First Description of Marinoquinoline Derivatives’ Activity against Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
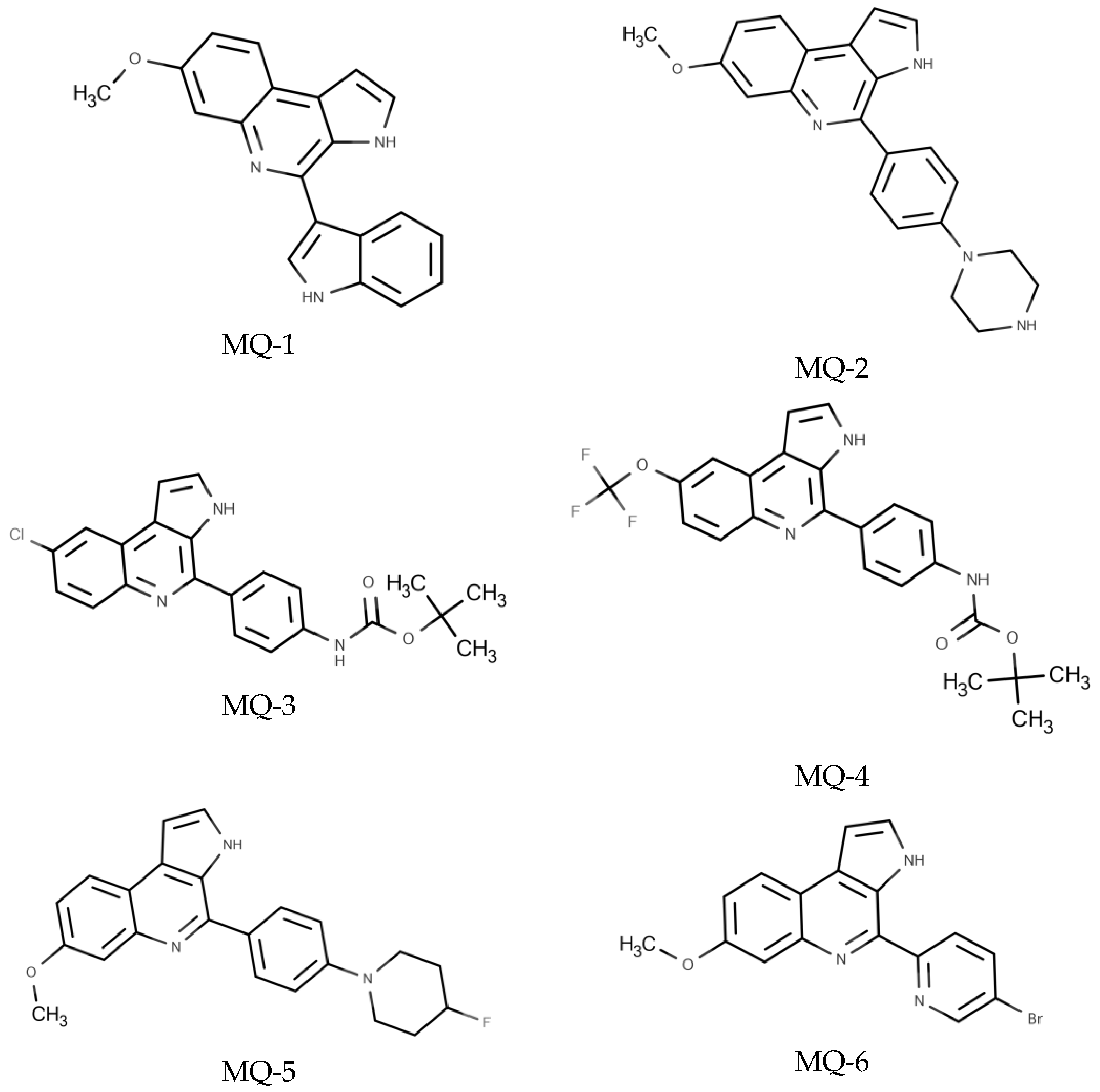
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of MQs
2.2. ADMET Predictions
2.3. In Vitro Study
2.3.1. Cell Culture and Parasite Propagation
2.3.2. Assay for Evaluating Anti-T. gondii Activity
2.3.3. Assay for Evaluating Mammalian Cytotoxicity
2.4. In Vivo Study
2.4.1. Acute Model
2.4.2. Chronic Model
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Characterization of MQs Derivatives Evaluated against T. gondii
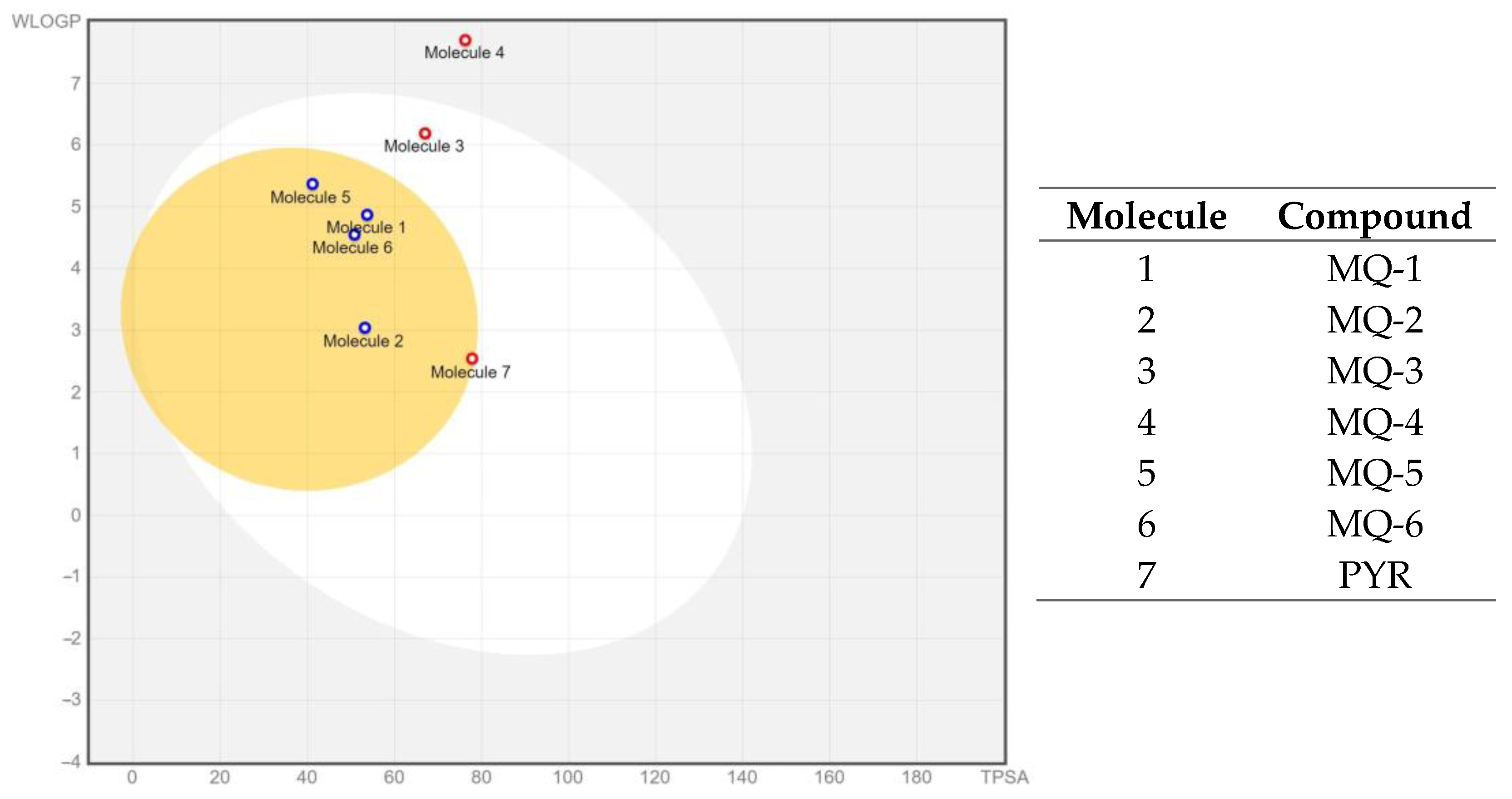
3.2. In Silico Results
ADMET Predictions
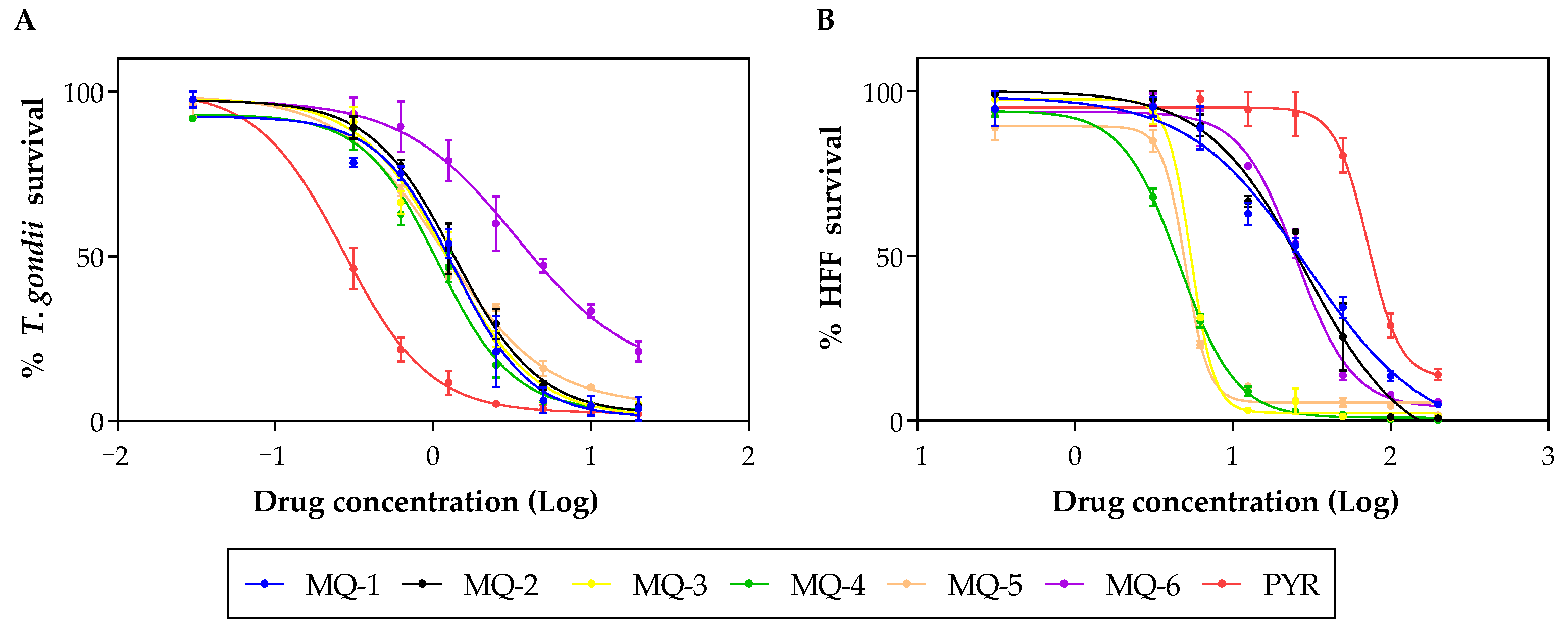
3.3. In Vitro Results
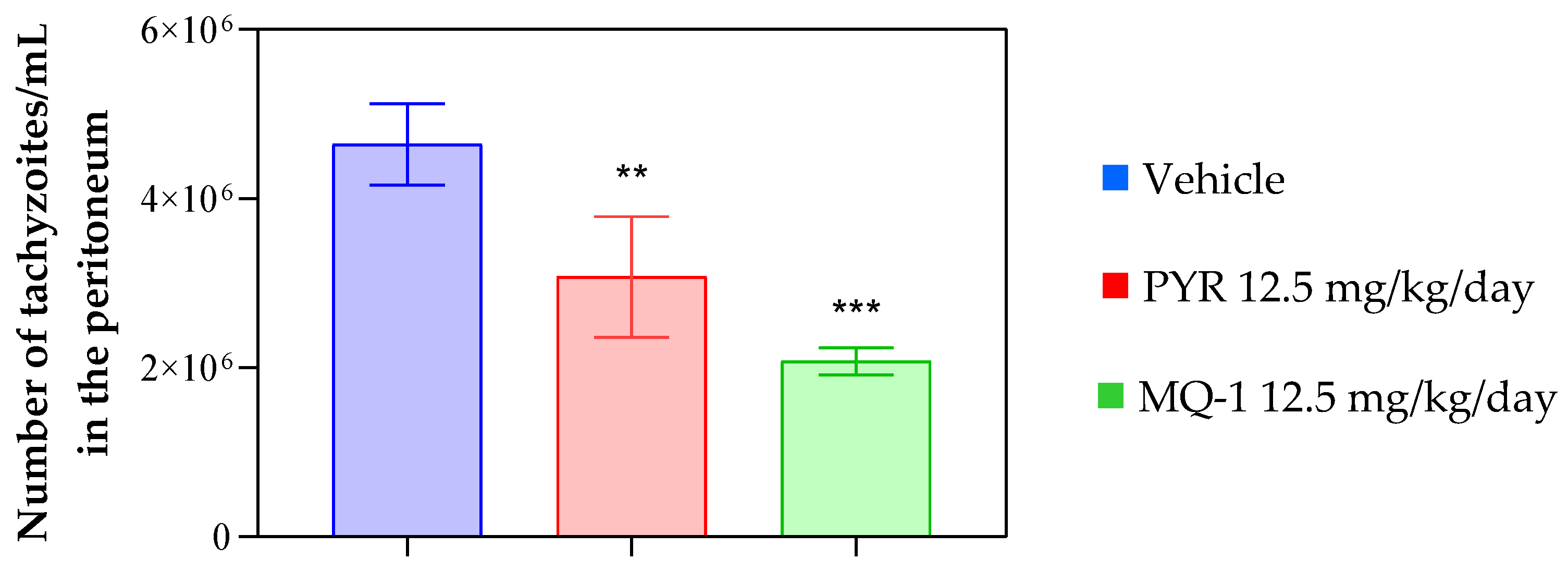
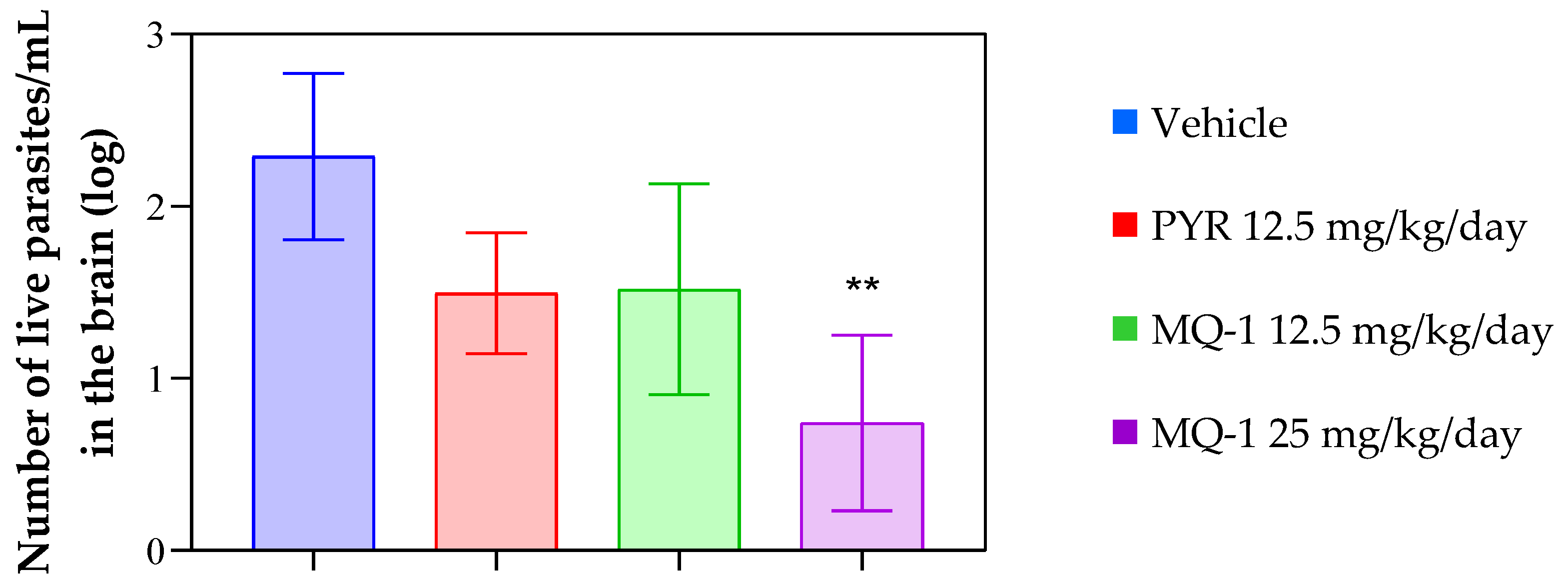
3.4. In Vivo Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robert-Gangneux, F.; Dardé, M.L. Epidemiology of and diagnostic strategies for toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 264–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, J.M.; Smith, J.R.; Belfort, R., Jr.; Gattey, D.; Winthrop, K.L. Toxoplasmosis: A global threat. J. Global Dis. 2011, 3, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dian, S.; Ganiem, A.R.; Ekawardhani, S. Cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients: A review. Pathog. Glob. Health 2023, 117, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carellos, E.V.; Caiaffa, W.T.; Andrade, G.M.; Abreu, M.N.; Januário, J.N. UFMG Congenital Toxoplasmosis Brazilian Group (UFMG-CTBG). Congenital toxoplasmosis in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil: A neglected infectious disease? Epidemiol. Infect. 2014, 142, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.G.; Liesenfeld, O. Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 2004, 363, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Gajurel, K.; Dhakal, R.; Liesenfeld, O.; Montoya, J.G. Treatment of Toxoplasmosis: Historical Perspective, Animal Models, and Current Clinical Practice. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 17–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhai, S.Q.; Li, C.H. Recent progress on anti-Toxoplasma drugs discovery: Design, synthesis and screening. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangnoi, Y.; Sakulkeo, O.; Yuenyongsawad, S.; Kanjanaopas, A.; Ingkaninan, K.; Plubrukarn, A.; Suwanborirux, K. Acetylcholines-terase-inhibiting activity of pyrrole derivatives from a novel marine gliding bacterium, Rapidithrix thailandica. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, A.C.C.; Panciera, M.; dos Santos, E.F.S.; Singh, M.K.; Garcia, M.L.; de Souza, G.E.; Nakabashi, M.; Costa, J.L.; Garcia, C.R.S.; Oliva, G.; et al. Discovery of Marinoquinolines as Potent and Fast-Acting Plasmodium falciparum Inhibitors with in Vivo Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5547–5568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Xing, G.; Liu, H.; Lu, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Drug repositioning: Progress and challenges in drug discov-ery for various diseases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 234, 114239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 3, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An open-source program for chemistry aware data visuali-zation and analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lou, C.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, G.; Tang, Y. admetSAR 2.0: Web-service for prediction and optimization of chemical ADMET properties. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, J.; Wu, Z.; Liu, G.; Lee, P.W.; Tang, Y. admetSAR: A com-prehensive source and free tool for evaluating chemical ADMET properties. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3099–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.S.; Alves, C.M.; Angeloni, M.B.; Gomes, A.O.; Barbosa, B.F.; Franco, P.S.; Silva, D.A.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Mineo, J.R.; Mineo, T.W.; et al. Trophoblast cells are able to regulate monocyte activity to control Toxoplasma gondii infection. Placenta 2013, 34, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Sibley, L.D. Assays for Monitoring Toxoplasma gondii Infectivity in the Laboratory Mouse. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2071, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teo, C.F.; Zhou, X.W.; Bogyo, M.; Carruthers, V.B. Cysteine protease inhibitors block Toxoplasma gondii microneme secretion and cell invasion. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, B.R.; Ramos, A.B.D.S.B.; de Menezes, R.P.B.; Scotti, M.T.; Colombo, F.A.; Marques, M.J.; Reimão, J.Q. Repurposing the Medicines for Malaria Venture’s COVID Box to discover potent inhibitors of Toxoplasma gondii, and in vivo efficacy evaluation of almitrine bismesylate (MMV1804175) in chronically infected mice. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0288335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.A.; Oliveira, A.B.; Ribeiro, M.F.; Tafuri, W.L.; Vitor, R.W. Toxoplasma gondii: In vitro and in vivo activities of the hydroxynaphthoquinone 2-hydroxy-3-(1′-propen-3-phenyl)-1,4-naphthoquinone alone or combined with sulfadiazine. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wu, M.; Hua, Q.; Lu, D.; Tian, Y.; Yu, H.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Y.; Cao, J.; Hu, X.; et al. Two old drugs, NVP-AEW541 and GSK-J4, repurposed against the Toxoplasma gondii RH strain. Parasit. Vectors 2020, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, L.; Santana, P.L.; Evangelista, F.F.; Beletini, L.F.; Souza, A.H.; Mantelo, F.M.; Souza-Kaneshima, A.M.; Costa, I.N.; Falavig-na-Guilherme, A.L. Rosuvastatin reduced brain parasite burden in a chronic toxoplasmosis in vivo model and influenced the neuropathological pattern of ME-49 strain. Parasitology 2020, 147, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, J.B.; Burrows, J.N.; Goldberg, D.E.; Sibley, L.D. Evaluation of Current and Emerging Antimalarial Medicines for Inhibition of Toxoplasma gondii Growth in Vitro. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arisue, N.; Hashimoto, T. Phylogeny and evolution of apicoplasts and apicomplexan parasites. Parasitol. Int. 2015, 64, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. From Medicinal Chemistry to Human Health: Current Approaches to Drug Dis-covery for Cancer and Neglected Tropical Diseases. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, S. In silico ADME-Tox modeling: Progress and prospects. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aungst, B.J. Optimizing Oral Bioavailability in Drug Discovery: An Overview of Design and Testing Strategies and Formu-lation Options. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G.; Kitchen, D.B. Computational models to predict blood-brain barrier permeation and CNS activity. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2003, 17, 643–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backman, J.T.; Filppula, A.M.; Niemi, M.; Neuvonen, P.J. Role of Cytochrome P450 2C8 in Drug Metabolism and Interactions. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 168–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, C.W. Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier: Molecular Mechanism of Transport of Drugs and Physiologically Im-portant Compounds. J. Membr. Biol. 2015, 248, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciera, M.; Lence, E.; Rodríguez, Á.; Gracia, B.; Aínsa, J.A.; Marco-Marín, C.; Rubio, V.; Correia, C.R.D.; González-Bello, C. Dis-covery of 3H-pyrrolo[2,3-c]quinolines with activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by allosteric inhibition of the glutamate-5-kinase enzyme. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 15, 114206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienkiewicz, N.; Ong, H.B.; Fairlamb, A.H. Characterization of a putative glutamate 5-kinase from Leishmania donovani. FEBS J. 2018, 14, 2662–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco-Marín, C.; Gil-Ortiz, F.; Pérez-Arellano, I.; Cervera, J.; Fita, I.; Rubio, V. A novel two-domain architecture within the amino acid kinase enzyme family revealed by the crystal structure of Escherichia coli glutamate 5-kinase. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 5, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempone, A.G.; de Oliveira, C.M.; Berlinck, R.G. Current approaches to discover marine antileishmanial natural products. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, B.R.; Ramos, A.B.D.S.B.; de Menezes, R.P.B.; Scotti, M.T.; Colombo, F.A.; Marques, M.J.; Reimão, J.Q. Anti-Toxoplasma gondii screening of MMV pandemic response box and evaluation of RWJ-67657 efficacy in chronically infected mice. Parasitology 2023, 150, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, W.K.; Segarra, I.; Ambu, S.; Mak, J.W. Significant reduction of brain cysts caused by Toxoplasma gondii after treatment with spiramycin coadministered with metronidazole in a mouse model of chronic toxoplasmosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsheikha, H.M.; Marra, C.M.; Zhu, X.Q. Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 25, e00115-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | GI 1 | BBB 1 | Mut 2 | Tum 2 | RE 2 | AOT 3 | RT 4 | SC 4 | SI 4 | SS 4 | MT 4 | NT 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQ-1 | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − |
| MQ-2 | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| MQ-3 | + | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | − | + |
| MQ-4 | − | − | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | + |
| MQ-5 | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| MQ-6 | + | + | − | − | − | − | + | − | − | − | − | − |
| PYR 5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | − | + | + |
| Compound | CYP 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP1A2 | CYP2C19 | CYP2C9 | CYP2D6 | CYP3A4 | |
| MQ-1 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| MQ-2 | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| MQ-3 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| MQ-4 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| MQ-5 | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| MQ-6 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| PYR 2 | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Compound | CC50 (µM) 1 | EC50 (µM) 2 | SI 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MQ-1 | 30.51 ± 1.80 | 1.46 ± 0.45 | 20.85 |
| MQ-2 | 29.11 ± 0.84 | 1.67 ± 0.40 | 17.39 |
| MQ-3 | 5.36 ± 0.91 | 1.60 ± 0.54 | 3.35 |
| MQ-4 | 4.16 ± 1.05 | 1.31 ± 0.31 | 3.18 |
| MQ-5 | 5.05 ± 1.63 | 1.43 ± 0.37 | 3.52 |
| MQ-6 | 28.55 ± 7.33 | 3.78 ± 0.67 | 7.55 |
| PYR 4 | 68.11 ± 4.26 | 0.29 ± 0.19 | 237.65 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diethelm, L.T.H.; Ramos, A.B.d.S.B.; de Lorena, G.B.; Trajano, B.I.; do Espírito Santo, R.D.; de Menezes, R.P.B.; Scotti, M.T.; Colombo, F.A.; Marques, M.J.; Correia, C.R.D.; et al. First Description of Marinoquinoline Derivatives’ Activity against Toxoplasma gondii. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020262
Diethelm LTH, Ramos ABdSB, de Lorena GB, Trajano BI, do Espírito Santo RD, de Menezes RPB, Scotti MT, Colombo FA, Marques MJ, Correia CRD, et al. First Description of Marinoquinoline Derivatives’ Activity against Toxoplasma gondii. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(2):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020262
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiethelm, Luiza Tamie Hirata, Amanda Bruno da Silva Bellini Ramos, Giovanna Braga de Lorena, Bruna Inácio Trajano, Rafael Dias do Espírito Santo, Renata Priscila Barros de Menezes, Marcus Tullius Scotti, Fabio Antonio Colombo, Marcos José Marques, Carlos Roque Duarte Correia, and et al. 2024. "First Description of Marinoquinoline Derivatives’ Activity against Toxoplasma gondii" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 2: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020262
APA StyleDiethelm, L. T. H., Ramos, A. B. d. S. B., de Lorena, G. B., Trajano, B. I., do Espírito Santo, R. D., de Menezes, R. P. B., Scotti, M. T., Colombo, F. A., Marques, M. J., Correia, C. R. D., & Reimão, J. Q. (2024). First Description of Marinoquinoline Derivatives’ Activity against Toxoplasma gondii. Pharmaceutics, 16(2), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020262










