Quantification of Microsphere Drug Release by Fluorescence Imaging with the FRET System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
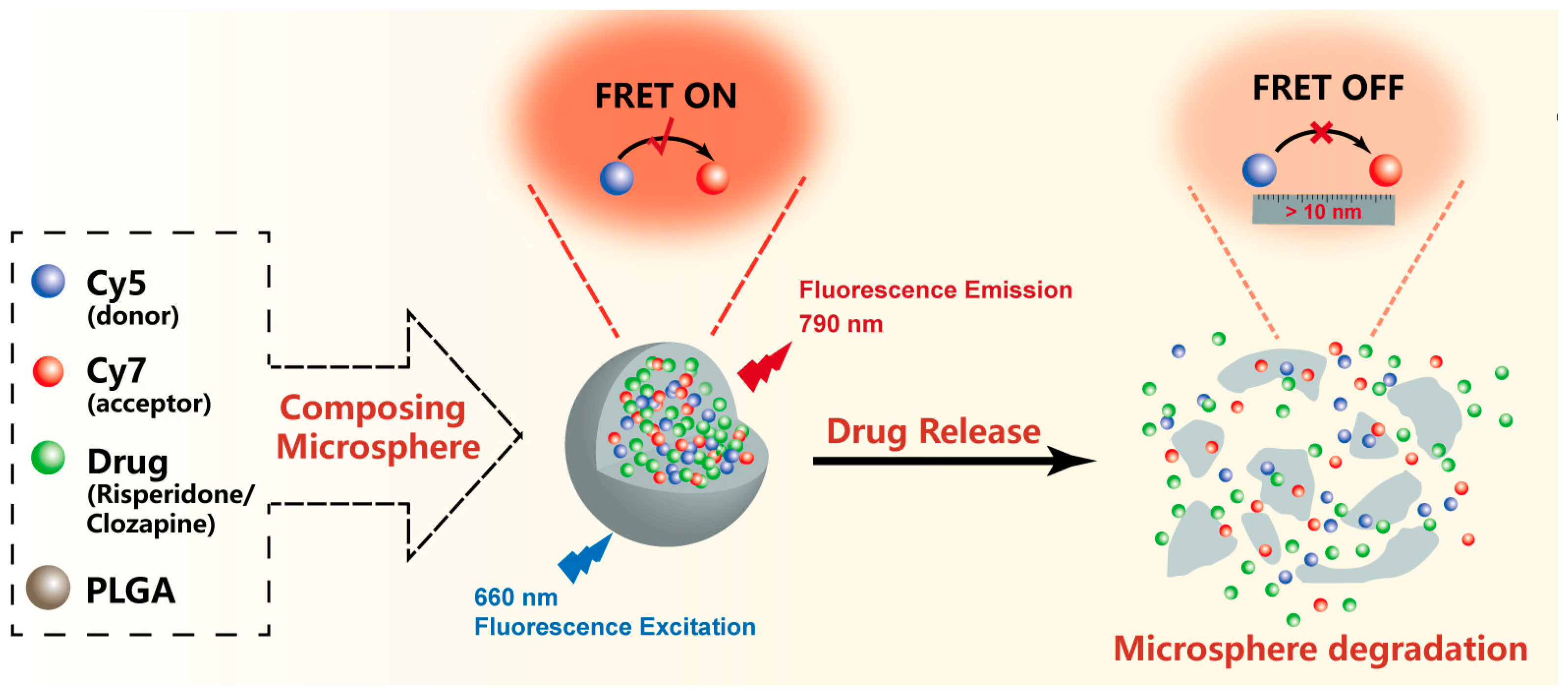
2.2. Preparations of Clo-FRET-PLGA/M and Ris-FRET-PLGA/M
2.3. Determination of Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency of Clo-FRET-PLGA/M and Ris-FRET-PLGA/M
2.4. In Vitro Drug Release
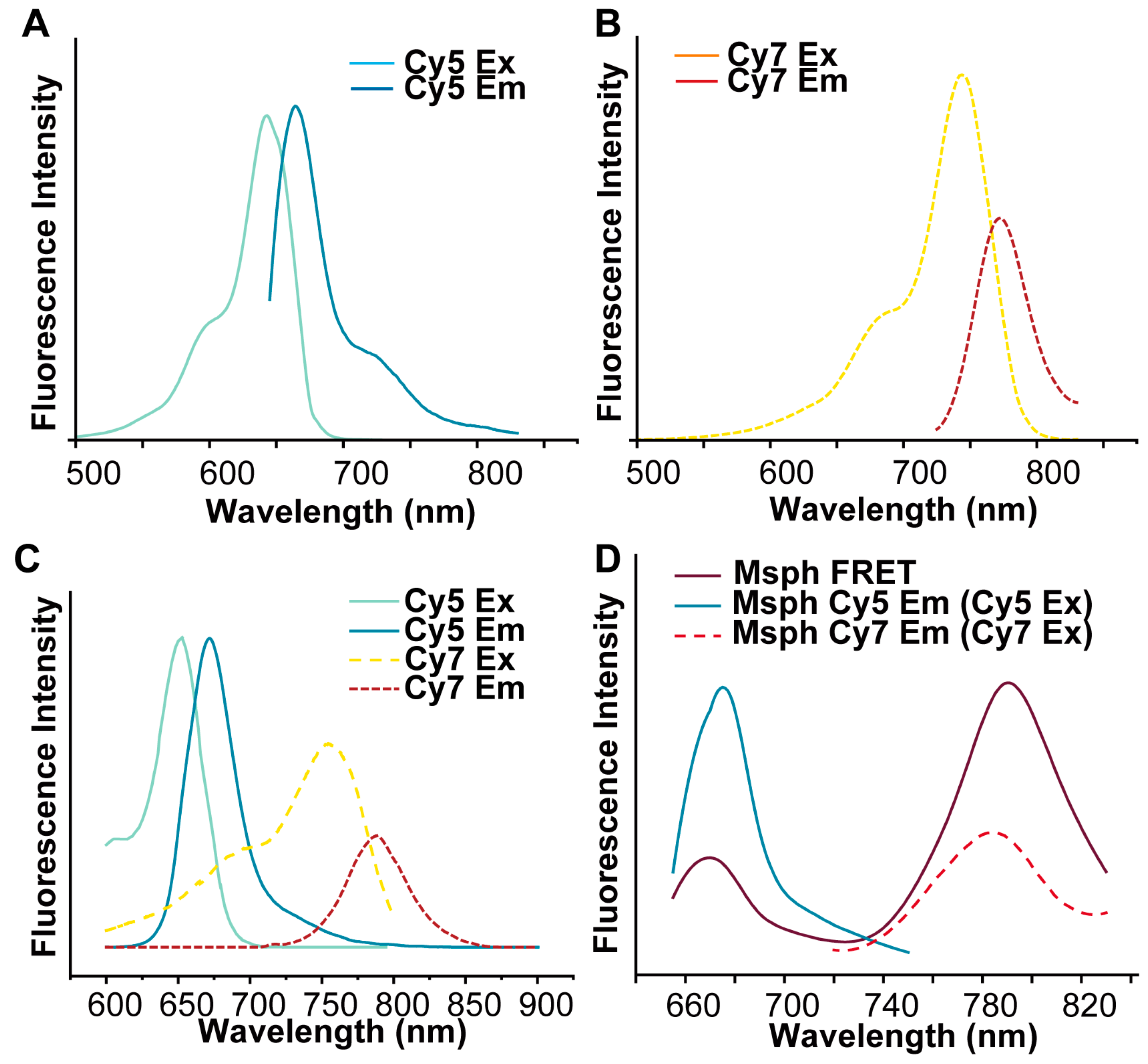
2.5. Detection of Fluorescence Intensity
2.6. Determination of Weight Loss of PLGA Microspheres
2.7. Determination of Water Absorption of PLGA Microspheres
2.8. Confocal Laser Microscopy Scanning
2.9. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.10. Relation Study
3. Results
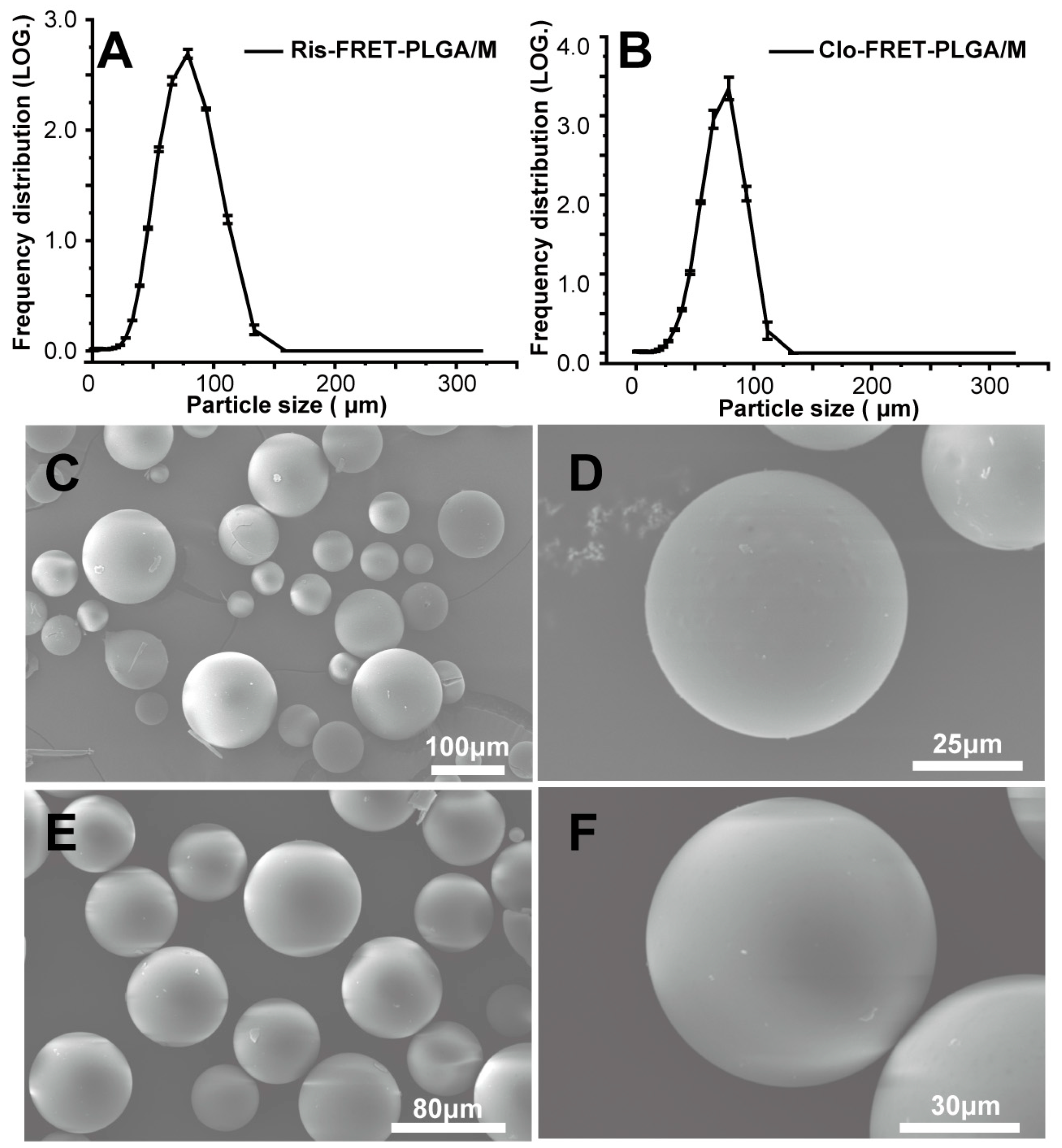
3.1. Preparations and Characterizations of Ris-FRET-PLGA/M and Clo-FRET-PLGA/M
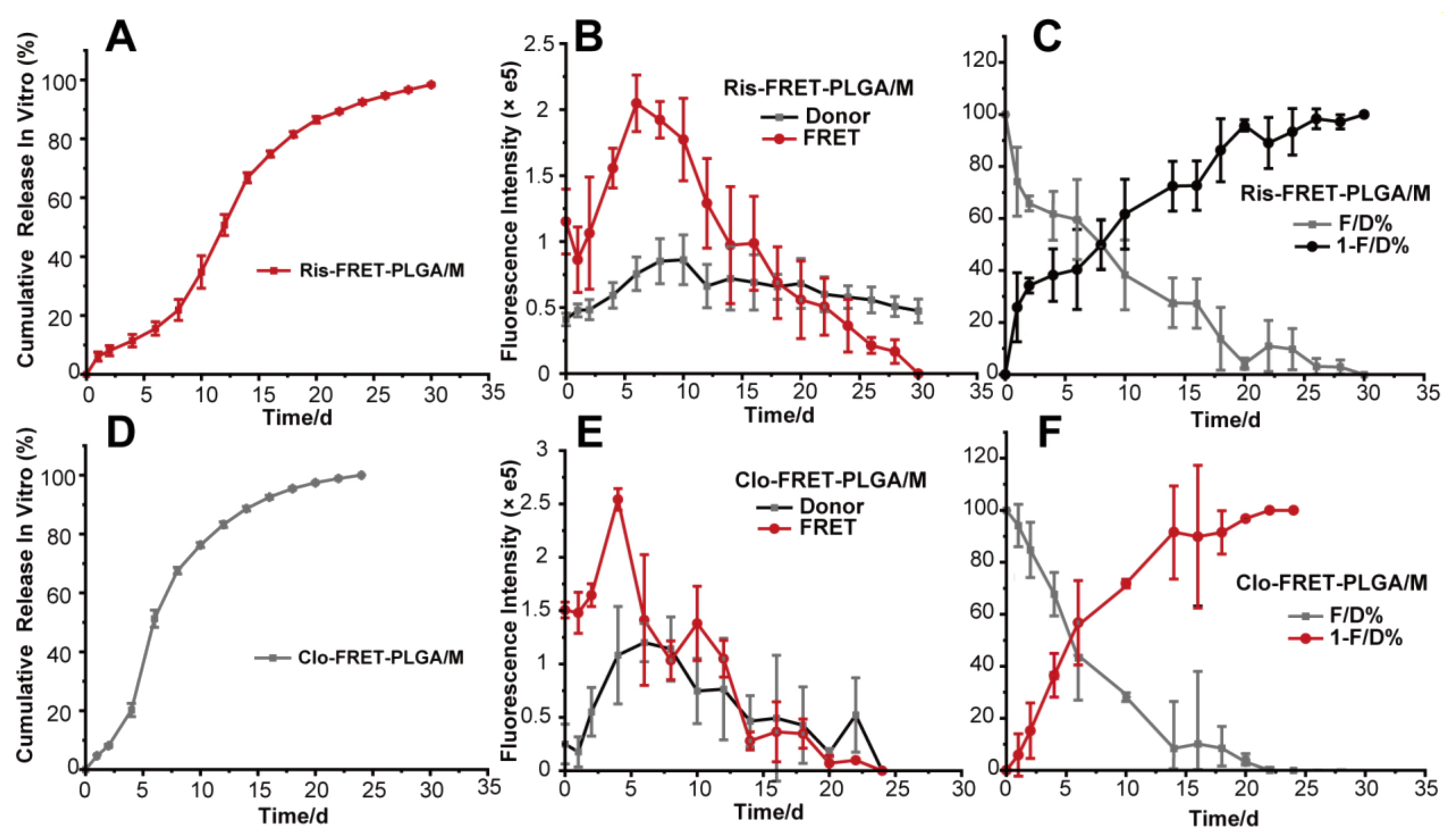
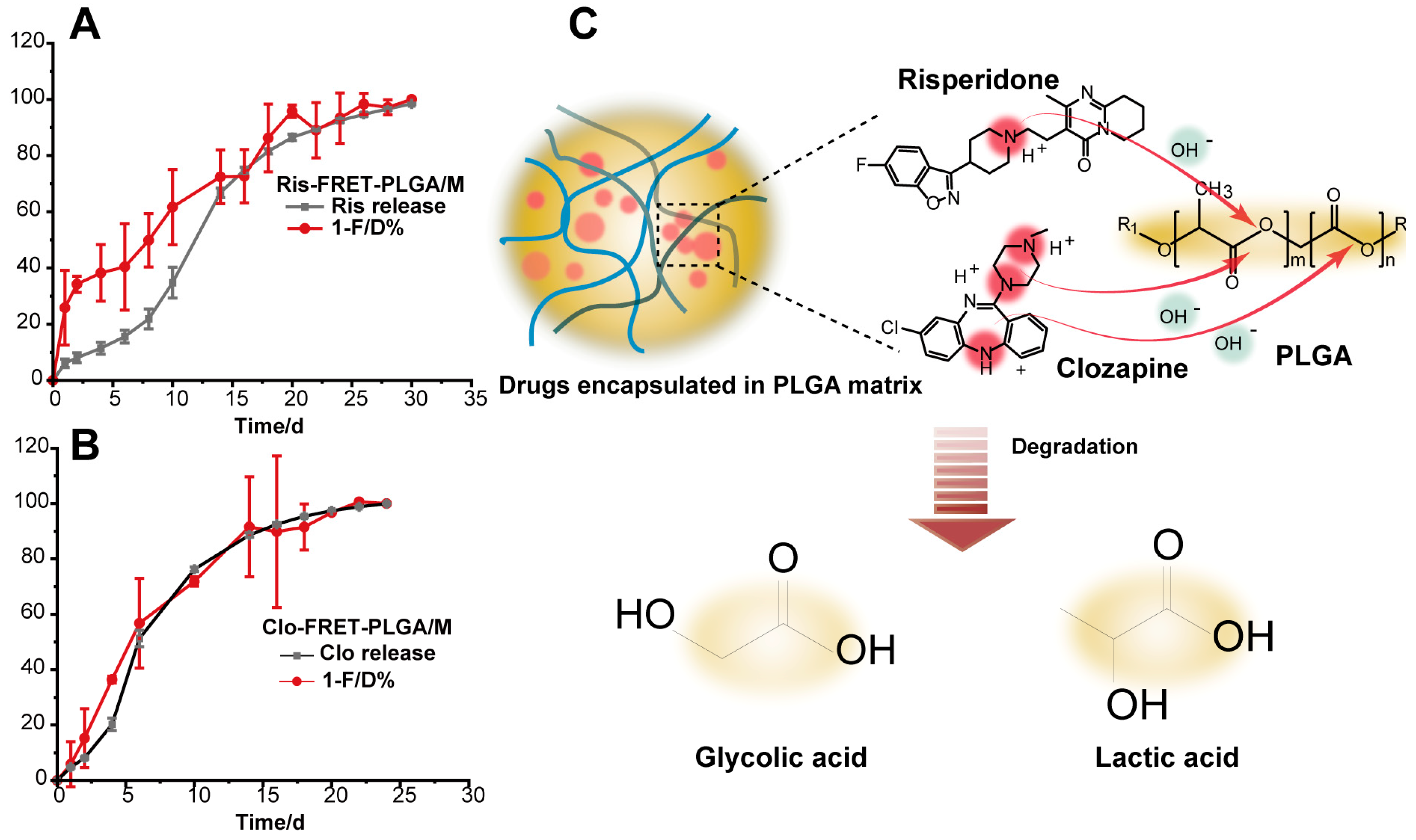
3.2. In Vitro Drug Release
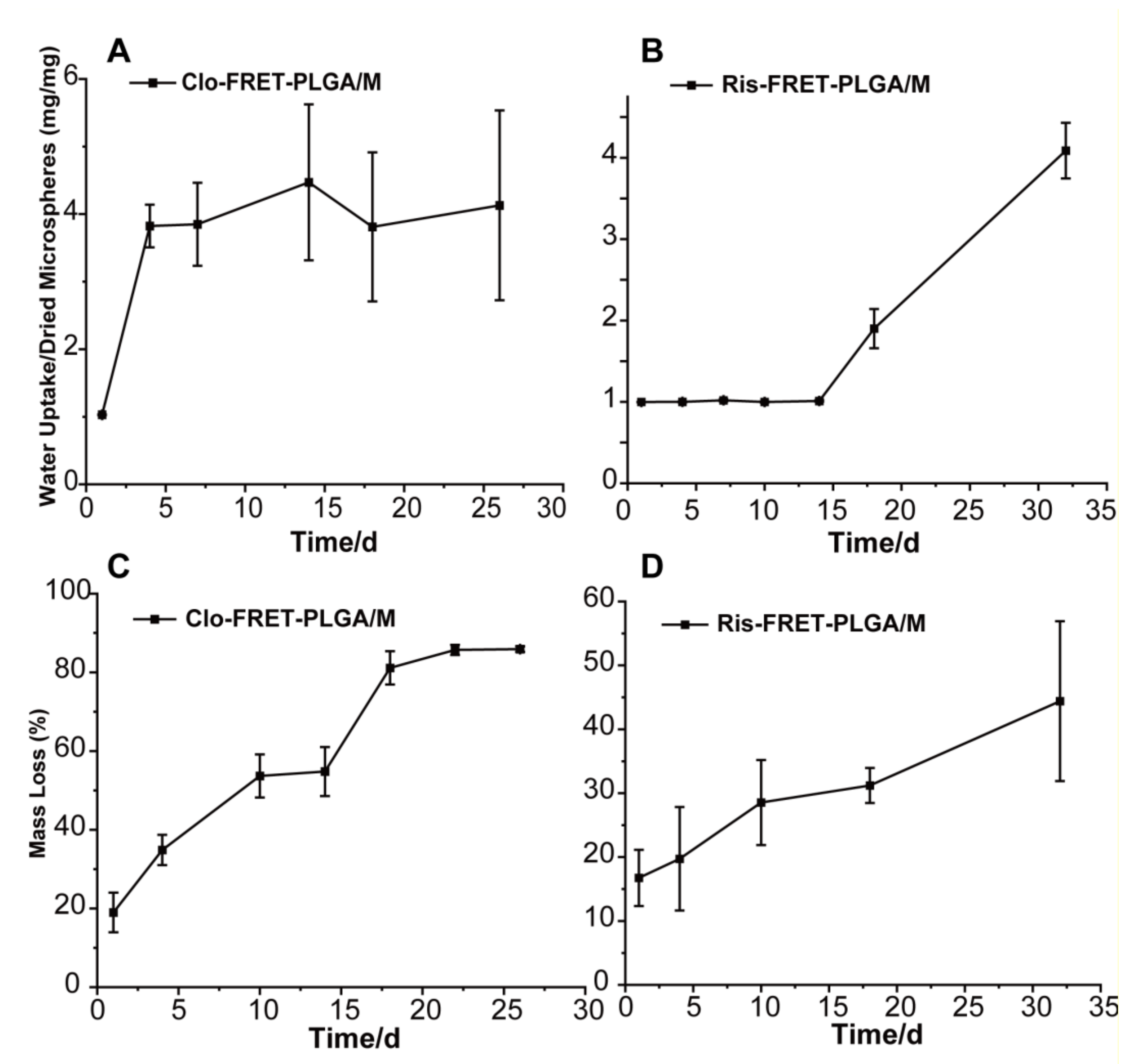
3.3. Determination of Weight Loss and Water Absorption of PLGA Microspheres
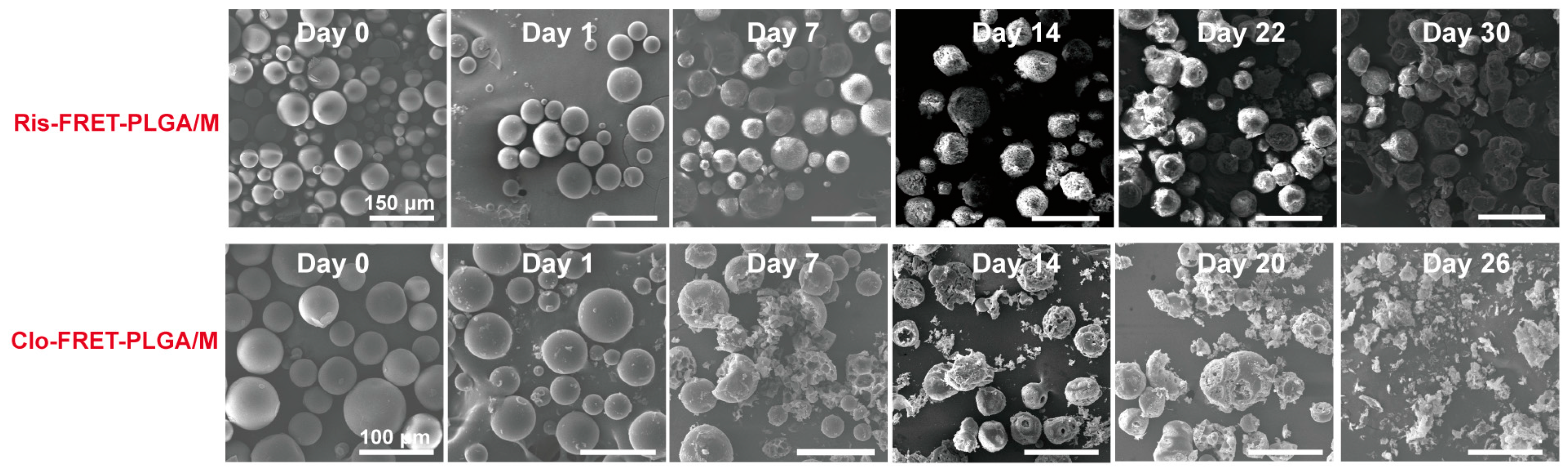
3.4. Degradation of Ris-FRET-PLGA/M and Clo-FRET-PLGA/M over Time by Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
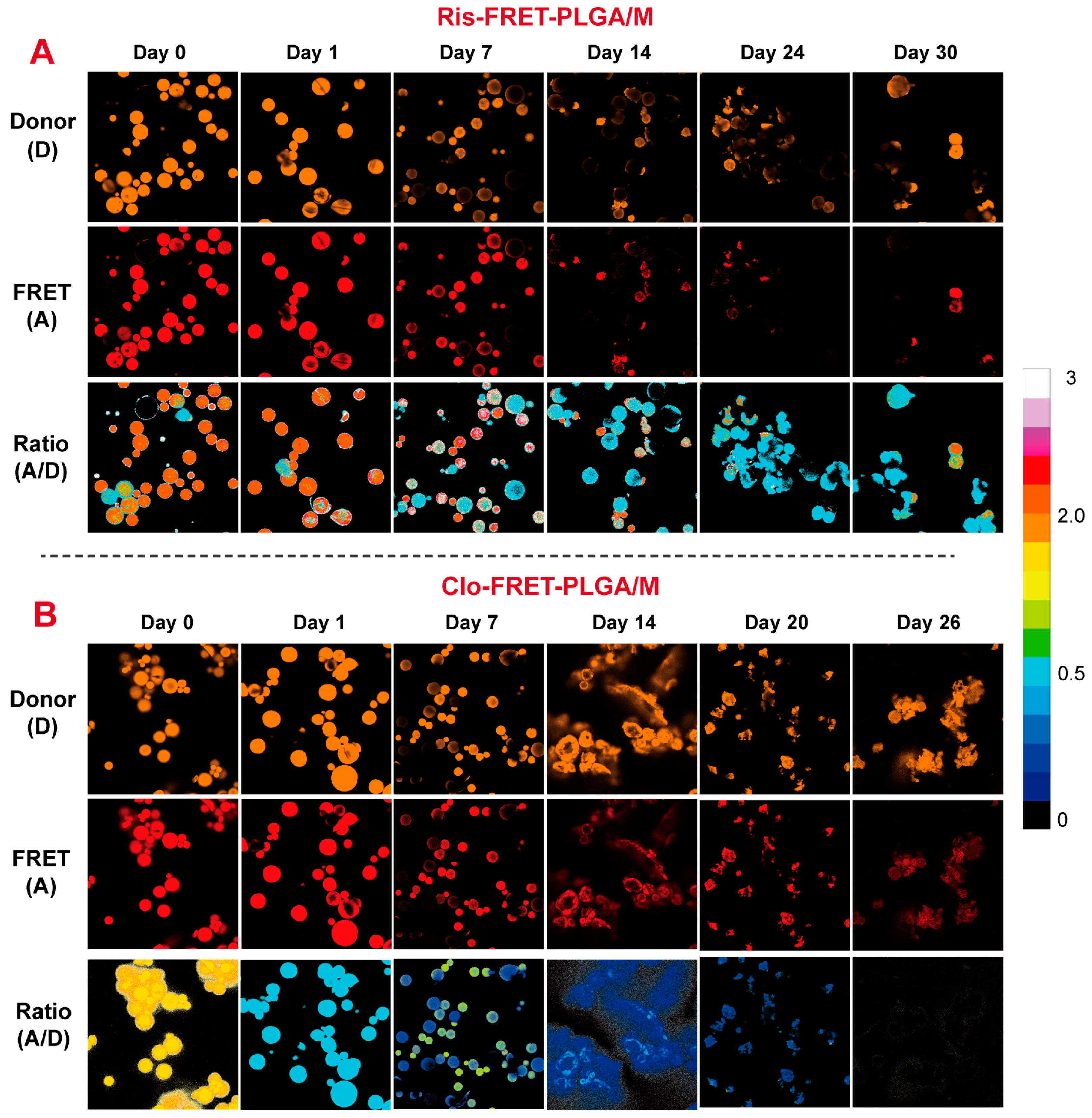
3.5. Degradation of Ris-FRET-PLGA/M and Clo-FRET-PLGA/M over Time by Confocal Laser Microscopy Scanning
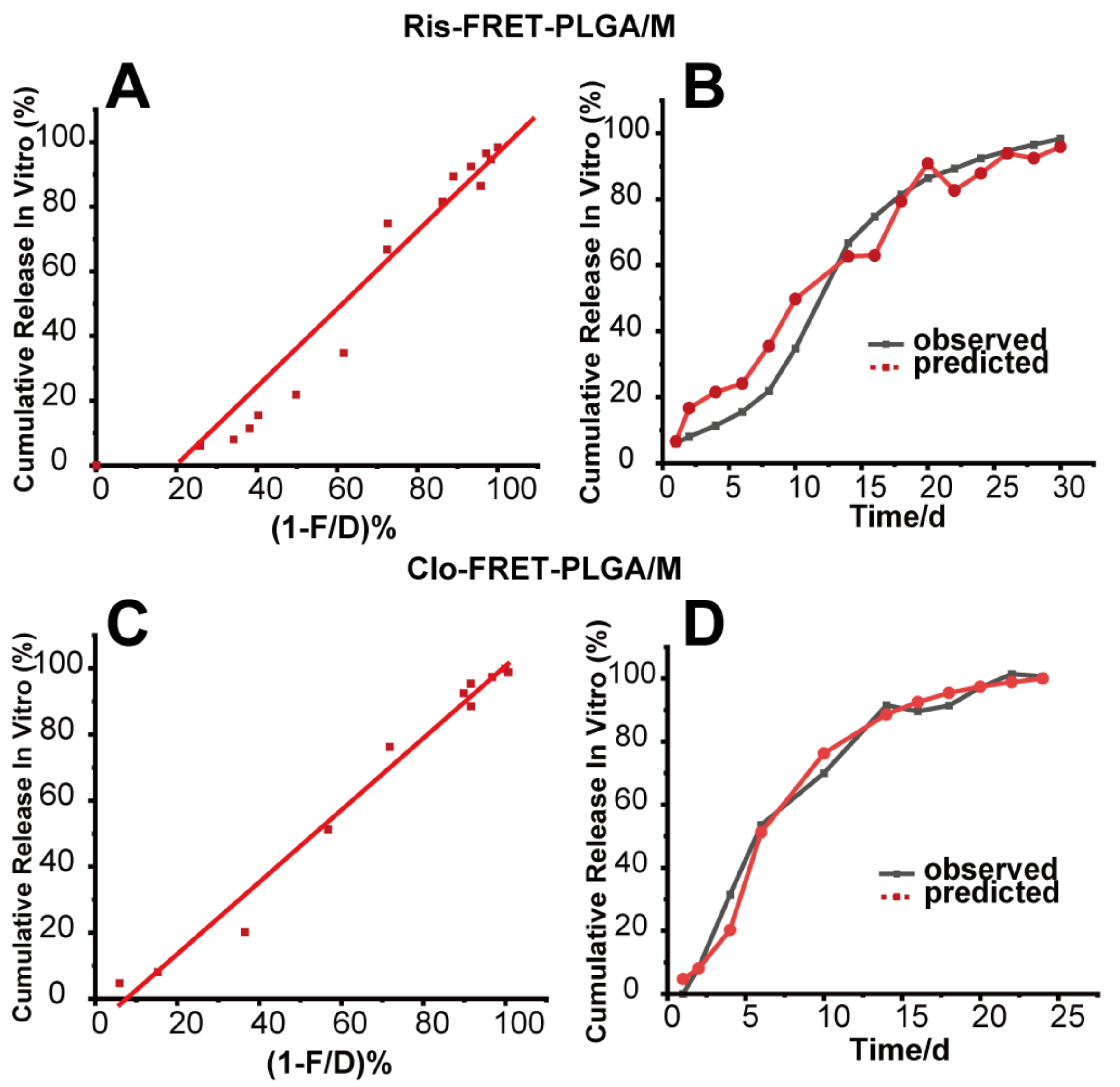
3.6. Correlation and Prediction Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alvarado, A.T.; Rojas-Macetas, A.; Medalla-Garro, G.; Saravia, M.; Losno, R.; Valderrama-Wong, M.; Pariona, R. Potential polymorphic CYP1A2 and CYP2D6-mediated pharmacokinetic interactions between risperidone or olanzapine and selected drugs intended to treat COVID-19. Drug Metab. Lett. 2022, 16, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, L.; Liu, W. Clozapine affects the pharmacokinetics of risperidone and inhibits its metabolism and P-glycoprotein–mediated transport in vivo and in vitro: A safety attention to antipsychotic polypharmacy with clozapine and risperidone. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 422, 115560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulejmanpasic, G.; Bise, S. Clozapine augmented with risperidone in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2017, 41, S385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopko, T.C.; Lindsley, C.W. Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Risperidone. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, S.; Taylor, D. Alternative Routes of Administration of Clozapine. CNS Drugs 2022, 36, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, S.; Mazza, M.; Roy, G.; England, R.M.; Zhou, L.; Nourian, S.; Anand Subramony, J. Evolution of nanomedicine formulations for targeted delivery and controlled release. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 200, 114962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Jha, A.; Patel, R. Potential application of PLGA microsphere for tissue engineering. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, F.; Naderpour, S.; Nejad, B.G.; Rahimzadegan, M.; Ebrahimi, Z.N.; Kamali, H.; Nosrati, R. The recent insight in the release of anticancer drug loaded into PLGA microspheres. Med. Oncol. 2023, 40, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bee, S.-L.; Hamid, Z.A.A.; Mariatti, M.; Yahaya, B.H.; Lim, K.; Bee, S.-T.; Sin, L.T. Approaches to Improve Therapeutic Efficacy of Biodegradable PLA/PLGA Microspheres: A Review. Polym. Rev. 2018, 58, 495–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, M.; Andhariya, J.V.; Wan, B.; Bao, Q.; Rothstein, S.; Hezel, M.; Wang, Y.; Burgess, D.J. The effect of PLGA molecular weight differences on risperidone release from microspheres. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 582, 119339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlęk, J.; Pacławski, A.; Lau, R.; Jachowicz, R.; Kazemi, P.; Mendyk, A. Empirical search for factors affecting mean particle size of PLGA microspheres containing macromolecular drugs. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 134, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawbaa, H.M.; Szlȩk, J.; Grosan, C.; Jachowicz, R.; Mendyk, A. Computational Intelligence Modeling of the Macromolecules Release from PLGA Microspheres-Focus on Feature Selection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andhariya, J.V.; Jog, R.; Shen, J.; Choi, S.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Y.; Burgess, D.J. In vitro-in vivo correlation of parenteral PLGA microspheres: Effect of variable burst release. J. Control. Release 2019, 314, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Sun, X.; Papadimitrakopoulos, F.; Burgess, D.J. Seeing is believing, PLGA microsphere degradation revealed in PLGA microsphere/PVA hydrogel composites. J. Control. Release 2016, 228, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ju, J.; Wang, D.; Yuan, H.; Hao, L.; Tan, Y. Aggregation-induced emission for the visualization of the structure and properties of polymers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 11484–11496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Pan, Y.; Manghnani, P.N.; Liu, B. AIE Polymers: Synthesis, Properties, and Biological Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 17, 1600433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Hu, X.; Dong, X.; Lu, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhao, W.; Wu, W. Towards more accurate bioimaging of drug nanocarriers: Turning aggregation-caused quenching into a useful tool. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 143, 206–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, A.; Dhakal, S. Invited Review: Recent applications of FRET-based multiplexed techniques. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 123, 115777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charron, D.M.; Zheng, G. Nanomedicine development guided by FRET imaging. Nano Today 2018, 18, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenken, J.A. Introduction to Fluorescence Sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredenberg, S.; Wahlgren, M.; Reslow, M.; Axelsson, A. The mechanisms of drug release in poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-based drug delivery systems—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexis, F. Factors affecting the degradation and drug-release mechanism of poly(lactic acid) and poly[(lactic acid)-co-(glycolic acid)]. Polym. Int. 2005, 54, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yan, P.; Wang, K.; Chen, R. Inhibition of Fusarium graminearum growth and deoxynivalenol production by geocarpospheric bacterial strains. J. Earth Sci. 2010, 21, 306–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Bian, Y.; Ren, G.; Hong, M. Insight into the Behavior Regulation of Drug Transfer of Nimodipine Loaded PLGA Microspheres by Emulsion Evaporation Method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 670, 131569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X.; Li, M.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, F.; et al. An Accelerated Release Method of Risperidone Loaded PLGA Microspheres with Good IVIVC. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2017, 15, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Xie, Y.; Lv, Y.; Qi, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, W.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. Bioimaging of Intact Polycaprolactone Nanoparticles Using Aggregation-Caused Quenching Probes: Size-Dependent Translocation via Oral Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1800711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yicheng, F.; Nan, Z.; Qi, L.; Jianting, C.; Subin, X.; Weisan, P. Characterizing the release mechanism of donepezil-loaded PLGA microspheres in vitro and in vivo. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 51, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolnik, B.S.; Burgess, D.J. Effect of acidic pH on PLGA microsphere degradation and release. , , –. J. Control. Release 2007, 122, 338–344. [Google Scholar]
- Aart, A.v.A.; van Manen, H.-J.; Jeroen, M.B.; Joost, D.d.B.; Clemens, A.v.B.; Cees, O. Raman Imaging of PLGA Microsphere Degradation Inside Macrophages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13226–13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, S.; Faraj, J.A.; Giovagnoli, S.; Deluca, P.P. IVIVC from Long Acting Olanzapine Microspheres. Int. J. Biomater. 2014, 2014, 407065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Choi, J.; Kim, A.; Lee, J.H.; Nam, Y.; Park, J.; Sun, B.K.; Suh, H.; Kim, C.-J.; Hwang, S.-J. Sustained release of risperidone from biodegradable microspheres prepared by in-situ suspension-evaporation process. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 503, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Cai, Y.; Dong, X.; Wu, W.; Zhao, W. Selection of an aggregation-caused quenching-based fluorescent tracer for imaging studies in nano drug delivery systems. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 9290–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford Versypt, A.N.; Pack, D.W.; Braatz, R.D. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery from autocatalytically degradable PLGA microspheres—A review. J. Control. Release 2012, 165, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonios, V.; Georgia, K.; Evangelia, B.; Vasileios, D.; Theocharis, K.; Myrika, S.; Nikolaos, D.B.; Evi, C.; Ioanna, K.; Evangelos, K.; et al. Poly(Lactic Acid)-Based Microparticles for Drug Delivery Applications: An Overview of Recent Advances. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busatto, C.; Berkenwald, E.; Mariano, N.; Casis, N.; Luna, J.; Estenoz, D. Homogeneous hydrolytic degradation of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres: Mathematical modeling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 125, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Microsphere | Total Drug Absorbed/Released In Vitro (%) | 1 − A/D (%) | f2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ris-FRET-PLGA/M | 98.39 | 100 | 39.10 |
| Clo-FRET-PLGA/M | 100 | 100 | 59.70 |
| Microsphere | Correlation Equation | R2 | f2 Observed/Predicted | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In vitro | Ris-FRET-PLGA/M | a = −24.480 + 1.204 × b | 0.932 | 47.1 |
| Clo-FRET-PLGA/M | a= −8.2214 + 1.089 × b | 0.983 | 73.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; He, Q.; Yang, J.; Lu, H.; Han, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, P. Quantification of Microsphere Drug Release by Fluorescence Imaging with the FRET System. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081019
Chen Y, Lu H, He Q, Yang J, Lu H, Han J, Zhu Y, Hu P. Quantification of Microsphere Drug Release by Fluorescence Imaging with the FRET System. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(8):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081019
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuying, Huangjie Lu, Qingwei He, Jie Yang, Hong Lu, Jiongming Han, Ying Zhu, and Ping Hu. 2024. "Quantification of Microsphere Drug Release by Fluorescence Imaging with the FRET System" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 8: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081019
APA StyleChen, Y., Lu, H., He, Q., Yang, J., Lu, H., Han, J., Zhu, Y., & Hu, P. (2024). Quantification of Microsphere Drug Release by Fluorescence Imaging with the FRET System. Pharmaceutics, 16(8), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16081019






