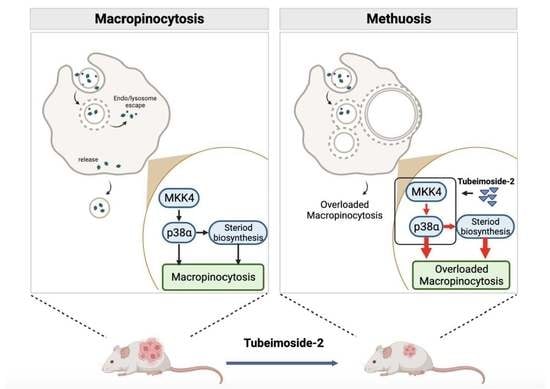
Tubeimoside-2 Triggers Methuosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells through the MKK4–p38α Axis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Dextran/Lucifer Yellow Uptake Assay
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.6. Proteomic Analysis
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Total Cholesterol Assay
2.9. Xenograft Experiments
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TBM-2 Treatment Induced Methuosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells
3.2. TBM-2 Enhanced Lipid Metabolism to Support Methuosis
3.3. TBM-2 Treatment Hyperactivated the MAPK Signal Pathway
3.4. TBM-2 Induced Methuosis via the MKK4–p38α Axis
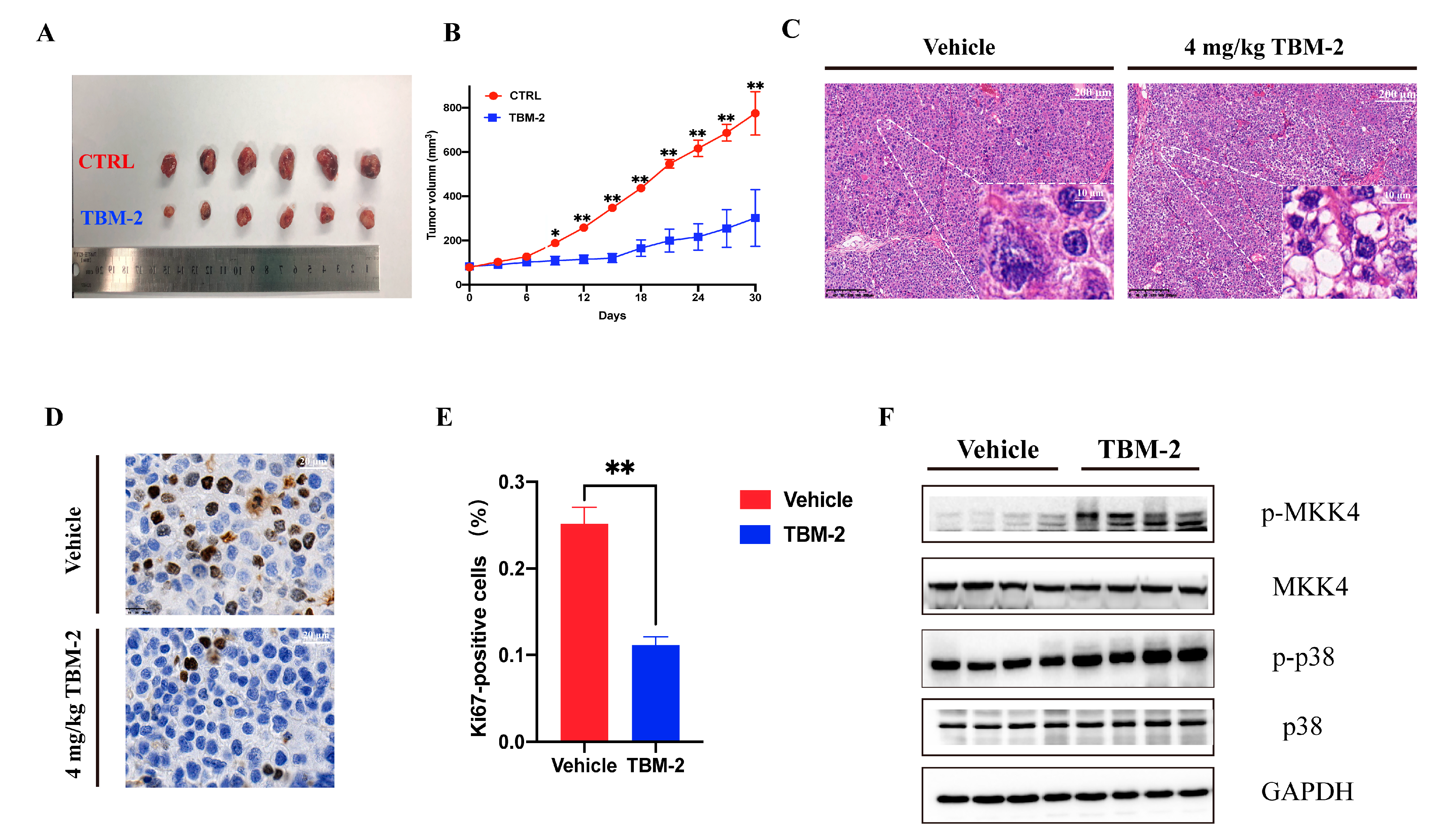
3.5. TBM-2 Triggered Methuosis and Suppressed Hepatocarcinoma Tumor Growth In Vivo
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Qu, C.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, H.; Sun, K.; Gu, X.; Xia, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, W.; et al. Liver cancer incidence and mortality in China: Temporal trends and projections to 2030. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 30, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Q.; Wen, W.; Wang, H. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Challenges and opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2019, 460, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X. New agents on the horizon in hepatocellular carcinoma. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2013, 5, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Rong, D.; Reiter, F.P.; et al. The mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Theoretical basis and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holohan, C.; Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Longley, D.B.; Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: An evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Ren, J.; Lai, P.B.S.; Chen, G.G. New insights into sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Responsible mechanisms and promising strategies. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, E.; Fuchs, Y. Modes of Regulated Cell Death in CancerModes of Regulated Cell Death in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 245–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Agostinis, P.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Amelio, I.; Andrews, D.W.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 486–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltese, W.A.; Overmeyer, J.H. Methuosis: Nonapoptotic Cell Death Associated with Vacuolization of Macropinosome and Endosome Compartments. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1630–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Commisso, C. Macropinocytosis in Cancer: A Complex Signaling Network. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayashankar, V.; Edinger, A.L. Macropinocytosis confers resistance to therapies targeting cancer anabolism. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.-X.; Pang, H.-B. Macropinocytosis as a cell entry route for peptide-functionalized and bystander nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2020, 329, 1222–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, J.; Helenius, A. Virus entry by macropinocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recouvreux, M.V.; Commisso, C. Macropinocytosis: A metabolic adaptation to nutrient stress in cancer. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, Z.; Cai, H.; Long, Y.; Sirka, O.K.; Padmanaban, V.; Ewald, A.J.; Devreotes, P.N. Statin-induced GGPP depletion blocks macropinocytosis and starves cells with oncogenic defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4158–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, P.M.; Zheng, Z.G.; Zhou, Y.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Jing, D.; Cheng, H.M.; Li, J.; Li, P.; Xu, X. Phellodendrine chloride suppresses proliferation of KRAS mutated pancreatic cancer cells through inhibition of nutrients uptake via macropinocytosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 850, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, S.; Nishizawa, S.; Nakagawa, H.; Funata, M.; Nishimura, K.; Soga, T.; Hara, T. Cancer with low cathepsin D levels is susceptible to vacuolar (H(+))-ATPase inhibition. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efferth, T.; Li, P.C.; Konkimalla, V.S.B.; Kaina, B. From traditional Chinese medicine to rational cancer therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Wang, C.; Zheng, J.; Paudyal, N.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, H. The potential role of tubeimosides in cancer prevention and treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Li, G. Tubeimoside-1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis through downregulation of CXCR4 chemokine receptor expression. BMB Rep. 2016, 49, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; He, P. Tubeimoside-1 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by increasing the Bax to Bcl-2 ratio and decreasing COX-2 expression in lung cancer A549 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2011, 4, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, A.I. Pharmacological inhibition of endocytic pathways: Is it specific enough to be useful? In Exocytosis and Endocytosis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 15–33. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wan, T.; Wan, M.; Liu, B.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, R. The effect of the size of fluorescent dextran on its endocytic pathway. Cell Biol. Int. 2015, 39, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, M.C.; Teasdale, R.D. Defining Macropinocytosis. Traffic 2009, 10, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, C.; Hauser, A.D.; Vucic, E.A.; Bar-Sagi, D. Plasma membrane V-ATPase controls oncogenic RAS-induced macropinocytosis. Nature 2019, 576, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, M.; Kawai, K.; Egami, Y.; Araki, N. Dissecting the roles of Rac1 activation and deactivation in macropinocytosis using microscopic photo-manipulation. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stow, J.L.; Hung, Y.; Wall, A.A. Macropinocytosis: Insights from immunology and cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 65, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, D.; Xuan, Y.; Hao, P.; Ke, X.; Zhou, X.; Qu, Y. Eltrombopag binds SDC4 directly and enhances MAPK signaling and macropinocytosis in cancer cells. Am. J. Cancer. Res. 2022, 12, 2697–2710. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.K.; Li, C.; Khan, J.; Banerjee, N.S.; Chow, L.T.; Athar, M. Combined mTORC1/mTORC2 inhibition blocks growth and induces catastrophic macropinocytosis in cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 24583–24592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Pavez, E.; Villar, P.; Trigo, C.; Caamaño, E.; Niechi, I.; Pérez, P.; Muñoz, J.P.; Aguayo, F.; Burzio, V.A.; Varas-Godoy, M. CK2 inhibition with silmitasertib promotes methuosis-like cell death associated to catastrophic massive vacuolization of colorectal cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.C.; Martinez, O.; Honko, A.N.; Hensley, L.E.; Olinger, G.G.; Basler, C.F. Pyridinyl imidazole inhibitors of p38 MAP kinase impair viral entry and reduce cytokine induction by Zaire ebolavirus in human dendritic cells. Antivir. Res. 2014, 107, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Gram, H.; Zhao, M.; New, L.; Gu, J.; Feng, L.; Di Padova, F.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Han, J. Characterization of the Structure and Function of the Fourth Member of p38 Group Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases, p38δ. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30122–30128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motamedi, N.; Sewald, X.; Luo, Y.; Mothes, W.; DiMaio, D. SV40 Polyomavirus Activates the Ras-MAPK Signaling Pathway for Vacuolization, Cell Death, and Virus Release. Viruses 2020, 12, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, J.D.; Fulton, D.L.; Richard, S.; Almazan, G. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Regulates Genes during Proliferation and Differentiation in Oligodendrocytes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charni-Natan, M.; Aloni-Grinstein, R.; Osher, E.; Rotter, V. Liver and Steroid Hormones-Can a Touch of p53 Make a Difference? Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Hua, L.; Fang, H.; Li, S.; Chai, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y. Tubeimoside-2 Triggers Methuosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells through the MKK4–p38α Axis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041093
Gan Y, Wang C, Chen Y, Hua L, Fang H, Li S, Chai S, Xu Y, Zhang J, Gu Y. Tubeimoside-2 Triggers Methuosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells through the MKK4–p38α Axis. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041093
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Yichao, Chen Wang, Yunyun Chen, Linxin Hua, Hui Fang, Shu Li, Shoujie Chai, Yang Xu, Jiawei Zhang, and Ying Gu. 2023. "Tubeimoside-2 Triggers Methuosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells through the MKK4–p38α Axis" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041093
APA StyleGan, Y., Wang, C., Chen, Y., Hua, L., Fang, H., Li, S., Chai, S., Xu, Y., Zhang, J., & Gu, Y. (2023). Tubeimoside-2 Triggers Methuosis in Hepatocarcinoma Cells through the MKK4–p38α Axis. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041093