Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of pDNA
2.1.2. Animals
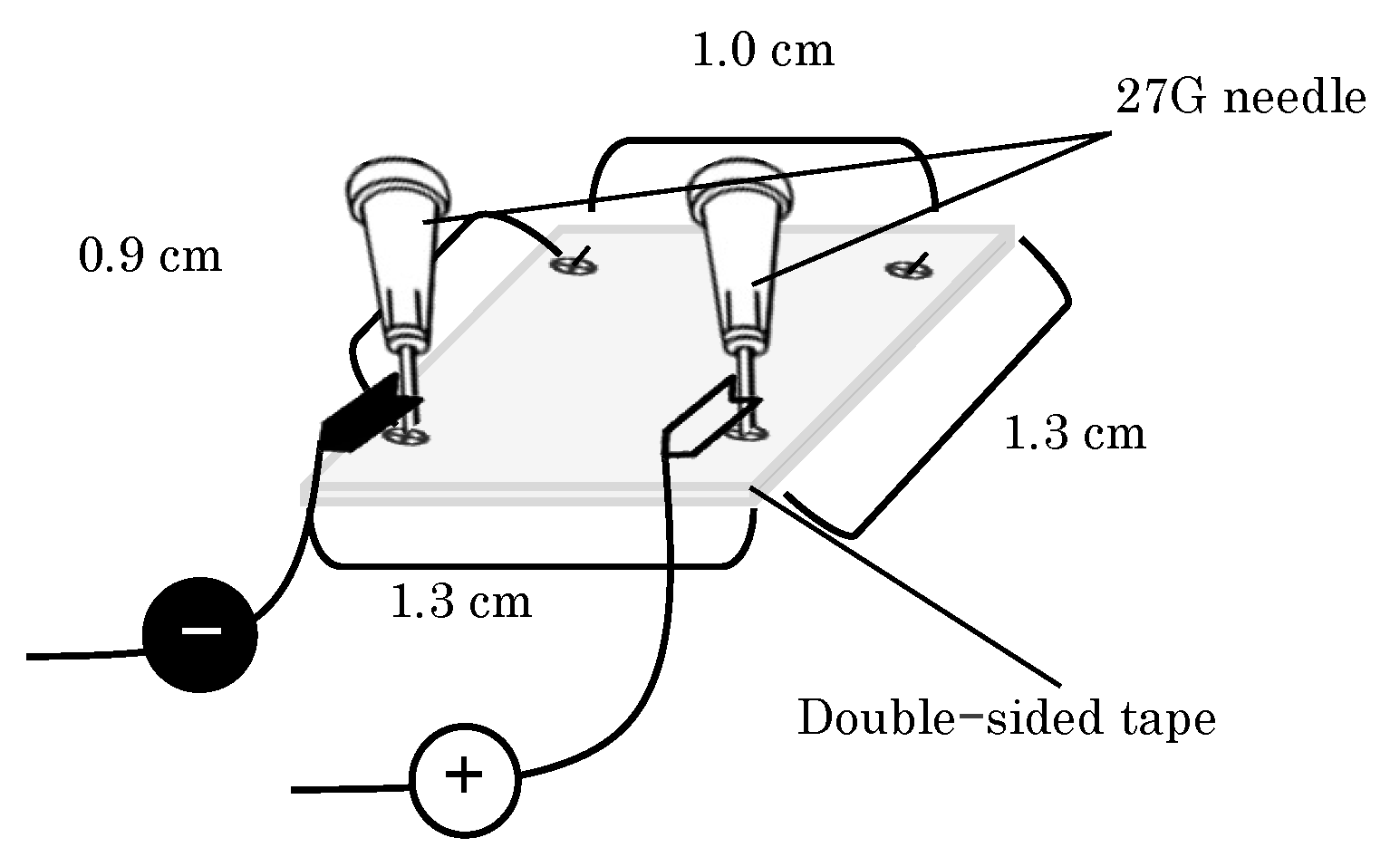
2.1.3. EP Device Preparation
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Observation of GFP Expression in Mice Abdominal Skin Using a Laser Scanning Microscope
2.2.2. In Vivo Imaging System Observation
2.2.3. Quantification Analysis of Luciferase Expression
2.2.4. Thickness of the Skin
2.2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
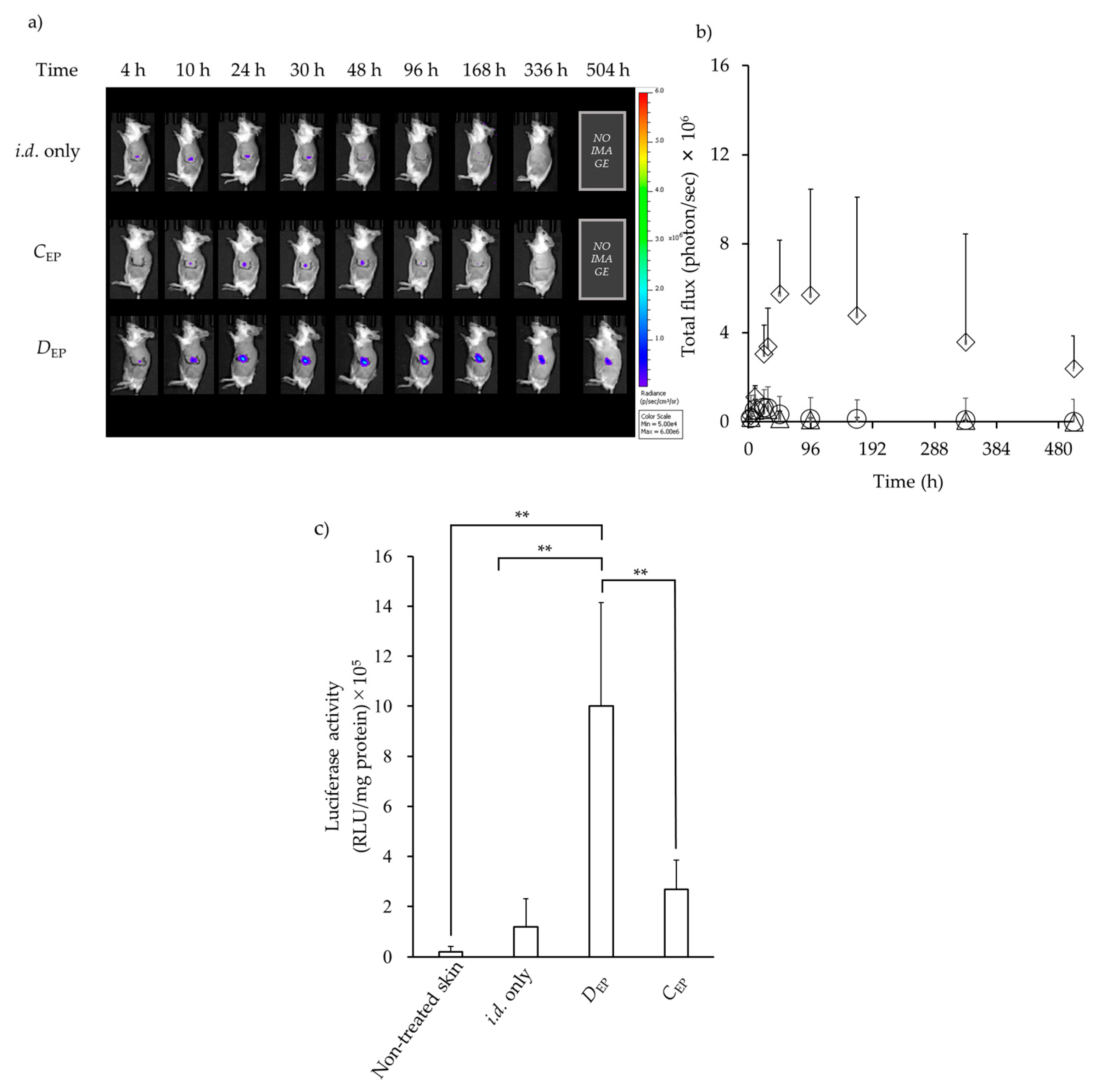
3.1. GFP Expression in the Skin after i.d. Administration Followed by EP Application
3.2. Luciferase Expression in the Skin after i.d. Administration Followed by EP Application
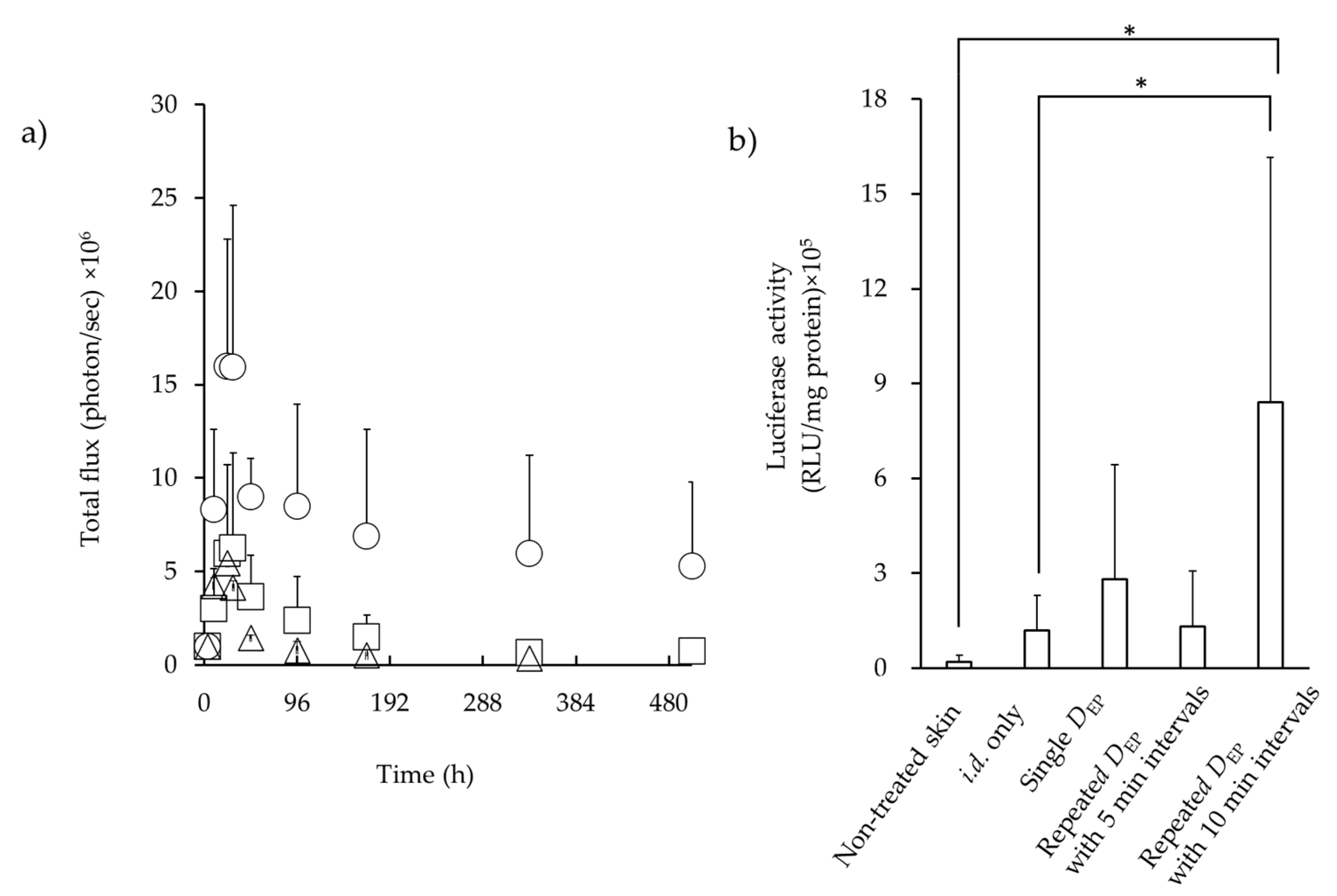
3.3. Luciferase Expression in the Skin after i.d. Administration Followed by EP Application
3.4. Skin Thickness Observation after EP Applications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| ANOVA | one-way analysis of variance |
| CEP | conventional stratum corneum electroporation |
| CLSM | confocal laser scanning microscope |
| DEP | direct electroporation at an intradermal site |
| EGFP | enhanced green fluorescent protein |
| EP | electroporation |
| GFP | green fluorescent protein |
| H.E. | hematoxylin and eosin |
| hMN | hollow-type microneedle |
| i.d. | intradermal |
| IVIS | in vivo imaging system |
| MN | microneedle |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| pDNA | plasmid DNA |
| RLU | relative light units |
| ROI | region of interest |
| SC | stratum corneum |
References
- Neumann, E.; Schaefer-Ridder, M.; Wang, Y.; Hofschneider, P.H. Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rols, M.P.; Teissié, J. Electropermeabilization of mammalian cells to macromolecules: Control by pulse duration. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argus, F.; Boyd, B.; Becker, S.M. Electroporation of tissue and cells: A three-equation model of drug delivery. Comput. Biol. Med. 2017, 84, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosazza, C.; Deschout, H.; Buntz, A.; Braeckmans, K.; Rols, M.P.; Zumbusch, A. Endocytosis and endosomal trafficking of DNA after gene electrotransfer in vitro. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Bose, V.G.; Langer, R.; Weaver, J.C. Electroporation of mammalian skin: A mechanism to enhance transdermal drug delivery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 10504–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, N.; Van Deŕ Smissen, P.; Préat, V. Topical gene transfer into rat skin using electroporation. Pharm. Res. 2001, 18, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, L.; An, Z.; Hoffman, R.M.; Hofmann, G.A. In vivo transdermal delivery of large molecules by pressure-mediated electroincorporation and electroporation: A novel method for drug and gene delivery. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1997, 42, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermeulen, G.; Richiardi, H.; Escriou, V.; Ni, J.; Fournier, P.; Schirrmacher, V.; Scherman, D.; Préat, V. Skin-specific promoters for genetic immunisation by DNA electroporation. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4272–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, F.; Tötterman, T.; Maltais, A.K.; Pisa, P.; Yachnin, J. DNA vaccine coding for the rhesus prostate specific antigen delivered by intradermal electroporation in patients with relapsed prostate cancer. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3843–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pliquett, U.F.; Zewert, T.E.; Chen, T.; Langer, R.; Weaver, J.C. Imaging of fluorescent molecule and small ion transport through human stratum corneum during high voltage pulsing: Localized transport regions are involved. Biophys. Chem. 1996, 58, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xie, J. A Review on Electroporation-Based Intracellular Delivery. Molecules 2018, 23, 3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannaman, D.; Dupuy, L.C.; Ellefsen, B.; Schmaljohn, C.S. A Phase 1 clinical trial of a DNA vaccine for Venezuelan equine encephalitis delivered by intramuscular or intradermal electroporation. Vaccine 2016, 34, 3607–3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvet, C.Y.; Thalmensi, J.; Liard, C.; Pliquet, E.; Bestetti, T.; Huet, T.; Langlade-Demoyen, P.; Mir, L.M. Optimization of a gene electrotransfer procedure for efficient intradermal immunization with an hTERT-based DNA vaccine in mice. Molecular therapy. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugimont, L.; Baron, N.; Vandermeulen, G.; Pavselj, N.; Miklavcic, D.; Jullien, M.C.; Cabodevila, G.; Mir, L.M.; Préat, V. Hollow microneedle arrays for intradermal drug delivery and DNA electroporation. J. Membr. Biol. 2010, 236, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, J.R.; Mendoza, J.M.; Spik, K.W.; Badger, C.; Gomez, A.F.; Schmaljohn, C.S.; Sardesai, N.Y.; Broderick, K.E. A multi-head intradermal electroporation device allows for tailored and increased dose DNA vaccine delivery to the skin. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyško-Ptašinskė, V.; Staigvila, G.; Novickij, V. Invasive and non-invasive electrodes for successful drug and gene delivery in electroporation-based treatments. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 10, 1094968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogev, D.; Goldberg, T.; Arami, A.; Tejman-Yarden, S.; Winkler, T.E.; Maoz, B.M. Current state of the art and future directions for implantable sensors in medical technology: Clinical needs and engineering challenges. APL Bioeng. 2023, 7, 031506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naegele, T.E.; Gurke, J.; Rognin, E.; Willis-Fox, N.; Dennis, A.; Tao, X.; Daly, R.; Keyser, U.F.; Malliaras, G. Redox Flow Iontophoresis for Continuous Drug Delivery, Adv. Material. Technol. 2024, 9, 2301641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarruel Mendoza, L.A.; Scilletta, N.A.; Bellino, M.G.; Desimone, M.F.; Catalano, P.N. Recent Advances in Micro-Electro-Mechanical Devices for Controlled Drug Release Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, K.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Shkunov, M.; Silva SR, P.; Castro, F.A.; et al. Minimally invasive power sources for implantable electronics. Exploration 2023, 4, 20220106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Kawamoto, K. Preparation of Thin Frozen Sections from Nonfixed and Undecalcified Hard Tissues Using Kawamoto’s Film Method (2020). Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2230, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, L.R.; He, Z.B.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.T.; Han, B.Z.; Chen, X.J.; He, X.F.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, B.; Qiao, L. Electroporation-mediated nucleic acid delivery during non-embryonic stages for gene-function analysis in Anopheles sinensis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 128, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, K.E.; Humeau, L.M. Enhanced Delivery of DNA or RNA Vaccines by Electroporation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1499, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novickij, V.; Rembiałkowska, N.; Szlasa, W.; Kulbacka, J. Does the shape of the electric pulse matter in electroporation? Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 958128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foldvari, M.; Babiuk, S.; Badea, I. DNA delivery for vaccination and therapeutics through the skin. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2006, 3, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Nishizawa, M. Electrical aspects of skin as a pathway to engineering skin devices. APL Bioeng. 2021, 5, 041509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadoul, A.; Bouwstra, J.; Préat, V.V. Effects of iontophoresis and electroporation on the stratum corneum. Review of the biophysical studies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 35, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, V.; Kamensek, U.; Sersa, G.; Cemazar, M. Changing electrode orientation, but not pulse polarity, increases the efficacy of gene electrotransfer to tumors in vivo. Bioelectrochemistry 2014, 100, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorec, B.; Becker, S.; Rebersek, M.; Miklavcic, D.; Pavselj, N. Skin electroporation for transdermal drug delivery: The influence of the order of different square wave electric pulses. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 457, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavselj, N.; Préat, V. DNA electrotransfer into the skin using a combination of one high- and one low-voltage pulse. J. Control. Release 2005, 106, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavselj, N.; Préat, V.; Miklavcic, D. A numerical model of skin electropermeabilization based on in vivo experiments. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 35, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirao, L.A.; Wu, L.; Khan, A.S.; Satishchandran, A.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Weiner, D.B. Intradermal/subcutaneous immunization by electroporation improves plasmid vaccine delivery and potency in pigs and rhesus macaques. Vaccine 2008, 26, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, K.E.; Shen, X.; Soderholm, J.; Lin, F.; McCoy, J.; Khan, A.S.; Yan, J.; Morrow, M.P.; Patel, A.; Kobinger, G.P.; et al. Prototype development and preclinical immunogenicity analysis of a novel minimally invasive electroporation device. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain, Q.U.; Campos EV, R.; Huynh, A.; Witzigmann, D.; Hedtrich, S. Gene Delivery to the Skin—How Far Have We Come? Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, J.L.; Dean, D.A. Electroporation-mediated gene delivery. Adv. Genet. 2015, 89, 49–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escoffre, J.M.; Portet, T.; Wasungu, L.; Teissié, J.; Dean, D.; Rols, M.P. What is (still not) known of the mechanism by which electroporation mediates gene transfer and expression in cells and tissues. Mol. Biotechnol. 2009, 41, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, H.; Rols, M.P.; Boldt, E.; Neumann, E.; Teissié, J. Control by pulse parameters of electric field-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Biophys. J. 1994, 66 Pt 1, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugibayashi, K.; Yoshida, M.; Mori, K.; Watanabe, T.; Hasegawa, T. Electric field analysis on the improved skin concentration of benzoate by electroporation. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 219, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshida, Y.; Aoki, M.; Nagase, K.; Marubashi, K.; Kojima, H.; Itakura, S.; Komatsu, S.; Sugibayashi, K.; Todo, H. Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091219
Yoshida Y, Aoki M, Nagase K, Marubashi K, Kojima H, Itakura S, Komatsu S, Sugibayashi K, Todo H. Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(9):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091219
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshida, Yuya, Manami Aoki, Kalin Nagase, Koichi Marubashi, Hiroyuki Kojima, Shoko Itakura, Syuuhei Komatsu, Kenji Sugibayashi, and Hiroaki Todo. 2024. "Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 9: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091219
APA StyleYoshida, Y., Aoki, M., Nagase, K., Marubashi, K., Kojima, H., Itakura, S., Komatsu, S., Sugibayashi, K., & Todo, H. (2024). Plasmid DNA Delivery into the Skin via Electroporation with a Depot-Type Electrode. Pharmaceutics, 16(9), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16091219







