Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instruments
2.2. Drugs and Reagents
2.3. Animals and Cells
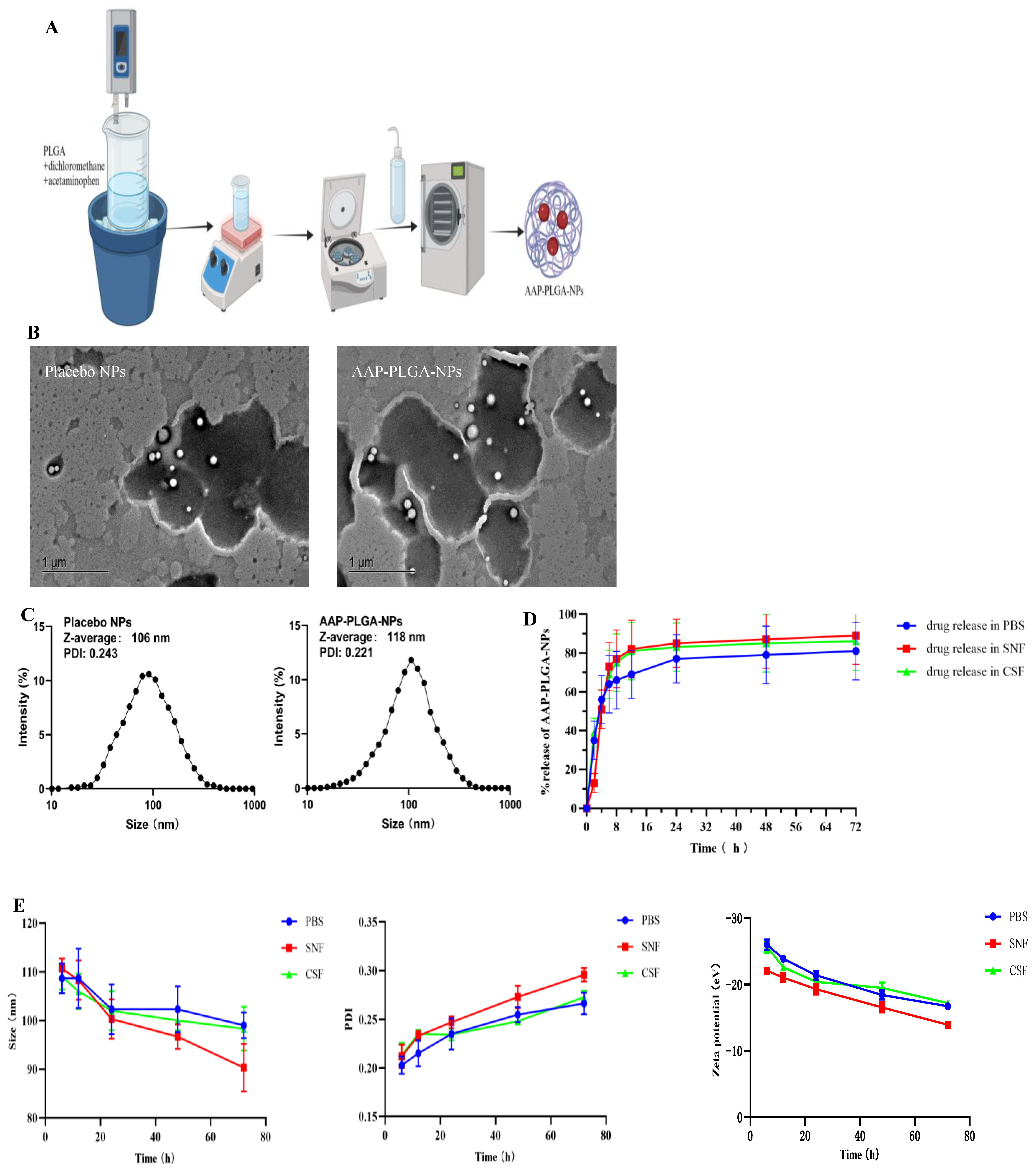
2.4. Preparation of AAP PLGA NPs
2.5. Characterization of AAP PLGA NPs
2.5.1. Determination of Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
2.5.2. Determination of Particle Size and Zeta Potential
2.5.3. Morphological Characterization
2.6. Evaluation of In Vitro Release Behavior and Stability
2.7. Cytotoxicity Evaluation
2.7.1. CCK-8 Assay
2.7.2. Live/Dead Cell Staining
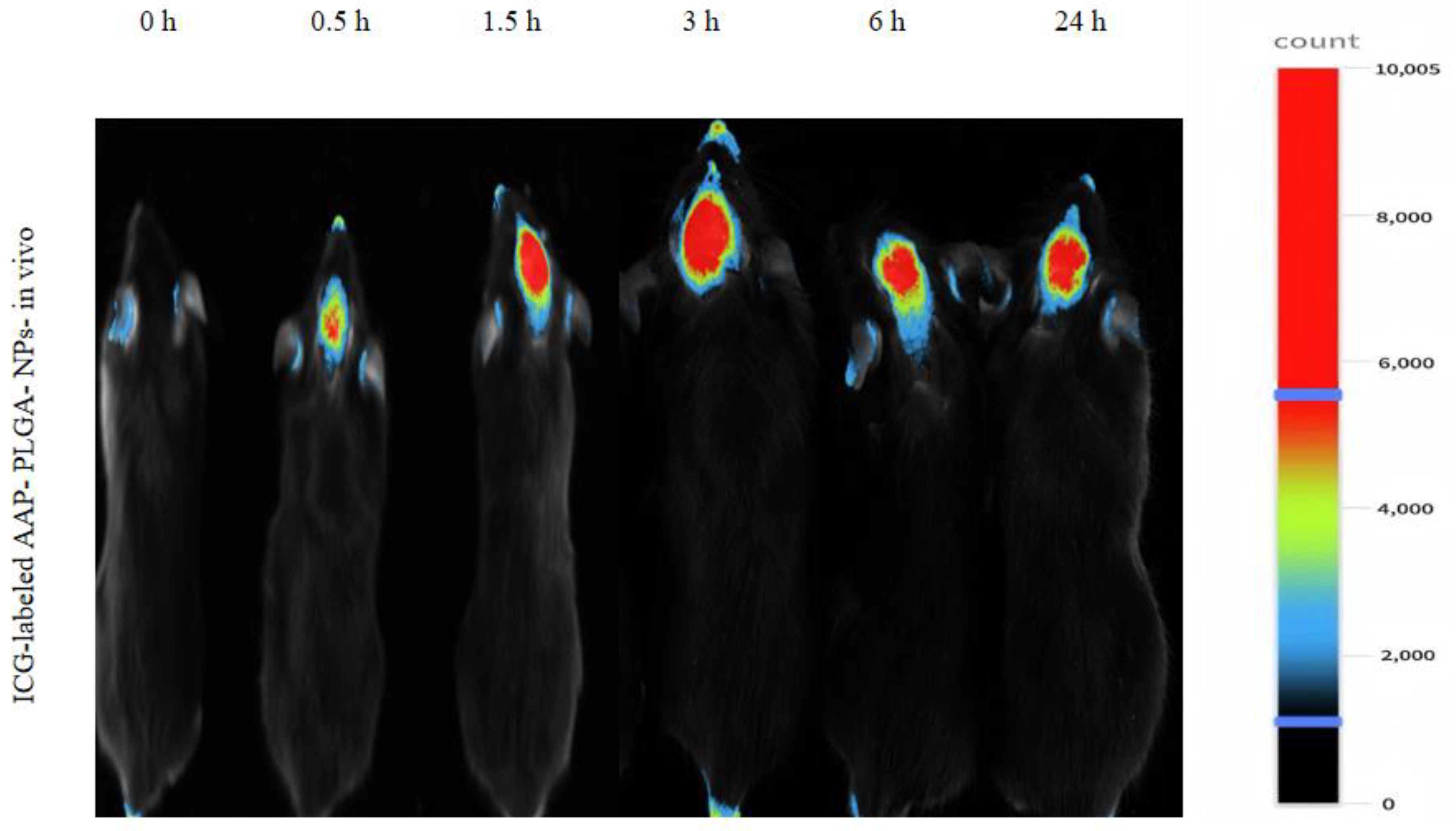
2.8. In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging
2.9. Determination of AAP PLGA NPs in the Murine Blood and Brain
2.10. Pharmacodynamic Study of AAP PLGA NPs
2.10.1. Hot-Plate Test [14]
2.10.2. Tail-Flick Test [15]
2.10.3. Model Establishment
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Properties of AAP PLGA NPs
3.2. In Vitro Release Behavior and Stability
3.3. Results of Cytotoxicity Assessment
3.4. Live/Dead Staining
3.5. Live Fluorescence Imaging
3.6. Drug Levels in Murine Blood and Brain
3.7. Pharmacodynamic Observation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Jia, T.; Zhu, W.; Fan, L. High-altitude environments enhance the ability of Eothenomys miletus to regulate body mass during food limitation, with a focus on gut microorganisms and physiological markers. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1499028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suri, R.; Markovic, D.; Woo, H.; Arjomandi, M.; Barr, R.G.; Bowler, R.P.; Criner, G.; Curtis, J.L.; Dransfield, M.T.; Drummond, M.B.; et al. The Effect of Chronic Altitude Exposure on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Outcomes in the SPIROMICS Cohort: An Observational Cohort Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Yang, X.Y.; Su, R.; Ma, H.; Li, H. Temporal Effects of Hypoxia Exposure at High Altitudes on Compensatory Brain Function: Evidence from Functional Connectivity of Resting-State EEG Brain Networks. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noël-Jorand, M.C.; Bragard, D.; Plaghki, L. Pain perception under chronic high-altitude hypoxia. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 2075–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Han, K.; Lu, H.; Illangamudalige, S.; Shaheed, C.A.; Chen, L.; McLachlan, A.J.; Patanwala, A.E.; Maher, C.G.; Lin, C.W.C.; et al. Paracetamol Combination Therapy for Back Pain and Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Drugs 2024, 84, 953–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.S.; Wenzel, R.P.; Thomas, S.H. High altitude headache: Efficacy of acetaminophen vs. ibuprofen in a randomized, controlled trial. J. Emerg. Med. 2003, 24, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsafty, M.; Abdeen, A.; Aboubakr, M. Allicin and Omega-3 fatty acids attenuates acetaminophen mediated renal toxicity and modulates oxidative stress, and cell apoptosis in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2024, 397, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanza, C.; Saglietti, F.; Giamello, J.D.; Savioli, G.; Biancone, D.M.; Balzanelli, M.G.; Giordano, B.; Trompeo, A.C.; Longhitano, Y. Effectiveness of Intranasal Analgesia in the Emergency Department. Medicina 2023, 59, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, X.; Yu, S.; Gong, G.; Shu, H. Research progress in brain-targeted nasal drug delivery. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1341295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pandey, A.N.; Jain, S.K. Nasal-nanotechnology: Revolution for efficient therapeutics delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, Q. Pharmacokinetics and disposition of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles. Curr. Drug Metab. 2010, 11, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanna, V.; Vora, A.; Shah, P.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Sawarkar, S.P. PLGA Nanoparticles Based Mucoadhesive Nasal In Situ Gel for Enhanced Brain Delivery of Topiramate. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshan-Sefidi, M.; Bakhshi, B.; Rasekhi, A. Vibriocidal efficacy of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus acidophilus cell-free supernatants encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles against multi-drug resistant Vibrio cholerae O1 El Tor. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Su, D.; Li, Z.C.; Sun, S.; Ge, Z. Metformin attenuates central sensitization by regulating neuroinflammation through the TREM2-SYK signaling pathway in a mouse model of chronic migraine. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandulenko, I.V.; Belozertseva, I.V.; Zvartau, E.E.; Zelentsova, M.V.; Ambartsumyan, A.A.; Smol’yakov, A.F.; Moiseev, S.K. C(21)-fluorinated thevinol scaffold for opioid ligands. 21,21,21-Trifluoro-6-O-nororvinols: Design, synthesis and analgesic activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 252, 115296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamani, F.; Bassand, C.; Hamoudi, M.C.; Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J. Mechanistic explanation of the (up to) 3 release phases of PLGA microparticles: Monolithic dispersions studied at lower temperatures. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 596, 120220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodoplu, D.; Boyaci, I.H.; Bozkurt, A.G.; Eksi, H.; Zengin, A.; Tamer, U.; Aydogan, N.; Ozcan, S.; Tugcu-Demiröz, F. Quantitative Characterization of Magnetic Mobility of Nanoparticle in Solution-Based Condition. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 5389–5400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Tang, L.; Yang, H.; Yan, M.; Yuan, P.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, T.; Wang, Y.; Gou, J.; et al. Effect of mPEG-PLGA on Drug Crystallinity and Release of Long-Acting Injection Microspheres: In Vitro and In Vivo Perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2024, 41, 1271–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boltnarova, B.; Durinova, A.; Jandova, L.; Micuda, S.; Kucera, O.; Pavkova, I.; Machacek, M.; Nemeckova, I.; Vojta, M.; Dusek, J.; et al. Dexamethasone Acetate-Loaded PLGA Nanospheres Targeting Liver Macrophages. Macromol. Biosci. 2024, 25, e2400411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Almazán, J.P.; Castro-Ceseña, A.B.; Aguila, S.A. Evaluation of the release kinetics of hydrophilic and lipophilic compounds from lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 15801–15814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernert, M.; Bignoux, M.J.; Madhav, C.; Gqeba, S.; Otgaar, T.C.; Morris, G.; Weiss, S.F.; Ferreira, E. PLGA nanocapsules as a delivery system for a recombinant LRP-based therapeutic. FEBS Open Bio 2024, 14, 1072–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H. Exploring the Effects of Process Parameters during W/O/W Emulsion Preparation and Supercritical Fluid Extraction on the Protein Encapsulation and Release Properties of PLGA Microspheres. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marecki, E.K.; Oh, K.W.; Knight, P.R.; Davidson, B.A. Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticle fabrication, functionalization, and biological considerations for drug delivery. Biomicrofluidics 2024, 18, 051503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Palma, E.; Pasqua, A.; Gagliardi, A.; Britti, D.; Fresta, M.; Cosco, D. Antileishmanial Activity of Amphotericin B-loaded-PLGA Nanoparticles: An Overview. Materials 2018, 11, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kaur, A.; Nigam, K.; Tyagi, A.; Dang, S. A Preliminary Pharmacodynamic Study for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Memantine-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuglianello, C.; França, A.P.; de Souza, B.S.; Agnes, J.P.; Prediger, R.D.; Lemos-Senna, E. Intranasal administration of dextran-pramlintide polyelectrolyte complex-coated nanoemulsions improves cognitive impairments in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 281 Pt 1, 136158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, K.; Kaplan, M.; Çalış, S. Effects of nanoparticle size, shape, and zeta potential on drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 666, 124799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Lupi, M.; Colombo, C.; Morbidelli, M.; D’Incalci, M.; Moscatelli, D. Investigation of size, surface charge, PEGylation degree and concentration on the cellular uptake of polymer nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkland, C.; Pollauf, E.; Raman, C.; Silverman, R.; Kim, K.; Pack, D.W. Macromolecule release from monodisperse PLG microspheres: Control of release rates and investigation of release mechanism. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 1176–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkman, R. Central antinociceptive effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and paracetamol. Experimental studies in the rat. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. Suppl. 1995, 103, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Q.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Hou, J.; Yu, S.; Zhou, S.; Gong, G.; Shu, H. Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030341
Huang Q, Han X, Li J, Li X, Chen X, Hou J, Yu S, Zhou S, Gong G, Shu H. Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(3):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030341
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Qingqing, Xingyue Han, Jin Li, Xilin Li, Xin Chen, Jianwen Hou, Sixun Yu, Shaobing Zhou, Gu Gong, and Haifeng Shu. 2025. "Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 3: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030341
APA StyleHuang, Q., Han, X., Li, J., Li, X., Chen, X., Hou, J., Yu, S., Zhou, S., Gong, G., & Shu, H. (2025). Intranasal Administration of Acetaminophen-Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles Increases Pain Threshold in Mice Rapidly Entering High Altitudes. Pharmaceutics, 17(3), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17030341






