoparticles for effective drug delivery and cancer therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Feng, Y. Recent Progress of Glutathione (GSH) Specific Fluorescent Probes: Molecular Design, Photophysical Property, Recognition Mechanism and Bioimaging. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 52, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shi, N.; Yang, L.; Glass, Z.; Bolinger, J.; Finkel, I.J.; Li, W.; Yang, T.; Xu, Q. Combinatorial library of chalco-gen-containing lipidoids for intracellular delivery of genome-editing proteins. Biomaterials 2018, 178, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Glass, Z.; Chen, J.; Haas, M.; Jin, X.; Zhao, X.; Rui, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; et al. Lipid nanoparticle-mediated codelivery of Cas9 mRNA and single-guide RNA achieves liver-specific in vivo genome editing of Angptl3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020401118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, X.; Sun, T.; Mao, L.; Xu, Q.; Wang, M. Fast and Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing In Vivo Enabled by Bioreducible Lipid and Messenger RNA Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, F.; Yang, L.; Sun, Z.; Chen, J.; Rui, X.; Glass, Z.; Xu, Q. Neurotransmitter-derived lipidoids (NT-lipidoids) for enhanced brain delivery through intravenous injection. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, M.; Ansell, S.M.; Mui, B.L.; Tam, Y.K.; Chen, J.; Du, X.; Butler, D.; Eltepu, L.; Matsuda, S.; Narayanannair, J.K.; et al. Maximizing the Potency of siRNA Lipid Nanoparticles for Hepatic Gene Silencing In Vivo**. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8529–8533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramishetti, S.; Hazan-Halevy, I.; Palakuri, R.; Chatterjee, S.; Naidu Gonna, S.; Dammes, N.; Freilich, I.; Kolik Shmuel, L.; Da-nino, D.; Peer, D. A combinatorial library of lipid nanoparticles for RNA delivery to leukocytes. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, H.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Cleavable hydrophobic derivatization strategy for enrichment and identification of phosphorylated lysine peptides. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 4159–4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Ibrahim, N.M.; Cheng, K. The Importance of Apparent pKa in the Development of Nanoparticles Encapsulating siRNA and mRNA. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, S.; Kumarasinghe, E.S.; Salerno, T.; Mihai, C.; Ketova, T.; Senn, J.J.; Lynn, A.; Bulychev, A.; McFadyen, I.; Chan, J.; et al. A Novel Amino Lipid Series for mRNA Delivery: Improved Endosomal Escape and Sustained Pharmacology and Safety in Non-Human Primates. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Entry | Name | size (nm) | PDI | Stability | Entry | Name | Size (nm) | PDI | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | C4S10 | 100 ± 23.1 | 0.266 | II | 9 | C4S18B | 62.1 ± 1.29 | 0.338 | I |
| 2 | C4S12 | 52.0 ± 0.49 | 0.251 | II | 10 | C4AS18A | 104 ± 1.88 | 0.131 | I |
| 3 | C4S14 | 102 ± 3.79 | 0.139 | II | 11 | C3S18A | 101 ± 1.41 | 0.207 | I |
| 4 | C4S16 | 68.1 ± 0.62 | 0.120 | II | 12 | C2S18A | 63.2 ± 0.85 | 0.323 | I |
| 5 | C4S18 | 122 ± 2.05 | 0.128 | II | 13 | C3AS18A | 101 ± 1.41 | 0.267 | I |
| 6 | C3S14 | 89.6 ± 2.84 | 0.297 | II | 14 | C3BS18A | 100 ± 1.99 | 0.183 | I |
| 7 | C3S16 | 110 ± 2.81 | 0.383 | II | 15 | C3CS18A | 82.8 ± 1.26 | 0.325 | I |
| 8 | C4S18A | 103 ± 1.03 | 0.177 | I | 16 | C3DS18A | 64.7 ± 1.08 | 0.146 | I |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Z.; Liu, C.; Wang, Z.; Xie, F.; Liu, X.; Dong, L.; Pan, X.; Zeng, C.; Wang, P.G. Development of a Library of Disulfide Bond-Containing Cationic Lipids for mRNA Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020477
Shen Z, Liu C, Wang Z, Xie F, Liu X, Dong L, Pan X, Zeng C, Wang PG. Development of a Library of Disulfide Bond-Containing Cationic Lipids for mRNA Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020477
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Zhigao, Cong Liu, Ziqian Wang, Fengfei Xie, Xingwu Liu, Lingkai Dong, Xuehua Pan, Chen Zeng, and Peng George Wang. 2023. "Development of a Library of Disulfide Bond-Containing Cationic Lipids for mRNA Delivery" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020477
APA StyleShen, Z., Liu, C., Wang, Z., Xie, F., Liu, X., Dong, L., Pan, X., Zeng, C., & Wang, P. G. (2023). Development of a Library of Disulfide Bond-Containing Cationic Lipids for mRNA Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 477. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020477






