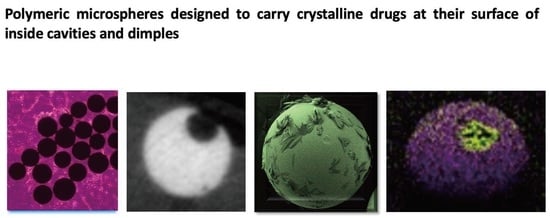
Polymeric Microspheres Designed to Carry Crystalline Drugs at Their Surface or Inside Cavities and Dimples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microsphere Synthesis
2.3. Microparticle Characterization
2.4. Loading of Particles with Voriconazole
2.5. Antifungal Experiment
2.6. In Vitro Drug Release
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microsphere Synthesis and Observations Made by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.2. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic (XPS) Analysis
3.3. Micro X-ray Computed Tomography (Micro-CT)
3.4. Voriconazole-Loaded Particles
3.5. Antifungal Effect of Spherical Voriconazole-Loaded Particles In Vitro
3.6. Voriconazole-Loaded Spherical Particles with a Cavity, Quantification
3.7. Release of Voriconazole, Measured In Vitro
3.8. Drug Release Mechanism
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Battiston, K.; Parrag, I.; Statham, M.; Louka, D.; Fischer, H.; Mackey, G.; Daley, A.; Gu, F.; Baldwin, E.; Yang, B.; et al. Polymer-free corticosteroid dimer implants for controlled and sustained drug delivery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, S.; Doloff, J.C.; Mueller, P.; Sadraei, A.; Han, H.J.; Olafson, K.; Vyas, K.; Kam, H.H.; Hollister-Lock, J.; Kowalski, P.S.; et al. Long-term implant fibrosis prevention in rodents and non-human primates using crystallized drug formulations. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farah, S.; Domb, A.J. Crystalline paclitaxel coated DES with bioactive protective layer development. J. Control. Release 2018, 271, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Obaidi, H.; Majumber, M.; Bari, F. Amorphous and Crystalline Particulates: Challenges and Perspectives in Drug Delivery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadgraft, J.; Lane, M.E. Drug crystallization—Implications for topical and transdermal delivery. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshosaz, J.; Ghassami, E.; Ahmadipour, S. Crystal Engineering for Enhanced Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2473–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Khan, W.; Domb, A.J. Crystalline coating of rapamycin onto a stent: Process development and characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 445, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursharan, S.; Preuss, C.V. Triamcinolone; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gaballa, S.A.; Kompella, U.B.; Elgarhy, O.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Pierscionek, B.; Alany, R.G.; Abdelkader, H. Corticosteroids in ophthalmology: Drug delivery innovations, pharmacology, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 866–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S. Protective Layer Development for Enhancing Stability and Drug-Delivery Capabilities of DES Surface-Crystallized Coatings. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 9010–9022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.R.; Muya, L.; Cansara, V.; Ciulla, T.A. Suprachoroidal Delivery of Small Molecules, Nanoparticles, Gene and Cell Therapies for Ocular Diseases. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhail, A.S.; Negussie, A.H.; Mauda-Havakuk, M.; Owen, J.W.; Pritchard, W.F.; Lewis, A.L.; Wood, B.J. Drug-eluting embolic microspheres: State-of-the-art and emerging clinical applications. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 383–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.P.; Zhang, J.L.; Zou, Y.; Wu, L. Recent Advances on Polymeric Beads or Hydrogels as Embolization Agents for Improved Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE). Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.W.; Hong, H.P.; Kim, M.S.; Shin, B.S.; Kwon, H.-J.; Kim, B.I.; Sohn, W. Comparison of Clinical Efficacy and Safety between 70–150 µm and 100–300 µm Doxorubicin Drug-Eluting Bead Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Life 2022, 12, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ye, C.; Wang, S.; An, X. Development of PVA-based microsphere as a potential embolization agent. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 135, 112677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Liang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wen, J.; Chen, K.; Su, X.; Teng, Z.; Lu, G.; Xu, J. Magnetic mesoporous embolic microspheres in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for liver cancer. Acta Biomater. 2021, 130, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Q.; Fu, C.; Tan, L.; Ren, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; Ren, J.; Meng, X. Porous PLGA microspheres with recruited ions and doxorubicin for triple-combination therapy of larger hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 9025–9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassef, M.; Pelage, J.P.; Velzenberger, E.; Namur, J.; Schwartz-Cornil, I.; Taylor, R.R.; Lewis, A.L.; Laurent, A. Anti-inflammatory effect of ibuprofen-loaded embolization beads in sheep uterus. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 86B, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.R.; Tang, Y.; Gonzalez, M.V.; Stratford, P.W.; Lewis, A.L. Irinotecan drug eluting beads for use in chemoembolization: In vitro and in vivo evaluation of drug release properties. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, K.; Tang, Y.; Britton, H.; Domenge, O.; Blino, D.; Bushby, A.J.; Shuturminska, K.; den Hartog, M.; Radaelli, A.; Negussie, A.H.; et al. Characterization of a novel intrinsically radiopaque Drug-eluting Bead for image-guided therapy: DC Bead LUMI™. J. Control. Release 2017, 250, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnutzmann, D.M.; Mechel, J.; Schmitz, A.; Kohler, K.; Krone, D.; Belleman, N.; Gockner, T.L.; Mokry, T.; Kortes, N.; Sommer, C.-M.; et al. Evaluation of the Plasmatic and Parenchymal Elution Kinetics of Two Different Irinotecan-Loaded Drug-Eluting Embolics in a Pig Model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015, 26, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagari, K.; Pomoni, M.; Moschouris, H.; Kelekis, A.; Charokopakis, A.; Bouma, E.; Spyridopoulos, T.; Chatziioannou, A.; Sotirchos, V.; Karampelas, T.; et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with HepaSphere 30–60 μm. Safety and efficacy study. J. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 37, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Plotkin, S.; Yu, R.; Sutter, A.; Wu, Y.; Cruise, G.M. An In Vitro Evaluation of Four Types of Drug-Eluting Microspheres Loaded with Doxorubicin. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, H.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Xiang, H.; Zheng, C.; Ma, C.; Luo, C.; Qiu, H.; et al. Comparison of treatment efficacy and safety between drug-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization with CalliSpheres® microspheres and conventional transarterial chemoembolization as first-line treatment in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 7456–7470. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, M.V.; Tang, Y.; Phillips, G.I.; Lloyd, A.W.; Hall, B.; Stratford, P.W.; Lewis, A.L. Doxorubicin eluting beads—2: Methods for evaluating drug elution and in-vitro: In-vivo correlation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldenhoff, Y.B.J.; Kruft, M.A.; Pijpers, A.P.; van der Veen, F.H.; Bulstra, S.K.; Kuijer, R.; Koole, L.H. Stability of radiopaque iodine-containing biomaterials. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hooy-Corstjens, C.S.J.; Saralidze, K.; Knetsch, M.L.W.; Emans, P.J.; de Haan, M.W.; Magusin, P.C.; Mezari, B.; Koole, L.H. New Intrinsically Radiopaque Hydrophilic Microspheres for Embolization: Synthesis and Characterization. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saralidze, K.; Knetsch, M.L.W.; van Berkel, R.G.; Mostert, C.; Koole, L.H. Radiopaque microspheres for improved transarterial chemical embolization (TACE). J. Control. Release 2011, 152 (Suppl. S1), e74–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karina, A.; Benzina, A.; Tazhibayeva, S.; Fan, H.; Koole, L.H. Polymer microparticles with a cavity designed for trans arterial chemoembolization with crystalline drug formulations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2021, 109B, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, A. Microspheres and Nonspherical Particles for Embolization. Tech. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 4, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelage, J.P.; Laurent, A.; Wassef, M.; Bonneau, M.; Germain, D.; Rymer, R.; Flaud, P.; Martal, J.; Merland, J.-J. (Uterine Artery Embolization in Sheep: Comparison of Acute Effects with Polyvinyl Alcohol Particles and Calibrated Microspheres. Radiology 2002, 224, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkow, E.L.; Lockhart, S.R.; Ostrosky-Zeichner, L. Antifungal Susceptibility Testing: Current Approaches. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00069-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, E.R. Aseptic Laboratory Techniques: Plating Methods. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 63, e3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinubabu, G.; Raju, C.A.I.; Sarath, N.; Kiran Kumar, P.; Seshagiri Rao, J.V.L.N. Development and validation of a HPLC method for the determination of voriconazole in pharmaceutical formulation using an experimental design. Talanta 2007, 71, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinsky, S.; Park, J.I.; Gourevich, I.; Chan, C.; Deetz, M.; Kumacheva, E. Microfluidic Synthesis of Macroporous Copolymer Particles. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 3555–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.W. Handbook of Polymer Reaction Engineering; Meyer, T., Keurentjes, J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH GmbH: Hamburg, Germany, 2005; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; van Ravensteijn, B.G.P.; Kegel, W.K. Dimple Colloids with Tunable Cavity Size and Surface Functionalities. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 4287–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, S.; Li, Q.; Shan, B.; Tong, W.; Gao, C. Fabrication of Red-Blood-Cell-Like Polyelectrolyte Microcapsules and Their Deformation and Recovery Behavior Through a Microcapillary. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5814–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, N.; Zahr, A.S.; Bhaskar, S.; Lahann, J.; Mitragotri, S. Red blood cell-mimicking synthetic biomaterial particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21495–21499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Ren, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liao, S. Large-Scale Synthesis of Monodisperse Red Blood Cell (RBC)-Like Polymer Particles. ACS Macro Lett. 2016, 5, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meester, V.; Kraft, D.J. Spherical, Dimpled, and Crumpled Hybrid Colloids with Tunable Surface Morphology. Langmuir 2016, 32, 10668–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangin, D.; Garcia, E.; Veesler, S. Modeling of the dissolution of a pharmaceutical compound. J. Cryst. Growth 2006, 286, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G.; Igarashi, K.; Ooshima, H. Dissolution kinetics of crystals in suspension and its application to l-aspartic acid crystals. Chem. Eng. J. 2002, 88, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, M.; Zheng, L.; Koole, L.H. Polymeric Microspheres Designed to Carry Crystalline Drugs at Their Surface or Inside Cavities and Dimples. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082146
Shen M, Zheng L, Koole LH. Polymeric Microspheres Designed to Carry Crystalline Drugs at Their Surface or Inside Cavities and Dimples. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(8):2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082146
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Meitong, Ling Zheng, and Leo H. Koole. 2023. "Polymeric Microspheres Designed to Carry Crystalline Drugs at Their Surface or Inside Cavities and Dimples" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 8: 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082146
APA StyleShen, M., Zheng, L., & Koole, L. H. (2023). Polymeric Microspheres Designed to Carry Crystalline Drugs at Their Surface or Inside Cavities and Dimples. Pharmaceutics, 15(8), 2146. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15082146