Physicochemical Stability of Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions: Effect of Changes in Composition and Storage Protocol
Abstract
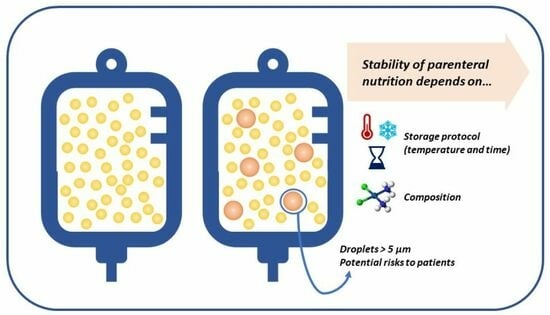
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Storage
2.2. Study of Droplet Diameter
2.3. Density, Viscosity and pH Variation
2.4. Visual Controls
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Droplet Diameter
3.2. pH
3.3. Viscosity and Density
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boullata, J.I.; Gilbert, K.; Sacks, G.; Labossiere, R.J.; Crill, C.; Goday, P.; Kumpf, V.J.; Mattox, T.W.; Plogsted, S.; Holcombe, B.; et al. ASPEN clinical Guidelines: Parenteral Nutrition Ordering, Order Review, Compounding, Labeling, and Dispensing. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2014, 38, 334–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibault, R.; Abbasoglu, O.; Ioannou, E.; Meija, L.; Ottens-Oussoren, K.; Pichard, C.; Rothenberg, E.; Rubin, D.; Siljamäki-Ojansuu, U.; Vaillant, M.-F.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Hospital Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5684–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boullata, J.I.; Berlana, D.; Pietka, M.; Klek, S.; Martindale, R. Use of Intravenous Lipid Emulsions with Parenteral Nutrition: Practical Handling Aspects. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2020, 44 (Suppl. S1), S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, D.C.; Peris, M.C.; Arévalo, M.F.; Muñoz, P.G.; Tutor, M.J.M.; Corrales, G.P.; Penín, I.R.; Polo, A.V. Consenso Español Sobre la Preparación de Mezclas Nutrientes Parenterales. Farm. Hosp. 2009, 33, 81–107. [Google Scholar]
- Planas, M. Conceptos Prácticos en Nutrición Enteral y Parenteral, 1st ed.; Ediciones Mayo: Barcelona, Spain, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, P.G.; Zanuy, M.V. Nutrición Parenteral; Hernández, Á.G., De Nutrición, T., Eds.; Médica Panamericana: Madrid, Spain, 2010; pp. 143–169. [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Nehne, J.; Peterss, H.; Klütsch, K.; Bistrian, B.R.; Niemann, W. Physicochemical Stability of Intravenous Lipid Emulsions as All-in-One Admixtures Intended for the Very Young. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Thoma, A.; Franke, R.; Klütsch, K.; Nehne, J.; Bistrian, B.R. Lipid Globule Size in Total Nutrient Admixtures Prepared in Three-Chamber Plastic Bags. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2009, 66, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero-Millán, L.; Lago Rivero, N.; Blanco Rodicio, A.; García Beloso, N.; Legido Soto, J.L.; Piñeiro-Corrales, G. Stability of Lipid Emulsion in Total Parenteral Nutrition: An Overview of Literature. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 45, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockville, M.D. Globule Size Distribution in Lipid Injectable Emulsions. In United States Pharmacopeia; General Chapter, (729); United States Pharmacopeia (USP-NF): Frederick, MD, USA, 2023; Available online: https://doi.org/10.31003/USPNF_M99505_02_01 (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Skouroliakou, M.; Matthaiou, C.; Chiou, A.; Panagiotakos, D.; Gounaris, A.; Nunn, T.; Andrikopoulos, N. Physicochemical Stability of Parenteral Nutrition Supplied as All-in-One for Neonates. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2008, 32, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Parikh, M.; Silvestri, A.P.; Klütsch, K.; Bistrian, B.R.; Nehne, J. Establishing a Stability Window for Medium- and Long-Chain-Triglyceride Lipid-Based Total Nutrient Admixtures Using USP Standards. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2006, 63, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Giampietro, K.; Wichelhaus, D.P.; Peterss, H.; Nehne, J.; Niemann, W.; Bistrian, B.R. Physico-Chemical Stability Assessments of Lipid Emulsions of Varying Oil Composition. Clin. Nutr. 2001, 20, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Silvestri, A.P.; Nehne, J.; Klütsch, K.; Bistrian, B.R.; Niemann, W. Physicochemical Stability of Highly Concentrated Total Nutrient Admixtures for Fluid-Restricted Patients. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2006, 63, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, D.W.; Driscoll, D.F. Calcium and Phosphate Compatibility: Revisited Again. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2008, 65, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foinard, A.; Perez, M.; Barthélémy, C.; Lannoy, D.; Flamein, F.; Storme, L.; Addad, A.; Bout, M.-A.; Décaudin, B.; Odou, P. In Vitro Assessment of Interaction Between Amino Acids and Copper in Neonatal Parenteral Nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2016, 40, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.M.; Skillman, H.E.; Irving, S.Y.; Coss-Bu, J.A.; Vermilyea, S.; Farrington, E.A.; McKeever, L.; Hall, A.M.; Goday, P.S.; Braunschweig, C. Guidelines for the Provision and Assessment of Nutrition Support Therapy in the Pediatric Critically Ill Patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 706–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihatsch, W.A.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Desci, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN Guidelines on Pediatric Parenteral Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2303–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero-Millán, L.; Bea-Mascato, B.; Legido Soto, J.L.; Martínez-López-De-Castro, N.; Lago-Rivero, N. Evaluation of the Stability of Newborn Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Ling, P.-R.; Quist, W.C.; Bistrian, B.R. Pathological Consequences from the Infusion of Unstable Lipid Emulsion Admixtures in Guinea Pigs. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.F. Quality, stability and safety of lipid emulsions. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 2 (Suppl. S3), 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Gerard-Boncompain, M.; Claudel, J.P.; Gaussorgues, P.; Salord, F.; Sirodot, M.; Chevallier, M.; Robert, D. Hepatic Cytolytic and Cholestatic Changes Related to a Change of Lipid Emulsions in Four Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition Patients with Short Bowel. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1992, 16, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toce, S.S.; Keenan, W.J. Lipid Intolerance in Newborns Is Associated with Hepatic Dysfunction but Not Infection. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 1995, 149, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mckinnon, B.T. FDA Safety Alert: Hazards of Precipitation Associated with Parenteral Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 1996, 11, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, A.; Rivas, M.A.; Legido, J.; Iglesias, T.P. Study of Static Permittivity and Density of the Systems {(n-Nonane+monoglyme or Diglyme)} at Various Temperatures. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2009, 41, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Casanova, C.; Legido, J.L.; Piñeiro, M.M. CuO in Water Nanofluid: Influence of Particle Size and Polydispersity on Volumetric Behaviour and Viscosity. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2011, 300, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastoriza-Gallego, M.J.; Casanova, C.; Páramo, R.; Barbés, B.; Legido, J.L.; Piñeiro, M.M. A Study on Stability and Thermophysical Properties (Density and Viscosity) of Al2O3 in Water Nanofluid. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 064301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero, M.I.; Pozo, M.; Legido, J.L.; Fernández-González, M.V.; Delgado, R.; Gómez, I.; Armijo, F.; Maraver, F. Assessment of Three Spanish Clays for Their Use in Pelotherapy. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 99, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casás, L.M.; Pozo, M.; Gómez, C.P.; Pozo, E.; Bessières, L.D.; Plantier, F.; Legido, J.L. Thermal Behavior of Mixtures of Bentonitic Clay and Saline Solutions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 72, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.F.; Silvestri, A.P.; Bistrian, B.R. Stability of MCT/LCT-Based Total Nutrient Admixtures for Neonatal Use over 30 Hours at Room Temperature: Applying Pharmacopeial Standards. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2010, 34, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watrobska-Swietlikowska, D.; Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, A.; Łuszkiewicz, K. Evaluation of Physical Stability of All in One Parenteral Admixtures for Pediatric Home Care with High Electrolytes Concentrations. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 31, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watrobska-Swietlikowska, D.; Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, A.; MacLoughlin, R. The Presence of Inorganic Calcium in Pediatric Parenteral Admixtures. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonyon, T.; Tomaso, A.E.; Kotha, P.; Owen, H.; Patel, D.; Carter, P.W.; Cronin, J.; Green, J.-B.D. Interactions between Parenteral Lipid Emulsions and Container Surfaces. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ribeiro, D.O.; Lobo, B.W.; Volpato, N.M.; da Veiga, V.F.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Influence of the Calcium Concentration in the Presence of Organic Phosphorus on the Physicochemical Compatibility and Stability of All-in-One Admixtures for Neonatal Use. Nutr. J. 2009, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janů, M.; Brodská, H.; Vecka, M.; Masteiková, R.; Kotrlíková, E.; Lažauskas, R.; Pečiūra, R.; Bernatonienė, J. Comparison of Long-Term Stability of Parenteral All-in-One Admixtures Containing New Lipid Emulsions Prepared under Hospital Pharmacy Conditions. Medicina 2011, 47, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne-James, J.; Grimble, G.; Silk, D. Parenteral Nutrition Formulation. In Artificial Nutrition Support in Clinical Practise; Simon, A., Ed.; Medical Media: Greenwich, UK, 1995; pp. 321–332. [Google Scholar]
- Chaieb, D.S.; Chaumeil, J.C.; Jebnoun, S.; Khrouf, N.; Hedhili, A.; Sfar, S. Effect of the Intravenous Lipid Emulsions on the Availability of Calcium When Using Organic Phosphate in TPN Admixtures. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CIMA. Ficha Técnica Aminoplasmal b. Braun 10% Solución Para Perfusión. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/p/67054/P_67054.html (accessed on 29 June 2023).
- CIMA. Ficha Técnica Aminoven Infant 10% Solución Para Perfusión. Available online: https://cima.aemps.es/cima/dochtml/ft/59628/FT_59628.html (accessed on 29 June 2023).






| Sample | N (g/L) | Prot (g/L) | Gluc (g/L) | Lip (g/L) | Na (mMol/L) | K (mMol/L) | Mg (mMol/L) | Ca (mMol/L) | P (mMol/L) | OSM (mOsm/L) | CAN (mMol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PN BASE | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1030.00 | 2020.00 |
| PN1 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 50.00 | 12.50 | 1130.00 | 3620.00 |
| PN2 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 62.50 | 12.50 | 1180.00 | 4420.00 |
| PN3 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 75.00 | 12.50 | 1230.00 | 5220.00 |
| PN4 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 87.50 | 12.50 | 1280.00 | 6020.00 |
| PN5 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 12.50 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1060.00 | 2500.00 |
| PN6 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1110.00 | 3300.00 |
| PN7 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 37.50 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1160.00 | 4100.00 |
| PN8 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 50.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1210.00 | 4900.00 |
| PN9 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 20.00 | 1043.50 | 2020.00 |
| PN10 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 48.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 30.00 | 1101.50 | 2028.00 |
| PN11 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 80.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 50.00 | 1217.50 | 2060.00 |
| PN12 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 120.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 100.00 | 1507.50 | 2100.00 |
| PN13 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 15.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1015.00 | 2020.00 |
| PN14 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 10.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 1000.00 | 2020.00 |
| PN15 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 5.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 985.00 | 2020.00 |
| PN16 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 2.50 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 977.50 | 2020.00 |
| PN17 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 75.00 | 1.24 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 973.75 | 2020.00 |
| PN18 | 3.50 | 21.87 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 995.63 | 2020.00 |
| PN19 | 3.00 | 18.75 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 961.25 | 2020.00 |
| PN20 | 2.50 | 15.62 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 926.88 | 2020.00 |
| PN21 | 1.50 | 9.37 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 858.13 | 2020.00 |
| PN22 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 75.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 5.00 | 25.00 | 12.50 | 755.00 | 2020.00 |
| Sample | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 10 | Day 14 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 °C | 4 °C | RT | 4 °C | RT | 4 °C | RT | |
| PN13 | 1.415 ± 0.004 | 1.402 ± 0.003 | 1.394 ± 0.003 | 1.399 ± 0.003 | 1.397 ± 0.004 | 1.411 ± 0.007 | 1.394 ± 0.004 |
| PN14 | 1.365 ± 0.008 | 1.361 ± 0.005 | 1.368 ± 0.005 | 1.369 ± 0.004 | 1.365 ± 0.004 | 1.375 ± 0.003 | 1.387 ± 0.005 |
| PN15 | 1.370 ± 0.004 | 1.344 ± 0.003 | 1.343 ± 0.004 | 1.347 ± 0.006 | 1.343 ± 0.004 | 1.357 ± 0.004 | 1.351 ± 0.004 |
| PN16 | 1.343 ± 0.004 | 1.329 ± 0.003 | 1.321 ± 0.005 | 1.334 ± 0.005 | 1.356 ± 0.002 | 1.334 ± 0.005 | 1.331 ± 0.004 |
| PN17 | 1.327 ± 0.005 | 1.316 ± 0.003 | 1.316 ± 0.003 | 1.320 ± 0.005 | 1.346 ± 0.003 | 1.320 ± 0.004 | 1.318 ± 0.003 |
| Sample | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 10 | Day 14 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 °C | 4 °C | RT | 4 °C | RT | 4 °C | RT | |
| PN13 | 1.045 | 1.049 | 1.045 | 1.049 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 |
| PN14 | 1.044 | 1.044 | 1.044 | 1.044 | 1.044 | 1.044 | 1.044 |
| PN15 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 |
| PN16 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.046 | 1.045 |
| PN17 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 | 1.045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otero-Millán, L.; Bea-Mascato, B.; Legido Soto, J.L.; Martínez-López-De-Castro, N.; Lago-Rivero, N. Physicochemical Stability of Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions: Effect of Changes in Composition and Storage Protocol. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050572
Otero-Millán L, Bea-Mascato B, Legido Soto JL, Martínez-López-De-Castro N, Lago-Rivero N. Physicochemical Stability of Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions: Effect of Changes in Composition and Storage Protocol. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(5):572. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050572
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtero-Millán, Luis, Brais Bea-Mascato, Jose Luis Legido Soto, Noemi Martínez-López-De-Castro, and Natividad Lago-Rivero. 2024. "Physicochemical Stability of Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions: Effect of Changes in Composition and Storage Protocol" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 5: 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050572
APA StyleOtero-Millán, L., Bea-Mascato, B., Legido Soto, J. L., Martínez-López-De-Castro, N., & Lago-Rivero, N. (2024). Physicochemical Stability of Hospital Parenteral Nutrition Solutions: Effect of Changes in Composition and Storage Protocol. Pharmaceutics, 16(5), 572. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16050572