Chemical Insights into Topical Agents in Intraocular Pressure Management: From Glaucoma Etiopathology to Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Glaucoma Etiopathology
2.1. Types of Glaucoma
2.2. Risk Factors
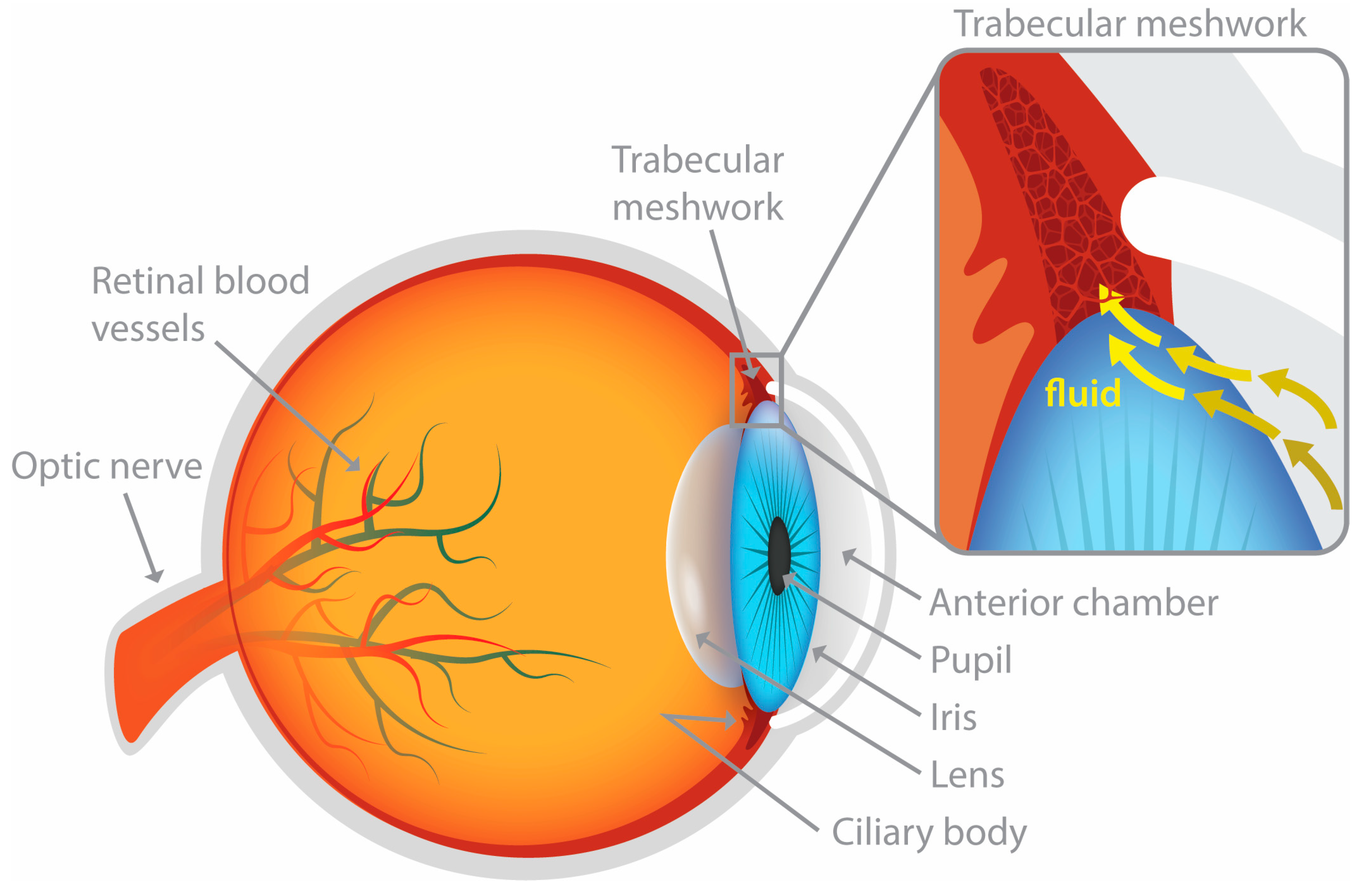
2.3. Aqueous Humor Dynamics
3. Diagnosis of Glaucoma
3.1. Tonometry
3.2. Gonioscopy
3.3. Optic Nerve Assessment
3.4. Visual Field Test
4. Glaucoma Therapeutics
4.1. Prostaglandin Analogs
4.2. Beta Blockers
4.3. Alpha Agonists
4.4. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
4.5. Rho Kinase Inhibitors
4.6. Cholinergic (Miotic) Agents
4.7. Adjunctive Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinreb, R.N.; Aung, T.; Medeiros, F.A. The Pathophysiology and Treatment of Glaucoma: A Review. JAMA 2014, 311, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cho, K.-S.; Vu, T.H.K.; Shen, C.-H.; Kaur, M.; Chen, G.; Mathew, R.; McHam, M.L.; Fazelat, A.; Lashkari, K.; et al. Commensal microflora-induced T cell responses mediate progressive neurodegeneration in glaucoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, T.; Crowston, J. Asia Pacific Glaucoma Guidelines; Kugler Publications: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, P.J.; Buhrmann, R.; Quigley, H.A.; Johnson, G.J. The definition and classification of glaucoma in prevalence surveys. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 86, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwerth, R.S.; Wheat, J.L.; Fredette, M.J.; Anderson, D.R. Linking structure and function in glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersey, J.P.; Broadway, D.C. Corticosteroid-induced glaucoma: A review of the literature. Eye 2006, 20, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wiggs, J.L. Common and rare genetic risk factors for glaucoma. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a017244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Lai, J.-Y. Advancing the stimuli response of polymer-based drug delivery systems for ocular disease treatment. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 6988–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, R.J.; Chidlow, G.; Wood, J.P.M.; Crowston, J.G.; Goldberg, I. Definition of glaucoma: Clinical and experimental concepts. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 40, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.; Swanson, W.H.; Garway-Heath, D.F. ‘Structure–function relationship’ in glaucoma: Past thinking and current concepts. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 40, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.H.; Fingert, J.H.; Kuehn, M.H.; Alward, W.L. Primary open-angle glaucoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeb Ahmad, S.; Abdul Ghani, S.; Hemalata Rajagopal, T. Current Concepts in the Biochemical Mechanisms of Glaucomatous Neurodegeneration. J. Curr. Glaucoma Pract. 2013, 7, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Leung, C.K.; Crowston, J.G.; Medeiros, F.A.; Friedman, D.S.; Wiggs, J.L.; Martin, K.R. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijl, A.; Leske, M.C.; Bengtsson, B.; Hyman, L.; Bengtsson, B.; Hussein, M.; Group, E.M.G.T. Reduction of Intraocular Pressure and Glaucoma Progression: Results from the Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2002, 120, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanakis, V.V.; Chan, M.P.Y.; Foster, P.J.; Cook, D.G.; Owen, C.G.; Rudnicka, A.R. Global variations and time trends in the prevalence of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowski, A.; Och, M.; Kanclerz, P.; Leffler, C.; De Moraes, C.G. Primary open angle glaucoma and vascular risk factors: A review of population based studies from 1990 to 2019. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Khaw, P.T. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet 2004, 363, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, H. Causal inference in primary open angle glaucoma: Specific discussion on intraocular pressure. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2006, 13, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, H.A.; McKinnon, S.J.; Zack, D.J.; Pease, M.E.; Kerrigan–Baumrind, L.A.; Kerrigan, D.F.; Mitchell, R.S. Retrograde axonal transport of BDNF in retinal ganglion cells is blocked by acute IOP elevation in rats. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 3460–3466. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, M.-L.; Peng, P.-H.; Ma, M.-C.; Ritch, R.; Chen, C.-F. Dynamic changes in reactive oxygen species and antioxidant levels in retinas in experimental glaucoma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, M.R. The optic nerve head in glaucoma: Role of astrocytes in tissue remodeling. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2000, 19, 297–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, T.; Nakazawa, C.; Matsubara, A.; Noda, K.; Hisatomi, T.; She, H.; Michaud, N.; Hafezi-Moghadam, A.; Miller, J.W.; Benowitz, L.I. Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates oligodendrocyte death and delayed retinal ganglion cell loss in a mouse model of glaucoma. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 12633–12641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, H.A. Neuronal death in glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1999, 18, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, P.; Tezel, G.l.N.; Patil, R.V.; Hernandez, M.R.; Wax, M.B. Induction of HLA-DR expression in human lamina cribrosa astrocytes by cytokines and simulated ischemia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Stasi, K.; Nagel, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, R.-F.; Ren, L.; Podos, S.M.; Mittag, T.; Danias, J. Complement component 1Q (C1Q) upregulation in retina of murine, primate, and human glaucomatous eyes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Li, Y.; Jiang, B. Prevalence of Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma in the Last 20 Years: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 624179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondkar, A.A. Updates on Genes and Genetic Mechanisms Implicated in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma. Appl. Clin. Genet. 2021, 14, 89–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.-Y.; Cringle, S.J.; Chen, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, C. Primary angle closure glaucoma: What we know and what we don’t know. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 57, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsbirk, F.H. Anatomical risk factors in primary angle-closure glaucoma: A ten year follow up survey based on limbal and axial anterior chamber depths in a high risk population. Int. Ophthalmol. 1992, 16, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.Y.; Au, S.C.L. Glaukomflecken: The classic and uncommon ocular sign after acute primary angle closure attack. Vis. J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 31, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihota, R. Classification of primary angle closure disease. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2011, 22, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.C.L. From acute angle-closure to COVID-19 during Omicron outbreak. Vis. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 29, 101514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.C.L.; Tsang, A.; Ko, C.K.L. Ocular events following the surge of cough and cold medications use during the Omicron outbreak in Hong Kong. QJM Int. J. Med. 2023, 116, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, S.C.L. Cluster of ocular acute primary angle closure cases and increased antitussive or nasal decongestants usage following the surge in acute COVID-19 infection. QJM Int. J. Med. 2023, 116, 601–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ouyang, J.; Zhou, W.; Lai, M.; Ye, T.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J. Multiple patterns of angle closure mechanisms in primary angle closure glaucoma in Chinese. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi Chin. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 36, 46–51, discussion 45–46. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri-Mahdavi, K.; Supawavej, C.; Bitrian, E.; Giaconi, J.A.; Law, S.K.; Coleman, A.L.; Caprioli, J. Patterns of damage in chronic angle-closure glaucoma compared to primary open-angle glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 152, 74–80.e72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatham, A.J.; Miki, A.; Weinreb, R.N.; Zangwill, L.M.; Medeiros, F.A. Defects of the lamina cribrosa in eyes with localized retinal nerve fiber layer loss. Ophthalmology 2014, 121, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobe, L.A.; Harris, A.; Hussain, R.M.; Eckert, G.; Huck, A.; Park, J.; Egan, P.; Kim, N.J.; Siesky, B. The role of retrobulbar and retinal circulation on optic nerve head and retinal nerve fibre layer structure in patients with open-angle glaucoma over an 18-month period. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killer, H.E.; Pircher, A. Normal tension glaucoma: Review of current understanding and mechanisms of the pathogenesis. Eye 2018, 32, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, J.; Devi, L.; Malik, P.K.; Mallick, J. Update on Normal Tension Glaucoma. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2016, 11, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetry, D.; Singh, J.; Chhetri, A.; Katiyar, V.K.; Singh, D.S. Effect of yoga on intra-ocular pressure in patients with glaucoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 71, 1757–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shields, M.B. Normal-tension glaucoma: Is it different from primary open-angle glaucoma? Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2008, 19, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, F.; Papadopoulos, M.; Khaw, P.T. Chapter 9—Primary congenital glaucoma. In Progress in Brain Research; Bagetta, G., Nucci, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 221, pp. 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, J. Congenital glaucoma and its inheritance. Ophthalmologica 1980, 181, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allingham, R.; Damji, K.; Freeman, S.; Moroi, S.; Shafranov, G. Congenital glaucomas and developmental glaucomas with associated anomalies. Shields Textb. Glaucoma 2005, 5, 235–271. [Google Scholar]
- Badawi, A.H.; Al-Muhaylib, A.A.; Al Owaifeer, A.M.; Al-Essa, R.S.; Al-Shahwan, S.A. Primary congenital glaucoma: An updated review. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 33, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, M.; Lui, F. Neuroanatomy, Neural Crest; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.L.; Walton, D.S. Primary Congenital Glaucoma: 2004 Update. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2004, 41, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J. Secondary glaucoma. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2000, 83, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barac, I.R.; Pop, M.D.; Gheorghe, A.I.; Taban, C. Neovascular Secondary Glaucoma, Etiology and Pathogenesis. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 59, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.-Q.; Yao, L.; Wang, D.-B.; Jin, R.; Wang, Y.-X. Causes and Treatments of Traumatic Secondary Glaucoma. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 19, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, G.B.; Abe, R.Y.; Zangalli, C.; Sodre, S.L.; Donini, F.A.; Costa, D.C.; Leite, A.; Felix, J.P.; Torigoe, M.; Diniz-Filho, A.; et al. Neovascular glaucoma: A review. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2016, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiello, L.P.; Avery, R.L.; Arrigg, P.G.; Keyt, B.A.; Jampel, H.D.; Shah, S.T.; Pasquale, L.R.; Thieme, H.; Iwamoto, M.A.; Park, J.E. Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 331, 1480–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.C.; Borisuth, N.S.; Tripathi, B.J. Detection, quantification, and significance of basic fibroblast growth factor in the aqueous humor of man, cat, dog and pig. Exp. Eye Res. 1992, 54, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyadurupola, N.; Broadway, D.C. Pigment dispersion syndrome and pigmentary glaucoma—A major review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 36, 868–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.W.; Sakiyalak, D.; Krupin, T. Pigmentary glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2001, 10, S30–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglior, S.; Bertuzzi, F. Chapter 12–Exfoliative glaucoma: New evidence in the pathogenesis and treatment. In Progress in Brain Research; Bagetta, G., Nucci, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 221, pp. 233–241. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, M.; Kee, C. Initial central scotomas vs peripheral scotomas in normal-tension glaucoma: Clinical characteristics and progression rates. Eye 2014, 28, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarieh, M.; Flammer, J. New insights in the pathogenesis and treatment of normal tension glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doucette, L.P.; Rasnitsyn, A.; Seifi, M.; Walter, M.A. The interactions of genes, age, and environment in glaucoma pathogenesis. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2015, 60, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudnicka, A.R.; Mt-Isa, S.; Owen, C.G.; Cook, D.G.; Ashby, D. Variations in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Prevalence by Age, Gender, and Race: A Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 4254–4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuck, M.W.; Crick, R.P. The age distribution of primary open angle glaucoma. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 1998, 5, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toris, C.B.; Yablonski, M.E.; Wang, Y.L.; Camras, C.B. Aqueous humor dynamics in the aging human eye. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 127, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabelt, B.A.T.; Kaufman, P.L. Changes in aqueous humor dynamics with age and glaucoma. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2005, 24, 612–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggs, J.L.; Pasquale, L.R. Genetics of glaucoma. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R21–R27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.F.; Gaier, E.D.; Wiggs, J.L. Genetics of primary inherited disorders of the optic nerve: Clinical applications. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a017277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.; Picciani, R.G.; Lee, R.K.; Bhattacharya, S.K. Aqueous humor dynamics: A review. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2010, 4, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, M.; Yağcı, R.; Erdurmuş, M. Chapter 9–Glaucoma and Antioxidant Status. In Handbook of Nutrition, Diet and the Eye; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Hassan, D.W.; Acott, T.S.; Kelley, M.J. The trabecular meshwork: A basic review of form and function. J. Ocul. Biol. 2014, 2, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.S.; Mohindroo, C.; Weinreb, R.N. Aqueous humor outflow structure and function imaging at the bench and bedside: A review. J. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 7, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Yoo, C.; Chung, H.W.; Kim, Y.Y. Effect of prostaglandin analogues on anterior scleral thickness and corneal thickness in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costagliola, C.; Dell’Omo, R.; Agnifili, L.; Bartollino, S.; Fea, A.M.; Uva, M.G.; Zeppa, L.; Mastropasqua, L. How many aqueous humor outflow pathways are there? Surv. Ophthalmol. 2020, 65, 144–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toris, C.B.; Gagrani, M.; Ghate, D. Current methods and new approaches to assess aqueous humor dynamics. Expert Rev. Ophthalmol. 2021, 16, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; McLaren, J.W.; Overby, D.R. Unconventional aqueous humor outflow: A review. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 158, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Toris, C.B.; B’Ann, T.G.; Lindsey, J.D.; Kaufman, P.L. Effects of prostaglandins on the aqueous humor outflow pathways. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2002, 47, S53–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Mackey, D.A. Glaucoma—Risk factors and current challenges in the diagnosis of a leading cause of visual impairment. Maturitas 2022, 163, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D. Glaucoma Diagnosis and Management; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shiose, Y. Intraocular pressure: New perspectives. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1990, 34, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, R.A. The Goldmann Applanation Tonometer. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1958, 46, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloster, J.; Perkins, E. The validity of the Imbert-Fick law as applied to applanation tonometry. Exp. Eye Res. 1963, 2, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.A.; Botello, A.P.; Elders, A.; Fathi Ali, A.; Azuara-Blanco, A.; Fraser, C.; McCormack, K.; Margaret Burr, J. Systematic Review of the Agreement of Tonometers with Goldmann Applanation Tonometry. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1552–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppieri, M.; Gurnani, B. Applanation Tonometry. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.; Sheu, M.; Hsu, A.; Wu, K.; Yeh, J.; Tien, J.; Tsai, R. Comparisons of intraocular pressure measurements: Goldmann applanation tonometry, noncontact tonometry, Tono-Pen tonometry, and dynamic contour tonometry. Eye 2009, 23, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.; Pandav, S.S. Ocular response analyzer. J. Curr. Glaucoma Pract. 2012, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamper, R.L. A history of intraocular pressure and its measurement. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, E16–E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, I. Understanding and caring for a Schiotz tonometer. Community Eye Health 2014, 27, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Bhan, A.; Browning, A.C.; Shah, S.; Hamilton, R.; Dave, D.; Dua, H.S. Effect of corneal thickness on intraocular pressure measurements with the pneumotonometer, Goldmann applanation tonometer, and Tono-Pen. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1389–1392. [Google Scholar]
- Mok, K.H.; Wong, C.S.-L.; Lee, V.W.-H. Tono-Pen tonometer and corneal thickness. Eye 1999, 13, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Sony, P.; Agarwal, H.C.; Sihota, R.; Sharma, A. Inter-instrument agreement and influence of central corneal thickness on measurements with Goldmann, pneumotonometer and noncontact tonometer in glaucomatous eyes. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2006, 54, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutzscher, A.E.; Kumar, R.S.; Ramgopal, B.; Rackenchath, M.V.; Sathi, D.; Nagaraj, S.; Moe, C.A.; Fry, D.M.; Stamper, R.L.; Keenan, J.D. Reproducibility of 5 Methods of Ocular Tonometry. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2019, 2, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.C.; Liu, C.J.; Hsu, W.M. Varying effects of corneal thickness on intraocular pressure measurements with different tonometers. Eye 2005, 19, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belovay, G.W.; Goldberg, I. The thick and thin of the central corneal thickness in glaucoma. Eye 2018, 32, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, F.A.; Weinreb, R.N. Is corneal thickness an independent risk factor for glaucoma? Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellman, R. Gonioscopy. In Atlas of Glaucoma; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 57–76. [Google Scholar]
- Selhorst, J.B.; Chen, Y. The Optic Nerve. Semin. Neurol. 2009, 29, 029–035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.B.; Budde, W.M.; Panda-Jonas, S. Ophthalmoscopic Evaluation of the Optic Nerve Head. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1999, 43, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.A.; Cioffi, G.A.; Liebmann, J.R.; Sample, P.A.; Zangwill, L.M.; Weinreb, R.N. The relationship between structural and functional alterations in glaucoma: A review. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2000, 15, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, D.S.; Weinreb, R.N. Role of Optic Nerve Imaging in Glaucoma Clinical Practice and Clinical Trials. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 145, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.R.F.; Gommer, E.D.; Aries, M.J.H.; Ertl, M.; Mess, W.H.; Huberts, W.; Delhaas, T. Optic nerve sheath diameter assessment by neurosonology: A review of methodologic discrepancies. J. Neuroimaging 2021, 31, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waisberg, E.; Micieli, J.A. Neuro-Ophthalmological Optic Nerve Cupping: An Overview. Eye Brain 2021, 13, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cong, J.; Sun, Z.; Du, Y.; Yang, G.; Ding, D.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, G. Stereoscopic vs. monoscopic photographs on optic disc evaluation and glaucoma diagnosis among general ophthalmologists: A cloud-based real-world multicenter study. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 990611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podoleanu, A.G. Optical coherence tomography. J. Microsc. 2012, 247, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRocca, F.; Dhalla, A.-H.; Kelly, M.; Farsiu, S.; Izatt, J. Optimization of confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope design. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 076015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrescu, C.; Dascalu, A.M.; Panca, A.; Sescioreanu, A.; Mitulescu, C.; Ciuluvica, R.; Voinea, L.; Celea, C. Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscopy in glaucoma diagnosis and management. J. Med. Life 2010, 3, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Dada, T.; Sharma, R.; Angmo, D.; Sinha, G.; Bhartiya, S.; Mishra, S.K.; Panda, A.; Sihota, R. Scanning laser polarimetry in glaucoma. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsapakis, S.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Diagourtas, A.; Kandarakis, S.; Droutsas, K.; Andreanos, K.; Brouzas, D. Home-based visual field test for glaucoma screening comparison with Humphrey perimeter. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 12, 2597–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingeret, M.; Gaddie, I.B.; Bloomenstein, M. Latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic solution 0.024%: A new treatment option for open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leske, M.C.; Heijl, A.; Hussein, M.; Bengtsson, B.; Hyman, L.; Komaroff, E.; Group, E.M.G.T. Factors for glaucoma progression and the effect of treatment: The early manifest glaucoma trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijl, A. Glaucoma treatment: By the highest level of evidence. Lancet 2015, 385, 1264–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Gutiérrez, Á.; Baladrón, V. The role of prostaglandins in different types of cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhan, W.; Wei, X. Clinical pharmacology and pharmacogenetics of prostaglandin analogues in glaucoma. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1015338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Matsugi, T.; Goto, W.; Kageyama, M.; Mori, N.; Matsumura, Y.; Hara, H. New fluoroprostaglandin F2α derivatives with prostanoid FP-receptor agonistic activity as potent ocular-hypotensive agents. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 1691–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, W.J. A retrospective review of non-responders to latanoprost. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 18, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.G.; Group, L.S. Latanoprost: Two years’ experience of its use in the United Kingdom. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, A. Latanoprost in the treatment of glaucoma. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 1967–1985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tatham, A.J. The Use of Generic Medications for Glaucoma. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 2020, 1651265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asendrych-Wicik, K.; Zarczuk, J.; Walaszek, K.; Ciach, T.; Markowicz-Piasecka, M. Trends in development and quality assessment of pharmaceutical formulations-F2α analogues in the glaucoma treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 180, 106315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bito, L.Z.; Baroody, R.A. The ocular pharmacokinetics of eicosanoids and their derivatives. 1. Comparison of ocular eicosanoid penetration and distribution following the topical application of PGF2α, PGF2α-1-methyl ester, and PGF2α-1-isopropyl ester. Exp. Eye Res. 1987, 44, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stjernschantz, J.W. From PGF2α-Isopropyl Ester to Latanoprost: A Review of the Development of Xalatan the Proctor Lecture. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 1134–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist, B.; Stjernschantz, J. Ocular and systemic pharmacokinetics of latanoprost in humans. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2002, 47, S6–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camras, C.B.; Alm, A. Initial clinical studies with prostaglandins and their analogues. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41, S61–S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, A.; Camras, C.B.; Watson, P.G. Phase III latanoprost studies in Scandinavia, the United Kingdom and the United States. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41, S105–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedman, K.; Watson, P.G.; Alm, A. The effect of latanoprost on intraocular pressure during 2 years of treatment. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2002, 47, S65–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, A.; Widengård, I. Latanoprost: Experience of 2-year treatment in Scandinavia. Acta Ophthalmol. Scand. 2000, 78, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alm, A.; Schoenfelder, J.; McDermott, J. A 5-Year, Multicenter, Open-Label, Safety Study of Adjunctive LatanoprostTherapy for Glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garway-Heath, D.F.; Crabb, D.P.; Bunce, C.; Lascaratos, G.; Amalfitano, F.; Anand, N.; Azuara-Blanco, A.; Bourne, R.R.; Broadway, D.C.; Cunliffe, I.A. Latanoprost for open-angle glaucoma (UKGTS): A randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, S.; Rosenfeld, E.; Shemesh, G.; Kurtz, S. Original and generic latanoprost for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension: Are they really the same? Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, D.F.; Phelps, R.L.; Krauss, A.H.-P.; Weber, A.; Short, B.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Wheeler, L.A. Bimatoprost: A Novel Antiglaucoma Agent. Cardiovasc. Drug Rev. 2004, 22, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamer, W.D.; Perkumas, K.M.; Kang, M.H.; Dibas, M.; Robinson, M.R.; Rhee, D.J. Proposed Mechanism of Long-Term Intraocular Pressure Lowering with the Bimatoprost Implant. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, D.F.; Krauss, A.H.-P.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y.; Li, C.; Protzman, C.E.; Bogardus, A.; Chen, R.; Kedzie, K.M.; Krauss, H.A.; et al. Pharmacological Characterization of a Novel Antiglaucoma Agent, Bimatoprost (AGN 192024). J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brubaker, R.F. Mechanism of Action of Bimatoprost (Lumigan™). Surv. Ophthalmol. 2001, 45, S347–S351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodward, D.F.; Krauss, A.H.P.; Chen, J.; Lai, R.K.; Spada, C.S.; Burk, R.M.; Andrews, S.W.; Shi, L.; Liang, Y.; Kedzie, K.M.; et al. The Pharmacology of Bimatoprost (Lumigan™). Surv. Ophthalmol. 2001, 45, S337–S345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Z.; Woodward, D.F.; Cornell, C.L.; Fliri, H.G.; Martos, J.L.; Pettit, S.N.; Wang, J.W.; Kharlamb, A.B.; Wheeler, L.A.; Garst, M.E. Bimatoprost, prostamide activity, and conventional drainage. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4107–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noecker, R.S.; Dirks, M.S.; Choplin, N.T.; Bernstein, P.; Batoosingh, A.L.; Whitcup, S.M. A six-month randomized clinical trial comparing the intraocular pressure-lowering efficacy of bimatoprost and latanoprost in patients with ocular hypertension or glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 135, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrish, R.K.; Palmberg, P.; Sheu, W.-P.; Group, X.S. A comparison of latanoprost, bimatoprost, and travoprost in patients with elevated intraocular pressure: A 12-week, randomized, masked-evaluator multicenter study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 135, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.S.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Sukumaran, S.; Koyiparambath, V.P.; Pappachen, L.K.; Rangarajan, T.M.; Kim, H.; Mathew, B. FDA-Approved Trifluoromethyl Group-Containing Drugs: A Review of 20 Years. Processes 2022, 10, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yale, H.L. The Trifluoromethyl Group in Medical Chemistry. J. Med. Pharm. Chem. 1959, 1, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orengo-Nania, S.; Landry, T.; Von Tress, M.; Silver, L.H.; Weiner, A.; Davis, A.A.; Group, T.S. Evaluation of travoprost as adjunctive therapy in patients with uncontrolled intraocular pressure while using timolol 0.5%. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 132, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellberg, M.R.; Sallee, V.L.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Sharif, N.A.; Desantis, L.; Dean, T.R.; Zinke, P.W. Preclinical efficacy of travoprost, a potent and selective FP prostaglandin receptor agonist. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 17, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waugh, J.; Jarvis, B. Travoprost. Drugs Aging 2002, 19, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netland, P.A.; Landry, T.; Sullivan, E.K.; Andrew, R.; Silver, L.; Weiner, A.; Mallick, S.; Dickerson, J.; Bergamini, M.; Robertson, S. Travoprost compared with latanoprost and timolol in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 132, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, I.; Cunha-Vaz, J.; Jakobsen, J.-E.; Nordmann, J.-P.; Trost, E.; Sullivan, E.K.; Group, I.T.S. Comparison of topical travoprost eye drops given once daily and timolol 0.5% given twice daily in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. J. Glaucoma 2001, 10, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadia, M.; Bagnis, A.; Scotto, R.; Traverso, C.E. Tafluprost for glaucoma. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2011, 12, 2393–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukano, Y.; Kawazu, K. Disposition and metabolism of a novel prostanoid antiglaucoma medication, tafluprost, following ocular administration to rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, A.; Gouws, P.; Ropo, A. Tafluprost, a new potent prostanoid receptor agonist: A dose-response study on pharmacodynamics and tolerability in healthy volunteers. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 46, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traverso, C.E.; Ropo, A.; Papadia, M.; Uusitalo, H. A phase II study on the duration and stability of the intraocular pressure-lowering effect and tolerability of Tafluprost compared with latanoprost. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihara, M. Clinical appraisal of tafluprost in the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2010, 4, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, E.; Ropo, A.; Group, T.a.t.S. Adjunctive use of tafluprost with timolol provides additive effects for reduction of intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 19, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, S.M. Latanoprostene Bunod Ophthalmic Solution 0.024%: A Review in Open-Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension. Drugs 2018, 78, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoonen, R.; Sips, P.Y.; Bloch, K.D.; Buys, E.S. Pathophysiology of hypertension in the absence of nitric oxide/cyclic GMP signaling. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2013, 15, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buys, E.S.; Potter, L.R.; Pasquale, L.R.; Ksander, B.R. Regulation of intraocular pressure by soluble and membrane guanylate cyclases and their role in glaucoma. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavet, M.E.; DeCory, H.H. The role of nitric oxide in the intraocular pressure lowering efficacy of latanoprostene bunod: Review of nonclinical studies. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muenster, S.; Lieb, W.S.; Fabry, G.; Allen, K.N.; Kamat, S.S.; Guy, A.H.; Dordea, A.C.; Teixeira, L.; Tainsh, R.E.; Yu, B. The ability of nitric oxide to lower intraocular pressure is dependent on guanylyl cyclase. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 4826–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavet, M.E.; Vittitow, J.L.; Impagnatiello, F.; Ongini, E.; Bastia, E. Nitric oxide (NO): An emerging target for the treatment of glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 5005–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, I.M.; Ostwald, P.; Roth, S. Nitric oxide: A review of its role in retinal function and disease. Vis. Res. 1996, 36, 2979–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, N.; Nakanishi-Toda, M. Nitric oxide: Ocular blood flow, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 205–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmetterer, L.; Polak, K. Role of nitric oxide in the control of ocular blood flow. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2001, 20, 823–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, A.H.; Impagnatiello, F.; Toris, C.B.; Gale, D.C.; Prasanna, G.; Borghi, V.; Chiroli, V.; Chong, W.K.; Carreiro, S.T.; Ongini, E. Ocular hypotensive activity of BOL-303259-X, a nitric oxide donating prostaglandin F2α agonist, in preclinical models. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, T.; Tsuruga, H.; Aihara, M.; Araie, M.; Rittenhouse, K. Dose-response profile of PF-03187207 (PF-207) and peak IOP lowering response following single topical administration to FP receptor knockout mice vs. wild type mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4064. [Google Scholar]
- Cavet, M.E.; Vollmer, T.R.; Harrington, K.L.; VanDerMeid, K.; Richardson, M.E. Regulation of endothelin-1–induced trabecular meshwork cell contractility by latanoprostene bunod. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araie, M.; Sforzolini, B.S.; Vittitow, J.; Weinreb, R.N. Evaluation of the effect of latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic solution, 0.024% in lowering intraocular pressure over 24 h in healthy Japanese subjects. Adv. Ther. 2015, 32, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Ong, T.; Sforzolini, B.S.; Vittitow, J.L.; Singh, K.; Kaufman, P.L. A randomised, controlled comparison of latanoprostene bunod and latanoprost 0.005% in the treatment of ocular hypertension and open angle glaucoma: The VOYAGER study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, F.A.; Martin, K.R.; Peace, J.; Sforzolini, B.S.; Vittitow, J.L.; Weinreb, R.N. Comparison of latanoprostene bunod 0.024% and timolol maleate 0.5% in open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: The LUNAR study. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 168, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Sforzolini, B.S.; Vittitow, J.; Liebmann, J. Latanoprostene bunod 0.024% versus timolol maleate 0.5% in subjects with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: The APOLLO study. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Liebmann, J.M.; Martin, K.R.; Kaufman, P.L.; Vittitow, J.L. Latanoprostene bunod 0.024% in subjects with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: Pooled phase 3 study findings. J. Glaucoma 2018, 27, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawase, K.; Vittitow, J.L.; Weinreb, R.N.; Araie, M.; JUPITER Study Group. Long-term safety and efficacy of latanoprostene bunod 0.024% in Japanese subjects with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension: The JUPITER study. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 1612–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, N.V.; Toris, C.B. Current status of unoprostone for the management of glaucoma and the future of its use in the treatment of retinal disease. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2013, 14, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacherjee, P.; Paterson, C.A.; Percicot, C. Studies on receptor binding and signal transduction pathways of unoprostone isopropyl. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 17, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg, D.L.; Camras, C.B. A Preliminary Risk-Benefit Assessment of Latanoprost and Unoprostone in Open-Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension. Drug Saf. 1999, 20, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, C.A.; Kaufman, P.L.; Kiland, J.A. Benzalkonium chloride and glaucoma. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 30, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, C.; Stolwijk, T.; Kuppens, E.; de Keizer, R.; van Best, J. Topical timolol with and without benzalkonium chloride: Epithelial permeability and autofluorescence of the cornea in glaucoma. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1994, 232, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, L.; Ferreras, A.; Iester, M. Timolol 0.1% in Glaucomatous Patients: Efficacy, Tolerance, and Quality of Life. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 4146124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, A.M.; Gillies, W.E. Ocular beta-blockers in glaucoma management. Clinical pharmacological aspects. Drugs Aging 1992, 2, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demailly, P. Biodisponibilité des medicaments hypotonisants. J. Français D’ophtalmologie 2000, 23, 518–522. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzo, D.J.; Loper, A.E. Timolol Maleate. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1987; Volume 16, pp. 641–692. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, C.; Gerber, J.G.; Gal, J.; Nies, A.S. Beta-adrenergic receptors in the elderly are not less sensitive to timolol. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1986, 40, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Chiou, G. Action mechanism of timolol to lower the intraocular pressure in rabbits. Ophthalmic Res. 1983, 15, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, T.J.; Kaufman, H.E. Timolol: Dose response and duration of action. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1977, 95, 605–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, T.J.; Kaufman, H.E. Timolol: A β-adrenergic blocking agent for the treatment of glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1977, 95, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, C.G.; Zhu, Y.P.; Frier, M.; Rao, L.; Gilchrist, P.; Perkins, A.C. Ocular contact time of a carbomer gel (GelTears) in humans. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 82, 1131–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Valk, R.; Webers, C.A.; Schouten, J.S.; Zeegers, M.P.; Hendrikse, F.; Prins, M.H. Intraocular pressure–lowering effects of all commonly used glaucoma drugs: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ophthalmology 2005, 112, 1177–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouland, J.-F.; Morel-Mandrino, P.; Elena, P.-P.; Polzer, H.; Sunder Raj, P. Timolol 0.1% gel (Nyogel 0.1%®) once daily versus conventional timolol 0.5% solution twice daily: A comparison of efficacy and safety. Ophthalmologica 2002, 216, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buskirk, E.M. Adverse reactions from timolol administration. Ophthalmology 1980, 87, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, T.J.; Baumann, J.D.; Hetherington, J. Side effects of timolol. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1983, 28, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenwald, R.D.; Huang, H.S. Corneal penetration behavior of β-blocking agents I: Physicochemical factors. J. Pharm. Sci. 1983, 72, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlo, F.J.D.; Leinweber, F.-J.; Szpiech, J.M.; Davidson, I.W. Metabolism of l-bunolol. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1977, 22, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, U.; Vollmer, K. Binding of beta-adrenoceptor antagonists to rat and rabbit lung: Special reference to levobunolol. Arzneim.-Forsch. 1984, 34, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Novack, G.D. Levobunolol for the long-term treatment of glaucoma. Gen. Pharmacol. 1986, 17, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, J.P.; Clissold, S.P. Ocular Levobunolol. Drugs 1987, 34, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensinger, R.E.; Keates, E.U.; Gofman, J.D.; Novack, G.D.; Duzman, E. Levobunolol: A three-month efficacy study in the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1985, 103, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandel, T.; Charap, A.D.; Lewis, R.A.; Partamian, L.; Cobb, S.; Lue, J.C.; Novack, G.D.; Gaster, R.; Smith, J.; Duzman, E. Glaucoma Treatment with Once-Daily Levobunolol. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 101, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, F.G.; Cohen, H.B.; Foerster, R.J.; Lass, J.H.; Novack, G.D.; Duzman, E. Levobunolol compared with timolol for the long-term control of elevated intraocular pressure. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1985, 103, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henness, S.; Harrison, T.S.; Keating, G.M. Ocular carteolol: A review of its use in the management of glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Drugs Aging 2007, 24, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, M.; Brémont, B.; Rousselle, D.; Gaudy, F. Structural analysis by the comparative molecular field analysis method of the affinity of β-adrenoreceptor blocking agents for 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 244, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujio, N.; Kusumoto, N.; Odomi, M. Ocular distribution of carteolol after single and repeated ocular instillation in pigmented rabbits. Acta Ophthalmol. 1994, 72, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Uchida, M.; Odomi, M. Metabolism of carteolol by cDNA-expressed human cytochrome P450. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 52, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Matsuki, S.; Uemura, N.; Muraguchi, R.; Nakagawa, M.; Nakano, S.; Nakatsuka, K. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic differences between ocular and nasal instillation of carteolol on intraocular pressure and heart rate in Japanese men with high CYP2D6 activity. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 42, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier, D.; Smith, S. Ocular and cardiovascular response to topical carteolol 2% and timolol 0.5% in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1988, 72, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuki, K.; Yamazaki, Y. Effect of carteolol hydrochloride on ocular blood flow dynamics in normal human eyes. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 44, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.G.; Barnett, M.F.; Parker, V.; Haybittle, J. A 7 year prospective comparative study of three topical β blockers in the management of primary open angle glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 85, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Tai, M.-C.; Lu, D.-W. Efficacy and safety of carteolol long-acting solution 2% compared with timolol gel-forming solution 0.5% in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension: A randomized, parallel-group, open-label phase IV study in Taiwan. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 34, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Jensvold-Vetsch, B. Drug-Induced Ocular Side Effects; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, I. Betaxolol. Aust. N. Z. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 17, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Ganellin, C.R. Analogue-based drug discovery. Chem. Int. Newsmag. IUPAC 2010, 32, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.C.; Hertzmark, E.; Walker, A.M.; Epstein, D.L. A double-masked comparison of betaxolol vs timolol in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 101, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Caldwell, D.R.; Goode, S.M.; Horwitz, B.L.; Laibovitz, R.; Shrader, C.E.; Stewart, R.H.; Williams, A.T. A double-masked three-month comparison between 0.25% betaxolol suspension and 0.5% betaxolol ophthalmic solution. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1990, 110, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, N.; Cazevieille, C.; Carvalho, A.; Larsen, A.; DeSantis, L. In vivo and in vitro experiments show that betaxolol is a retinal neuroprotective agent. Brain Res. 1997, 751, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abshagen, U.; Betzien, G.; Kaufmann, B.; Endele, G. Pharmacokinetics of metipranolol in normal man. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1982, 21, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dausch, D.; Brewitt, H.; Edelhoff, R. Metipranolol Eye Drops—Clinical Suitability in the Treatment of Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Merte, H.; Stryz, J.; Mertz, M. Comparative studies of initial pressure reduction using 0.3% metipranolol and 0.25% timolol in eyes with wide-angle glaucoma. Klin. Monatsblatter Fur Augenheilkd. 1983, 182, 286–289. [Google Scholar]
- Battershill, P.E.; Sorkin, E.M. Ocular metipranolol: A preliminary review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic efficacy in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Drugs 1988, 36, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demailly, P.; Lecherpie, F. Métipranolol 0, 1%: L’effet d’une dose unique sur la courbe tensionnelle nycthémérale d’un œil porteur d’un glaucome chronique primitif à angle ouvert. J. Français D’Ophtalmologie 1987, 10, 447–449. [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, A.C.; Conemans, J. Contact allergy to metipranolol. Contact Dermat. 1988, 18, 107–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, S.; Cantor, L.B. Update on the role of alpha-agonists in glaucoma management. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, J.R. Subtypes of functional α1-adrenoceptor. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilsbach, R.; Röser, C.; Beetz, N.; Brede, M.; Hadamek, K.; Haubold, M.; Leemhuis, J.; Philipp, M.; Schneider, J.; Urbanski, M. Genetic dissection of α2-adrenoceptor functions in adrenergic versus nonadrenergic cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, P.L.; Gabelt, B.A. α2Adrenergic Agonist Effects on Aqueous Humor Dynamics. J. Glaucoma 1995, 4, S8–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsamer, H.; Posey, M.; Kiel, J. Effects of a topical α2 adrenergic agonist on ciliary blood flow and aqueous production in rabbits. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittag, T.; Tormay, A. Drug responses of adenylate cyclase in iris-ciliary body determined by adenine labelling. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1985, 26, 396–399. [Google Scholar]
- Costagliola, C.; Dell’Omo, R.; Romano, M.R.; Rinaldi, M.; Zeppa, L.; Parmeggiani, F. Pharmacotherapy of intraocular pressure: Part I. Parasympathomimetic, sympathomimetic and sympatholytics. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2009, 10, 2663–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamer, W.D.; Huang, Y.; Seftor, R.; Svensson, S.; Snyder, R.W.; Regan, J.W. Cultured human trabecular meshwork cells express functional alpha 2A adrenergic receptors. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 2426–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, T.; Ohguro, H.; Mamiya, K.; Ohguro, I.; Nakazawa, M. Effects of antiglaucoma drops on MMP and TIMP balance in conjunctival and subconjunctival tissue. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkouh, A.; Frigo, P.; Czejka, M. Systemic side effects of eye drops: A pharmacokinetic perspective. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 2433–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jampel, H.D.; Robin, A.L.; Quigley, H.A.; Pollack, I.P. Apraclonidine: A one-week dose-response study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1988, 106, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasubramanian, S.; Hitchings, R.A.; Demailly, P.; Chuniaud, M.; Pannarale, M.R.; Pecori-Giraldi, J.; Stodtmeister, R.; Parsons, D.G. Comparison of apraclonidine and timolol in chronic open-angle glaucoma: A three-month study. Ophthalmology 1993, 100, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.C.; Robin, A.L. Adjunctive glaucoma therapy: A comparison of apraclonidine to dipivefrin when added to timolol maleate. Ophthalmology 1989, 96, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasini, M.; Shields, M.B. Apraclonidine hydrochloride as an adjunct to timolol maleate therapy. J. Glaucoma 1992, 1, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vocci, M.J.; Robin, A.L.; Wahl, J.C.; Mayer, P.; Graves, A.; York, B.; Enger, C.; Sutton, J. Reformulation and drop size of apraclonidine hydrochloride. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1992, 113, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, D.-S.; Homsy, J.J.; Gluchowski, C.; Tang-Liu, D.D.-S. Corneal and conjunctival/scleral penetration of p-aminoclonidine, AGN 190342, and clonidine in rabbit eyes. Curr. Eye Res. 1990, 9, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, G.; Kunikane, E.; Shigemi, W.; Shinno, K.; Kozai, S.; Kurata, M.; Kawamura, A. Ocular and systemic pharmacokinetics of brimonidine and brinzolamide after topical administration in rabbits: Comparison between fixed-combination and single-drug formulations. Curr. Eye Res. 2021, 46, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adkins, J.C.; Balfour, J.A. Brimonidine. Drugs Aging 1998, 12, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A.; Tang-Liu, D.D. Measurement of brimonidine concentrations in human plasma by a highly sensitive gas chromatography/mass spectrometric assay. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1995, 13, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheampong, A.A.; Chien, D.S.; Lam, S.; Vekich, S.; Breau, A.; Usansky, J.; Harcourt, D.; Munk, S.A.; Nguyen, H.; Garst, M.; et al. Characterization of brimonidine metabolism with rat, rabbit, dog, monkey and human liver fractions and rabbit liver aldehyde oxidase. Xenobiotica 1996, 26, 1035–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derick, R.J.; Robin, A.L.; Walters, T.; Barnebey, H.S.; Choplin, N.; Schuman, J.; Kelley, E.P.; Chen, K.; Stoecker, J.F. Brimonidine tartrate: A one-month dose response study. Ophthalmology 1997, 104, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, T.R. Development and use of brimonidine in treating acute and chronic elevations of intraocular pressure: A review of safety, efficacy, dose response, and dosing studies. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1996, 41, S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serle, J.B.; The Brimonidine Study Group III. A comparison of the safety and efficacy of twice daily brimonidine 0.2% versus betaxolol 0.25% in subjects with elevated intraocular pressure. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1996, 41, S39–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuman, J.S. Clinical experience with brimonidine 0.2% and timolol 0.5% in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1996, 41, S27–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, D.F.; Lindsley, K. Neuroprotection for treatment of glaucoma in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 1, CD006539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, J.S.; Horwitz, B.; Choplin, N.T.; David, R.; Albracht, D.; Chen, K. A 1-year study of brimonidine twice daily in glaucoma and ocular hypertension: A controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997, 115, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, I.P.; Smitha, R.; Aggarwal, D.; Kapil, M. Acetazolamide: Future perspective in topical glaucoma therapeutics. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 248, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supuran, C.T.; Altamimi, A.S.A.; Carta, F. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition and the management of glaucoma: A literature and patent review 2013–2019. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyei, S.; Adu, P.; Wiredu, F.; Antwi, E.; Baidoo, E. Safety Concerns of Glaucoma Chemotherapy among G6PD Deficient Glaucoma Patients: A Pilot Study. J. Hematol. Blood Disord. 2019, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Glaucoma and the applications of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Subcell Biochem. 2014, 75, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Th, M.; Robinson, B. The pharmacology of acetazolamide as related to cerebrospinal fluid and the treatment of hydrocephalus. Bull. Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1960, 106, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann, B.; Linnér, E.; Wistrand, P.J. The Pharmacokinetics of Acetazolamide in Relation to its Use in the Treatment of Glaucoma and to its Effects as an Inhibitor of Carbonic Anhydrases. In Proceedings of the Schering Workshop on Pharmacokinetics, Berlin, Germany, 8–9 May 1969; Raspé, G., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1970; pp. 197–217. [Google Scholar]
- Sisson, G.; Maren, T.H. Pharmacology of 5-acetylimino-4-methyl-Δ2-1, 3, 4-thiadiazoline-2-sulfonamide (CL 13,912), a new carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Fed. Proc. 1956, 15, 430–484. [Google Scholar]
- Maren, T.; Haywood, J.; Chapman, S.; Zimmerman, T. The pharmacology of methazolamide in relation to the treatment of glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1977, 16, 730–742. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, B. Use of Methazolamide (Neptazane) in the Therapy of Glaucoma*: Comparison with Acetazolamide (Diamox). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1960, 49, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B. Carbonic anhydrase and the formation of aqueous humor: The Friedenwald Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1959, 47, 342–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, A.A.; Sayyad, F.E.; Ayres, B.; Lee, R.K. Acute bilateral angle closure glaucoma induced by methazolamide. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2013, 7, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jiang, S.; Liu, D.; Bi, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Q. A potential new therapeutic system for glaucoma: Solid lipid nanoparticles containing methazolamide. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, L.; Jiang, S.; He, J.; Zhang, X.; Peng, J.; Xu, Q.; Li, R. Optimization of methazolamide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for ophthalmic delivery using Box–Behnken design. J. Liposome Res. 2014, 24, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, A.; Harris, A.; Oddone, F.; Belamkar, A.; Vercellin, A.C.V.; Shin, J.; Januleviciene, I.; Siesky, B. Topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and glaucoma in 2021: Where do we stand? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Banditt, P. Clinical pharmacokinetics of dorzolamide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2002, 41, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balfour, J.A.; Wilde, M.I. Dorzolamide. Drugs Aging 1997, 10, 384–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugrue, M.F. Pharmacological and ocular hypotensive properties of topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2000, 19, 87–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippa, E.A.; Carlson, L.-E.; Ehinger, B.; Eriksson, L.-O.; Finnström, K.; Holmin, C.; Nilsson, S.-E.G.; Nyman, K.; Raitta, C.; Ringvold, A. Dose response and duration of action of dorzolamide, a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konowal, A.; Morrison, J.; Brown, S.; Cooke, D.; Maguire, L.; Verdier, D.; Fraunfelder, F.; Dennis, R.; Epstein, R. Irreversible corneal decompensation in patients treated with topical dorzolamide. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 127, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamsons, I. Irreversible corneal decompensation in patients treated with topical dorzolamide. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 128, 774–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, N. Dorzolamide: Development and clinical application of a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1997, 42, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iester, M. Brinzolamide ophthalmic suspension: A review of its pharmacology and use in the treatment of open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2008, 2, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetkovic, R.S.; Perry, C.M. Brinzolamide. Drugs Aging 2003, 20, 919–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, L.H. Clinical efficacy and safety of brinzolamide (Azopt™), a new topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor for primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 126, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusthaus, J.A.; Goldberg, I. Brimonidine and brinzolamide for treating glaucoma and ocular hypertension; a safety evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 16, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnebey, H.; Kwok, S.Y. Patients’ acceptance of a switch from dorzolamide to brinzolamide for the treatment of glaucoma in a clinical practice setting. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riento, K.; Ridley, A.J. Rocks: Multifunctional kinases in cell behaviour. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiberg, J.C.; von Spreckelsen, A.; Kolko, M.; Azuara-Blanco, A.; Virgili, G. Rho kinase inhibitor for primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 6, 1465–1858. [Google Scholar]
- Wettschureck, N.; Offermanns, S. Rho/Rho-kinase mediated signaling in physiology and pathophysiology. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 80, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukata, Y.; Kaibuchi, K.; Amano, M. Rho–Rho-kinase pathway in smooth muscle contraction and cytoskeletal reorganization of non-muscle cells. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2001, 22, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honjo, M.; Tanihara, H.; Inatani, M.; Kido, N.; Sawamura, T.; Yue, B.Y.; Narumiya, S.; Honda, Y. Effects of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on intraocular pressure and outflow facility. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Goldhagen, B.; Proia, A.D.; Epstein, D.L.; Rao, P.V. Elevated levels of RhoA in the optic nerve head of human eyes with glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2012, 21, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.K.; Chang, R.T. An emerging treatment option for glaucoma: Rho kinase inhibitors. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rao, V.P.; Epstein, D.L. Rho GTPase/Rho kinase inhibition as a novel target for the treatment of glaucoma. BioDrugs 2007, 21, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, M.; Gupta, S.; Nair, A.B.; Dhanawat, M.; Sandal, S.; Morsy, M.A. Netarsudil: A new ophthalmic drug in the treatment of chronic primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-F.; Williamson, J.E.; Kopczynski, C.; Serle, J.B. Effect of 0.04% AR-13324, a ROCK, and norepinephrine transporter inhibitor, on aqueous humor dynamics in normotensive monkey eyes. J. Glaucoma 2015, 24, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.W.; Sherman, B.; Moore, L.A.; Laethem, C.L.; Lu, D.W.; Pattabiraman, P.P.; Rao, P.V.; deLong, M.A.; Kopczynski, C.C. Discovery and Preclinical Development of Netarsudil, a Novel Ocular Hypotensive Agent for the Treatment of Glaucoma. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacharach, J.; Dubiner, H.B.; Levy, B.; Kopczynski, C.C.; Novack, G.D.; AR-13324-CS202 Study Group. Double-masked, randomized, dose–response study of AR-13324 versus latanoprost in patients with elevated intraocular pressure. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serle, J.B.; Katz, L.J.; McLaurin, E.; Heah, T.; Ramirez-Davis, N.; Usner, D.W.; Novack, G.D.; Kopczynski, C.C. Two phase 3 clinical trials comparing the safety and efficacy of netarsudil to timolol in patients with elevated intraocular pressure: Rho kinase elevated IOP treatment trial 1 and 2 (ROCKET-1 and ROCKET-2). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 186, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahook, M.Y.; Serle, J.B.; Mah, F.S.; Kim, T.; Raizman, M.B.; Heah, T.; Ramirez-Davis, N.; Kopczynski, C.C.; Usner, D.W.; Novack, G.D. Long-term Safety and Ocular Hypotensive Efficacy Evaluation of Netarsudil Ophthalmic Solution: Rho Kinase Elevated IOP Treatment Trial (ROCKET-2). Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 200, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyng, P.F.J.; van Beek, L.M. Pharmacological Therapy for Glaucoma. Drugs 2000, 59, 411–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, G.L.; Sagesaka, A.; Todo, H.; Wierzba, K.; Sugibayashi, K. Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Pilocarpine After Application to Eyelid Skin of Rats. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 2942–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, A.B.; Kraus, G.P. Physiology, Cholinergic Receptors. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.K.; Agarwal, R.; Galpalli, N.D.; Srivastava, S.; Agrawal, S.S.; Saxena, R. Comparative efficacy of pilocarpine, timolol and latanoprost in experimental models of glaucoma. Methods Find Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 29, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaat, A.; Rosman, M.S.; Chien, J.L.; Mogil, R.S.; Ren, R.; Liebmann, J.M.; Ritch, R.; Park, S.C. Effect of Pilocarpine Hydrochloride on the Schlemm Canal in Healthy Eyes and Eyes with Open-Angle Glaucoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, L.S.; Galin, M.A. Dose response analysis of pilocarpine-induced ocular hypotension. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1970, 84, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drance, S.M. The dose response of human intraocular pressure of pilocarpine. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 1971, 6, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hitchings, R.A.; Powell, D.J. Pilocarpine and narrow-angle glaucoma. Trans. Ophthalmol. Soc. U K 1981, 101, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Noecker, R.; Miller, K.V. Benzalkonium chloride in glaucoma medications. Ocul. Surf. 2011, 9, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmier, J.K.; Hulme-Lowe, C.K.; Covert, D.W. Adjunctive therapy patterns in glaucoma patients using prostaglandin analogs. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2014, 8, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitson, J.T. Glaucoma: A review of adjunctive therapy and new management strategies. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2007, 8, 3237–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monem, A.S.; Ali, F.M.; Ismail, M.W. Prolonged effect of liposomes encapsulating pilocarpine HCl in normal and glaucomatous rabbits. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 198, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, C.L.; Poling, T.R.; Mint, J.O. A medical device/drug delivery system for treatment of glaucoma. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2009, 92, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavik, E.; Kuehn, M.H.; Kwon, Y.H. Novel drug delivery systems for glaucoma. Eye 2011, 25, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Types of Glaucoma | Associated Genes |
|---|---|
| Primary Open Angle Glaucoma (POAG) | MYOC (Myocilin) OPTN (Optineurin) CYP1B1 (Cytochrome P450 1B1) WDR36 (WD Repeat Domain 36) TMCO1 (Transmembrane and Coiled-Coil Domains 1) TXNRD2 (Thioredoxin Reductase 2) TBK1 (TANK binding kinase 1) |
| Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma (PACG) | ADAMTS10 (A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs 10) COL11A1 (Collagen Type XI Alpha 1 Chain) PCMTD1 (Protein-L-Isoaspartate O-Methyltransferase Domain Containing 1) GLC1N (Primary Congenital Glaucoma 1N) LOXL1 (Lysyl Oxidase-Like 1) |
| Normal Tension Glaucoma (NTG) | CDKN2B-AS1 (CDKN2B Antisense RNA 1) CAV1/CAV2 (Caveolin 1 and 2) SIX1/SIX6 (Sine Oculis Homeobox Homolog 1 and 6) TMEM136 (Transmembrane Protein 136) ABCC5 (ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 5) |
| Secondary Glaucoma | MYOC (Myocilin) CYP1B1 (Cytochrome P450 1B1) TBK1 (TANK Binding Kinase 1) ASB10 (Ankyrin Repeat and SOCS Box Containing 10) FOXC1 (Forkhead Box C1) |
| Primary Congenital Glaucoma (PCG) | CYP1B1 (Cytochrome P450 1B1) LTBP2 (Latent Transforming Growth Factor Beta Binding Protein 2) MYOC (Myocilin) CYP19A1 (Cytochrome P450 Family 19 Subfamily A Member 1) LTBP2 (Latent Transforming Growth Factor Beta Binding Protein 2) |
| Pigmentary Glaucoma | ADAMTS10 (A Disintegrin and Metalloproteinase with Thrombospondin Motifs 10) OPA1 (Mitochondrial Dynamin Like GTPase) TYR (Tyrosinase) TYRP1 (Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1) MVP (Major Vault Protein) |
| Exfoliative Glaucoma | LOXL1 (Lysyl Oxidase-Like 1) TGFBI (Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Induced) APOE (Apolipoprotein E) SRPX2 (Sushi Repeat Containing Protein X-Linked 2) PEX11B (Peroxisomal Biogenesis Factor 11 Beta) |
| Classification | Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients |
|---|---|
| Prostaglandin Analogs | Latanoprost, Bimatoprost, Travoprost, Tafluprost, Latanoprostene Bunod, Unoprostone |
| Beta Blockers | Timolol, Levobunolol, Carteolol, Betaxolol, Metipranolol |
| Alpha Agonists | Apraclonidine, Brimonidine |
| Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | Acetazolamide, Methazolamide, Dorzolamide, Brinzolamide |
| Rho Kinase Inhibitors | Netarsudil |
| Cholinergic (Miotic) Agents | Pilocarpine, Carbachol |
| Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients | Trade Names |
| Latanoprost | Xalatan, Xelpros, Monoprost, |
| Bimatoprost | Eyreida, Lumigan, Sturiban |
| Travoprost | Travatan, iDose TR, Travatan Z, Izba |
| Tafluprost | Taflotan, Zioptan, Saflutan |
| Latanoprostene Bunod | Vyzultar |
| Unoprostone | Rescula |
| Timolol | Betimol, Blocadren, Istalol, Timoptic, Timol |
| Levobunolol | AKBeta, Betagan, Vistagan |
| Carteolol | Arteolol, Arteoptic, Calte, Carteabak, Cateol, Cartrol, Elbloc, Endak, Glauteolol, Mikelan, Ocupress, Poenglaucol, Singlauc, Teopic |
| Betaxolol | Betoptic |
| Metipranolol | OptiPranolol, Betanol, Disorat, Trimepranol |
| Apraclonidine | Iopidine |
| Brimonidine | Alphagan, Mirvaso, Lumify, Brymont |
| Acetazolamide | Diamox |
| Methazolamide | Neptazane |
| Dorzolamide | Trusopt |
| Brinzolamide | Azopt |
| Netarsudil | Rhopressa |
| Pilocarpine | Diocarpine, Isopto carpine, Miocarpine, Pilopine HS |
| Carbachol | Miostat |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patton, G.N.; Lee, H.J. Chemical Insights into Topical Agents in Intraocular Pressure Management: From Glaucoma Etiopathology to Therapeutic Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020274
Patton GN, Lee HJ. Chemical Insights into Topical Agents in Intraocular Pressure Management: From Glaucoma Etiopathology to Therapeutic Approaches. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(2):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020274
Chicago/Turabian StylePatton, Geewoo Nam, and Hyuck Jin Lee. 2024. "Chemical Insights into Topical Agents in Intraocular Pressure Management: From Glaucoma Etiopathology to Therapeutic Approaches" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 2: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020274
APA StylePatton, G. N., & Lee, H. J. (2024). Chemical Insights into Topical Agents in Intraocular Pressure Management: From Glaucoma Etiopathology to Therapeutic Approaches. Pharmaceutics, 16(2), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16020274









