Effect of Multiple-Cycle Collections of Conditioned Media from Different Cell Sources towards Fibroblasts in In Vitro Wound Healing Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells Isolation and Culture
2.2. Preparation and Collection of Multiple Cycles of Conditioned Medium
2.3. Protein Filtration and Concentration
2.4. Evaluation of Protein Molecular Weight
2.5. Proliferation and Migration Rate Activities
2.5.1. Fibroblast Proliferation
2.5.2. Immunocytochemistry Staining for Proliferative Cells
2.5.3. Scratch Wound Healing Assays
2.6. Fabrication of DFCM/WJCM with Collagen Hydrogel Construct
2.7. Protein Release Profile
2.8. Sample Size Calculation
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
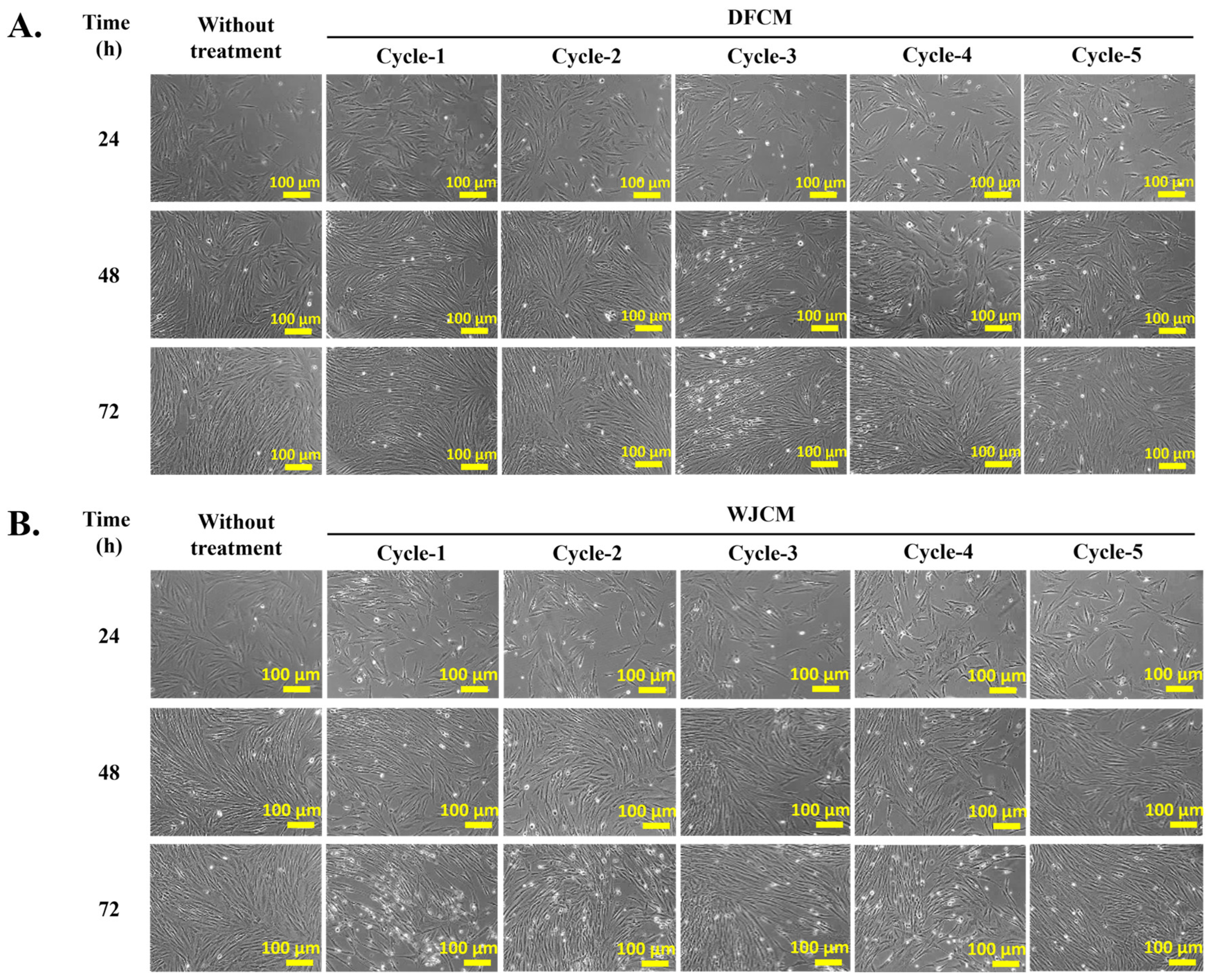
3.1. Effect of DFCM and WJCM on the Cells Morphology
3.2. Concentrations of Secreted Proteins from DFCM and WJCM
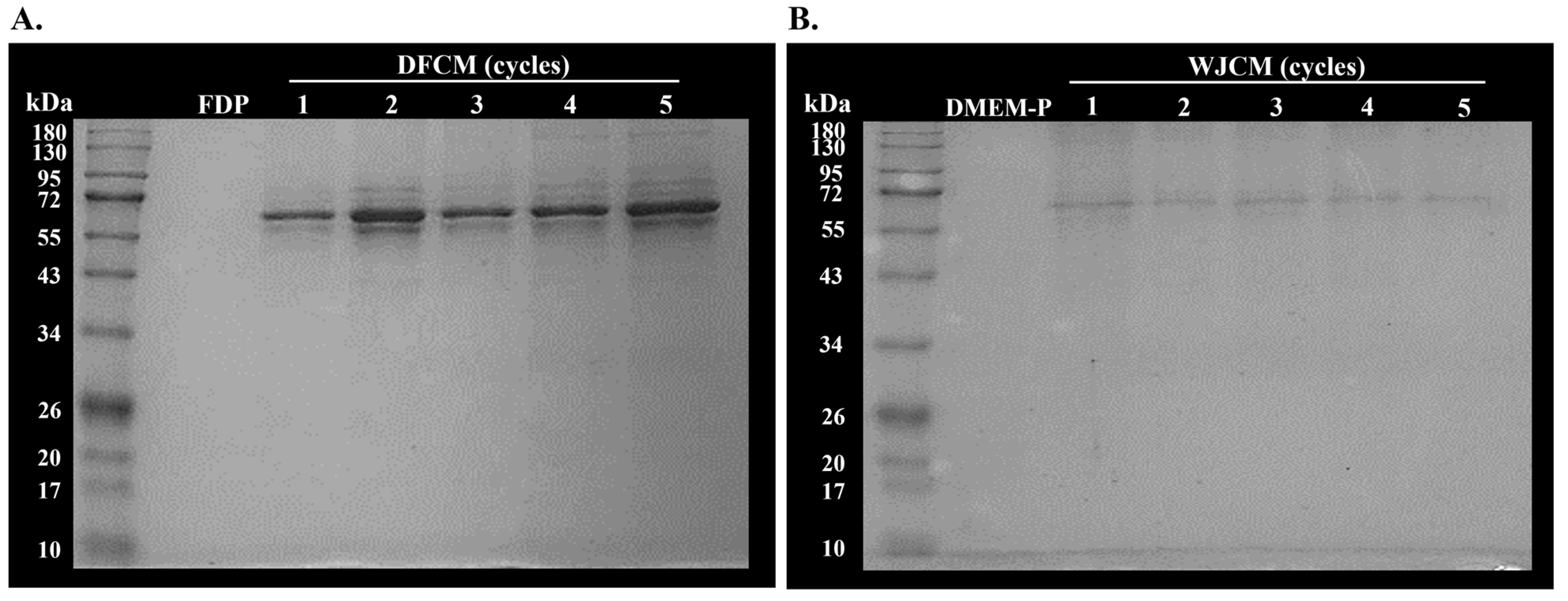
3.3. Determination of Molecular Weight of Secreted Proteins from DFCM and WJCM by SDS-PAGE
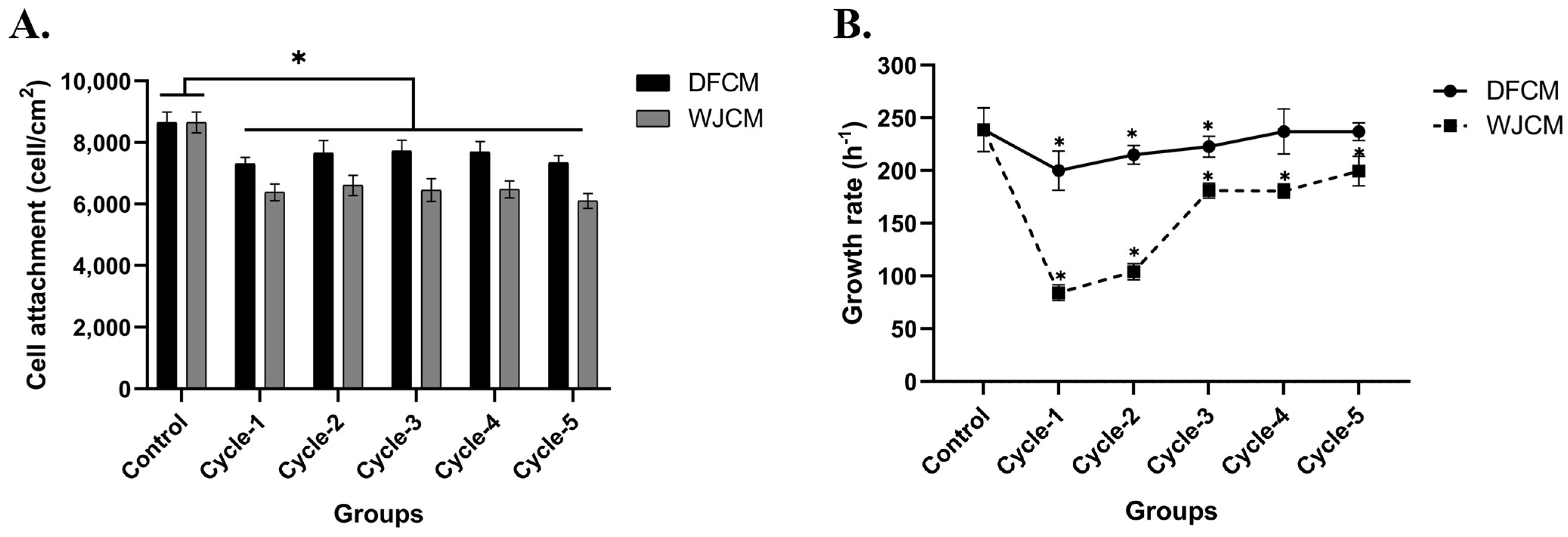
3.4. Effect of DFCM and WJCM on the Fibroblast Proliferation
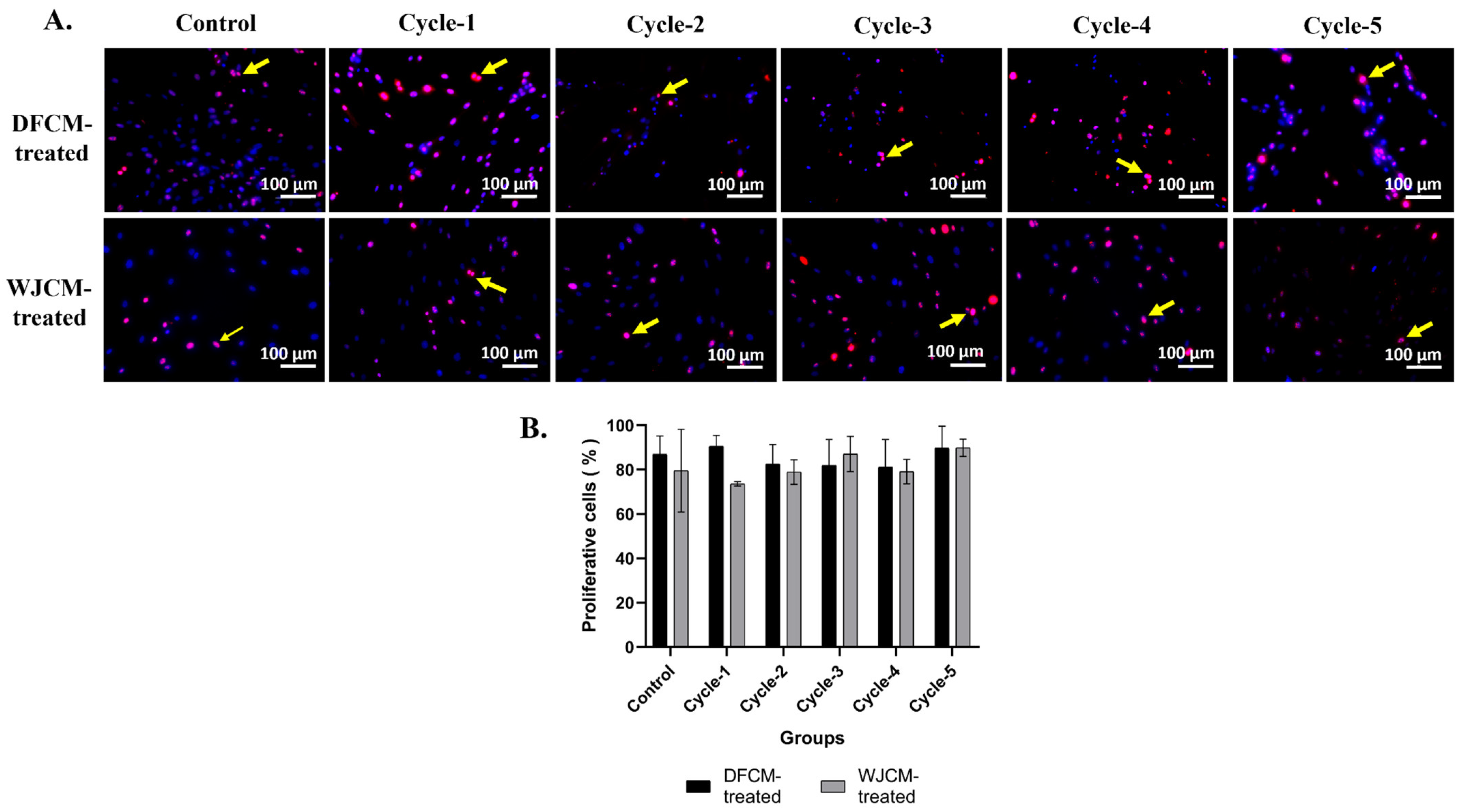
3.5. Immunocytochemistry Staining for Proliferative Cells
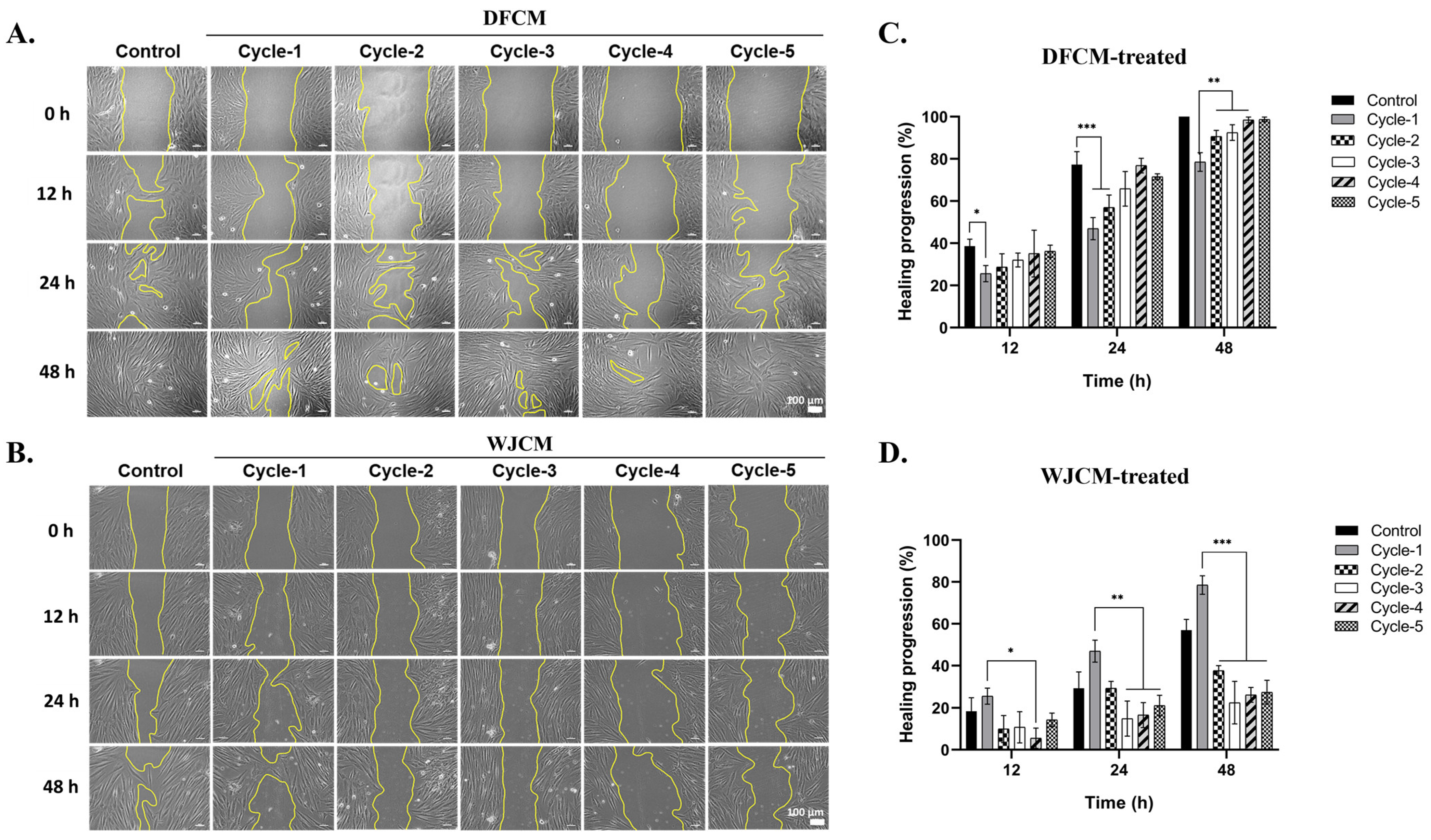
3.6. Effect of Dermal Fibroblast-Conditioned Medium (DFCM) on Fibroblast Migration
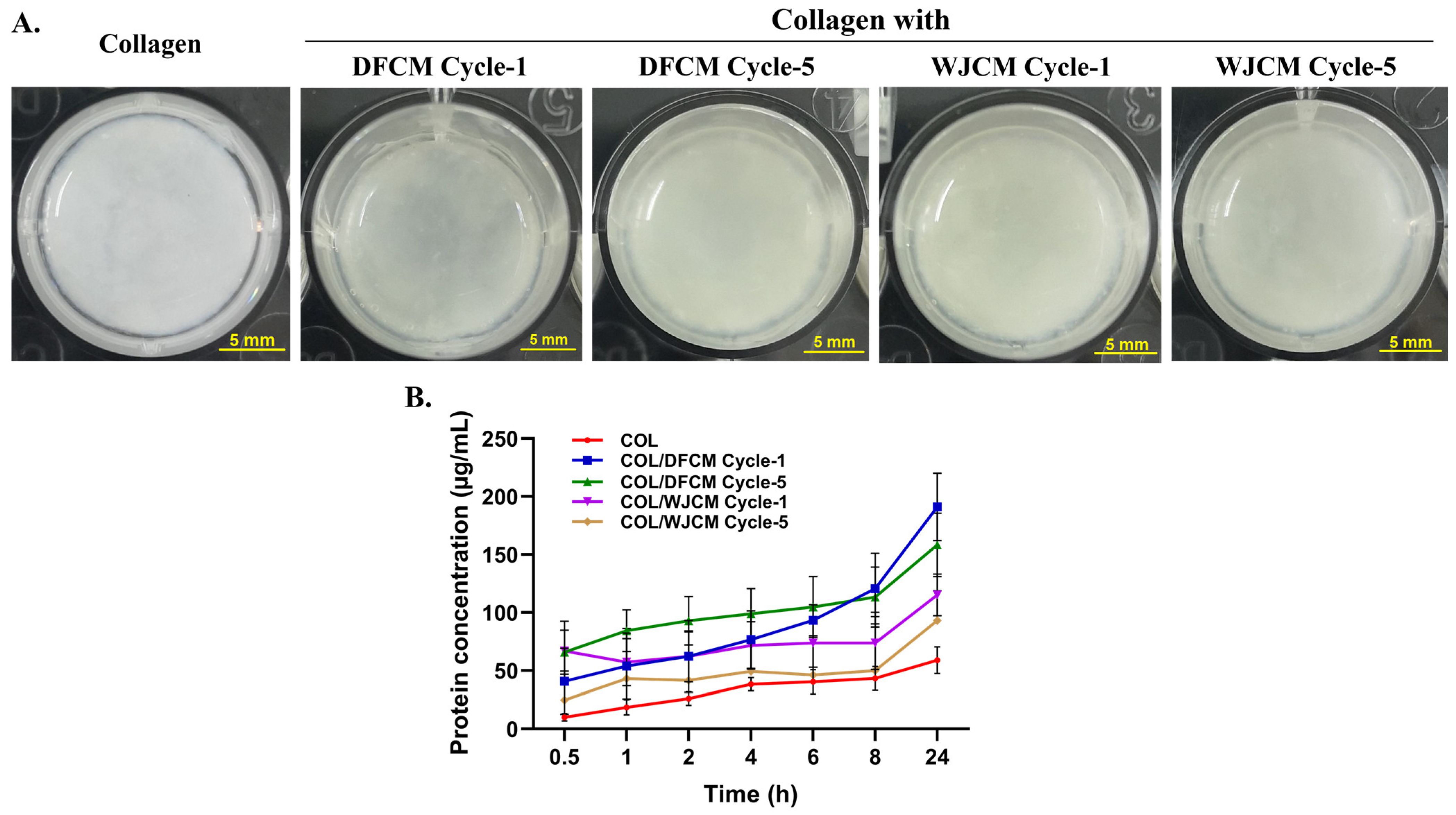
3.7. Fabrication of 3D Construct of Collagen/Conditioned-Medium and Protein Release Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heydari, M.B.; Ghanbari-Movahed, Z.; Heydari, M.; Farzaei, M.H. In vitro study of the mesenchymal stem cells-conditional media role in skin wound healing process: A systematic review. Int. Wound J. 2022, 19, 2210–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Isa, I.L.M.; Zaman, W.S.W.K.; Tabata, Y.; Fauzi, M.B. The effect of nanoparticle-incorporated natural-based biomaterials towards cells on activated pathways: A systematic review. Polymers 2022, 14, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazlyzam, A.L.; Aminuddin, B.S.; Fuzina, N.H.; Norhayati, M.M.; Fauziah, O.; Isa, M.R.; Saim, L.; Ruszymah, B.H. Reconstruction of living bilayer human skin equivalent utilizing human fibrin as a scaffold. Burns 2007, 33, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seet, W.T.; Manira, M.; Khairul Anuar, K.; Chua, K.-H.; Ahmad Irfan, A.W.; Ng, M.H.; Saim Aminuddin, B.; Idrus Ruszymah, B.H. Correction: Shelf-Life Evaluation of Bilayered Human Skin Equivalent, MyDerm™. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrus, R.B.; Rameli, M.A.; Low, K.C.; Law, J.X.; Chua, K.H.; Latiff, M.B.; Saim, A.B. Full-thickness skin wound healing using autologous keratinocytes and dermal fibroblasts with fibrin: Bilayered versus single-layered substitute. Adv Ski. Wound Care 2014, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damayanti, R.H.; Rusdiana, T.; Wathoni, N. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome for dermatology application: A review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1401–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirthalingam, M.; Bhat, S.; Dighe, P.A.; Seetharam, R. Human mesenchymal stromal cells-derived conditioned medium based formulation for advanced skin care: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Stem Cells Res. Dev. Ther. 2019, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pawitan, J.A. Prospect of stem cell conditioned medium in regenerative medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 965849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, A.G.; Cibrão, J.R.; Silva, N.A.; Monteiro, S.; Salgado, A.J. Cell secretome: Basic insights and therapeutic opportunities for CNS disorders. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarof, M.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Saim, A.; Bt Hj Idrus, R.; Lokanathan, Y. Concentration dependent effect of human dermal fibroblast conditioned medium (Dfcm) from three various origins on keratinocytes wound healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarof, M.; Mh Busra, M.F.; Lokanathan, Y.; Bt Hj Idrus, R.; Rajab, N.F.; Chowdhury, S.R. Safety and efficacy of dermal fibroblast conditioned medium (DFCM) fortified collagen hydrogel as acellular 3D skin patch. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarof, M.; Lokanathan, Y.; Ruszymah, H.I.; Saim, A.; Chowdhury, S.R. Proteomic Analysis of Human Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium (DFCM). Protein J. 2018, 37, 589–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collawn, S.S.; Mobley, J.A.; Banerjee, N.S.; Chow, L.T. Conditioned media from adipose-derived stromal cells accelerates healing in 3-dimensional skin cultures. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2016, 76, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Hao, H.; Liu, J.; Ti, D.; Tong, C.; Hou, Q.; Li, M.; Zheng, J.; Liu, G.; Fu, X. A conditioned medium of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing Wnt7a promotes wound repair and regeneration of hair follicles in mice. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 3738071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wang, B.; Tang, T.; Lv, L.; Ding, Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, R.; Wei, Q.; Shen, A.; Fu, Y.; et al. Three-dimensional culture of MSCs produces exosomes with improved yield and enhanced therapeutic efficacy for cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahangar, P.; Mills, S.J.; Cowin, A.J. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome as an emerging cell-free alternative for improving wound repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocchi, M.; Dotti, S.; Del Bue, M.; Villa, R.; Bari, E.; Perteghella, S.; Torre, M.L.; Grolli, S. Veterinary regenerative medicine for musculoskeletal disorders: Can mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and their secretome be the new frontier? Cells 2020, 9, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, M.N.; Wright, K.T.; Fuller, H.R.; MacNeil, S.; Johnson, W.E.B. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium accelerates skin wound healing: An in vitro study of fibroblast and keratinocyte scratch assays. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Jailani, M.S.M.A.K.; Hisham, M.A.I.B.; Raj, N.S.; Shamsuddin, S.A.; Ng, M.H.; Fauzi, M.B.; Maarof, M. Cell secretomes for wound healing and tissue regeneration: Next generation acellular based tissue engineered products. J. Tissue Eng. 2022, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tredget, E.E.; Wu, P.Y.; Wu, Y. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-S.; Park, B.-S.; Sung, J.-H.; Yang, J.-M.; Park, S.-B.; Kwak, S.-J.; Park, J.-S. Wound healing effect of adipose-derived stem cells: A critical role of secretory factors on human dermal fibroblasts. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2007, 48, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangadaran, P.; Oh, E.J.; Rajendran, R.L.; Oh, J.M.; Kim, H.M.; Kwak, S.; Chung, H.Y.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.-C.; Hong, C.M. Three-dimensional culture conditioned bone marrow MSC secretome accelerates wound healing in a burn injury mouse model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 673, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, Q. The Healing Effects of Conditioned Medium Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Radiation-Induced Skin Wounds in Rats. Cell Transpl. 2019, 28, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauzi, M.; Lokanathan, Y.; Aminuddin, B.; Ruszymah, B.; Chowdhury, S. Ovine tendon collagen: Extraction, characterisation and fabrication of thin films for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, M.; Morimoto, N.; Ogino, S.; Jinno, C.; Taira, T.; Suzuki, S. Efficacy of gelatin gel sheets in sustaining the release of basic fibroblast growth factor for murine skin defects. J. Surg. Res. 2016, 201, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ejiri, H.; Nomura, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Tatsumi, C.; Imai, M.; Sakakibara, S.; Terashi, H. Use of synthetic serum-free medium for culture of human dermal fibroblasts to establish an experimental system similar to living dermis. Cytotechnology 2015, 67, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitz, H.d.S.; Pereira, A.; Blasius, M.B.; Voytena, A.P.L.; Affonso, R.C.; Fanan, S.; Trevisan, A.C.; Ribeiro-do-Valle, R.M.; Maraschin, M. In vitro evaluation of the antioxidant activity and wound healing properties of Jaboticaba (Plinia peruviana) fruit peel hydroalcoholic extract. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3403586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Ahmad, H.; Abdul Rahman, M.B.; Chia, S.L.; Ng, S.-F.; Leong, S.W. Synthesis and in vitro biological evaluations of novel tetrapeptide as therapeutic agent for wound treatment. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.-Q.; Hu, Z.; Lin, Z.-P.; Quan, W.-Y.; Deng, Y.-F.; Li, S.-D.; Li, P.-W.; Chen, Y. Chitosan hydrogel in combination with marine peptides from tilapia for burns healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 112, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniandy, K.; Gothai, S.; Tan, W.S.; Kumar, S.S.; Mohd Esa, N.; Chandramohan, G.; Al-Numair, K.S.; Arulselvan, P. In vitro wound healing potential of stem extract of Alternanthera sessilis. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 3142073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Motta, A.; Tabata, Y.; Fauzi, M.B. The discovery and development of natural-based biomaterials with demonstrated wound healing properties: A reliable approach in clinical trials. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Riha, S.M.; Mazlan, Z.; Wen, A.P.Y.; Hao, L.Q.; Joseph, B.; Maarof, M.; Thomas, S.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B. Functionalised-biomatrix for wound healing and cutaneous regeneration: Future impactful medical products in clinical translation and precision medicine. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1160577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capo, J.T.; Kokko, K.P.; Rizzo, M.; Adams, J.E.; Shamian, B.; Abernathie, B.; Melamed, E. The use of skin substitutes in the treatment of the hand and upper extremity. Hand 2014, 9, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, G.B.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.W.; Jung, E.; Jeong, G.J.; Wang, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, D.I.; Kim, T.H.; et al. Enhancing the Wound Healing Effect of Conditioned Medium Collected from Mesenchymal Stem Cells with High Passage Number Using Bioreducible Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, X.; Lin, F.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, X.; Meng, Q.; Ma, X.; Wei, L.; Fan, H.; et al. Conditioned medium from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing through enhanced angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, S.; Aminuddin, B.; Ruszymah, B. Effect of supplementation of dermal fibroblasts conditioned medium on expansion of keratinocytes through enhancing attachment. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 50, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rapizzi, E.; Benvenuti, S.; Deledda, C.; Martinelli, S.; Sarchielli, E.; Fibbi, B.; Luciani, P.; Mazzanti, B.; Pantaleo, M.; Marroncini, G. A unique neuroendocrine cell model derived from the human foetal neural crest. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2020, 43, 1259–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarof, M.; Law, J.X.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Khairoji, K.A.; Saim, A.B.; Idrus, R.B.H. Secretion of wound healing mediators by single and bi-layer skin substitutes. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.L.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Y.C.; Cheng, L.; Liu, M.; Shi, J.; Yang, Y.Z.; Pan, C.; Ge, J.; Phillips, M.I. Autologous mesenchymal stem cell transplantation induce VEGF and neovascularization in ischemic myocardium. Regul. Pept. 2004, 117, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.M.; Hur, S.-M.; Park, K.-Y.; Kim, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, H.-S.; Shin, H.-C.; Won, M.-H.; Ha, K.-S.; Kwon, Y.-G. Multiple paracrine factors secreted by mesenchymal stem cells contribute to angiogenesis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 63, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi-Yuyama, E.; Matsubara, H.; Murohara, T.; Ikeda, U.; Shintani, S.; Masaki, H.; Amano, K.; Kishimoto, Y.; Yoshimoto, K.; Akashi, H. Therapeutic angiogenesis for patients with limb ischaemia by autologous transplantation of bone-marrow cells: A pilot study and a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 360, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, T.; Legesse-Miller, A.; Hameed, M.R.; Aisner, S.C.; Randolph-Habecker, J.; Coller, H.A. An immunohistochemical method for identifying fibroblasts in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2008, 56, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, H.; Dong, L.; Liu, J.; Han, W.; Fu, X. Umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal stromal cell–conditioned medium exerts in vitro antiaging effects in human fibroblasts. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Phang, S.J.; Kamaruzaman, N.; Salleh, A.; Zawani, M.; Sanyal, A.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Antioxidant biomaterials in cutaneous wound healing and tissue regeneration: A critical review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Rahman, M.B.A.; Yusof, L.M.; Mustapha, N.M.; Ahmad, H. The therapeutic effect and in vivo assessment of Palmitoyl-GDPH on the wound healing process. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radstake, W.E.; Gautam, K.; Van Rompay, C.; Vermeesen, R.; Tabury, K.; Verslegers, M.; Baatout, S.; Baselet, B. Comparison of in vitro scratch wound assay experimental procedures. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2023, 33, 101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.N.; Willis, E.; Chan, V.T.; Muffley, L.A.; Isik, F.F.; Gibran, N.S.; Hocking, A.M. Mesenchymal stem cells induce dermal fibroblast responses to injury. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Ahmat, N.; Hao, L.Q.; Maarof, M.; Rajab, N.F.; Idrus, R.B.H.; Fauzi, M.B. Biological Safety Assessments of High-Purified Ovine Collagen Type I Biomatrix for Future Therapeutic Product: International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) and Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) Settings. Polymers 2023, 15, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarof, M.; Mohd Nadzir, M.; Sin Mun, L.; Fauzi, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Idrus, R.B.H.; Lokanathan, Y. Hybrid Collagen Hydrogel/Chondroitin-4-Sulphate Fortified with Dermal Fibroblast Conditioned Medium for Skin Therapeutic Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9001:2015; Malaysian Standard—Quality Management System—Requirement. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadilah, N.I.M.; Fauzi, M.B.; Maarof, M. Effect of Multiple-Cycle Collections of Conditioned Media from Different Cell Sources towards Fibroblasts in In Vitro Wound Healing Model. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060767
Fadilah NIM, Fauzi MB, Maarof M. Effect of Multiple-Cycle Collections of Conditioned Media from Different Cell Sources towards Fibroblasts in In Vitro Wound Healing Model. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(6):767. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060767
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadilah, Nur Izzah Md, Mh Busra Fauzi, and Manira Maarof. 2024. "Effect of Multiple-Cycle Collections of Conditioned Media from Different Cell Sources towards Fibroblasts in In Vitro Wound Healing Model" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 6: 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060767
APA StyleFadilah, N. I. M., Fauzi, M. B., & Maarof, M. (2024). Effect of Multiple-Cycle Collections of Conditioned Media from Different Cell Sources towards Fibroblasts in In Vitro Wound Healing Model. Pharmaceutics, 16(6), 767. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16060767







