Use of Poly(vinyl alcohol) in Spray-Dried Dispersions: Enhancing Solubility and Stability of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
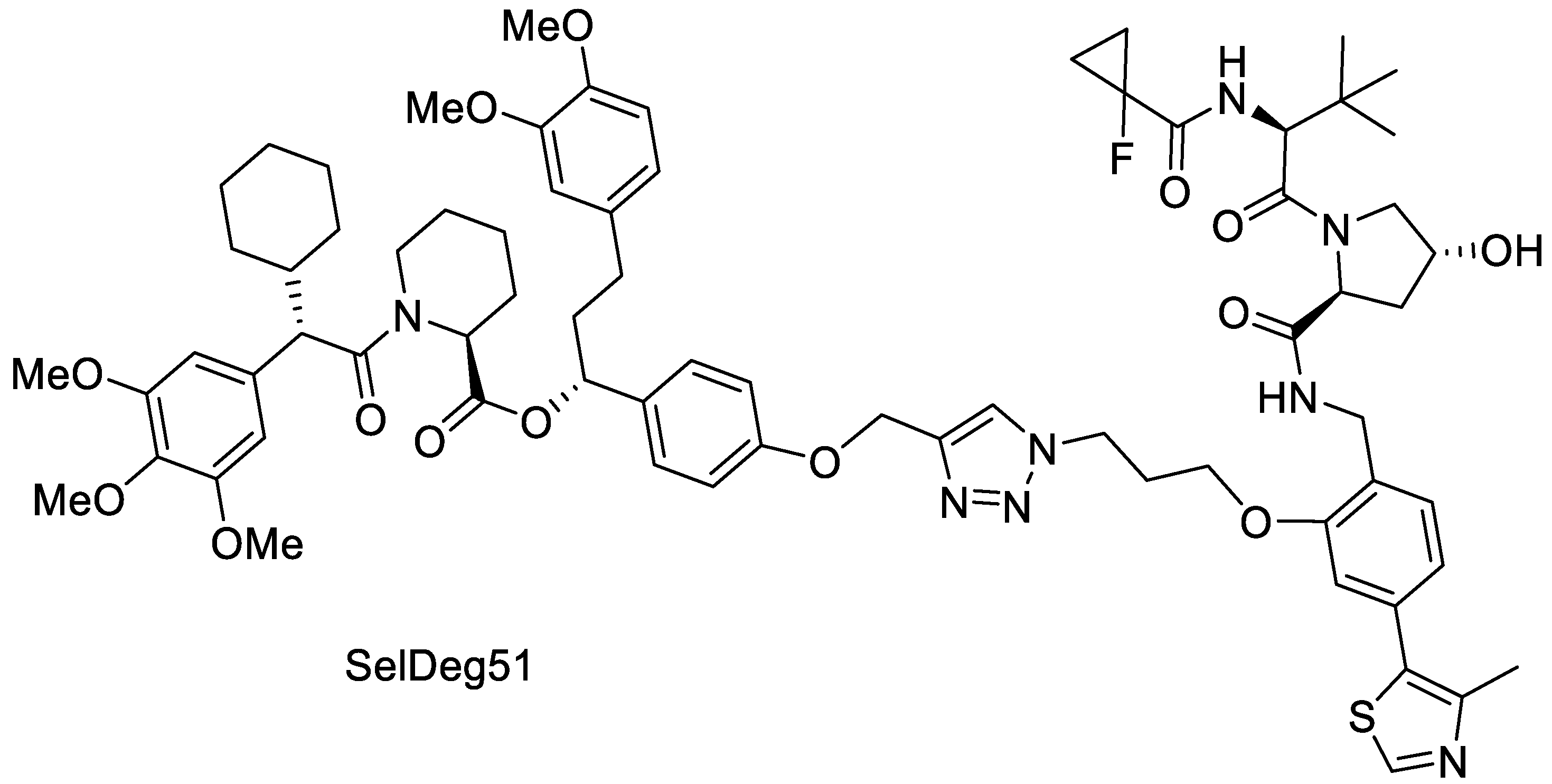
2.2.1. Synthesis of SelDeg51
2.2.2. Spray Drying
2.2.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
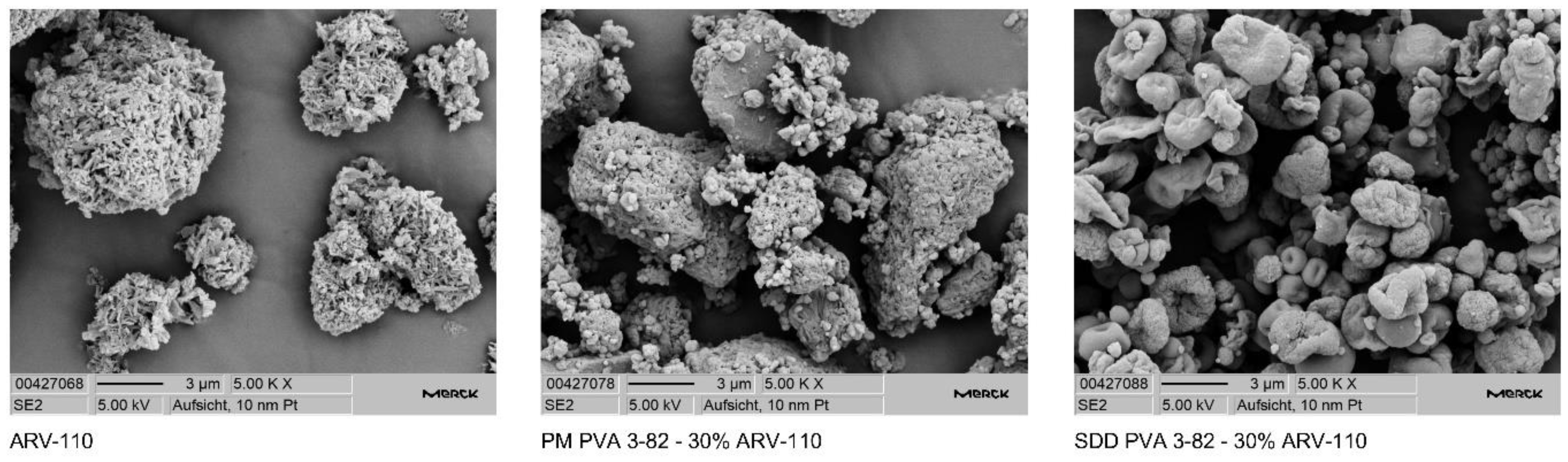
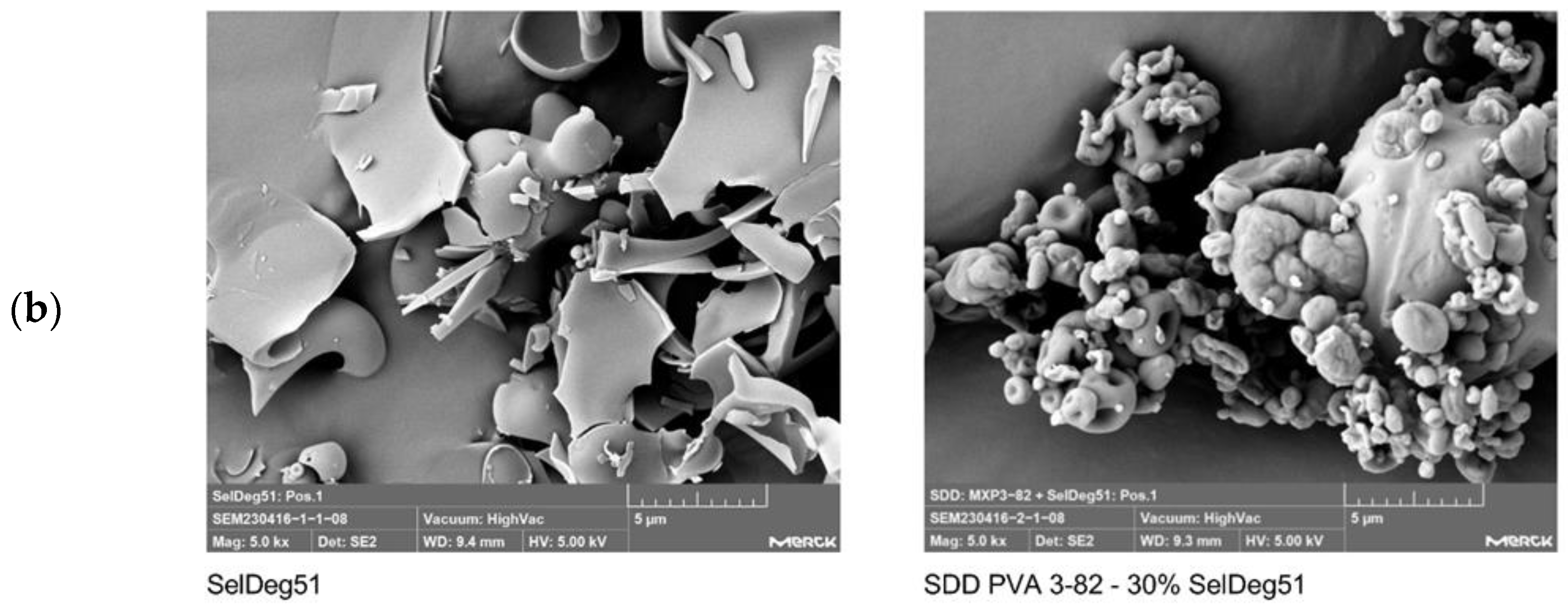
2.2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
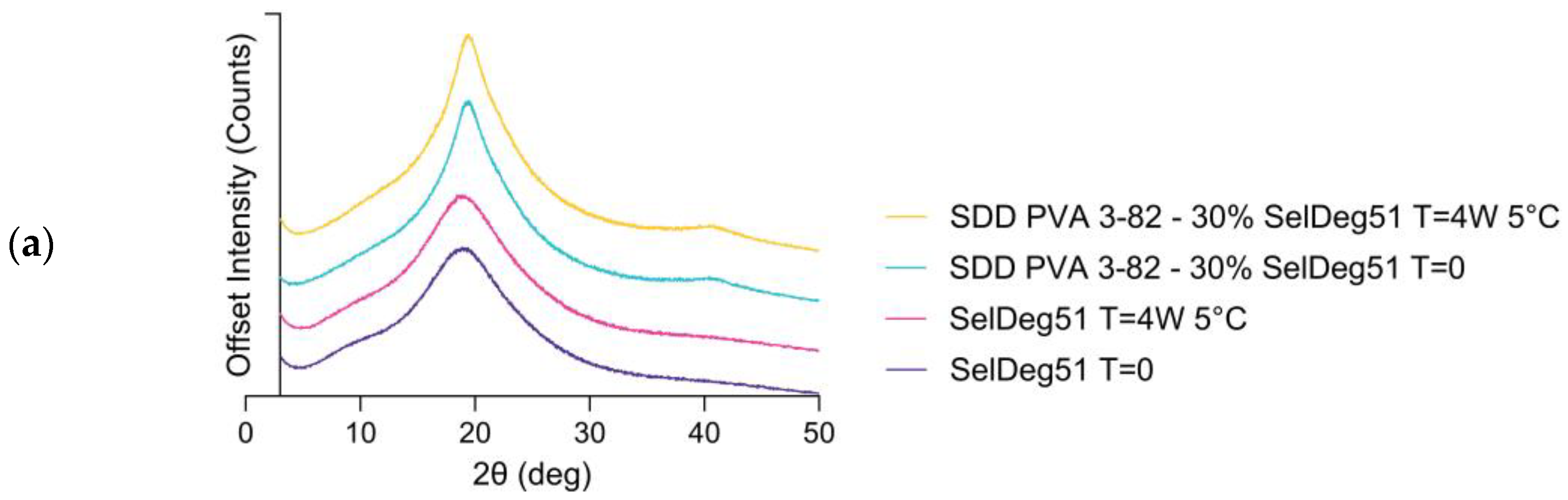
2.2.5. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
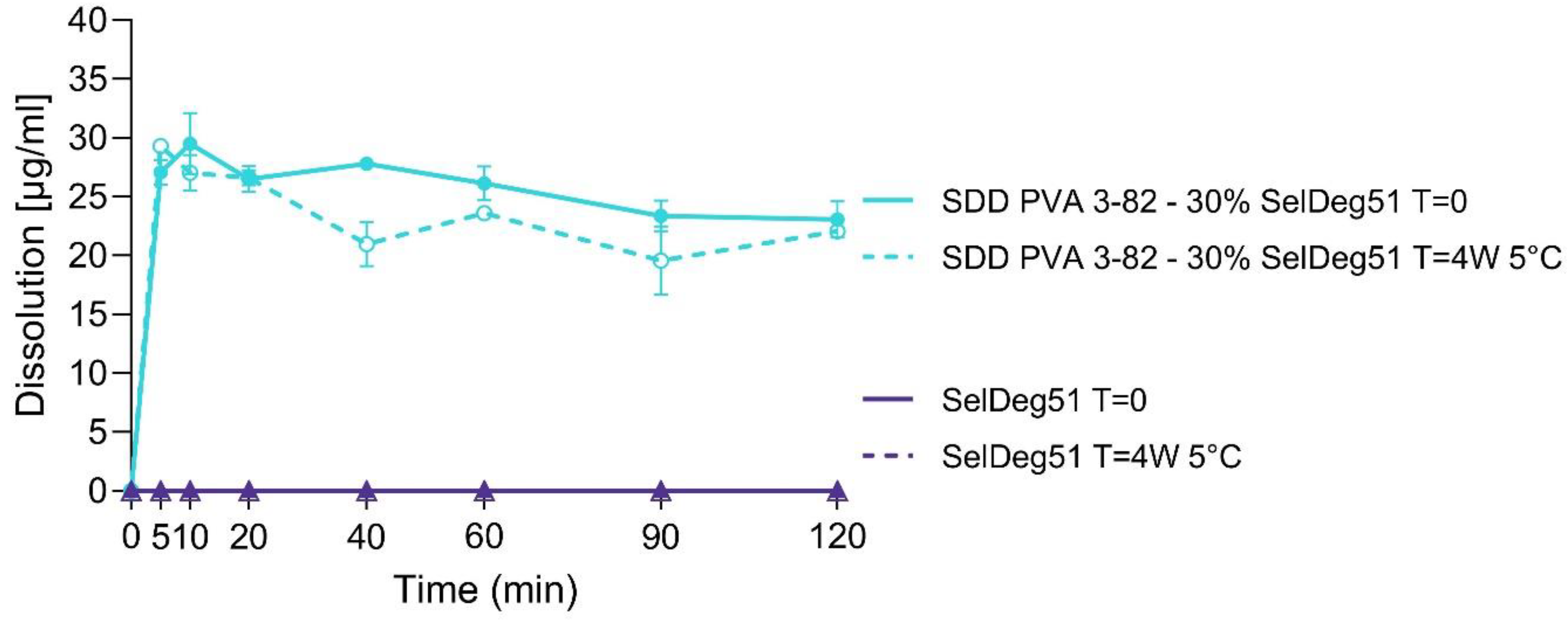
2.2.6. Dissolution
2.2.7. Reversed-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (RP-HPLC)
2.2.8. Microtransfer
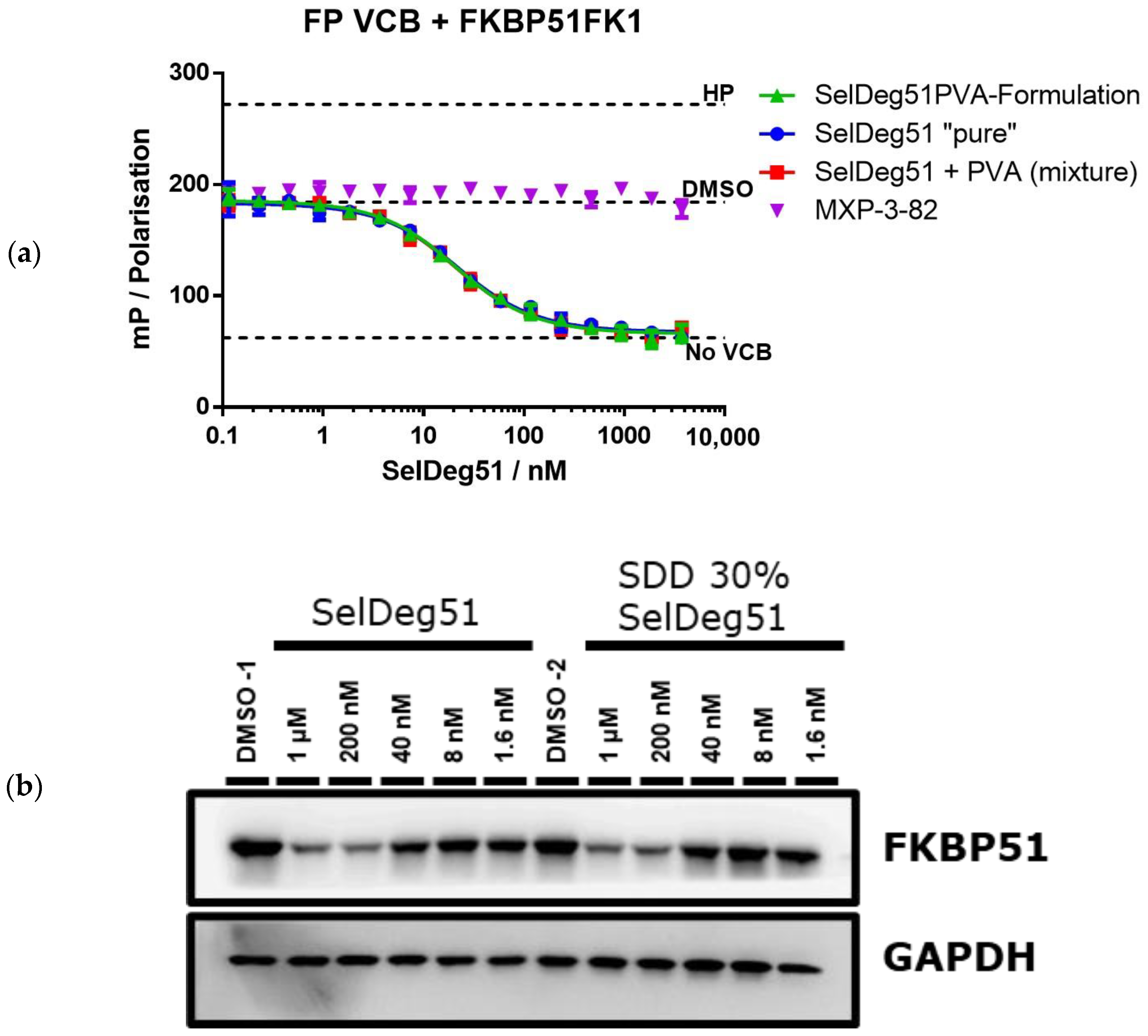
2.2.9. Activity Assay
2.2.10. Fluorescence Polarization Assay for VCB binding
2.2.11. Stability Studies
3. Results and Discussion
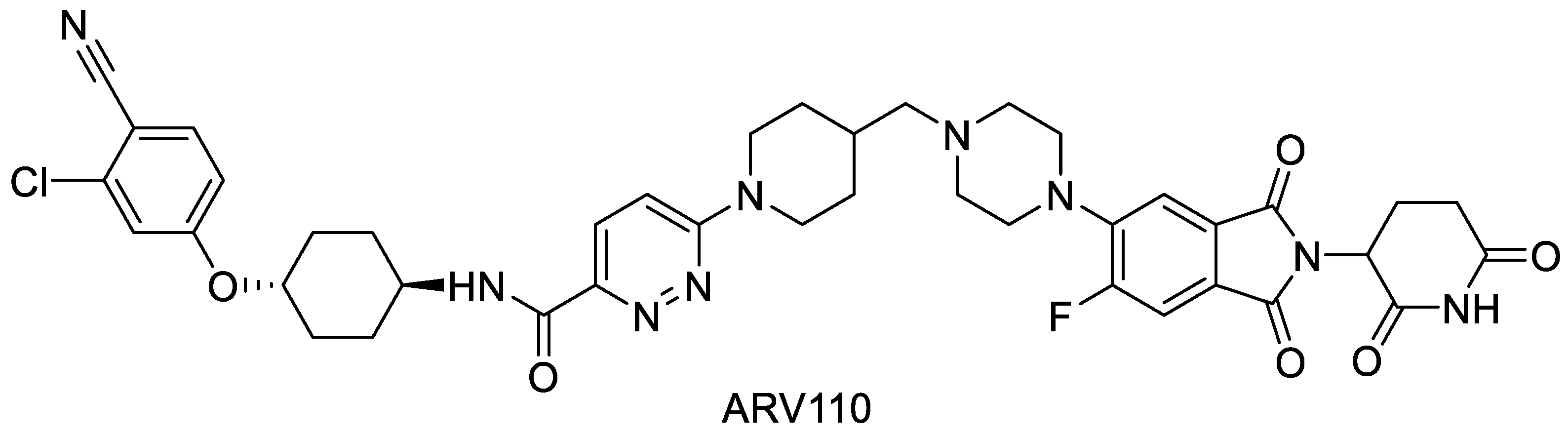
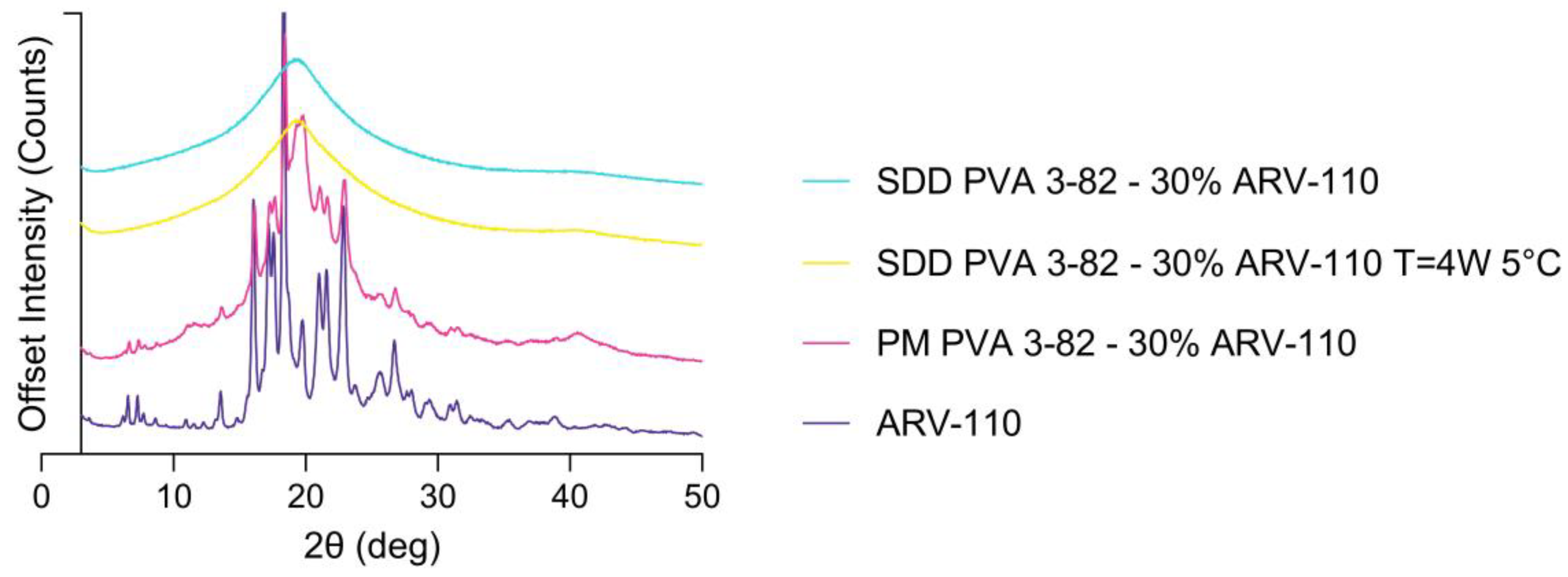
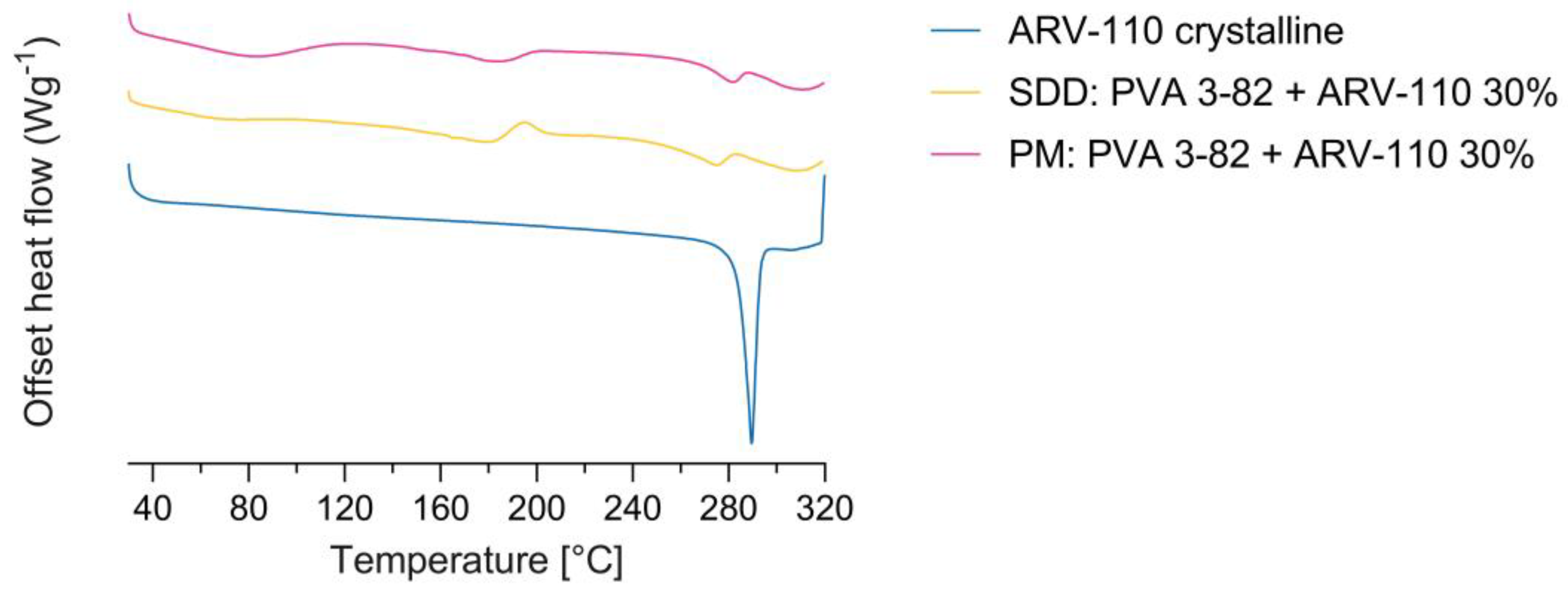
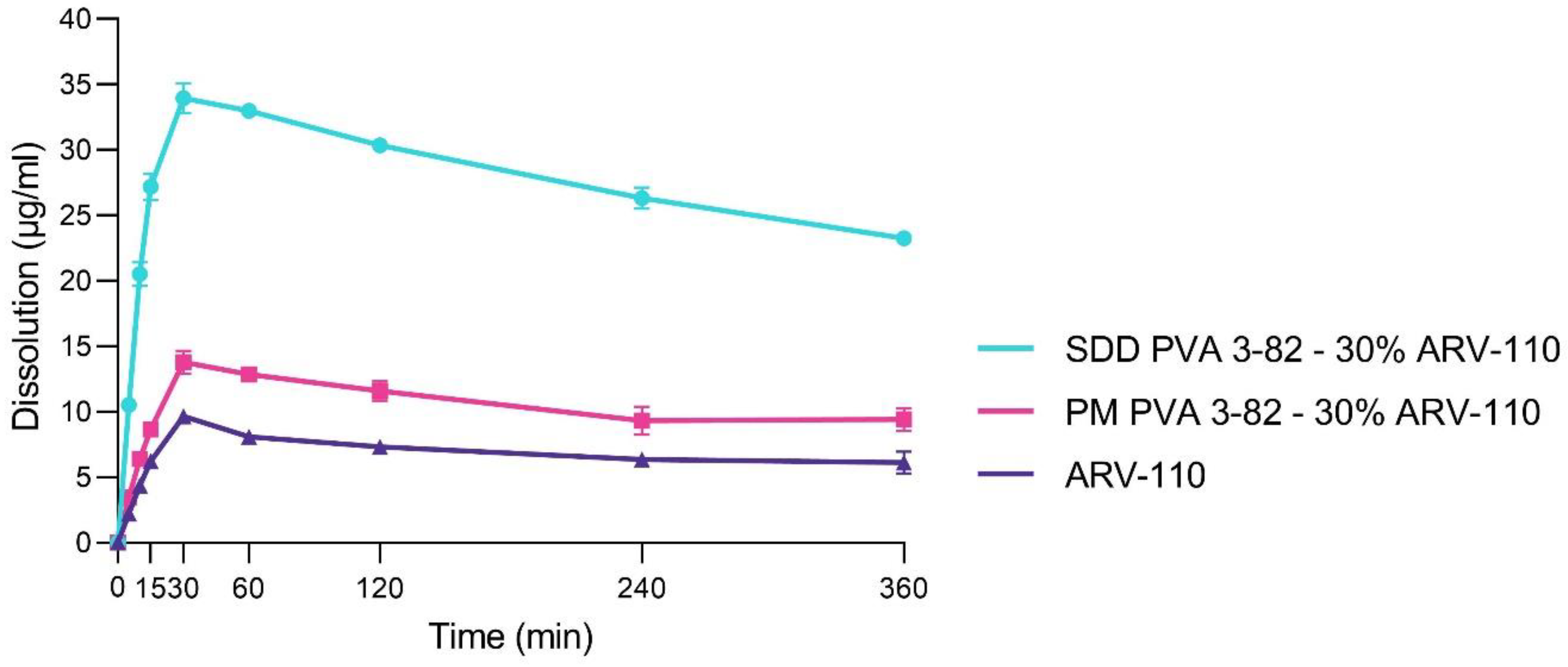
3.1. Spray Drying of Crystalline PROTAC ARV-110 with PVA
3.2. Spray Drying of Amorphous PROTAC SelDeg51 with PVA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toure, M.; Crews, C.M. Small-Molecule PROTACS: New Approaches to Protein Degradation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1966–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.C.; Crews, C.M. Induced protein degradation: An emerging drug discovery paradigm. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; He, M.; Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Tong, Y.; Rao, Y. PROTACs: Great opportunities for academia and industry. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scudellari, M. Protein-slaying drugs could be the next blockbuster therapies. Nature 2019, 567, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Ando, H.; Suzuki, T.; Ogura, T.; Hotta, K.; Imamura, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Handa, H. Identification of a primary target of thalidomide teratogenicity. Science 2010, 327, 1345–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hon, W.C.; Wilson, M.I.; Harlos, K.; Claridge, T.D.; Schofield, C.J.; Pugh, C.W.; Maxwell, P.H.; Ratcliffe, P.J.; Stuart, D.I.; Jones, E.Y. Structural basis for the recognition of hydroxyproline in HIF-1α by pVHL. Nature 2002, 417, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinidou, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Shaabani, S.; Ter Brake, F.; Essa, K.; Domling, A. PROTACs- a game-changing technology. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Gadgil, P.; Krishnamurthy, V.R.; Landis, M.; Mallick, P.; Patel, D.; Patel, P.J.; Reid, D.L.; Sanchez-Felix, M. The Evolving Druggability and Developability Space: Chemically Modified New Modalities and Emerging Small Molecules. AAPS J. 2020, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Saboo, S.; Zhou, L.; Askin, S.; Bak, A. Early evaluation of opportunities in oral delivery of PROTACs to overcome their molecular challenges. Drug Discov. Today 2024, 29, 103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, J.M.; Dressman, J.B. The developability classification system: Application of biopharmaceutics concepts to formulation development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4940–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yedla, P.; Babalghith, A.O.; Andra, V.V.; Syed, R. PROTACs in the Management of Prostate Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhujbal, S.V.; Mitra, B.; Jain, U.; Gong, Y.; Agrawal, A.; Karki, S.; Taylor, L.S.; Kumar, S.; Tony Zhou, Q. Pharmaceutical amorphous solid dispersion: A review of manufacturing strategies. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2505–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Van den Mooter, G. Spray drying formulation of amorphous solid dispersions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 100, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauppinen, A.; Broekhuis, J.; Grasmeijer, N.; Tonnis, W.; Ketolainen, J.; Frijlink, H.W.; Hinrichs, W.L.J. Efficient production of solid dispersions by spray drying solutions of high solid content using a 3-fluid nozzle. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 123, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, L.K.; Halstenberg, L.; Di Gallo, N.; Kipping, T. Evaluation of a Three-Fluid Nozzle Spraying Process for Facilitating Spray Drying of Hydrophilic Polymers for the Creation of Amorphous Solid Dispersions. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, N.; Harms, M.; Mader, K. ASDs of PROTACs: Spray-dried solid dispersions as enabling formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 650, 123725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, T.M.; Walz, M.; Meyners, C.; Kuehn, A.; Dreizler, J.K.; Sugiarto, W.O.; Maciel, E.V.S.; Zheng, M.; Lermyte, F.; Hausch, F. Discovery of a Potent Proteolysis Targeting Chimera Enables Targeting the Scaffolding Functions of FK506-Binding Protein 51 (FKBP51). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202309706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauder, M.; Meyners, C.; Purder, P.L.; Merz, S.; Sugiarto, W.O.; Voll, A.M.; Heymann, T.; Hausch, F. Structure-Based Design of High-Affinity Macrocyclic FKBP51 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 3320–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voll, A.M.; Meyners, C.; Taubert, M.C.; Bajaj, T.; Heymann, T.; Merz, S.; Charalampidou, A.; Kolos, J.; Purder, P.L.; Geiger, T.M.; et al. Macrocyclic FKBP51 Ligands Define a Transient Binding Mode with Enhanced Selectivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13257–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozany, C.; Marz, A.; Kress, C.; Hausch, F. Fluorescent probes to characterise FK506-binding proteins. Chembiochem 2009, 10, 1402–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Burris, H.A., III; Vuky, J.; Dreicer, R.; Sartor, A.O.; Sternberg, C.N.; Percent, I.J.; Hussain, M.H.A.; Kalebasty, A.R.; Shen, J.; et al. Phase 1/2 study of ARV-110, an androgen receptor (AR) PROTAC degrader, in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekes, M.; Langley, D.R.; Crews, C.M. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, F.; Kipping, T.; Weitschies, W.; Krause, J. Understanding the Interaction of Thermal, Rheological, and Mechanical Parameters Critical for the Processability of Polyvinyl Alcohol-Based Systems during Hot Melt Extrusion. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Han, C.H.; Oh, I.H.; Allu, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.S.; Park, B.J. Fabrication and evaluation of stable amorphous polymer-drug composite particles via a nozzle-free ultrasonic nebulizer. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 657, 124177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dedroog, S.; Pas, T.; Vergauwen, B.; Huygens, C.; Van den Mooter, G. Solid-state analysis of amorphous solid dispersions: Why DSC and XRPD may not be regarded as stand-alone techniques. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, M.M.; Wendelboe, J.; Holm, R.; Rades, T. Effect of amorphous phase separation and crystallization on the in vitro and in vivo performance of an amorphous solid dispersion. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 130, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postges, F.; Kayser, K.; Appelhaus, J.; Monschke, M.; Gutschow, M.; Steinebach, C.; Wagner, K.G. Solubility Enhanced Formulation Approaches to Overcome Oral Delivery Obstacles of PROTACs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baischew, A.; Engel, S.; Geiger, T.M.; Taubert, M.C.; Hausch, F. Structural and biochemical insights into FKBP51 as a Hsp90 co-chaperone. J. Cell. Biochem. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baischew, A.; Engel, S.; Taubert, M.C.; Geiger, T.M.; Hausch, F. Large-scale, in-cell photocrosslinking at single-residue resolution reveals the molecular basis for glucocorticoid receptor regulation by immunophilins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1857–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mareczek, L.; Mueller, L.K.; Halstenberg, L.; Geiger, T.M.; Walz, M.; Zheng, M.; Hausch, F. Use of Poly(vinyl alcohol) in Spray-Dried Dispersions: Enhancing Solubility and Stability of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070924
Mareczek L, Mueller LK, Halstenberg L, Geiger TM, Walz M, Zheng M, Hausch F. Use of Poly(vinyl alcohol) in Spray-Dried Dispersions: Enhancing Solubility and Stability of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(7):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070924
Chicago/Turabian StyleMareczek, Lena, Lena K. Mueller, Laura Halstenberg, Thomas M. Geiger, Michael Walz, Min Zheng, and Felix Hausch. 2024. "Use of Poly(vinyl alcohol) in Spray-Dried Dispersions: Enhancing Solubility and Stability of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 7: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070924
APA StyleMareczek, L., Mueller, L. K., Halstenberg, L., Geiger, T. M., Walz, M., Zheng, M., & Hausch, F. (2024). Use of Poly(vinyl alcohol) in Spray-Dried Dispersions: Enhancing Solubility and Stability of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras. Pharmaceutics, 16(7), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16070924




