Antibiofilm, Anti-Inflammatory, and Regenerative Properties of a New Stable Ozone-Gel Formulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ozone Gel
2.2. Microorganisms
2.3. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) Assay
2.4. Ozone-Gel Effect on Biofilm Formation
2.5. Effect of Ozone Gel on Biofilm Dispersion
100)/OD control-gel-treated preformed biofilm
2.6. Peripheral Human Mononuclear Cells (PBMC) Isolation
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.8. Cytokine Determination
2.9. Scratch Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ozone-Gel Stability
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity
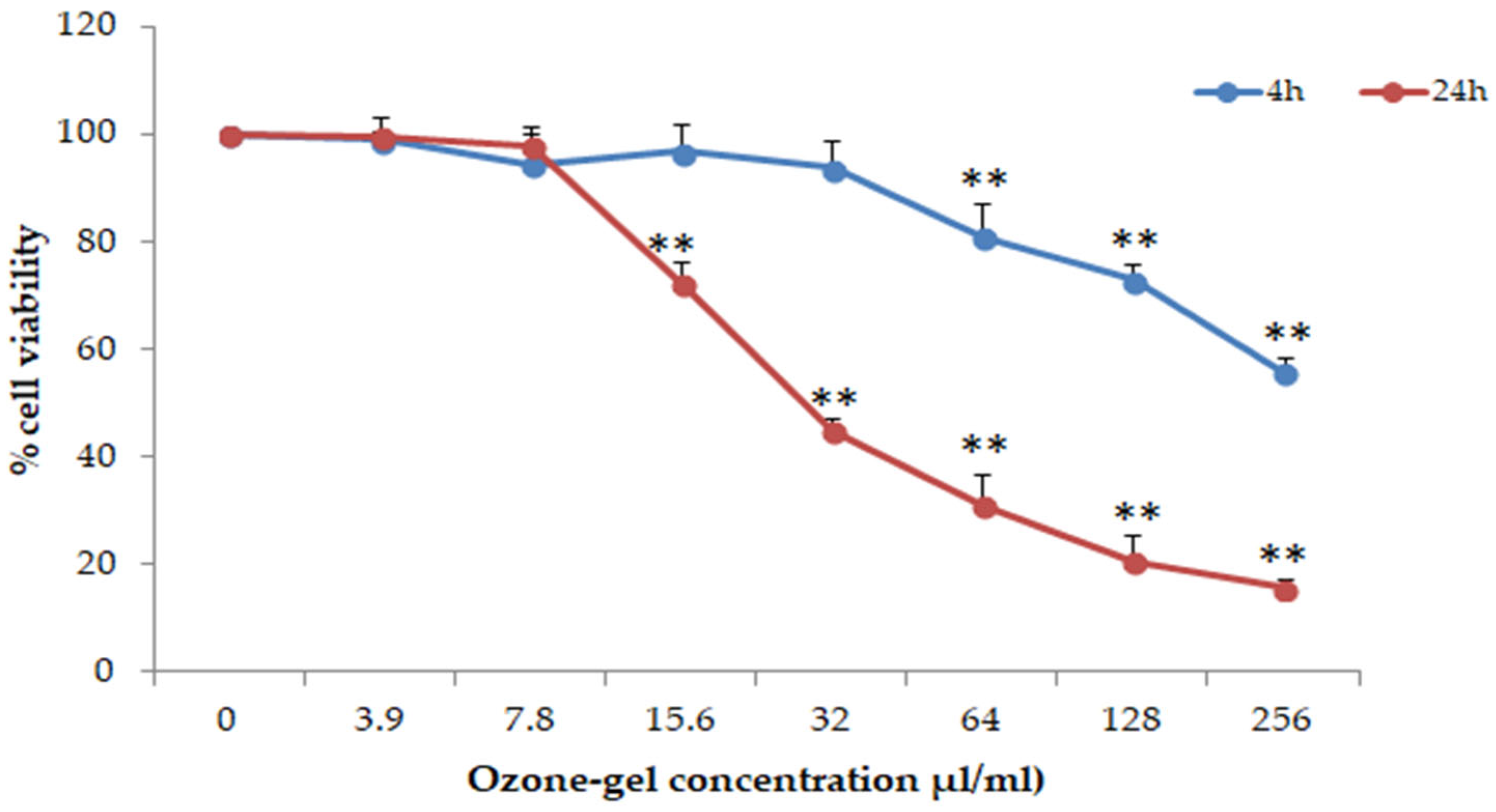
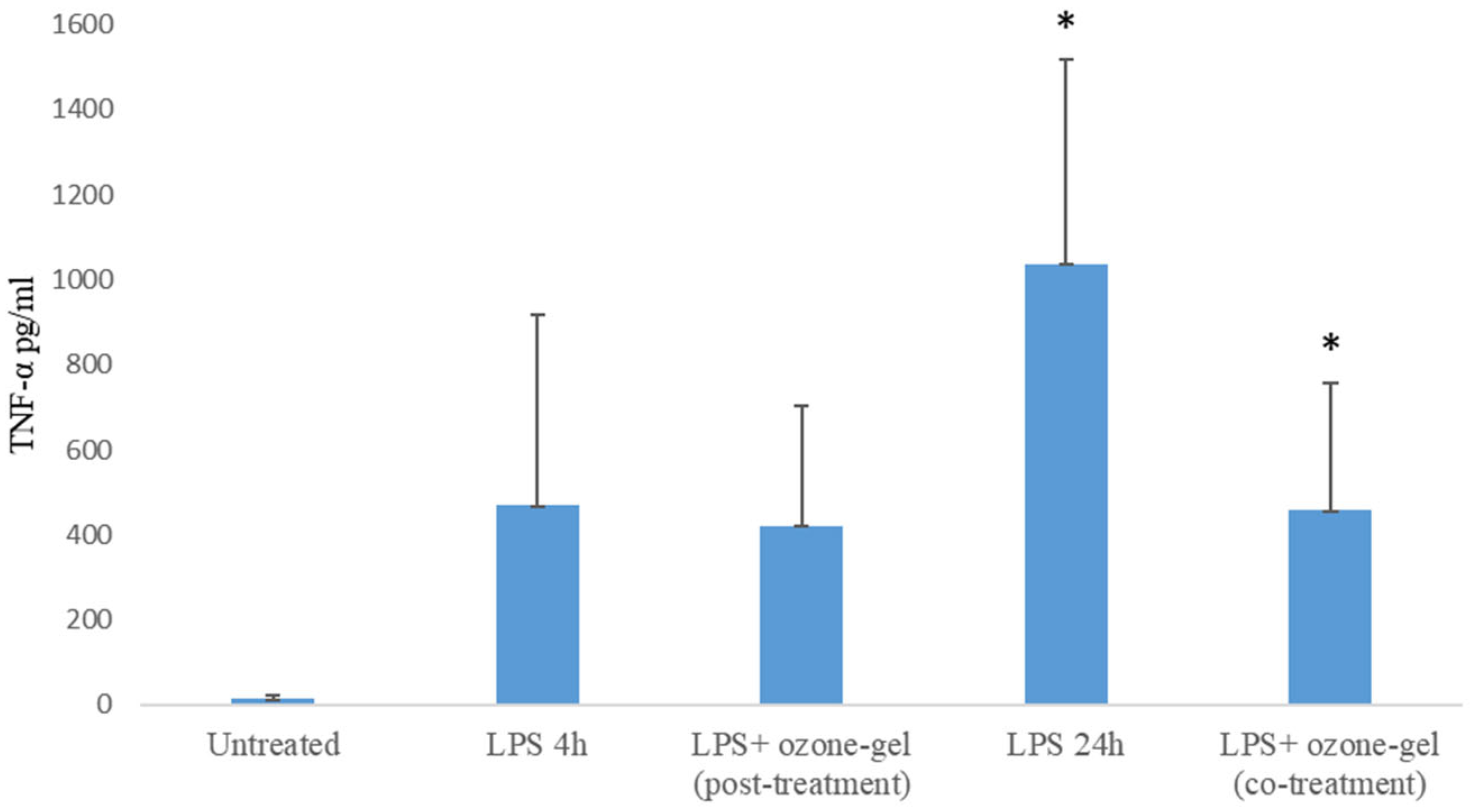
3.3. Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Activity
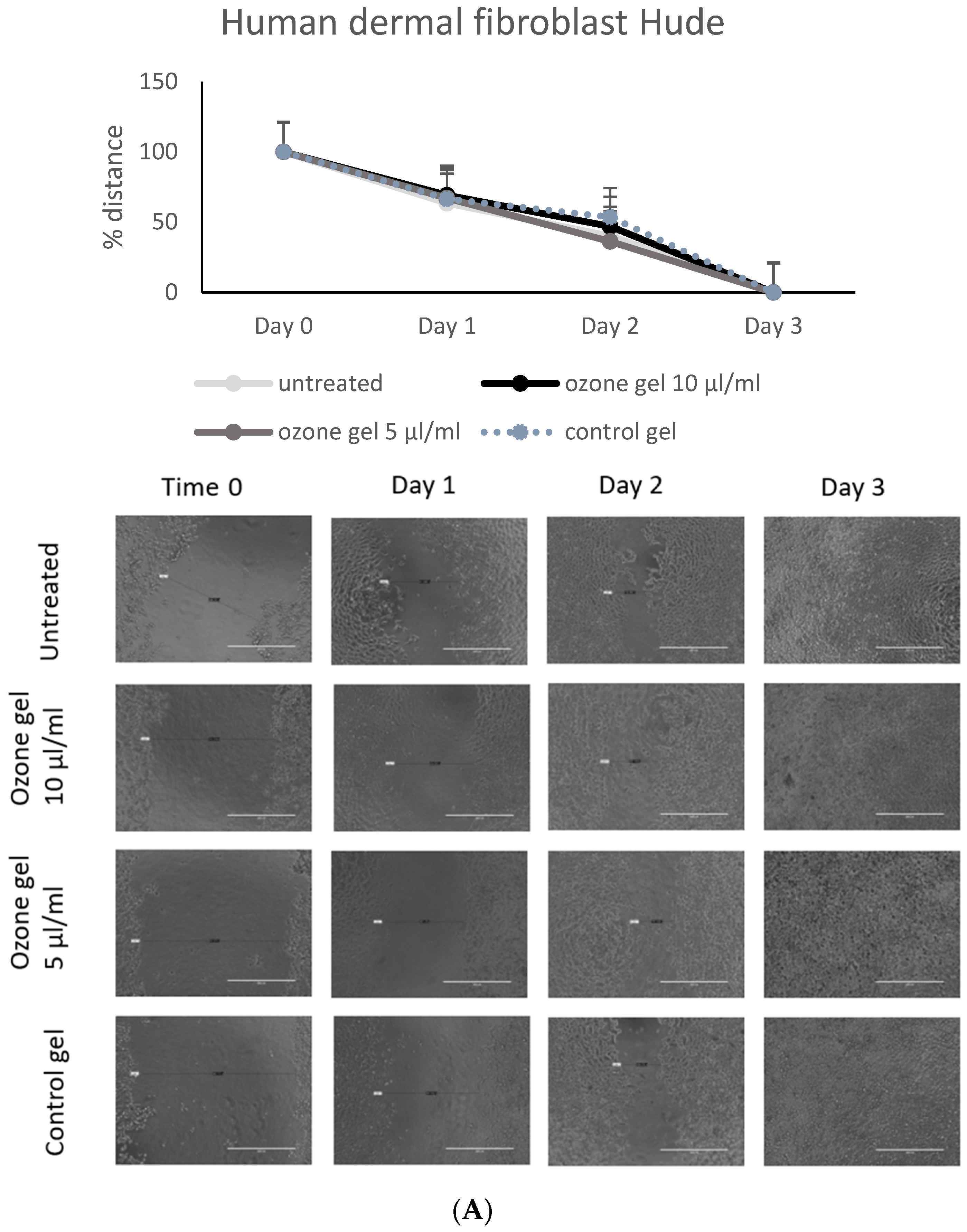
3.4. Regenerative Activity of Ozone Gel
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Raziyeva, K.; Kim, Y.; Zharkinbekov, Z.; Kassymbek, K.; Jimi, S.; Saparov, A. Immunology of Acute and Chronic Wound Healing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayate, A.S.; Nagoba, B.S.; Mumbre, S.S.; Mavani, H.B.; Gavkare, A.M.; Deshpande, A.S. Current Scenario of Traditional Medicines in Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Review. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uberoi, A.; McCready-Vangi, A.; Grice, E.A. The Wound Microbiota: Microbial Mechanisms of Impaired Wound Healing and Infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzopardi, E.A.; Azzopardi, E.; Camilleri, L.; Villapalos, J.; Boyce, D.E.; Dziewulski, P.; Dickson, W.A.; Whitaker, I.S. Gram Negative Wound Infection in Hospitalised Adult Burn Patients-Systematic Review and Metanalysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Pulakat, L.; Anderson, D.W. Challenges and New Therapeutic Approaches in the Management of Chronic Wounds. Curr. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ng, P.H.; Pinheiro Marques, A.R.; Cheng, T.H.; Man, K.Y.; Lim, K.Z.; MacKinnon, B.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jahangiri, L.; et al. Effect of Ozone Nanobubbles on the Microbial Ecology of Pond Water and Safety for Jade Perch (Scortum barcoo). Aquaculture 2023, 576, 739866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, Q.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Yang, X.H. Effects of Ozone on Membrane Permeability and Ultrastructure in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, K.; Cabral, F.O.; Lechuga, G.C.; Carvalho, J.P.R.S.; Villas-Bôas, M.H.S.; Midlej, V.; De-Simone, S.G. Detrimental Effect of Ozone on Pathogenic Bacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitter, K.; Vlassakidis, A.; Niepel, M.; Hoedke, D.; Schulze, J.; Neumann, K.; Moter, A.; Noetzel, J. Effects of Diode Laser, Gaseous Ozone, and Medical Dressings on Enterococcus faecalis Biofilms in the Root Canal Ex Vivo. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, E.; Holland, O.J.; Vanderlelie, J.J. Ozone Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Wounds: A Systematic Review. Int. Wound J. 2018, 15, 633–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocci, V.; Borrelli, E.; Travagli, V.; Zanardi, I. The Ozone Paradox: Ozone Is a Strong Oxidant as Well as a Medical Drug. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29, 646–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koundle, P.; Nirmalkar, N.; Momotko, M.; Boczkaj, G. Ozone Nanobubble Technology as a Novel AOPs for Pollutants Degradation under High Salinity Conditions. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zeng, L.; Gao, L.; Zeng, J.; Lu, J. Ozone Therapy for Skin Diseases: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms. Int. Wound J. 2022, 20, 2376–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Li, C.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Thermoresponsive Ozone-Enriched Spray Gel for Postsurgical Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 3518–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khachatryan, G.; Khachatryan, L.; Krystyjan, M.; Lenart-Boroń, A.; Krzan, M.; Kulik, K.; Białecka, A.; Grabacka, M.; Nowak, N.; Khachatryan, K. Preparation of Nano/Microcapsules of Ozonated Olive Oil in Hyaluronan Matrix and Analysis of Physicochemical and Microbiological (Biological) Properties of the Obtained Biocomposite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, L.J.; Lahiri, B.; Penumatsa, N.V.; Soans, C.R.; Sekar, A.; Nasyam, F.A. Effectiveness of Topical Ozone Gel Application in the Management of Postextraction Wound Healing: An In Vivo Study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2024, 24, 887–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Gallo, S.; Garofoli, A.; Poggio, C.; Arciola, C.R.; Scribante, A. Ozone Gel in Chronic Periodontal Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial on the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ozone Application. Biology 2021, 10, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakonechna, A.; Dore, P.; Dixon, T.; Khan, S.; Deacock, S.; Holding, S.; Abuzakouk, M. Immediate Hypersensitivity to Chlorhexidine Is Increasingly Recognised in the United Kingdom. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2014, 42, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R. Ozone Therapy in Dentistry: A Strategic Review. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2011, 2, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, B.R.; Romary, D.J.; Landsberger, S.A.; Bradner, K.N.; Ramirez, M.; Lubitz, R.M. Risks of Ozonated Oil and Ozonated Water on Human Skin: A Systematic Review. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcaro, G.; Amosso, E.; Baldoni, M. Treatment of Osteoradionecrosis of the Jaw with Ozone in the Form of Oil-Based Gel: 1-Year Follow-Up. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2019, 20, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, R.; Kommedal, R.; Kalvenes, S. Quantification of Biofilm Accumulation by an Optical Approach. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Białoszewski, D. The Impact of Liquid Ozone on the Quality of Surgical Cement Fillings in the Marrow Cavity of Long Bones. Ortop. Traumatol. Rehabil. 2004, 6, 789–792. [Google Scholar]
- Uzun, G.; Mutluoğlu, M.; Karagöz, H.; Memiş, A.; Karabacak, E.; Ay, H. Pitfalls of Intralesional Ozone Injection in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Case Study. J. Am. Coll. Clin. Wound Spec. 2014, 4, 81–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielko, K.A.; Jabłoński, S.J.; Milczewska, J.; Sands, D.; Łukaszewicz, M.; Młynarz, P. Metabolomic Studies of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00020-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.K.L.; Tay, W.H.; Janela, B.; Yong, A.M.H.; Liew, T.H.; Madden, L.; Keogh, D.; Barkham, T.M.S.; Ginhoux, F.; Becker, D.L.; et al. Enterococcus Faecalis Modulates Immune Activation and Slows Healing During Wound Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, S.; Negri, M.; Henriques, M.; Oliveira, R.; Williams, D.W.; Azeredo, J. Candida Glabrata, Candida Parapsilosis and Candida Tropicalis: Biology, Epidemiology, Pathogenicity and Antifungal Resistance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 288–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuno, E.; Jarros, I.C.; Bonfim-Mendonça, P.S.; Vicente de Rezende, G.; Negri, M.; Svidzinski, T.E. Candida Parapsilosis Isolates from Burn Wounds Can Penetrate an Acellular Dermal Matrix. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.M.; Schellhorn, H.E. Regulators of Oxidative Stress Response Genes in Escherichia coli and Their Functional Conservation in Bacteria. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 525, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J. Reactive Species Formed on Proteins Exposed to Singlet Oxygen. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2004, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtman, E.R. Protein Oxidation and Aging. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 1250–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, T. Translational Fidelity, Protein Oxidation, and Senescence: Lessons from Bacteria. Ageing Res. Rev. 2002, 1, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialoszewski, D.; Bocian, E.; Bukowska, B.; Czajkowska, M.; Sokol-Leszczynska, B.; Tyski, S. Antimicrobial Activity of Ozonated Water. Med. Sci. Monit. 2010, 16, MT71–MT75. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Dou, J.; Gao, L.; Xiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Ding, S.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Q.; Luo, Z.; Tan, W.; et al. Topical Ozone Therapy Restores Microbiome Diversity in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 80, 106191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, A.; Elkashif, A.; Selvamani, V.; Stucky, R.A.; Seleem, M.N.; Ziaie, B.; Rahimi, R. Wearable and Flexible Ozone Generating System for Treatment of Infected Dermal Wounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prebeg, D.; Katunarić, M.; Budimir, A.; Pavelić, B.; Šegović, S.; Anić, I. Antimicrobial Effect of Ozone Made by KP Syringe of High-Frequency Ozone Generator. Acta Stomatol. Croat. 2016, 50, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghal Asghari, F.; Dehghani, M.H.; Dehghanzadeh, R.; Farajzadeh, D.; Shanehbandi, D.; Mahvi, A.H.; Yaghmaeian, K.; Rajabi, A. Performance Evaluation of Ozonation for Removal of Antibiotic-Resistant Escherichia Coli and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Genes from Hospital Wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 24519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breidablik, H.J.; Lysebo, D.E.; Johannessen, L.; Skare, Å.; Andersen, J.R.; Kleiven, O. Effects of Hand Disinfection with Alcohol Hand Rub, Ozonized Water, or Soap and Water: Time for Reconsideration? J. Hosp. Infect. 2020, 105, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, W.; Yam, W.C.; Huang, H.; Leung, D.Y.C. The Efficacy of Vacuum-Ultraviolet Light Disinfection of Some Common Environmental Pathogens. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, E.P.; Stephens, M.D.; Dufresne, S.; Silver, B.; Gerbarg, P.; Gerbarg, Z.; Dela Cruz, C.S.; Sharma, L. Disinfection of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa from N95 Respirators with Ozone: A Pilot Study. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2021, 8, e000781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, B.; Portugal, S.; Mastanaiah, N.; Johnson, J.A.; Roy, S. Inactivation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in an Open Water System with Ozone Generated by a Compact, Atmospheric DBD Plasma Reactor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, L.D.R.; Ferreira, R.; Costa, A.R.; Oliveira, H.; Azeredo, J. Author Correction: Efficacy and Safety Assessment of Two Enterococci Phages in an in Vitro Biofilm Wound Model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncay, Ö.; Er, Ö.; Demirbuga, S.; Zorba, Y.O.; Topçuoğlu, H.S. Effect of Gaseous Ozone and Light-Activated Disinfection on the Surface Hardness of Resin-Based Root Canal Sealers. Scanning 2016, 38, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbezoglu, I.; Zan, R.; Tunc, T.; Sumer, Z. Antibacterial Efficacy of Aqueous Ozone in Root Canals Infected by Enterococcus Faecalis. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, e11411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shichiri-Negoro, Y.; Tsutsumi-Arai, C.; Arai, Y.; Satomura, K.; Arakawa, S.; Wakabayashi, N. Ozone Ultrafine Bubble Water Inhibits the Early Formation of Candida Albicans Biofilms. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargaran, M.; Fatahinia, M.; Zarei Mahmoudabadi, A. The Efficacy of Gaseous Ozone against Different Forms of Candida Albicans. Curr. Med. Mycol. 2017, 3, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noites, R.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rocha, R.; Carvalho, M.F.; Gonçalves, A.; Pina-vaz, I. Synergistic Antimicrobial Action of Chlorhexidine and Ozone in Endodontic Treatment. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 592423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzillo, V.; Lallitto, F.; Russo, A.; Poggio, C.; Scribante, A.; Arciola, C.R.; Bertuccio, F.R.; Colombo, M. Ozonized Gel Against Four Candida Species: A Pilot Study and Clinical Perspectives. Materials 2020, 13, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, V.; Quagliariello, V.; Franzini, M.; Iaffaioli, R.V.; Maurea, N.; Valdenassi, L. Ozone Exerts Cytoprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Cardiomyocytes and Skin Fibroblasts after Incubation with Doxorubicin. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 2019, 2169103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scassellati, C.; Galoforo, A.C.; Bonvicini, C.; Esposito, C.; Ricevuti, G. Ozone: A Natural Bioactive Molecule with Antioxidant Property as Potential New Strategy in Aging and in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 63, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, K.; Li, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, N.; Zeng, Q.; Pang, H.; Wang, C.; Xiao, L.; et al. Ozone Promotes Regeneration by Regulating the Inflammatory Response in Zebrafish. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2015, 28, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araneda, S.; Commin, L.; Atlagich, M.; Kitahama, K.; Parraguez, V.H.; Pequignot, J.-M.; Dalmaz, Y. VEGF Overexpression in the Astroglial Cells of Rat Brainstem Following Ozone Exposure. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacchi, G.; Lim, Y.; Belmonte, G.; Miracco, C.; Zanardi, I.; Bocci, V.; Travagli, V. Ozonated Sesame Oil Enhances Cutaneous Wound Healing in SKH1 Mice. Wound Repair Regen. 2011, 19, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Heng, H.; Liu, X.; Geng, H.; Liang, J. Evaluation of the Healing Potential of Short-Term Ozone Therapy for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1304034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, G.S.; Jeong, M.-J.; Ashworth, J.J.; Hardman, M.; Jin, W.; Moutsopoulos, N.; Wild, T.; McCartney-Francis, N.; Sim, D.; McGrady, G.; et al. TNFα Is a Therapeutic Target for Impaired Cutaneous Wound Healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2012, 20, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocci, V. Preparation of Ozonated Water and Oil for the Topical Therapy—Ozone as a Drinking Water Disinfectant: Ozone Disinfection to Prevent Nosocomial Infections. In OZONE; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MIC (µL/mL) | Positive Control MIC (µL/mL) a | |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC® 25923 ™ | 125 | 1 |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis ATCC® 35984 ™ | 250 | 0.25 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC® PAO-1 ™ | 250 | 2 |
| Escherichia coli ATCC® 86963 ™ | 250 | 1 |
| Candida albicans ATCC MYA-2876 | 62.5 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, C.; Curcio, G.; Graziani, A.; Mencacci, A.; Pietrella, D. Antibiofilm, Anti-Inflammatory, and Regenerative Properties of a New Stable Ozone-Gel Formulation. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121580
Russo C, Curcio G, Graziani A, Mencacci A, Pietrella D. Antibiofilm, Anti-Inflammatory, and Regenerative Properties of a New Stable Ozone-Gel Formulation. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(12):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121580
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Carla, Giuseppe Curcio, Alessandro Graziani, Antonella Mencacci, and Donatella Pietrella. 2024. "Antibiofilm, Anti-Inflammatory, and Regenerative Properties of a New Stable Ozone-Gel Formulation" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 12: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121580
APA StyleRusso, C., Curcio, G., Graziani, A., Mencacci, A., & Pietrella, D. (2024). Antibiofilm, Anti-Inflammatory, and Regenerative Properties of a New Stable Ozone-Gel Formulation. Pharmaceutics, 16(12), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121580








