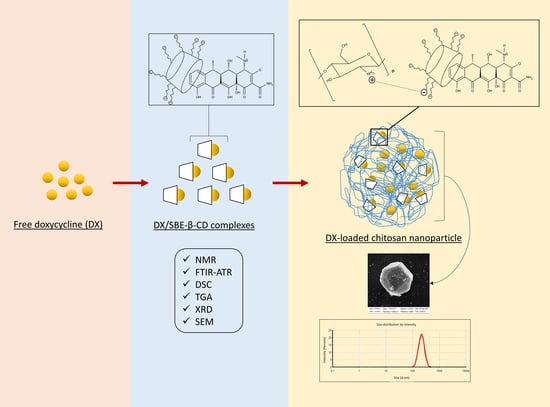
Supramolecular Arrangement of Doxycycline with Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin: Impact on Nanostructuration with Chitosan, Drug Degradation and Antimicrobial Potency
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Drug Content and Impurities by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. DX/SBE-β-CD Complex Preparation
2.4. Stability of DX/SBE-β-CD Complex in Different pHs
2.5. Job’s Plot
2.6. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry (ITC)
2.7. Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) and 2D-NOESY Spectra
2.8. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.9. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.10. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.11. Hydrodynamic Diameter and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.12. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.13. Chitosan Nanoparticles Formulation
2.14. Drug Content and Encapsulation Efficiency in NPs
2.15. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of DX/SBE-β-CD Complexes in Aqueous Solution
3.1.1. The Stability of the DX/SBE-β-CD Complex in Different pHs
3.1.2. DX/SBE-β-CD Complex Stoichiometry and Binding Studies
3.1.3. 1H NMR and 2D-NOESY Spectra
3.1.4. Hydrodynamic Diameter (Size)
3.2. Characterization of DX/SBE-β-CD Complexes in Solid State
3.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2.2. Thermal Analysis
3.2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. Development and Characterization of Empty and DX-Loaded Nanoparticles
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feitosa, R.C.; Ishikawa, E.S.A.; da Silva, M.F.A.; da Silva-Júnior, A.A.; Oliveira-Nascimento, L. Five decades of doxycycline: Does nanotechnology improve its properties? Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Pan, X.; Su, W.; Liang, D.; Wu, C. Doxycycline and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex in poloxamer thermal sensitive hydrogel for ophthalmic delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2011, 1, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, M.; Wen, X.; Quan, G.; Huang, X.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Optimization of a doxycycline hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex based on computational modeling. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2013, 3, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M.; He, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; He, Z.; Wan, Q.; Liang, D.; Repka, M.A.; Wu, C. Molecular modeling-based inclusion mechanism and stability studies of doxycycline and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex for ophthalmic delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2013, 14, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogawa, A.C.; Zoppi, A.; Quevedo, M.A.; Nunes Salgado, H.R.; Longhi, M.R. Increasing doxycycline hyclate photostability by complexation with β-cyclodextrin. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suárez, D.F.; Consuegra, J.; Trajano, V.C.; Gontijo, S.M.L.; Guimarães, P.P.G.; Cortés, M.E.; Denadai, Â.L.; Sinisterra, R.D. Structural and thermodynamic characterization of doxycycline/β-cyclodextrin supramolecular complex and its bacterial membrane interactions. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 118, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, O.; Ghate, V.M.; Lewis, S.A. Utility of sulfobutyl ether β-Cyclodextrin inclusion complexes in drug delivery: A review. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 81, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Syeda, J.T.M.; Wasan, K.M.; Wasan, E.K. An overview of chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug delivery. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cover, N.F.; Lai-yuen, S.; Parsons, A.K. Synergetic effects of doxycycline-loaded chitosan nanoparticles for improving drug delivery and efficacy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 2411–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Parle, M.; Sharma, N.; Dhingra, S.; Raina, N.; Jindal, D.K. Brain targeted oral delivery of doxycycline hydrochloride encapsulated tween 80 coated chitosan nanoparticles against ketamine induced psychosis: Behavioral, biochemical, neurochemical and histological alterations in mice. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1429–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zegan, G.; Toma, V.; Cernei, E.R.; Anistoroaei, D.; Carausu, E.M.; Moscu, M. Study on antibiotic loaded nanoparticles for oral infection treatment. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 1712–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Qiu, X.; Ji, Q. The effect of doxycycline-containing chitosan/carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles on NLRP3 inflammasome in periodontal disease. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo El-Ela, F.I.; Hussein, K.H.; El-Banna, H.A.; Gamal, A.; Rouby, S.; Menshawy, A.M.S.; EL-Nahass, E.L.S.; Anwar, S.; Zeinhom, M.M.A.; Salem, H.F.; et al. Treatment of Brucellosis in Guinea Pigs via a Combination of Engineered Novel pH-Responsive Curcumin Niosome Hydrogel and Doxycycline-Loaded Chitosan–Sodium Alginate Nanoparticles: An In Vitro and In Vivo Study. AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 2020, 21, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhum, W.N.; Zaidan, I.A. The synergistic effects of chitosan-alginate nanoparticles loaded with doxycycline antibiotic against multidrug resistant proteus mirabilis, Escherichia coli and enterococcus faecalis. Iraqi J. Sci. 2020, 61, 3187–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leichner, C.; Jelkmann, M.; Prüfert, F.; Laffleur, F.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Intestinal enzyme delivery: Chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles providing a targeted release behind the mucus gel barrier. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 144, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, R.M.; Dmour, I.; Taha, M.O. Stable Chitosan-Based Nanoparticles Using Polyphosphoric Acid or Hexametaphosphate for Tandem Ionotropic/Covalent Crosslinking and Subsequent Investigation as Novel Vehicles for Drug Delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juschten, J.; Ingelse, S.A.; Bos, L.D.J.; Girbes, A.R.J.; Juffermans, N.P.; van der Poll, T.; Schultz, M.J.; Tuinman, P.R.; de Beer, F.M.; Claushuis, T.A.; et al. Alkaline phosphatase in pulmonary inflammation—A translational study in ventilated critically ill patients and rats. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2020, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Raloxifene/SBE-β-CD Inclusion Complexes Formulated into Nanoparticles with Chitosan to Overcome the Absorption Barrier for Bioavailability Enhancement. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Tang, B.; Tang, P.; Sun, Q.; Suo, Z.; Zhang, M.; Gan, N. Chitosan/Sulfobutylether-b-Cyclodextrin Nanoparticles for Ibrutinib Delivery: A Potential Nanoformulation of Novel Kinase Inhibitor. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, T.; Lin, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, G.; Bu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J. Preparation and in vitro release of buccal tablets of naringenin-loaded MPEG-PCL nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 33672–33679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Antoniou, J.; Li, Y.; Majeed, H.; Liang, R.; Ma, Y.; Ma, J. Chitosan/sulfobutylether-b-cyclodextrin nanoparticles as a potential approach for tea polyphenol encapsulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoover, R.K.; Alcorn, H.; Lawrence, L.; Paulson, S.K.; Quintas, M.; Luke, D.R.; Cammarata, S.K. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin in Patients With Varying Degrees of Renal Impairment. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, 814–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Job, P. Formation and Stability of Inorganic Complexes in Solution. Ann. Chim. 1928, 9, 113–203. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, A.A.; El-feky, G.S.; Kamel, R.; Awad, G.E.A. Chitosan/sulfobutylether-b-cyclodextrin nanoparticles as a potential approach for ocular drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 413, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 30th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standard Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; ISBN 9781684400669. [Google Scholar]
- Remmers, E.G.; Sieger, G.M.; Doerschuk, A.P. Some observations on the kinetics of the C·4 epimerization of tetracycline. J. Pharm. Sci. 1963, 52, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazek-Kęsik, A.; Nosol, A.; Płonka, J.; Śmiga-Matuszowicz, M.; Student, S.; Brzychczy-Włoch, M.; Krok-Borkowicz, M.; Pamuła, E.; Simka, W. Physico-chemical and biological evaluation of doxycycline loaded into hybrid oxide-polymer layer on Ti–Mo alloy. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, O.M.M.; Silva, D.M.; Martins, F.T.; Legendre, A.O.; Azarias, L.C.; Rosa, I.M.L.; Neves, P.P.; De Araujo, M.B.; Doriguetto, A.C. Protonation pattern, tautomerism, conformerism, and physicochemical analysis in new crystal forms of the antibiotic doxycycline. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 3711–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojica, E.R.E.; Nguyen, E.; Rozov, M.; Bright, F.V. PH-dependent spectroscopy of tetracycline and its analogs. J. Fluoresc. 2014, 24, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidong, W.; Hua, S.; Roets, E.; Busson, R.; Hoogmartens, J. Investigation of keto-enol tautomerism and ionization of doxycycline in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 96, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, A.; Palilis, L.P.; Lino, C.M.; Silveira, M.I.; Calokerinos, A.C. Determination of tetracycline and its major degradation products by chemiluminescence. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 405, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.; Yen, C.H.; Schneider, M.; Lowry, B.; Yerlikaya, F.; Whitesell, G.; Leisssa, B.; Faustino, P.J.; Khan, S.R. Development and validation of a stability-indicating ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) method for doxycycline hyclate: An optimization of the analytical methodology for a medical countermeasure (MCM) drug. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monser, L.; Darghouth, F. Rapid liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of tetracyclines antibiotics and 6-Epi-doxycycline in pharmaceutical products using porous graphitic carbon column. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranaboripan, W.; Lang, W.; Motomura, E.; Sakairi, N. Preparation and characterization of polymeric host molecules, β-cyclodextrin linked chitosan derivatives having different linkers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkour, Y.; Vermeersch, G.; Morcellet, M.; Boschin, F.; Martel, B.; Azaroual, N. Formation of cyclodextrin inclusion complexes with doxycyclin-hyclate: NMR investigation of their characterisation and stability. J. Incl. Phenom. 2006, 54, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbert, D.B.; Thordarson, P. The death of the Job plot, transparency, open science and online tools, uncertainty estimation methods and other developments in supramolecular chemistry data analysis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 12792–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, V.M.; de Oliveira-Nascimento, L.; Cabeça, L.F.; Geraldes, D.C.; Costa, J.S.R.; Riske, K.A.; Franz-Montan, M.; Yokaychiya, F.; Dias Franco, M.K.K.; de Paula, E. Capsaicin-cyclodextrin complex enhances mepivacaine targeting and improves local anesthesia in inflamed tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denadai, Â.M.L.; Ianzer, D.; Alcântara, A.F.d.C.; Santoro, M.M.; Santos, C.F.F.; Lula, I.S.; de Camargo, A.C.M.; Faljoni-Alario, A.; dos Santos, R.A.S.; Sinisterra, R.D. Novel pharmaceutical composition of bradykinin potentiating penta peptide with β-cyclodextrin: Physical-chemical characterization and anti-hypertensive evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, P.; Guimarães, G.; Coelho, A.; Karina, D.M.; Rosa, I.; Denadai, Â.M.L.; Fills, R.A.; Esperanza, M.; Rubén, C.; Sinisterra, D. Enhanced efficacy against bacterial biofilms via host: Guest cyclodextrin—Doxycycline inclusion complexes. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2021, 99, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, M.; Kurkov, S.V.; Flavià-piera, R.; Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Self-assembly of cyclodextrins: The effect of the guest molecule. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto-Ferreira, J.C.; Ilharco, L.M.; Garcia, A.R.; Vieira Ferreira, L.F. Characterization of solid complexes between aromatic ketones and β-cyclodextrin using diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 10392–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyed, O. Spectroscopic studies on β-cyclodextrin. Vib. Spectrosc. 1990, 1, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer. Doxycycline [Doxycycline Hyclate Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, for Solution]. Available online: https://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=952. (accessed on 16 March 2023).
- de Barros, J.O.; Kogawa, A.C.; Regina, H.; Salgado, N. Short-Term Stability Study of Doxycycline Tablets by High Performance Liquid Chromatography, Spectrophotometry in the Ultraviolet Region and Turbidimetry. J. Pharmacol. Clin. Trials 2018, 1, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, A.O.; Silva, L.R.R.; Silva, D.M.; Rosa, I.M.L.; Azarias, L.C.; De Abreu, P.J.; De Araújo, M.B.; Neves, P.P.; Torres, C.; Martins, F.T.; et al. Solid state chemistry of the antibiotic doxycycline: Structure of the neutral monohydrate and insights into its poor water solubility. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2012, 14, 2532–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Qian, F.; Yin, C. Preparation and characterization of mucoadhesive polymer-coated nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 316, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Nienhaus, K.; Nienhaus, G.U. Engineered nanoparticles interacting with cells: Size matters. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2014, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, R.J.C.; Tharmalingam, N.; Choi, Y.; Madheswaran, T.; Paulmurugan, R.; McCarthy, J.R.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H. Combating intracellular pathogens with nanohybrid-facilitated antibiotic delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8437–8449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Duchêne, D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, J.E.; Jones, R.N. MIC quality control guidelines for doxycycline when testing Gram- positive control strains by the reference methods. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2004, 50, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, M.P.; Weir, S.; Macone, A.; Donatelli, J.; Trieber, C.A.; Tanaka, S.K.; Levy, S.B. Mechanism of Action of the Novel Aminomethylcycline Antibiotic. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1279–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matynia, B.; Młodzinska, E.; Hryniewicz, W. Antimicrobial susceptibility patterns of Staphylococcus aureus in Poland obtained by the National Quality Assurance Programme. Eur. Soc. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation. ICH Harmonised Guideline: Validation of Analytical Procedures Q2(R2). Available online: https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines (accessed on 30 March 2023).









| pH | DX Complex (%) | DX Free Drug (%) | DX-IP Complex (%) | DX-IP Free Drug (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | 0 h | 24 h | |
| 2 | 95.33 | 95.76 | 96.44 | 93.15 | 1.64 | 1.63 | 1.61 | 1.63 |
| 5 | 102.11 | 100.39 | 100.17 | 98.70 | 1.52 | 2.09 | 1.55 | 2.07 |
| 8 | 95.87 | 76.75 | 91.01 | 75.05 | 1.61 | 8.12 | 1.63 | 8.43 |
| 11 | 91.09 | 68.86 | 89.45 | 69.17 | 4.86 | 25.35 | 4.40 | 24.63 |
| Sample | CS (mg/mL) | SBE-β-CD (mg/mL) | CS/SBE-β-CD Mass Ratio | Visual Analysis | PS (nm) | PDI | ZP (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.2 | 0.8 | 1:1.3 | Clear to opalescent dispersion | 523.0 ± 18.5 | 0.353 ± 0.073 | +41.1 ± 1.5 |
| B | 0.2 | 1.2 | 1:2 | Opalescent dispersion | 208.8 ± 4.4 | 0.020 ± 0.018 | +18.7 ± 1.4 |
| C | 0.2 | 2.0 | 1:3.3 | Aggregates | - | - | - |
| D | 0.2 | 3.0 | 1:5 | Aggregates | - | - | - |
| E | 0.5 | 1.8 | 1:1.2 | Opalescent dispersion | 438.9 ± 4.9 | 0.276 ± 0.020 | +44.3 ± 1.0 |
| F | 0.5 | 3.0 | 1:2 | Aggregates | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvalho Feitosa, R.; Souza Ribeiro Costa, J.; van Vliet Lima, M.; Sawa Akioka Ishikawa, E.; Cogo Müller, K.; Bonin Okasaki, F.; Sabadini, E.; Garnero, C.; Longhi, M.R.; Lavayen, V.; et al. Supramolecular Arrangement of Doxycycline with Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin: Impact on Nanostructuration with Chitosan, Drug Degradation and Antimicrobial Potency. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041285
Carvalho Feitosa R, Souza Ribeiro Costa J, van Vliet Lima M, Sawa Akioka Ishikawa E, Cogo Müller K, Bonin Okasaki F, Sabadini E, Garnero C, Longhi MR, Lavayen V, et al. Supramolecular Arrangement of Doxycycline with Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin: Impact on Nanostructuration with Chitosan, Drug Degradation and Antimicrobial Potency. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(4):1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041285
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvalho Feitosa, Renata, Juliana Souza Ribeiro Costa, Marcelo van Vliet Lima, Elina Sawa Akioka Ishikawa, Karina Cogo Müller, Fernando Bonin Okasaki, Edvaldo Sabadini, Claudia Garnero, Marcela Raquel Longhi, Vladimir Lavayen, and et al. 2023. "Supramolecular Arrangement of Doxycycline with Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin: Impact on Nanostructuration with Chitosan, Drug Degradation and Antimicrobial Potency" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 4: 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041285
APA StyleCarvalho Feitosa, R., Souza Ribeiro Costa, J., van Vliet Lima, M., Sawa Akioka Ishikawa, E., Cogo Müller, K., Bonin Okasaki, F., Sabadini, E., Garnero, C., Longhi, M. R., Lavayen, V., da Silva-Júnior, A. A., & Oliveira-Nascimento, L. (2023). Supramolecular Arrangement of Doxycycline with Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin: Impact on Nanostructuration with Chitosan, Drug Degradation and Antimicrobial Potency. Pharmaceutics, 15(4), 1285. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15041285