Green Synthesis of Blue-Emitting Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for In Vitro CT26 and In Vivo Zebrafish Nano-Imaging as Diagnostic Probes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Instrumental Measurements of GOQDs
2.3. Synthesis of GOQDs
2.4. Determination of the Fluorescence Quantum Yield of GOQDs
2.5. Biocompatibility Assays
2.6. In Vitro Imaging of GOQDs by Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
2.7. In Vivo Zebrafish Compatibility and Fluorescence Imaging of GOQDs
3. Results and Discussion
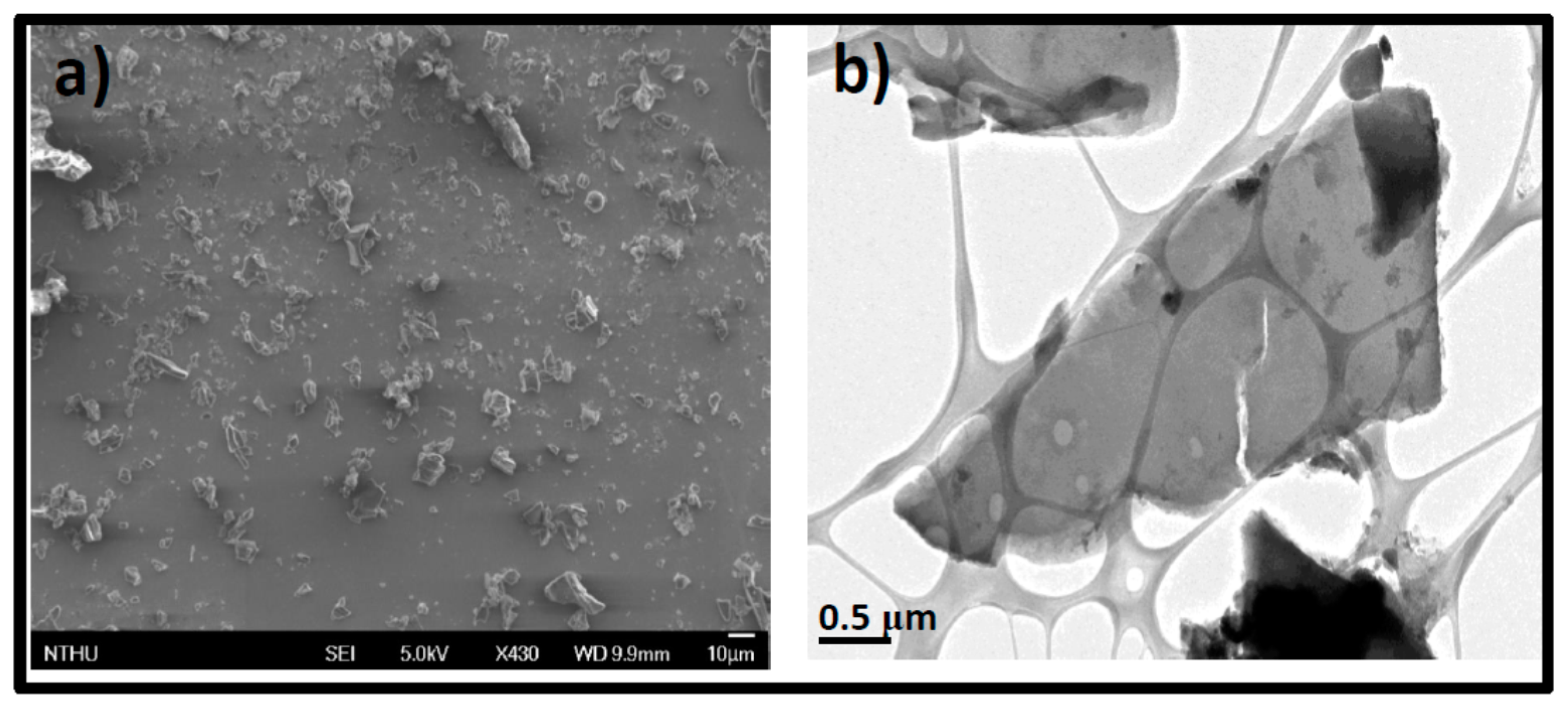
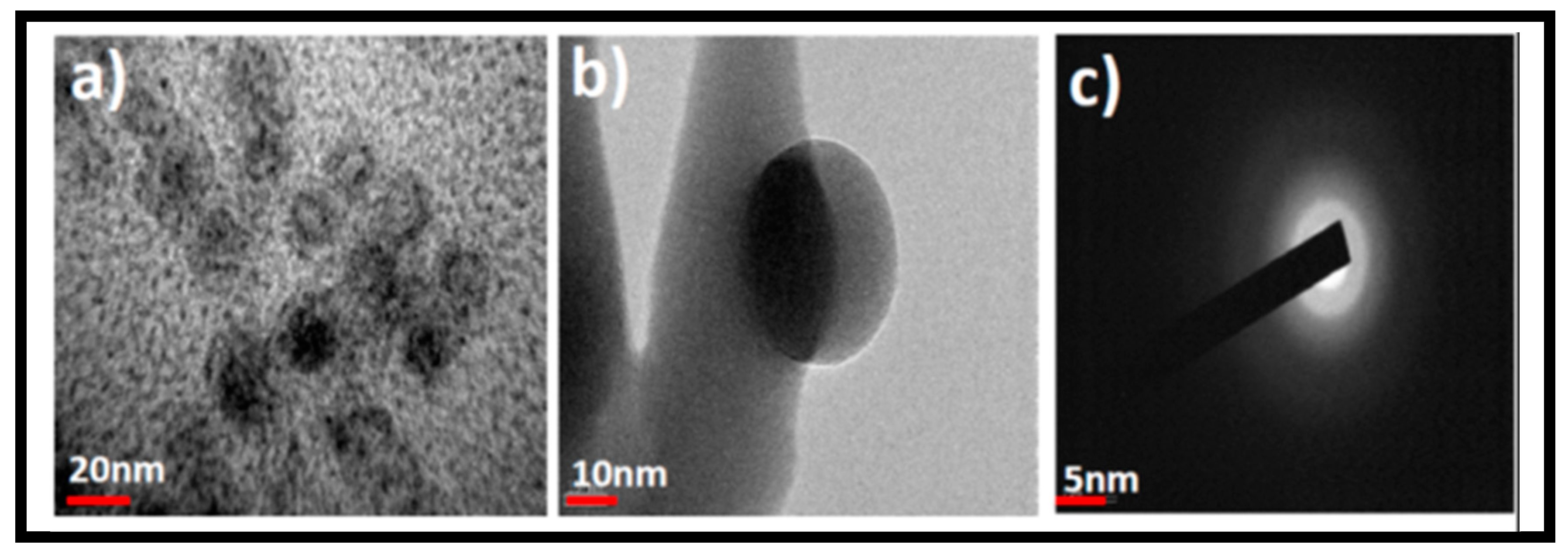
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of GOQDs
3.2. Optical Properties of GOQDs
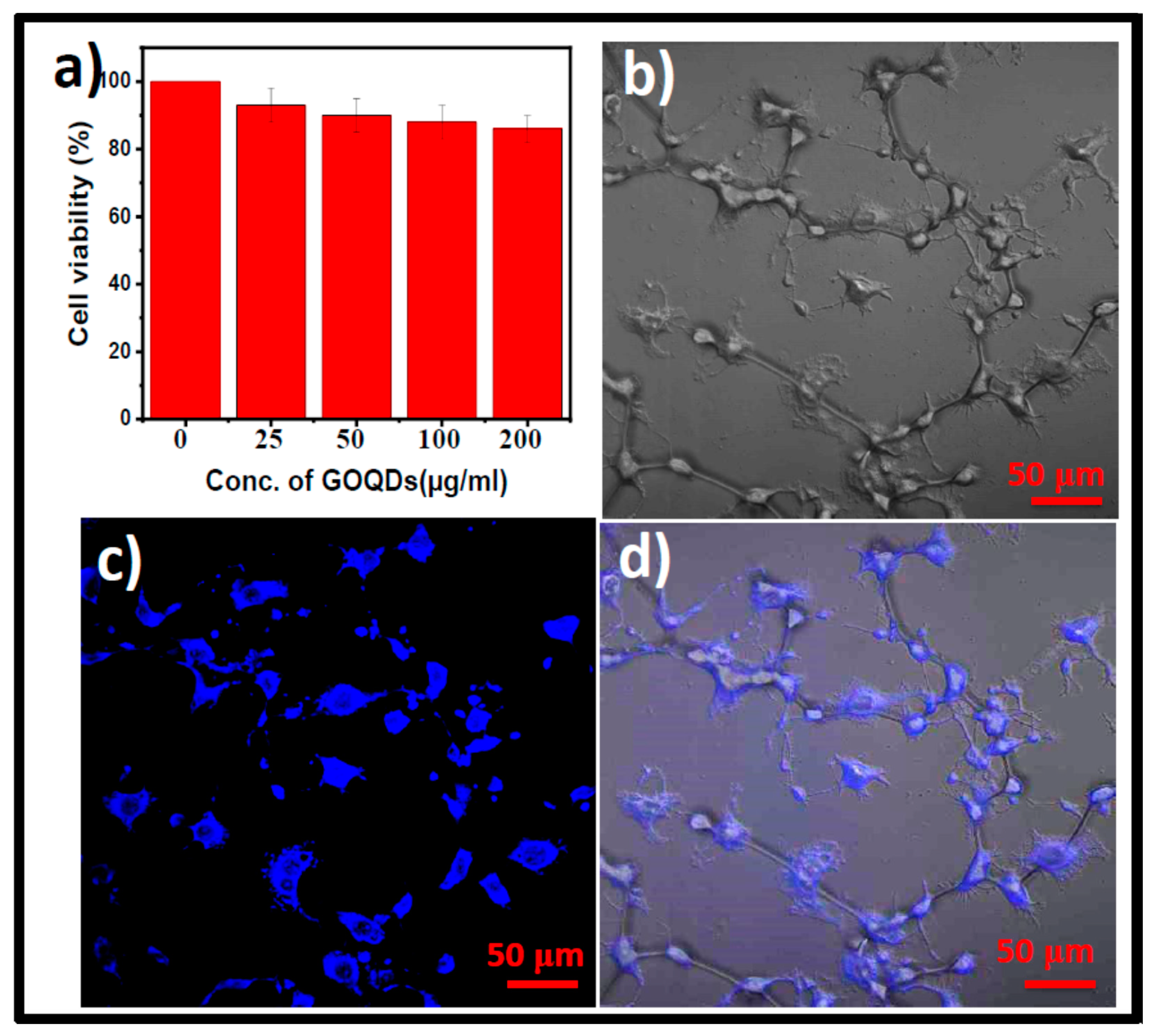
3.3. In Vitro Biocompatibility and Nano-Imaging of GOQDs in CT26 Cells
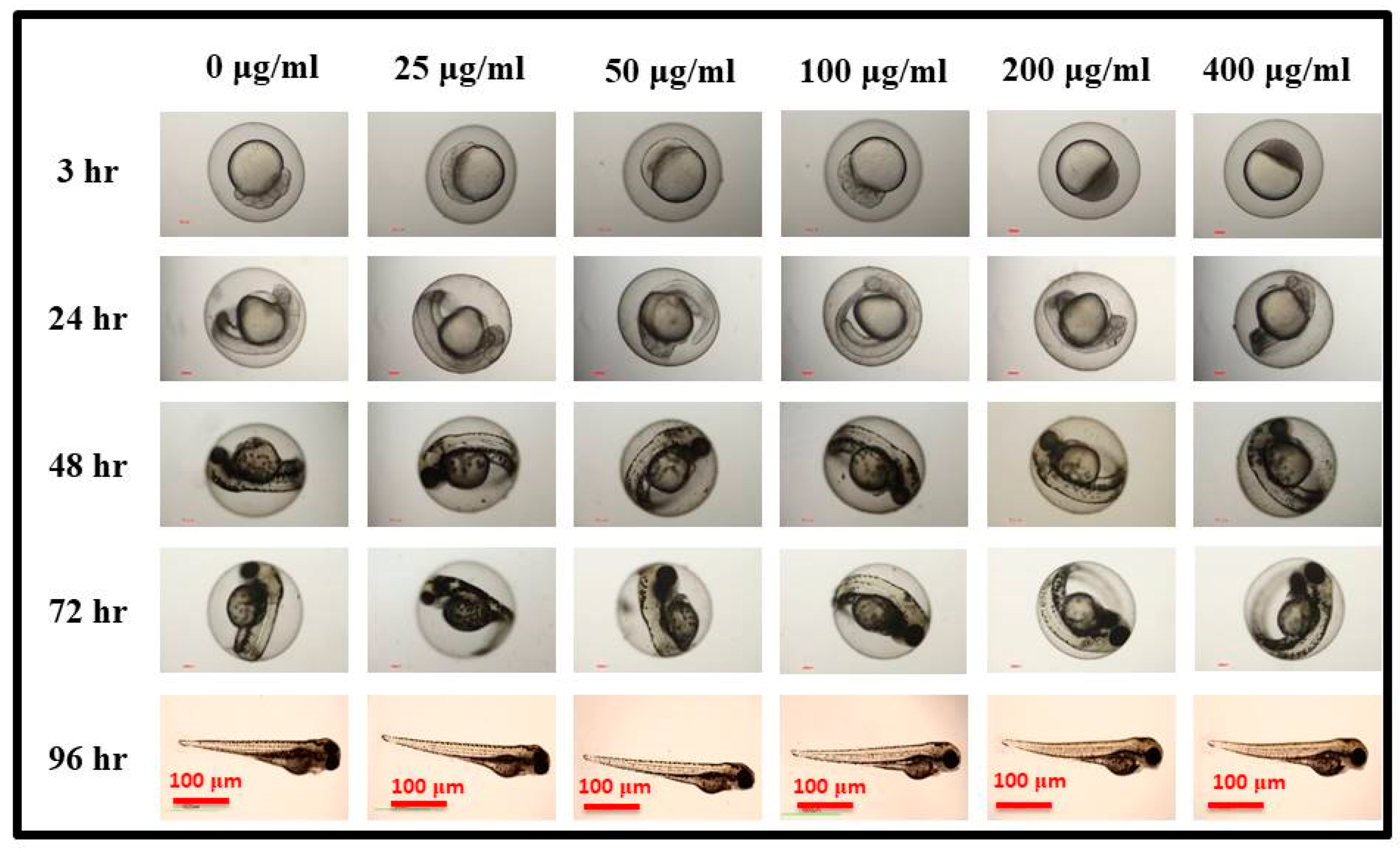
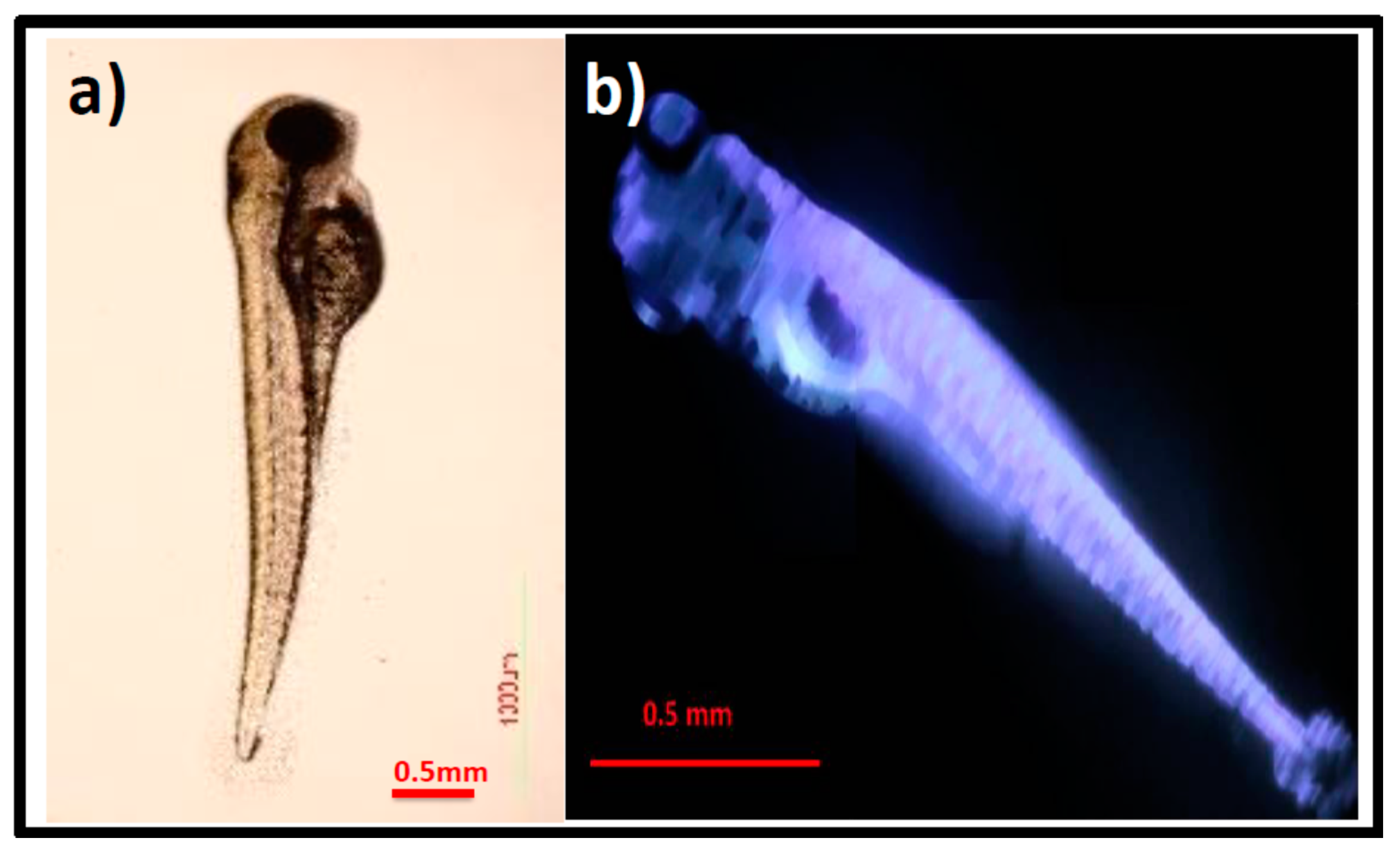
3.4. In Vivo Biocompatibility and Nano-Imaging of GOQDs in Zebrafish Embryos
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Hu, G.; Pu, X.; Tang, T.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Li, W. Size Effect of Graphene Quantum Dots on Photoluminescence. Molecules 2021, 26, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Song, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ye, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zhang, M.; et al. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots and their applications in drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, M.R.; He, G.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots for Bioimaging Applications. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, M. Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkan, E.; Barati, A.; Rahmanpanah, M.; Hosseinzadeh, L.; Moradi, S.; Hajialyani, M. Green synthesis of carbon dots derived from walnut oil and an investigation of their cytotoxic and apoptogenic activities toward cancer cells. Adv. Pharm. Bull 2018, 8, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, S.; Pourmadadi, M.; Yazdian, F.; Ghadami, A. The synthesis and characterization of targeted delivery curcumin using chitosan-magnetite-reduced graphene oxide as nano-carrier. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 186, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, C.; Tang, S.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Li, B.; Tian, L.; Liu, F.; Hu, R.; et al. Strongly green-photoluminescent graphenequantum dots for bioimaging applications. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6858–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaela, B.N.; Ndlovu, K.S.; Tshangana, C.S.; Muleja, A.A.; Mamba, B.B.; Nyokong, T.; Managa, M. Photodegradation of ibuprofen using 5-10-15-20-tetrakis(4-bromophenyl) porphyrin conjugated to graphene quantum dots. Opt. Mater. 2022, 134, 113147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, K.; Makarov, V.I.; Avalos, J.; Guinel, M.J.F.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. Luminescent graphene quantum dots fabricated by pulsed laser synthesis. Carbon N. Y. 2013, 64, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, C.; Qiu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, P.; King, G.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Kim, J.Y.T.; Cullen, D.A.; Zheng, D.; et al. General synthesis of single-atom catalysts with high metal loading using graphene quantum dots. Nat. Chem. 2021, 13, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.; Ni, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Lu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lu, Y.R.; Chan, T.S.; Chen, J. A Universal Graphene Quantum Dot Tethering Design Strategy to Synthesize Single-Atom Catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 21885–21889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressi, V.; Ferlazzo, A.; Iannazzo, D.; Espro, C. Graphene Quantum Dots by Eco-Friendly Green Synthesis for Electrochemical Sensing: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Jeong, Y.K.; Jung, K.H.; Son, Y.; Choi, S.C.; An, G.S.; Han, H.; Kim, K.M. Simple preparation of graphene quantum dots with controllable surface states from graphite. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38447–38453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, D.; Pinilla, J.L.; Gálvez, E.M.; Suelves, I. Graphene quantum dots from fishbone carbon nanofibers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 48504–48514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Jahdaly, B.A.; Elsadek, M.F.; Ahmed, B.M.; Farahat, M.F.; Taher, M.M.; Khalil, A.M. Outstanding Graphene Quantum Dots from Carbon Source for Biomedical and Corrosion Inhibition Applications: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Yeo, P.S.; Gan, C.K.; Wu, P.; Loh, K.P. Transforming C60 molecules into graphene quantum dots. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; He, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.; Nian, Q.; Li, S.; Qian, S.; Li, W.; Liu, C.; Liang, Z. Preparation of high-quality graphene oxide-carbon quantum dots composites and their application for electrochemical sensing of uric acid and ascorbic acid. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 135501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.; Park, M.; Kim, J.; Novak, T.G.; Lee, S.; Jeon, S. Toward highly efficient luminescence in graphene quantum dots for optoelectronic applications. Chem. Phys. Rev. 2021, 2, 031303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Jung, K.H.; Mhin, S.; Son, Y.; Lee, K.; Kim, W.R.; Choi, H.; Ryu, J.H.; Han, H.; Kim, K.M. Fundamental Understanding of the Formation Mechanism for Graphene Quantum Dots Fabricated by Pulsed Laser Fragmentation in Liquid: Experimental and Theoretical Insight. Small 2020, 16, e2003538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, M.J.; Dutta, A.; Chowdhury, D. Tuning the wettability and photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots via covalent modification. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, L.; Hu, G.; Tang, T.; Wen, J.; Li, X. Tuning the Photoluminescence of Graphene Quantum Dots by Fluorination. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 9682846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shen, H.; Tu, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, J.; Dai, J.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Z. The in vitro and in vivo toxicity of graphene quantum dots. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5041–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasbender, S.; Zimmermann, L.; Cadeddu, R.P.; Luysberg, M.; Moll, B.; Janiak, C.; Heinzel, T.; Haas, R. The Low Toxicity of Graphene Quantum Dots is Reflected by Marginal Gene Expression Changes of Primary Human Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, K.M.; Dai, Q.; Alman, B.A.; Chan, W.C. Are quantum dots toxic? Exploring the discrepancy between cell culture and animal studies. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Tabish, T.A.; Bull, S.J.; Lim, T.M.; Phan, A.N. High yield synthesis of graphene quantum dots from biomass waste as a highly selective probe for Fe3+ sensing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xie, J.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Lv, J.; Ge, H.; Ren, N.; Su, H.; Xie, X.; et al. From Graphite to Graphene Oxide and Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots. Small 2017, 13, 1601001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, M.; Gotou, T.; Horiuchi, S.; Fujiwara, M.; Ohba, M. Thin-film particles of graphite oxide 1: High-yield synthesis and flexibility of the particles. Carbon 2004, 42, 2929–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zhong, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T. Facile hydrothermal method to prepare graphene quantum dots from graphene oxide with different photoluminescences. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40422–40426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lv, G.; Hu, W.; Li, D.; Chen, S.; Dai, Z. Synthesis and applications of graphene quantum dots: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2018, 7, 157–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Zhao, C.; Yu, Y.; Yang, J. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers for oxidation of dopamine. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2016, 31, 1294–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, J.P.; Ríos, P.L.; Povea, P.; Morales-Verdejo, C.; Camarada, M.B. Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as the Support for the Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles and Their Applications as New Catalysts for the Decomposition of Composite Solid Propellants. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Quan, H.; Zhong, B.; Li, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, D. A Reduced Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot-Based Adsorbent for Efficiently Binding with Organic Pollutants. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6502–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-C.; Lu, S.-Y. Carbon black-derived graphene quantum dots composited with carbon aerogel as a highly efficient and stable reduction catalyst for the iodide/tri-iodide couple. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 1209–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, R.; Yang, B. Carbon Dots: A New Type of Carbon-Based Nanomaterial with Wide Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 2179–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, S. A facile and simple method for synthesis of graphene oxide quantum dots from black carbon. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabolle, M.; Spieles, M.; Lesnyak, V.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A.; Resch-Genger, U. Determination of the Fluorescence Quantum Yield of Quantum Dots: Suitable Procedures and Achievable Uncertainties. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6285–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuthala, N.; Shanmugam, M.; Kong, X.; Chiang, C.-S.; Hwang, K.C. Salt-mediated, plasmonic field-field/field-lattice coupling-enhanced NIR-II photodynamic therapy using core-gap-shell gold nanopeanuts. Nanoscale Horiz. 2022, 7, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-Y.; Choi, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-R.; Choe, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.P.; Alves, F.; Stringasci, M.D.; Buzzá, H.H.; Ciol, H.; Inada, N.M.; Bagnato, V.S. One-Pot Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Carbon Dots and in vivo and in vitro Antimicrobial Photodynamic Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.R.; Kumar, D.R.; Singh, D.; Savu, R.; Moshkalev, S. Progress in microwave-assisted synthesis of quantum dots(graphene/carbon/semiconducting) for bio applications: A review. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 282–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Pramanik, A.; Tchounwou, C.; Pedraza, F.; Crouch, R.A.; Chavva, S.R.; Vangara, A.; Sinha, S.S.; Jones, S.; Sardar, D.; et al. Multifunctional Biocompatible Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots Decorated Magnetic Nanoplatform for Efficient Capture and Two-Photon Imaging of Rare Tumor Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 10935–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, T.; Edamana, P. White-Light Emission from Unmodified Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 150126160901000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Ha, H.D.; Kim, Y.T.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Seo, T.S. Combination of a Sample Pretreatment Microfluidic Device with a Photoluminescent Graphene Oxide Quantum Dot Sensor for Trace Lead Detection. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 10969–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Qiu, J.; Ren, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, S.; Weeks, B. Size Sorted Multicolor Fluorescence Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots Obtained by Differential Velocity Centrifugation. Sci. Adv. Mater. 2014, 6, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, K.M.; Jung, K.; Son, Y.; Mhin, S.; Ryu, J.H.; Shim, K.B.; Lee, B.; Han, H.; Song, T. Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots Derived from Coal for Bioimaging: Facile and Green Approach. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, T.-F.; Teng, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-J.; Teng, H. Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Overall Water-Splitting under Visible Light Illumination. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3297–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.-X.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Wang, M. One- and two-photon luminescence in graphene oxide quantum dots. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, N.; Du, Y. Intrinsic magnetism of monolayer graphene oxide quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 033105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Fu, F.; Chi, Y.; Chen, G. Graphene quantum dots, graphene oxide, carbon quantum dots and graphite nanocrystals in coals. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7410–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.; Tian, L.; Xiang, W.; Wang, T.; Hu, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, Z. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from natural polymer starch for cell imaging. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Guo, Q.; Chen, D.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Xu, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, G. Facile and Highly Effective Synthesis of Controllable Lattice Sulfur-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots via Hydrothermal Treatment of Durian. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5750–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Li, F.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots derived from lignin biomass. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-L.; Huang, C.-C.; Mai, F.-D.; Yen, C.-L.; Tzing, S.-H.; Hsieh, H.-T.; Ling, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-Y. Application of paramagnetic graphene quantum dots as a platform for simultaneous dual-modality bioimaging and tumor-targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.-Y.; Gedda, G.; Girma, W.M.; Yen, C.-L.; Ling, Y.-C.; Chang, J.-Y. Magneto fluorescent Carbon Dots Derived from Crab Shell for Targeted Dual-Modality Bioimaging and Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13887–13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Niu, J.; Liu, B. Facile synthesis and photoluminescence of graphene oxide quantum dots and their reduction products. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4970–4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Jalal, M.; Prasad, S.; Bose, S. Aggregation-induced enhanced photoluminescence in magnetic graphene oxide quantum dots as a fluorescence probe for As(iii) sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, Y.; Lu, C. Rapid Screening of Oxygen States in Carbon Quantum Dots by Chemiluminescence Probe. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12520–12526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhong, X.; He, J. Synthesis of Yellow-Fluorescent Carbon Nano-dots by Microplasma for Imaging and Photocatalytic Inactivation of Cancer Cells. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2021, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Gao, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Quantum dots in cell imaging and their safety issues. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5765–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Peng, X.; Sun, F.; Kong, Z.; Shen, J.-W. A review on the cytotoxicity of graphene quantum dots: From experiment to simulation. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Lan, M.; Zhou, B.; Liu, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, H.; Jia, Q.; Niu, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. A graphene quantum dot photodynamic therapy agent with high singlet oxygen generation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Hai, X.; Xia, C.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, J.H. Preparation of excitation-independent photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with visible-light excitation/emission for cell imaging. Chemistry 2013, 19, 15918–15923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, M.; Mewada, A.; Pandey, S.; Bhori, M.; Singh, K.; Sharon, M.; Sharon, M. Milk-derived multi-fluorescent graphene quantum dot-based cancer theranostic system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 67, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.T.; Gonzalez-Rodriguez, R.; Ryan, C.; Faerber, N.; Coffer, J.L.; Naumov, A.V. Photo-and Electroluminescence from Nitrogen-Doped and Nitrogen–Sulfur Codoped Graphene Quantum Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Hu, J.; Zhao, J.; An, N.; Liang, K.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, R.; Zhang, F. Eco friendly synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots for the sensitive detection of ferric ions and cell imaging. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Sang, Y.; Tang, W.; Rivera Gil, P.; Liu, H. Fluorescent graphene quantum dots as traceable, pH-sensitive drug delivery systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6709–6724. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Chen, D.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Huang, N.; Gu, Y.; Wang, C.; et al. Eco-friendly synthesis of size-controllable amine-functionalized graphene quantum dots with antimycoplasma properties. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Wang, K.; Sun, L.; Sun, B.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, L. Application of graphene quantum dots for simultaneous fluorescence imaging and tumor-targeted drug delivery. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.V.; Thomas, R.T.; Sankar, V.; Muhammad, H.; Dong, M.; Pillai, S. Rapid, Acid-Free Synthesis of High-Quality Graphene Quantum Dots for Aggregation Induced Sensing of Metal Ions and Bioimaging. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8051–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, A.; Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Zhou, T.; Hosta-Rigau, L.; Sun, Y. One-Pot Green Synthesis of Biocompatible Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Cell Uptake Studies. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunci, L.; González-Colón, V.; Vargas-Pérez, B.L.; Ortiz-Santiago, J.; Pagán, M.; Carrion, P.; Cruz, J.; Molina-Ontoria, A.; Martinez, N.; Silva, W.; et al. Multicolor Fluorescent Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for Sensing Cancer Cell Biomarkers. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Ren, Y.; Bick, M.; Dudek, A.; Hong-Wang Waworuntu, E.; Tang, J.; Chen, J.; Chang, B. Highly fluorescent copper nanoclusters for sensing and bioimaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 154, 112078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.K.; Thakur, M.; Bahadur, R.; Kaku, T.; Prabhuraj, R.S.; Ninawe, A.; Srivastava, R. Preparation of graphene oxide-graphene quantum dots hybrid and its application in cancer theranostics. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 103, 109774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollavelli, G.; Ling, Y.C. Multi-functional graphene as an in vitro and in vivo imaging probe. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2532–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hason, M.; Bartůněk, P. Zebrafish Models of Cancer-New Insights on Modeling Human Cancer in a Non-Mammalian Vertebrate. Genes 2019, 10, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollavelli, G.; Chang, C.-C.; Ling, Y.-C. Facile Synthesis of Smart Magnetic Graphene for Safe Drinking Water: Heavy Metal Removal and Disinfection Control. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W.; Yang, W.; He, Z.; Sun, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, F. Synthesis of multi-functional green fluorescence carbon dots and their applications as a fluorescent probe for Hg2+ detection and zebrafish imaging. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 10400–10405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.F.; Li, Y.H.; Fang, Y.W.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X.M.; Yin, X.B. Carbon Quantum Dots for Zebrafish Fluorescence Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Li, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, F.; Zhu, X. Red-Emissive Ruthenium-Containing Carbon Dots for Bioimaging and Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, G.; De Luca, G.; Nocito, G.; Rizzo, M.G.; Lombardo, S.P.; Chisari, G.; Forte, S.; Sciuto, E.L.; Conoci, S. Carbon Dots: An Innovative Tool for Drug Delivery in Brain Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskewycz, A.; Yin, H.; Halberg, N.; Lai, D.T.H.; Ball, A.S.; Truong, V.K.; Rybicka, A.M.; Cole, I. Carbon Dot Therapeutic Platforms: Administration, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion, Toxicity, and Therapeutic Potential. Small 2022, 18, 2106342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, P.; Dev, A. Carbon quantum dots: A promising nanocarrier for bioimaging and drug delivery in cancer. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| S. No | Precursor | Synthetic Process (Method, Reagents, Time) | Post-Processing Steps | Time | Ref. No |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Graphite Powder | Step 1: Oxidation method H2SO4/KMnO4/NaNO3/H2O2, >1 d Step 2: Hydrothermal method, Ndimethylformamide, 6 h | Dialysis, filtration, and rotary evaporation | >8 h | [42] |
| 2 | Graphite | Step 1: Oxidation method H2SO4/KMnO4/NaNO3/H2O2, >1 d Step 2: Acid refluxing, HNO3, 8 h Step 3: Ultrasonic, NaOH, 0.5 h | Centrifugation, dialysis, and filtration. | >1 week | [43] |
| 3 | Graphite Nanoparticles | Step 1: Ultrasonication H2SO4/HNO3, Step 2: Acid refluxing, H2SO4/HNO3 12 h | Centrifugation, and dialysis | >2 d | [44] |
| 4 | Graphene nanofibers | Step 1: Acid oxidizing, NaClO3, fuming HNO3, 12 h Step 2: Acid refluxing, NaClO3, fuming HNO3, HNO3, 6 h Step 3: Ultrasonication, HCl, 1 h | Dialysis and vacuum drying | 1 week | [45] |
| 5 | Coal | The coal and ethanol added in 50 mL of Bottom of a glass vessel, and applied Q-switch ND:YAG laser system, pulsed laser beam with an ablation energy of 0.1 J. | Filtered microporous membrane and dialysis for two days | 5 min | [46] |
| 6 | Graphite | Step 1: Oxidation by Hummers method, H2SO4/KMnO4/NaNO3/H2O2, >1 d Step 2: further oxidation by Hummers method, H2SO4/KMnO4/NaNO3/H2O2, >1 d | Centrifugation, and dialysis. | >2 d | [47] |
| 7 | XC-72 carbon black | Step 1: Ultrasonication, HNO3, 2 h Step 2: Acid refluxing, HNO3, 24 h | Centrifugation, evaporation, and redispersion | >24 h | [48] |
| 8 | XC-72 carbon black | Acid refluxing, HNO3, 24 h | Centrifugation, vacuum filtration, and vacuum freeze drying | >24 h | [49] |
| 9 | Coal | Acid refluxing, HNO3, 12 h | Centrifugation, vacuum dry, and redispersion | >12 h | [50] |
| 10 | Starch | Starch solution in water, Hydrothermal method at 190 °C for 120 min. | Centrifugation, and dialysis | 2 h | [51] |
| 11 | Durian extract | Durian flesh suspension in water, Hydrothermal method at 150 °C for 12 h. | Filter membrane, and centrifugation. | 12 h | [52] |
| 12 | Lignin | Lignin acidic solution, Hydrothermal method at 180 °C for 12 h. | Filter membrane, and centrifugation | 12 h | [53] |
| 13 | Crab shells | Step 1: Dried crab shells powder in acetic acid solution by stirring for 12 h at TR Step 2: The upper layer solution and GdCl3 added in glass vessel then heated using a single-mode microwave reactor at 220 °C for 10 min. | Filter membrane, and centrifugation | 12 h | [54] |
| 14 | Graphite | Step 1: oxidation by Hummer’s method, H2SO4/KMnO4/NaNO3/H2O2, >1 d Step 2: Graphene oxide in water was hydrothermally treated at 120 °C for 10 h. GQDs were purified by membrane filtration. | Filter membrane, and centrifugation | 22 h | [55] |
| 15 | Black carbon | Microwave-assisted method. No chance of heavy metal contamination and required excessive purification with acids or other solvents | Simple membrane filtration. | 2 min | This work |
| S. No | Materials | Size | PL Color | Emission (nm) | Quantum Yield (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GQDs | 2−6 | Red | 600 | 1.4 | [62] |
| 2 | GQDs | 3−5 | Blue | 427, 516 (shoulder) | 4.1 | [63] |
| 3 | GQDs-Cyc-HCl | 5 | Green | 400−500 | 58 | [64] |
| 4 | N-GQD/N−S-GQD | 5.5−3.9 avg. | Green | 425, 448 | 60 | [65] |
| 5 | Carbon dots (CDs). | 3 | Blue | 442 | 25 | [66] |
| 6 | GQD-RGD | 4 | Blue-green | 420 | NA | [67] |
| 7 | GQD-amine | 7.5 | Green | 500 | 1.5 | [68] |
| 8 | GQD-RGD | 3.7 | Yellow-green | 460 | NA | [69] |
| 9 | Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) | 5 | Blue | 430 | 23.8 | [70] |
| 10 | GQDs | 6 | Blue | 400 | 28 | [71] |
| 11 | GOQDS | 20 | Blue | 400 | 3.13 | Present work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorle, G.; Gollavelli, G.; Nelli, G.; Ling, Y.-C. Green Synthesis of Blue-Emitting Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for In Vitro CT26 and In Vivo Zebrafish Nano-Imaging as Diagnostic Probes. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020632
Gorle G, Gollavelli G, Nelli G, Ling Y-C. Green Synthesis of Blue-Emitting Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for In Vitro CT26 and In Vivo Zebrafish Nano-Imaging as Diagnostic Probes. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020632
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorle, Govinda, Ganesh Gollavelli, Gowreeswari Nelli, and Yong-Chien Ling. 2023. "Green Synthesis of Blue-Emitting Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for In Vitro CT26 and In Vivo Zebrafish Nano-Imaging as Diagnostic Probes" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020632
APA StyleGorle, G., Gollavelli, G., Nelli, G., & Ling, Y.-C. (2023). Green Synthesis of Blue-Emitting Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots for In Vitro CT26 and In Vivo Zebrafish Nano-Imaging as Diagnostic Probes. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020632








