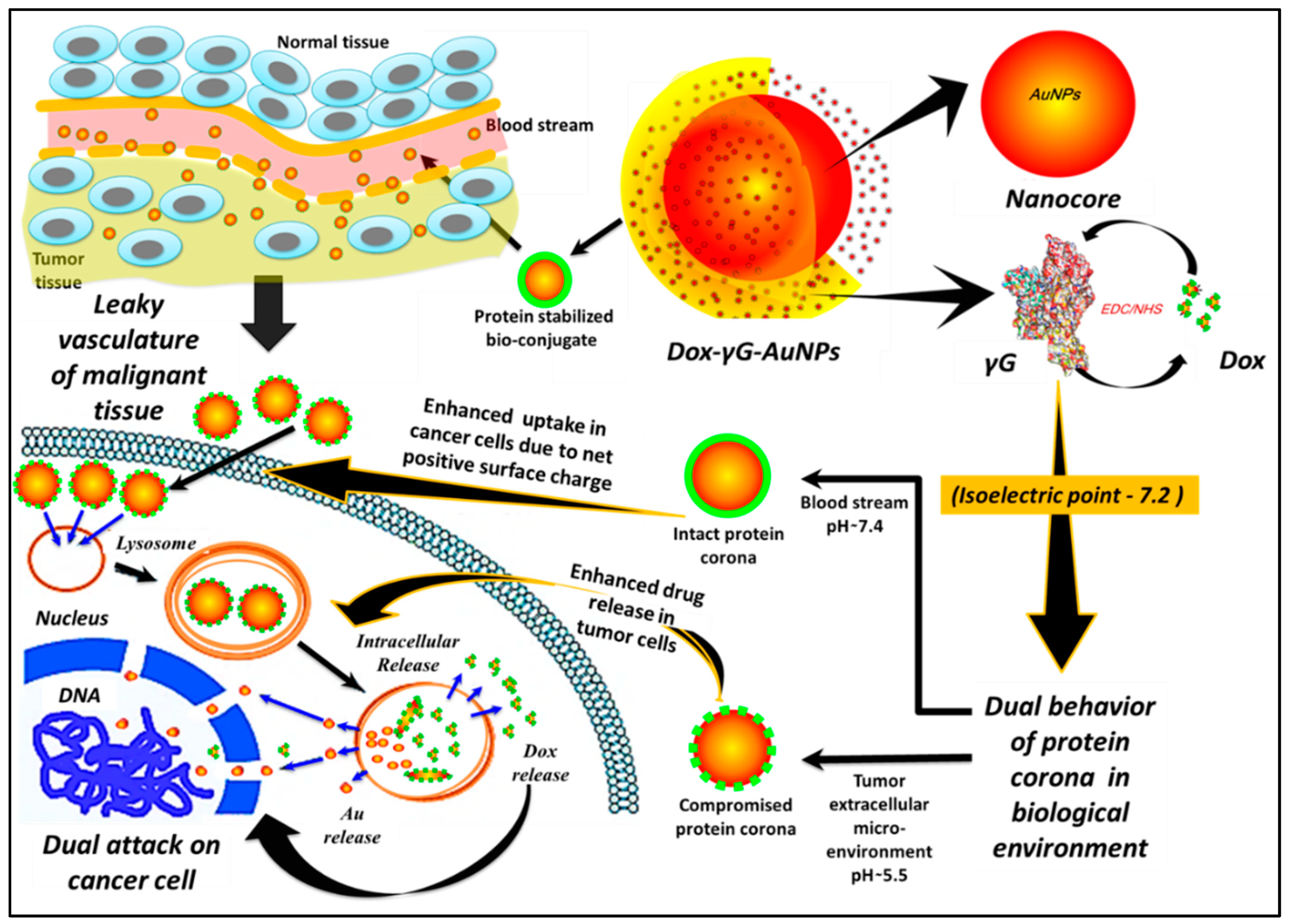
Doxorubicin Conjugated γ-Globulin Functionalised Gold Nanoparticles: A pH-Responsive Bioinspired Nanoconjugate Approach for Advanced Chemotherapeutics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of γ-Globulin (γG) Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles (γG-AuNPs)
2.2. Quantification Tightly Bound Hard (γG) Corona: Standard Bicinchoninic Acid “BCA” Assay
2.3. Synthesis of Dox Conjugated γG-AuNPs, i.e., “Dox-γG-AuNPs”
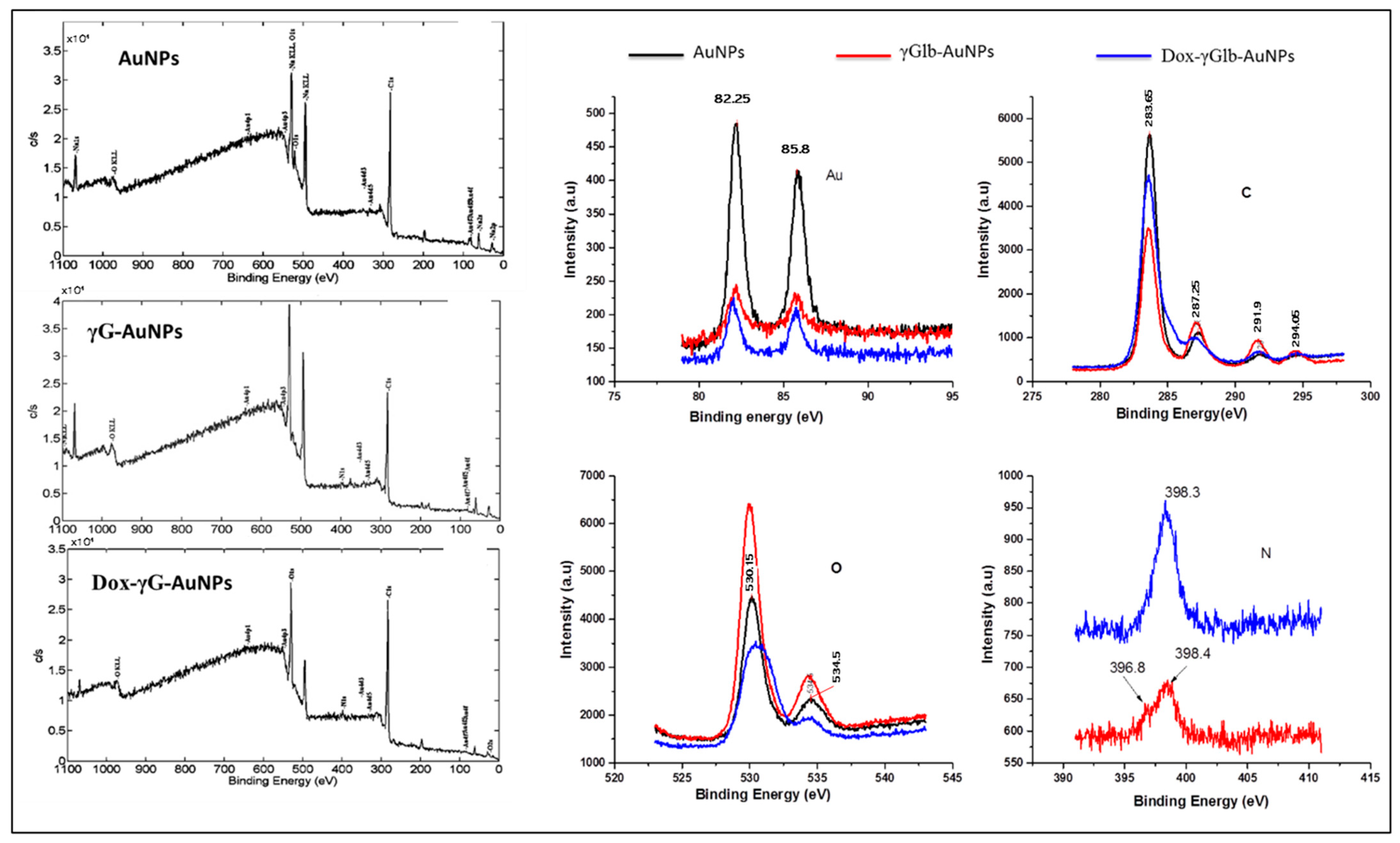
2.4. Characterisation
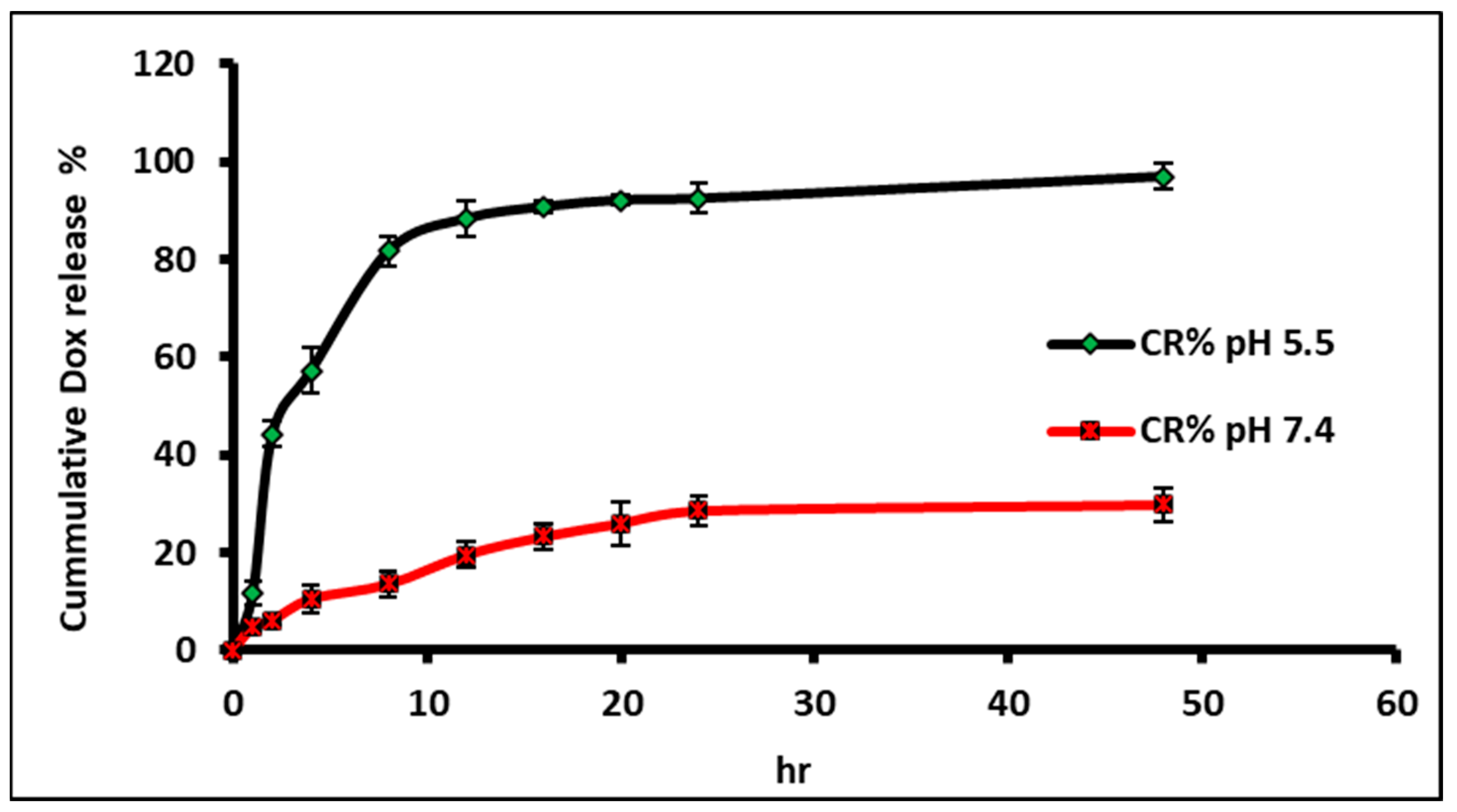
2.5. In Vitro Release Studies
2.6. Cellular Experiments
2.6.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.6.2. Cell Cytotoxicity
2.6.3. Live/Dead Analysis
2.6.4. Cell Uptake of Dox
2.6.5. Cellular Uptake of Gold
2.6.6. Cell Morphology Using SEM
2.6.7. Intracellular ROS Detection
2.6.8. qPCR Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis, Characterisation of γ-Globulin Stabilized Gold Nanoparticles “γG-AuNPs” and Estimation of Hard Protein Corona
3.2. In Vitro Release and Release Kinetics
3.3. Cellular Experiments
3.3.1. Cytotoxicity in Glioma Cells and Biocompatibility in Fibroblasts
3.3.2. Live/Dead Analysis
3.3.3. Cellular Uptake of Dox
3.3.4. Cellular Uptake of Gold
3.3.5. Cellular Morphology Using SEM
3.3.6. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Detection
3.3.7. qPCR
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gaurav, C.; Nikhil, G.; Deepti, S.; Kalra, S.; Goutam, R.; Amit, G.K. Albumin stabilized silver nanoparticles–clotrimazole β-cyclodextrin hybrid nanocomposite for enriched anti-fungal activity in normal and drug resistant Candida cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 71190–71202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisselier, E.; Astruc, D. Gold nanoparticles in nanomedicine: Preparations, imaging, diagnostics, therapies and toxicity. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1759–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Chopra, V.; Tyagi, A.; Rath, G.; Sharma, R.K.; Goyal, A.K. “Gold nanoparticles composite-folic acid conjugated graphene oxide nanohybrids” for targeted chemo-thermal cancer ablation: In vitro screening and in vivo studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 96, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaurav, C.; Saurav, B.; Goutam, R.; Goyal, A.K. Nano-systems for advanced therapeutics and diagnosis of atherosclerosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 4498–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, G.; Lujambio Ángeles, A.; Gonzalez-González, E.; Kulkarni, M.M.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Madou, M.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O. Carbon-Nanogold Hierarchical Micro/Nano Topographies for Cell Guidance. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Ángeles, A.L.; Gonzalez-González, E.; Kulkarni, M.M.; Cardenas-Benitez, B.; Jiménez, M.F.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Madou, M.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O. Nano-spaced Gold on Glassy Carbon Substrate for Controlling Cell Behavior. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.K.; Choi, E.-J.; Webster, T.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Khang, D. Effect of the protein corona on nanoparticles for modulating cytotoxicity and immunotoxicity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 97–113. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, D.-H.; DelRio, F.W.; Keene, A.M.; Tyner, K.M.; MacCuspie, R.I.; Cho, T.J.; Zachariah, M.R.; Hackley, V.A. Adsorption and conformation of serum albumin protein on gold nanoparticles investigated using dimensional measurements and in situ spectroscopic methods. Langmuir 2011, 27, 2464–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, A.; Chandran, P.; Monteiro-Riviere, N.A. Biocorona Bound Gold Nanoparticles Augment Their Hematocompatibility Irrespective of Size or Surface Charge. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, K.; Rahimi, M.; Yazdani, M.; Kim, S.T.; Moyano, D.F.; Hou, S.; Das, R.; Mout, R.; Rezaee, F.; Mahmoudi, M. Regulation of Macrophage Recognition through the Interplay of Nanoparticle Surface Functionality and Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4421–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, S.H.D.P.; Park, J.J.; Meuse, C.; Pristinski, D.; Becker, M.L.; Karim, A.; Douglas, J.F. Interaction of gold nanoparticles with common human blood proteins. ACS Nano 2009, 4, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Jin, R.; Mirkin, C.A. DNA-modified core-shell Ag/Au nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7961–7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, B.D.; Lin, Q.-Y.; Wu, H.; Luijten, E.; Mirkin, C.A.; Dravid, V.P. Size-Selective Nanoparticle Assembly on Substrates by DNA Density Patterning. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 5679–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, B.; Ren, X.; Li, S.; Ma, Y.; Cui, S.; Gu, Y. Multifunctional near-infrared-emitting nano-conjugates based on gold clusters for tumor imaging and therapy. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 8461–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volsi, A.L.; de Aberasturi, D.J.; Henriksen-Lacey, M.; Giammona, G.; Licciardi, M.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Inulin coated plasmonic gold nanoparticles as a tumor-selective tool for cancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoti, A.S.; Shukla, R.; Shanker, R.; Singh, S. Surface functionalization of quantum dots for biological applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 215, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culver, H.R.; Steichen, S.D.; Herrera-Alonso, M.; Peppas, N.A. A versatile route to colloidal stability and surface functionalization of hydrophobic nanomaterials. Langmuir 2016, 32, 5629–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.-C.; Chang, Y.; Kang, I.-K. Immobilization of biomolecules on the surface of inorganic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2016, 11, 014101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirshafiee, V.; Kim, R.; Park, S.; Mahmoudi, M.; Kraft, M.L. Impact of protein pre-coating on the protein corona composition and nanoparticle cellular uptake. Biomaterials 2016, 75, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safra, T.; Muggia, F.; Jeffers, S.; Tsao-Wei, D.; Groshen, S.; Lyass, O.; Henderson, R.; Berry, G.; Gabizon, A. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (doxil): Reduced clinical cardiotoxicity in patients reaching or exceeding cumulative doses of 500 mg/m2. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacar, O.; Sriamornsak, P.; Dass, C.R. Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 65, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banu, H.; Sethi, D.K.; Edgar, A.; Sheriff, A.; Rayees, N.; Renuka, N.; Faheem, S.; Premkumar, K.; Vasanthakumar, G. Doxorubicin loaded polymeric gold nanoparticles targeted to human folate receptor upon laser photothermal therapy potentiates chemotherapy in breast cancer cell lines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2015, 149, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkune, N.W.; Abrahamse, H. The Efficacy of Zinc Phthalocyanine Nanoconjugate on Melanoma Cells Grown as Three-Dimensional Multicellular Tumour Spheroids. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Mishra, P.K.; Talegaonkar, S.; Vaidya, B. Metal nanoparticles: A theranostic nanotool against cancer. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Chanda, N.; Zambre, A.; Upendran, A.; Katti, K.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Nune, S.K.; Casteel, S.W.; Smith, C.J.; Vimal, J. Laminin receptor specific therapeutic gold nanoparticles (198AuNP-EGCg) show efficacy in treating prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12426–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvizo, R.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P. Gold nanoparticles: Opportunities and challenges in nanomedicine. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giljohann, D.A.; Seferos, D.S.; Daniel, W.L.; Massich, M.D.; Patel, P.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Gold nanoparticles for biology and medicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3280–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Z.-Z.J.; Li, J.-E.J.; Ng, C.-T.; Yung, L.-Y.L.; Bay, B.-H. Gold nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilár, F.; Simon, I.; Lakatos, S.; Vonderviszt, F.; Medgyesi, G.A.; Závodszky, P. Conformation of human IgG subclasses in solution. Eur. J. Biochem. 1985, 147, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righetti, P.G.; Tudor, G.; Gianazza, E. Effect of 2-mercaptoethanol on pH gradients in isoelectric focusing. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1982, 6, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.J. Amine coupling through EDC/NHS: A practical approach. In Surface Plasmon Resonance; Springer: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Gaurav, C.; Goutam, R.; Rohan, K.N.; Sweta, K.T.; Abhay, C.S.; Amit, G.K. (Copper–curcumin) β-cyclodextrin vaginal gel: Delivering a novel metal–herbal approach for the development of topical contraception prophylaxis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 65, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. In-vitro anti-viral screening and cytotoxicity evaluation of copper-curcumin complex. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2013, 41, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezgui, R.; Blumer, K.; Yeoh-Tan, G.; Trexler, A.J.; Magzoub, M. Precise quantification of cellular uptake of cell-penetrating peptides using fluorescence-activated cell sorting and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2016, 1858, 1499–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes-Rius, A.; de Puig, H.; Kah, J.C.Y.; Borros, S.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Optimizing the properties of the protein corona surrounding nanoparticles for tuning payload release. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 10066–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kah, J.C.Y.; Grabinski, C.; Untener, E.; Garrett, C.; Chen, J.; Zhu, D.; Hussain, S.M.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Protein coronas on gold nanorods passivated with amphiphilic ligands affect cytotoxicity and cellular response to penicillin/streptomycin. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4608–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Sakhtianchi, R.; Müller, B.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D.; Mahmoudi, M. Protein corona change the drug release profile of nanocarriers: The “overlooked” factor at the nanobio interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, T.L.; Rodriguez-Lorenzo, L.; Hirsch, V.; Balog, S.; Urban, D.; Jud, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Lattuada, M.; Petri-Fink, A. Nanoparticle colloidal stability in cell culture media and impact on cellular interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6287–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.P.; Lim, D.-K. Photothermal Effect of Gold Nanoparticles as a Nanomedicine for Diagnosis and Therapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Moitra, P.; Bashir, M.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Natural tripeptide capped pH-sensitive gold nanoparticles for efficacious doxorubicin delivery both in vitro and in vivo. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboyewa, J.A.; Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Meyer, M.; Oguntibeju, O.O. Gold Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Extracts of Cyclopia intermedia, Commonly Known as Honeybush, Amplify the Cytotoxic Effects of Doxorubicin. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, E. The role of surface charge in cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of medical nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5577–5591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarska, M.; Novotny, F.; Havel, F.; Sramek, M.; Babelova, A.; Benada, O.; Novotny, M.; Saran, H.; Kuca, K.; Musilek, K. A two-step mechanism of cellular uptake of cationic gold nanoparticles modified by (16-mercaptohexadecyl) trimethylammonium bromide (MTAB). Bioconjugate Chem. 2016, 27, 2558–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Kaur, T.; Chauhan, A.; Kumar, R.; Kuanr, B.K.; Sharma, D. Tailoring nanoparticles design for enhanced heating efficiency and improved magneto-chemo therapy for glioblastoma. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 139, 213021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banstola, A.; Poudel, K.; Emami, F.; Ku, S.K.; Jeong, J.-H.; Kim, J.O.; Yook, S. Localized therapy using anti-PD-L1 anchored and NIR-responsive hollow gold nanoshell (HGNS) loaded with doxorubicin (DOX) for the treatment of locally advanced melanoma. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2021, 33, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chauhan, G.; Chopra, V.; Alvarado, A.G.; Gómez Siono, J.A.; Madou, M.J.; Martinez-Chapa, S.O.; Kulkarni, M.M. Doxorubicin Conjugated γ-Globulin Functionalised Gold Nanoparticles: A pH-Responsive Bioinspired Nanoconjugate Approach for Advanced Chemotherapeutics. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020208
Chauhan G, Chopra V, Alvarado AG, Gómez Siono JA, Madou MJ, Martinez-Chapa SO, Kulkarni MM. Doxorubicin Conjugated γ-Globulin Functionalised Gold Nanoparticles: A pH-Responsive Bioinspired Nanoconjugate Approach for Advanced Chemotherapeutics. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(2):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020208
Chicago/Turabian StyleChauhan, Gaurav, Vianni Chopra, América García Alvarado, Jocelyn Alexandra Gómez Siono, Marc J. Madou, Sergio Omar Martinez-Chapa, and Manish M. Kulkarni. 2024. "Doxorubicin Conjugated γ-Globulin Functionalised Gold Nanoparticles: A pH-Responsive Bioinspired Nanoconjugate Approach for Advanced Chemotherapeutics" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 2: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020208
APA StyleChauhan, G., Chopra, V., Alvarado, A. G., Gómez Siono, J. A., Madou, M. J., Martinez-Chapa, S. O., & Kulkarni, M. M. (2024). Doxorubicin Conjugated γ-Globulin Functionalised Gold Nanoparticles: A pH-Responsive Bioinspired Nanoconjugate Approach for Advanced Chemotherapeutics. Pharmaceutics, 16(2), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020208






