Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Loop Diuretics on Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Analyses
| Author | Year | Antibiotic | Diuretic | Population | N Subjects | Age (Years) | Weight (kg) | Baseline eGFR (mL/min) | Follow-Up Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brass et al. [13] | 1974 | Ampicillin 2 G IV bolus | Furosemide 40 mg PO | Healthy volunteers | 8 | 27 | 75 | 8 h | |
| Tice et al. [14] | 1975 | Cephalothin 500 mg bolus IV followed by continuous infusion 500 mg/h | Furosemide 70.5 mg IV bolus at hour 3 of continuous infusion | Healthy volunteers | 5 | 25 | 70.5 | 133 | 6 h |
| Norrby et al. [15] | 1976 | Cephaloridine 1 G IM or 0.5 G IM if renal impaired | Furosemide 80 mg PO | Hospital patients | 16 | 64.5 | NA | NA | NA |
| Tilstone et al. 1 [16] | 1977 | Cephaloridine 250 mg IV bolus | Furosemide 20 mg IV bolus | Healthy volunteers | 5 | 23 | 70 | 129 | NA |
| Morgant et al. [17] | 1984 | Cefazolin 680 mg/h IV continuous infusion | Furosemide 20.4 mg IV bolus 1 h after start of cefazolin infusion | Healthy volunteers | 6 | 24 | 68 | 113.4 | 2 h |
| Morgant et al. 1 [17] | 1984 | Cefazolin 680 mg/h IV continuous infusion | Piretanide 6.8 mg IV bolus 1 h after start of cefazolin infusion | Healthy volunteers | 6 | 24 | 68 | 113.4 | 2 h |
| Chrysos et al. [18] | 1995 | Ceftazidime 1 G IM | Furosemide 40 mg PO 1 h prior to ceftazidime dose. | Healthy volunteers | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 8 h |
| Chrysos et al. 1 [18] | 1995 | Ceftazidime 1 G IM | Furosemide 40 mg PO 3 h prior to ceftazidime dose. | Healthy volunteers | 6 | NA | NA | NA | 8 h |
| Schück et al. [19] | 1975 | Chloramphenicol 1 G PO | Furosemide 10 mg IV bolus | Healthy volunteers | 7 | 43.43 | NA | NA | 4 h |
| Schück et al. [20] | 1978 | Chloramphenicol 1 G PO | Ethacrynic acid 150 mg PO | Healthy volunteers | 8 | 38 | NA | NA | 4 h |
| Tilstone et al. 1 [16] | 1977 | Gentamicin 20 mg IV bolus | Furosemide 20 mg IV bolus | Healthy volunteers | 5 | 23 | 70 | 129 | |
| Whiting et al. [3] | 1981 | Gentamicin 74 mg IV bolus | Furosemide 18.5 mg IV bolus | Healthy volunteers | 6 | 27.5 | 74 | 139 | 7 h |
| Whiting et al. 1 [3] | 1981 | Gentamicin 74 mg IV bolus | Piretanide 7.4 mg IV bolus | Healthy volunteers | 6 | 27.5 | 74 | 139 | 7 h |
| Lawson et al. [21] | 1982 | Gentamicin 80 mg IV bolus | Furosemide 40 mg IV bolus | Hospital patients | 7 | 65 | 58 | 104 | 5 h |
| Hannedouche et al. [22] | 1986 | Gentamicin IV infusion over 30 min | Muzolimine 30 mg PO 90 min prior to gentamicin dose | Healthy volunteers | 6 | 26.5 | 77 | 101.23 | 24 h |
| Sudoh et al. [23] | 1993 | Lomefloxacin 100 mg PO | Furosemide 40 mg PO | Healthy volunteers | 8 | 30 | 67 | NA | 8 h |
| Author | Year | Study Design | Antibiotic | Diuretic | Population | N Subjects | Age (Years) | Weight (kg) | Study Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adam et al. [24] | 1978 | Prospective cohort | Cephradine single dose infused over 20 min | Furosemide | Patients undergoing brain surgery | 11 | NA | NA | There were 11 patients in the cephradine group, where 6 of 11 received TID 40 mg PO furosemide 2–6 days prior to surgery with last dose 12 h prior to surgery. |
| Trollfors et al. [25] | 1978 | Prospective cohort | Cefoxitin 1 G IV infused over 30 min | Furosemide 80 mg PO | Patients with chronic infection | 27 | 76.81 | 71.85 | There were four study groups with antibiotic (antibiotic alone N = 7, antibiotic and daily 80 mg PO furosemide N = 12, antibiotic and 80 mg PO furosemide on days 9–11 of therapy and septic shock patients with acute renal failure). No significant changes were observed in baseline eGFR or plasma clearance of cefoxitin throughout antibiotic therapy in the no diuretic and daily diuretic groups. |
| Trollfors et al. [26] | 1980 | Prospective cohort | Cefoxitin 1–2 G IV or Cefuroxime | Furosemide 40–160 mg PO | Patients with acute or chronic infection | 91 | NA | NA | A total of 50 patients received cefoxitin (26 with no furosemide and 24 with furosemide), while 41 patients received cefuroxime (28 without furosemide and 13 with furosemide). No significant differences were observed in half-life of cefuroxime or cefoxitin with or without furosemide. |
| Marlowe et al. [27] | 2003 | Retrospective cohort | Vancomycin 10–25 mg/kg per dose | Furosemide | Neonates, infants and children admitted to a cardiac hospital unit | 36 | 1.62 | 9.3 | While not explicitly stated, the study implied that all patients were treated with furosemide. A statistically significant negative correlation between Vd and furosemide dose was found. However, there was no significant trend between fluid balance and Vd, confounding the trend between Vd and furosemide. The effect of daily furosemide dose on vancomycin CL was not reported. |
| Hirai et al. [28] | 2021 | Retrospective cohort | Vancomycin 1000–2000 mg/day | Furosemide | Hospitalized patients | 208 | 74 | 53 | Furosemide alone had no statistically significant association with dose-normalized vancomycin troughs. However, a statistically significant increase in dose-normalized vancomycin trough was observed in patients receiving furosemide/thiazide diuretics combined compared to those without. |
| Author | Year | Antibiotic | Diuretic | Population | N Subjects | N Subjects on Loop Diuretic | Age (years) | Weight | eGFR | Results of Loop Diuretic Covariate Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuchs et al. [29] | 2014 | Gentamicin | Furosemide | Hospitalized infants | 1449 | 5 | 0.65 | 2.17 | NA | There was a non-statistically significant reduction in systemic gentamicin clearance by 34% (p = 0.012). There was no mention of testing on Vc. BW and age were accounted for in model. |
| Thibault et al. [30] | 2019 | Piperacillin–tazobactam | Furosemide | Hospitalized infants and children | 89 | 25 | 1.5 | 11.4 | NA | There was a statistically significant reduction (p < 0.05) in piperacillin CL (24%) and tazobactam CL (25%). Volume parameters were not evaluated. Weight was accounted for in model. |
| Lin et al. [31] | 2016 | Vancomycin | Furosemide | Post-craniotomy patients | 100 | 16 | 51.6 | 59.1 | 104.7 | Furosemide had no statistically significant effect on CL. No effect size was reported. |
| Medellín-Garibay et al. [32] | 2016 | Vancomycin | Furosemide | Hospitalized trauma patients | 118 | 28 | 74.3 | 72 | 90.5 | There was a statistically significant reduction (p < 0.05 on forward inclusion and p < 0.001 on backward elimination) in vancomycin CL (34%). Creatinine clearance was accounted for in model. |
| Medellín-Garibay et al. [33] | 2017 | Vancomycin | Furosemide | Patients on mechanical ventilation | 54 | 26 | 65 | 75 | 106.3 | Furosemide was not statistically significant; no effect size was reported. |
| Milovanovic et al. [34] | 2019 | Vancomycin | Furosemide | Patients with long bone fractures | 99 | 23 | 61.12 | 80.32 | 93.23 | Furosemide was not statistically significant; no effect size was reported |
| Xu et al. [35] | 2021 | Vancomycin | Furosemide | Infants with meningitis | 82 | 26 | 1.13 | 8.27 | 39.24 | Furosemide was not statistically significant; no effect size was reported |
| Buckwalter et al. [36] | 2005 | Dalbavancin | Furosemide | Hospitalized patients | 532 | 79 | 46 | 88 | 120.6 | Furosemide was not statistically significant; no effect size was reported. |
2.5. Meta-Analysis and Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results
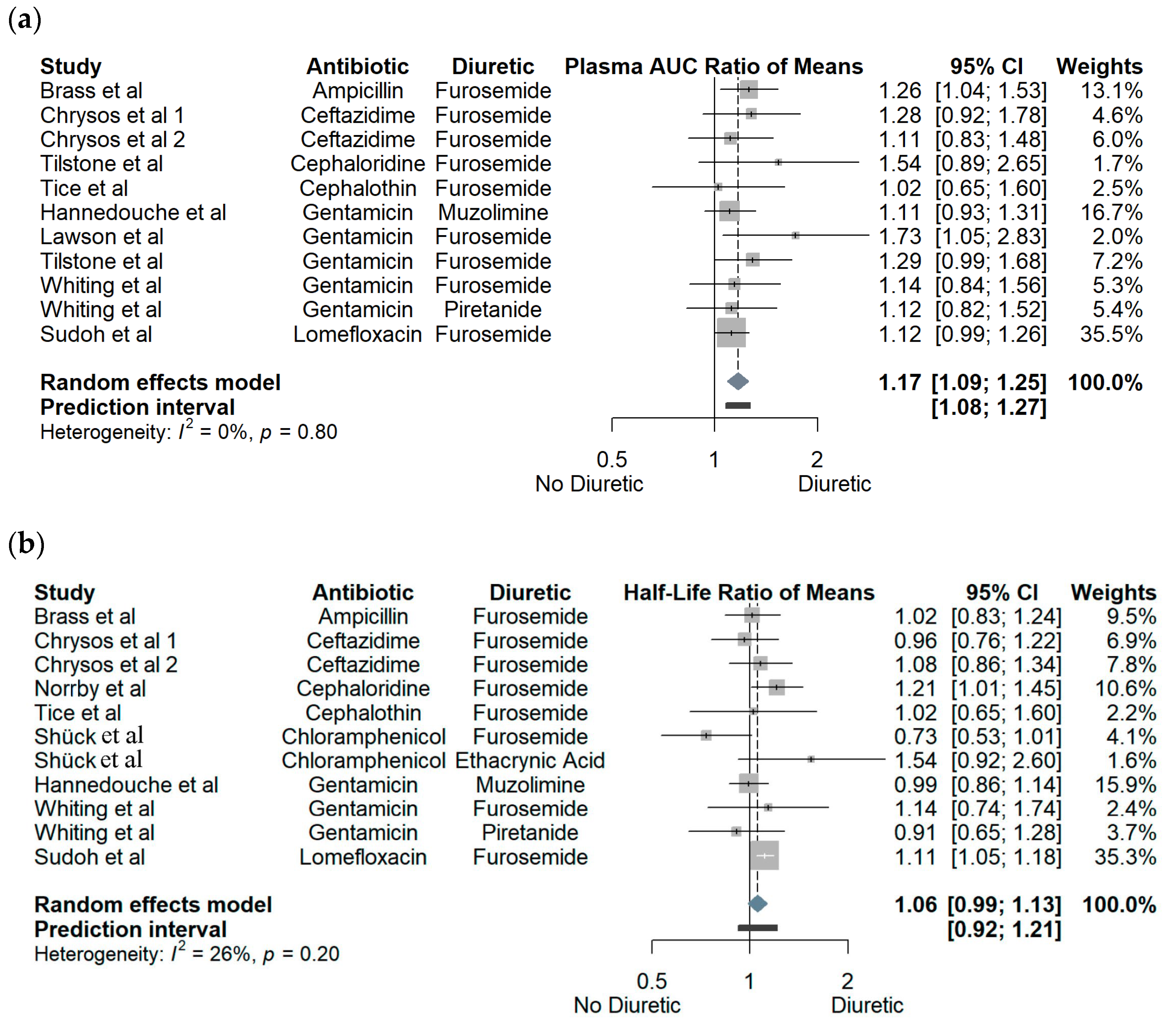
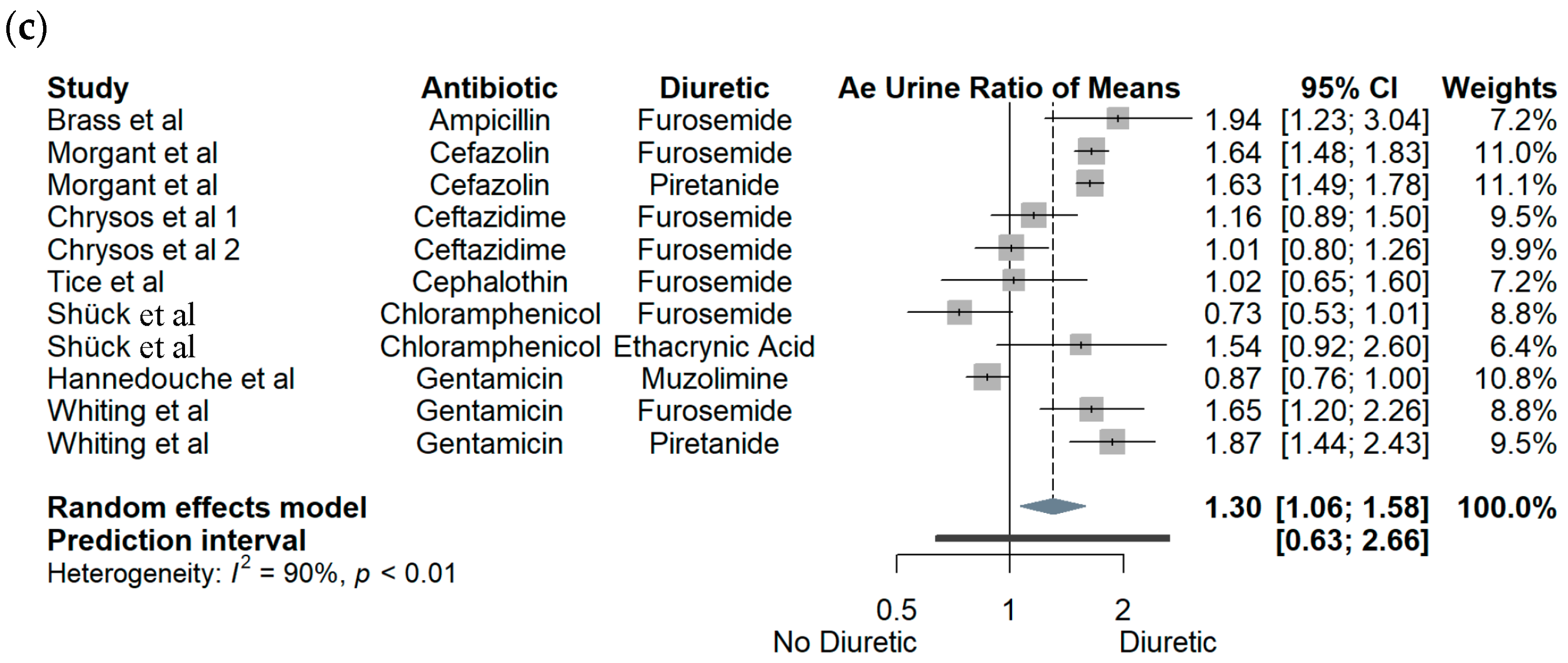
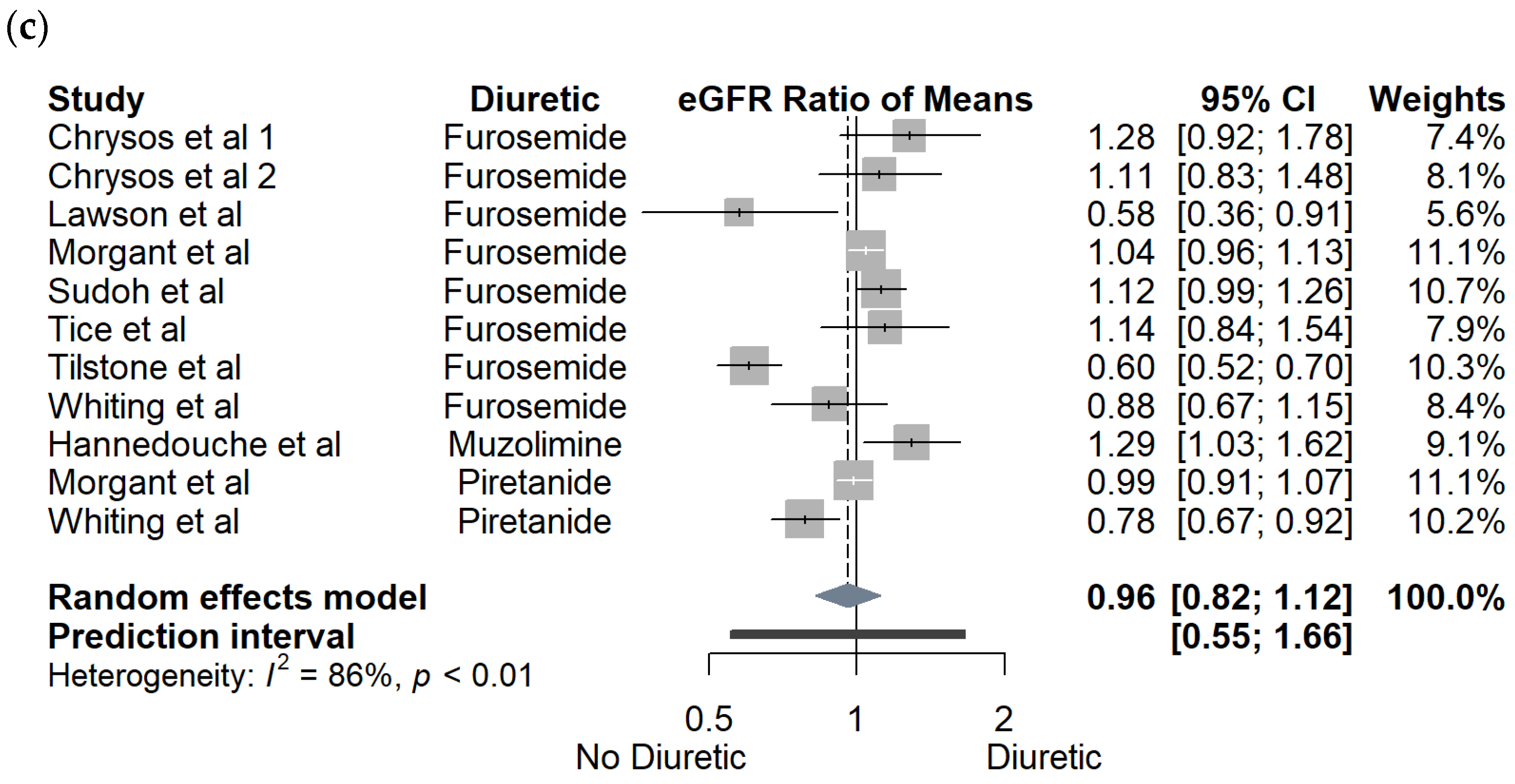
3.1. Crossover Studies
3.2. Observational Cohort Studies
3.3. Population Pharmacokinetic Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felker, G.M.; Ellison, D.H.; Mullens, W.; Cox, Z.L.; Testani, J.M. Diuretic Therapy for Patients With Heart Failure: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxel, C.; Raja, A.; Ollivierre-Lawrence, M.D. Loop Diuretics. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Whiting, P.H.; Barber, H.E.; Petersen, J. The effect of frusemide and piretanide on the renal clearance of gentamicin in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1981, 12, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallon, V.; Rieg, T.; Ahn, S.Y.; Wu, W.; Eraly, S.A.; Nigam, S.K. Overlapping in vitro and in vivo specificities of the organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3 for loop and thiazide diuretics. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2008, 294, F867–F873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burckhardt, G. Drug transport by Organic Anion Transporters (OATs). Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 136, 106–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wile, D. Diuretics: A review. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2012, 49 Pt 5, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Jiang, H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Sha, D.; Wang, J. Effect of continuous furosemide infusion on outcome of acute kidney injury. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, A. Diuretics in Acute Kidney Injury. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. Peer-Rev. Off. Publ. Indian Soc. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24 (Suppl. S3), S98–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarons, L.; Ogungbenro, K. Optimal design of pharmacokinetic studies. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 106, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, G.M. Clinical pharmacology of furosemide in neonates: A review. Pharmaceuticals 2013, 6, 1094–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Lewis, T.; Gauda, E.; Gobburu, J.; Ivaturi, V. Mechanistic Population Pharmacokinetics of Morphine in Neonates with Abstinence Syndrome After Oral Administration of Diluted Tincture of Opium. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Neely, M.; Lipman, J.; Sime, F.; Roberts, J.A.; Kiel, P.J.; Avedissian, S.N.; Rhodes, N.J.; Scheetz, M.H. Development of Population and Bayesian Models for Applied Use in Patients Receiving Cefepime. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brass, H.; Walther, O.E.; Amort, H. Effect of furosemide-induced increased diuresis on the pharmacodynamics of ampicillin. MMW Munch. Med. Wochenschr. 1974, 116, 2089–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Tice, A.D.; Barza, M.; Bergeron, M.G.; Brusch, J.L.; Weinstein, L. Effect of diuretics on urinary excretion of cephalothin in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1975, 7, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrby, R.; Stenqvist, K.; Elgefors, B. Interaction between cephaloridine and furosemide in man. Scand. J. Infect Dis. 1976, 8, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstone, W.J.; Semple, P.F.; Lawson, D.H.; Boyle, J.A. Effects of furosemide on glomerular filtration rate and clearance of practolol, digoxin, cephaloridine, and gentamicin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1977, 22, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgant, C.; Contrepois, A.; Chau, N.P.; Romaru, A.; Fourtillan, J.B.; Carbon, C. Effects of furosemide, piretanide, and water loading on urinary excretion of cefazolin in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1984, 25, 618–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysos, G.; Gargalianos, P.; Lelekis, M.; Stefanou, J.; Kosmidis, J. Pharmacokinetic interactions of ceftazidime and frusemide. J. Chemother. 1995, 7 (Suppl. S4), 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Schück, O.; Grafnetterová, J.; Prát, V.; Kotanová, E. The influence of furosemide on the renal excretion of chloramphenicol and its metabolites. Experientia 1975, 31, 1434–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schück, O.; Nádvorníková, H.; Grafnetterová, J. The influence of ethacrynic acid, hydrochlorothiazide and clopamide on the renal excretion of chloramphenicol and its metabolites. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Biopharmacy 1978, 16, 217–219. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, D.H.; Tilstone, W.J.; Gray, J.M.; Srivastava, P.K. Effect of furosemide on the pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in patients. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1982, 22, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannedouche, T.; Morin, J.P.; Leroy, A. Influence of muzolimine administration on pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in healthy subjects. Therapie 1986, 41, 421–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sudoh, T.; Fujimura, A.; Shiga, T.; Sasaki, M.; Harada, K.; Tateishi, T.; Ohashi, K.; Ebihara, A. Renal clearance of lomefloxacin is decreased by furosemide. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1994, 46, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, D.; Jacoby, W.; Raff, W.K. Interference of the tissue concentration of antibiotics with a salidiuretic. Behaviour of cephradine and cephalothin in brain tissue after additional administration of furosemide (author’s transl). Klin. Wochenschr. 1978, 56, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trollfors, B.; Norrby, R.; Kristianson, K.; Nilsson, N.J. Effects on renal function of treatment with cefoxitin alone or in combination with furosemide. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 1978, 13, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trollfors, B.; Norrby, R. Effect of frusemide on the elimination of cefuroxime and cefoxitin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1980, 6, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlowe, K.F.; Chicella, M.F.; Claridge, T.E.; Pittman, S.W. An assessment of vancomycin pharmacokinetic variability in pediatric cardiology patients. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 8, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, T.; Hanada, K.; Iwamoto, T.; Itoh, T. Involvement of the effect of renal hypoperfusion medications on vancomycin trough concentration: A secondary analysis using a retrospective observational data. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 129, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Guidi, M.; Giannoni, E.; Werner, D.; Buclin, T.; Widmer, N.; Csajka, C. Population pharmacokinetic study of gentamicin in a large cohort of premature and term neonates. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 78, 1090–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, C.; Lavigne, J.; Litalien, C.; Kassir, N.; Theoret, Y.; Autmizguine, J. Population Pharmacokinetics and Safety of Piperacillin-Tazobactam Extended Infusions in Infants and Children. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e01260-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.W.; Wu, W.; Jiao, Z.; Lin, R.F.; Jiang, C.Z.; Huang, P.F.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, C.L. Population pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in adult Chinese patients with post-craniotomy meningitis and its application in individualised dosage regimens. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellin-Garibay, S.E.; Ortiz-Martin, B.; Rueda-Naharro, A.; Garcia, B.; Romano-Moreno, S.; Barcia, E. Pharmacokinetics of vancomycin and dosing recommendations for trauma patients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medellín-Garibay, S.E.; Romano-Moreno, S.; Tejedor-Prado, P.; Rubio-Álvaro, N.; Rueda-Naharro, A.; Blasco-Navalpotro, M.A.; García, B.; Barcia, E. Influence of mechanical ventilation on the pharmacokinetics of vancomycin administered by continuous infusion in critically ill patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01249-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, J.; Zaric, R.Z.; Rosic, N.; Zecevic, D.R.; Milovanovic, D.; Folic, M.; Jankovic, S.M. Population pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in adult patients with long bones’ fractures. Serb. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2021, 22, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Niu, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Jiang, L.; Shi, D. Establishment and application of population pharmacokinetics model of vancomycin in infants with meningitis. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2022, 63, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckwalter, M.; Dowell, J.A. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of dalbavancin, a novel lipoglycopeptide. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marier, J.F.; Teuscher, N.; Mouksassi, M.S. Evaluation of covariate effects using forest plots and introduction to the coveffectsplot R package. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharm. 2022, 11, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Statistical Approaches to Establishing Bioequivalence; Food and Drug Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2001.
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduzzi, S.; Rucker, G.; Schwarzer, G. How to perform a meta-analysis with R: A practical tutorial. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2019, 22, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jadhav, P.R.; Lala, M.; Gobburu, J.V. Clarification on precision criteria to derive sample size when designing pediatric pharmacokinetic studies. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 1601–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonathan Sterne, J.H.; Reeves, B.; Savović, J.; Turner, L. RoB 2 for Crossover Trials. Available online: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tool/rob-2-for-crossover-trials (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Jonathan Sterne, J.H.; Reeves, B.; Savović, J.; Turner, L. Robvis Visualization Tool. Available online: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/robvis-visualization-tool (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Trollfors, B.; Norrby, R.; Kristianson, K. Effects on renal function of treatment with cefoxitin sodium alone or in combination with furosemide. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1978, 4, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selig, D.J.; Akers, K.S.; Chung, K.K.; Kress, A.T.; Livezey, J.R.; Por, E.D.; Pruskowski, K.A.; DeLuca, J.P. Comparison of Piperacillin and Tazobactam Pharmacokinetics in Critically Ill Patients with Trauma or with Burn. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.S.; Yuan, M.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Pinheiro, J. Full covariate modelling approach in population pharmacokinetics: Understanding the underlying hypothesis tests and implications of multiplicity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 1525–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanis, E.; Parks, J.; Austin, D.L. Structural Analysis and Protein Binding of Cephalosporins. ACS Pharm. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik, M.; Goral, A.M.; Jasinski, M.; Dominiak, P.M.; Trylska, J. Electrostatic interactions in aminoglycoside-RNA complexes. Biophys. J. 2015, 108, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 3467. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Gentamicin (accessed on 26 January 2023).
- Akhavan, B.J.; Khanna, N.R.; Vijhani, P. Amoxicillin. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.; Barton, G.; Fischer, A. Pharmacokinetic considerations and dosing strategies of antibiotics in the critically ill patient. J. Intensive Care Soc. 2015, 16, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves-Pereira, J.; Povoa, P. Antibiotics in critically ill patients: A systematic review of the pharmacokinetics of beta-lactams. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponto, L.L.; Schoenwald, R.D. Furosemide (frusemide). A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic review (Part I). Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1990, 18, 381–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerling, D.A.; Clarke, S.C.; DeLuca, J.P.; Evans, M.O.; Kress, A.T.; Nadeau, R.J.; Selig, D.J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Loop Diuretics on Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051411
Kerling DA, Clarke SC, DeLuca JP, Evans MO, Kress AT, Nadeau RJ, Selig DJ. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Loop Diuretics on Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(5):1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051411
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerling, David A., Sarah C. Clarke, Jesse P. DeLuca, Martin O. Evans, Adrian T. Kress, Robert J. Nadeau, and Daniel J. Selig. 2023. "Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Loop Diuretics on Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 5: 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051411
APA StyleKerling, D. A., Clarke, S. C., DeLuca, J. P., Evans, M. O., Kress, A. T., Nadeau, R. J., & Selig, D. J. (2023). Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Loop Diuretics on Antibiotic Pharmacokinetics. Pharmaceutics, 15(5), 1411. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051411







