Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
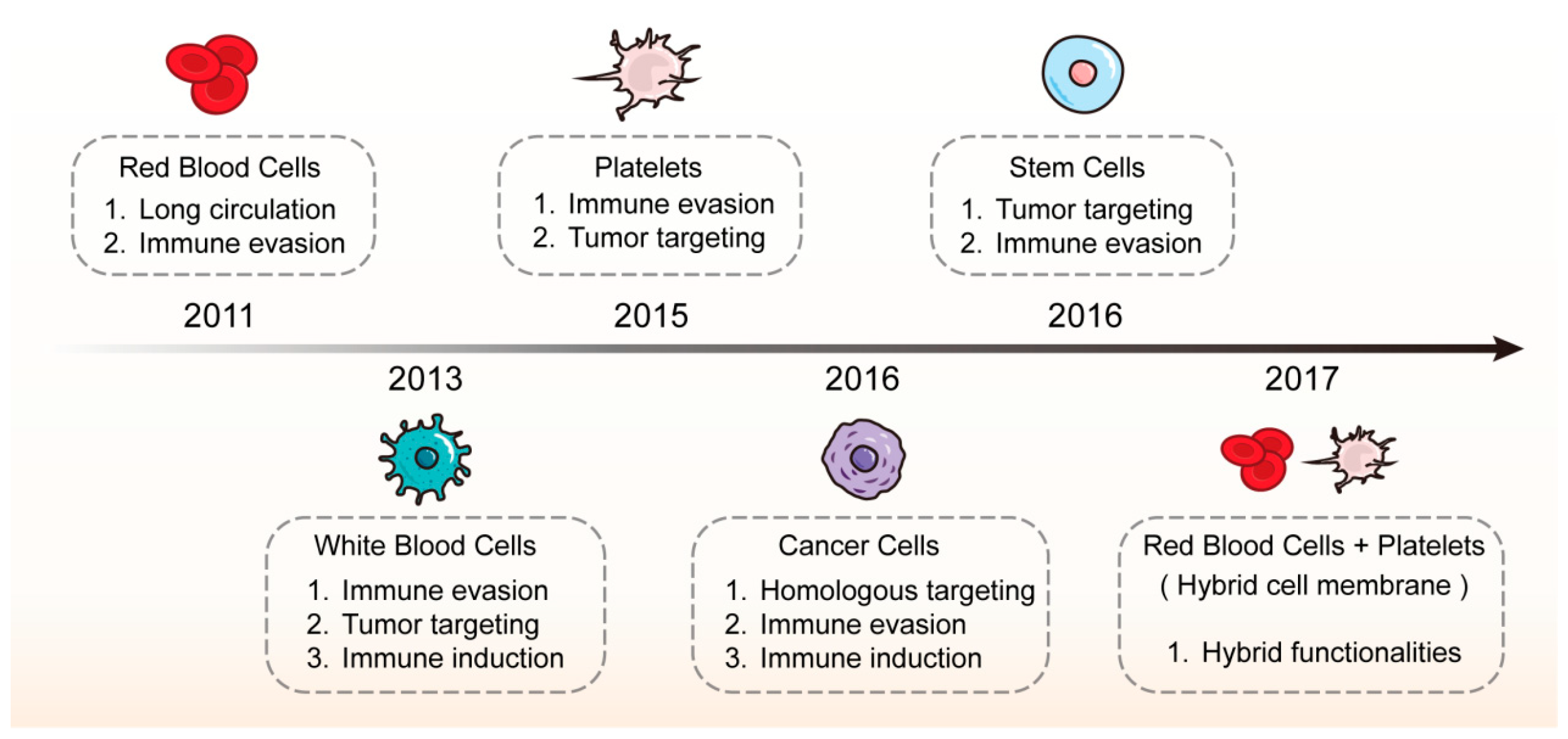
2. Classification of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles
3. Preparation of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles
3.1. Co-Extrusion
3.2. Sonication
3.3. Microfluidic Electroporation
4. Application of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment
4.1. Red Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (RBCm@NPs)
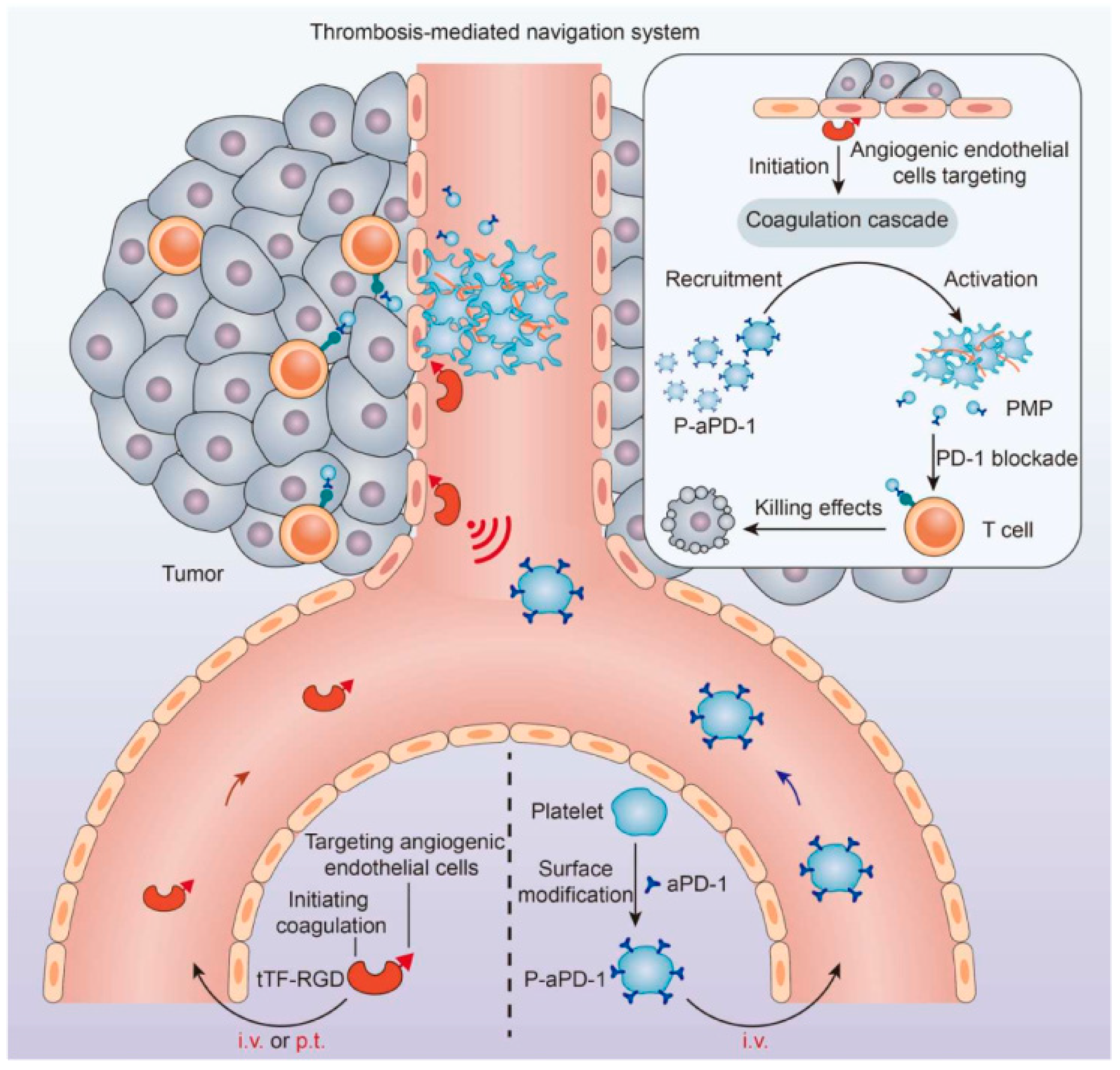
4.2. Platelet Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (PLTm@NPs)
4.3. White Blood Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (WBCm@NPs)
4.3.1. Neutrophil Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (Nm@NPs)
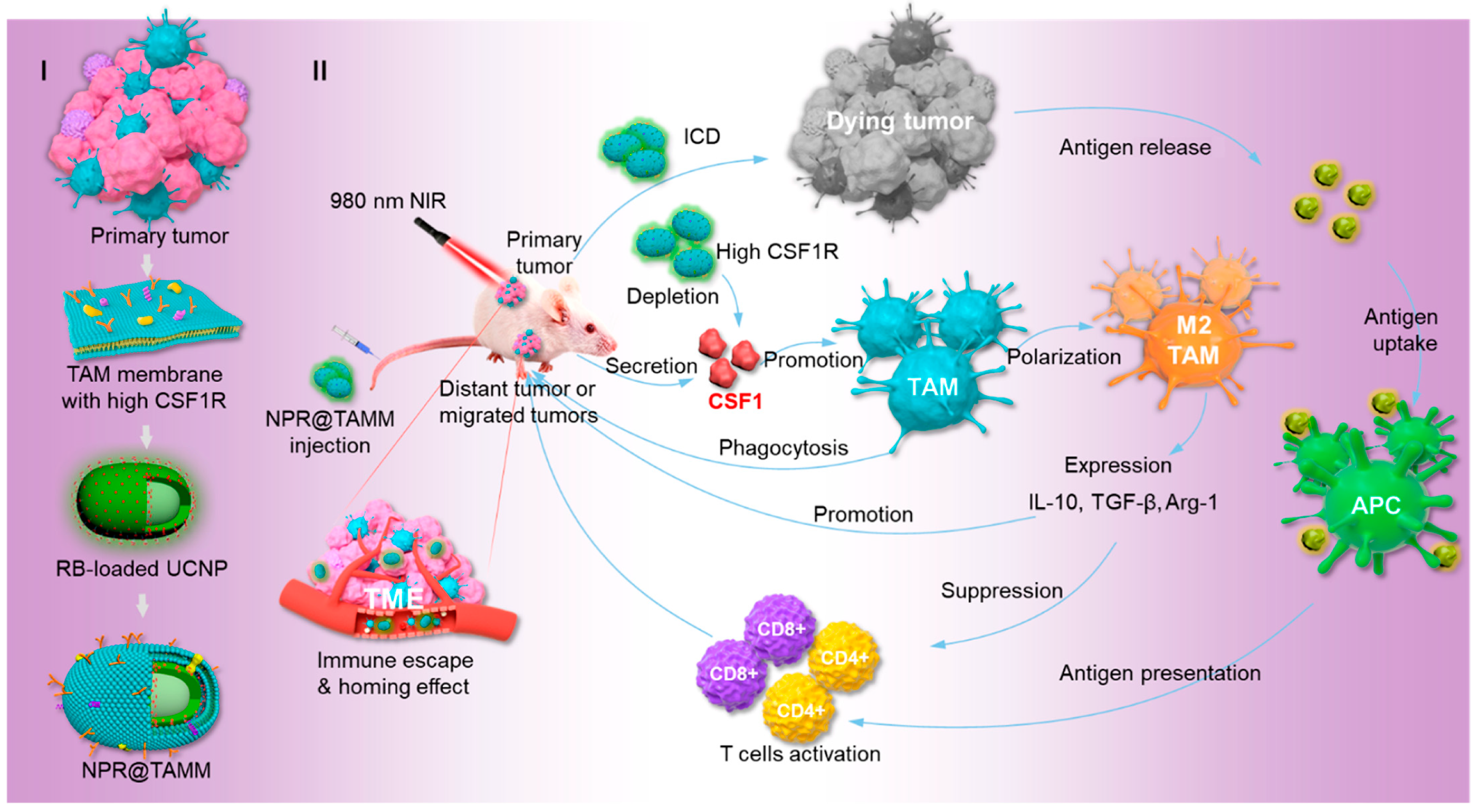
4.3.2. Macrophage Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (Mm@NPs)
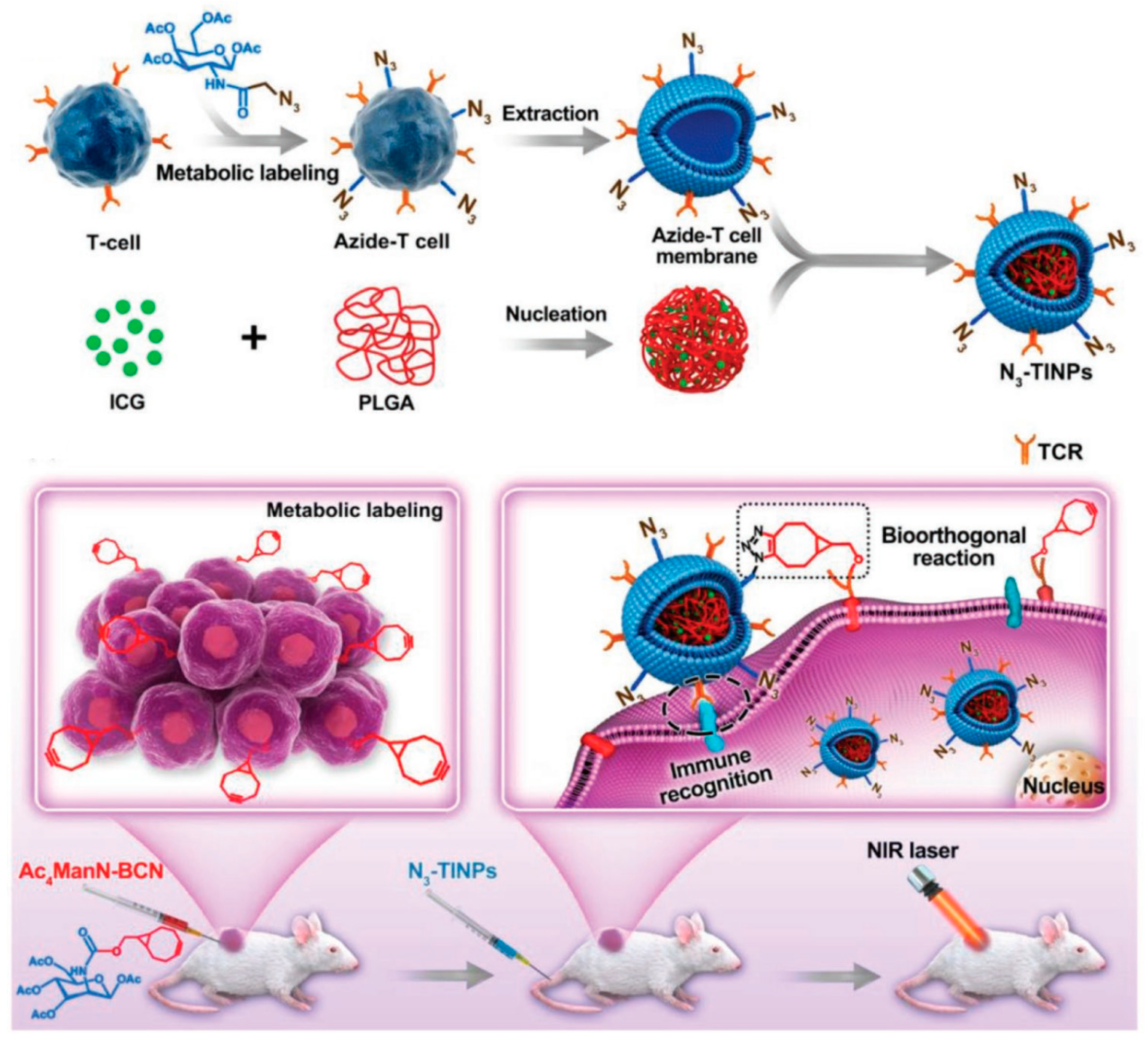
4.3.3. T Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (Tm@NPs)
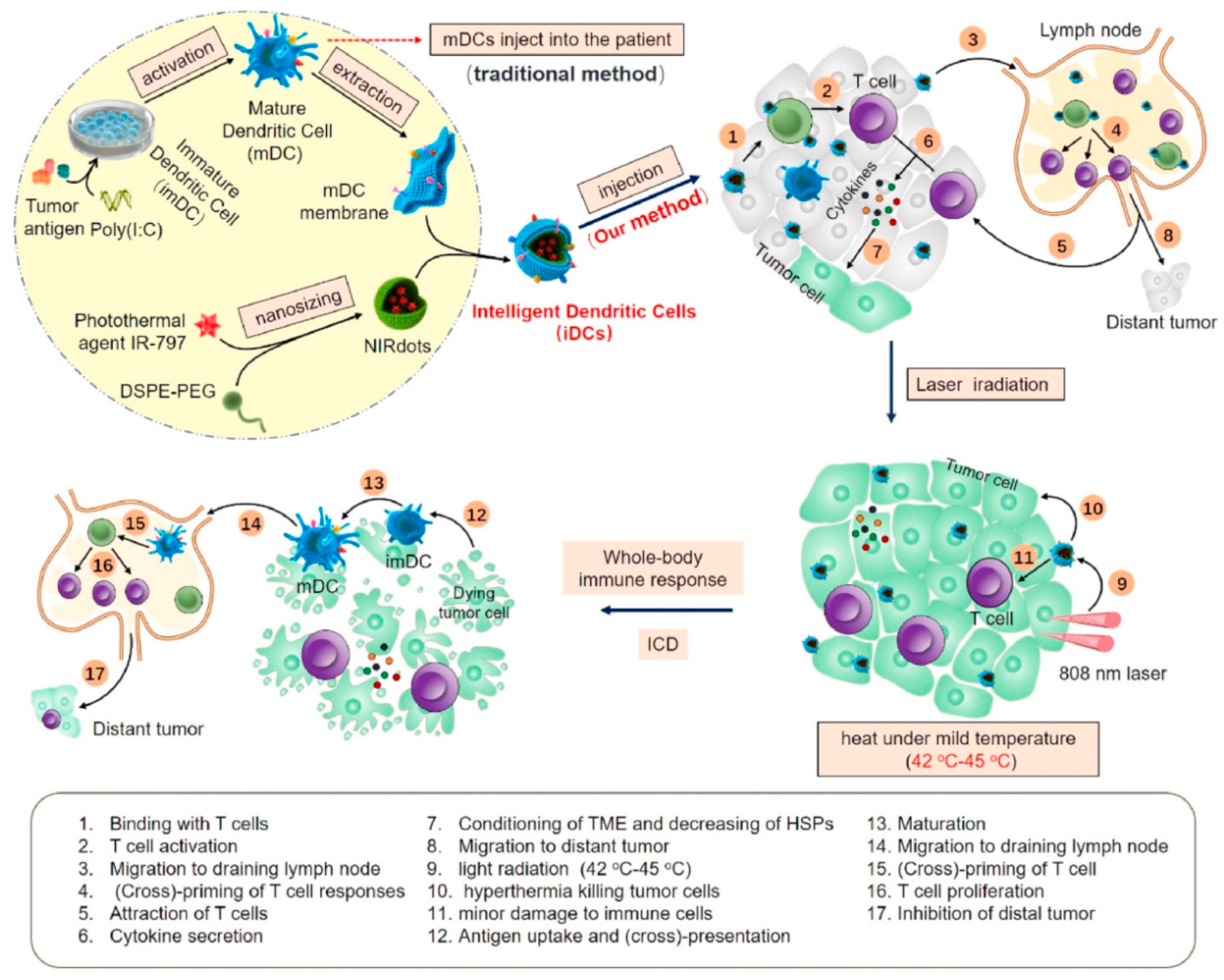
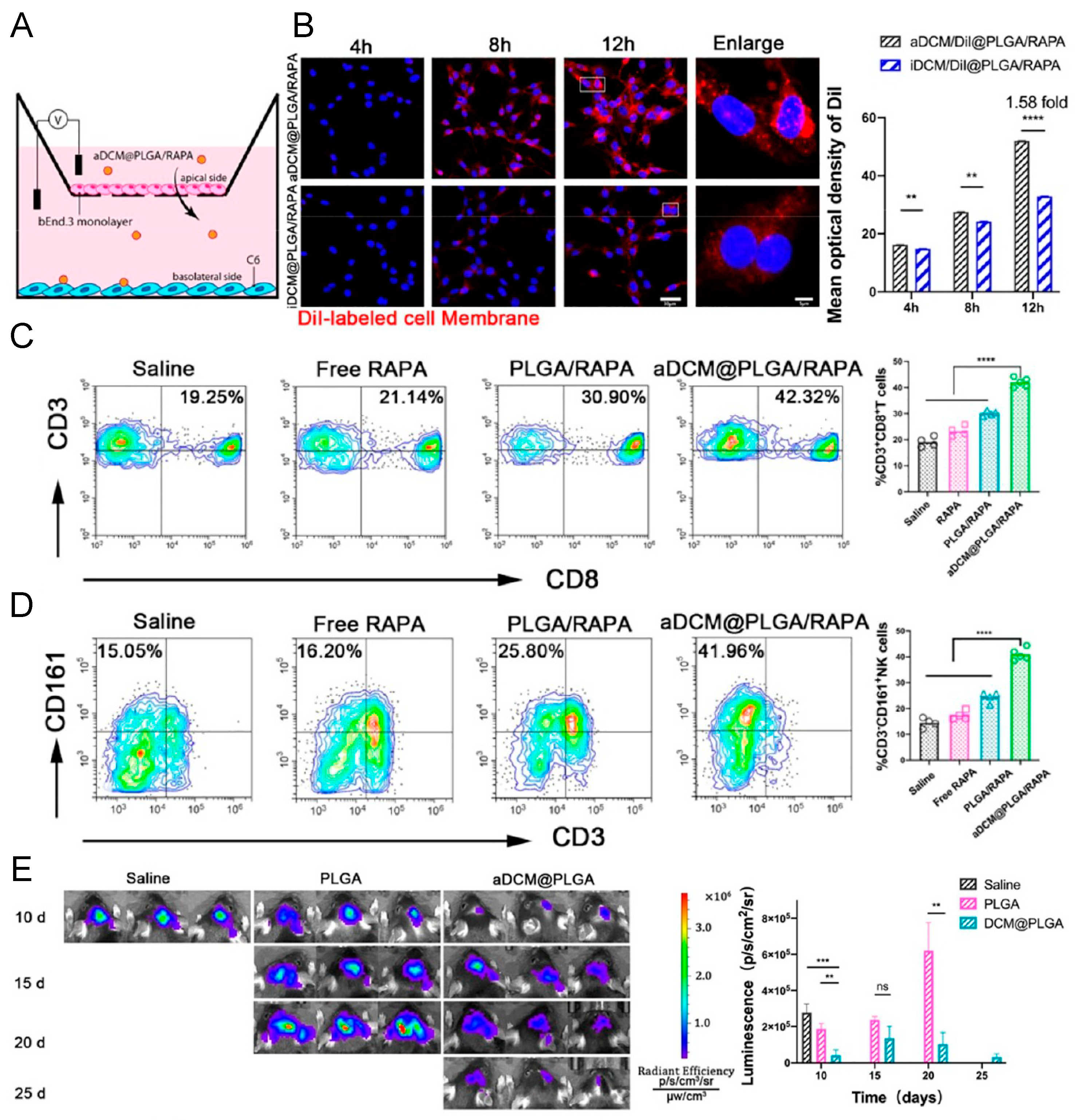
4.3.4. Dendritic Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (DCm@NPs)
4.3.5. Natural Killer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (NKm@NPs)
4.4. Stem Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (SCm@NPs)
| Source Cell | Inner Cores | Therapeutics | Key Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stem cells | PLGA | Chemotherapy | Tumor targeting | [68] |
| Polydopamine | Chemotherapy–PTT | Tumor targeting, long circulation, immune evasion | [69] | |
| Polydopamine | Chemotherapy, gene therapy | Tumor targeting | [70] | |
| Fe3O4@PDA | MRI, PTT, gene therapy | Tumor targeting | [135] |
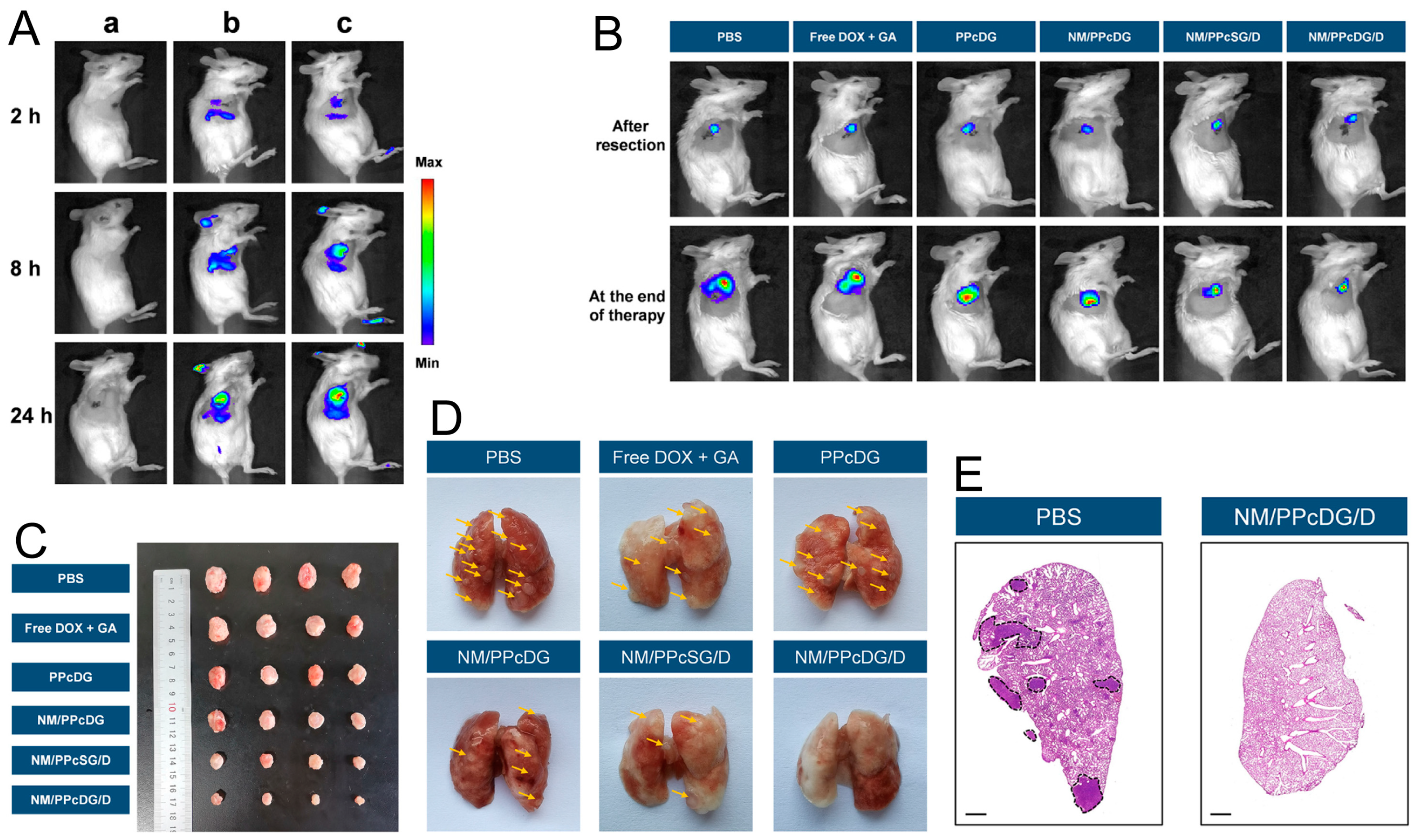
4.5. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (CCm@NPs)
4.6. Hybrid Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles (Hym@NPs)
5. Advantages and Limitations
6. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| DDSs | Drug delivery systems |
| PEGs | Glycol polymers |
| PLGA | Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) |
| CMC@NPs | Cell membrane-coated NPs |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| SDT | Sonodynamic therapy |
| RBCs | Red blood cells |
| RBCm | Red blood cell membrane |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
| PDT | Photodynamic therapy |
| PTT | Photothermal therapy |
| HSCs | Hematopoietic stem cells |
| Nm | Neutrophil membrane |
| PLTs | Platelets |
| PLTm | Platelet membrane |
| R848 | Resiquimod |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| WBCs | White blood cells |
| WBCm | White blood cell membrane |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| APCs | Antigen presenting cells |
| DCm | Dendritic cell membrane |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| NKs | Natural killer cells |
| SCs | Stem cells |
| CTCs | Circulating tumor cells |
| Mm | Macrophage membrane |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TAMs | Tumor-associated macrophages |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide |
| CSF1 | Colony-stimulating factor 1 |
| CTLs | Cytotoxic T lymphocytes |
| ICG | Indocyanine green |
| CAR-T | Chimeric antigen receptor T |
| HCCs | Hepatocellular carcinomas |
| AIE | Aggregation-induced emission |
| MHCs | Major histocompatibility complexes |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| ICD | Immunogenic cell death |
| Hym | Hybrid membrane |
| Nm@NPs | Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| CCm@NPs | Cancer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| RBCm@NPs | Red blood cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| PLTm@NPs | Platelet membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| WBCm@NPS | White blood cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| MSCm@NPs | MSC membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| SCm@NPs | Stem cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| Hym@NPs | Hybrid membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| Mm@NPs | Macrophage membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| Tm@NPs | T cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| DCm@NPs | Dendritic cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
| NKm@NPs | Natural killer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N. Challenges in development of nanoparticle-based therapeutics. AAPS J. 2012, 14, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zuo, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, R.; Ahmed, A.; Hu, Y.; Ouyang, J. Doxorubicin-loaded platelets as a smart drug delivery system: An improved therapy for lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubich, C.; Allacher, P.; Maurus, D.L.R.; Bauer, A.; Prenninger, T.; Horling, F.M.; Siekmann, J.; Oldenburg, J.; Scheiflinger, F.; Reipert, B.M. The Mystery of Antibodies Against Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)—What do we Know? Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2239–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Jeong, Y.; Park, J.M.; Lee, K.H.; Hong, J.W.; Choi, J. Biomimetics: Forecasting the future of science, engineering, and medicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5701–5713. [Google Scholar]
- Kroll, A.V.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Biointerfacing and Applications of Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Bioconjugate Chem. 2017, 28, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Bai, W.; Deng, T.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; He, Q. Sponge-like nano-system suppresses tumor recurrence and metastasis by restraining myeloid-derived suppressor cells-mediated immunosuppression and formation of pre-metastatic niche. Acta Biomater. 2023, 158, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Jiang, X.; Yang, T.; Xu, H.; Xie, Q.; Hu, M.; Yang, C.; Kong, L.; Zhang, Z. Enhancing cancer chemo-immunotherapy by biomimetic nanogel with tumor targeting capacity and rapid drug-releasing in tumor microenvironment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2550–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.M.; Zhang, L.; Aryal, S.; Cheung, C.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte membrane-camouflaged polymeric nanoparticles as a biomimetic delivery platform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10980–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parodi, A.; Quattrocchi, N.; van de Ven, A.L.; Chiappini, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Martinez, J.O.; Brown, B.S.; Khaled, S.Z.; Yazdi, I.K.; Enzo, M.V.; et al. Synthetic nanoparticles functionalized with biomimetic leukocyte membranes possess cell-like functions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Sun, W.; Qian, C.; Wang, C.; Bomba, H.N.; Gu, Z. Anticancer Platelet-Mimicking Nanovehicles. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7043–7050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Bu, L.L.; Cai, B.; Xu, J.H.; Li, A.; Zhang, W.F.; Sun, Z.J.; Guo, S.S.; Liu, W.; Wang, T.H.; et al. Cancer Cell Membrane-Coated Upconversion Nanoprobes for Highly Specific Tumor Imaging. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3460–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Lin, Z.; Jurado-Sánchez, B.; Lin, X.; Wu, Z.; He, Q. Stem Cell Membrane-Coated Nanogels for Highly Efficient In Vivo Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery. Small 2016, 12, 4056–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehaini, D.; Wei, X.; Fang, R.H.; Masson, S.; Angsantikul, P.; Luk, B.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, M.; Jiang, Y.; Kroll, A.V.; et al. Erythrocyte-Platelet Hybrid Membrane Coating for Enhanced Nanoparticle Functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, R.B.; Ye, M.; Carlson, P.M.; Jaquish, A.; Zangl, L.; Ma, B.; Wang, Y.; Arthur, I.; Xie, R.; Brown, R.J.; et al. Development of an In Situ Cancer Vaccine via Combinational Radiation and Bacterial-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1902626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H.; Mohapatra, A.; Zhou, J.; Holay, M.; Krishnan, N.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Virus-Mimicking Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Cytosolic Delivery of mRNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202113671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Lin, J.; Chew, S.Y. Neural Cell Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Targeted and Enhanced Uptake by Central Nervous System Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 55840–55850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X. Macrophage-evading and tumor-specific apoptosis inducing nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 327–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Sun, C.; Guo, T.; Pang, Z.; Zhang, B.; et al. Cytokine nanosponges suppressing overactive macrophages and dampening systematic cytokine storm for the treatment of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z.; Huang, X. Biomimetic cell membrane-coated glucose/oxygen-exhausting nanoreactor for remodeling tumor microenvironment in targeted hypoxic tumor therapy. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Deng, W.W.; Zan, M.; Rao, L.; Yu, G.T.; Zhu, D.M.; Wu, W.T.; Chen, B.; Ji, L.W.; Chen, L.; et al. Cancer Cell Membrane Camouflaged Nanoparticles to Realize Starvation Therapy Together with Checkpoint Blockades for Enhancing Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Qiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, G.; Chai, L.; Ren, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, S. Design of red blood cell membrane-cloaked dihydroartemisinin nanoparticles with enhanced antimalarial efficacy. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 618, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yang, X.Q.; An, J.; Cheng, K.; Hou, X.L.; Zhang, X.S.; Hu, Y.G.; Liu, B.; Zhao, Y.D. Red blood cell membrane-enveloped O(2) self-supplementing biomimetic nanoparticles for tumor imaging-guided enhanced sonodynamic therapy. Theranostics 2020, 10, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Han, S.; Du, C.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Platelet-membrane-camouflaged bismuth sulfide nanorods for synergistic radio-photothermal therapy against cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3450–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.X.; Liu, J.H.; Wu, J.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Qiu, X.H.; Xu, W.J.; Xu, P.; Xiang, D.X. Hybrid Cell Membrane-Functionalized Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Therapy of Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 837–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Jen, C.; Huang, M.; Wu, C.; Lin, X. Electroporation microchips for continuous gene transfection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 79, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Nakamura, H.; Watano, S. MD simulation study of direct permeation of a nanoparticle across the cell membrane under an external electric field. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11897–11906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Lin, Z.; Zhao, C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Lai, J.; Meng, Q.F.; Yao, G.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, X.Z.; et al. Neutrophil membrane-coated immunomagnetic nanoparticles for efficient isolation and analysis of circulating tumor cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 213, 114425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, L.; Cai, B.; Bu, L.L.; Liao, Q.Q.; Guo, S.S.; Zhao, X.Z.; Dong, W.F.; Liu, W. Microfluidic Electroporation-Facilitated Synthesis of Erythrocyte Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Enhanced Imaging-Guided Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3496–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Wu, M.; Wang, Q.; Ding, S.; Dong, X.; Xue, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xia, F.; Wang, S.; et al. Red blood cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles loaded with AIEgen and Poly(I:C) for enhanced tumoral photodynamic-immunotherapy. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwab039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Li, Y.; Long, H.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, F.; Li, M.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z. Cell membrane-camouflaged DOX-loaded β-glucan nanoparticles for highly efficient cancer immunochemotherapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Yu, P.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Wu, M. Facile phase transfer of hydrophobic Fe3O4@Cu2−xS nanoparticles by red blood cell membrane for MRI and phototherapy in the second near-infrared window. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Q.; Hu, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Jing, X.; Xie, Z. Light-Activatable Red Blood Cell Membrane-Camouflaged Dimeric Prodrug Nanoparticles for Synergistic Photodynamic/Chemotherapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1630–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fang, H.; Liu, Q.; Gai, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Gao, M.; Lan, X. Red blood cell membrane-coated upconversion nanoparticles for pretargeted multimodality imaging of triple-negative breast cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 1802–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, X.; Su, J.; Guo, P.; Kamal, Z.; Xu, E.; Liu, S.; Chen, J.; Qiu, M. Study on preparation, characterization and multidrug resistance reversal of red blood cell membrane-camouflaged tetrandrine-loaded PLGA nanoparticles. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, Q.; Li, Y.; Jin, S.; Mao, Q.; Liu, C.; Fan, X.; Lin, H. Cell membrane-coated human hair nanoparticles for precise disease therapies. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qiu, K.; Liao, X.; Rees, T.W.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. Fabrication of red blood cell membrane-camouflaged Cu(2-x)Se nanoparticles for phototherapy in the second near-infrared window. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 6523–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Lai, W.; Li, G.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Liao, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, Q.; et al. Platelet Membrane-Coated and VAR2CSA Malaria Protein-Functionalized Nanoparticles for Targeted Treatment of Primary and Metastatic Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 25635–25648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Kong, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Xi, Y.; Ji, J.; Ye, L.; et al. A ROS-responsive biomimetic nano-platform for enhanced chemo-photodynamic-immunotherapy efficacy. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 6583–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gao, F.; Fan, F.; Yang, L. Platelet membrane coating coupled with solar irradiation endows a photodynamic nanosystem with both improved antitumor efficacy and undetectable skin damage. Biomaterials 2018, 159, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, S.; Lyu, M.; Zhu, D.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Tang, B.Z. Type-I AIE Photosensitizer Loaded Biomimetic System Boosting Cuproptosis to Inhibit Breast Cancer Metastasis and Rechallenge. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 10206–10217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmani, B.; Gong, H.; Luk, B.T.; Haushalter, K.J.; DeTeresa, E.; Previti, M.; Zhou, J.; Gao, W.; Bui, J.D.; Zhang, L.; et al. Intratumoral immunotherapy using platelet-cloaked nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in solid tumors. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Mo, F.; Chen, Y.; Iida, M.; Wheeler, D.L.; Hu, Q. Active recruitment of anti-PD-1-conjugated platelets through tumor-selective thrombosis for enhanced anticancer immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chu, T.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, F.; Lu, Z.; Gao, C.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, E.; Xu, J.; et al. Platelet-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles Enable Vascular Disrupting Agent Combining Anti-Angiogenic Drug for Improved Tumor Vessel Impairment. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2588–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, D.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, S. Biodegradable Hypocrellin B nanoparticles coated with neutrophil membranes for hepatocellular carcinoma photodynamics therapy effectively via JUNB/ROS signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 99, 107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, H.; Xu, D.; Sun, R.; Fang, C.; Zhao, Q.; He, C.; Pan, Y.; Xu, F.; Jiang, T. Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles for enhanced nanosecond pulsed electric field treatment of pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2022, 39, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Hu, Y.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Gong, T.; Sun, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Z. Neutrophil-mimicking therapeutic nanoparticles for targeted chemotherapy of pancreatic carcinoma. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Macrophage Membrane-Coated Nano-Gemcitabine Promotes Lymphocyte Infiltration and Synergizes AntiPD-L1 to Restore the Tumoricidal Function. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 322–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qian, R.; Li, T.; Fu, W.; Fang, L.; Cai, Y.; Guo, H.; Xi, L.; Cheang, U.K. Imaging-Guided Biomimetic M1 Macrophage Membrane-Camouflaged Magnetic Nanorobots for Photothermal Immunotargeting Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 56548–56559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Song, M.; Du, Y.; Yu, Y.; Li, C.; Han, Y.; Yan, F.; Shi, Z.; Feng, S. Tumor-Associated-Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Improved Photodynamic Immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 5522–5531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W. Macrophage membrane-coated nanovesicles for dual-targeted drug delivery to inhibit tumor and induce macrophage polarization. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 23, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, T.; He, M.; Xu, F.; Fan, Y.; Jia, B.; Shen, M.; Wang, H.; Shi, X. Macrophage Membrane-Camouflaged Responsive Polymer Nanogels Enable Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Chemotherapy/Chemodynamic Therapy of Orthotopic Glioma. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 20377–20390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Wu, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C. T cell membrane cloaking tumor microenvironment-responsive nanoparticles with a smart “membrane escape mechanism” for enhanced immune-chemotherapy of melanoma. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 3453–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Hong, J.; Jung, M.; Kwon, S.P.; Song, S.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.R.; Kang, S.; Han, J.; Koo, J.H.; et al. T-Cell-Mimicking Nanoparticles for Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2003368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zhu, D.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, W.; Jiang, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, G.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Z.; et al. Coating biomimetic nanoparticles with chimeric antigen receptor T cell-membrane provides high specificity for hepatocellular carcinoma photothermal therapy treatment. Theranostics 2020, 10, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, F.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Genetically edited T-cell membrane coated AIEgen nanoparticles effectively prevents glioblastoma recurrence. Biomaterials 2023, 293, 121981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
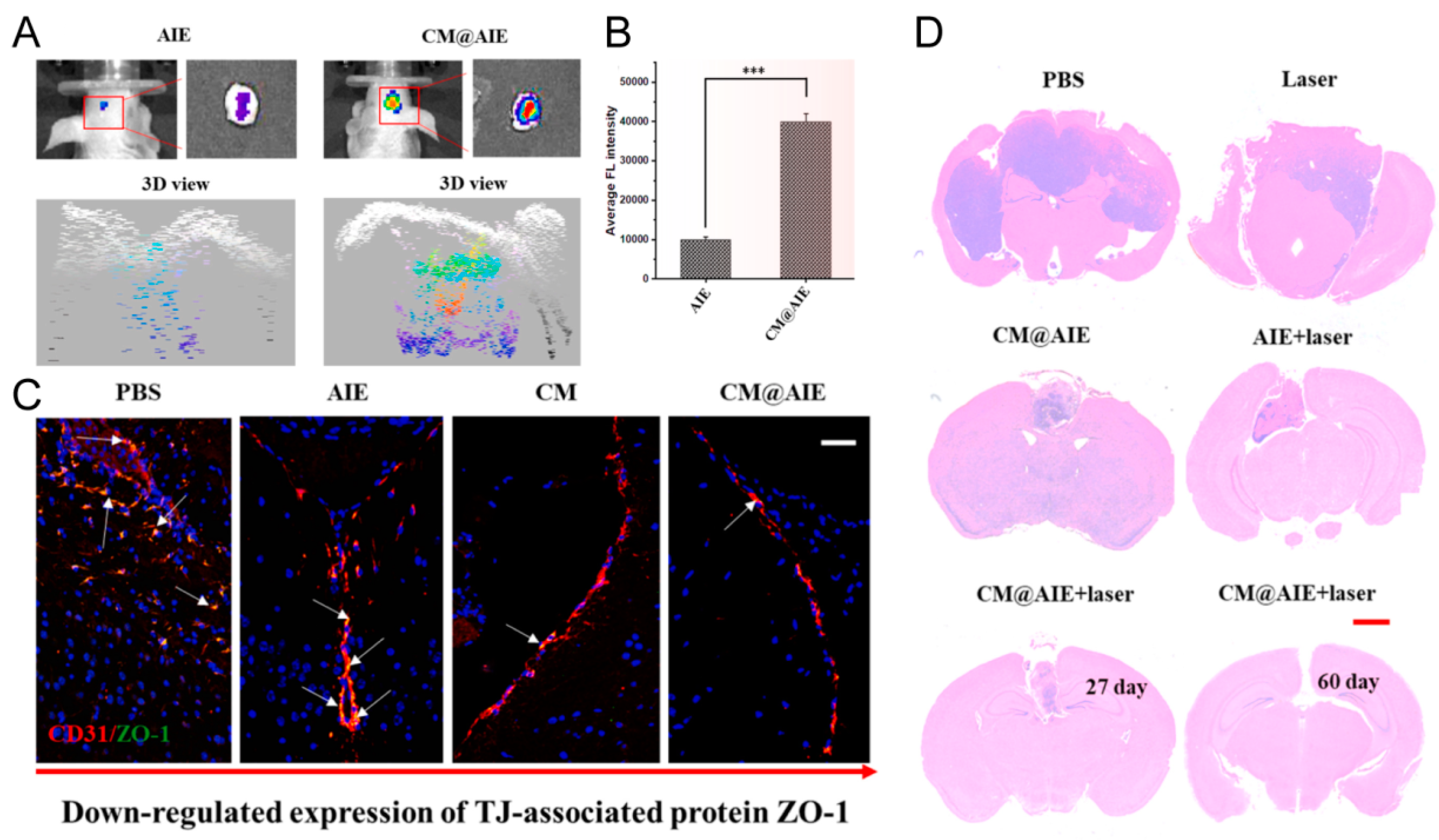
- Han, Y.; Pan, H.; Li, W.; Chen, Z.; Ma, A.; Yin, T.; Liang, R.; Chen, F.; Ma, Y.; Jin, Y.; et al. T Cell Membrane Mimicking Nanoparticles with Bioorthogonal Targeting and Immune Recognition for Enhanced Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Geng, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, J. Biomimetic Nanoparticles Enabled by Cascade Cell Membrane Coating for Direct Cross-Priming of T Cells. Small 2022, 18, e2104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Engineering Nanoscale Artificial Antigen-Presenting Cells by Metabolic Dendritic Cell Labeling to Potentiate Cancer Immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Deng, G.; Sun, Z.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, P.; Liu, G.; Zhang, P.; et al. A Biomimetic Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizer with Antigen-Presenting and Hitchhiking Function for Lipid Droplet Targeted Photodynamic Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Deng, G.; Peng, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Peng, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wen, A.; Wang, Y.; et al. Intelligent photothermal dendritic cells restart the cancer immunity cycle through enhanced immunogenic cell death. Biomaterials 2021, 279, 121228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, B.; Zheng, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Liao, N.; Wang, P.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Remodeling Tumor-Associated Neutrophils to Enhance Dendritic Cell-Based HCC Neoantigen Nano-Vaccine Efficiency. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2105631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Kuang, L.; Yin, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Wang, B.; Dong, Z.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.; et al. Tumor-Antigen Activated Dendritic Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles with Orchestrating Immune Responses Promote Therapeutic Efficacy against Glioma. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2341–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitchaimani, A.; Nguyen, T.D.T.; Marasini, R.; Eliyapura, A.; Azizi, T.; Jaberi-Douraki, M.; Aryal, S. Biomimetic Natural Killer Membrane Camouflaged Polymeric Nanoparticle for Targeted Bioimaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Wu, M.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Natural Killer Cell Membrane-Cloaked Virus-Mimicking Nanogenerator with NIR-Triggered Shape Reversal and •C/•OH Storm for Synergistic Thermodynamic-Chemodynamic Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2103498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, J.; Gu, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, R.; Zhou, X. A Trojan-Horse-Like Biomimetic Nano-NK to Elicit an Immunostimulatory Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced GBM Chemo-Immunotherapy. Small 2023, 19, 2301439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, G.; Peng, X.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, W.; Yu, J.; Du, L.; Chen, H.; Gong, P.; Zhang, P.; Cai, L.; et al. Natural-Killer-Cell-Inspired Nanorobots with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for Near-Infrared-II Fluorescence-Guided Glioma Theranostics. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 11452–11462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, K.; Huang, Y.; Taleb, M.; Zhao, J.; Dong, W.F.; et al. Surface Functionalization of Polymeric Nanoparticles with Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Membrane for Tumor-Targeted Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22963–22973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, F.; Liu, T.; Shao, P.; Duan, L.; Yan, J.; Mu, X.; Jiang, J. Polydopamine Nanoparticles Camouflaged by Stem Cell Membranes for Synergistic Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Malignant Bone Tumors. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 10183–10197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, A.; Yin, F.; Wang, Y.; Hu, K.; Jiang, J. Doxorubicin and PD-L1 siRNA co-delivery with stem cell membrane-coated polydopamine nanoparticles for the targeted chemoimmunotherapy of PCa bone metastases. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 8998–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; He, Y.; Chen, F.M.; Zhang, F.; Shao, D.; Wang, Z. Leveraging β-Adrenergic Receptor Signaling Blockade for Improved Cancer Immunotherapy Through Biomimetic Nanovaccine. Small 2023, 19, 2207029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Feng, Y.J.; Guo, X.Y.; Li, T.; Meng, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, D.Q.; Tian, H.Y. CD47KO/CRT dual-bioengineered cell membrane-coated nanovaccine combined with anti-PD-L1 antibody for boosting tumor immunotherapy. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 22, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.S.; Sun, S.H.; Wang, P.; Sun, L.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Xu, M.H.; Chen, J.; Wu, R.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; et al. Genetically Engineering Cell Membrane-Coated BTO Nanoparticles for MMP2-Activated Piezocatalysis-Immunotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2300964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.C.; Luo, Q.Z.; He, Y.Q.; He, Y.C.; Zhang, X.W.; Wang, J.; Ni, S.; Gao, D.W.; Wang, D.S. Endogenous Nitric Oxide Releases In Situ for RNS/ROS Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 11, 2314536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Karges, J.; Xiong, K.; Chen, Y.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. Cancer cell membrane camouflaged iridium complexes functionalized black-titanium nanoparticles for hierarchical-targeted synergistic NIR-II photothermal and sonodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 275, 120979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.Q.; Qiao, B.; Lin, X.H.; Cao, J.; Zhang, N.; Guo, H.L.; Liu, W.W.; Zhu, L.Y.; Xie, X.; Wan, L.; et al. A hydrogen peroxide economizer for on-demand oxygen production-assisted robust sonodynamic immunotherapy. Theranostics 2022, 12, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, D.; He, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y. A Defect-Engineered Nanozyme for Targeted NIR-II Photothermal Immunotherapy of Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2022, 36, 2206401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Peng, H.; Shen, T.; Wang, M.; Luo, M.; Qu, X.; Qu, F.; Liu, W.; Lei, B.; et al. Bioactive cytomembrane@poly(citrate-peptide)-miRNA365 nanoplatform with immune escape and homologous targeting for colon cancer therapy. Mater. Today Bio 2022, 15, 100294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X.; Fu, J.; He, C. Tumor cell membrane-camouflaged responsive nanoparticles enable MRI-guided immuno-chemodynamic therapy of orthotopic osteosarcoma. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 17, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Huang, Y.F.; Feng, H.X.; Lin, J.M.; Huang, A.F.; Hu, J.X.; Tang, Q.L.; Zhu, X.J.; Han, S.S.; Lu, J.C.; et al. A nanodrug combining CD47 and sonodynamic therapy efficiently inhibits osteosarcoma deterioration. J. Control Release 2023, 355, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Li, J.Y.; Nie, D.; Zhuo, Y.; Lv, Y.S.; Wang, N.; Chen, H.; Guo, S.Y.; Gan, Y.; et al. Cell membrane-coated mesoporous silica nanorods overcome sequential drug delivery barriers against colorectal cancer. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Pan, Q.Y.; Bai, Y.; Yu, M.F.; Zhou, Y. Targeted Therapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma with Cancer Cell Membrane Coated Co-Fc Nanoparticles Via Autophagy Inhibition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, L.; Lai, W.F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Qi, X.; et al. R11 modified tumor cell membrane nanovesicle-camouflaged nanoparticles with enhanced targeting and mucus-penetrating efficiency for intravesical chemotherapy for bladder cancer. J. Control Release 2022, 351, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Liu, C.; You, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Bacterial Vesicle-Cancer Cell Hybrid Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles for Tumor Specific Immune Activation and Photothermal Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 41138–41147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Wang, K.; Lu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Kan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Sun, J. Nanosponges of circulating tumor-derived exosomes for breast cancer metastasis inhibition. Biomaterials 2020, 242, 119932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, X.; Fu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wan, Z.; Zhao, Y. Intelligent Nanoplatform Integrating Macrophage and Cancer Cell Membrane for Synergistic Chemodynamic/Immunotherapy/Photothermal Therapy of Breast Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 59117–59133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Xian, Y. Multivalent Aptamer Functionalized Ag2S Nanodots/Hybrid Cell Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanobioprobe for the Ultrasensitive Isolation and Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Cai, H.; Yang, Y.; Peng, F.; Song, M.; Sun, K.; Yan, F.; Liu, Y. Hybrid membrane camouflaged copper sulfide nanoparticles for photothermal-chemotherapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Biomater. 2020, 111, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, W.; Hu, L.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, X.; Cao, Z.; Cao, J. Long Circulating Cancer Cell-Targeted Bionic Nanocarriers Enable Synergistic Combinatorial Therapy in Colon Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 22843–22853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Mu, N.; Ding, Y.; Huang, R.; Wu, W.; Li, L.; Chen, T. Tumor microenvironment targeting for glioblastoma multiforme treatment via hybrid cell membrane coating supramolecular micelles. J. Control Release 2024, 366, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, H.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Biomimetic Nanocomposites Camouflaged with Hybrid Cell Membranes for Accurate Therapy of Early-Stage Glioma. Angew. Chem. 2023, 62, e202304419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Cui, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, Z.; Gong, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. Hybrid membrane-coated nanosuspensions for multi-modal anti-glioma therapy via drug and antigen delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Tang, W.; Ma, X.; Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Hu, F.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Biomimetic neutrophil and macrophage dual membrane-coated nanoplatform with orchestrated tumor-microenvironment responsive capability promotes therapeutic efficacy against glioma. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; et al. Cancer-Erythrocyte Hybrid Membrane-Camouflaged Magnetic Nanoparticles with Enhanced Photothermal-Immunotherapy for Ovarian Cancer. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 19756–19770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fan, J.; Yuan, L.; Tong, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, B. A hybrid membrane coating nanodrug system against gastric cancer via the VEGFR2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 3838–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.M.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Erythrocyte-inspired delivery systems. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, A.N.; Van den Berg, T.K. The interaction between signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPα) and CD47: Structure, function, and therapeutic target. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Baruah, K.; Cox, E.; Vanrompay, D.; Bossier, P. Structure-Functional Activity Relationship of β-Glucans From the Perspective of Immunomodulation: A Mini-Review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Graaff, P.; Berrevoets, C.; Rӧsch, C.; Schols, H.A.; Verhoef, K.; Wichers, H.J.; Debets, R.; Govers, C. Curdlan, zymosan and a yeast-derived β-glucan reshape tumor-associated macrophages into producers of inflammatory chemo-attractants. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lovell, J.F.; Yoon, J.; Chen, X. Clinical development and potential of photothermal and photodynamic therapies for cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, L.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Han, Y.; Chen, D.F.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Cui, Z.; et al. Lysozyme-Assisted Photothermal Eradication of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Accelerated Tissue Repair with Natural Melanosome Nanostructures. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11153–11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Gong, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, W.; Fang, R.H.; Zhang, L. Targeted gene silencing in vivo by platelet membrane-coated metal-organic framework nanoparticles. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ye, J.J.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, C.X.; Wang, X.S.; Yu, W.; Song, W.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.Z. Platelet-Mimicking Biotaxis Targeting Vasculature-Disrupted Tumors for Cascade Amplification of Hypoxia-Sensitive Therapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 14230–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Shi, M.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W. Glycoprotein Ib-regulated micro platelet ghost for biosafe distribution and photothermal oncotherapy. J. Control Release 2022, 351, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yan, Q.; Xia, C.; Wang, X.; Kumar, A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J. Recent advances in cell membrane coated metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for tumor therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 4459–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Fan, Q.; Hu, F.; Ma, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B.; Kuang, L.; Hu, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y. Engineered Macrophage-Membrane-Coated Nanoparticles with Enhanced PD-1 Expression Induce Immunomodulation for a Synergistic and Targeted Antiglioblastoma Activity. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 6606–6614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Cheng, Z.; Li, N.; Ma, X.; Nie, G.; Zhao, X. Biomimetic Nanoparticles Carrying a Repolarization Agent of Tumor-Associated Macrophages for Remodeling of the Inflammatory Microenvironment Following Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15166–15179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Peng, X.; Li, W.; Zhou, L.; Ma, Y.; Gong, P.; Cai, L. Cell-Membrane Immunotherapy Based on Natural Killer Cell Membrane Coated Nanoparticles for the Effective Inhibition of Primary and Abscopal Tumor Growth. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 12096–12108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.M.; Zeng, D.; Lei, X.C.; Huang, J.; Deng, Y.F.; Ji, Y.B.; Liu, J.; Dai, F.F.; Li, Y.Z.; Shi, D.D.; et al. KLF2 regulates neutrophil migration by modulating CXCR1 and CXCR2 in asthma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dehaini, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Fang, R.H.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L. Neutrophil membrane-coated nanoparticles inhibit synovial inflammation and alleviate joint damage in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, M.; Wu, L.; Song, Y.; Yu, S.; Wan, Y.; Cheng, W.; Yang, B.; Mou, X.; Yu, H.; et al. Peptide-anchored neutrophil membrane-coated biomimetic nanodrug for targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhuang, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, H.; de Ávila, B.E.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yin, L.; Karshalev, E.; et al. Nanoparticle-modified microrobots for in vivo antibiotic delivery to treat acute bacterial pneumonia. Nat. Mater. 2022, 21, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez Perdiguero, E.; Schulz, C.; Geissmann, F. Development and homeostasis of “resident” myeloid cells: The case of the microglia. Glia 2013, 61, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, W.; Song, W.; Zhao, Z.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhu, T.; Yin, J.; Bai, J.; et al. Antiviral and Anti-Inflammatory Treatment with Multifunctional Alveolar Macrophage-Like Nanoparticles in a Surrogate Mouse Model of COVID-19. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gao, D.; An, K.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.; Chen, X.; Lyv, Y.; Cui, C.; et al. A programmable polymer library that enables the construction of stimuli-responsive nanocarriers containing logic gates. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Shi, J. Nanoplatform-based cascade engineering for cancer therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 9057–9094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Xiong, X.; Yang, G.; Xiao, W.; Hou, J.; Pan, T.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, S. A macrophage membrane-coated mesoporous silica nanoplatform inhibiting adenosine A2AR via in situ oxygen supply for immunotherapy. J. Control Release 2023, 353, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.W.; Liu, P.P.; Wang, Z.X.; Chen, C.Y.; Xie, H. Macrophages in Osteosarcoma Immune Microenvironment: Implications for Immunotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 586580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buechler, M.B.; Fu, W.; Turley, S.J. Fibroblast-macrophage reciprocal interactions in health, fibrosis, and cancer. Immunity 2021, 54, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadi, S.; Chhangawala, S.; Whitlock, B.M.; Franklin, R.A.; Luo, C.T.; Oh, S.A.; Toure, A.; Pritykin, Y.; Huse, M.; Leslie, C.S.; et al. Cancer Immunosurveillance by Tissue-Resident Innate Lymphoid Cells and Innate-like T Cells. Cell 2016, 164, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roybal, K.T.; Rupp, L.J.; Morsut, L.; Walker, W.J.; McNally, K.A.; Park, J.S.; Lim, W.A. Precision Tumor Recognition by T Cells With Combinatorial Antigen-Sensing Circuits. Cell 2016, 164, 770–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Pan, H.; He, H.; Meng, X.; Ren, Q.; Gong, P.; Jiang, X.; Liang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zheng, M.; et al. Bio-Orthogonal T Cell Targeting Strategy for Robustly Enhancing Cytotoxicity against Tumor Cells. Small 2019, 15, e1804383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wculek, S.K.; Cueto, F.J.; Mujal, A.M.; Melero, I.; Krummel, M.F.; Sancho, D. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucikova, J.; Palova-Jelinkova, L.; Bartunkova, J.; Spisek, R. Induction of Tolerance and Immunity by Dendritic Cells: Mechanisms and Clinical Applications. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehner, R.; Dietze, K.; Bachmann, M.; Schmitz, M. The bidirectional crosstalk between human dendritic cells and natural killer cells. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trachootham, D.; Alexandre, J.; Huang, P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical therapeutic approach? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uccelli, A.; Moretta, L.; Pistoia, V. Mesenchymal stem cells in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, T. Cell Membrane Coating Technology: A Promising Strategy for Biomedical Applications. Nanomicro Lett. 2019, 11, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Du, L.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Tumour-associated mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: Emerging therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, J.; Dong, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, J. Combined chemical and structural signals of biomaterials synergistically activate cell-cell communications for improving tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Shin, Y.M.; Chung, S.; Kim, D.; Park, D.B.; Baek, S.; Park, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Yi, S.W.; et al. Cell-Membrane-Derived Nanoparticles with Notch-1 Suppressor Delivery Promote Hypoxic Cell-Cell Packing and Inhibit Angiogenesis Acting as a Two-Edged Sword. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2101558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Albero, M.; Encinas-Giménez, M.; Sebastián, V.; Pérez, E.; Luján, L.; Santamaría, J.; Martin-Duque, P. Transfer of photothermal nanoparticles using stem cell derived small extracellular vesicles for in vivo treatment of primary and multinodular tumours. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Li, J.; Yan, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, J. siRNA Delivery with Stem Cell Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy and Gene Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Chen, G.B.; Chen, H.H.; Zhang, J.B.; Li, H.Z.; Sheng, M.X.; Weng, W.B.; Guo, S.M. Cancer cell membrane-cloaked mesoporous silica nanoparticles with a pH-sensitive gatekeeper for cancer treatment. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.H.; Hu, C.M.; Luk, B.T.; Gao, W.; Copp, J.A.; Tai, Y.; O’Connor, D.E.; Zhang, L. Cancer cell membrane-coated nanoparticles for anticancer vaccination and drug delivery. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, P.; Shen, X.; Lyu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, L.; Huang, Y. Cascade Delivery to Golgi Apparatus and On-Site Formation of Subcellular Drug Reservoir for Cancer Metastasis Suppression. Small 2023, 19, 2204747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.W.; Lee, G.; Niidome, T.; Komohara, Y.; Lee, R.; Park, Y.I. Platelet-Like Gold Nanostars for Cancer Therapy: The Ability to Treat Cancer and Evade Immune Reactions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M.; Shi, B. Cancer cell-mitochondria hybrid membrane coated Gboxin loaded nanomedicines for glioblastoma treatment. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, G.; Wu, W.; Wang, J.; Hu, J.; Mao, J.; Chu, P.K.; Bai, H.; Tang, G. A Hybrid Eukaryotic-Prokaryotic Nanoplatform with Photothermal Modality for Enhanced Antitumor Vaccination. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Bai, F.; Xing, S.; Wang, M.; Dang, Z.; Lin, J.; Huang, P. Genetically engineered eukaryocyte-bacteria hybrid membrane-camouflaged nanoemulsion for three-pronged synergistic cancer therapy. Nano Today 2024, 54, 102076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Sun, H.; Meng, Q.; Yin, Q.; Tang, S.; Zhang, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, Y. Long Circulation Red-Blood-Cell-Mimetic Nanoparticles with Peptide-Enhanced Tumor Penetration for Simultaneously Inhibiting Growth and Lung Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M. Biomimetic cell membrane-coated DNA nanoparticles for gene delivery to glioblastoma. J. Control Release 2021, 338, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Pan, D.; Chen, S.; Martikainen, M.V.; Kårlund, A.; Ke, J.; Pulkkinen, H.; Ruhanen, H.; Roponen, M.; Käkelä, R.; et al. Systematic design of cell membrane coating to improve tumor targeting of nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Cao, Z.P.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.Y.; Lin, S.S.; Wu, F.; Pang, Y.; Liu, J.Y. Multimodal oncolytic bacteria by coating with tumor cell derived nanoshells. Nano Today 2022, 45, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



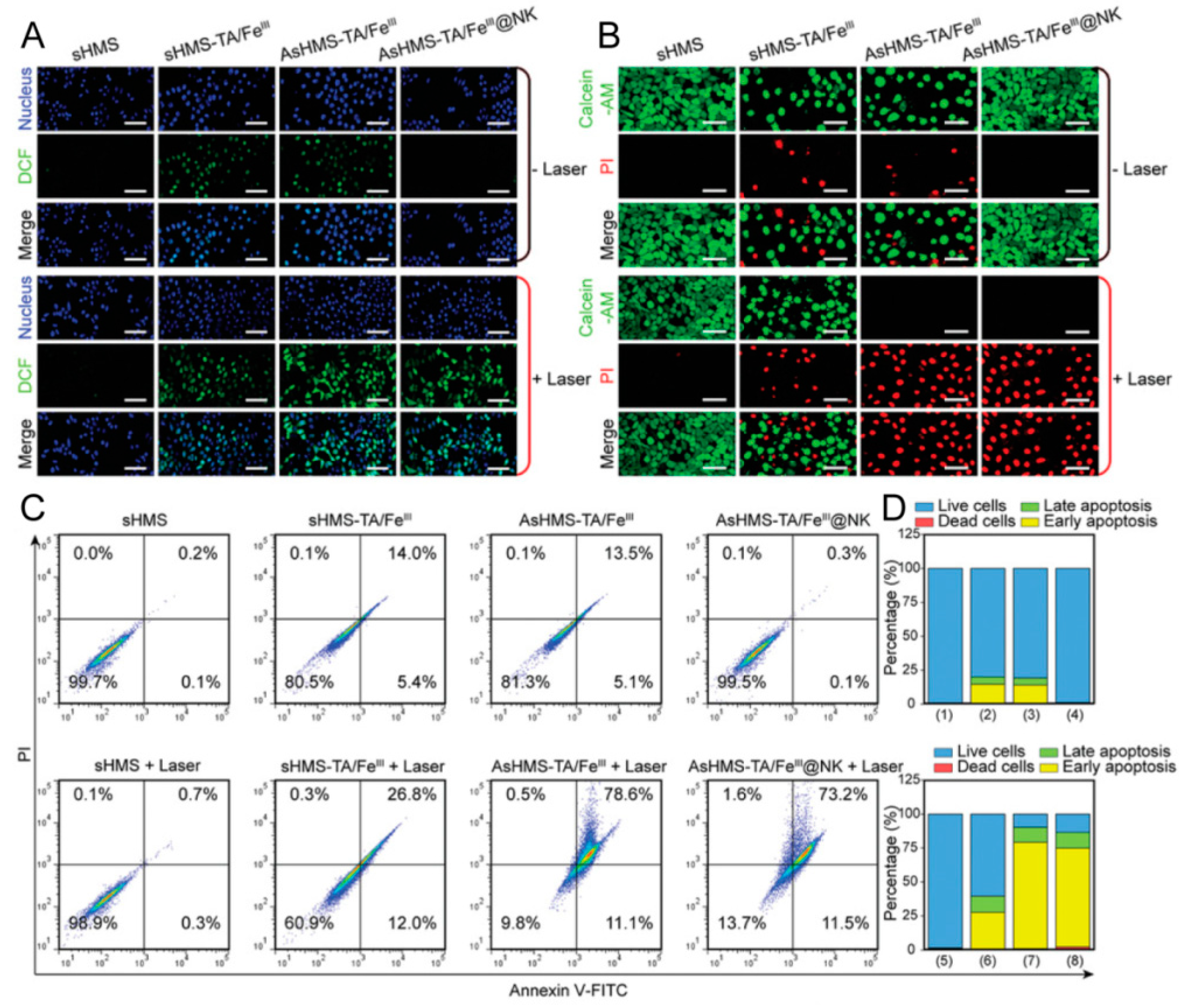
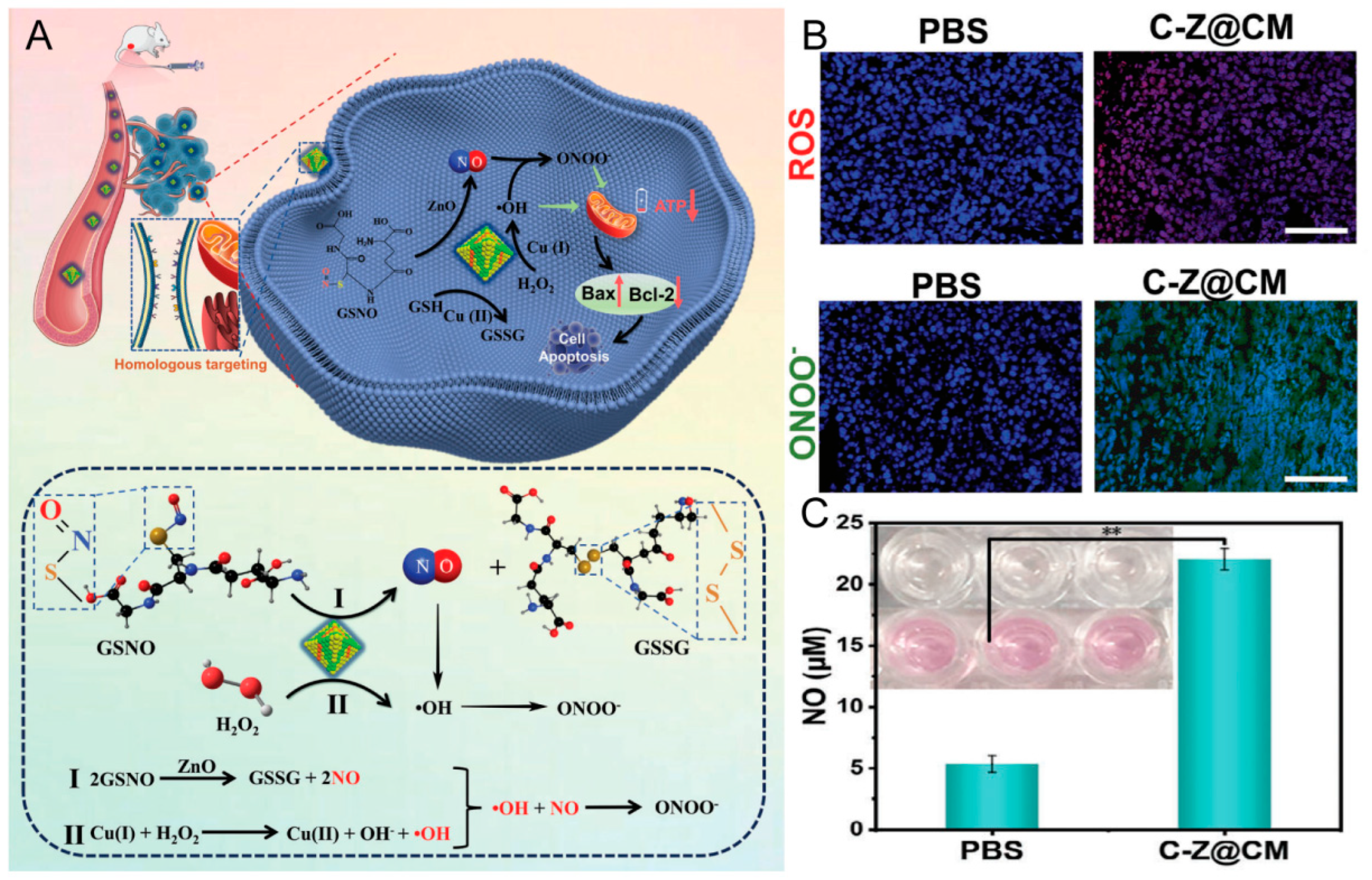

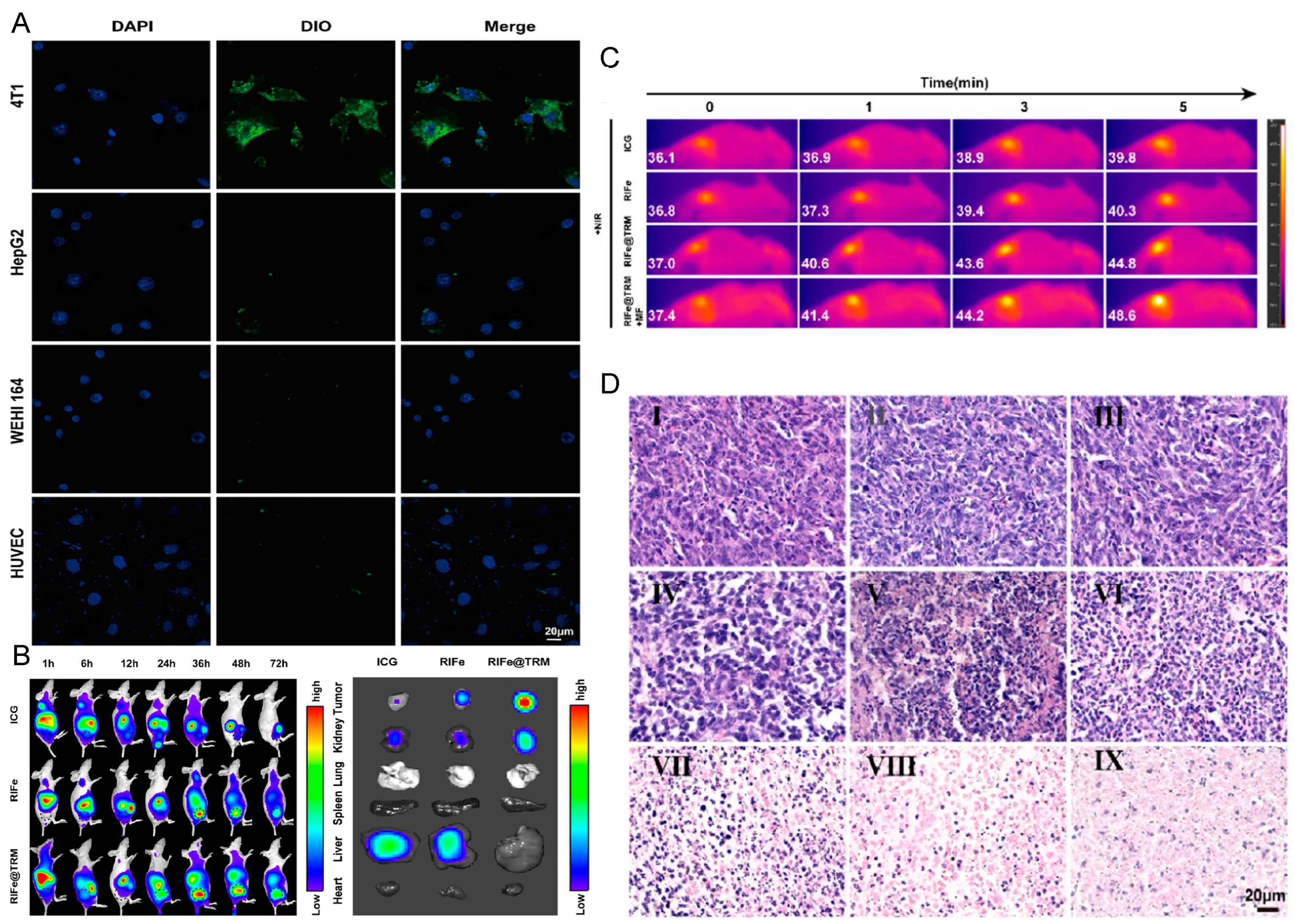


| Type of CMC@NPs | Cancer Models | References |
|---|---|---|
| RBCm@NPs | Melanoma | [30,31] |
| Cervical cancer | [32,33] | |
| Breast cancer | [34,35] | |
| Colon cancer | [23] | |
| Liver cancer | [36,37] | |
| PLTm@NPs | Melanoma | [38,39] |
| PLTm@NPs | Breast cancer | [40,41,42] |
| Colon cancer | [42,43] | |
| Liver cancer | [44] | |
| Nm@NPs | Breast cancer | [7,28] |
| Liver cancer | [45] | |
| Pancreatic cancer | [46,47] | |
| Mm@NPs | Breast cancer | [48,49,50] |
| Osteosarcoma | [51] | |
| Glioma | [52] | |
| Tm@NPs | Melanoma | [53,54] |
| Liver cancer | [55] | |
| Glioma | [56] | |
| Lymphoma | [57] | |
| DCm@NPs | Melanoma | [58,59] |
| Breast cancer | [60,61] | |
| Liver cancer | [62] | |
| Glioma | [63] | |
| NKm@NPs | Breast cancer | [64] |
| Liver cancer | [65] | |
| Glioma | [66,67] | |
| SCm@NPs | Liver cancer | [68] |
| Bone cancer | [69] | |
| Prostate cancer | [70] | |
| CCm@NPs | Melanoma | [71,72,73] |
| Cervical cancer | [74,75] | |
| Breast cancer | [76,77] | |
| Colon cancer | [78] | |
| Osteosarcoma | [79,80] | |
| Colorectal cancer | [81] | |
| Oral squamous cell carcinoma | [82] | |
| Bladder cancer | [83] | |
| Hym@NPs | Melanoma | [84] |
| Breast cancer | [85,86,87] | |
| Liver cancer | [88] | |
| Colon cancer | [89] | |
| Osteosarcoma | [25] | |
| Glioma | [90,91,92,93] | |
| Ovarian cancer | [94] | |
| Gastric cancer | [95] |
| Source Cell | Inner Cores | Therapeutics | Key Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBCs | Curdlan | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Long circulation, immune evasion | [31] |
| Melanin | PTT | Long circulation, good biocompatibility | [36] | |
| PLGA/AIEgen/Poly(I:C) | PDT, immunotherapy | Long circulation, homing to spleen | [30] | |
| Fe3O4@Cu2−xS | MRI, PTT | Immune evasion | [32] | |
| UCNP | Tumor imaging | Good biocompatibility | [34] | |
| Ag2S | MRI, SDT | Long circulation, good biocompatibility | [23] | |
| PLGA | Chemotherapy | Long circulation, immune evasion | [35] | |
| PEG-b-PDLLA | Chemotherapy, PDT | Long circulation | [33] |
| Source Cell | Inner Cores | Therapeutics | Key Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLTs | PLA | Immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, good biocompatibility | [42] |
| - | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, responds to coagulation signals | [43] | |
| PLGA | PDT | Long circulation, tumor targeting | [40] | |
| Cu2O | PDT, cuproptosis | Long circulation, tumor targeting | [41] | |
| PLGA-ss-HA | Chemotherapy | Tumor targeting | [38] | |
| MSN | Chemotherapy | Tumor and damage vessel targeting | [44] | |
| MOF | Gene therapy | Tumor targeting | [102] | |
| MSN | Hypoxia-sensitive chemotherapy | Tumor and damage vessel targeting | [103] | |
| HGN | PTT | Long circulation, tumor targeting | [104] |
| Source Cell | Inner Cores | Therapeutics | Key Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutrophils | PPDG | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Inflammation targeting, immune induction | [7] |
| IMN | Isolation and analysis of CTCs | Tumor targeting, immune evasion | [28] | |
| Lip-GEM | Nanosecond pulsed electric field, chemotherapy | Tumor targeting | [46] | |
| PLGA | PDT | Tumor targeting, immune evasion | [45] | |
| PEG-PLGA | Chemotherapy | Tumor targeting | [47] | |
| Macrophages | PEG-PDPA | Immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction | [48] |
| - | Immunotherapy | Tumor and macrophage targeting | [51] | |
| PLGA | Immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, BBB crossing, immune induction | [107] | |
| Fe3O4 | Chemotherapy, phototherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction | [49] | |
| Polydopamine | PTT, immunotherapy | Tumor and inflammation targeting | [108] | |
| PLGA | MRI, chemotherapy, chemodynamic therapy | Long circulation, BBB crossing, tumor targeting | [52] | |
| UCNP | PDT, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune evasion, immune induction | [50] | |
| T cells | AIE | Gene editing, PTT | Tumor targeting, BBB crossing, good biocompatibility | [56] |
| HA | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction and evasion | [53] | |
| MSN | Gene editing, PTT | Tumor targeting | [55] | |
| PLGA | Immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction | [54] | |
| PLGA | PTT | Tumor targeting | [57] | |
| Dendritic cells | PLGA | Immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, BBB crossing, immune induction | [63] |
| MSN | PDT, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction | [62] | |
| PLGA | Immunotherapy | Immune induction | [58] | |
| AIE | PDT, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction | [60] | |
| PLGA | Click chemistry, immunotherapy | Immune induction | [59] | |
| Polymer NPs | Immunotherapy, PTT | Immune induction and evasion | [61] | |
| Natural killer cells | PLGA | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Long circulation, tumor targeting, BBB crossing | [66] |
| AsHMS-TA/FeIII | Thermodynamic–chemodynamic therapy | Long circulation, tumor targeting | [65] | |
| AIE | Fluorescence imaging, PTT | Tumor targeting, BBB crossing | [67] | |
| PLGA | Fluorescence imaging, MRI | Tumor targeting | [64] | |
| mPEG-PLGA | PDT, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune induction | [109] |
| Source Cell | Inner Cores | Therapeutics | Key Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cancer cells | Nanogel | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Homologous targeting, long circulation | [8] |
| Silica | Chemotherapy | Homologous targeting | [81] | |
| Cu-ZnO | NO therapy | Tumor targeting, immune evasion | [74] | |
| MSN | Tumor vaccine, immunotherapy | Immune induction | [71] | |
| PEI | Tumor vaccine, gene editing | Homologous targeting, immune induction | [72] | |
| HMnO2 | Immunotherapy, chemodynamic therapy | Long circulation, homologous targeting | [79] | |
| Fe-PDAP | SDT, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting | [76] | |
| CMOx | PTT, immunotherapy | Tumor targeting, immune evasion | [77] | |
| TiO2 | SDT, PTT | Tumor targeting | [75] |
| Source Cell | Inner Cores | Therapeutics | Key Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLTm-Nm | Gold nanocage | Chemotherapy, PTT | High affinity for CTCs and exosomes | [85] |
| Mm-CCm | Fe3O4 | Chemodynamic therapy, immunotherapy, PDT | Immune evasion, homologous targeting | [86] |
| Mm-CCm-mH | CPC@MTIC | Chemotherapy | BBB crossing, homologous and inflammation targeting | [90] |
| CCm-CCm | OA-LnNPs | PTT | BBB crossing, homologous targeting | [91] |
| DCm-CCm | HPMC | Chemotherapy, immunotherapy | Homologous targeting, immune induction | [92] |
| RBCm-CCm | TK-PPE | PTT, immunotherapy | Long circulation, homologous targeting | [94] |
| RBCm-CCm | PLGA | Chemotherapy, PDT | Long circulation, homologous targeting | [89] |
| WBCm-CCm | Fe3O4 | Isolation and analysis of CTCs | Tumor targeting, immune evasion | [87] |
| Mm-Nm | Ag2S | Immunotherapy | Homologous and inflammation targeting, BBB crossing | [93] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, B. Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040531
Zhang S, Zhang X, Gao H, Zhang X, Sun L, Huang Y, Zhang J, Ding B. Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(4):531. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040531
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shu, Xiaojuan Zhang, Huan Gao, Xiaoqin Zhang, Lidan Sun, Yueyan Huang, Jie Zhang, and Baoyue Ding. 2024. "Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 4: 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040531
APA StyleZhang, S., Zhang, X., Gao, H., Zhang, X., Sun, L., Huang, Y., Zhang, J., & Ding, B. (2024). Cell Membrane-Coated Biomimetic Nanoparticles in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics, 16(4), 531. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16040531







