Abstract
Background/Objectives: Fexofenadine hydrochloride is a widely prescribed drug for treating histamine-mediated allergic reactions. This review systematically collates existing research on the clinical pharmacokinetics (PK) of fexofenadine, with a copious emphasis on examining the impact of stereoisomerism, disease states, and drug interactions. Methods: The search engines PubMed, Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Cochrane were scanned systematically for articles concerning the clinical PK of fexofenadine in humans. The extensive literature search yielded 85 articles meeting the inclusion standards. Results: The PK parameters of fexofenadine showed a linear correlation between increasing doses and proportional elevations in PK parameters such as area under the curve from time 0 to infinity (AUC0–∞) and maximum plasma concentration (Cmax). Under fed conditions, its bioavailability was reduced by approximately 50%. Findings from patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) displayed a 63% decline in oral clearance (CL/F) of fexofenadine. A drug–food interaction study has displayed that grapefruit juice decreased Cmax (201 ng/mL vs. 128 ng/mL), accompanied by a 30% reduction in the bioavailability of fexofenadine. Furthermore, a drug–herb interaction study with St John’s Wort (SJW) has reported a reduction in CL/F by 10% after a single dose, but long-term administration reversed this effect, resulting in elevated CL/F by 17% of fexofenadine. Conclusions: Since no prior systematic review on the PK of this drug exists, this review amalgamates all pertinent PK parameters in humans by pooling up-to-date data from published studies. This detailed literature review can be advantageous for researchers who want to develop and assess PK models.
1. Introduction
Fexofenadine hydrochloride is a second-generation, peripheral histamine H1- receptor antagonist drug [1,2]. It was developed by Hoechst Marion Roussel and granted a patent approval in 1979 [3,4]. The drug was originally synthesized in 1993 by the Massachusetts-based biotechnology company Sepracor [5] and approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on 30 July 1996 [6] for the relief of chronic idiopathic urticaria and seasonal allergic rhinitis [7]. Fexofenadine is commonly considered an ‘inverse agonist’ because it stabilizes the inactive configuration of the H1 receptor, which in turn helps to alleviate the histamine-induced allergic responses. It is a non-sedating drug because of its negligible impact on cognitive performance [8]. In patients with chronic urticaria, it appeared to reduce the levels of tryptase, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) suggesting anti-inflammatory benefits through cytokine regulation [9]. This medication can be used off-label to treat allergic conjunctivitis, angioedema, eczema, and reactions to insect bites and stings [10]. The drug is available as tablets, suspension, and orally disintegrating tablets and is administered at a dose of 60 mg, 120 mg, and 180 mg [11].
Fexofenadine is a carboxylate metabolite of terfenadine that had been backed off from the US market due to potential cardiotoxic effects, including ventricular dysrhythmias and QTc interval prolongation [10]. Unlike terfenadine, fexofenadine is a safer drug and does not cause detrimental cardiac effects even when used in conjunction with cytochrome P450 (CYP3A) inhibitors such as erythromycin or ketoconazole [11].
Fexofenadine is categorized as a Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) class III drug with low permeability and high solubility [12]. It has a low bioavailability of 33% [13] and is quickly absorbed after oral absorption, achieving peak plasma concentration (Cmax) in approximately 1–3 h [14]. The volume of distribution (Vd) of the drug is reported to be 5.4–5.8 L/kg [15]. It predominantly binds to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein, constituting 60% to 70% of plasma protein binding [16]. It is a racemic blend of equipotent (R)- and (S)- enantiomers and has a renal clearance (CLR) of 4.32 L/h [12,16]. About 5% of the drug is metabolized by intestinal mucosa [17], and the remaining 92% of the administered drug is excreted unchanged in urine (12%) and feces (80%) [18]. Fexofenadine serves as a substrate for various transporters like P-glycoprotein (P-gp), organic anion-transporting polypeptides (OATPs), and multi-drug resistance proteins (MRP2). Due to negligible metabolism by CYP450, these transporters play a requisite role in the disposition of the drug [19].
Fexofenadine hydrochloride has an empirical formula C32H39NO4. HCl, with a molecular weight of 538.1 g/mol [20]. It is a hydrophilic zwitterion having a Log-p value of 0.49 and water solubility of approximately 0.81 mg/mL [21]. The effective jejunal permeability (Peff) of the drug is 0.06 ± 0.07 × 10−4 cm/s [22]. Moreover, the octanol-to-water partition coefficient is reported to be 2.81 [23].
Fexofenadine belongs to pregnancy category C, and it does not cross the blood-brain barrier [17,24]. The adverse effects linked to the drug include back pain, dyspepsia, dysmenorrhea, dizziness, nausea, fatigue, drowsiness, dry mouth, and the most commonly stated effect is headache. The drug does not cause any cardiotoxicity and entails minimal hepatotoxicity [17,25,26]. Rare side effects of Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) have been reported in the post-marketing surveillance [27]. It is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to fexofenadine or its ingredients [17], and caution is recommended in phenylketonuria patients [11].
The rationale of this research is to systematically assess all the pertinent pharmacokinetic (PK) parameters of fexofenadine in humans by pooling up-to-date data from published studies so that unexplored gaps involving the clinical utilization of the drug can be addressed. Different review articles have been published shedding light on fexofenadine usage, which focused on safety and efficacy in children [28], management of allergic disorders [9,29], and pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and biochemical properties [30]. Two systematic reviews have been reported on the antihistamine effects and safety of fexofenadine, and one on the efficacy of fexofenadine [26,31]. Although extensive literature is available regarding the PK of the drug, there is no report of a single systematic review that integrates all the factors influencing its clinical PK, such as genetic variability, transporters, stereoisomerism, co-existing disease states, physiological changes in special populations and interactions with other drugs, food, and herbs. The objective of this review is to critically evaluate all the PK aspects of fexofenadine up to the present and execute a unified overview exploring variations in drug PK exposure among different populations and anticipating potential drug interactions alongside the influence of transporters, stereoisomerism, and genetic variations, which may assist clinicians in dose optimization and clinical decision making. Additionally, this may also aid researchers in developing and evaluating PK models.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Design
This systematic review was meticulously executed in alignment with the Cochrane Handbook guidelines [32] and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [33] and has been registered in PROSPERO with the registration number “CRD42024530096”. The PRISMA Checklist is explicated in Supplementary Table S1.
2.2. Search Strategy
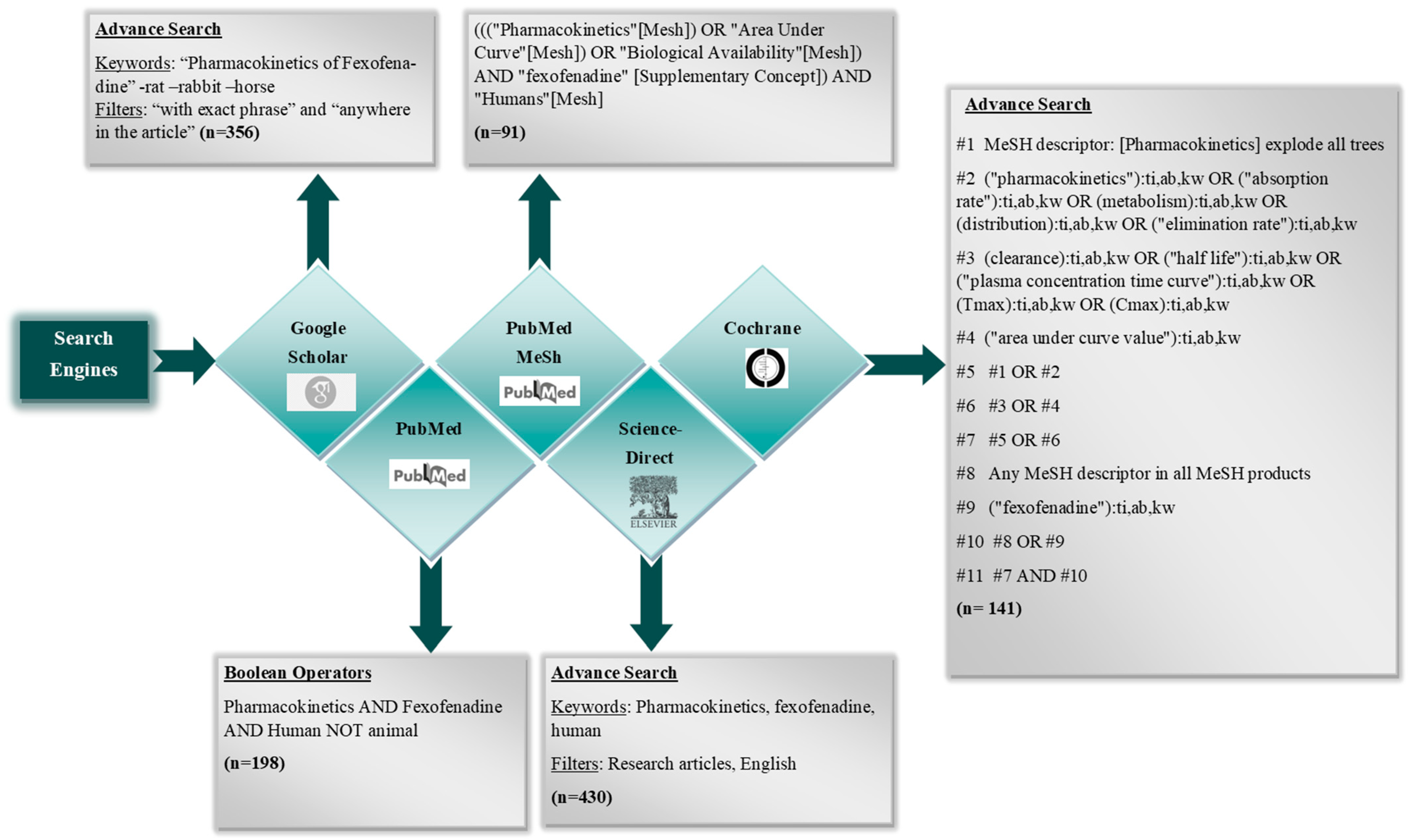
The online search engines (PubMed, Google Scholar, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library) were scrutinized comprehensively to ensure a thorough retrieval of all published studies detailing the PK of fexofenadine in humans. The search strategy was initiated by selecting the keywords based on Medical subject headings (MeSH), Boolean operators, and additional keywords from published articles. The searches were carried out from 13 September 2023 to 9 October 2023. The search methodologies are depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
Literature Search Strategy.
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
The inclusion criteria dictate that an original research article should present at least one PK parameter of fexofenadine. No restrictions were imposed on the publication year, and only articles written in English were deemed eligible.
2.4. Data Extraction and Study Selection
After conducting comprehensive searches through different search engines, all retrieved articles were imported into EndNote version 20, and duplicates were eradicated using the “remove duplicate” option. Then screening was executed based on titles, abstracts, animal studies, and non-accessibility. Letters to the editor, investigative reports, and short reviews were also omitted from the analysis. Articles that met the eligibility criteria underwent additional screening through full-text reading, resulting in the selection of the pertinent studies. The process of data extraction and eligibility evaluation was further finalized by two independent reviewers. The excluded articles are documented in Supplementary Table S2. The PK parameters to be assessed included area under the curve from time 0 to infinity (AUC0-∞), maximum plasma concentration (Cmax), time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax), half-life (t1/2), and clearance (CL). The standardization of PK parameter units was carried out to facilitate consistency in data comparison.
2.5. Quality Assessment
The quality assessment of all relevant studies was conducted using Jadad scoring, the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP) scoring system, and the Critical Appraisal Clinical Pharmacokinetic Tool (CACPK). Jadad scoring assigns a score from 0 to 5 based on the reporting of randomization, blinding, and drop-outs in the relevant article [34]. Studies having scores < 3, 3–4, and >4 are categorized as low, moderate, and high quality, respectively. CASP scoring, based on a 10-point scale, with a score of >6 signifies high quality, 4–6 implies moderate quality, and <4 shows low quality [35]. The CACPK, a 21-question checklist, categorizes articles into low, high, or moderate quality based on their score < 12, >13, or 12–13, respectively [36]. The Cochrane Collaboration tool was apprenticed to assess the risk of bias, and studies were categorized based on their scores, which indicated either a high, moderate, or low risk of bias. Scores falling < 3 indicated a high risk, 3–4 suggested a moderate risk, and >4 signified a low risk of bias [37]. The detailed scoring is documented in Supplementary Tables S3–S6.
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
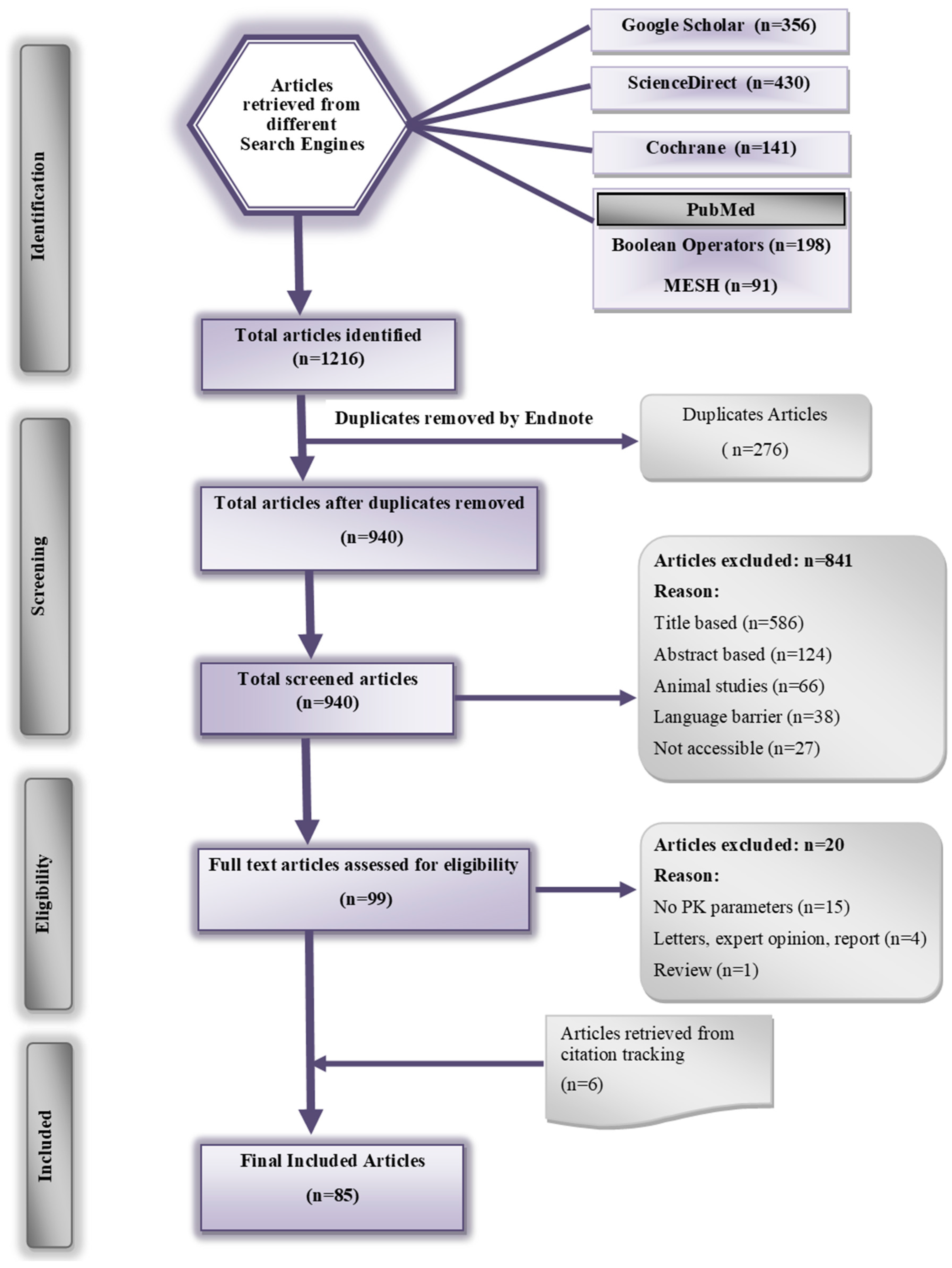
By utilizing different search engines, 1216 articles were identified, of which 276 were duplicates. The remaining 940 articles were subjected to further screening by applying both inclusion and exclusion criteria, resulting in a final inclusion of 85 articles. The PRISMA flow diagram displaying the final count of studies is illustrated in Figure 2.
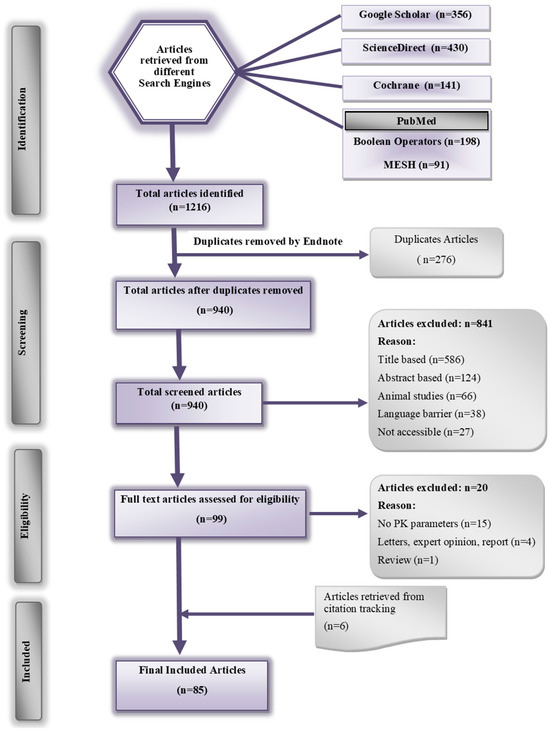
Figure 2.
PRISMA Flow Diagram.
The first article discussing the PK of fexofenadine was published in 1996 [38], and then the number of related publications increased gradually throughout the ensuing years. The included articles are further arranged by the year of publication in Figure 3.
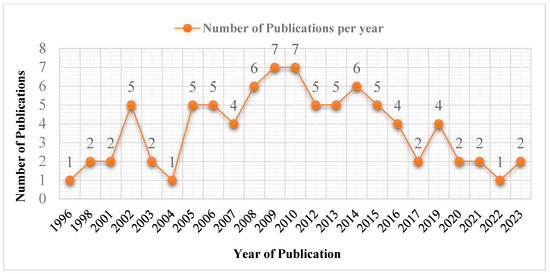
Figure 3.
Number of articles published per year.
3.2. Quality of Included Studies
A total of 85 articles were scrutinized for quality assessment using Jadad scoring, CASP scoring, and the CACPK tool. Jadad scoring categorized 72 articles as low quality and 13 as moderate quality. CASP scoring revealed that all articles are of high quality. In CACPK scoring, high, moderate, and poor quality were indicated by 60, 21, and 4 studies, respectively. According to Cochrane Collaboration, 21, 40, and 24 articles have a high, moderate, or low risk of bias, respectively.
3.3. Study Characteristics
The demographic characteristics of studies are delineated in Table 1, incorporating various aspects such as population, age, drug, dose, frequency, dosage form, and analytical method.

Table 1.
Study Characteristics.
3.4. Studies Including Healthy Population
3.4.1. Intravenous Administration
A single study was carried out after intravenous (IV) administration of fexofenadine. The study aimed to investigate the disposition kinetics between two 100 μg intravenous non-radiolabeled fexofenadine doses. One IV microdose dose was administered alone, while the other was given alongside a 120 mg oral therapeutic dose. Both doses showed closely similar CL values of 13 L/h and 16 L/h, respectively [21].
3.4.2. Oral Administration
A total of 22 oral studies were conducted with a healthy population. The PK of fexofenadine displayed linearity within the therapeutic dose range of 20–120 mg but elicited a minor disproportional increase in AUC0–∞ by 9% and Cmax by 25% at 240 mg dose [40]. A study has reported that Cmax varied between 45.6 ng/mL and 6383 ng/mL following a single dose range of 10–800 mg and between 57.9 ng/mL and 4677 ng/mL with multiple doses ranging from 20–690 mg [39]. In a clinical study, phenylalanine-free taste-masked orodispersible tablet (ODT) of fexofenadine demonstrated significantly higher AUC0-∞ of 1856.098 ± 692.314 ng.h/mL as compared to immediate release (IR) tablet [56]. One of the studies compared the PK of a therapeutic dose (120 mg) and microdose (100 μg), depicting a Cmax of 318 ng/mL in the former and 0.31 ng/mL in the latter dose [21]. In another clinical study, the PK of fexofenadine/pseudoephedrine combination tablet was evaluated in the fasted and fed states which indicated a 1.2-fold decrease in drug exposure in the latter [48].
Moreover, a study has narrated that the (R)-enantiomer displayed considerably greater AUC0–∞ as compared to the (S)-enantiomer—i.e., 843 ± 153 ng.h/mL vs. 496 ± 131 ng.h/mL, respectively [46].
3.4.3. Effect of Genes Encoding Drug Transporters
Two studies have explored the influence of MDR1 gene polymorphism on fexofenadine disposition by analyzing variant alleles for the G2677T polymorphism in exon 21 and the C3435T polymorphism in exon 26 after an oral dose of 180 mg [41,43]. A study preceded the activity of variant A allele based on genotype combinations of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) revealed that Cmax values were 494 ± 81 ng.h/mL for 2677AA/3435CC and 958 ± 408 ng.h/mL for 2677TT/3435TT [43]. Upon stratification by the C3435T, individuals homozygous for the TT genotype showed elevated AUC0–∞ values of 3910.1 ± 1894.8 ng.h/mL in comparison to the CC genotype, which displayed values of 3567.1 ± 1535.5 ng.h/mL [41]. Moreover, a study involving an in vivo cocktail approach to investigate drug transporter P-gp and CYP isoforms activity revealed varied CL/F of 205.87 L/h, 293.56 L/h, and 106.21 L/h for EM (all CYPs extensive metabolizer), CYP2C9 *3/*3, and CYP2D6 *4/*4 genotypes, respectively [60].
Furthermore, a clinical study investigating the association of drug-transporter polymorphisms has reported that (S)-enantiomer carrying the SLCO2B1*1/*1 allele exhibited significantly reduced AUC0–24 relative to the SLCO2B1*1/*3 + *3/*3 allele, i.e., 446 ng.h/mL vs. 675 ng.h/mL, respectively [51].
The PK parameters in healthy populations, segregated by the different groups, are depicted in Table 2.

Table 2.
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine in Healthy Population.
3.5. Studies with Diseased Population
The PK of fexofenadine remained consistent between cystic fibrosis patients and age-mates healthy participants when it was administered alone, but probenecid coadministration significantly augmented its Cmax to 470–1210 ng/mL [18]. One study was conducted on patients with advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that exhibited a surge in Cmax by 76% and 25% following single and multiple dose administration, respectively [59]. Moreover, a study executed on patients suffering from end-stage renal disease (ESRD) has displayed a significant decline in CL/F from 102.8 ± 37.9 L/h to 37.9 ± 19.5 L/h [50]. Furthermore, another study has reported no significant alterations in fexofenadine PK between the “before hemodialysis” and “after hemodialysis” investigations depicting that hemodialysis did not alter the AUC0–∞, i.e., 2355 ng.h/mL vs. 2785 ng.h/mL [62].
The remaining PK parameters of diseased populations are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine in Diseased Population.
3.6. Studies with Special Population
A clinical study revealed that children suffering from allergic rhinitis aged 2–5 years had a Cmax value of 224 ng/mL following a 30 mg dose of oral suspension [49]. Another study entailed the enantioselective disposition of fexofenadine in parturient women and displayed AUC0-∞ values of 267.67 ng.h/mL for (S)-fexofenadine and 423.2 ng.h/mL for (R)-fexofenadine [61].
The related PK parameters of special populations are explicated in Table 4.

Table 4.
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine in Special Population.
3.7. Drug–Drug Interactions (DDI) of Fexofenadine
A higher potential for drug interactions is associated with increased polytherapy. In 1999, a report indicated that drug transporters like OATP and P-gp potentially mediate drug interactions of antihistamines, including fexofenadine [66]. The mechanism underpinning drug interactions involves the induction or inhibition of drug transporters that facilitate the cellular efflux and uptake of the xenobiotics. The majority of drug–drug interactions (DDI) of fexofenadine were conducted using the probe substrate-based cocktail approach, which involves concurrent administration of subtherapeutic doses of probe substrates to evaluate the P-gp transport activity [60].
A total of 31 studies analyzed the interaction between fexofenadine and various drugs. A study was undertaken to assess the collective effect of fexofenadine and azalide antibiotic azithromycin, indicating an elevation in mean Cmax from 199 ng/mL to 349 ng/mL [66]. One of the studies looked into the impact of transporting inhibitors on fexofenadine and displayed a 1.5-fold increase in its AUC0–∞ with probenecid treatment and a 2.9-fold increase in its Cmax with verapamil treatment. Additionally, cimetidine’s inhibitory effect led to a decrease in CLR of fexofenadine from 13.8 ± 4.68 L/h to 9.12 ± 4.2 L/h without any discernible changes in other PK parameters [74].
Another study has highlighted a substantial drop in fexofenadine Cmax from 133 ± 67 ng/mL to 100 ± 43 ng/mL on simultaneous administration with nelfinavir [85]. A study analyzing the in vivo effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) on fexofenadine has demonstrated that co-administration with fluvoxamine led to a notable increase in its Cmax by 57% and an elevation in its AUC0–∞ by 38% was observed with paroxetine [93]. One of the studies has depicted that both acute and steady-state ritonavir caused a time and dose-dependent spike in fexofenadine AUC0–∞ by 2.8-fold and 1.4-fold, respectively [83].
Furthermore, a clinical study has reported that the combined impact of Vitamin D3 with fexofenadine showed a significant elevation in fexofenadine’s Cmax from 184.5 nmol/L to 317.5 nmol/L [106]. No discernible changes in the PK of fexofenadine were depicted with diltiazem [78], sertraline [93], breviscapine [113], and metronidazole [89].
3.7.1. Effect of Enantiomers on DDI of Fexofenadine
A clinical study has reported that concomitant use of carbamazepine induced a substantial decrease in Cmax from 100 ng/mL to 68 ng/mL for (S)-fexofenadine and from 132 ng/mL to 85 ng/mL for (R)-fexofenadine [16]. One of the clinical studies has narrated the cumulative effect of fexofenadine with a single dose of rifampicin and displayed a reduction in CL/F of both (S)- and (R)-enantiomer by 77% and 73%, respectively [19]. Another study has delineated that multiple doses of rifampicin markedly elevated the AUC0–24 of (R)- and (S)-fexofenadine by 3.1-fold and 3.48-fold, respectively [104].
3.7.2. Effect of Genotypes on DDI of Fexofenadine
An oral study involving MDR1 genetic polymorphism has exhibited a significant escalation in Cmax values from 713.8 ± 311.4 ng/mL to 2136.2 ± 897.9 ng/mL for 2677TT/3435TT genotype and from 510.8 ± 262.6 ng/mL to 1376.3 ± 340.5 ng/mL for 2677GG/3435CC genotype when itraconazole was co-administered with fexofenadine [72]. Another study has concluded that the breviscapine effect on fexofenadine PK was independent of MDR1 C3435T genetic polymorphism [113].
All the remaining PK parameters of DDI are listed in Table 5.

Table 5.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of DDI of fexofenadine.
3.8. Drug–Food Interactions (DFI) of Fexofenadine
3.8.1. Interactions of Fexofenadine with Fruit Juices
A clinical study has investigated the outcomes concerning the administration of 60 mg fexofenadine with grapefruit juice (GFJ) and showed a decrease in Cmax from 201 ng/mL to 128 ng/mL accompanied by a 30% reduction in the bioavailability of fexofenadine [69]. Another study has reported a volume-dependent decline in AUC0–∞ by 53% and 33% after consuming 300 mL and 1200 mL of GFJ, respectively [75]. An interaction study focusing on dietary constituents of GFJ has reported different Cmax values of 269 ng/mL, 380 ng/mL, and 463 ng/mL when fexofenadine was consumed with GFJ, naringin solution, and water, respectively [81].
One of the studies has highlighted that fexofenadine showed a decrease in AUC0-∞, i.e., 1598 ± 496 ng.h/mL, 1072 ± 429 ng.h/mL, and 668 ± 163 ng.h/mL with increasing apple juice (AJ) volume of 150 mL, 300 mL, and 600 mL [108].
A clinical study has mentioned the combined effect of different fruit juices with fexofenadine and displayed varied Cmax values of 288 ± 24 ng/mL, 110 ± 14 ng/mL, 96 ± 7 ng/mL, and 81 ± 13 ng/mL for water, GFJ, orange juice, and AJ, respectively. However, CLR, Tmax, and t1⁄2 remain unchanged across all treatments [70].
3.8.2. Interactions of Fexofenadine with Green Tea Extract (GTE)
The effect of GTE containing (−)-epigallocatechin gallate on the fexofenadine PK has demonstrated a lower Cmax value compared to water—i.e., 82.6 ng/mL vs. 278.7 ng/mL. No disparities were observed in the CLR, Tmax, and t1/2 between the water and GTE phases [114].
3.8.3. Effect of Enantiomers on DFI of Fexofenadine
A clinical study has depicted a reduction in AUC0–24 of both (R)- and (S)-enantiomers by 59% and 49%, respectively, after a single intake of AJ [101]. Another study has reported that co-administration with GFJ resulted in increased CL/F of both (R)-fexofenadine—i.e., 41 L/h vs. 75 L/h—and (S)-fexofenadine—i.e., 62 L/h vs. 143 L/h [105].
3.8.4. Effect of Transporter Genotypes on DFI of Fexofenadine
An interaction study focusing on the genotype-dependent effect of the SLCO2B1 c.1457C > T polymorphism has revealed significantly reduced Cmax values of 43.6 ± 9.8 ng/mL, 44.7 ± 16.4 ng/mL, 46.2 ± 18.6 ng/mL for CC allele, CT allele, and TT allele, respectively, when fexofenadine was administered with AJ [91].
All the necessary PK parameters of the DFI of fexofenadine are expounded in Table 6.

Table 6.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of DFI of fexofenadine.
3.9. Drug–Herb Interactions (DHI) of Fexofenadine
An interaction study has depicted that concurrent intake of St John’s Wort (SJWs) caused an escalation in Cmax from 163 ± 43 ng/mL to 236 ± 96 ng/mL after a single dose, but long-term administration led to the reversal of these changes with a decrease in Cmax value of 154 ± 75 ng/mL [68]. A study investigating quercetin’s inhibitory effect on fexofenadine has shown a significant decline in CL/F by 37% [86]. Another study was executed to assess the collective impact of fexofenadine and resveratrol, resulting in increased AUC0–∞ values from 2541.65 ± 527.18 ng.h/mL to 4512.33 ± 1265.17 ng.h/mL [100]. An in vivo study investigating the effect of multiple doses of danshen ethanol extract on MDR1 activity has resulted in enhanced CL/F of fexofenadine—i.e., 44.35 ± 25.57 L/h vs. 77.88 ± 31.20 L/h [102]. All the related PK parameters of DHI studies are reported in Table 7.

Table 7.
Pharmacokinetic Parameters of DHI of fexofenadine.
4. Discussion
This systematic review aimed to compile and assess human PK data of fexofenadine from published literature concerning the effects of dosage, age, stereoisomerism, disease states, genotypes, and drug interactions. Within the pool of retrieved articles, 21 examined healthy populations, 7 pertained to diseased populations, 4 delved into specific populations, 31 examined drug–drug interactions, 10 addressed drug–food interactions, and 14 investigated drug–herb interactions. The included studies have consistently cited Cmax and AUC0-∞ as primary PK parameters. Merely one report exists on the IV administration of fexofenadine in humans, which has shown comparable PK parameters to an oral therapeutic dose, suggesting a possibility of the potential use of this research in future studies [21].
A study conducted on oral administration of fexofenadine has reported that the drug exhibited dose-proportional PK at doses ranging from 20–120 mg. However, following 240 mg, there was a little disproportional increase in exposure due to the saturation of transporters, which led to decreased permeability efficiency with elevating doses [40]. A clinical study has demonstrated that the bioavailability of fexofenadine drops by approximately 50% under fed conditions; hence, the drug is suggested to be taken on an empty stomach [48]. Another study has narrated that phenylalanine-free taste-masked fexofenadine ODT exhibited a greater extent of drug absorption probably because of quick disintegration and dissolution in saliva even without water; hence, it is cogitated to be appropriate for both geriatric and pediatric patients [56]. Furthermore, one study has revealed that subjects with the 2677AA/3435CC genotype combination had lower Cmax values than those with other combinations of the 2677TT/3435TT SNPs. This difference was attributed to the fact that 2677TT/3435TT carriers had a higher concentration of P-gp substrate relative to 2677AA/3435CC carriers, indicating a significant interethnic variability in MDR1 haplotypes [43].
A clinical study elucidating the stereoselectivity of fexofenadine in healthy subjects has shown a significantly greater AUC0-∞ for the R-enantiomer relative to the S-enantiomer, likely due to the potential of chiral discrimination by P-glycoprotein [46]. Another study has displayed considerably reduced AUC0–24 values for S-fexofenadine in persons with the SLCO2B1*1/*1 allele relative to the SLCO2B1*1/*3 + *3/*3 allele. This indicates that the association of SLCO (encoding OATP) affects drug exposure in the liver and small intestine, resulting in different enantiomer dispositions [51]. Furthermore, a probe substrate-based cocktail study evaluating CYP enzymes and transporters activity influenced by genetic factors has revealed decreased CL/F of fexofenadine related to the CYP2D6 polymorphisms. This might be because individuals with the non-functional CYP2D64/*4 PM genotype lack CYP2D6 activity, which may lead to the accumulation of P-gp inhibitors, ultimately decreasing fexofenadine CL/F by impeding its efflux [60].
In patients suffering from advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the concurrent use of fexofenadine with single or multiple doses of osimertinib has resulted in increased fexofenadine exposure. Close monitoring is advised for patients receiving osimertinib alongside disposition-dependent P-gp drugs, as there is a risk of increased exposure to the concomitant medication, potentially leading to changes in tolerability [59]. Another study has depicted that PK of fexofenadine remained consistent in cystic fibrosis patients and age-mate healthy participants, but probenecid co-administration considerably augmented its Cmax due to OAT3 inhibition in the kidneys [18,74]. Moreover, a study carried out in patients with ESRD undergoing conventional hemodialysis has reported a 63% decline in CL/F, and this decrease could impact the PK disposition via nonrenal clearance pathways, leading to reduced hepatic OATP and intestinal P-gp activity [50].
A study assessing the tolerability of fexofenadine oral suspension in children aged 2–5 years has exhibited a similar exposure level compared to children aged 6–11 years and adults. Therefore, it was considered a well-tolerated nonsedating treatment for children who find difficulty in swallowing tablets [49]. In parturient women, maternal-fetal PK of fexofenadine enantiomers has revealed approximately 18% transplacental transfer for both enantiomers, with the (R)-enantiomer exhibiting higher AUC0–∞ due to the interplay of efflux P-gp and uptake OATP transporters for chiral discrimination [61].
Most drug–drug interactions (DDI) of fexofenadine occur as a result of induction or inhibition of intestinal efflux or hepatic uptake transporters. A research study has demonstrated that ritonavir, as well as combination tablets of lopinavir/ritonavir and ritonavir/indinavir, substantially raised the systemic drug exposure of fexofenadine possibly by inhibiting hepatic and intestinal P-gp activity [76,87,96,99]. A different study has described that nelfinavir potentially lowered fexofenadine Cmax as a result of elevated intestinal efflux and gastrointestinal P-gp activity; thus, dose adjustment is advisable to prevent potential side effects [85]. Another study was carried out in which cimetidine, a potent OCT inhibitor, when administered with fexofenadine, showed no significant plasma PK changes, indicating that alterations in OCT activity do not impact the in vivo disposition of fexofenadine [74]. Moreover, some research findings have highlighted that simultaneous use with azithromycin, Vitamin D3, and SSRI—i.e., paroxetine and fluvoxamine—resulted in a notable elevation of fexofenadine exposure, possibly due to the inhibition of P-gp activity; however, these changes were perceived to be well-tolerated [66,93,106]. Moreover, no anticipated PK changes were observed when fexofenadine was administered with diltiazem, sertraline, breviscapine, and metronidazole, suggesting that no dose adjustment is necessary [78,89,93,113].
A genotype-based DDI study has indicated that the T/T haplotype has 40% higher Cmax than the G/C haplotype, and itraconazole co-administration boosts the Cmax of both haplotypes by 3-fold due to P-gp inhibition with no association with MDR1 genetic variations [72]. A stereoisomerism-based DDI study has explicated that CL/F of both enantiomers of fexofenadine was significantly decreased by a single dose of rifampicin, likely by inhibiting hepatic or renal OATP1B3 and intestinal P-gp; thus, the dose adjustment is recommended to attain the desired therapeutic effect [19].
Drug–food interactions (DFI) play a vital role in clinical practice by altering drug effects. A clinical study has exhibited that AJ induced a volume-dependent decline in fexofenadine exposure through intestinal OATP2B1 activity; hence, taking the drug with water is preferred for optimal antihistamine effects [108]. Another study has narrated that co-administration of fexofenadine with GTE resulted in reduced exposure due to inhibition of intestinal OATP1A2 activity; hence, refraining the drug with green tea is suggested to prevent the possibility of therapeutic failure [114].
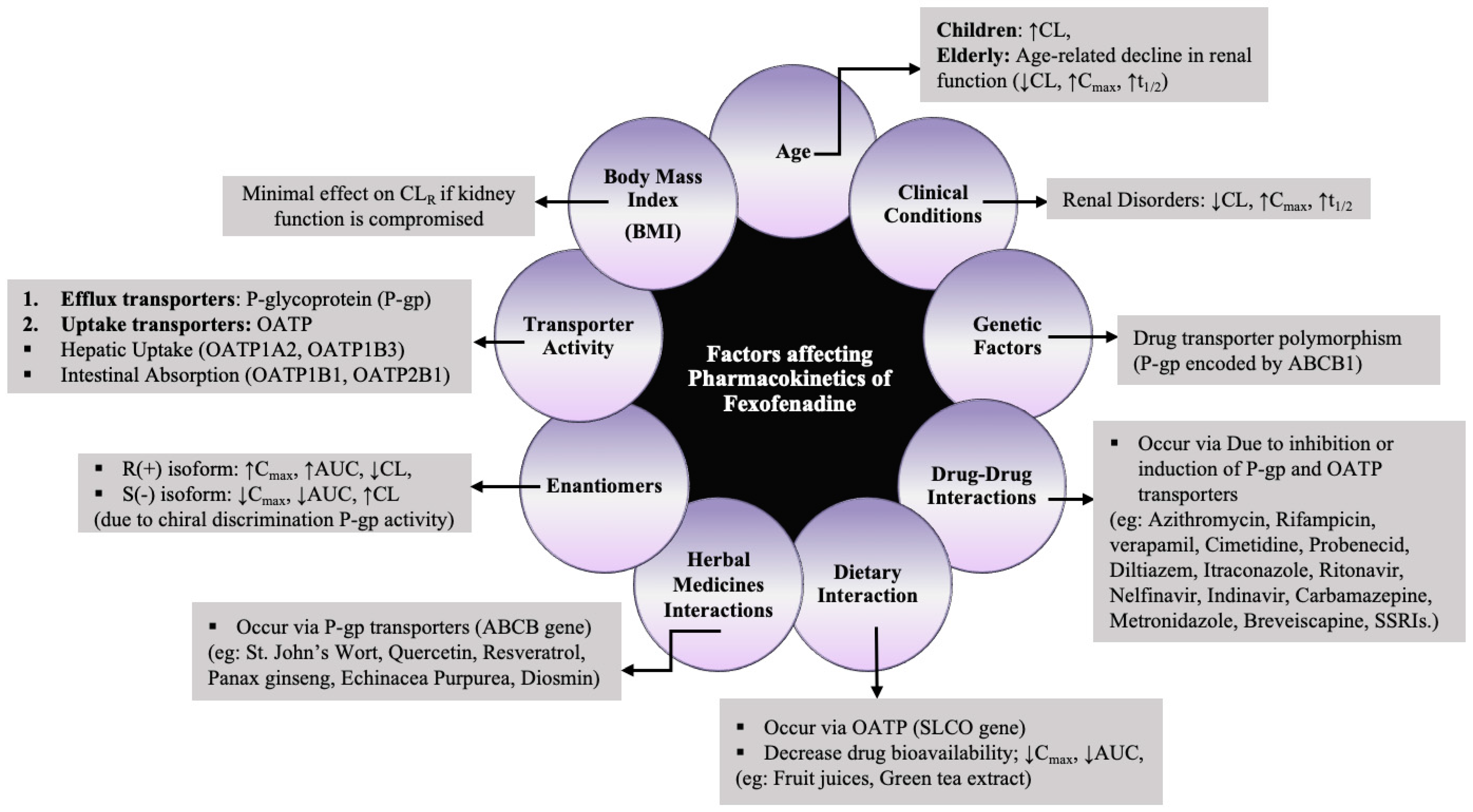
In general, drug–herb interactions (DHI) pose a serious safety concern as they may lead to potentially fatal consequences. A study has revealed that the Cmax of fexofenadine increased with SJWs over short-term use due to P-gp inhibition, while long-term use resulted in decreased Cmax due to P-gp induction [68]. Different studies have reported that fexofenadine’s PK was unaffected by ginkgo biloba extract, Echinacea purpurea, Panax ginseng, and radix astragali extract granules; hence, these substances can be used together without any dosage adjustments [82,90,92,98]. Furthermore, a clinical study evaluating the inter-ethnic disparities in interaction with SJW has illustrated diverse CL/F of fexofenadine in various populations, possibly stemming from genetic variations and allelic differences in CYP3A4 and P-gp functionality [73]. In summary, all the factors influencing the PK of fexofenadine are elucidated in Figure 4.
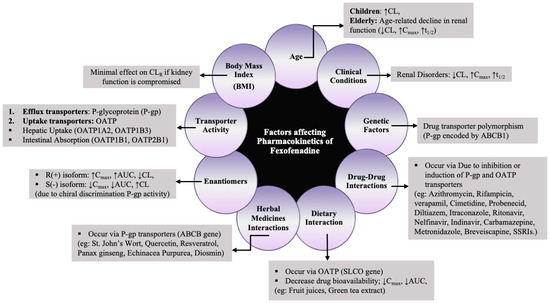
Figure 4.
Factors affecting PK of fexofenadine. (↓ Relative decrease in a specific parameter; ↑ Relative increase in a specific parameter).
The strength of the study lies in its comprehensive inclusion of PK studies from 1996 to 2023, spanning healthy, diseased, and special populations, alongside detailed analyses of drug interactions. The retrieval of 85 articles from four separate search engines reduces the potential for overlooking relevant studies. The limitation of this systematic review is the inclusion of only English language papers, which may overlook important research from other linguistic sources. Moreover, the presence of only one article focusing on parturient women limits the extent to which strong conclusions can be drawn regarding the pregnant population.
5. Conclusions
This review presents a comprehensive overview of the clinical PK of fexofenadine by compiling up-to-date information from all pertinent published studies. The analysis of the studies indicates a correlation between increasing doses and proportional elevations in PK parameters such as Cmax and AUC0–∞. The PK variations were significant between healthy and diseased populations, exhibiting reduced CL/F values in the case of renal disease. Racemic fexofenadine displayed notably higher drug exposure for the R-enantiomer relative to the S-enantiomer. The induction or inhibition of drug transporters like P-gp and OATP potentiate the clinical relevance of fexofenadine interactions with other drugs, food, and herbs. Various fruit juices also influenced the fexofenadine PK, but the impact was deemed clinically important following the interactions with grapefruit juice and apple juice. Genetic variations also perpetrate drug interactions, resulting in changes to its effectiveness. The knowledge of these PK parameters and disparities in fexofenadine PK among healthy, diseased, and special populations, alongside the impact of stereoisomerism and genetic polymorphism, can assist clinicians in developing and evaluating the fexofenadine PK model. Moreover, the understanding of alterations in PK parameters regarding drug-drug, drug-food, and drug–herb interactions offers practitioners valuable insights into preempting adverse reactions, refining dosage strategies, and choosing appropriate treatments to achieve the intended outcomes.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmaceutics16121619/s1. Supplementary Table S1: PRISMA Checklist 2020. Supplementary Table S2: Screening of articles based on title, abstract, involvement of animals, and accessibility. Supplementary Table S3: JADAD Scoring. Supplementary Table S4: Critical Appraisal Skill Program (CASP). Supplementary Table S5: Critical Appraisal Clinical Pharmacokinetic (CACPK) Tool. Supplementary Table S6: Cochrane Collaboration Tool.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: M.B., M.F.R. and F.A.; Methodology and acquisition of data: M.B., A.Z. and T.A.; Formal Interpretation of data: A.Z., H.S. and F.A.; Writing—Original draft preparation: M.B., A.Z. and T.A.; Writing—Review and editing: M.F.R., H.S. and T.A.; Supervision: M.F.R. and F.A.; Funding Acquisition: F.A. All authors have made substantial contributions to the design, extraction, analysis, and interpretation of data and have actively participated in drafting and revising the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Distinguished Scientist Fellowship program at King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, through research supporting project number (RSP2024R131).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data used for this publication are either presented in the main article or is available as Supplementary Information.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the effort of Imran Imran (I.I.), Anees ur Rehman (A.R.), and Waseem Ashraf (W.A.) in the presented work. The authors extend their appreciation to the Distinguished Scientist Fellowship program at King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for funding this work through research supporting project number (RSP2024R131).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
References
- Dicpinigaitis, P.V.; Gayle, Y.E. Effect of the second-generation antihistamine, fexofenadine, on cough reflex sensitivity and pul-monary function. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 56, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciprandi, G.; Tosca, M.A.; Cosentino, C.; Riccio, A.M.; Passalacqua, G.; Canonica, G.W. Effects of fexofenadine and other antihistamines on components of the allergic response: Adhesion molecules. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, S78–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handley, D.A. Advancement of the Third Generation of Antihistamines. Pediatr. Asthma Allergy Immunol. 1999, 13, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Ganellin, C.R. Analogue-based drug discovery. Chem. Int. Newsmag. IUPAC 2010, 32, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Asha, P.K.; Raghu, M.S.; Devi, V.S.A. Properties of Potassium Permanganate as Oxidant in the Determination of Fexofenadine in Pharmaceuticals. Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, A.A. FDA approves safer form of terfenadine. Lancet 1996, 348, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Akamine, Y.; Kaneko, S.; Uno, T. Effects of the P-glycoprotein inducer carbamazepine on fexofenadine phar-macokinetics. Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devillier, P.; Roche, N.; Faisy, C. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Desloratadine, Fexofenadine and Levocetirizine: A comparative review. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 47, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelrod, D.; Bielory, L. Fexofenadine hydrochloride in the treatment of allergic disease: A review. J. Asthma Allergy 2008, 1, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team DSbHJ. Fexofenadine. Available online: https://healthjade.net/fexofenadine/ (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Craun, K.L.; Schury, M.P. Fexofenadine: StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556104/#_article-21720_s11_ (accessed on 23 April 2024).
- Helmy, S.A.; El-Bedaiwy, H.M.; El-Masry, S.M. Applying Biopharmaceutical Classification System Criteria to Predict the Potential Effect of Cremophor ® RH 40 on Fexofenadine Bioavailability at Higher Doses. Ther. Deliv. 2020, 11, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, A.; Kumagai, Y.; Yamane, N.; Tozuka, Z.; Sugiyama, Y.; Fujita, T.; Yokota, S.; Maeda, M. Microdose study of a P-glycoprotein substrate, fexofenadine, using a non-radioisotope-labelled drug and LC/MS/MS. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2010, 35, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, F.E.; Simons, K.J. Clinical pharmacology of new histamine H1 receptor antagonists. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 36, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molimard, M.; Diquet, B.; Benedetti, M.S. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and metabolism of desloratadine, fexofenadine, levocetirizine and mizolastine in humans. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 18, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamine, Y.; Miura, M.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Kojima, M.; Uno, T. Carbamazepine differentially affects the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine enantiomers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 73, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abilash, K.; Dinesh, G.; Janartanan, S.; Praveena, J.; Vanitha, G.; Gokul Manikandan, P.; Jeevanandham, S. Formulation and evaluation of mouth dissolving films of fexofenadine hydrocloride by solvent casting method. World J. Pharm. Res. 2022, 11, 1699–1721. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Beringer, P.M.; Hidayat, L.; Rao, A.P.; Louie, S.; Burckart, G.J.; Shapiro, B. Probenecid, but Not Cystic Fibrosis, Alters the Total and Renal Clearance of Fexofenadine. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 48, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuhara, H.; Miura, M.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Yoshida, K.; Akamine, Y.; Yokochi, M.; Fukizawa, S.; Ikejiri, K.; Kanamitsu, K.; Uno, T.; et al. Effect of Coadministration of Single and Multiple Doses of Rifampicin on the Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine Enantiomers in Healthy Subjects. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, H.; Leila, B.; Jalilian, H.; Islambulchilar, Z.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Bioequivalence of Fexofenadine Tablet Formulations Assessed in Healthy Iranian Volunteers. Arzneimittelforschung 2009, 59, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappin, G.; Shishikura, Y.; Jochemsen, R.; Weaver, R.J.; Gesson, C.; Houston, B.; Oosterhuis, B.; Bjerrum, O.J.; Rowland, M.; Garner, C. Pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine: Evaluation of a microdose and assessment of absolute oral bioavailability. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 40, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannergren, C.; Petri, N.; Knutson, L.; Hedeland, M.; Bondesson, U.; Lennernäs, H. Multiple transport mechanisms involved in the intestinal absorption and first-pass extraction of fexofenadine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 74, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Alam, M.S.; Meena, C.L.; Jain, R.; Bansal, A.K. Fexofenadine Hydrochloride. Profiles of Drug Substances, Excipients and Related Methodology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 34, pp. 153–192. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, L.; Moreira, F.d.L.; Nardotto, G.H.B.; Cavalli, R.C.; Moisés, E.C.D.; Duarte, G.; Lanchote, V.L. Chiral Discrimination of P-glycoprotein in Parturient Women: Effect of Fluoxetine on Maternal-Fetal Fexofenadine Pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compalati, E.; Baena-Cagnani, R.; Penagos, M.; Badellino, H.; Braido, F.; Gómez, R.; Canonica, G.; Baena-Cagnani, C. Systematic Review on the Efficacy of Fexofenadine in Seasonal Allergic Rhinitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 156, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Peng, H. Antihistamine effects and safety of fexofenadine: A systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancano, M.A. ISMP Adverse Drug Reactions: Propofol-Related Infusion Syndrome (PRIS) 1, 2; Ivermectin-Induced Ste-vens-Johnson Syndrome; Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis From Fexofenadine; Memantine-Related Drug Eruption. Hosp. Pharm. 2018, 53, 220–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, E.O.; Rosario, N.A.; Van Bever, H.; Lucio, L. Fexofenadine: Review of safety, efficacy and unmet needs in children with allergic rhinitis. Allergy, Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, K.; Jarvis, B. Fexofenadine: A review of its use in the management of seasonal allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria. Drugs 2000, 59, 301–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M.; Gums, J.G. Fexofenadine: Biochemical, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties and its unique role in allergic disorders. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnovale, C.; Battini, V.; Gringeri, M.; Volonté, M.; Uboldi, M.C.; Chiarenza, A.; Passalacqua, G. Safety of fexofenadine and other second-generation oral antihistamines before and after the removal of the prescription requirement in Italy and other European countries: A real-world evidence study and systematic review. World Allergy Organ. J. 2022, 15, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Green, S.; Ben Van Den, A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.D.; Wells, G.A.; Huët, C.; McAlister, F.A.; Salmi, L.R.; Fergusson, D.; Laupacis, A. Assessing the quality of randomized trials: Reliability of the Jadad scale. Control. Clin. Trials 1999, 20, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dirini, R.M.A.; Thewlis, D.; Paul, G. A Comprehensive Literature Review of the Pelvis and the Lower Extremity FE Human Models under Quasi-static Conditions. Work. 2012, 41 (Suppl. S1), 4218–4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliman, A.B.E.; Pawluk, S.A.; Wilby, K.J.; Rachid, O. The use of a modified Delphi technique to develop a critical appraisal tool for clinical pharmacokinetic studies. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. Weekbl. 2022, 44, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savović, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C.; et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, F.E.R.; Bergman, J.N.; Watson, W.T.A.; Simons, K. The clinical pharmacology of fexofenadine in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 1062–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, T.; Stoltz, M.; Weir, S. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and tolerance of single- and multiple-dose fexofenadine hydrochloride in healthy male volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 64, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, D.K.; Castles, M.A.; Pack, D.J.; Bhargava, V.O.; Weir, S.J. Dose proportionality and comparison of single and multiple dose pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine (MDL 16455) and its enantiomers in healthy male volunteers. Biopharm Drug Dispos 1998, 19, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, S.; Schaeffeler, E.; Hitzl, M.; Hofmann, U.; Schwab, M.; Brinkmann, U.; Eichelbaum, M.; Fromm, M.F. MDR1 gene polymorphisms and disposition of the P-glycoprotein substrate fexofena-dine. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 53, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, U.; Seiler, M.; Drescher, S.; Fromm, M.F. Determination of fexofenadine in human plasma and urine by liquid chromatog-raphy-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2002, 766, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.Y.; Hong, K.S.; Lim, H.S.; Chung, J.Y.; Oh, D.S.; Kim, J.R.; Jung, H.R.; Cho, J.Y.; Yu, K.S.; Jang, I.J.; et al. A variant 2677A allele of the MDR1 gene affects fexofenadine disposition. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2004, 76, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J.; Ridout, F.; Meadows, R.; Johnsen, S.; Hindmarch, I. Suppression of the histamine-induced wheal and flare response by fexofenadine HCl 60 mg twice daily, loratadine 10 mg once daily and placebo in healthy Japanese volunteers. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2005, 21, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, L.; Begany, P.; Dyrhonova, M.; Emritte, N.; Svobodova, X. Bioequivalence of two fexofenadine formulations in healthy human volunteers after single oral administration. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc 2007, 151, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, M.; Uno, T.; Tateishi, T.; Suzuki, T. Pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine enantiomers in healthy subjects. Chirality 2007, 19, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, G.; Teng, L.; Wu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liu, L.; Gu, J. Rapid and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Quantification of Fexofenadine in Human Plas-ma—Application to a Bioequivalence Study in Chinese Volunteers. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2007, 23, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, V.D.; Radharani, K.; Jagadeesh, B.; Ramulu, G.; Bhushan, I.; Naidu, A.; Mullangi, R. LC–MS–MS Assay for Simultaneous Quantification of Fexofenadine and Pseudoephedrine in Human Plasma. Chromatographia 2008, 67, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segall, N.; Grubbe, R.E.; Levy, A.L.; Maloney, M.J.; Nayak, A.S.; Kittner, B.; Quesada, J.T. Pharmacokinetics, safety and tolerability of an oral suspension of fexofenadine for children with allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008, 29, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolin, T.D.; Frye, R.F.; Le, P.; Sadr, H.; Naud, J.; Leblond, F.A.; Pichette, V.; Himmelfarb, J. ESRD Impairs Nonrenal Clearance of Fexofenadine but not Midazolam. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamine, Y.; Miura, M.; Sunagawa, S.; Kagaya, H.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Uno, T. Influence of drug-transporter polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine enantiomers. Xenobiotica 2010, 40, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Zou, J.; Zhu, Y.; Lou, S.; Fan, H.; Qin, Q. Measurement of fexofenadine concentration in micro-sample human plasma by a rapid and sensitive LC-MS/MS employing protein precipitation: Application to a clinical pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muppavarapu, R.; Guttikar, S.; Rajappan, M.; Kamarajan, K.; Mullangi, R. Sensitive LC-MS/MS-ESI method for simultaneous determination of montelukast and fexofenadine in human plasma: Application to a bioequivalence study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-A.; Hsu, K.-Y. Pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine in healthy Taiwanese volunteers. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 1261–1264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joy, M.S.; Frye, R.F.; Nolin, T.D.; Roberts, B.V.; La, M.K.; Wang, J.; Brouwer, K.L.; Dooley, M.A.; Falk, R.J. In Vivo Alterations in Drug Metabolism and Transport Pathways in Patients with Chronic Kidney Diseases. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2014, 34, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehia, S.A.; El-Ridi, M.S.; Tadros, M.I.; El-Sherif, N.G. Phenylalanine-free taste-masked orodispersible tablets of fexofenadine hydrochloride: Development, in vitro evaluation and in vivo estimation of the drug pharmacokinetics in healthy human volunteers. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2015, 20, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, B.K.; Nolin, T.D.; Velenosi, T.J.; Feere, D.A.; Knauer, M.J.; Asher, L.J.; House, A.A.; Urquhart, B.L. Effect of CKD and Dialysis Modality on Exposure to Drugs Cleared by Nonrenal Mechanisms. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, S.A.; El Bedaiwy, H.M. HPLC Determination of Fexofenadine in Human Plasma for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Pharmacokinetic Studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2016, 30, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Moreno, V.; Carpeno, J.D.; Weilert, D.; Laus, G.; Mann, H.; Vishwanathan, K. Modulation of Fexofenadine Pharmacokinetics by Osimertinib in Patients with Advanced EGFR-Mutated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 59, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusinato, D.A.C.; Filgueira, G.C.d.O.; Rocha, A.; Cintra, M.A.C.; Lanchote, V.L.; Coelho, E.B. LC-MS/MS analysis of the plasma concentrations of a cocktail of 5 cytochrome P450 and P-glycoprotein probe substrates and their metabolites using subtherapeutic doses. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, L.S.R.; Vale, G.T.D.; Moreira, F.d.L.; Marques, M.P.; Coelho, E.B.; Cavalli, R.C.; Lanchote, V.L. Direct chiral LC-MS/MS analysis of fexofenadine enantiomers in plasma and urine with application in a maternal-fetal pharmacokinetic study. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1145, 122094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeland, E.J.; Witczak, B.J.; Zaré, H.K.; Christensen, H.; Åsberg, A.; Robertsen, I. Chronic Inhibition of CYP3A is Temporarily Reduced by Each Hemodialysis Session in Patients with End-Stage Renal Disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 108, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everardo, P.G.; Magdalena, G.S.; Elena, G.P.M.; Vanessa, C.M.; Gabriela, S.C. Bioavailability assessment of fexofenadine and montelukast in a fixed-dose combination tablet versus the components administered simultaneously. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2021, 49, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, C.; Lucio, L.; De Fer, B.B.; Lheritier-Barrand, M. Bioequivalence of 2 Pediatric Formulations of Fexofenadine Hydrochloride Oral Suspension. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2023, 12, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chretien, M.L.; Bailey, D.G.; Asher, L.; Parfitt, J.; Driman, D.; Gregor, J.; Dresser, G.K. Severity of coeliac disease and clinical management study when using a non-metabolised medication: A phase I pharmacokinetic study. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e057151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Banfield, C.; Kantesaria, B.; Marino, M.; Clement, R.; Affrime, M.; Batra, V. Pharmacokinetic and safety profile of desloratadine and fexofenadine when coad-ministered with azithromycin: A randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Clin. Ther. 2001, 23, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, M.A.; Bruce, M.A.; Haehner-Daniels, B.D.; Hall, S.D. The effect of rifampin administration on the disposition of fexofenadine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 69, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Hamman, M.A.; Huang, S.M.; Lesko, L.J.; Hall, S.D. Effect of St John’s wort on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 71, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banfield, C.; Gupta, S.; Marino, M.; Lim, J.; Affrime, M. Grapefruit Juice Reduces the Oral Bioavailability of Fexofenadine But Not Desloratadine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresser, G.K.; Bailey, D.G.; Leake, B.F.; Schwarz, U.I.; Dawson, P.A.; Freeman, D.J.; Kim, R.B. Fruit juices inhibit organic anion transporting polypeptide–mediated drug uptake to decrease the oral availability of fexofenadine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 71, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresser, G.K.; Schwarz, U.I.; Wilkinson, G.R.; Kim, R.B. Coordinate induction of both cytochrome P4503A and MDR1 by St John’s wort in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, J.H.; Yoon, Y.R.; Hongm, W.S.; Nguyen, P.M.; Lee, S.S.; Choi, Y.G.; Cha, I.J.; Shin, J.G. Effect of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of fexofenadine in relation to the MDR1 genetic polymorphism. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 78, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Tan, L.H.; Polasek, E.C.; Hong, C.; Teillol-Foo, M.; Gordi, T.; Sharma, A.; Nickens, D.J.; Arakawa, T.; Knuth, D.W.; et al. CYP3A and P-glycoprotein activity induction with St. John’s Wort in healthy volunteers from 6 ethnic populations. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 45, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuifurukori, N.; Uno, T.; Sugawara, K.; Tateishi, T. Different effects of three transporting inhibitors, verapamil, cimetidine, and probenecid, on fexofenadine pharmacokinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 77, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresser, G.K.; Kim, R.B.; Bailey, D.G. Effect of Grapefruit Juice Volume on the Reduction of Fexofenadine Bioavailability: Possible Role of Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptides*. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 77, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolf, P.G.; Heeswijk, v.; Bourbeau, M.; Campbell, P.; Seguin, I.; Chauhan, B.M.; Foster, B.C.; Cameron, D.W. Time-Dependent Interaction Between Lopinavir/Ritonavir and Fexofenadine. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 46, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemma, G.L.; Wang, Z.; Hamman, M.A.; Zaheer, N.A.; Gorski, J.C.; Hall, S.D. The effect of short- and long-term administration of verapamil on the disposition of cytochrome P450 3A and P-glycoprotein substrates. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 79, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Uno, T.; Sugawara, K.; Tateishi, T. Effects of itraconazole and diltiazem on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 61, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sugawara, K.; Tateishi, T. Lack of Dose-Dependent Effects of Itraconazole on the Pharmacokinetic Interaction with Fexofenadine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2006, 34, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Uno, T.; Sugawara, K.; Tateishi, T. Effects of single and multiple doses of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics of fexofen-adine, a substrate of P-glycoprotein. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2006, 62, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.G.; Dresser, G.K.; Leake, B.F.; Kim, R.B. Naringin is a major and selective clinical inhibitor of organic anion-transporting poly-peptide 1A2 (OATP1A2) in grapefruit juice. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 81, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, S.M.; Davey, R.T.; Voell, J.; Formentini, E.; Alfaro, R.M.; Penzak, S.R. Effect of Ginkgo biloba extract on lopinavir, midazolam and fexofenadine pharma-cokinetics in healthy subjects. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2008, 24, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Bedynek, P.S.; Walker, A.; Whittington, D.; Hoffer, C. Mechanism of ritonavir changes in methadone pharmacokinetics and pharmaco-dynamics: II. Ritonavir effects on CYP3A and P-glycoprotein activities. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 84, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, T.; Miura, M.; Suzuki, T.; Uno, T. The different effects of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine enantiomers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Walker, A.; Whittington, D.; Hoffer, C.; Bedynek, P.S. Methadone metabolism and clearance are induced by nelfinavir despite inhibition of cytochrome P4503A (CYP3A) activity. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2009, 101, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-A.; Park, P.-W.; Park, J.-Y. Short-term effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a substrate of P-glycoprotein, in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Hoffer, C.; Whittington, D.; Walker, A.; Bedynek, P.S. Methadone pharmacokinetics are independent of cytochrome P4503A (CYP3A) activity and gastrointestinal drug transport: Insights from methadone interactions with ritonavir/indinavir. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakugawa, T.; Miura, M.; Hokama, N.; Suzuki, T.; Tateishi, T.; Uno, T. Enantioselective disposition of fexofenadine with the P-glycoprotein inhibitor vera-pamil. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 67, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.A.; Park, J.Y. Effect of metronidazole on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a P-glycoprotein substrate, in healthy male volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penzak, S.R.; Robertson, S.M.; Hunt, J.D.; Chairez, C.; Malati, C.Y.; Alfaro, R.M.; Stevenson, J.M.; Kovacs, J.A. Echinacea purpurea significantly induces cytochrome P450 3A activity but does not alter lopinavir-ritonavir exposure in healthy subjects. Pharmacotherapy 2010, 30, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanaga, J.; Kotegawa, T.; Imai, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; Yoshizato, T.; Ohyama, T.; Shirasaka, Y.; Tamai, I.; Tateishi, T.; Ohashi, K.; et al. The effects of the SLCO2B1 c.1457C > T polymorphism and apple juice on the pharma-cokinetics of fexofenadine and midazolam in humans. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2011, 21, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malati, C.Y.; Robertson, S.M.; Hunt, J.D.; Chairez, C.; Alfaro, R.M.; Kovacs, J.A.; Penzak, S.R. Influence of Panax ginseng on Cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A and P-glycoprotein (P-gp) Activity in Healthy Participants. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 52, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruwatari, J.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Niioka, T.; Akamine, Y.; Takashima, A.; Kaneko, S.; Uno, T. Different Effects of the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Fluvoxamine, Paroxetine, and Sertraline on the Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine in Healthy Volunteers. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 32, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Bedynek, P.S.; Hoffer, C.; Walker, A.; Whittington, D. Lack of Indinavir Effects on Methadone Disposition Despite Inhibition of Hepatic and Intestinal Cytochrome P4503A (CYP3A). Anesthesiology 2012, 116, 432–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M.; Keely, B.; Morris, I.; Tann, L.; Lappin, G. Predicting Drug Candidate Victims of Drug-Drug Interactions, using Microdosing. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharasch, E.D.; Stubbert, K. Cytochrome P4503A Does Not Mediate the Interaction between Methadone and Ritonavir-Lopinavir. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, C.S.; Lan, T.; VanderMolen, K.M.; Dawso, P.A.; Oberlies, N.H.; Widner, W.W.; Scarlett, Y.V.; Paine, M.F. A Modified Grapefruit Juice Eliminates Two Compound Classes as Major Mediators of the Grapefruit Juice–Fexofenadine Interaction: An In Vitro–In Vivo “Connect”. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 53, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Ye, Z.; Ruan, Z.; Zeng, S. Investigation on modulation of human P-gp by multiple doses of Radix Astragali extract granules using fexofenadine as a phenotyping probe. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 146, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieiri, I.; Tsunemitsu, S.; Maeda, K.; Ando, Y.; Izumi, N.; Kimura, M.; Yamane, N.; Okuzono, T.; Morishita, M.; Kotani, N.; et al. Mechanisms of pharmacokinetic enhancement between ritonavir and saquinavir; mi-cro/small dosing tests using midazolam (CYP3A4), fexofenadine (p-glycoprotein), and pravastatin (OATP1B1) as probe drugs. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 53, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedada, S.K.; Yakkanti, S.A.; Neerati, P. Resveratrol enhances the bioavailability of fexofenadine in healthy human male volunteers: Involvement of P-glycoprotein inhibition. J. Bioequiv Avail. 2014, 6, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamine, Y.; Miura, M.; Komori, H.; Saito, S.; Kusuhara, H.; Tamai, I.; Ieiri, I.; Uno, T.; Yasui-Furukori, N. Effects of one-time apple juice ingestion on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine en-antiomers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 70, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Zeng, J.; Liu, S.; He, M.; Zhu, L.; Ye, Y.; Miao, P.; Shen, S.; Jiang, J. Effects of Danshen Ethanol Extract on the Pharmacokinetics of Fexofenadine in Healthy Volunteers. Evidence-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 473213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaru, A.; Takeda-Morishita, M.; Maeda, K.; Banba, H.; Takayama, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Kusuhara, H.; Sugiyama, Y. Effects of Cremophor EL on the absorption of orally administered saquinavir and fexofenadine in healthy subjects. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 30, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamine, Y.; Miura, M.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Ieiri, I.; Uno, T. Effects of multiple-dose rifampicin 450 mg on the pharmacokinetics of fexof-enadine enantiomers in Japanese volunteers. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamine, Y.; Miura, M.; Komori, H.; Tamai, I.; Ieiri, I.; Yasui-Furukori, N.; Uno, T. The change of pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine enantiomers through the single and simultaneous grapefruit juice ingestion. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2015, 30, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Gubler, C.; Spanaus, K.; Ismair, M.G.; da Silva, T.C.; Jetter, A. No major effects of vitamin D3 (1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3) on absorption and pharmacokinetics of folic acid and fexofenadine in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 72, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Kim, Y.; Jeon, J.Y.; Kim, D.S. Effect of fermented red ginseng on cytochrome P450 and P-glycoprotein activity in healthy subjects, as evaluated using the cocktail approach. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Imai, H.; Ohyama, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Hasunuma, T.; Inoue, Y.; Kotegawa, T.; Ohashi, K.; Uemura, N. The Pharmacokinetic Exposure to Fexofenadine is Volume-Dependently Reduced in Healthy Subjects Following Oral Administration With Apple Juice. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2016, 9, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedada, S.K.; Boga, P.K.; Kotakonda, H.K. The effect of diosmin on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine in healthy human vol-unteers. Xenobiotica 2017, 47, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedada, S.K.; Boga, P.K. The influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a P-glycoprotein substrate, in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 73, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusinato, D.A.; Martinez, E.Z.; Cintra, M.T.; Filgueira, G.C.; Berretta, A.A.; Lanchote, V.L.; Coelho, E.B. Evaluation of potential herbal-drug interactions of a standardized propolis extract (EPP-AF®) using an in vivo cocktail approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 245, 112174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilkovska, M.; Magliocco, G.; Desmeules, J.; Samer, C.; Daali, Y. Interaction between Fexofenadine and CYP Phenotyping Probe Drugs in Geneva Cocktail. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Miao, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, X.; Lai, Y. Effects of breviscapine and C3435T MDR1 gene polymorphism on the pharmacokinetics of fexofenadine, a P-glycoprotein substrate, in healthy volunteers. Xenobiotica 2021, 51, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaka, S.; Ono, Y.; Taudte, R.V.; Hoier, E.; Ogata, H.; Ono, T.; König, J.; Watanabe, H.; Fromm, M.F.; Shimomura, K. Exposure of Fexofenadine, but Not Pseudoephedrine, Is Markedly Decreased by Green Tea Extract in Healthy Volunteers. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).