Roles for Exosomes in the Pathogenesis, Drug Delivery and Therapy of Psoriasis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Biogenesis of Exosomes
3. The Immunological Function of Exosomes That Are or Are Not Associated with Psoriasis
3.1. Immune Cell-Derived Exosomes
3.1.1. Dendritic Cell-Derived Exosomes
3.1.2. Neutrophil-Derived Exosomes
3.1.3. Macrophage-Derived Exosomes
3.1.4. Mast Cell-Derived Exosomes
3.1.5. T Cell-Derived Exosomes
3.2. Non-Immune Cell-Derived Exosomes
3.2.1. Keratinocyte-Derived Exosomes
3.2.2. Adipocyte-Derived Exosomes
3.2.3. Fibroblast-Derived Exosomes
4. Exosome Contents May Serve as Biomarkers for the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Psoriasis
5. Exosome-Based Therapeutic Applications in Psoriasis
5.1. Exosomes as Therapeutic Agents for Psoriasis Treatment
5.2. Exosomes as Drug Delivery Systems for Psoriasis Treatment
6. Clinical Application of Exosomes for Treating Psoriasis
7. Challenges and Future Directions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Armstrong, A.W.; Read, C. Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Armstrong, A.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Barker, J.N.W.N. Psoriasis. Lancet 2021, 397, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, G.K.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. Psoriasis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2012, 7, 385–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owczarek, W.; Dzik, M.; Narbutt, J.; Walecka, I.; Kowalczyk, M. Real-world evidence on time to relapse of plaque psoriasis after discontinuation of biologic treatment in Poland. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blauvelt, A.; Leonardi, C.L.; Gooderham, M.; Papp, K.A.; Philipp, S.; Wu, J.J.; Igarashi, A.; Flack, M.; Geng, Z.; Wu, T.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Continuous Risankizumab Therapy vs Treatment Withdrawal in Patients With Moderate to Severe Plaque Psoriasis: A Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarla, R.; Hur, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Chwae, Y.J. Apoptotic cell-derived exosomes: Messages from dying cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Q.; Lin, L.; Sha, C.; Li, T.; Liu, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.; Gao, W.; et al. Regulation of exosome production and cargo sorting. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Fang, H.; Li, Q.; Wang, G. Extracellular vesicles in Inflammatory Skin Disorders: From Pathophysiology to Treatment. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9937–9955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, S.Y.; You, G.E.; Park, C.W.; Kim, H.O.; Chung, B.Y. Exosomes released by environmental pollutant-stimulated Keratinocytes/PBMCs can trigger psoriatic inflammation in recipient cells via the AhR signaling pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 10, 1324692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Min, X.; Ouyang, L.; Jia, S.; Lu, Q.; et al. Keratinocyte-to-macrophage communication exacerbate psoriasiform dermatitis via LRG1-enriched extracellular vesicles. Theranostics 2024, 14, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.; Fang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, M.; Xue, K.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Neutrophil exosomes enhance the skin autoinflammation in generalized pustular psoriasis via activating keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 6813–6828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Lai, R.C.; Sim, W.K.; Choo, A.B.H.; Lane, E.B.; Lim, S.K. Topical Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes Alleviates the Imiquimod Induced Psoriasis-Like Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Feng, H.; Zeng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Hou, K.; Wu, M. Exosomes: The emerging mechanisms and potential clinical applications in dermatology. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 1778–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.-H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, J.; Hur, J.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, H.-J.; Chwae, Y.-J. Molecular mechanisms of biogenesis of apoptotic exosome-like vesicles and their roles as damage-associated molecular patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11721–E11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonbhadra, S.; Mehak; Pandey, L.M. Biogenesis, Isolation, and Detection of Exosomes and Their Potential in Therapeutics and Diagnostics. Biosensors 2023, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henne, W.M.; Buchkovich, N.J.; Emr, S.D. The ESCRT pathway. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, R.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Azari, A.; Taghipour, N.; Soleimani, M.; Rahimpour, A.; Abbaszadeh, H.A. The Current Status and Future Direction of Extracellular Nano-vesicles in the Alleviation of Skin Disorders. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 19, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.Q.; Akhtar, S.; Prabhu, K.S.; Zarif, L.; Khan, R.; Alam, M.; Buddenkotte, J.; Ahmad, A.; Steinhoff, M.; Uddin, S. Exosomes: Emerging Diagnostic and Therapeutic Targets in Cutaneous Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henne, W.M.; Stenmark, H.; Emr, S.D. Molecular mechanisms of the membrane sculpting ESCRT pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a016766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, T.; Fürthauer, M. Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurian, T.K.; Banik, S.; Gopal, D.; Chakrabarti, S.; Mazumder, N. Elucidating Methods for Isolation and Quantification of Exosomes: A Review. Mol. Biotechnol. 2021, 63, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschuschke, M.; Kocherova, I.; Bryja, A.; Mozdziak, P.; Angelova Volponi, A. Inclusion Biogenesis, Methods of Isolation and Clinical Application of Human Cellular Exosomes. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subra, C.; Grand, D.; Laulagnier, K.; Stella, A.; Lambeau, G.; Paillasse, M.; De Medina, P.; Monsarrat, B.; Perret, B.; Silvente-Poirot, S.; et al. Exosomes account for vesicle-mediated transcellular transport of activatable phospholipases and prostaglandins. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2105–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 29, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K. Immunotherapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, E.; Amigorena, S.; Théry, C. Mature dendritic cells secrete exosomes with strong ability to induce antigen-specific effector immune responses. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2005, 35, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkach, M.; Kowal, J.; Zucchetti, A.E.; Enserink, L.; Jouve, M.; Lankar, D.; Saitakis, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Théry, C. Qualitative differences in T-cell activation by dendritic cell-derived extracellular vesicle subtypes. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 3012–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segura, E.; Guérin, C.; Hogg, N.; Amigorena, S.; Théry, C. CD8+ dendritic cells use LFA-1 to capture MHC-peptide complexes from exosomes in vivo. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, K.; Guo, T.; Yang, S.; Jia, H. Par3 regulates the asymmetric division of basal stem cells in psoriasis via the Par3/mInsc/LGN signaling axis. Cell. Immunol. 2022, 373, 104496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skokos, D.; Botros, H.G.; Demeure, C.; Morin, J.; Peronet, R.; Birkenmeier, G.; Boudaly, S.; Mécheri, S. Mast cell-derived exosomes induce phenotypic and functional maturation of dendritic cells and elicit specific immune responses in vivo. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3037–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.L.; Jarrett, R.; Subramaniam, S.; Salimi, M.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D. Psoriatic T cells recognize neolipid antigens generated by mast cell phospholipase delivered by exosomes and presented by CD1a. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefler, I.; Pasmanik-Chor, M.; Kidron, D.; Mekori, Y.A.; Hershko, A.Y. T cell-derived microvesicles induce mast cell production of IL-24: Relevance to inflammatory skin diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, L.A.; Ratnasothy, K.; Tsang, J.Y.; Boardman, D.; Warley, A.; Lechler, R.; Lombardi, G. CD73 expression on extracellular vesicles derived from CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ T cells contributes to their regulatory function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 2430–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, I.S.; Coomes, S.M.; Pelly, V.S.; Czieso, S.; Papayannopoulos, V.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Wilson, M.S. MicroRNA-containing T-regulatory-cell-derived exosomes suppress pathogenic T helper 1 cells. Immunity 2014, 41, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangino, G.; Iuliano, M.; Carlomagno, S.; Bernardini, N. Interleukin-17A affects extracellular vesicles release and cargo in human keratinocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.W.; Zhu, R.; Ran, L.; Li, Y.Q.; Huang, K.; Peng, J.; He, W.; Zhou, C.L.; Wang, R.P. A novel non-contact communication between human keratinocytes and T cells: Exosomes derived from keratinocytes support superantigen-induced proliferation of resting T cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 7032–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Fang, H.; Dang, E.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, P.; Yu, C.; Yang, A.; Wang, G. Small Extracellular Vesicles Containing miR-381-3p from Keratinocytes Promote T Helper Type 1 and T Helper Type 17 Polarization in Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzerke, K.; Mempel, M.; Aung, T.; Wulf, G.G.; Urlaub, H.; Wenzel, D.; Schön, M.P.; Braun, A. Immunostimulatory activity of murine keratinocyte-derived exosomes. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Fang, H.; Shao, S.; Dang, E.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, P.; Yang, A.; Wang, G. Keratinocyte exosomes activate neutrophils and enhance skin inflammation in psoriasis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13241–13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; She, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Y. Vitamin D receptor-deficient keratinocytes-derived exosomal miR-4505 promotes the macrophage polarization towards the M1 phenotype. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gao, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.; Wan, Z.; Dong, Y.; Chen, X.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G. Visceral Adipose Tissue Derived Exosomes Exacerbate Colitis Severity via Pro-inflammatory MiRNAs in High Fat Diet Fed Mice. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 5099–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlecki-Zaniewicz, L.; Pils, V.; Bobbili, M.R.; Lämmermann, I.; Perrotta, I.; Grillenberger, T.; Schwestka, J.; Weiß, K.; Pum, D.; Arcalis, E.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles in Human Skin: Cross-Talk from Senescent Fibroblasts to Keratinocytes by miRNAs. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2425–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.N.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, J.M.; Park, A.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Seok, J.; Yoo, K.H.; Kim, B.J. Exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblasts (HDFn-Ex) alleviate DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis (AD) via PPARα. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Sarkar, M.K.; Tsoi, L.C.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Psoriasis: A mixed autoimmune and autoinflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 49, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, A.; Xing, X.; Wolterink, L.; Barnes, D.H.; Yin, Z.; Reingold, L.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Harms, P.W.; Gudjonsson, J.E. IL-1 and IL-36 are dominant cytokines in generalized pustular psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, W.; Kong, B.; Ouyang, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wang, X.; et al. IL-17D-induced inhibition of DDX5 expression in keratinocytes amplifies IL-36R-mediated skin inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, C.M.; Sullivan, G.P.; Clancy, D.M.; Afonina, I.S.; Kulms, D.; Martin, S.J. Neutrophil-Derived Proteases Escalate Inflammation through Activation of IL-36 Family Cytokines. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewood, C.; Fearnley, G.W.; Berekmeri, A.; Laws, P.; Macleod, T.; Ponnambalam, S.; Stacey, M.; Graham, A.; Wittmann, M. IL-36γ Is a Strong Inducer of IL-23 in Psoriatic Cells and Activates Angiogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.A.; Kupper, T.S. Misbehaving macrophages in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2084–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, K.; Olivier, M. Immunomodulatory impact of leishmania-induced macrophage exosomes: A comparative proteomic and functional analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyman, O.; Hefti, H.P.; Conrad, C.; Nickoloff, B.J.; Suter, M.; Nestle, F.O. Spontaneous development of psoriasis in a new animal model shows an essential role for resident T cells and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Peng, X.; Dai, H.; Li, L. Mast Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Th2 Cell Differentiation via OX40L-OX40 Ligation. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 3623898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, W.; Lee, E.; Krueger, J.G. Psoriasis genomics: Analysis of proinflammatory (type 1) gene expression in large plaque (Western) and small plaque (Asian) psoriasis vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 150, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Di Meglio, P.; Nestle, F.O. The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, X.Q.; Cheng, J.; Hui, R.S.; Gao, T.W. Increased Th17 cells are accompanied by FoxP3(+) Treg cell accumulation and correlated with psoriasis disease severity. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 135, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, J.; Duan, H.; Jia, T.; Lei, Q.; et al. Characterization of Th17 and FoxP3(+) Treg Cells in Paediatric Psoriasis Patients. Scand. J. Immunol. 2016, 83, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, H.; Gyulai, R.; Toichi, E.; Garaczi, E.; Shimada, S.; Stevens, S.R.; McCormick, T.S.; Cooper, K.D. Dysfunctional blood and target tissue CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in psoriasis: Mechanism underlying unrestrained pathogenic effector T cell proliferation. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, R.; Mazzeo, C.; Rodriguez, M.C.; Marsh, M.; Fraile-Ramos, A.; Calvo, V.; Avila-Flores, A.; Merida, I.; Izquierdo, M. Diacylglycerol kinase α regulates the formation and polarisation of mature multivesicular bodies involved in the secretion of Fas ligand-containing exosomes in T lymphocytes. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Wu, J.; Tian, J.; Wang, S. Role of T cell-derived exosomes in immunoregulation. Immunol. Res. 2018, 66, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlgren, J.; Karlson Tde, L.; Glader, P.; Telemo, E.; Valadi, H. Activated human T cells secrete exosomes that participate in IL-2 mediated immune response signaling. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedlund, M.; Nagaeva, O.; Kargl, D.; Baranov, V.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L. Thermal- and oxidative stress causes enhanced release of NKG2D ligand-bearing immunosuppressive exosomes in leukemia/lymphoma T and B cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Deng, Y.; Munegowda, M.A.; Chibbar, R.; Qureshi, M.; Xiang, J. Dendritic cells recruit T cell exosomes via exosomal LFA-1 leading to inhibition of CD8+ CTL responses through downregulation of peptide/MHC class I and Fas ligand-mediated cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 5268–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dang, G.; Lü, S.; Liu, H.; Ma, X.; Han, L.; Deng, J.; Miao, Y.; Li, X.; Shao, F.; et al. T-cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate B-cell IgG production via pyruvate kinase muscle isozyme 2. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 12780–12799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Messina, L.; Rodríguez-Galán, A.; de Yébenes, V.G.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Tenreiro, S.; Seabra, M.C.; Ramiro, A.R.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Transfer of extracellular vesicle-microRNA controls germinal center reaction and antibody production. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e48925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, U.T.T.; Guanzon, D.; Broadbent, J.A.; Leavesley, D.I.; Salomon, C.; Parker, T.J. Differential Expression of Keratinocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Mirnas Discriminate Exosomes From Apoptotic Bodies and Microvesicles. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Muñoz, C.; Morse, J.; Kilani, R.; Ghahary, A. Primary human keratinocytes externalize stratifin protein via exosomes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 2165–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Bi, J.; Owen, G.R.; Chen, W.; Rokka, A.; Koivisto, L.; Heino, J.; Häkkinen, L.; Larjava, H. Keratinocyte Microvesicles Regulate the Expression of Multiple Genes in Dermal Fibroblasts. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 3051–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.J. Emerging Roles of Adipose Tissue in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis in Obesity. JID Innov. 2022, 2, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Candia, P.; De Rosa, V.; Gigantino, V.; Botti, G.; Ceriello, A.; Matarese, G. Immunometabolism of human autoimmune diseases: From metabolites to extracellular vesicles. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 3119–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaherty, S.E., 3rd; Grijalva, A.; Xu, X.; Ables, E.; Nomani, A.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. A lipase-independent pathway of lipid release and immune modulation by adipocytes. Science 2019, 363, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranendonk, M.E.; Visseren, F.L.; van Herwaarden, J.A.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; de Jager, W.; Wauben, M.H.; Kalkhoven, E. Effect of extracellular vesicles of human adipose tissue on insulin signaling in liver and muscle cells. Obesity 2014, 22, 2216–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ballantyne, L.L.; Yu, Y.; Funk, C.D. Perivascular adipose tissue-derived extracellular vesicle miR-221-3p mediates vascular remodeling. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 12704–12722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadey, R.M.; Connolly, K.D.; Mathew, D.; Walters, G.; Rees, D.A.; James, P.E. Inflammatory adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles promote leukocyte attachment to vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2019, 283, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Han, M.; Lou, F.; Sun, Y.; Yin, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Z.; et al. Tenascin C(+) papillary fibroblasts facilitate neuro-immune interaction in a mouse model of psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Plazyo, O.; Billi, A.C.; Tsoi, L.C.; Xing, X.; Wasikowski, R. Single cell and spatial sequencing define processes by which keratinocytes and fibroblasts amplify inflammatory responses in psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shao, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Li, K.; Liang, H.; Wang, N.O.; et al. The mechano-chemical circuit in fibroblasts and dendritic cells drives basal cell proliferation in psoriasis. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Dong, C.; Lin, J.; Lu, X.; Zhu, J.; Lin, L.; Xu, J. MMP2hi Fibroblasts Regulate CD8+ T Cell Residency and Inflammation via CD100 in Psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 191, 405–418. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Niu, Z.; Huang, Q.; Han, L.; Du, J.; Liang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, R.; Yawalkar, N.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Identification of an exosomal miRNA-mRNA regulatory network contributing to methotrexate efficacy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolino, G.; Buratta, S.; Mercuri, S.R.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Urbanelli, L.; Emiliani, C.; Bertuccini, L.; Iosi, F.; Huber, V.; Brianti, P.; et al. Lipidic Profile Changes in Exosomes and Microvesicles Derived From Plasma of Monoclonal Antibody-Treated Psoriatic Patients. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 923769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, T.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Di, T.; Li, P. Protective effect of Yangxue Jiedu Soup against psoriasis-like lesions by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway mediated by secretion of exosome HSP70. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, T.; Li, P. Effects of luteolin on treatment of psoriasis by repressing HSP90. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 79, 106070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ni, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, R.D.; Fang, X.; Wang, P.; Pan, H.F. Exosomes as biomarkers and therapeutic delivery for autoimmune diseases: Opportunities and challenges. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.C.; Tan, T.T.; Sim, W.K.; Zhang, B.; Lim, S.K. A roadmap from research to clinical testing of mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes in the treatment of psoriasis. Cytotherapy 2023, 25, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Yan, J.J.; Li, Z.J.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Q. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022, 42, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Lee, S.Y.; You, G.E.; Kim, H.O.; Park, C.W.; Chung, B.Y. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Alleviate Psoriasis Serum Exosomes-Induced Inflammation by Regulating Autophagy and Redox Status in Keratinocytes. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 3699–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.C.; Cardoso, R.M.S.; Freire, P.C.; Gomes, C.F.; Duarte, F.V.; das Neves, R.P.; Simões-Correia, J. Immunomodulatory Properties of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles and Their Therapeutic Potential for Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Huang, Y.; Shao, K.; Yan, J.; Sun, Q. High Expression of miR-6785-5p in the Serum Exosomes of Psoriasis Patients Alleviates Psoriasis-Like Skin Damage by Interfering with the MNK2/p-eIF4E Axis in Keratinocytes. Inflammation 2024, 47, 1585–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, S.; Tehrani, F.R.; Tahmasebi, S.; Shafiee, A.; Hashemi, S.M. Exosome engineering in cell therapy and drug delivery. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 145–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Chakraborty, K.; Hwang, J.; Lee, Y.-K. Exosome-based drug delivery systems and their therapeutic applications. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 18475–18492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
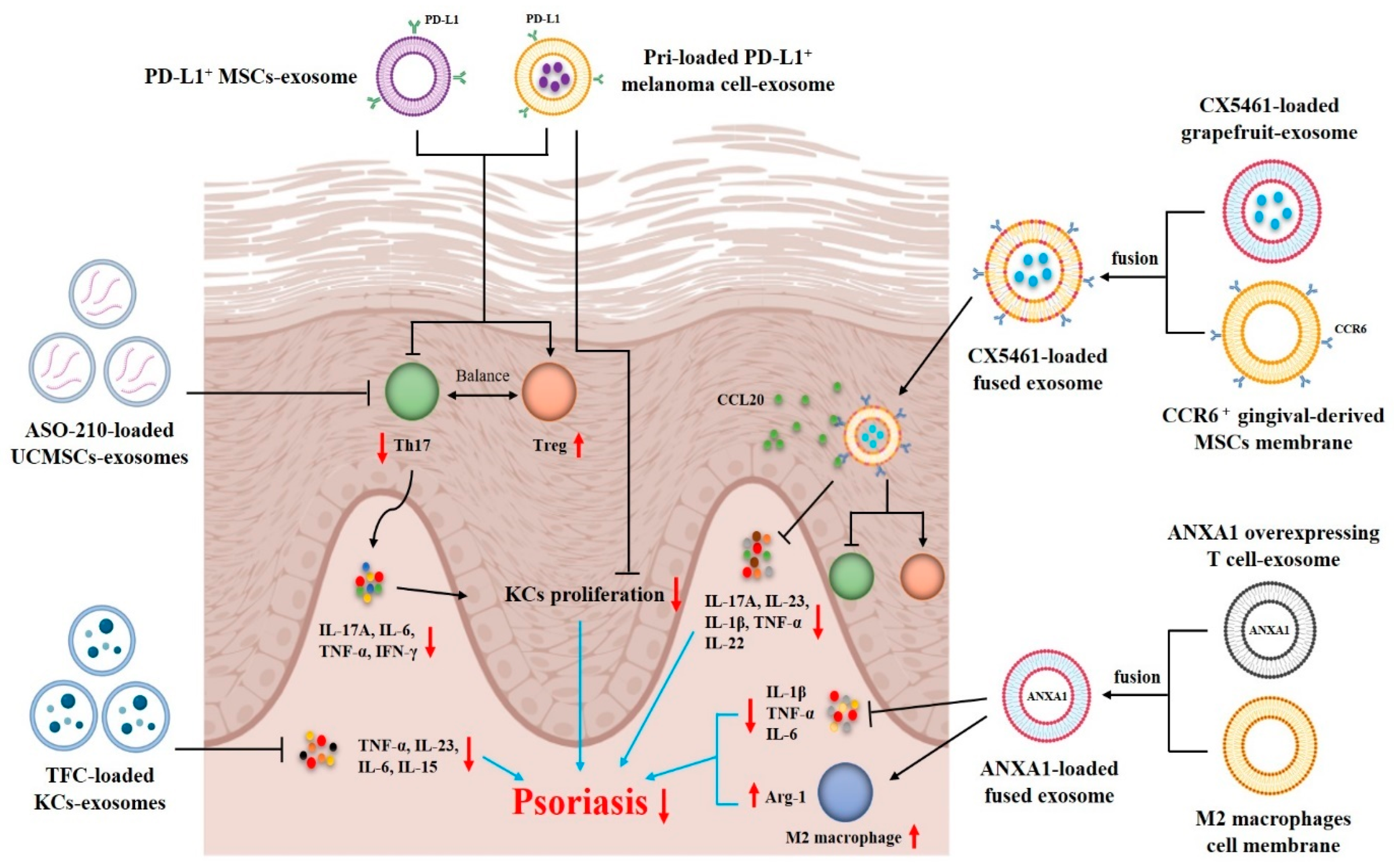
- Zhang, W.; Lin, J.; Shi, P.; Su, D.; Cheng, X.; Yi, W.; Yan, J.; Chen, H.; Cheng, F. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived From MSCs Have Immunomodulatory Effects to Enhance Delivery of ASO-210 for Psoriasis Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 842813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, P.; Varshosaz, J.; Mirian, M.; Minaiyan, M.; Kazemi, M.; Bodaghi, M. Keratinocyte Exosomes for Topical Delivery of Tofacitinib in Treatment of Psoriasis: An In Vitro/ In Vivo Study in Animal Model of Psoriasis. Pharm. Res. 2024, 41, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Fei, Z.; Dai, H.; Xu, J.; Fan, Q.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chu, J.; Peng, F.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles with High PD-L1 Expression for Autoimmune Diseases Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2021, 34, e2106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, T.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, H.; Fu, S.; Hong, J.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Tumor-Derived PD-L1+ Exosomes with Natural Inflammation Tropism for Psoriasis-Targeted Treatment. Bioconjugate Chem. 2023, 34, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qin, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Liang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, L.; et al. Engineering extracellular vesicles with macrophage membrane fusion for ameliorating imiquimod-induced psoriatic skin inflammation. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2023, 34, 2220445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Jia, B.; Su, D.; Li, M.; Xu, Z.; He, C.; Huang, Y.; Fan, H.; Chen, H.; Cheng, F. Plant exosomes fused with engineered mesenchymal stem cell-derived nanovesicles for synergistic therapy of autoimmune skin disorders. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2023, 12, e12361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohseni Meybodi, M.A.; Nilforoushzadeh, M.A.; KhandanDezfully, N.; Mansouri, P. The safety and efficacy of adipose tissue-derived exosomes in treating mild to moderate plaque psoriasis: A clinical study. Life Sci. 2024, 353, 122915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Source Cells | Contents | Target Cells | Effects | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immune cells | ||||
| DCs | MHC-II, CD86, ICAM-1 | T cells | Stimulating T cells activation | [31] |
| MHC-II, CD86, CD9, HLA-DR | CD4+ T cells | Activating CD4+ T cells and promoting secretion of IFN-γ | [32] | |
| ICAM-1, MHC-peptide complexes | DCs | Captured by DCs with high levels of LFA-1 | [33] | |
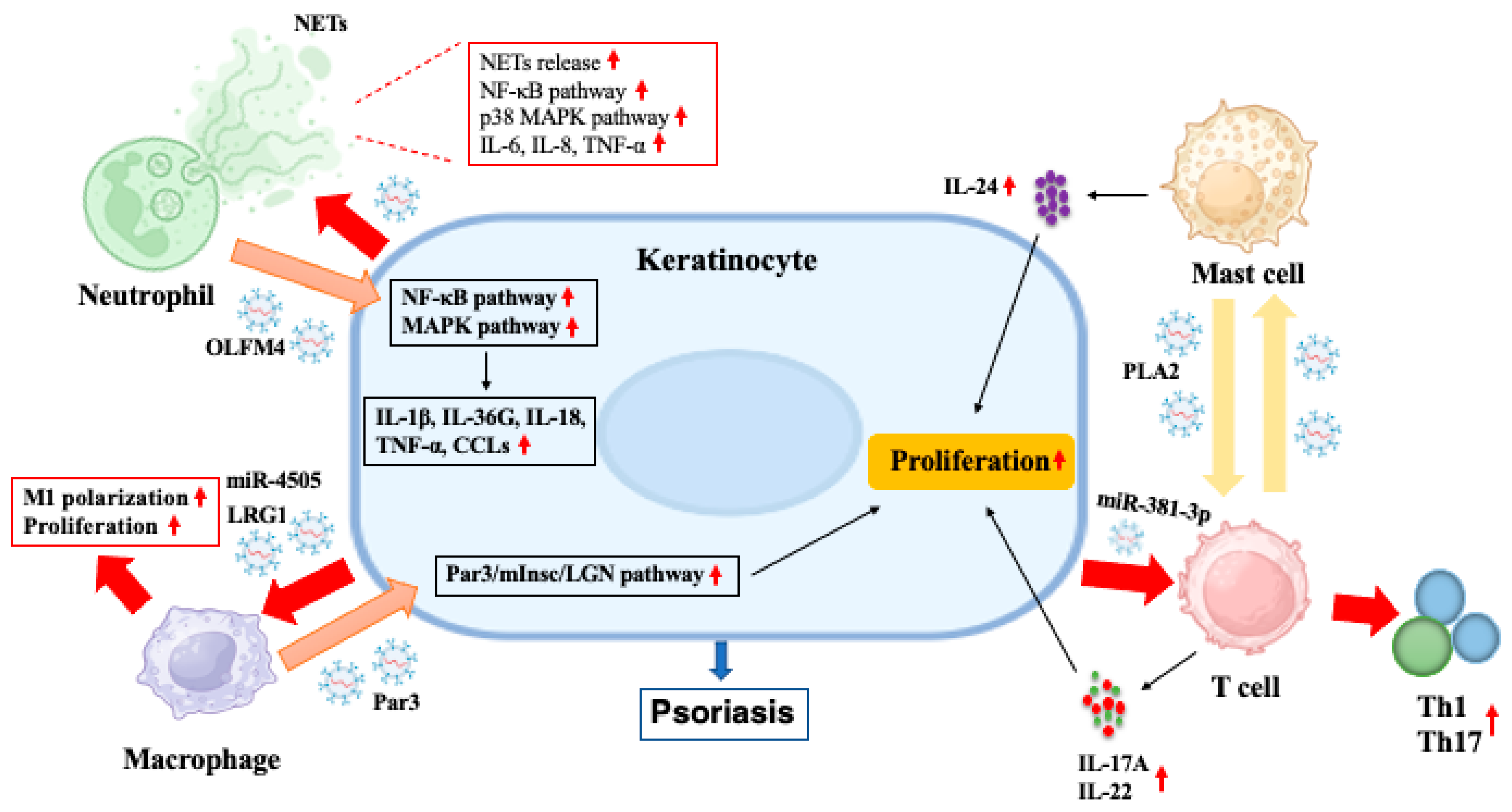
| Neutrophils | OLFM4 | Keratinocytes | Increasing the expression of IL-1β, IL-36G, IL-18, TNF-α and CCLs in keratinocytes by activating MAPK and NF-κB pathways, which modulate autoinflammation in generalized pustular psoriasis | [12] |
| Macrophages | Par3 | Keratinocytes | Enhancing the asymmetric division of basal stem cells by activating the Par3/mInsc/LGN signaling pathway in psoriatic mice | [34] |
| Mast cells | HSP60, HSP70 | DCs | Inducing immature DCs to upregulate MHC-II, CD80, CD86 and CD40 and to acquire potent Ag-presenting capacity. | [35] |
| PLA2 | CD1a-expressing cells | Increasing the generation of neolipid antigens in CD1a-expressing cells, which were subsequently recognized by lipid-specific CD1a-reactive T cells from psoriatic patients, thus inducing the production of IL-17A and IL-22 | [36] | |
| T cells | Non-specific | Mast cells | Stimulating mast cells to degranulate and release IL-24, which in turn activated keratinocytes | [37] |
| CD73 | Not specific | Converting extracellular adenosine-5-monophosphate to adenosine, thus promoting interactions with adenosine receptors expressed on target cells | [38] | |
| Let-7d | Th1 cells | Inhibiting proliferation and IFN-γ secretion of Th1 cells | [39] | |
| Non-immune cells | ||||
| Keratinocytes | β-Defensin 2, CCL20, CXCL1, CXCL3, CXCL5, CXCL6 | HaCaT cells | Upregulating mRNA expression of endogenous β-Defensin 2 in HaCaT cells | [40] |
| CD63, CD9, HSP70, Alix, TSG101 | Inducing the release of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α) and chemokines (CXCL1 and CXCL5) in HaCaT cells through AhR signaling | [10] | ||
| MHC- I, MHC-II | T cells | Enhancing the proliferation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in vitro | [41] | |
| miR-381-3p | Th1, Th17 cells | promoting T cell differentiation into Th1/Th17 cells under psoriatic conditions | [42] | |
| Flotillin, ALIX | DCs | Inducing maturation of DCs and their production of IL-6, IL-10 and IL-12 | [43] | |
| CD9, CD63, HSP70 | Neutrophils | Increasing the release of NETs and production of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α in neutrophils by activating NF-κB and p38 MAPK pathways, thus exacerbating psoriatic skin lesions in mice | [44] | |
| LRG1 | Macrophages | Promoting macrophage polarization through TGFβR1-dependent process, thus accelerating skin lesions in psoriatic mice | [11] | |
| miR-4505 | Enhancing macrophage proliferation and polarization towards M1 phenotype while inhibiting macrophage apoptosis | [45] | ||
| Adipocytes | miR-155 | Macrophages | Inducing macrophage polarization towards the M1 phenotype | [46] |
| Fibroblasts | miR-23a-3p | Keratinocytes | Accelerating scratch closure of epidermal keratinocytes and impairing keratinocyte differentiation in vitro | [47] |
| Non-specific | HaCaT cells | Inhibiting epidermal hyperplasia and increasing the levels of filaggrin and HAS1 by augmenting the expression of PPARα in HaCaT cells | [48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Yang, B.; Lu, W.; Dai, Z. Roles for Exosomes in the Pathogenesis, Drug Delivery and Therapy of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010051
Chen Y, Liu H, He Y, Yang B, Lu W, Dai Z. Roles for Exosomes in the Pathogenesis, Drug Delivery and Therapy of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yuchao, Huazhen Liu, Yuming He, Bin Yang, Weihui Lu, and Zhenhua Dai. 2025. "Roles for Exosomes in the Pathogenesis, Drug Delivery and Therapy of Psoriasis" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010051
APA StyleChen, Y., Liu, H., He, Y., Yang, B., Lu, W., & Dai, Z. (2025). Roles for Exosomes in the Pathogenesis, Drug Delivery and Therapy of Psoriasis. Pharmaceutics, 17(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010051







